In this network, a router and 2 PCs are used. Computers are connected with routers using a copper straight-through cable. After forming the network, to check network connectivity a simple PDU is transferred from PC0 to PC1. The network simulation status is successful. From this network, it can be observed that the router handles data transfers between multiple devices.
Procedure:
Step-1(Configuring Router1):
- Select the router and Open CLI.
- Press ENTER to start configuring Router1.
- Type enable to activate the privileged mode.
- Type config t(configure terminal) to access the configuration menu.
- Configure interfaces of Router1:
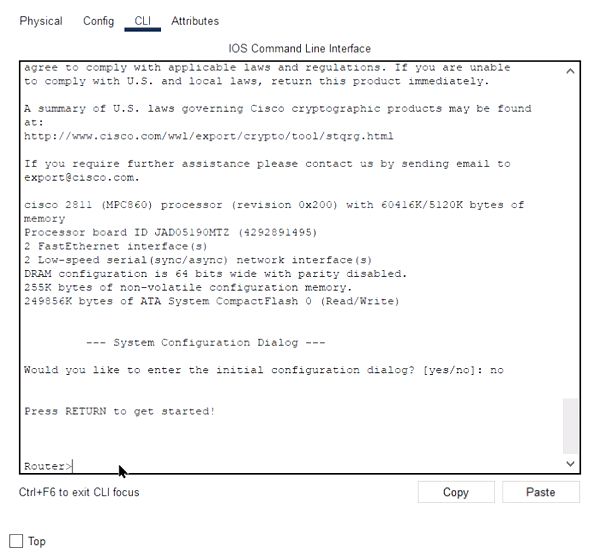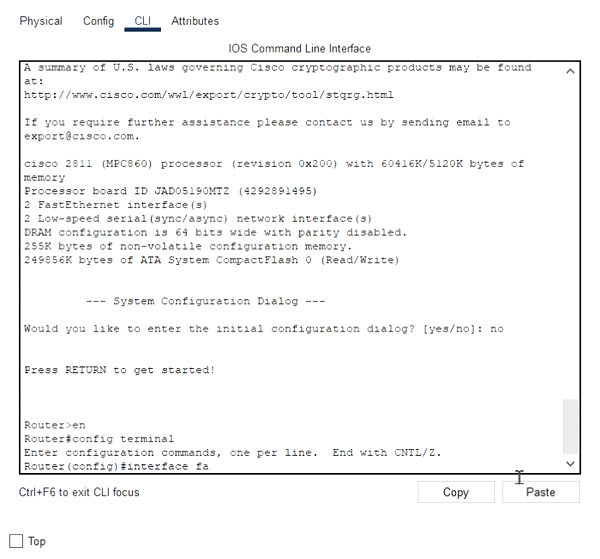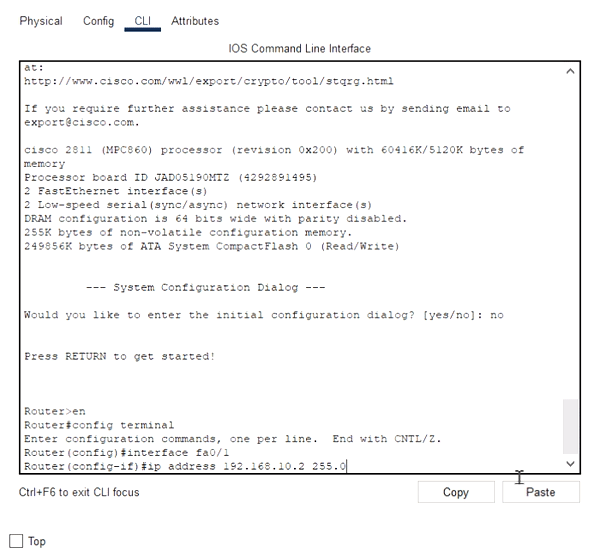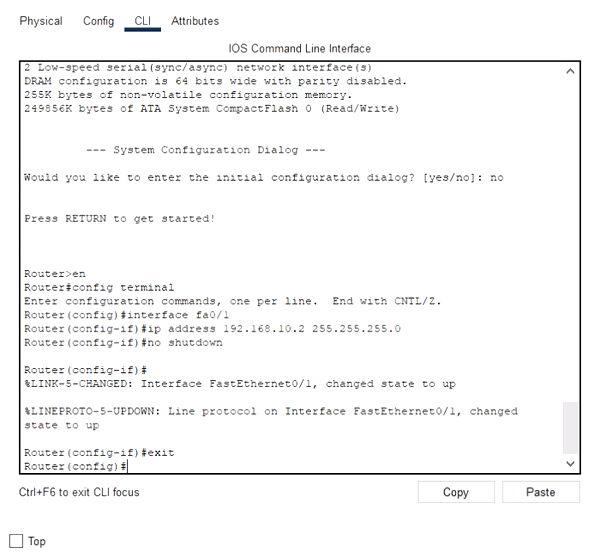
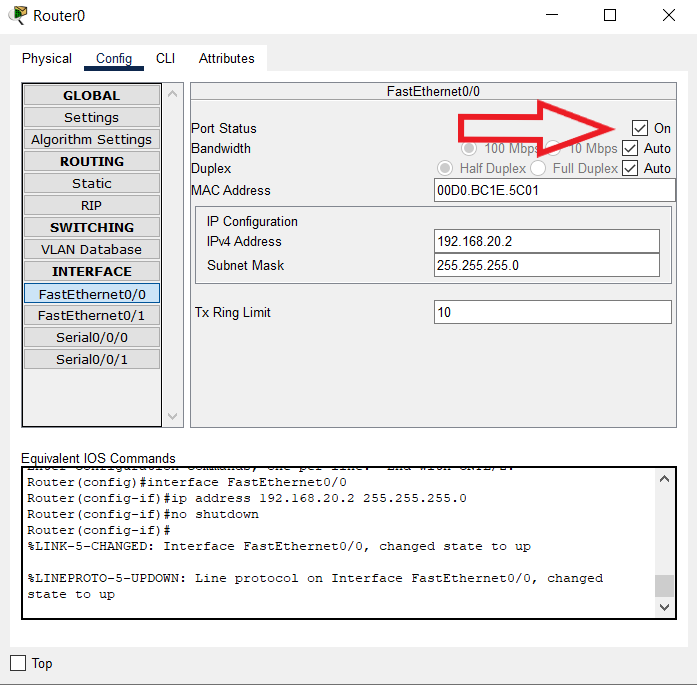
• Type interface FastEthernet0/0 to access FastEthernet0/0 and Configure the FastEthernet0/0 interface with the IP address 192.168.10.1 and Subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
• Type interface FastEthernet0/1 to access GigabitEthernet0/0 and Configure the FastEthernet0/1 interface with IP address 192.168.20.1 and Subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
6. Type no shutdown to finish.
Router1 Command Line Interface:
Router>enable
Router#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#interface FastEthernet0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Router(config-if)#interface FastEthernet0/1
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Step-2(Configuring PCs):
- Assign IP Addresses to every PC in the network.
- Select the PC, Go to the desktop and select IP Configuration and assign an IP address, Default gateway, Subnet Mask
- Assign the default gateway of PC0 as 192.168.10.1.
- Assign the default gateway of PC1 as 192.168.20.1.
Step-3(Connecting PCs with Router):
- Connect FastEthernet0 port of PC0 with FastEthernet0/0 port of Router1 using a copper straight-through cable.
- Connect FastEthernet0 port of PC1 with FastEthernet0/1 port of Router1 using a copper straight-through cable.
Router Configuration Table:
| Device Name | IP address FastEthernet0/0 | Subnet Mask | IP Address FastEthernet0/1 | Subnet Mask |
| Router1 | 192.168.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 |
PC Configuration Table:
| Device Name | IP address | Subnet Mask | Gateway |
| PC 0 | 192.168.10.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.1 |
| PC 1 | 192.168.20.2 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.1 |
Designed Network topology:
Simulation of Designed Network Topology:
Sending a PDU From PC0 to PC1:
Acknowledgment From PC1 to PC0:
Last Updated :
10 Nov, 2021
Like Article
Save Article
Cisco Packet Tracer является отличным инструментом моделирования и визуализации сети, полезным как для обучения как студентов, так и продвинутых пользователей, у которых под рукой нет физического оборудования компании Cisco. Программа-симулятор позволяет настраивать (виртуально) различное телекоммуникационное оборудование фирмы Cisco (коммутаторы, маршрутизаторы, ip-телефоны, шлюзы, сервера, межсетевые экрана Cisco ASA и многое другое). Интерфейс прост и понятен, и вы сможете создать и сконфигурировать простые сети в Packet Tracer даже если обладаете глубокими познаниями в сетевых технологиях или оборудовании Cisco. Многие используют данное ПО для проектирования и моделирования сетей, обучения студентов, подготовке к сертификационным экзаменам CCNA/CCNP, получения практических навыков поиска и устранения проблем в сетях на оборудовании Cisco.
Несмотря на то, что Cisco Packet Tracer недоступен для бесплатного скачивания (доступен только участникам программы сетевой академии Cisco Networking Academy), вы с легкостью найдете дистрибутив на просторах сети. На текущий момент актуальной является версия Cisco Packet Tracer 7.2.1. При использовании Cisco Packet Tracer вам нужно указать, что вы хотите использовать гостевой доступ. Кроме того, есть бесплатные версии Cisco Packet Tracer для Android и iOS.
Чтобы освоить основы использования Cisco Packet Tracer, изучим интерфейс программы и создадим небольшую сеть.
Интерфейс программы предельно прост. В интерфейсе программы нет сложных настроек, элементов управления и ветвящихся меню, что приятно удивляет пользователей.
- Верх окна программы выполнен в классическом стиле, в котором нет ничего лишнего (базовые функции операции с файлами, отмена действии, масштабирование, сохранение, копирование).
- В правой части окна собраны функции для пометок, выделения областей, удаления и перемещения объектов.
- В нижней части размещена основные инструменты Cisco Packet Tracer, которые используются для создания вашей сети. В левом нижнем углу программы содержатся различные виды сетевого оборудования (коммутаторы, маршрутизаторы, телефоны, шлюзы, сервера, хабы, беспроводные источники, устройства защиты сети, эмуляция WAN-соединения, компьютеры, принтеры, телевизоры, мобильные телефоны и многое другое). При постоянном использовании программы Cisco Packet Tracer, часто используемые вами устройства запоминаются и отображаются в специальной папке (Custom Made Devices).
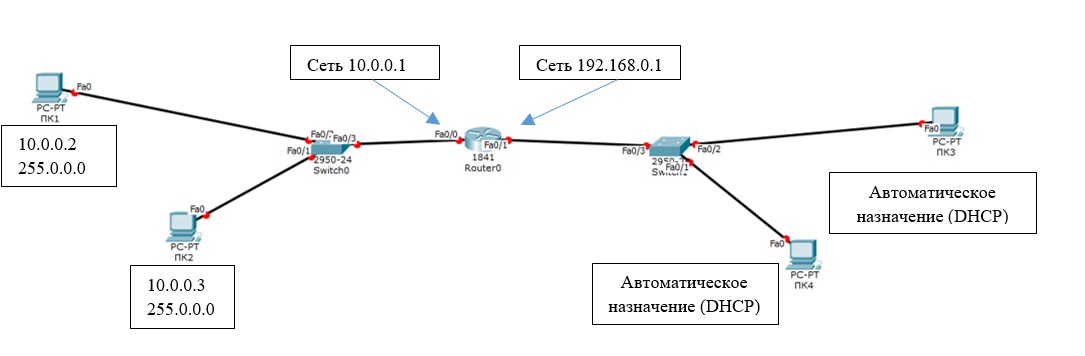
Создадим в Cisco Packet Tracer небольшую сеть, схема которой представлена ниже:
Общая сеть представляет из себя 2 сегмента (подсети 10.0.0.1/24 и 192.168.0.1/24), соединенных посредством маршрутизатора Cisco. Он будет осуществлять передачу данным между сетями в дуплексном режиме (прием и передача в обе стороны). К маршрутизатору (Router0) подключены 2 коммутатора. Интерфейс Fa 0/0 маршрутизатора подключен к порту Fa 0/3 левого коммутатора. С правым коммутатором (порт Fa 0/3) маршрутизатор подключен через интерфейс Fa 0/1. Switch0 будет осуществлять соединение ПК1 (Fa 0/2) и ПК2 (Fa 0/3), а ПК3 (Fa 0/2) и ПК4 (Fa 0/1) объединит Switch1. Порту Fa 0/0 маршрутизатора (слева) мы назначим адрес 10.0.0.1, а правому порту (Fa 0/1) – 192.186.0.1. На схеме мы видим, что все трассы (линии) подсвечены красным цветом. Это значит, что соединения нет и ни одно из устройств друг друга не «видят» в сети, потому что её ещё нет, а сетевые интерфейсы отключены (закрыты).
Настройки нашей сетей можно выполнить двумя способами:
- В графическом режиме
- В ручном режиме командами операционной системы Cisco IOS.
Левую половину сети будем настраивать графическим, а правую – ручным способами (изменения, которые мы вносим будут отражены выделены «жирным»).
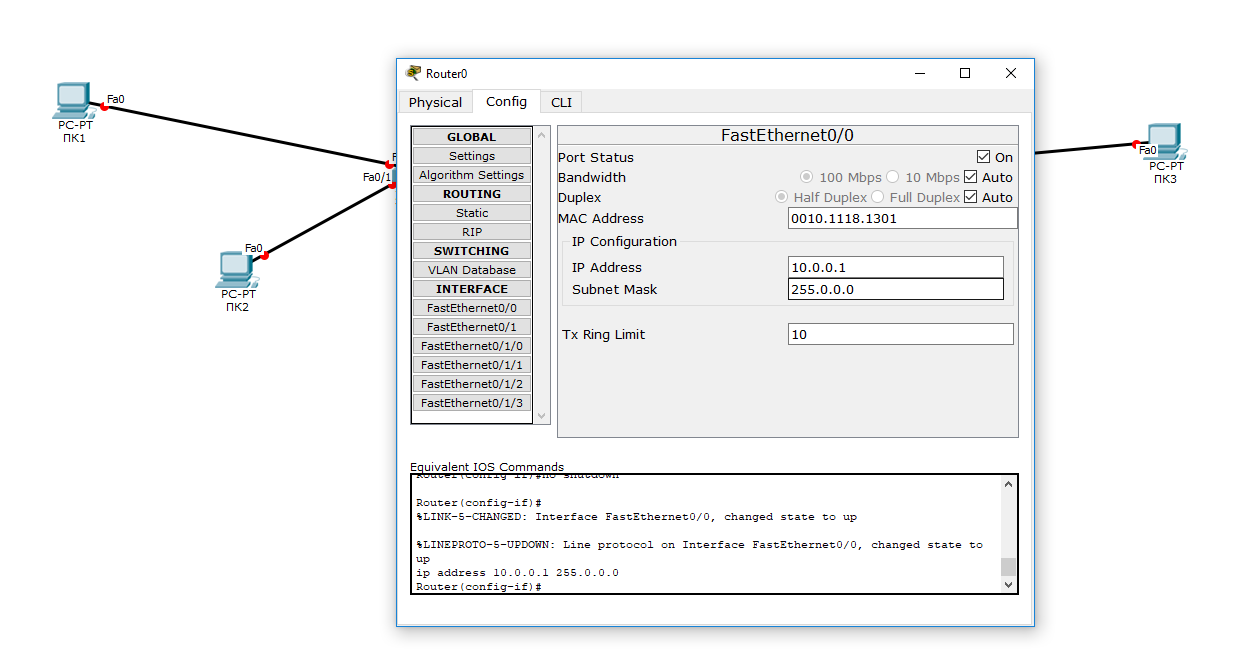
Прежде всего начнем с графической настройки маршрутизатора (левая сторона):
- Щелкните левой кнопкой мыши по маршрутизатору Router0 -> Config -> FastEthernet0/0;
- Включите порт (Port Status – On);
- Присваиваем IP-адрес и маску подсети интерфейсу маршрутизатора FastEtherner0/0 (
10.0.0.0/ 255.255.255.0
);
В ходе внесения нами изменений, автоматически формируется управляющая в окне Equivalent IOS Commands. В дальнейшем вы сможете использовать эти команды для ручной настройки маршрутизатора через команды CLI.
- Переходим к настройке FastEthernet 0/1 (правая часть);
- Включаем порт;
- Присваиваем IP адрес и маску (
192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
).
Теперь настроим коммутатор (левый):
- Нажали 1 раз левой кнопкой мышки > Config > FastEthernet0/1;
- Включаем порт (Port Status – On);
- Точно также включаем порты 0/2 и 0/3.
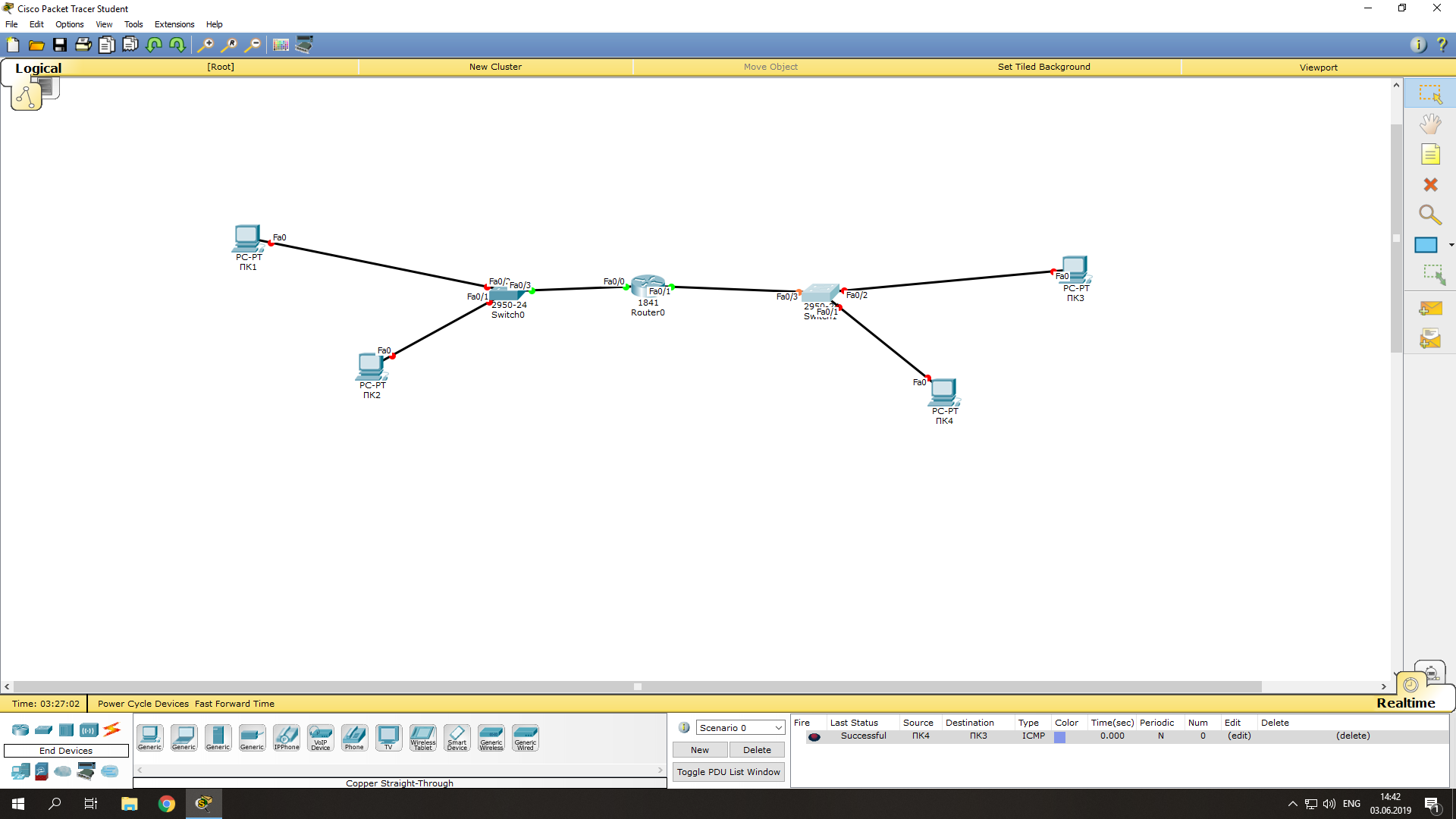
Теперь мы видим, что соединение установлено (индикация на соединениях стала зелёного цвета).
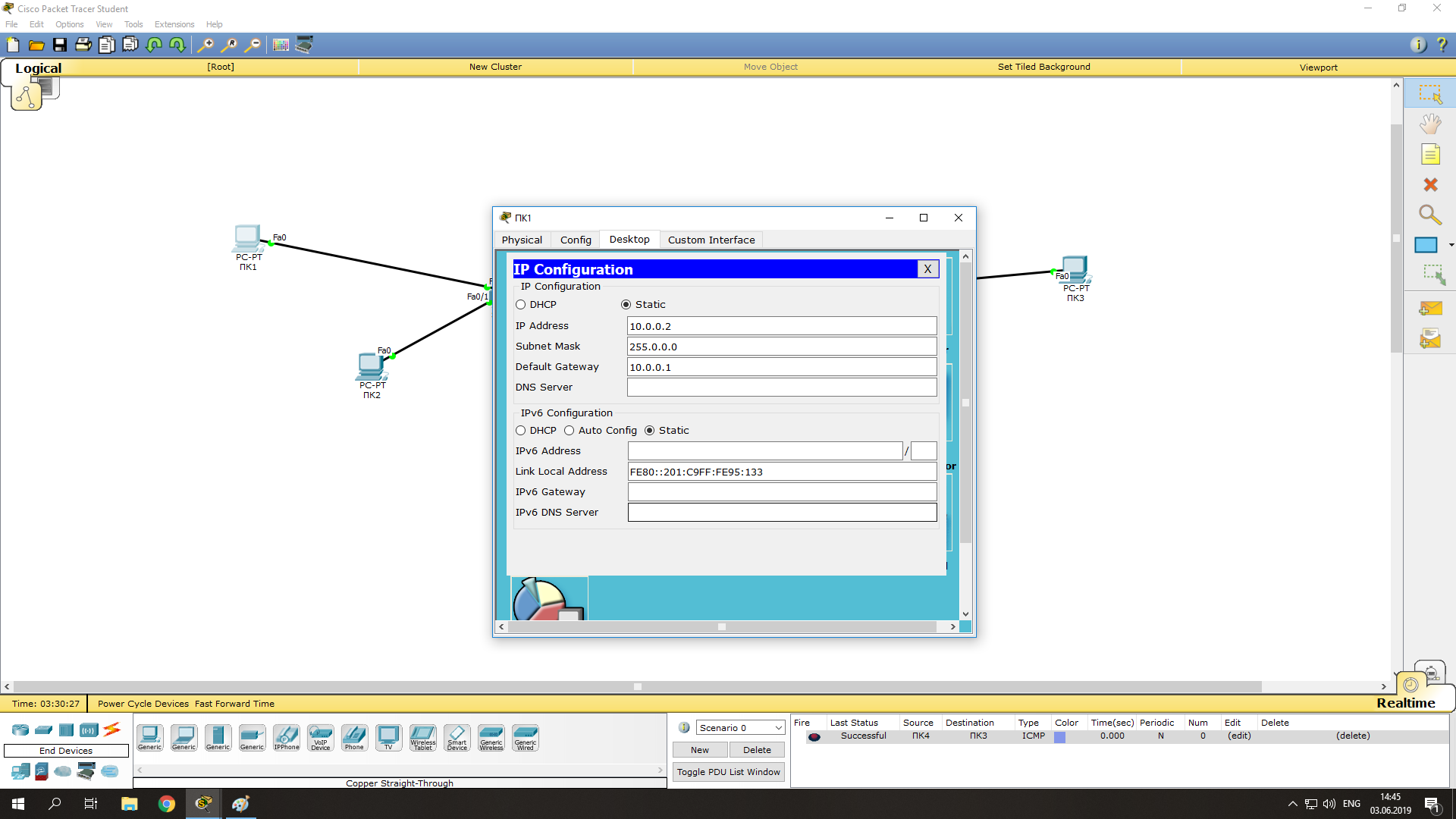
Зададим IP-адреса для компьютеров слева (в диапазоне указанных на маршрутизаторе адресов):
- Нажимаем на ПК1 левой кнопкой мыши -> Desktop -> IP Configuration;
- Указываем статический (опция Static) IP-адрес и маску, а также шлюз (Default Gateway – это будет IP адрес интерфейса Fa0/0 на маршрутизатор): IP:10.0.0.2 Mask:255.255.255.0 GW:10.0.0.1
- Нажимаем на ПК2 и производим аналогичные настройки, но с другим IP-адресом (10.0.0.3).
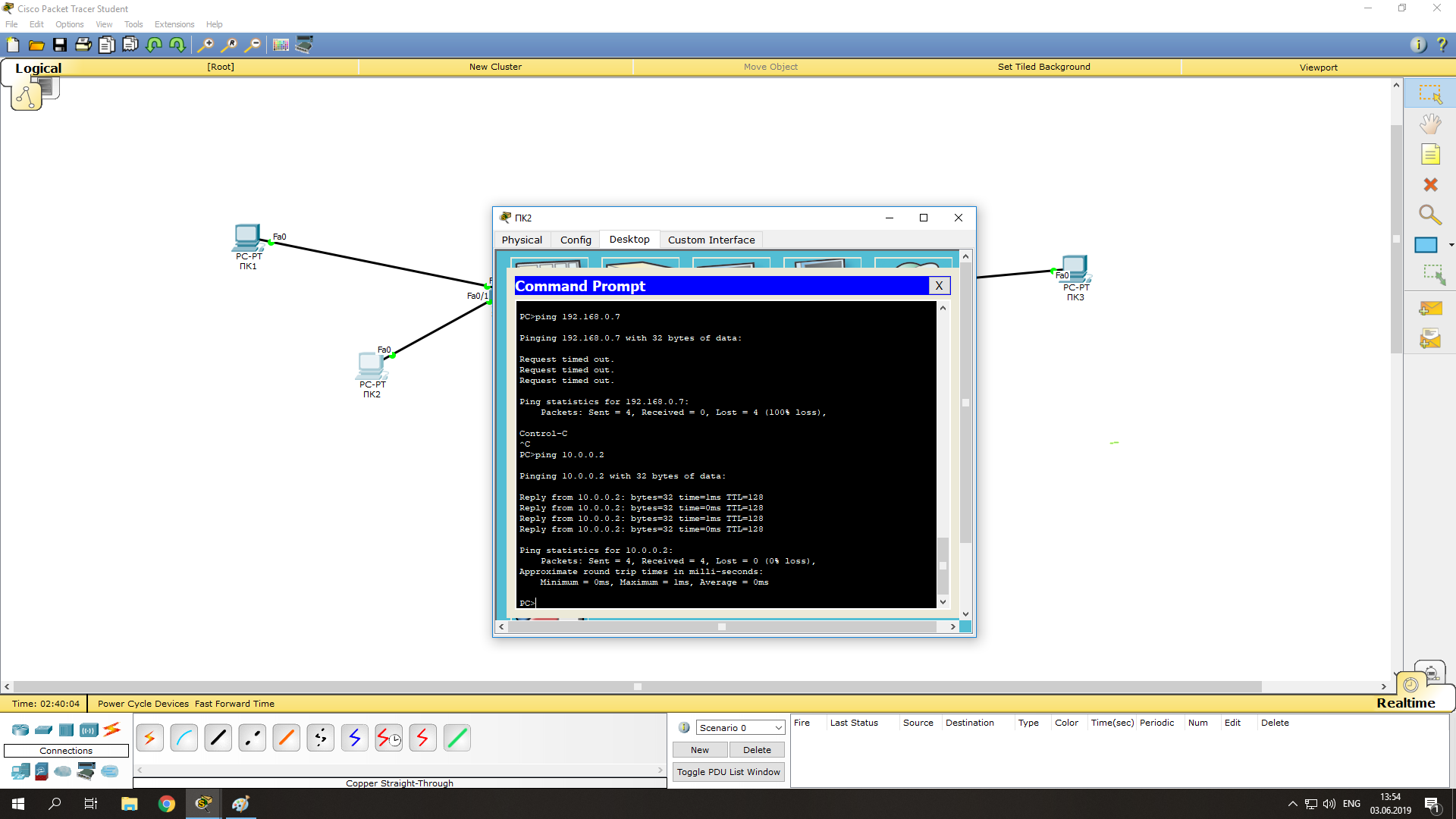
Проверим что оба компьютера стали доступны друг други (их пакеты проходят черех коммутатор):
- Нажимаем на ПК1 -> Desktop -> Command Prompt;
- В открывшемся окне командной строки, эмулирующей cmd выполните команду ping на ПК2:
ping 10.0.0.3
Соединение между ПК1 и ПК2 было установлено посредством логического соединения их через коммутатор. На этом графическая настройка левой части завершена.
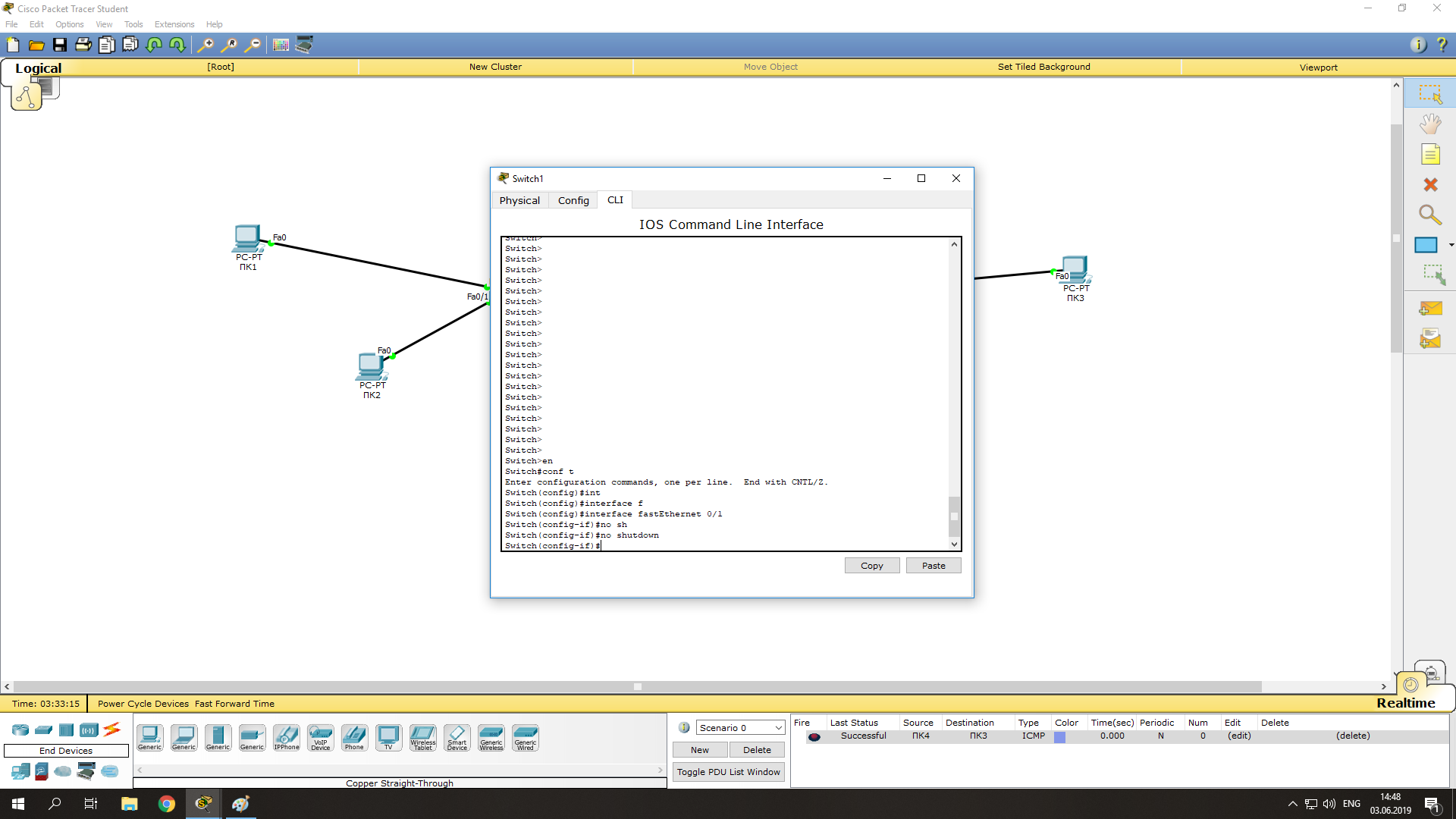
Чтобы настроить правую часть сети, нужно только открыть порты на коммутаторе и назначить IP-адреса ПК3 и ПК4. Начнём с маршрутизатора. Ручная настройка несколько сложнее, нежели графическая, но на данном уровне она не составит особого труда. Приступим:
- Заходим на коммутатор -> CLI (командная строка коммутатора);
- Заходим в привилегированный режим (пишем
enable
или
en
); - Заходим в режим конфигурирования (
configure terminal
или
conf t
); - Нам нужно включить 3 интерфейса (FastEthernet 0/1-0/3), поэтому начнем с 0/1 (пишем
int f
и нажимаем tab, затем дописываем
0/1
, enter); - Мы зашли на интерфейс 0/1. Теперь активируем его (разрешим передачу данных по нему) командой
no sh
и нажимаем tab, потом enter. Теперь этот порт открыт (активен); - Выходим из настроек интерфейса командой
ex
и enter; - Такие же настройки произведите с портами FastEthernet 0/2 и 0/3.
Осталось лишь назначить IP-адреса компьютерам ПК3 и ПК4. Но мы усложним задачу и настроим автоматическое получение IP-адресов компьютерами по протоколу DHCP. В качестве DHCP сервера, который раздает IP адреса клиентам будет выступать маршрутизатор:
- Заходим на маршрутизатор -> CLI;
- Так как мы уже производили настройки графическим методом, то мы изначально находимся в привилегированном режиме. Переходим в режим конфигурирования (
conf t
); - Пишем
ip dhcp pool XXX
(XXX – название пула формирования адресов DHCP):
network 192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0
(из этой сети будут присваиваться наши IP-адреса компьютерам)
default-router 192.168.0.1
(указываем адрес маршрутизатора, который будет шлюзом по-умолчанию для компьютеров)
ex
(вышли обратно в режим конфигурирования)
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.5
(этот диапазон адресов будет исключен из раздачи, назначить IP-адрес из этого диапазона можно будет только вручную); - Заходим на ПК3 -> Desktop -> IP Configuration;
- Выбираем DHCP и смотрим на правильность назначенного IP адреса. В большинстве сетей IP адреса компьютерам назначаются именно так, путем получения настроек с DHCP сервера. Это исключает возможность конфликта IP-адресов, а также экономит время настройки.
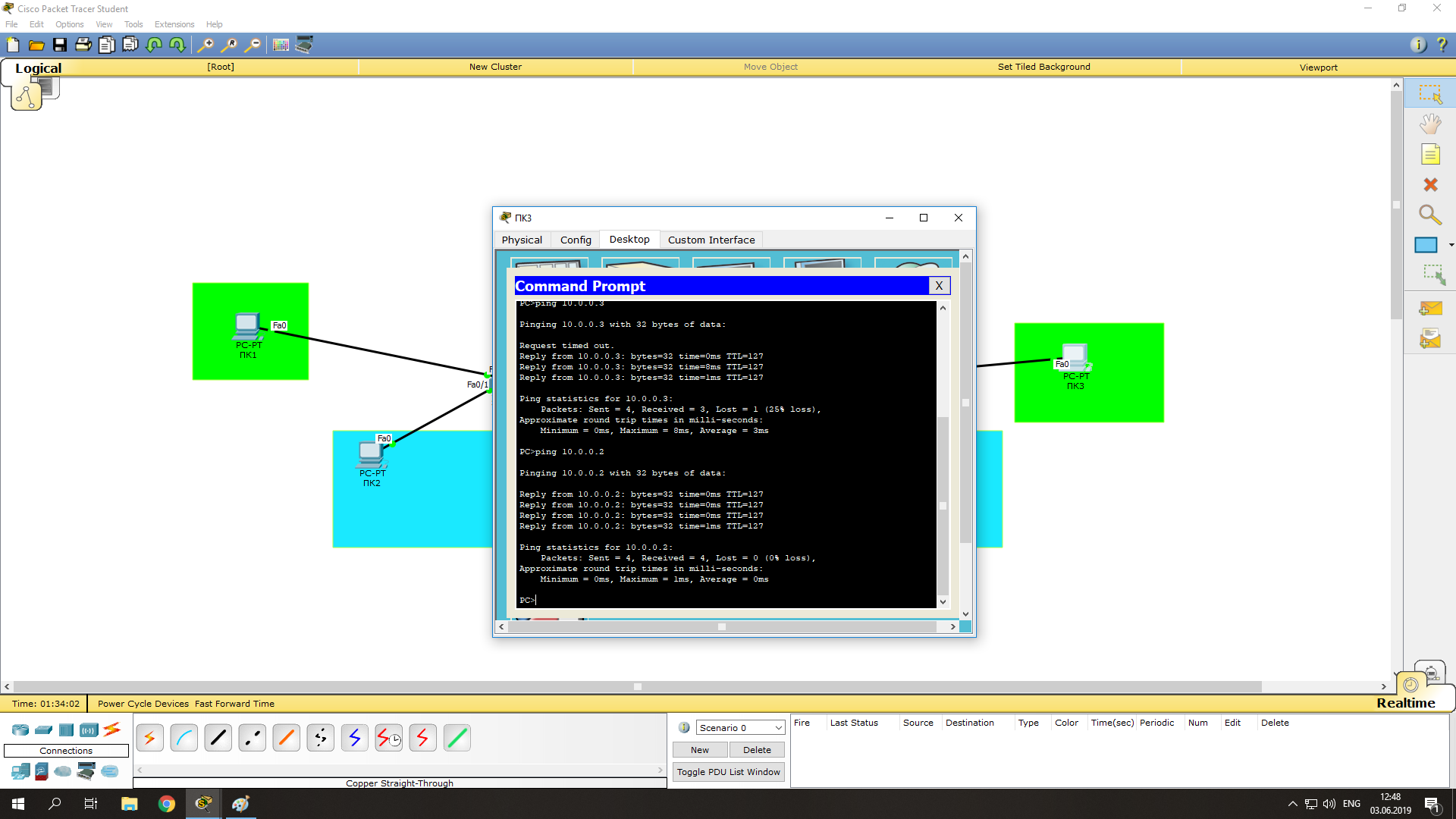
Проверяем соединение между компьютерами, соединёнными через маршрутизатор:
- Нажимаем на ПК3 -> Desktop -> Command Prompt;
- Выполняем ping на ПК1 и ПК2:
ping 10.0.0.2
ping 10.0.0.3
Теперь мы видим, что коммутация пакетов успешно установлена.
Усложним задачу. Свяжем между собой ПК1 и ПК2, а также ПК3 и ПК4. Выполнить эту задачу можно с помощью создания vlan (виртуальная локальная сеть). Она нужна для логического разграничения устройств. Так как мы не имеем возможности разделить сеть физически, воспользуемся vlan. Приступим:
- Создадим VLAN 10 на коммутаторах:
- Заходим на коммутатор (Switch0, затем также настраиваем и Switch1) -> CLI, пишем
conf t
vlan 10
(создался VLAN)
Interface FastEthernet 0/2
(для ПК1),
interface FastEthernet 0/1
(для ПК2),
interface FastEthernet 0/2
(для ПК3), или
interface FastEthernet 0/1
(для ПК4). Далее команды одинаковы для всех четырёх интерфейсов:
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan 10
Теперь ПК1 и ПК2 «общаются» в рамках своей сети, а ПК3 и ПК4, в рамках своей.
Вы можете получить текущую конфигурацию любого устройства в вашей сети, выполнив в CLI команду
show running-config
.
Итак, мы рассмотрели одну из самых простых схем типовой сети, использующейся для небольшой организации. Эта база, на которой строятся более сложные сети. Вы можете усложнить сеть путем добавления сетевого оборудования (дополнительные коммутаторы, маршрутизаторы, сервера, телефоны, беспроводные устройства и т.д.) и введением новых протоколов в работу (например, настройка IP-телефонов по протоколу SIP). Таким образом Cisco Packet Tracer будет отличным инструментом как для начинающего, так и для опытного сетевого инженера.
The interface is the port at which the router connects to a given network. It acts as an entry or exit point for data that is to be transmitted through the router. Every interface must be labeled or assigned an IP address, which should be unique among all the IP addresses in the network.
In Cisco Packet Tracer, to understand the process of assigning IP addresses, we will be using routers. This is because a router has many interfaces to connect to different networks and also after configuring a router by any routing protocol(RIP, static routing, etc.), we can observe how an interface and an IP address work in a router.
Steps to configure an IP address for an interface of a router in Cisco Packet Tracer:
Step 1: Open Cisco Packet Tracer and select the following devices:
S.NO |
Device |
Quantity |
|---|---|---|
1. |
PC | 4 |
2. |
Router | 2 |
IPv4 Addressing Table:
S.NO |
Device |
IPv4 Address |
Subnet Mask |
Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1. |
PC0 | 192.168.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.10.2 |
2. |
PC1 | 192.168.20.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.20.2 |
3. |
PC2 | 192.168.30.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.30.2 |
4. |
PC3 | 192.168.40.1 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.40.2 |
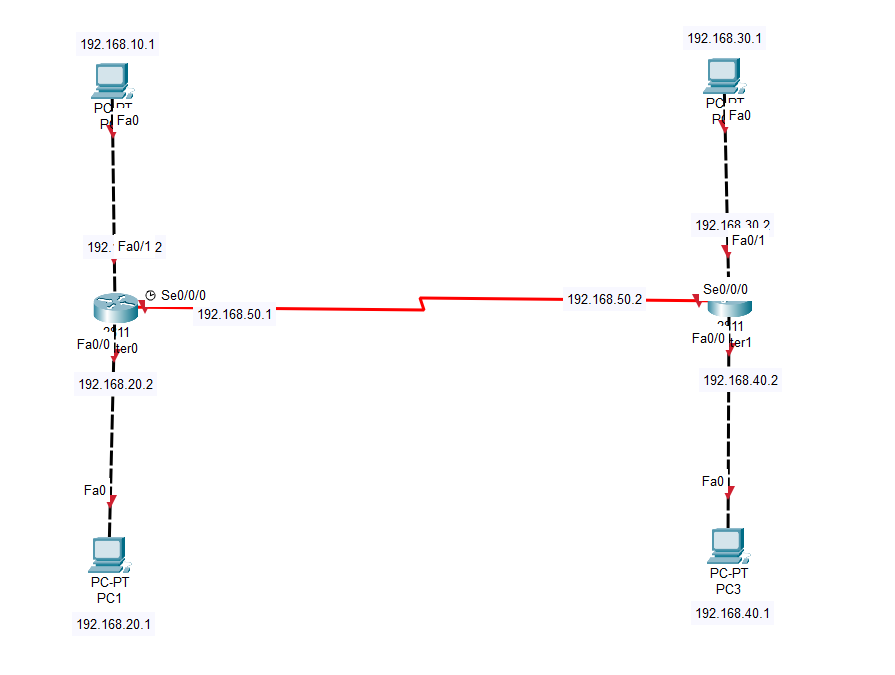
- Create the following topology and label the configuration as shown in the figure:
- Also, assign the respective IP addresses and default gateways to all 4 PCs.
Step 2: In Cisco Packet Tracer, assigning IP addresses to an interface of a router can either be done through the command line or the GUI mode. Both of them are discussed as follows:
Through command line mode:
- Firstly, enter the command line by clicking on any router and then selecting the CLI tab.
- Enter config mode by typing the following commands in the command line:
en config t
- Now we can assign IP addresses to their respective interfaces. To do this, firstly we need to enter into the interface we want to assign the IP address. This is done by typing the keyword interface followed by the label of the interface.
Interface [label of the interface]:
For example:
interface fa0/0
- After entering the interface, type the command IP address followed by the IP address you want to assign and also followed by the subnet mask of the IP address assigned.
IP address [IP address to be assigned] [subnet mask of the IP address]
For example:
IP address 192.168.20.2 255.255.255.0
- After assigning the IP address type, the command no shutdown to activate the port. Initially, all the ports of the router are switched off, so we need to manually activate them. You would also note that the color of the triangles representing the ports of the router changes to green and also start pointing upward.
For example:
no shutdown
- At last, exit the interface by typing the following command:
exit
- Repeat the above steps for all the interfaces of the router, and then for all interfaces of other routers as well.
Following is the image of the command line of the router after configuring all interfaces:
For a better understanding of the process, you may refer to the following simulation:
Through GUI mode:
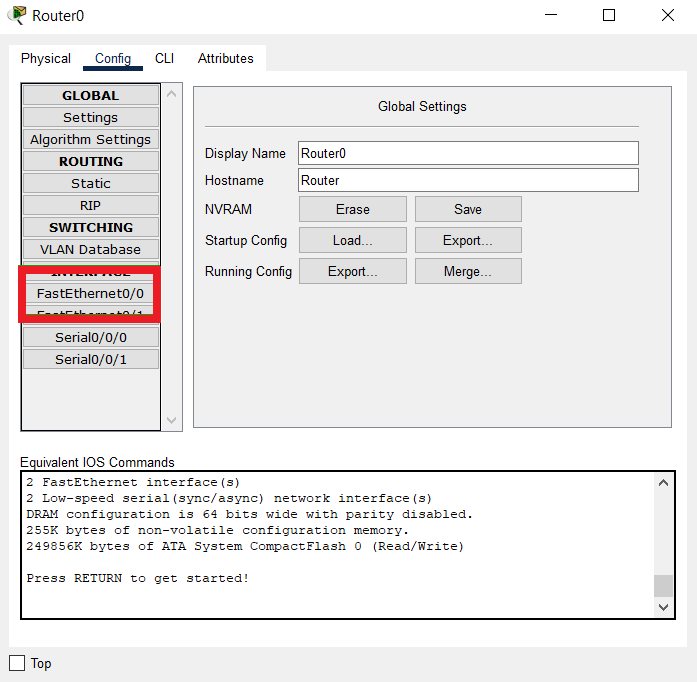
- Click on any router and select the Config tab from the above tabs.
- Now find the interface to which you want to assign the IP address, from the tabs available on the left side of the window.
For example:
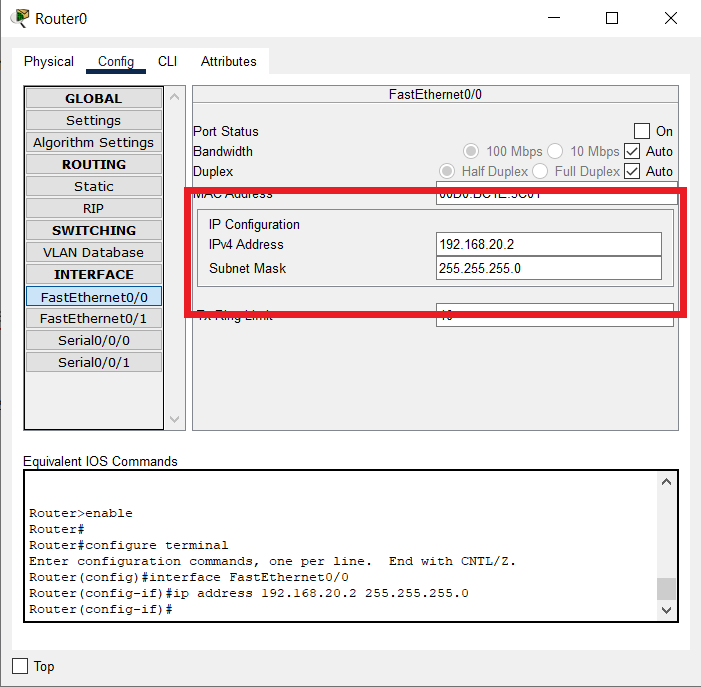
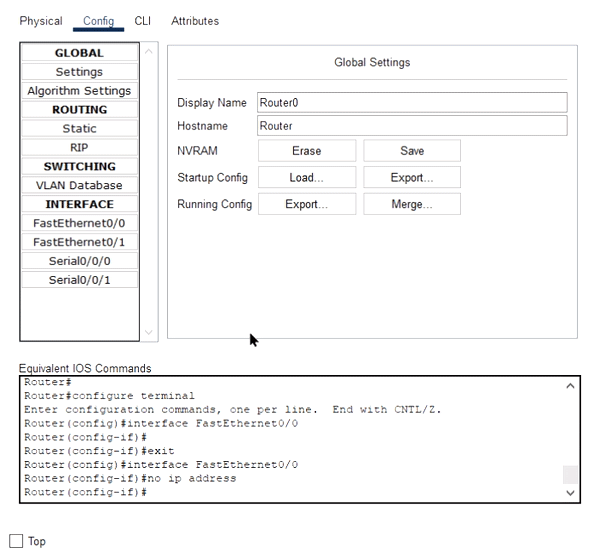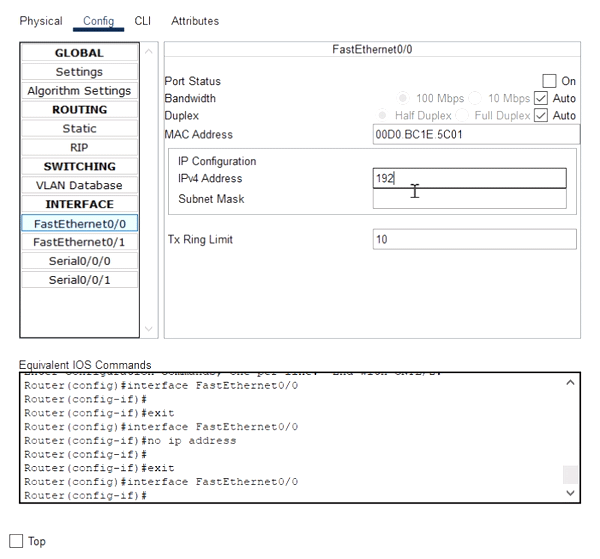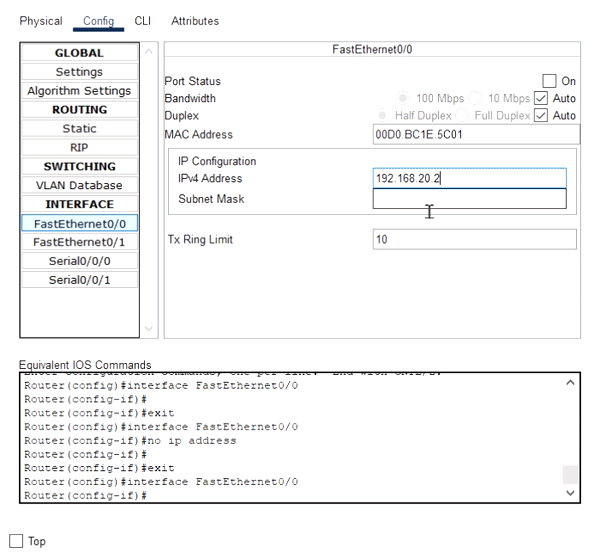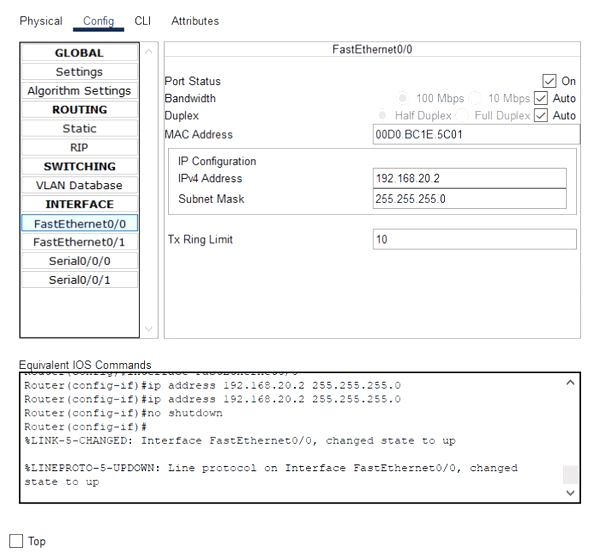
- After selecting the interface, fill in the IP address and the subnet mask in the fields named IPv4 Address and Subnet Mask.
For example:
- Activate the port by checking the checkbox labeled as On for the Port Status option.
For example:
The interface of the router has been assigned an IP address.
- Repeat the above steps for all the interfaces of the router, and then for all interfaces of other routers as well.
Simulation Result:
Last Updated :
21 Jul, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
Feb 13, 2020
Last Updated: May 15, 2023
CCNA v7 Course #2, CCNA v7.0
1.4.7 Packet Tracer – Configure Router Interfaces (Instructor Version)
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address/Prefix | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 172.16.20.1 /25 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 172.16.20.129 /25 | N/A | |
| S0/0/0 | 209.165.200.225 /30 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.16.20.10 /25 | 172.16.20.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.16.20.138 /25 | 172.16.20.129 |
| R2 | G0/0 | 2001:db8:c0de:12::1/64 | N/A |
| G0/1 | 2001:db8:c0de:13::1/64 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 2001:db8:c0de:11::1/64 | N/A | |
| fe80::2 | N/A | ||
| PC3 | NIC | 2001:db8:c0de:12::a/64 | fe80::2 |
| PC4 | NIC | 2001:db8:c0de:13::a/64 | fe80::2 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Configure IPv4 Addressing and Verify Connectivity
- Part 2: Configure IPv6 Addressing and Verify Connectivity
Background
Routers R1 and R2 each have two LANs. Your task is to configure the appropriate addressing on each device and verify connectivity between the LANs.
Note: The user EXEC password is cisco. The privileged EXEC password is class.
Instructions
Part 1: Configure IPv4 Addressing and Verify Connectivity
Step 1: Assign IPv4 addresses to R1 and LAN devices.
Referring to the Addressing Table, configure IP addressing for R1 LAN interfaces, PC1 and PC2. The serial interface has already configured.
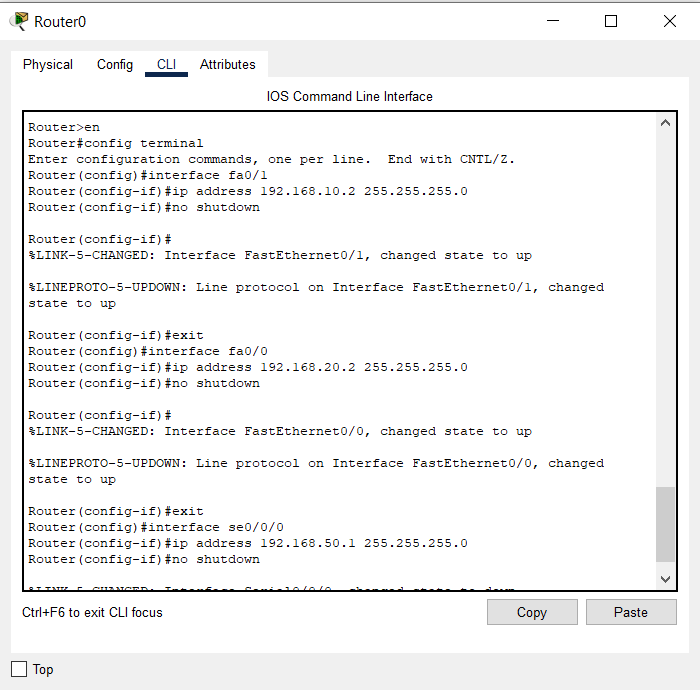
R1>enable Password: R1#configure terminal R1(config)#interface g0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.20.1 255.255.255.128 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#interface g0/1 R1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.20.129 255.255.255.128 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#
Step 2: Verify connectivity.
PC1 and PC2 should be able to ping each other and the Dual Stack Server.
C:\>PING 172.16.20.138
Pinging 172.16.20.138 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Reply from 172.16.20.138: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=127
Reply from 172.16.20.138: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=127 Reply from 172.16.20.138: bytes=32 time=13ms TTL=127 Ping statistics for 172.16.20.138: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 13ms, Average = 4ms C:\>ping 64.100.1.10
Pinging 64.100.1.10 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
Reply from 64.100.1.10: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=126
Reply from 64.100.1.10: bytes=32 time=13ms TTL=126
Reply from 64.100.1.10: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 64.100.1.10:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 13ms, Average = 5ms
C:\>
Part 2: Configure IPv6 Addressing and Verify Connectivity
Step 1: Assign IPv6 addresses to R2 and LAN devices.
Referring to the Addressing Table, configure IP addressing for R2 LAN interfaces, PC3 and PC4. The serial interface is already configured.
R2>enable Password: R2#configure terminal R2(config)#interface g0/0 R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8:c0de:12::1/64 R2(config-if)#no shutdown R2(config-if)#exit R2(config)#interface g0/1 R2(config-if)#ipv6 address 2001:db8:c0de:13::1/64 R2(config-if)#no shutdown
Step 2: Verify connectivity.
PC3 and PC4 should be able to ping each other and the Dual Stack Server.
C:\>ping 2001:db8:c0de:12::a
Pinging 2001:db8:c0de:12::a with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 2001:DB8:C0DE:12::A: bytes=32 time=13ms TTL=127
Reply from 2001:DB8:C0DE:12::A: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=127
Reply from 2001:DB8:C0DE:12::A: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=127
Reply from 2001:DB8:C0DE:12::A: bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=127 Ping statistics for 2001:DB8:C0DE:12::A: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 13ms, Average = 3ms C:\>ping 2001:db8:100:1::a
Pinging 2001:db8:100:1::a with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 2001:DB8:100:1::A: bytes=32 time=15ms TTL=126
Reply from 2001:DB8:100:1::A: bytes=32 time=7ms TTL=126
Reply from 2001:DB8:100:1::A: bytes=32 time=13ms TTL=126
Reply from 2001:DB8:100:1::A: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=126
Ping statistics for 2001:DB8:100:1::A:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 4ms, Maximum = 15ms, Average = 9ms
C:\>
Devices Config – Download PDF & PKA file:
Download Packet Tracer (.pka) file:
Configure A Router With Packet Tracer
Computer networking professionals getting started with Packet Tracer may find the interface to be flustered. Being a development program, this is only natural. However, learning how to configure a router with Packet Tracer will put professionals on the right track to mastering the program in about half an hour.
By this time, you should already have the Packet Tracer download and have it installed on your computer. Open the program and select the router from the lower left-hand corner, and drag it into the center of the sandbox screen as seen below. (Click for larger picture)
We will be setting up a very basic network that allows two computers to communicate, so the next step is to select end devices from the bottom left-hand corner and drag it to the sandbox screen. Do this twice to make two computers appear below the router.
Now select connections from the same bottom left-hand corner. When you connect like-devices(Such as a router and computer) you use a crossover cable, so you should select copper cross-over cable from the second menu to the immediate right. Click on Router0, and connect the cable via FastEthernet0/0 as seen below:
Now click the PC0 and select FastEthernet. You will notice that although a link is established, it is not functional. You can tell by the red dots that are present on both ends of the connection. Once the router is configured correctly, the red dots will turn green to indicate the devices are able to communicate.
Do the same operation to PC1, only this time connect the cable to FastEthernet0/1 since FastEthernet0/0 is already taken by PC0. Your network should be similar to the one below at this point:
Configuring The Router In Packet Tracer
A router that is turned off doesn’t work very well! Click on your router to bring up the configuration menu and verify that it is turned on.When on, there will be a small green light below the switch as seen in the diagram.
Next we have to open the Ethernet ports to allow communication. Although they are physically connected, they are in a state that is known as being in administrative shut down. Now click on the CLI tab to access the configuration menu. If you’ve used the Cisco IOS before, you will notice it looks and acts the same way.
1. Press RETURN to start the session
2. Type enable to get to privileged mode (this gives you more options in configuring the router)
3. Type config terminal (or config t for short) to access the configuration menu.
4. Type interface fastethernet0/0 to access Ethernet0/0
5. Type ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 to assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface.
6. Type no shutdown to open the interface up for business.
That’s it! You should now see a message similar to the following:
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
Now we have to do the same thing for fastethernet0/1. If you don’t, there still won’t be a connection to PC1! Make sure to enter the IP address carefully as seen below:
1. Press Ctrl + Z to go back to the previous mode.
1. Type interface fastethernet0/1
2. Type ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0
3. Type no shutdown
At this point our router is configured properly. If you test out a ping, you will notice that the computers still don’t communicate, however!
Configuring The Gateway In Packet Tracer
Our last step is to configure the gateway on each desktop computer. The gateway is the address we assigned to the Ethernet port that the desktop is connected to. It will allow the computer to interface with another network, so our ping won’t work without it!
Click on PC0 to bring up the configuration menu. Under global settings you will find a field for the gateway. Enter the corresponding IP address of the router’s interface, which is 192.168.10.1. Then click the FastEthernet tab on the left column to set the actual computer’s IP address to be on the network. Use 192.168.10.2 for the IP address, and 255.255.255.0 for the subnet mask.
Do the same thing for PC1, only use 192.168.20.1 for the gateway address, 192.168.20.2 for the IP address, and 255.255.255.0 for the subnet mask. You can confirm that your network works by sending out a packet of information from PC0 to PC1, and vice versa. Click the packet icon on the right menu as seen below:
Click on PC0 and then click PC1. On the lower right of the screen you will see a message box that says “Successful.” If it doesn’t, you may have had a syntax error when putting in an IP address or router configuration command. Review your work or ask for help among the community if you are stuck.
Closing Comments
Congratulations! You have a small working network. A real-world application of this very network would be to have two computers connected to the Internet, whereas the router would then be connected to your telecommunications company. (Or what we would call the “cloud”)
More advanced devices and topologies won’t be so easy, but you’re now on the right path to becoming qualified for the CCNA certification exam.