В этой статье я постарался собрать в одном месте основные команды cmd и PowerShell, которые полезны при настройке и управлении Windows Server Core. Думаю, этот гайд будет полезен как новичкам, так и опытным системным администраторам, как справочник по базовым командам Server Core.
Содержание:
- Настройка Windows Server Core с помощью SCONFIG
- Основные команды PowerShell для настройки Server Core
- Установка обновлений в Server Core
- Часто используемые команды в Server Core
Напомним, что Server Core это особый режим установки Windows Server без большинства графических инструментов и оболочек. Управление таким сервером выполняется из командной строки или удаленно.
Преимущества Windows Serve Core:
- Меньшие требования к ресурсам;
- Повышенная стабильность, безопасность, требует установки меньшего количества обновлений (за счет меньшего количества кода и используемых компонентов);
- Идеально подходит для использования в качестве сервера для инфраструктурных ролей (контроллер домена Active Directory, DHCP сервер, Hyper-V сервер, файловый сервер и т.д.).
Server Core лицензируется как обычный физический или виртуальный экземпляр Windows Server (в отличии от Hyper-V Server, который полностью бесплатен).
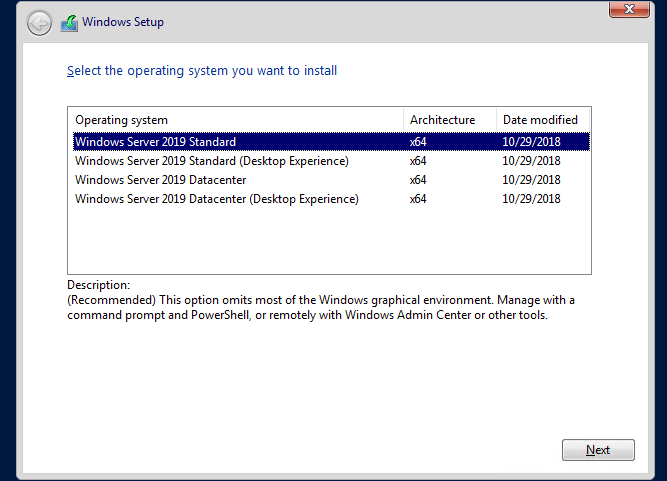
Для установки Windows Server 2016/2019 в режиме Core нужно выбрать обычную установку. Если вы выберите Windows Server (Desktop Experience), будет установлен GUI версия операционной системы (в предыдущих версиях Windows Server она называлась Server with a GUI).
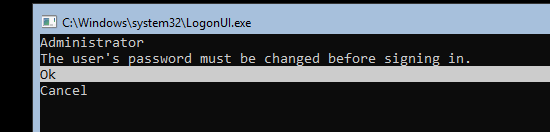
После установки Windows Server Core перед вами появляется командная строка, где нужно задать пароль локального администратора.
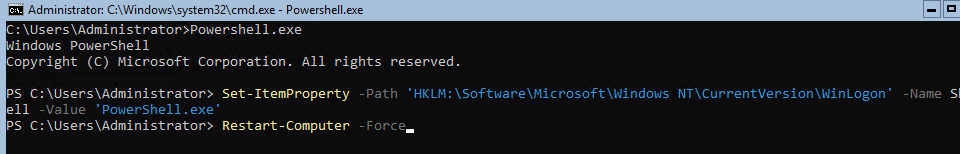
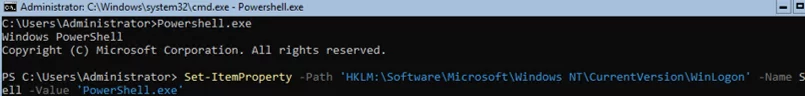
При входе на Server Core открывается командная строка (cmd.exe). Чтобы вместо командной строки у вас всегда открывалась консоль PowerShell.exe, нужно внести изменения в реестр. Выполните команды:
Powershell.exe
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\WinLogon' -Name Shell -Value 'PowerShell.exe'
И перезагрузите сервер:
Restart-Computer -Force
Если вы случайно закрыли окно командной строки, нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Alt+Delete, запустите Task Manager -> File -> Run -> выполните
cmd.exe
(или
PowerShell.exe
).
Настройка Windows Server Core с помощью SCONFIG
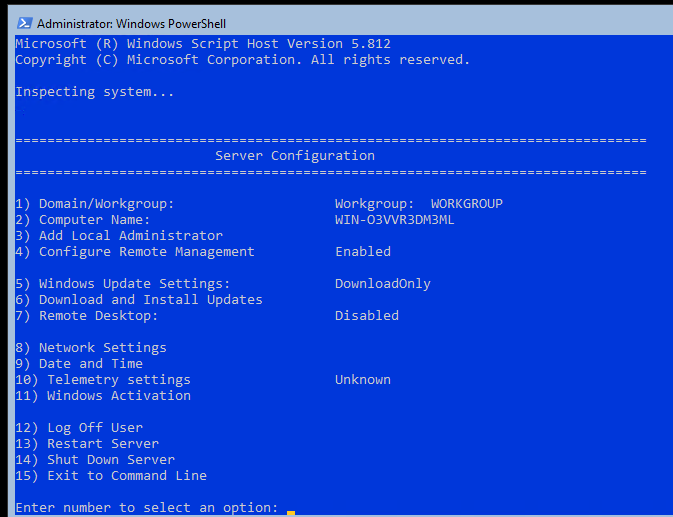
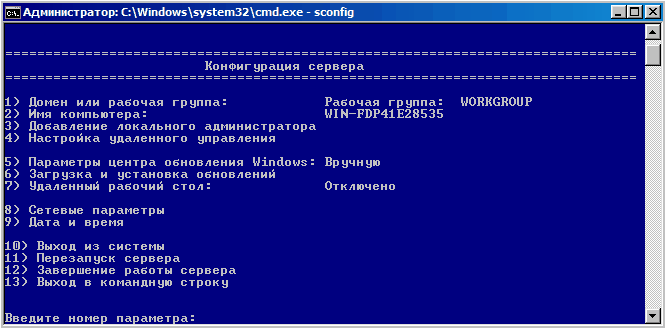
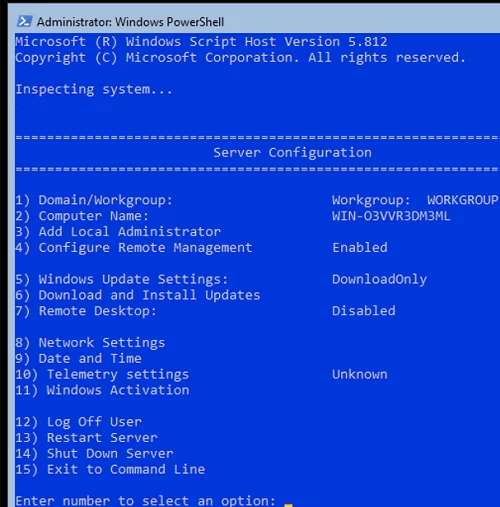
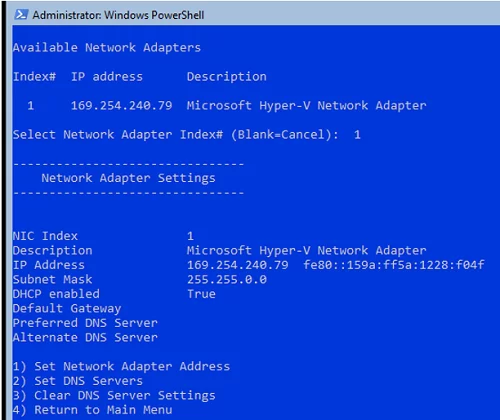
Для базовой настройки Server Core можно использовать встроенный скрипт sconfig. Просто выполните команду sconfig в консоли. Перед вами появиться меню с несколькими пунктами:
С помощью меню Server Configuration можно настроить:
- Добавить компьютер в домен или рабочую группу;
- Изменить имя компьютера (hostname);
- Добавить локального администратора;
- Разрешить/запретить удаленное управления и ответы на icmp;
- Настроить параметры обновления через Windows Update;
- Установить обновления Windows;
- Включить/отключить RDP;
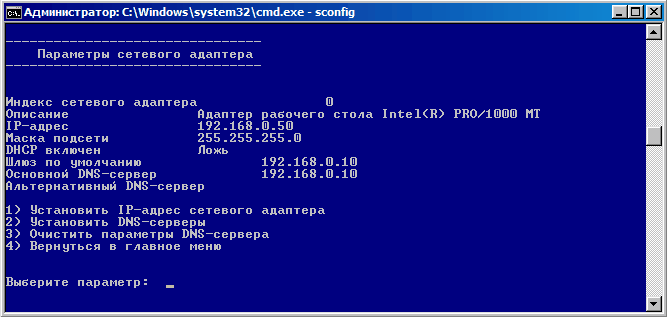
- Настроить параметры сетевых адаптеров (IP адрес, шлюз, DNS сервера);
- Настроить дату и время;
- Изменить параметры телеметрии;
- Выполнить logoff, перезагрузить или выключить сервер.
Все пункт в меню
sconfig
пронумерованы. Чтобы перейти в определенное меню наберите его номер и Enter.
В некоторых пунктах меню настройки sconfig есть вложенные пункты. Там также, чтобы перейти к определенной настройке, нужно сделать выбор цифры пункта меню.
Не будем подробно рассматривать все пункты настройки sconfig, т.к. там все достаточно просто и очевидно. Однако в большинстве случаев администраторы предпочитают использовать для настройки новых хостов с Server Core различные PowerShell скрипты. Это намного проще и быстрее, особенно при массовых развёртываниях.
Основные команды PowerShell для настройки Server Core
Рассмотрим основные команды PowerShell, которые можно использовать для настройки Server Core.
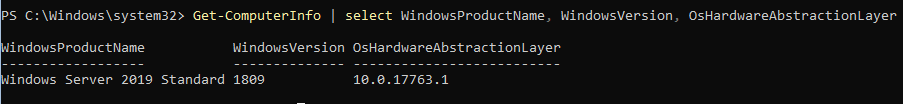
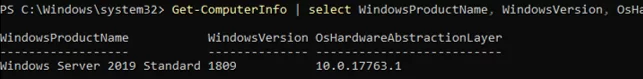
Узнать информацию о версии Windows Server и версии PowerShell:
Get-ComputerInfo | select WindowsProductName, WindowsVersion, OsHardwareAbstractionLayer
$PSVersionTable
Для перезагрузки Server Core нужно выполнить команду PowerShell :
Restart-Computer
Чтобы выполнить выход из консоли Server Core, наберите:
logoff
Настройка параметров сети
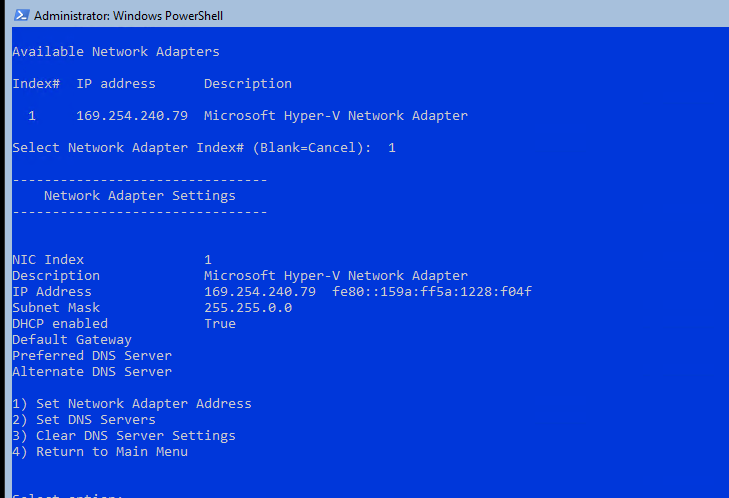
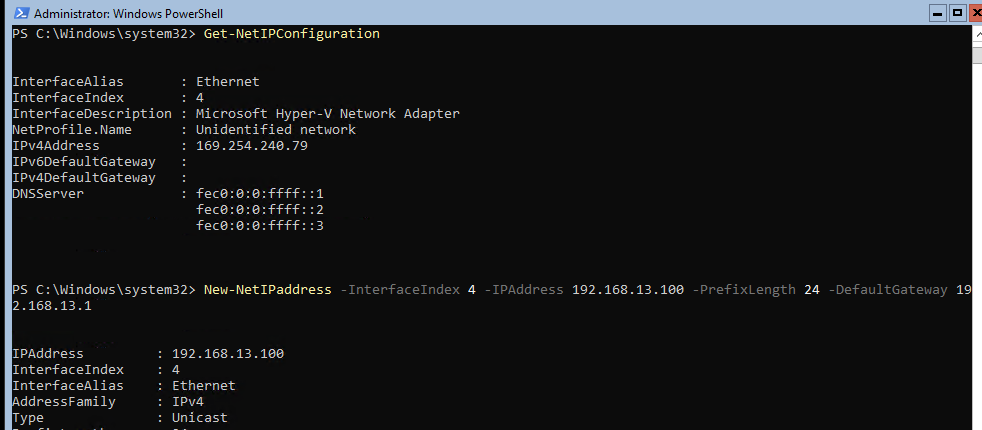
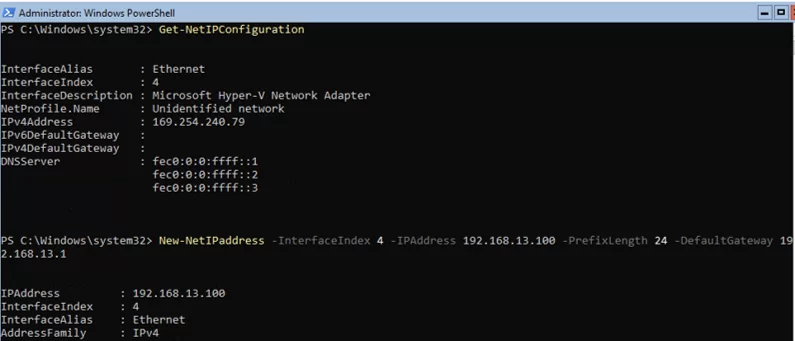
Теперь нужно из PowerShell нужно настроить параметры сети (по умолчанию Windows настроена на получение адреса от DHCP). Выведите список сетевых подключений:
Get-NetIPConfiguration
Теперь укажите индекс интерфейса сетевого адаптера (InterfaceIndex), который нужно изменить и задайте новый IP адрес:
New-NetIPaddress -InterfaceIndex 4 -IPAddress 192.168.13.100 -PrefixLength 24 -DefaultGateway 192.168.13.1
Set-DNSClientServerAddress –InterfaceIndex 4 -ServerAddresses 192.168.13.11,192.168.13.
111
Проверьте текущие настройки:
Get-NetIPConfiguration
Если нужно сбросить IP адрес и вернуться к получению адреса от DHCP, выполните:
Set-DnsClientServerAddress –InterfaceIndex 4 –ResetServerAddresses
Set-NetIPInterface –InterfaceIndex 4 -Dhcp Enabled
Включить/отключить сетевой адаптер:
Disable-NetAdapter -Name “Ethernet0”
Enable-NetAdapter -Name “Ethernet 0”
Включить, отключить, проверить статус поддержки IPv6 для сетевого адаптера:
Disable-NetAdapterBinding -Name "Ethernet0" -ComponentID ms_tcpip6
Enable-NetAdapterBinding -Name "Ethernet0" -ComponentID ms_tcpip6
Get-NetAdapterBinding -ComponentID ms_tcpip6
Настроить winhttp прокси сервер для PowerShell и системных подключений:
netsh Winhttp set proxy <servername>:<port number>
Настройка времени/даты
Вы можете настроить дату, время, часовой пояс с помощью графической утилиты
intl.cpl
или с помощью PowerShell:
Set-Date -Date "09/03/2022 09:00"
Set-TimeZone "Russia Time Zone 3
Задать имя компьютера, добавить в домен, активация
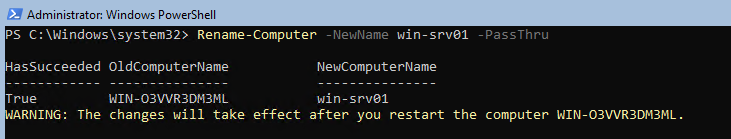
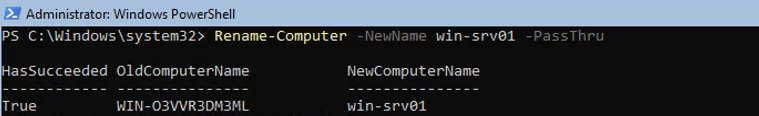
Чтобы изменить имя компьютера:
Rename-Computer -NewName win-srv01 -PassThru
Добавить сервер в домен Active Directory:
Add-Computer -DomainName "corp.winitpro.ru " -Restart
Если нужно добавить дополнительных пользователей в администраторы, можно настроить групповую политику или добавить вручную:
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group "Administrators" -Member "corp\anovikov"
Для активации Windows Server нужно указать ваш ключ:
slmgr.vbs –ipk <productkey>
slmgr.vbs –ato
Или можно активировать хост на KMS сервере (например, для Windows Server 2019):
slmgr /ipk N69G4-B89J2-4G8F4-WWYCC-J464C
slmgr /skms kms-server.winitpro.ru:1688
slmgr /ato
Разрешить удаленный доступ
Разрешить удаленный доступ к Server Core через RDP:
cscript C:\Windows\System32\Scregedit.wsf /ar 0
Разрешить удаленное управление:
Configure-SMRemoting.exe –Enable
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup “Windows Remote Management”
Текущие настройки:
Configure-SMRemoting.exe -Get
Разрешить Win-Rm PowerShell Remoting:
Enable-PSRemoting –force
Сервером с Windows Server можно управлять удаленно c другого сервера (с помощью ServerManager.exe), через браузер с помощью Windows Admin Center (WAC), с любой рабочей станции с помощью инструментов администрирования RSAT, подключаться к нему по RDP, PowerShell Remoting или SSH (в современных версиях Windows есть встроенный SSH сервер).
Настройка Windows Firewall
Информация о настройке Windows Firewall есть в статье по ссылке. Здесь оставлю несколько базовых команд.
Включить Windows Defender Firewall для всех профилей:
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain,Public,Private -Enabled True
Изменить тип сети с Public на Private:
Get-NetConnectionProfile | Set-NetConnectionProfile -NetworkCategory Private
Полностью отключить Windows Firewall (не рекомендуется):
Get-NetFirewallProfile | Set-NetFirewallProfile -enabled false
Разрешить подключение через инструменты удаленного управления:
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayName “Windows Management Instrumentation (DCOM-In)”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Event Log Management”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Service Management”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Volume Management”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Scheduled Tasks Management”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Windows Firewall Remote Management”
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Administration"
Установка обновлений в Server Core
Для управления параметрами обновлений предпочтительно использовать групповые политики Windows Update, но можно задать параметры и вручную.
Отключить автоматическое обновление:
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU -Name AUOptions -Value 1
Автоматически скачивать доступные обновления:
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU -Name AUOptions -Value 3
Получить список установленных обновлений:
Get-Hotfix
Или
wmic qfe list
Для ручной установки обновлений Windows можно использовать утилиту wusa:
Wusa update_name.msu /quiet
Также для установки и управления обновлениями из командной строки удобно использовать PowerShell модуль PSWindowsUpdate.
Управление ролями, службами и процессами Windows
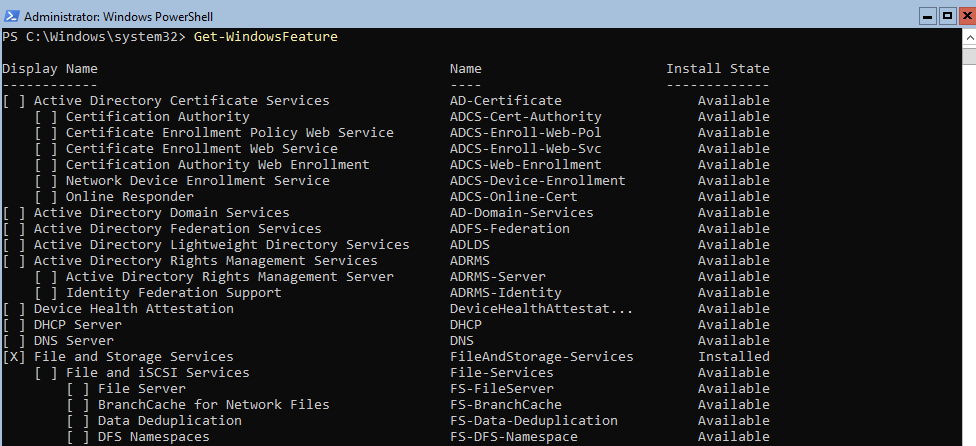
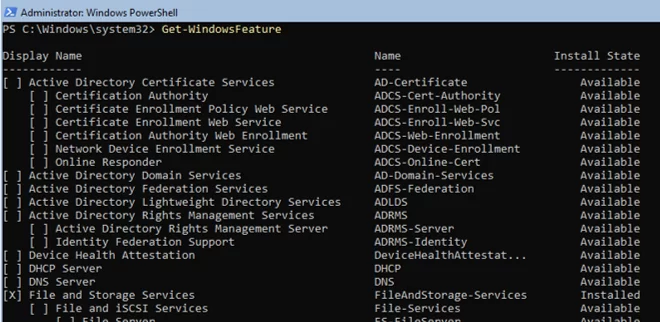
Для получения списка всех доступных ролей в Windows Server Core выполните команду PowerShell:
Get-WindowsFeature
Получить список всех установленных ролей и компонентов в Windows Server(можно быстро понять, для чего используется сервер):
Get-WindowsFeature | Where-Object {$_. installstate -eq "installed"} | ft Name,Installstate
Например, для установки службы DNS воспользуйтесь такой командой:
Install-WindowsFeature DNS -IncludeManagementTools
Список всех служб в Windows:
Get-Service
Список остановленных служб:
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.status -eq “stopped”}
Перезапустить службу:
Restart-Service -Name spooler
Для управление процессами можно использовать стандартный диспетчер задач (taskmgr.exe) или PowerShell модуль Processes:
Get-Process cmd, proc1* | Select-Object ProcessName, StartTime, MainWindowTitle, Path, Company|ft
Часто используемые команды в Server Core
Ну и наконец, приведу список различных полезных мне команд, которые я периодически использую в Server Core.
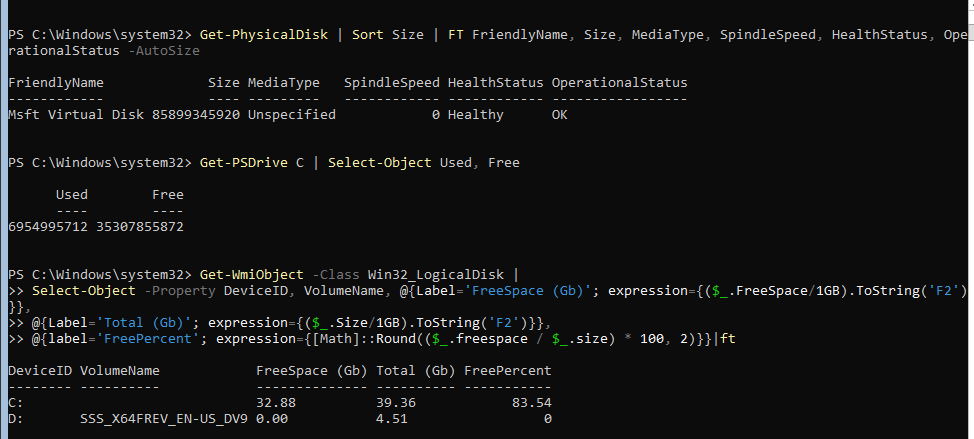
Информация о статусе и здоровье физических дисков (используется стандартный модуль управления дисками Storage):
Get-PhysicalDisk | Sort Size | FT FriendlyName, Size, MediaType, SpindleSpeed, HealthStatus, OperationalStatus -AutoSize
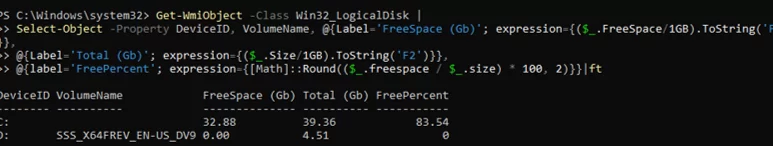
Информация о свободном месте на диске:
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_LogicalDisk |
Select-Object -Property DeviceID, VolumeName, @{Label='FreeSpace (Gb)'; expression={($_.FreeSpace/1GB).ToString('F2')}},
@{Label='Total (Gb)'; expression={($_.Size/1GB).ToString('F2')}},
@{label='FreePercent'; expression={[Math]::Round(($_.freespace / $_.size) * 100, 2)}}|ft
Информация о времени последних 10 перезагрузок сервера:
Get-EventLog system | where-object {$_.eventid -eq 6006} | select -last 10
Список установленных программ:
Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion, Publisher, InstallDate | Format-Table –AutoSize
Скачать и распаковать zip файл с внешнего сайта:
Invoke-WebRequest https://contoso/test.zip -outfile test.zip
Expand-Archive -path '.\test.zip' -DestinationPath C:\Users\Administrator\Documents\
Чтобы скопировать все файлы из каталога на удаленный компьютер по сети можно использовать Copy-Item:
$session = New-PSSession -ComputerName remotsnode1
Copy-Item -Path "C:\Logs\*" -ToSession $session -Destination "C:\Logs\" -Recurse -Force
Для установки драйвера можно использовать стандартную утилиту:
Pnputil –i –a c:\distr\hpdp.inf
Также Microsoft предлагает специальный пакет Server Core App Compatibility Feature on Demand (FOD), который позволяет установить в Windows Server 2019 некоторые графические инструменты и консоли (MMC, Eventvwr, Hyper-V Manager, PerfMon, Resmon, Explorer.exe, Device Manager, Powershell ISE). Этот FOD доступен для загрузки в виде ISO при наличии активной подписки. Установка выполняется командой:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name ServerCore.AppCompatibility~~~~0.0.1.0
Установка Server Core App Compatibility Feature on Demand будет использовать дополнительно около 200 Мб оперативной памяти в Server Core.
В этой статье я постарался собрать самые нужные команды, которые нужно постоянно держать под рукой при работе с Windows Server Core. Время от времени я буду обновлять статью и добавлять новые команды, которые покажутся мне нужными для повседневной работы.
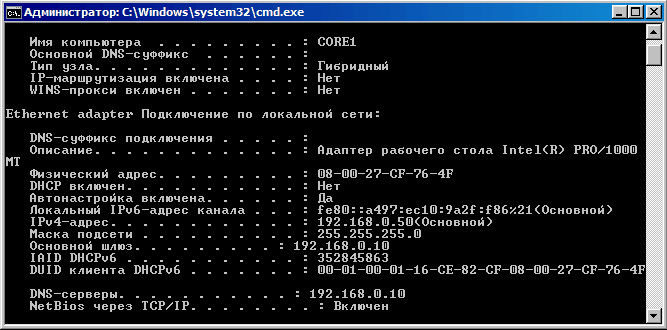
Все что мы видим после установки Windows Server 2008 в режиме Server Core — это пустой рабочий стол и командная строка. Для того чтобы управлять сервером, нам надо будет произвести некоторые первоначальные настройки — задать имя и IP-адрес, открыть нужные порты на файерволе и установить инструменты для удаленного управления. Настройку можно произвести двумя способами. Итак, способ первый:
Командная строка
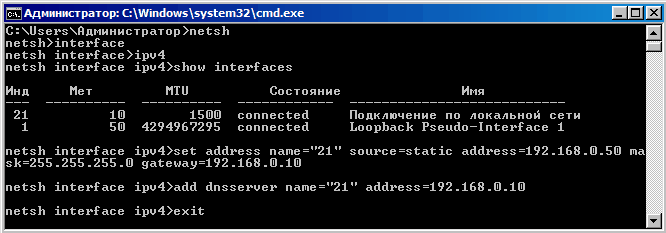
В первую очередь настраиваем сеть. Последовательно вводим команду netsh, затем interface, затем ipv4 (после каждой команды жмем Ввод) и попадаем в строку управления сетевыми интерфейсами. Смотрим имеющиеся в наличии:
show interfaces
Выбираем нужный нам и задаем его сетевые настройки (name — индекс выбранного сетевого интерфейса, в нашем случае 21):
set address name=″21″ source=static address=192.168.0.50 mask=255.255.255.0 gateway=192.168.0.10
И адрес DNS-сервера (если сервер не один, то задаем index=1,2…):
add dnsserver name=″21″ address=192.168.0.10 index=1
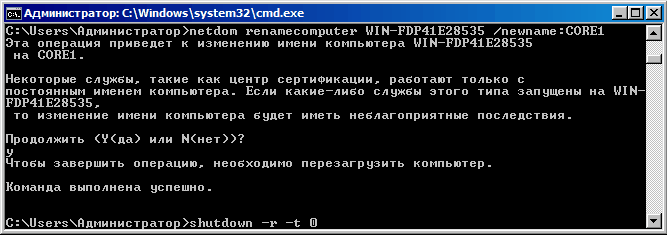
Теперь дадим нашему серверу имя. Вводим команду hostname и узнаем текущее имя, сгенерированное при установке. Поскольку оно нас не устраивает, зададим нашему серверу новое имя CORE1 :
netdom renamecomputer WIN-FDP41E28535 /newname:CORE1
Проверяем получившиеся настройки: ipconfig /all
Затем обязательно перезагружаем сервер: shutdown -r -t 0
Теперь наш сервер виден в сети.
Идем дальше и выставляем дату и время на сервере. Хоть в ServerCore и нет графической оболочки, но некоторыми оснастками панели управления воспользоваться можно. Так, введя команду control timedate.cpl мы откроем оснастку ″Дата и время″, а командой control intl.cpl — ″Региональные настройки″.
Активируем сервер с помощью менеджера лицензий slmgr.vbs :
slmgr -ipk <ключ продукта>
slmgr -ato
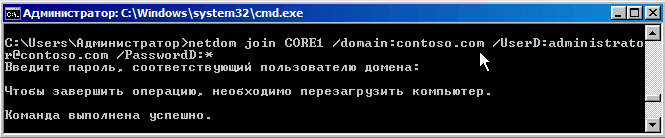
И теперь самое время вводить наш сервер в домен:
netdom join CORE1 /domain:contoso.com /UserD:administrator@contoso.com /PasswordD:*
Еще раз перезагружаемся.
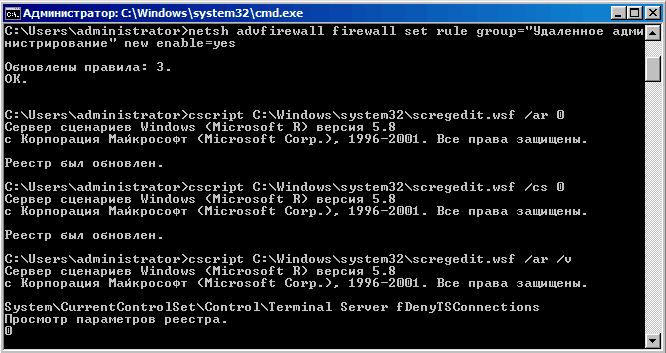
Теперь устанавливаем и настраиваем инструменты удаленного управления. В первую очередь открываем на файерволе порты, необходимые для удаленного управления помощью оснасток MMC:
netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group=″Удаленное администрирование″ new enable=yes
Примечание. Если у вас английская версия ОС, то вместо ″Удаленное администрирование″ вводим ″Remote administration″
Затем разрешаем подключение к удаленному рабочему столу:
cscript C:\windows\system32\scregedit.wsf /ar 0
Для возможности подключения к серверу с клиентов ниже, чем Windows Vista/Windows Server 2008, отключаем высокий уровень безопасности, установленный по умолчанию:
cscript C:\windows\system32\scregedit.wsf /cs 0
И проверяем результат:
cscript C:\windows\system32\scregedit.wsf /ar /v
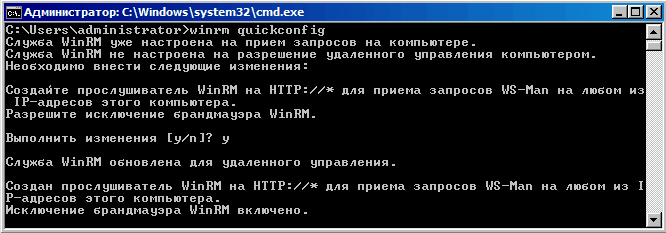
Еще один инструмен удаленного управления — Windows Remote Management (WinRM). Настроим его командой:
WinRM quickconfig
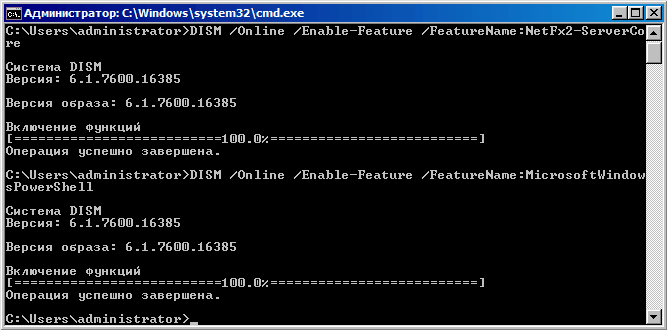
И теперь настроим удаленное управление сервером с помощью оснастки Server Manager. Для этого нам прийдется установить NetFramework и PowerShell:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:NetFx2-ServerCore
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:MicrosoftWindowsPowerShell
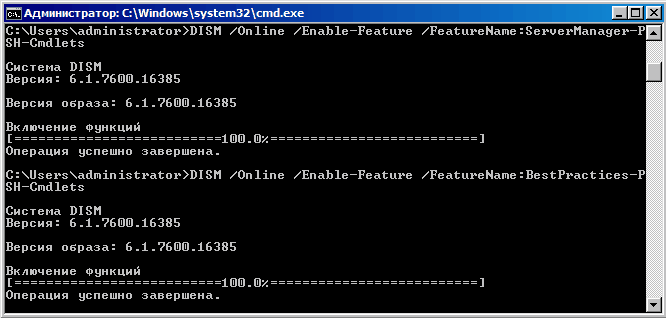
Устанавливаем остальные недостающие компоненты:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:ServerManager-PSH-Cmdlets
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:BestPractices-PSH-Cmdlets
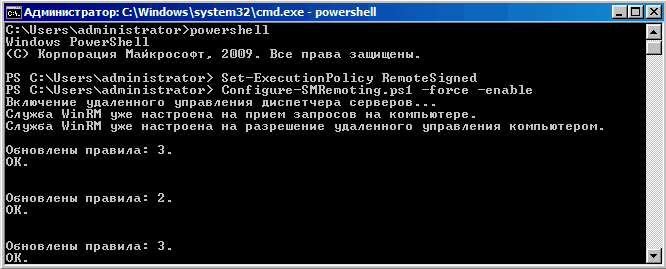
Перезагружаемся и вводим команду powershell. Затем меняем политику выполнения скриптов в PowerShell (по умолчанию выполнение скриптов запрещено):
Set-EsecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
И разрешаем удаленное управление в PowerShell:
Configure-SMRemoting.ps1 -force -enable
На этом первоначальная настройка закончена.
А теперь для тех, кто не переносит командную строку, второй способ настройки:
Скрипт первоначальной конфигурации Sconfig
Просто вводим в командной строке команду sconfig и попадаем в окно настроек:
Выбрав пункт 1, можем изменить имя компьютера. Однако, можно не делать этого отдельно, при вводе в домен программа сама выдаст запрос на изменение имени.
Для настройки сети выбираем номер параметра 8. Здесь задаем IP-адрес, маску и шлюз по умолчанию, а также DNS сервера.
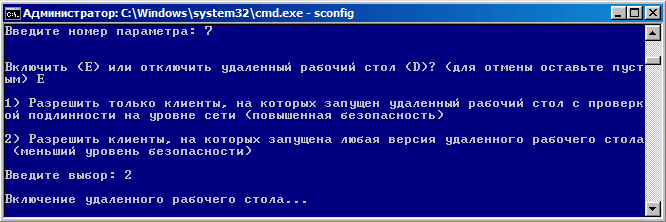
Выбрав пункт 7 мы включаем удаленный рабочий стол:
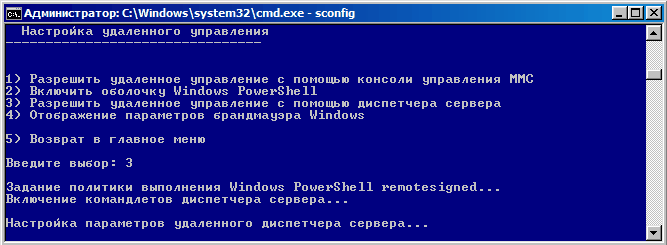
А пункт 4 позволяет нам настроить удаленное управление. Сначала устанавливаем открываем порты на файерволе (пункт 1), затем устанавливаем PowerShell (пункт 2). При этом все компоненты устанавливаются автоматически. После этого потребуется перезагрузка, а потом выбираем пункт 3 и разрешаем удаленное управление:
Вот и все. Теперь можно управлять сервером удаленно, с помощью любого из вышеперечисленных способов.
In this article, I tried to describe basic cmd and PowerShell commands used to configure and manage Windows Server Core. I think this guide will be useful both for beginners and experienced system administrators as a reference to basic Server Core administration commands.
Contents:
- Configure Windows Server Core Using SCONFIG
- Basic PowerShell Commands to Configure Server Core
- Useful Windows Server Core Commands
Server Core is a special Windows Server installation mode without most graphical tools and snap-ins. You can manage the Server Core from the command prompt or remotely (using Windows Admin Center or other tools).
Windows Server Core advantages:
- Lower resource requirements;
- Improved stability and security; fewer updates are required (due to less amount of code and used components);
- Ideally suits for use as an infrastructure role server (Active Directory domain controller, DHCP server, Hyper-V host, SMB file server, etc.).
Server Core is licensed as a common physical or virtual Windows Server instance (unlike Hyper-V Server that is totally free).
To install Windows Server 2016/2019 in the Core mode, you must select a typical installation. If you select Windows Server (Desktop Experience), the GUI version of the operating system will be installed (in previous Windows Server versions it was called a Server with a GUI).
You cannot switch between Full GUI and Core modes in Windows Server 2016/2019 without server reinstallation.
After Windows Server Core installation, you will be prompted to set a local administrator password.
When you log on to Server Core, the command prompt appears (cmd.exe). If you want the PowerShell console to be run instead of it, make some changes to the registry. Run the commands below:
Powershell.exe
Set-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\WinLogon' -Name Shell -Value 'PowerShell.exe'
And restart your server:
Restart-Computer -Force
If you have accidentally closed the command prompt window, press Ctrl+Alt+Delete, open the Task Manager -> File -> Run -> and run cmd.exe (or PowerShell.exe).
Configure Windows Server Core Using SCONFIG
You can use the built-in sconfig script for basic Server Core configuration. Just run the sconfig command in your console. You will see a menu with several items:
Using the Server Configuration menu, you can do the following:
- Add a computer to a domain or a workgroup
- Change a computer name (hostname)
- Add a local administrator
- Allow/deny remote management and ICMP response
- Configure Windows Update settings
- Install Windows updates
- Enable/disable RDP
- Configure network adapter settings (IP address, gateway, DNS server)
- Set date and time
- Change telemetry settings
- Activate your Windows Server instance
- Log off, restart or shut down your server
Each item in sconfig has its number. To open the item you want, just type its number and press Enter.
Some sconfig menu items have subitems. To get to a setting, you also need to enter its number.
We will not describe all sconfig settings, since they are easy to understand. However, in most cases, administrators prefer using various PowerShell scripts to configure new hosts running Server Core. It is easier and faster, especially in mass deployment scenarios.
Basic PowerShell Commands to Configure Server Core
Let’s take a look at the basic PowerShell commands that can be used to configure Server Core.
To get information about your Windows Server build and PowerShell version:
Get-ComputerInfo | select WindowsProductName, WindowsVersion, OsHardwareAbstractionLayer
$PSVersionTable
To restart Server Core, run this PowerShell command:
Restart-Computer
To log off your Server Core console, use the command below:
logoff
Configure Network Settings on Server Core with PowerShell
Now you need to configure network settings using PowerShell (by default, Windows is configured to receive an IP address from DHCP). Display a list of network adapters:
Get-NetIPConfiguration
Specify an index of your network adapter interface (InterfaceIndex) you want to change and set a new IP address and DNS servers:
New-NetIPaddress -InterfaceIndex 4 -IPAddress 192.168.1.100 -PrefixLength 24 -DefaultGateway 192.168.1.1
Set-DNSClientServerAddress –InterfaceIndex 4 -ServerAddresses 192.168.1.11,192.168.101.11
Check the current network settings:
Get-NetIPConfiguration
If you want to reset an IP address and return to getting an IP address from DHCP, run the command below:
Set-DnsClientServerAddress –InterfaceIndex 4 –ResetServerAddresses
Set-NetIPInterface –InterfaceIndex 4 -Dhcp Enabled
To enable/disable a network adapter:
Disable-NetAdapter -Name “Ethernet0”
Enable-NetAdapter -Name “Ethernet 0”
To enable, disable, or check the status of IPv6 support for your network adapter:
Disable-NetAdapterBinding -Name "Ethernet0" -ComponentID ms_tcpip6
Enable-NetAdapterBinding -Name "Ethernet0" -ComponentID ms_tcpip6
Get-NetAdapterBinding -ComponentID ms_tcpip6
To configure winhttp proxy server for PowerShell or system connections:
netsh Winhttp set proxy <servername>:<port number>
How to Set Date/Time?
You can set a date, time, or time zone using a graphical tool intl.cpl or PowerShell:
Set-Date -Date "07/21/2021 09:00"
Set-TimeZone "Central Europe Standard Time”
Set Computer Name, Join Domain, and Activate Server Core
To change a computer name (hostname):
Rename-Computer -NewName be-srv01 -PassThru
To add a server to your on-premises Active Directory domain:
Add-Computer -DomainName "corp.woshub.com" -Restart
If you want to add additional users to the local administrators group, you can configure a Group Policy or add them manually:
Add-LocalGroupMember -Group "Administrators" -Member "corp\jsmith"
To activate Windows Server, enter your product key:
slmgr.vbs –ipk <productkey>
slmgr.vbs –ato
Or you may activate your host on a KMS server. For example, to activate Windows Server Core 2019 Standart on a KMS host:
slmgr /ipk N69G4-B89J2-4G8F4-WWYCC-J464C
slmgr /skms kms.corp.woshub.com:1688
slmgr /ato
Enabling Remote Administration of Windows Server Core
To allow remote access to Server Core via RDP:
cscript C:\Windows\System32\Scregedit.wsf /ar 0
To allow remote management:
Configure-SMRemoting.exe –Enable
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup “Windows Remote Management”
To display current Remote Management settings:
Configure-SMRemoting.exe -Get
To allow Win-RM for PowerShell Remoting:
Enable-PSRemoting –force
You can manage a server running Windows Server Core remotely from another server (using ServerManager.exe), through a browser using Windows Admin Center (WAC), from any workstation using RSAT, you can also connect to it using RDP, PowerShell Remoting, or SSH (current Windows versions have build-in SSH server).
Configuring Windows Firewall on Server Core
You can find information about how to configure Windows Defender Firewall with PowerShell in this article. I will just show some basic commands here.
To enable Windows Defender Firewall for all profiles:
Set-NetFirewallProfile -Profile Domain,Public,Private -Enabled True
To change your network type from Public to Private:
Get-NetConnectionProfile | Set-NetConnectionProfile -NetworkCategory Private
To completely disable Windows Firewall (not recommended):
Get-NetFirewallProfile | Set-NetFirewallProfile -enabled false
To allow connection using remote management tools:
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayName “Windows Management Instrumentation (DCOM-In)”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Event Log Management”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Service Management”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Volume Management”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Scheduled Tasks Management”
Enable-NetFireWallRule -DisplayGroup “Windows Firewall Remote Management”
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Administration"
How to Install Updates on Windows Server Core?
To manage update options, it is better to use Windows Update Group Policies. However, you can set the update settings manually.
To disable automatic update:
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU -Name AUOptions -Value 1
To automatically download available updates:
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU -Name AUOptions -Value 3
To get the list of installed updates:
Get-Hotfix
Or
wmic qfe list
To install Windows updates manually, you can use the wusa tool:
wusa kbnamexxxxx.msu /quiet
To install and manage updates from the command prompt, it is convenient to use the PSWindowsUpdate module for PowerShell.
Managing Windows Core Roles, Services, and Processes
To get a list of all available roles on Windows Server Core, run the following PowerShell command:
Get-WindowsFeature
To get a list of all installed roles and features in Windows Server (thus you can quickly understand what the server is used for):
Get-WindowsFeature | Where-Object {$_. installstate -eq "installed"} | ft Name,Installstate
For example, to install the DNS role, run this command:
Install-WindowsFeature DNS -IncludeManagementTools
To get a list of all services in Windows:
Get-Service
To see all stopped services:
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.status -eq “stopped”}
To restart a service:
Restart-Service -Name spooler
To manage processes, you can use the Task Manager (taskmgr.exe) or the PowerShell Processes module:
Get-Process cmd, wuaucl* | Select-Object ProcessName, StartTime, MainWindowTitle, Path, Company|ft
Useful Windows Server Core Commands
Finally, I will show some useful PowerShell commands and scripts I often use to manage Server Core.
Information about the status and health of physical disks (the default Storage disk management module is used):
Get-PhysicalDisk | Sort Size | FT FriendlyName, Size, MediaType, SpindleSpeed, HealthStatus, OperationalStatus -AutoSize
Free disk space information:
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_LogicalDisk |
Select-Object -Property DeviceID, VolumeName, @{Label='FreeSpace (Gb)'; expression={($_.FreeSpace/1GB).ToString('F2')}},
@{Label='Total (Gb)'; expression={($_.Size/1GB).ToString('F2')}},
@{label='FreePercent'; expression={[Math]::Round(($_.freespace / $_.size) * 100, 2)}}|ft
Information about the last 10 reboots of your server:
Get-EventLog system | where-object {$_.eventid -eq 6006} | select -last 10
A list of installed programs:
Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion, Publisher, InstallDate | Format-Table –AutoSize
To download and extract a ZIP file from an external website:
Invoke-WebRequest https://servername/file.zip -outfile file.zip
Expand-Archive -path '.\file.zip' -DestinationPath C:\Users\Administrator\Documents\
To copy all files from a directory to a remote computer over the network, you can use the Copy-Item cmdlet:
$session = New-PSSession -ComputerName be-dc01
Copy-Item -Path "C:\Logs\*" -ToSession $session -Destination "C:\Logs\" -Recurse -Force
To install the device driver:
Pnputil –i –a c:\install\hpspp\hpdp.inf
Microsoft also offers a special package, Server Core App Compatibility Feature on Demand (FOD), which allows you to install some graphical tools and snap-ins on Windows Core Server 2019 (MMC, Eventvwr, Hyper-V Manager, PerfMon, Resmon, Explorer.exe, Device Manager, Powershell ISE). You can download FOD as an ISO file if your Microsoft subscription is active. You can install it as follows:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name ServerCore.AppCompatibility~~~~0.0.1.0
Server Core App Compatibility Feature on Demand installation will use about 200 MB of additional RAM on your Server Core.
In this article, I tried to collect the most useful commands needed to administer Windows Server Core. From time to time, I will update the article and add new commands if they seem necessary for everyday work.
В данной статье описывается 2 способа настройки сети в ОС Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Core: с помощью утилиты netsh в командной строке и консоли PowerShell.
Задача такая: необходимо настроить сеть машины с Windows Server 2019 Core с IP-адресом 192.168.1.54/24, шлюзом 192.168.1.1 и доступом к серверам доменных имён 8.8.8.8 и 8.8.4.4
Для выполнения всех действий необходимы права администратора.
Настройка сети с помощью утилиты netsh
В первую очередь нам необходимо выяснить, как в системе называется сетевой адаптер. Для этого вводим команду:
# ipconfig
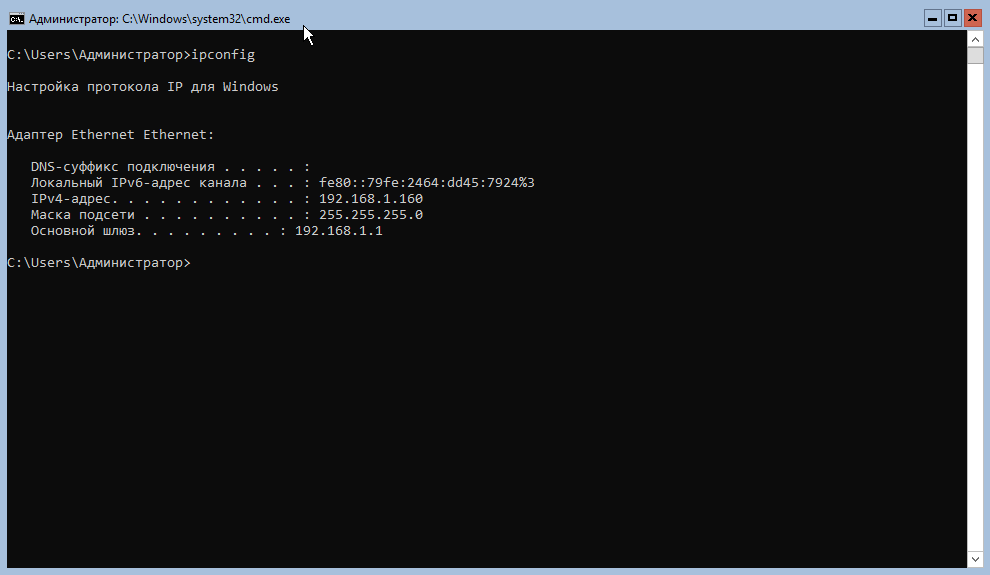
Из скриншота выше видим, что Адаптер Ethernet у нас называется Ethernet
Для того, чтобы настроить статический IP-адрес, маску и шлюз, вводим команду:
# netsh interface ip set address "Ethernet" static 192.168.1.54 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Ethernet — имя адаптера ethernet, как показано на скриншоте выше.
После этого пропишем IP-адреса первичного и альтернативного DNS-серверов:
# netsh interface ipv4 set dnsservers Ethernet static 8.8.8.8 primary # netsh interface ipv4 add dnsservers Ethernet 8.8.4.4 index=2
Готово!
Для того, чтобы вернуть все настройки обратно, необходимо ввести команды сброса сетевых настроек на получение от DHCP-сервера:
# netsh interface ipv4 set dnsservers Ethernet dhcp # netsh interface ip set address Ethernet dhcp
Настройка сети с помощью PowerShell
Выясняем, как называется сетевой адаптер на машине:
# Get-NetAdapter
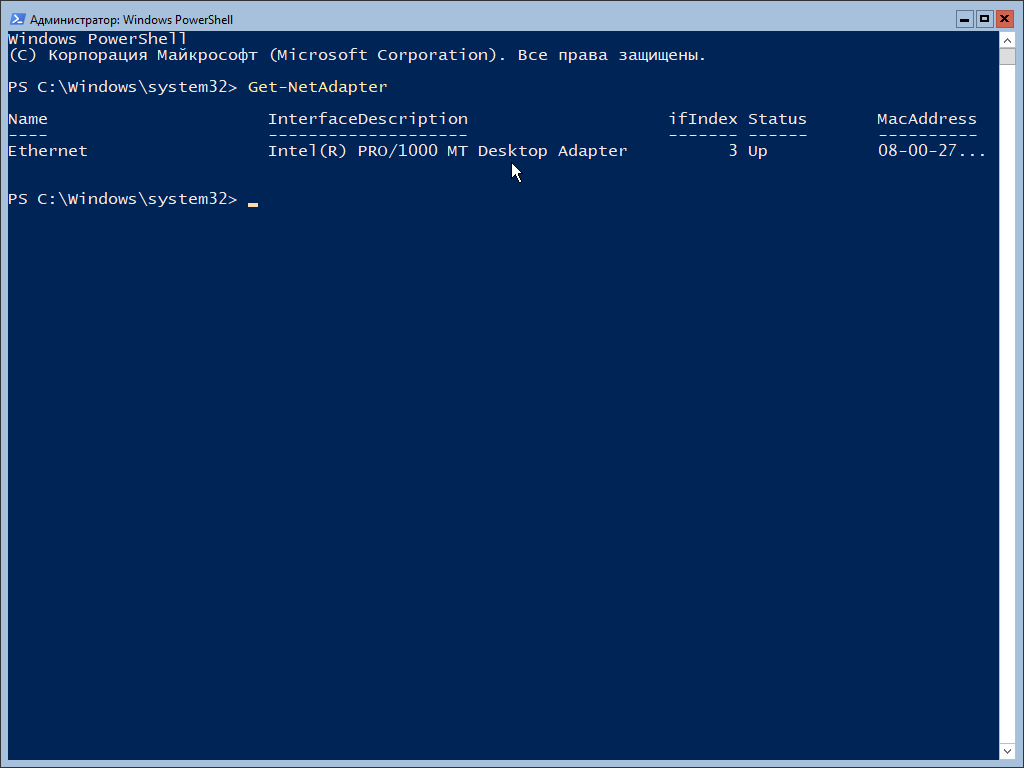
Из скриншота выше понятно, что имя сетевого интерфейса — Ethernet
Для того, чтобы настроить статический IP-адрес, маску и шлюз, вводим команду:
# Get-NetAdapter -Name Ethernet | New-NetIPAddress -IPAddress 192.168.1.54 -PrefixLength 24 -DefaultGateway 192.168.1.1
Ethernet — имя адаптера ethernet, как показано на скриншоте выше.
После этого пропишем IP-адреса первичного и альтернативного DNS-серверов:
# Get-NetAdapter -Name Ethernet | Set-DnsClientServerAddress -ServerAddresses 8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4
Проверяем конфигурацию сетевого интерфейса:
# Get-NetIPConfiguration -Detailed
Готово!
Для того, чтобы вернуть все настройки обратно, необходимо ввести команды сброса сетевых настроек на получение от DHCP-сервера
# Set-NetIPInterface -InterfaceAlias Ethernet -Dhcp Enabled # Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceAlias Ethernet -ResetServerAddresses
и перезапустим сетевой интерфейс для того, чтобы изменения вступили в силу
# Restart-NetAdapter -InterfaceAlias Ethernet
Готово!
Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel) and Windows Server 2016
Because Server Core doesn’t have a UI, you need to use Windows PowerShell cmdlets, command line tools, or remote tools to perform basic administration tasks. The following sections outline the PowerShell cmdlets and commands used for basic tasks. You can also use Windows Admin Center, a unified management portal currently in public preview, to administer your installation.
First from the cmd prompt start PowerShell
C:\Users\Administrator> powershell PS C:\Users\Administrator>
Administrative tasks using PowerShell cmdlets
Use the following information to perform basic administrative tasks with Windows PowerShell cmdlets.
Set a static IP address
When you install a Server Core server, by default it has A DHCP address. If you need a static IP address, you can set it using the following steps.
To view your current network configuration, use Get-NetIPConfiguration.
To view the IP addresses you’re already using, use Get-NetIPAddress.
To set a static IP address, do the following:
-
Run Get-NetIPInterface.
-
Note the number in the IfIndex column for your IP interface or the InterfaceDescription string. If you have more than one network adapter, note the number or string corresponding to the interface you want to set the static IP address for.
-
Run the following cmdlet to set the static IP address:
PowerShell
New-NetIPaddress -InterfaceIndex 12 -IPAddress 192.0.2.2 -PrefixLength 24 -DefaultGateway 192.0.2.1where:
- InterfaceIndex is the value of IfIndex from step 2. (In our example, 12)
- IPAddress is the static IP address you want to set. (In our example, 191.0.2.2)
- PrefixLength is the prefix length (another form of subnet mask) for the IP address you’re setting. (For our example, 24)
- DefaultGateway is the IP address to the default gateway. (For our example, 192.0.2.1)
-
Run the following cmdlet to set the DNS client server address:
PowerShell
Set-DNSClientServerAddress –InterfaceIndex 12 -ServerAddresses 192.0.2.4where:
- InterfaceIndex is the value of IfIndex from step 2.
- ServerAddresses is the IP address of your DNS server.
-
To add multiple DNS servers, run the following cmdlet:
PowerShell
Set-DNSClientServerAddress –InterfaceIndex 12 -ServerAddresses 192.0.2.4,192.0.2.5where, in this example, 192.0.2.4 and 192.0.2.5 are both IP addresses of DNS servers.
If you need to switch to using DHCP, run Set-DnsClientServerAddress –InterfaceIndex 12 –ResetServerAddresses.
Join a domain
Use the following cmdlets to join a computer to a domain.
-
Run Add-Computer. You’ll be prompted for both credentials to join the domain and the domain name.
-
If you need to add a domain user account to the local Administrators group, run the following command at a command prompt (not in the PowerShell window):
net localgroup administrators /add <DomainName>\<UserName> -
Restart the computer. You can do this by running Restart-Computer.
Rename the server
Use the following steps to rename the server.
- Determine the current name of the server with the hostname or ipconfig command.
- Run Rename-Computer -ComputerName <new_name>.
- Restart the computer.
Activate the server
Run slmgr.vbs –ipk<productkey>. Then run slmgr.vbs –ato. If activation succeeds, you won’t get a message.
Note
You can also activate the server by phone, using a Key Management Service (KMS) server, or remotely. To activate remotely, run the following cmdlet from a remote computer:
PowerShell
**cscript windows\system32\slmgr.vbs <ServerName> <UserName> <password>:-ato**
Configure Windows Firewall
You can configure Windows Firewall locally on the Server Core computer using Windows PowerShell cmdlets and scripts. See NetSecurity for the cmdlets you can use to configure Windows Firewall.
Enable Windows PowerShell remoting
You can enable Windows PowerShell Remoting, in which commands typed in Windows PowerShell on one computer run on another computer. Enable Windows PowerShell Remoting with Enable-PSRemoting.
For more information, see About Remote FAQ.
Administrative tasks from the command line
Use the following reference information to perform administrative tasks from the command line.
Configuration and installation
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Set the local administrative password | net user administrator * |
| Join a computer to a domain | netdom join %computername% /domain:<domain> /userd:<domain\username> /passwordd:* Restart the computer. |
| Confirm that the domain has changed | set |
| Remove a computer from a domain | netdom remove <computername> |
| Add a user to the local Administrators group | net localgroup Administrators /add <domain\username> |
| Remove a user from the local Administrators group | net localgroup Administrators /delete <domain\username> |
| Add a user to the local computer | net user <domain\username> * /add |
| Add a group to the local computer | net localgroup <group name> /add |
| Change the name of a domain-joined computer | netdom renamecomputer %computername% /NewName:<new computer name> /userd:<domain\username> /passwordd: * |
| Confirm the new computer name | set |
| Change the name of a computer in a work group | netdom renamecomputer <currentcomputername> /NewName:<newcomputername> Restart the computer. |
| Disable paging file management | wmic computersystem where name=»<computername>» set AutomaticManagedPagefile=False |
| Configure the paging file | wmic pagefileset where name=”<path/filename>” set InitialSize=<initialsize>,MaximumSize=<maxsize> Where path/filename is the path to and name of the paging file, initialsize is the starting size of the paging file, in bytes, and maxsize is the maximum size of the page file, in bytes. |
| Change to a static IP address | ipconfig /all Record the relevant information or redirect it to a text file (ipconfig /all >ipconfig.txt). netsh interface ipv4 show interfaces Verify that there is an interface list. netsh interface ipv4 set address name <ID from interface list> source=static address=<preferred IP address> gateway=<gateway address> Run ipconfig /all to verify that DHCP enabled is set to No. |
| Set a static DNS address. | netsh interface ipv4 add dnsserver name=<name or ID of the network interface card> address=<IP address of the primary DNS server> index=1 netsh interface ipv4 add dnsserver name=<name of secondary DNS server> address=<IP address of the secondary DNS server> index=2** Repeat as appropriate to add additional servers. Run ipconfig /all to verify that the addresses are correct. |
| Change to a DHCP-provided IP address from a static IP address | netsh interface ipv4 set address name=<IP address of local system> source=DHCP Run ipconfig /all to verify that DCHP enabled is set to Yes. |
| Enter a product key | slmgr.vbs –ipk <product key> |
| Activate the server locally | slmgr.vbs -ato |
| Activate the server remotely | cscript slmgr.vbs –ipk <product key><server name><username><password> cscript slmgr.vbs -ato <servername> <username> <password> Get the GUID of the computer by running cscript slmgr.vbs -did Run cscript slmgr.vbs -dli <GUID> Verify that License status is set to Licensed (activated). |
Networking and firewall
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Configure your server to use a proxy server | netsh Winhttp set proxy <servername>:<port number> Note: Server Core installations can’t access the Internet through a proxy that requires a password to allow connections. |
| Configure your server to bypass the proxy for Internet addresses | netsh winttp set proxy <servername>:<port number> bypass-list=»<local>» |
| Display or modify IPSEC configuration | netsh ipsec |
| Display or modify NAP configuration | netsh nap |
| Display or modify IP to physical address translation | arp |
| Display or configure the local routing table | route |
| View or configure DNS server settings | nslookup |
| Display protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections | netstat |
| Display protocol statistics and current TCP/IP connections using NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NBT) | nbtstat |
| Display hops for network connections | pathping |
| Trace hops for network connections | tracert |
| Display the configuration of the multicast router | mrinfo |
| Enable remote administration of the firewall | netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group=”Windows Firewall Remote Management” new enable=yes |
Updates, error reporting, and feedback
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Install an update | wusa <update>.msu /quiet |
| List installed updates | systeminfo |
| Remove an update | expand /f:* <update>.msu c:\test Navigate to c:\test\ and open <update>.xml in a text editor. Replace Install with Remove and save the file. pkgmgr /n:<update>.xml |
| Configure automatic updates | To verify the current setting: cscript %systemroot%\system32\scregedit.wsf /AU /v ** To enable automatic updates: **cscript scregedit.wsf /AU 4 To disable automatic updates: cscript %systemroot%\system32\scregedit.wsf /AU 1 |
| Enable error reporting | To verify the current setting: serverWerOptin /query To automatically send detailed reports: serverWerOptin /detailed To automatically send summary reports: serverWerOptin /summary To disable error reporting: serverWerOptin /disable |
| Participate in the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) | To verify the current setting: serverCEIPOptin /query To enable CEIP: serverCEIPOptin /enable To disable CEIP: serverCEIPOptin /disable |
Services, processes, and performance
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| List the running services | sc query or net start |
| Start a service | sc start <service name> or net start <service name> |
| Stop a service | sc stop <service name> or net stop <service name> |
| Retrieve a list of running applications and associated processes | tasklist |
| Start Task Manager | taskmgr |
| Create and manage event trace session and performance logs | To create a counter, trace, configuration data collection or API: logman ceate To query data collector properties: logman query To start or stop data collection: logman start|stop To delete a collector: logman delete To update the properties of a collector: logman update To import a data collector set from an XML file or export it to an XML file: logman import|export |
Event logs
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| List event logs | wevtutil el |
| Query events in a specified log | wevtutil qe /f:text <log name> |
| Export an event log | wevtutil epl <log name> |
| Clear an event log | wevtutil cl <log name> |
Disk and file system
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Manage disk partitions | For a complete list of commands, run diskpart /? |
| Manage software RAID | For a complete list of commands, run diskraid /? |
| Manage volume mount points | For a complete list of commands, run mountvol /? |
| Defragment a volume | For a complete list of commands, run defrag /? |
| Convert a volume to the NTFS file system | convert <volume letter> /FS:NTFS |
| Compact a file | For a complete list of commands, run compact /? |
| Administer open files | For a complete list of commands, run openfiles /? |
| Administer VSS folders | For a complete list of commands, run vssadmin /? |
| Administer the file system | For a complete list of commands, run fsutil /? |
| Take ownership of a file or folder | For a complete list of commands, run icacls /? |
Hardware
| Task | Command |
|---|---|
| Add a driver for a new hardware device | Copy the driver to a folder at %homedrive%\<driver folder>. Run pnputil -i -a %homedrive%\<driver folder>\<driver>.inf |
| Remove a driver for a hardware device | For a list of loaded drivers, run sc query type= driver. Then run sc delete <service_name> |
You can manage a Server Core server in the following ways:
You can also add hardware and manage drivers locally, as long as you do that from the command line.
There are some important limitations and tips to keep in mind when you work with Server Core:
Managing Server Core with Windows Admin Center
Windows Admin Center is a browser-based management app that enables on-premises administration of Windows Servers with no Azure or cloud dependency. Windows Admin Center gives you full control over all aspects of your server infrastructure and is particularly useful for management on private networks that are not connected to the Internet. You can install Windows Admin Center on Windows 10, on a gateway server, or on an installation of Windows Server with Desktop Experience, and then connect to the Server Core system that you want to manage.
Managing Server Core remotely with Server Manager
Server Manager is a management console in Windows Server that helps you provision and manage both local and remote Windows-based servers from your desktops, without requiring either physical access to servers, or the need to enable Remote Desktop protocol (RDP) connections to each server. Server Manager supports remote, multi-server management.
To enable your local server to be managed by Server Manager running on a remote server, run the Windows PowerShell cmdlet Configure-SMRemoting.exe –Enable.
Managing with Microsoft Management Console
You can use many snap-ins for Microsoft Management Console (MMC) remotely to manage your Server Core server.
To use an MMC snap-in to manage a Server Core server that is a domain member:
To use an MMC snap-in to manage a Server Core server that is not a domain member:
To configure Windows Firewall to allow MMC snap-in(s) to connect
To allow all MMC snap-ins to connect, run the following command:
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "Remote Administration"
To allow only specific MMC snap-ins to connect, run the following:
Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup "<rulegroup>"
Where rulegroup is one of the following, depending on which snap-in you want to connect:
| MMC snap-in | Rule group |
|---|---|
| Event Viewer | Remote Event Log Management |
| Services | Remote Service Management |
| Shared Folders | File and Printer Sharing |
| Task Scheduler | Performance Logs and Alerts, File and Printer Sharing |
| Disk Management | Remote Volume Management |
| Windows Firewall and Advanced Security | Windows Firewall Remote Management |
Note
Some MMC snap-ins don’t have a corresponding rule group that allows them to connect through the firewall. However, enabling the rule groups for Event Viewer, Services, or Shared Folders will allow most other snap-ins to connect.
Additionally, certain snap-ins require further configuration before they can connect through Windows Firewall:
Managing with Remote Desktop Services
You can use Remote Desktop to manage a Server Core server from remote computers.
Before you can access Server Core, you’ll need to run the following command:
cscript C:\Windows\System32\Scregedit.wsf /ar 0
This enables the Remote Desktop for Administration mode to accept connections.
Add hardware and manage drivers locally
To add hardware to a Server Core server, follow the instructions provided by the hardware vendor for installing new hardware.
If the hardware is not plug and play, you’ll need to manually install the driver. To do that, copy the driver files to a temporary location on the server, and then run the following command:
pnputil –i –a <driverinf>
Where driverinf is the file name of the .inf file for the driver.
If prompted, restart the computer.
To see what drivers are installed, run the following command:
sc query type= driver
Note
You must include the space after the equal sign for the command to complete successfully.
To disable a device driver, run the following:
sc delete <service_name>
Where service_name is the name of the service that you got when you ran sc query type= driver.
- Using Windows Admin Center
- Using Remote Server Administration Tools running on Windows 10
- Locally and remotely using Windows PowerShell
- Remotely using Server Manager
- Remotely using an MMC snap-in
- Remotely with Remote Desktop Services
- If you close all command prompt windows and want to open a new Command Prompt window, you can do that from the Task Manager. Press CTRL+ALT+DELETE, click Start Task Manager, click More Details > File > Run, and then type cmd.exe. (Type Powershell.exe to open a PowerShell command windows.) Alternatively, you can sign out and then sign back in.
- Any command or tool that attempts to start Windows Explorer will not work. For example, running start . from a command prompt won’t work.
- There is no support for HTML rendering or HTML help in Server Core.
- Server Core supports Windows Installer in quiet mode so that you can install tools and utilities from Windows Installer files. When installing Windows Installer packages on Server Core, use the /qb option to display the basic user interface.
- To change the time zone, run Set-Date.
- To change international settings, run control intl.cpl.
- Control.exe won’t run on its own. You must run it with either Timedate.cpl or Intl.cpl.
- Winver.exe isn’t available in Server Core. To obtain version information use Systeminfo.exe.
- Start an MMC snap-in, such as Computer Management.
- Right-click the snap-in, and then click Connect to another computer.
- Type the computer name of the Server Core server, and then click OK. You can now use the MMC snap-in to manage the Server Core server as you would any other PC or server.
-
Establish alternate credentials to use to connect to the Server Core computer by typing the following command at a command prompt on the remote computer:
-
cmdkey /add:<ServerName> /user:<UserName> /pass:<password>If you want to be prompted for a password, omit the /pass option.
-
When prompted, type the password for the user name you specified. If the firewall on the Server Core server is not already configured to allow MMC snap-ins to connect, follow the steps below to configure Windows Firewall to allow MMC snap-in. Then continue with step 3.
-
On a different computer, start an MMC snap-in, such as Computer Management.
-
In the left pane, right-click the snap-in, and then click Connect to another computer. (For example, in the Computer Management example, you would right-click Computer Management (Local).)
-
In Another computer, type the computer name of the Server Core server, and then click OK. You can now use the MMC snap-in to manage the Server Core server as you would any other computer running a Windows Server operating system.
- Disk Management. You must first start the Virtual Disk Service (VDS) on the Server Core computer. You must also configure the Disk Management rules appropriately on the computer that is running the MMC snap-in.
- IP Security Monitor. You must first enable remote management of this snap-in. To do this, at a command prompt, type Cscript \windows\system32\scregedit.wsf /im 1
- Reliability and Performance. The snap-in does not require any further configuration, but when you use it to monitor a Server Core computer, you can only monitor performance data. Reliability data is not available.
Patch a Server Core installation
You can patch a server running Server Core installation in the following ways:
View the updates installed on your Server Core server
Before you add a new update to Server Core, it’s a good idea to see what updates have already been installed.
To view updates by using Windows PowerShell, run Get-Hotfix.
To view updates by running a command, run systeminfo.exe. There might be a short delay while the tool inspects your system.
You can also run wmic qfe list from the command line.
Patch Server Core automatically with Windows Update
Use the following steps to patch the server automatically with Windows Update:
If the server is a member of a domain, you can also configure Windows Update using Group Policy. For more information, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=192470. However, when you use this method, only option 4 («Auto download and schedule the install») is relevant to Server Core installations because of the lack of a graphical interface. For more control over which updates are installed and when, you can use a script which provides a command-line equivalent of most of the Windows Update graphical interface. For information about the script, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=192471.
To force Windows Update to immediately detect and install any available updates, run the following command:
Wuauclt /detectnow
Depending on the updates that are installed, you may need to restart the computer, although the system will not notify you of this. To determine if the installation process has completed, use Task Manager to verify that the Wuauclt or Trusted Installerprocesses are not actively running. You can also use the methods in View the updates installed on your Server Core server to check the list of installed updates.
Patch the server with WSUS
If the Server Core server is a member of a domain, you can configure it to use a WSUS server with Group Policy. For more information, download the Group Policy reference information. You can also review Configure Group Policy Settings for Automatic Updates
Patch the server manually
Download the update and make it available to the Server Core installation. At a command prompt, run the following command:
Wusa <update>.msu /quiet
Depending on the updates that are installed, you may need to restart the computer, although the system will not notify you of this.
To uninstall an update manually, run the following command:
Wusa /uninstall <update>.msu /quiet -
Using Windows Update automatically or with Windows Server Update Services (WSUS). By using Windows Update, either automatically or with command-line tools, or Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), you can service servers running a Server Core installation.
-
Manually. Even in organizations that do not use Windows update or WSUS, you can apply updates manually.
-
Verify the current Windows Update setting:
%systemroot%\system32\Cscript scregedit.wsf /AU /v -
To enable automatic updates:
Net stop wuauserv %systemroot%\system32\Cscript scregedit.wsf /AU 4 Net start wuauserv -
To disable automatic updates, run:
Net stop wuauserv %systemroot%\system32\Cscript scregedit.wsf /AU 1 Net start wuauserv
Server Manager
Server Manager is a management console in Windows Server that helps IT professionals provision and manage both local and remote Windows-based servers from their desktops, without requiring either physical access to servers, or the need to enable Remote Desktop protocol (rdP) connections to each server. Although Server Manager is available in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2008, Server Manager was updated in Windows Server 2012 to support remote, multi-server management, and help increase the number of servers an administrator can manage.
In our tests, Server Manager in Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012 can be used to manage up to 100 servers, depending on the workloads that the servers are running. The number of servers that you can manage by using a single Server Manager console can vary depending on the amount of data that you request from managed servers, and hardware and network resources available to the computer running Server Manager. As the amount of data you want to display approaches that computer’s resource capacity, you can experience slow responses from Server Manager, and delays in the completion of refreshes. To help increase the number of servers that you can manage by using Server Manager, we recommend limiting the event data that Server Manager gets from your managed servers, by using settings in the Configure Event Data dialog box. Configure Event Data can be opened from the Tasks menu in the Events tile. If you need to manage an enterprise-level number of servers in your organization, we recommend evaluating products in the Microsoft System Center suite.
This topic and its subtopics provide information about how to use features in the Server Manager console. This topic contains the following sections.
Review initial considerations and system requirements
The following sections list some initial considerations that you need to review, as well as hardware and software requirements for Server Manager.
Hardware requirements
Server Manager is installed by default with all editions of Windows Server 2016. No additional hardware requirements exist for Server Manager.
Software and configuration requirements
Server Manager is installed by default with all editions of Windows Server 2016. You can use Server Manager in Windows Server 2016 to manage Server Core installation options of Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 , and Windows Server 2008 R2 that are running on remote computers. Server Manager does run on the Server Core installation option of Windows Server 2016.
Server Manager runs in the Minimal Server Graphical Interface; that is, when the Server Graphical Shell feature is not installed. The Server Graphical Shell feature is not installed by default on Windows Server 2016. If you are not running Server Graphical Shell, the Server Manager console runs, but some applications or tools available from the console are not available. Internet browsers cannot run without Server Graphical Shell, so webpages and applications such as HTML help (The mmc F1 help, for example) cannot be opened. You cannot open dialog boxes for configuring Windows automatic updating and feedback when Server Graphical Shell is not installed; commands that open these dialog boxes in the Server Manager console are redirected to run sconfig.cmd.
To manage servers that are running Windows Server releases older than Windows Server 2016, install the following software and updates to make the older releases of Windows Server manageable by using Server Manager in Windows Server 2016.
| Operating System | Required Software |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 | — .NET Framework 4.6 — Windows Management Framework 5.0. The Windows Management Framework 5.0 download package updates Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) providers on Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2012 . The updated WMI providers let Server Manager collect information about roles and features that are installed on the managed servers. Until the update is applied, servers that are running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 have a manageability status of Not accessible. — The performance update associated with Knowledge Base article 2682011 is no longer necessary on servers that are running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 . |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | — .NET Framework 4.5 — Windows Management Framework 4.0. The Windows Management Framework 4.0 download package updates Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) providers on Windows Server 2008 R2 . The updated WMI providers let Server Manager collect information about roles and features that are installed on the managed servers. Until the update is applied, servers that are running Windows Server 2008 R2 have a manageability status of Not accessible. — The performance update associated with Knowledge Base article 2682011 lets Server Manager collect performance data from Windows Server 2008 R2 . |
| Windows Server 2008 | — .NET Framework 4 — Windows Management Framework 3.0 The Windows Management Framework 3.0 download package updates Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) providers on Windows Server 2008 . The updated WMI providers let Server Manager collect information about roles and features that are installed on the managed servers. Until the update is applied, servers that are running Windows Server 2008 have a manageability status of Not accessible — verify earlier versions run Windows Management Framework 3.0. — The performance update associated with Knowledge Base article 2682011 lets Server Manager collect performance data from Windows Server 2008 . |
Manage remote computers from a client computer
The Server Manager console is included with Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10. Note that when Remote Server Administration Tools is installed on a client computer, you cannot manage the local computer by using Server Manager; Server Manager cannot be used to manage computers or devices that are running a Windows client operating system. You can only use Server Manager to manage Windows-based servers.
| Server Manager Source Operating System | Targeted at Windows Server 2016 | Targeted at Windows Server 2012 R2 | Targeted at Windows Server 2012 | Targeted at Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows Server 2008 | Targeted at Windows Server 2003 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016 | Full support | Full support | Full support | After Software and configuration requirements are satisfied, can perform most management tasks, but no role or feature installation or uninstallation | Not supported |
| Windows 8.1 or Windows Server 2012 R2 | Not supported | Full support | Full support | After Software and configuration requirements are satisfied, can perform most management tasks, but no role or feature installation or uninstallation | Limited support; online and offline status only |
| Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012 | Not supported | Not supported | Full support | After Software and configuration requirements are satisfied, can perform most management tasks, but no role or feature installation or uninstallation | Limited support; online and offline status only |
To start Server Manager on a client computer
for more information about running Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 to manage remote servers, see Remote Server Administration Tools on the TechNet Wiki.
Configure remote management on servers that you want to manage
Important
By default, Server Manager and Windows PowerShell remote management is enabled in Windows Server 2016.
To perform management tasks on remote servers by using Server Manager, remote servers that you want to manage must be configured to allow remote management by using Server Manager and Windows PowerShell. If remote management has been disabled on Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 , and you want to enable it again, perform the following steps.
To configure Server Manager remote management on Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 by using the Windows interface
To enable Server Manager remote management on Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 by using Windows PowerShell
To enable Server Manager and Windows PowerShell remote management on older operating systems
Tasks that you can perform in Server Manager
Server Manager makes server administration more efficient by allowing administrators to do tasks in the following table by using a single tool. In Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2012 , both standard users of a server and members of the Administrators group can perform management tasks in Server Manager, but by default, standard users are prevented from performing some tasks, as shown in the following table.
Administrators can use two Windows PowerShell cmdlets in the Server Manager cmdlet module, Enable-ServerManagerStandardUserremoting and Disable-ServerManagerStandardUserremoting, to further control standard user access to some additional data. The Enable-ServerManagerStandardUserremoting cmdlet can provide one or more standard, non-Administrator users access to event, service, performance counter, and role and feature inventory data.
Important
Server Manager cannot be used to manage a newer release of the Windows Server operating system. Server Manager running on Windows Server 2012 or Windows 8 cannot be used to manage servers that are running Windows Server 2012 R2 .
| Task Description | Administrators (including the built-in Administrator account) | Standard Server Users |
|---|---|---|
| add remote servers to a pool of servers that Server Manager can be used to manage. | Yes | No |
| create and edit custom groups of servers, such as servers that are in a specific geographic location or serve a specific purpose. | Yes | Yes |
| Install or uninstall roles, role services, and features on the local or on remote servers that are running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2012 . For definitions of roles, role services, and features, see Roles, Role Services, and Features. | Yes | No |
| View and make changes to server roles and features that are installed on either local or remote servers. Note: In Server Manager, role and feature data is displayed in the base language of the system, also called the system default GUI language, or the language selected during installation of the operating system. | Yes | Standard users can view and manage roles and features, and perform tasks such as viewing role events, but cannot add or remove role services. |
| start management tools such as Windows PowerShell or mmc snap-ins. You can start a Windows PowerShell session targeted at a remote server by right-clicking the server in the Servers tile, and then clicking Windows PowerShell. You can start mmc snap-ins from the Tools menu of the Server Manager console, and then point the mmc toward a remote computer after the snap-in is open. | Yes | Yes |
| Manage remote servers with different credentials by right-clicking a server in the Servers tile, and then clicking Manage As. You can use Manage As for general server and File and Storage Services management tasks. | Yes | No |
| Perform management tasks associated with the operational lifecycle of servers, such as starting or stopping services; and start other tools that allow you to configure a server’s network settings, users and groups, and Remote Desktop connections. | Yes | Standard users cannot start or stop services. They can change the local server’s name, workgroup, or domain membership and Remote Desktop settings, but are prompted by User Account Control to provide Administrator credentials before they can complete these tasks. They cannot change remote management settings. |
| Perform management tasks associated with the operational lifecycle of roles that are installed on servers, including scanning roles for compliance with best practices. | Yes | Standard users cannot run Best Practices Analyzer scans. |
| Determine server status, identify critical events, and analyze and troubleshoot configuration issues or failures. | Yes | Yes |
| Customize the events, performance data, services, and Best Practices Analyzer results about which you want to be alerted on the Server Manager dashboard. | Yes | Yes |
| Restart servers. | Yes | No |
| Refresh data that is displayed in the Server Manager console about managed servers. | Yes | No |
Note
Server Manager cannot be used to add roles and features to servers that are running Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows Server 2008 .
start Server Manager
Server Manager starts automatically by default on servers that are running Windows Server 2016 when a member of the Administrators group logs on to a server. If you close Server Manager, restart it in one of the following ways. This section also contains steps for changing the default behavior, and preventing Server Manager from starting automatically.
To start Server Manager from the start screen
To start Server Manager from the Windows desktop
To prevent Server Manager from starting automatically
Restart remote servers
You can restart a remote server from the Servers tile of a role or group page in Server Manager.
Important
Restarting a remote server forces the server to restart, even if users are still logged on to the remote server, and even if programs with unsaved data are still open. This behavior is different from shutting down or restarting the local computer, on which you would be prompted to save unsaved program data, and verify that you wanted to force logged-on users to log off. Be sure that you can force other users to log off of remote servers, and that you can discard unsaved data in programs that are running on the remote servers.
if an automatic refresh occurs in Server Manager while a managed server is shutting down and restarting, refresh and manageability status errors can occur for the managed server, because Server Manager cannot connect to the remote server until it is finished restarting.
To restart remote servers in Server Manager
Export Server Manager settings to other computers
In Server Manager, your list of managed servers, changes to Server Manager console settings, and custom groups that you have created are stored in the following two files. You can reuse these settings on other computers that are running the same release of Server Manager (or Windows 10 with Remote Server Administration Tools installed). Remote Server Administration Tools must be running on Windows client-based computers to export Server Manager settings to those computers.
Note
You can export Server Manager settings, make Server Manager settings portable, or use them on other computers in one of the following two ways.
To export Server Manager settings to other domain-joined computers
To export Server Manager settings to computers in workgroups
-
Review initial considerations and system requirements
-
Tasks that you can perform in Server Manager
-
start Server Manager
-
Restart remote servers
-
Export Server Manager settings to other computers
-
Follow instructions in Remote Server Administration Tools to install Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10.
-
On the start screen, click Server Manager. The Server Manager tile is available after you install Remote Server Administration Tools.
-
if neither the Administrative Tools nor the Server Manager tiles are displayed on the start screen after installing Remote Server Administration Tools, and searching for Server Manager on the start screen does not display results, verify that the Show administrative tools setting is turned on. To view this setting, hover the mouse cursor over the upper right corner of the start screen, and then click Settings. If Show administrative tools is turned off, turn the setting on to display tools that you have installed as part of Remote Server Administration Tools.
-
Note
The settings that are controlled by the Configure remote Management dialog box do not affect parts of Server Manager that use DCOM for remote communications.
Do one of the following to open Server Manager if it is not already open.
-
On the Windows taskbar, click the Server Manager button.
-
On the start screen, click Server Manager.
-
-
In the Properties area of the Local Servers page, click the hyperlinked value for the remote management property.
-
Do one of the following, and then click OK.
-
To prevent this computer from being managed remotely by using Server Manager (or Windows PowerShell if it is installed), clear the Enable remote management of this server from other computers check box.
-
To let this computer be managed remotely by using Server Manager or Windows PowerShell, select Enable remote management of this server from other computers.
-
-
Do one of the following.
-
To run Windows PowerShell as an administrator from the start screen, right-click the Windows PowerShell tile, and then click Run as Administrator.
-
To run Windows PowerShell as an administrator from the desktop, right-click the Windows PowerShell shortcut in the taskbar, and then click Run as Administrator.
-
-
type the following, and then press Enter to enable all required firewall rule exceptions.
Configure-SMremoting.exe -Enable
Note
This command also works in a command prompt that has been opened with elevated user rights (Run as Administrator).
if enabling remote management fails, see about_remote_Troubleshooting on Microsoft TechNet for troubleshooting tips and best practices.
-
Do one of the following.
-
To enable remote management on servers that are running Windows Server 2008 R2 , see remote Management with Server Manager in the Windows Server 2008 R2 help.
-
To enable remote management on servers that are running Windows Server 2008 , see Enable and Use remote Commands in Windows PowerShell.
-
- On the Windows start screen, click the Server Manager tile.
- On the Windows taskbar, click Server Manager.
-
In the Server Manager console, on the Manage menu, click Server Manager Properties.
-
In the Server Manager Properties dialog box, fill the check box for Do not start Server Manager automatically at logon. Click OK.
-
Alternatively, you can prevent Server Manager from starting automatically by enabling the Group Policy setting, Do not start Server Manager automatically at logon. The path to this policy setting, in the Local Group Policy editor console, is computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Server Manager.
-
Open a role or server group home page in Server Manager.
-
select one or more remote servers that you have added to Server Manager. Press and hold Ctrl as you click to select multiple servers at one time. For more information about how to add servers to the Server Manager server pool, see add Servers to Server Manager.
-
Right-click selected servers, and then click Restart Server.
-
%appdata%\Microsoft\Windows\ServerManager\Serverlist.xml
-
%appdata%\Local\Microsoft_Corporation\ServerManager.exe_StrongName_GUID\6.2.0.0\user.config
- Manage As (or alternate) credentials for servers in your server pool are not stored in the roaming profile. Server Manager users must add them on each computer from which they want to manage.
- The network share roaming profile is not created until a user logs on to the network, and then logs off for the first time. The Serverlist.xml file is created at this time.
-
To export settings to another domain-joined computer, configure the Server Manager user to have a roaming profile in active directory Users and computers. You must be a Domain Administrator to change user properties in active directory Users and computers.
-
To export settings to another computer in a workgroup, copy the preceding two files to the same location on the computer from which you want to manage by using Server Manager.
-
In active directory Users and computers, open the Properties dialog box for a Server Manager user.
-
On the Profile tab, add a path to a network share to store the user’s profile.
-
Do one of the following.
-
On U.S. English (en-us) builds, changes to the Serverlist.xml file are automatically saved to the profile. Go on to the next step.
-
On other builds, copy the following two files from the computer that is running Server Manager to the network share that is part of the user’s roaming profile.
-
%appdata%\Microsoft\Windows\ServerManager\Serverlist.xml
-
%localappdata%\Microsoft_Corporation\ServerManager.exe_StrongName_GUID\6.2.0.0\user.config
-
-
-
Click OK to save your changes and close the Properties dialog box.
-
On a computer from which you want to manage remote servers, overwrite the following two files with the same files from another computer that is running Server Manager, and that has the settings you want.
-
%appdata%\Microsoft\Windows\ServerManager\Serverlist.xml
-
%localappdata%\Microsoft_Corporation\ServerManager.exe_StrongName_GUID\6.2.0.0\user.config
-
This topic supports Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10.
Important
Starting with Windows 10 October 2018 Update, RSAT is included as a set of Features on Demand in Windows 10 itself. See When to use which RSAT version below for installation instructions.
RSAT lets IT admins manage Windows Server roles and features from a Windows 10 PC.
Remote Server Administration Tools includes Server Manager, Microsoft Management Console (mmc) snap-ins, consoles, Windows PowerShell cmdlets and providers, and some command-line tools for managing roles and features that run on Windows Server.
Remote Server Administration Tools includes Windows PowerShell cmdlet modules that can be used to manage roles and features that are running on Remote servers. Although Windows PowerShell remote management is enabled by default on Windows Server 2016, it is not enabled by default on Windows 10. To run cmdlets that are part of Remote Server Administration Tools against a Remote server, run Enable-PSremoting in a Windows PowerShell session that has been opened with elevated user rights (that is, Run as Administrator) on your Windows client computer after installing Remote Server Administration Tools.
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
Use Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 to manage specific technologies on computers that are running Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and in limited cases, Windows Server 2012 , or Windows Server 2008 R2 .
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 includes support for remote management of computers that are running the Server Core installation option or the Minimal Server Interface configuration of Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2 , and in limited cases, the Server Core installation options of Windows Server 2012. However, Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 cannot be installed on any versions of the Windows Server operating system.
Tools available in this release
for a list of the tools available in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, see the table in Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows operating systems.
System requirements
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 can be installed only on computers that are running Windows 10. Remote Server Administration Tools cannot be installed on computers that are running Windows RT 8.1, or other system-on-chip devices.
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 runs on both x86-based and x64-based editions of Windows 10.
Important
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 should not be installed on a computer that is running administration tools packs for Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2003 or Windows 2000 Server. Remove all older versions of Administration Tools Pack or Remote Server Administration Tools, including earlier prerelease versions, and releases of the tools for different languages or locales from the computer before you install Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10.
To use this release of Server Manager to access and manage Remote servers that are running Windows Server 2012 R2 , Windows Server 2012 , or Windows Server 2008 R2 , you must install several updates to make the older Windows Server operating systems manageable by using Server Manager. For detailed information about how to prepare Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2008 R2 for management by using Server Manager in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, see Manage Multiple, Remote Servers with Server Manager.
Windows PowerShell and Server Manager remote management must be enabled on remote servers to manage them by using tools that are part of Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10. Remote management is enabled by default on servers that are running Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012. For more information about how to enable remote management if it has been disabled, see Manage multiple, remote servers with Server Manager.
Use Features on Demand (FoD) to install specific RSAT tools on Windows 10 October 2018 Update, or later
Starting with Windows 10 October 2018 Update, RSAT is included as a set of Features on Demand right from Windows 10. Now, instead of downloading an RSAT package you can just go to Manage optional features in Settings and click Add a feature to see the list of available RSAT tools. Select and install the specific RSAT tools you need. To see installation progress, click the Back button to view status on the Manage optional features page.
See the list of RSAT tools available via Features on Demand. In addition to installing via the graphical Settings app, you can also install specific RSAT tools via command line or automation using DISM /Add-Capability.
One benefit of Features on Demand is that installed features persist across Windows 10 version upgrades!
To uninstall specific RSAT tools on Windows 10 October 2018 Update or later (after installing with FoD)
On Windows 10, open the Settings app, go to Manage optional features, select and uninstall the specific RSAT tools you wish to remove. Note that in some cases, you will need to manually uninstall dependencies. Specifically, if RSAT tool A is needed by RSAT tool B, then choosing to uninstall RSAT tool A will fail if RSAT tool B is still installed. In this case, uninstall RSAT tool B first, and then uninstall RSAT tool A. Also note that in some cases, uninstalling an RSAT tool may appear to succeed even though the tool is still installed. In this case, restarting the PC will complete the removal of the tool.
See the list of RSAT tools including dependencies. In addition to uninstalling via the graphical Settings app, you can also uninstall specific RSAT tools via command line or automation using DISM /Remove-Capability.
When to use which RSAT version
If you have a version of Windows 10 prior to the October 2018 Update (1809), you will not be able to use Features on Demand. You will need to download and install the RSAT package.
Download the RSAT package to install Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
To uninstall Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 (after RSAT package install)
Run Remote Server Administration Tools
Note
After installing Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, the Administrative Tools folder is displayed on the Start menu. You can access the tools from the following locations.
The tools installed as part of Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 cannot be used to manage the local client computer. Regardless of the tool you run, you must specify a remote server, or multiple remote servers, on which to run the tool. Because most tools are integrated with Server Manager, you add remote servers that you want to manage to the Server Manager server pool before managing the server by using the tools in the Tools menu. For more information about how to add servers to your server pool, and create custom groups of servers, see Add servers to Server Manager and Create and manage server groups.
In Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, all GUI-based server management tools, such as mmc snap-ins and dialog boxes, are accessed from the Tools menu of the Server Manager console. Although the computer that runs Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 runs a client-based operating system, after installing the tools, Server Manager, included with Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, opens automatically by default on the client computer. Note that there is no Local Server page in the Server Manager console that runs on a client computer.
To start Server Manager on a client computer
Although they are not listed in the Server Manager console Tools menu, Windows PowerShell cmdlets and Command prompt management tools are also installed for roles and features as part of Remote Server Administration Tools. For example, if you open a Windows PowerShell session with elevated user rights (Run as Administrator), and run the cmdlet Get-Command -Module RDManagement, the results include a list of remote Desktop Services cmdlets that are now available to run on the local computer after installing Remote Server Administration Tools, as long as the cmdlets are targeted at a remote server that is running all or part of the remote Desktop Services role.
To start Windows PowerShell with elevated user rights (Run as administrator)
Note
You can also start a Windows PowerShell session that is targeted at a specific server by right-clicking a managed server in a role or group page in Server Manager, and then clicking Windows PowerShell.
Known issues
Issue: RSAT FOD installation fails with error code 0x800f0954
Impact: RSAT FODs on Windows 10 1809 (October 2018 Update) in WSUS/SCCM environments
Resolution: To install FODs on a domain-joined PC which receives updates through WSUS or SCCM, you will need to change a Group Policy setting to enable downloading FODs directly from Windows Update or a local share. For more details and instructions on how to change that setting, see How to make Features on Demand and language packs available when you’re using WSUS/SCCM.
-
Install RSAT FODs directly from Windows 10, as outlined above: When installing on Windows 10 October 2018 Update (1809) or later, for managing Windows Server 2019 or previous versions.
-
Download and install WS_1803 RSAT package, as outlined below: When installing on Windows 10 April 2018 Update (1803) or earlier, for managing Windows Server, version 1803 or Windows Server, version 1709.
-
Download and install WS2016 RSAT package, as outlined below: When installing on Windows 10 April 2018 Update (1803) or earlier, for managing Windows Server 2016 or previous versions.
-
Download the Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 package from the Microsoft Download Center. You can either run the installer from the Download Center website, or save the download package to a local computer or share.
Important
You can only install Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 on computers that are running Windows 10. Remote Server Administration Tools cannot be installed on computers that are running Windows RT 8.1 or other system-on-chip devices.
-
If you save the download package to a local computer or share, double-click the installer program, WindowsTH-KB2693643-x64.msu or WindowsTH-KB2693643-x86.msu, depending on the architecture of the computer on which you want to install the tools.
-
When you are prompted by the Windows Update Standalone Installer dialog box to install the update, click Yes.
-
Read and accept the license terms. Click I accept.
-
Installation requires a few minutes to finish.
-
On the desktop, click Start, click All Apps, click Windows System, and then click Control Panel.
-
Under Programs, click Uninstall a program.
-
Click View installed updates.
-
Right-click Update for Microsoft Windows (KB2693643), and then click Uninstall.
-
When you are asked if you are sure you want to uninstall the update, click Yes. S
To turn off specific tools (after RSAT package install)
-
On the desktop, click Start, click All Apps, click Windows System, and then click Control Panel.
-
Click Programs, and then in Programs and Features click Turn Windows features on or off.
-
In the Windows Features dialog box, expand Remote Server Administration Tools, and then expand either Role Administration Tools or Feature Administration Tools.
-
Clear the check boxes for any tools that you want to turn off.
Note
If you turn off Server Manager, the computer must be restarted, and tools that were accessible from the Tools menu of Server Manager must be opened from the Administrative Tools folder.
-
When you are finished turning off tools that you do not want to use, click OK.
- The Tools menu in the Server Manager console.
- Control Panel\System and Security\Administrative Tools.
- A shortcut saved to the desktop from the Administrative Tools folder (to do this, right click the Control Panel\System and Security\Administrative Tools link, and then click Create Shortcut).
-
On the Start menu, click All Apps, and then click Administrative Tools.
-
In the Administrative Tools folder, click Server Manager.
-
On the Start menu, click All Apps, click Windows System, and then click Windows PowerShell.
-
To run Windows PowerShell as an administrator from the desktop, right-click the Windows PowerShell shortcut, and then click Run as Administrator.