На чтение 8 мин Просмотров 10.8к.
Кристина Горбунова
Высшее образование по специальности “Информационные системы”. В сфере более 7 лет, занимается разработкой сайтов на WordPress и Tilda.
Задать вопрос
При подключении к интернету у новичков часто возникает вопрос, что такое MTU в настройках роутера и как изменить этот параметр. Мы расскажем, как определить оптимальное значение этой характеристики и когда не стоит изменять максимальный размер полезного блока данных в пакете.
Содержание
- Что такое MTU и из чего складывается параметр
- Определяем оптимальное значение
- Установка MTU в роутере
- ASUS
- TP-Link
- D-Link
- Zyxel
- Keenetic
- Netis
- Tenda
- Upvel
- Mercusys
- Настройка на компьютере
- Что будет, если установить некорректное значение
Что такое MTU и из чего складывается параметр
В интернете информация передается в виде небольших пакетов данных. Каждый блок содержит служебную информацию – заголовок (header). Он нужен для определения типа пересылаемых данных, количества отправляемых пакетов и т. д. Величина передаваемого блока данных ограничена конкретным количеством байт.
Maximum transmission unit (MTU) – максимальное количество байт, которое сможет передать роутер без фрагментации. Чем больше этот параметр, тем выше скорость интернета. Для интерфейса Ethernet типовое значение этой характеристики – 1500. Реальная величина параметра MTU чуть меньше в пределах 1460-1480 байт.
Пример работы MTU. Роутеру нужно передать файл размером 9000 байт. Величина МТУ – 1470. Устройства фрагментирует передаваемую информацию на 7 частей – 6 фрагментов величиной 1470 байт и 1 фрагмент 180 байт.
Многие модели роутеров определяют МТУ самостоятельно при подключении к ПК и сети, но не всегда автоматически установленная величина совпадает с параметрами интернета.
За счет правильно настроенного значения МТУ можно:
- увеличить канал передачи, чтобы к нему одновременно смогли подключаться разные сетевые службы, приложения;
- сократить количество поврежденных пакетов при передаче данных;
- снизить нагрузку на канал передачи и увеличить скорость интернета.
Внимание! К изменению МТУ приступайте только при наличии проблем с интернетом или какими-то сетевыми службами. Если скорость соединения нормальная и сайты грузятся без проблем, лучше этот параметр не менять.
Современные ОС автоматически вычисляют оптимальное значение максимального размера блока данных или берут его из настроек роутера. Пользователи могут настроить МТУ самостоятельно с помощью командной строки.
Определяем оптимальное значение
Самый простой путь поиска оптимальной величины МТУ – узнать у провайдера. Большинство компаний предоставляют клиентам все настройки сети (VPI, VCI, имя IP-сервера). Если такой информации провайдер не предоставил, определить параметр можно самостоятельно.
Найти оптимальное значение MTU можно при помощи команды ping. Пропинговать можно любой ресурс.
Для этого отройте командную строку и введите команду:
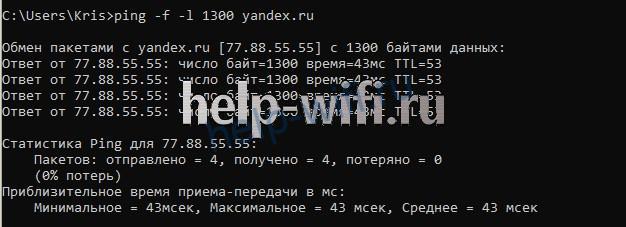
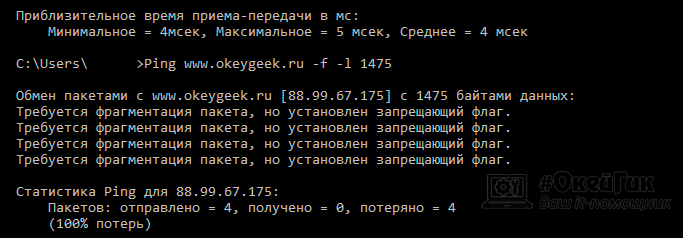
ping -f -l 1300 yandex.ru
Для открытия командной строки нажмите Win+R. В появившемся окне введите cmd, а затем нажмите на Enter. Откроется консоль с черным экраном. Это и есть командная строка.
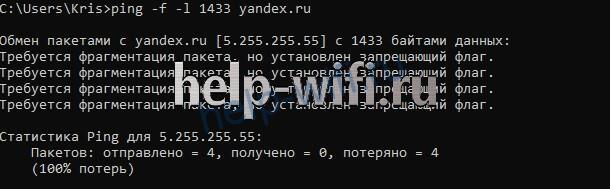
В введенной команде 1300 – размер пакета в байтах. Далее увеличивайте его, пока в командной строке не появится ошибка «Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг». Значение пакета, предшествующее появлению сообщения, равно максимальному количеству передаваемой информации.
Для нашего соединения этот параметр составляет 1432 байта. Если установить значение 1433, то появится ошибка. 1432 – это максимальна величина данных, передаваемая без заголовков (maximum segment size или MSS).
Для того, чтобы узнать размер MTU в байтах, прибавьте 28 к максимальному размеру пакета. В нашем случае это 1460 (1432+28). Это значение и нужно выставить в МТУ роутера.
Установка MTU в роутере
Сменить стандартное значение MTU можно в настройках роутерах. Для этого введите DNS или IP адрес устройства в адресную строку браузера. Он обычно указан на нижней части корпуса.
Самые популярные адреса:
- 192.168.0.1;
- 192.168.1.1.
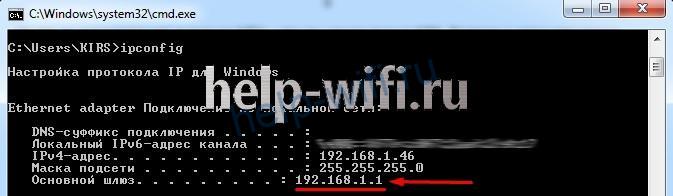
Еще один способ определения адреса – ввести в командную строку ipconfig.
IP роутера 192.168.1.1. После того как узнали адрес для входа, вводим его в адресной строке браузера. Следующим шагом нужно будет ввести логин и пароль администратора. По умолчанию это «admin» в оба поля.
Далее процесс настройки зависит от модели используемого устройства.
ASUS
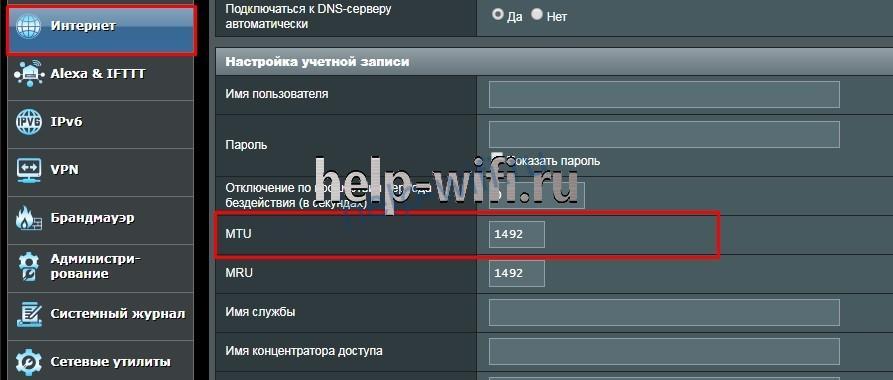
Откройте вкладку «Дополнительные настройки» и найдите там раздел «Интернет» или «Wan».
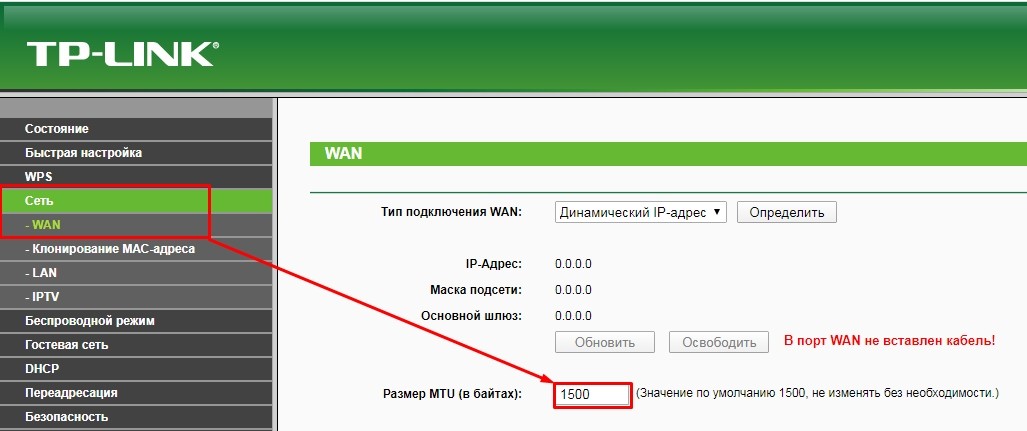
TP-Link
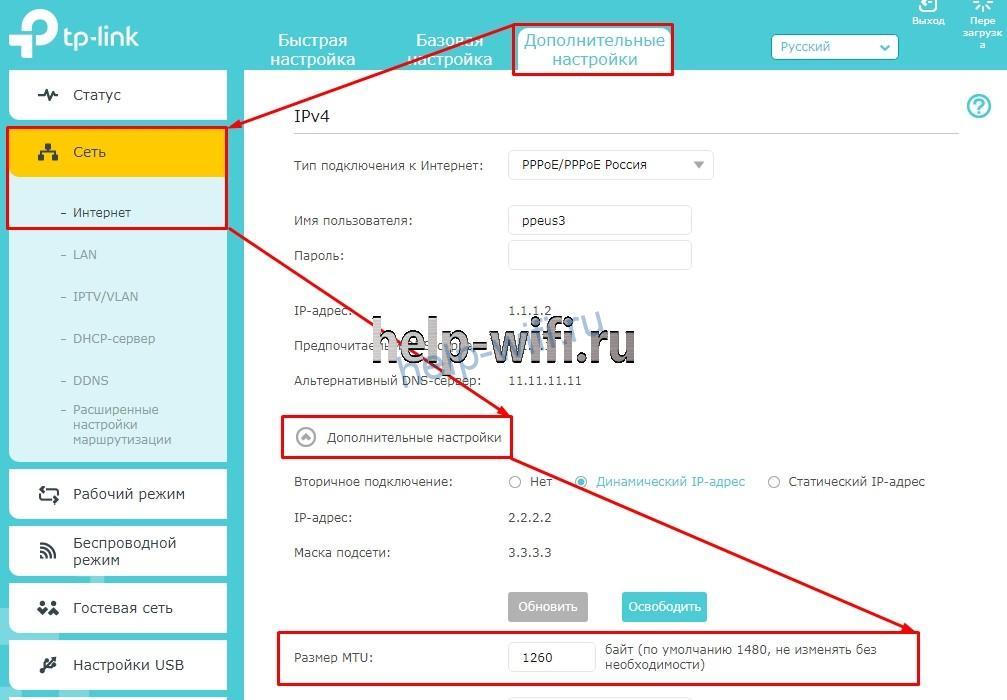
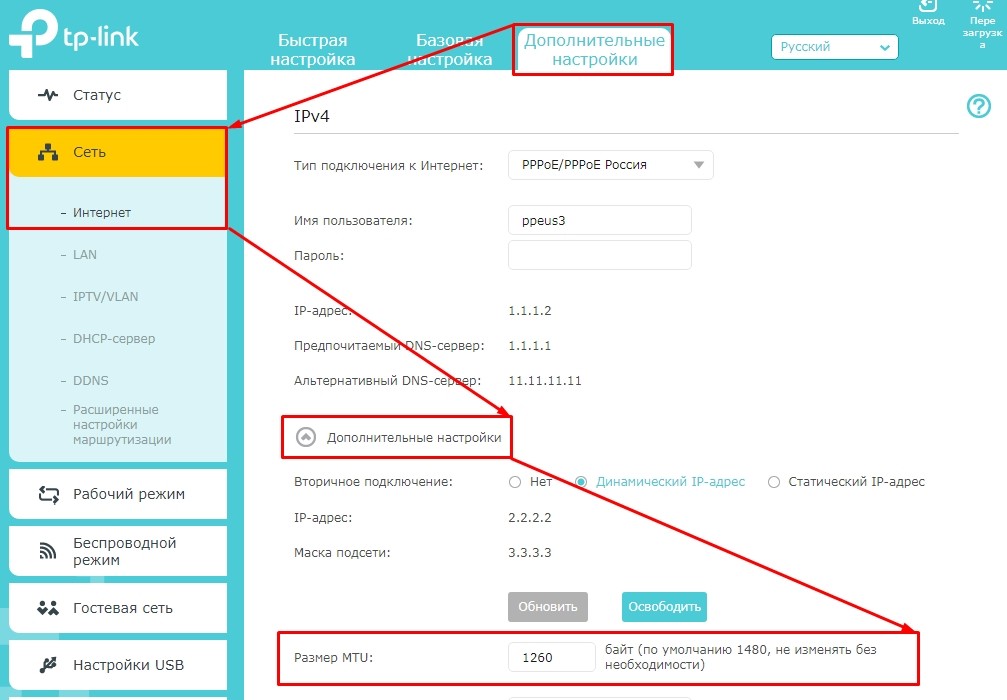
В старой прошивке роутеров откройте раздел «Сеть». В нижней части страницы вкладки WAN будет указан размер МТУ. Для замены просто введите новое значение и нажмите на кнопку «Сохранить».
В новых роутерах нужно перейти в раздел «Дополнительные настройки», открыть вкладку «Сеть» и открыть пункт «Интернет». В блоке «Дополнительные настройки» будет указан параметр MTU в роутере. После изменения параметров нажмите на кнопку «Сохранить». Новые настройки вступят в силу после перезагрузки роутера.
D-Link
Для настройки максимального размера блока данных откройте раздел «Сеть» подпункт «WAN». Выберите используемое подключение к интернету.
В появившемся списке настроек найдите пункт «MTU».
Zyxel
- Откройте раздел «Интернет» и откройте вкладку «Подключения». Выберите активное подключение или создайте новое.
- Найдите параметр «Размер MTU». Введите свое значение.
- Нажмите на кнопку «Применить» для сохранения параметров.
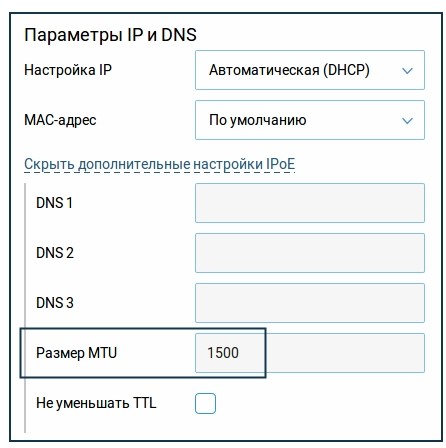
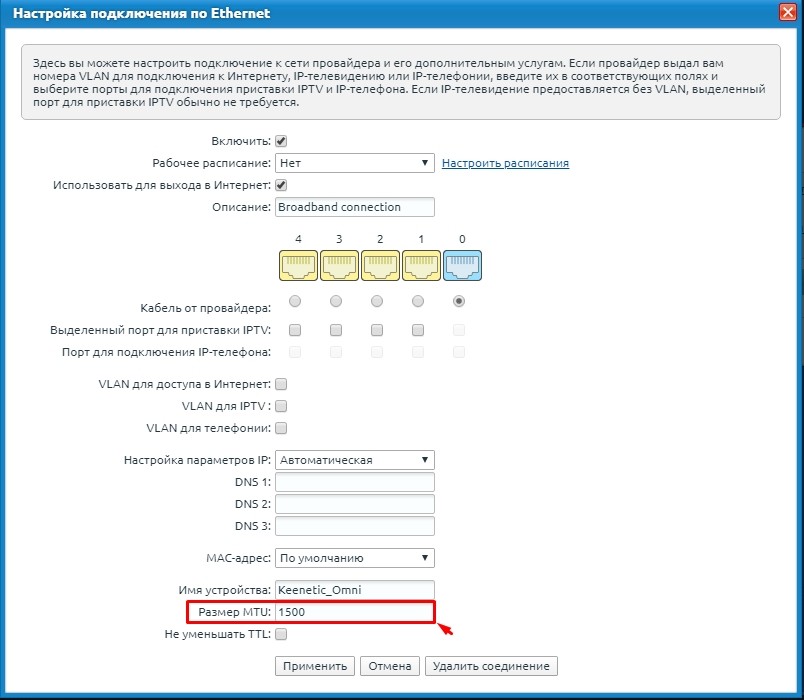
Keenetic
Чтобы изменить параметр MTU:
- В разделе «Интернет» откройте вкладку «Проводной».
- Найдите блок «Аутентификация у провайдера (PPPoE / PPTP / L2TP)» или «Параметры IP и DNS».
- Откройте дополнительные настройки. Найдите пункт «Размер MTU».
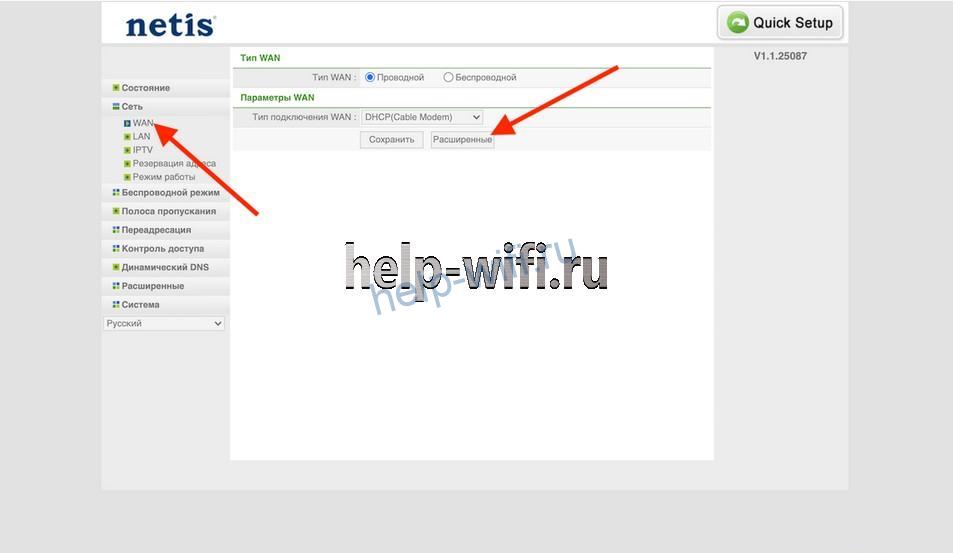
Netis
Нажмите на кнопку Advanced.
Откройте меню «Сеть». Выберите подпункт «Wan».
Чтобы поставить значение MTU в роутере Netis, откройте расширенные настройки WAN-соединения.
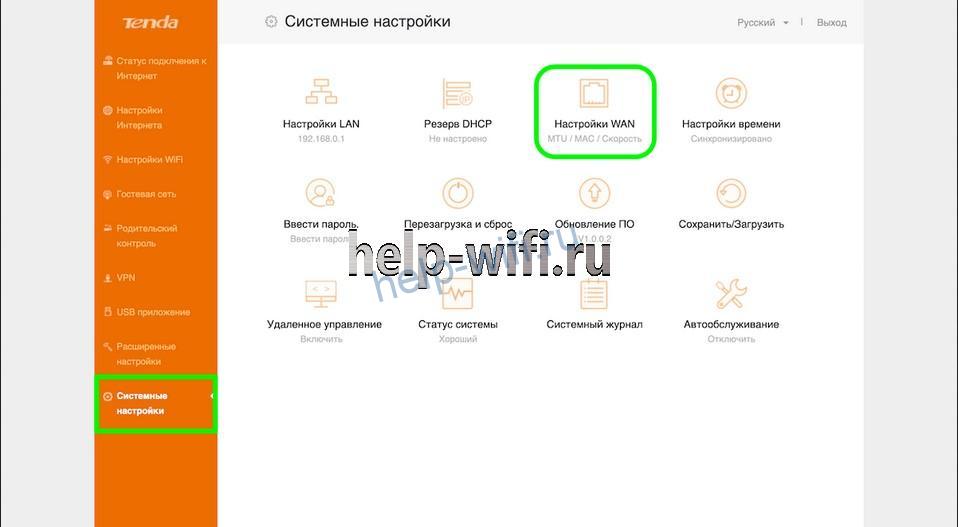
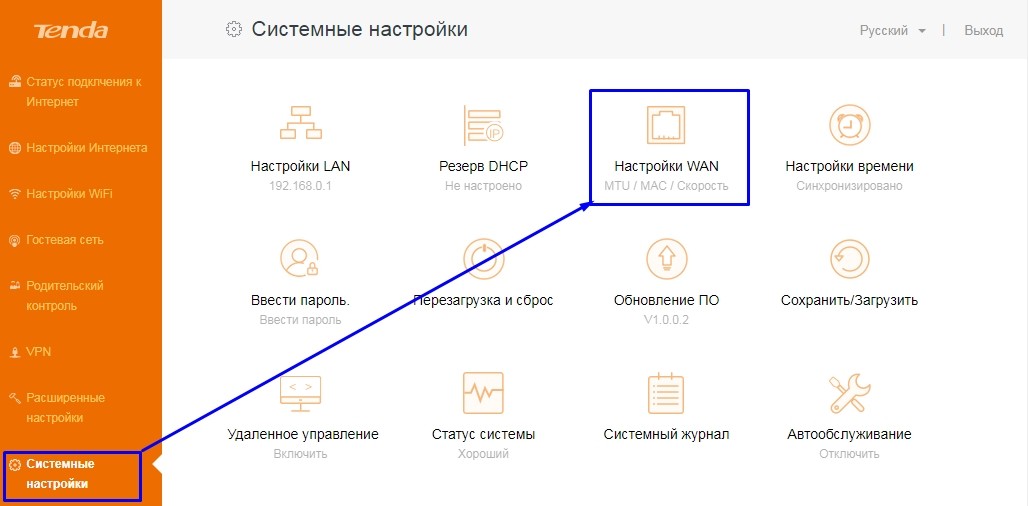
Tenda
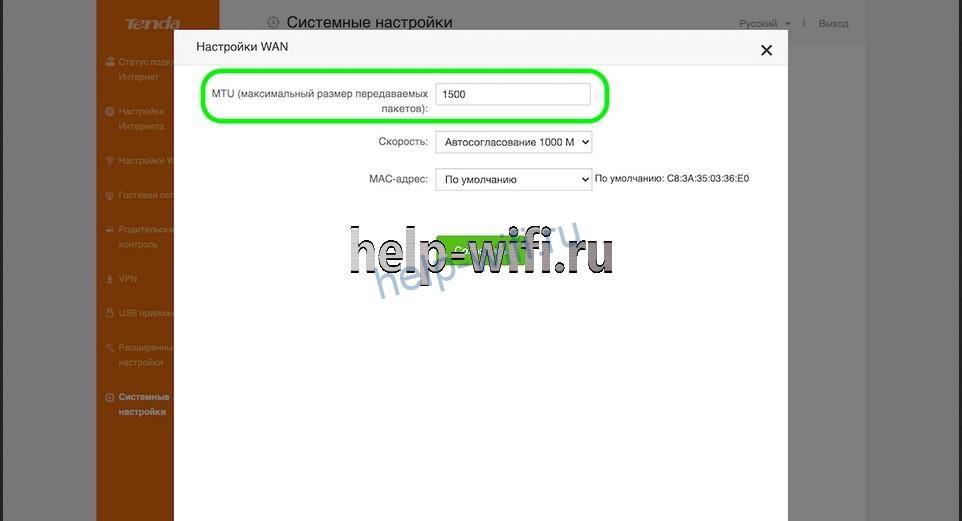
Откройте раздел «Системные настройки». Найдите там пункт «Настройки WAN».
В открывшемся окне на первой строчке находится «Максимальный размер передаваемых пакетов». Его нужно уменьшить или увеличить.
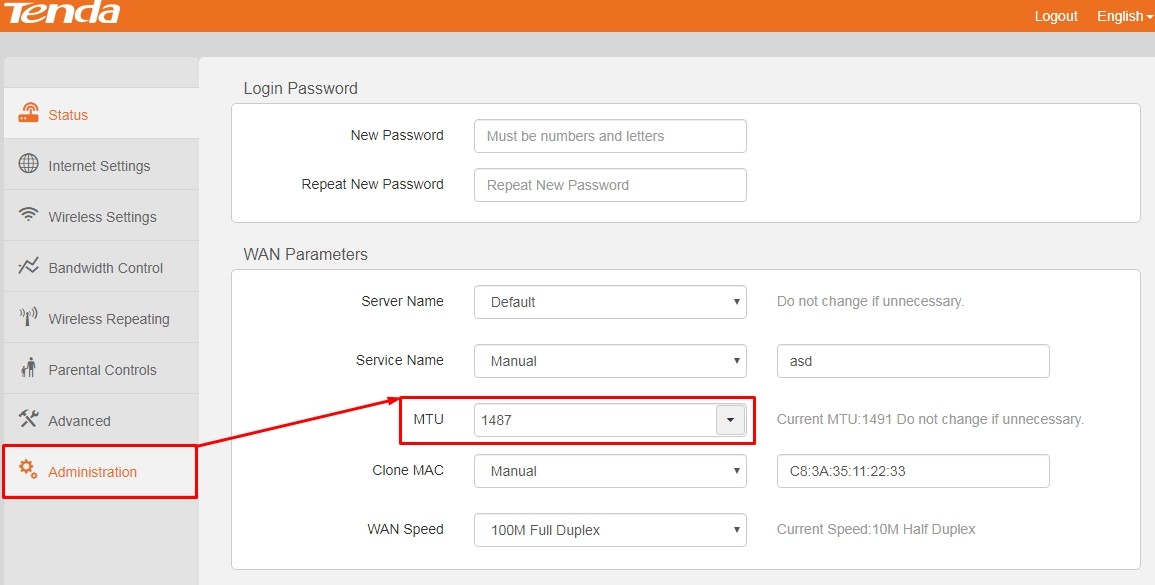
В роутерах Tenda с обновленной прошивкой нужные настройки расположены в разделе «Administration».
Upvel
Откройте раздел «Настройки», выберите там «Интерфейс WAN».
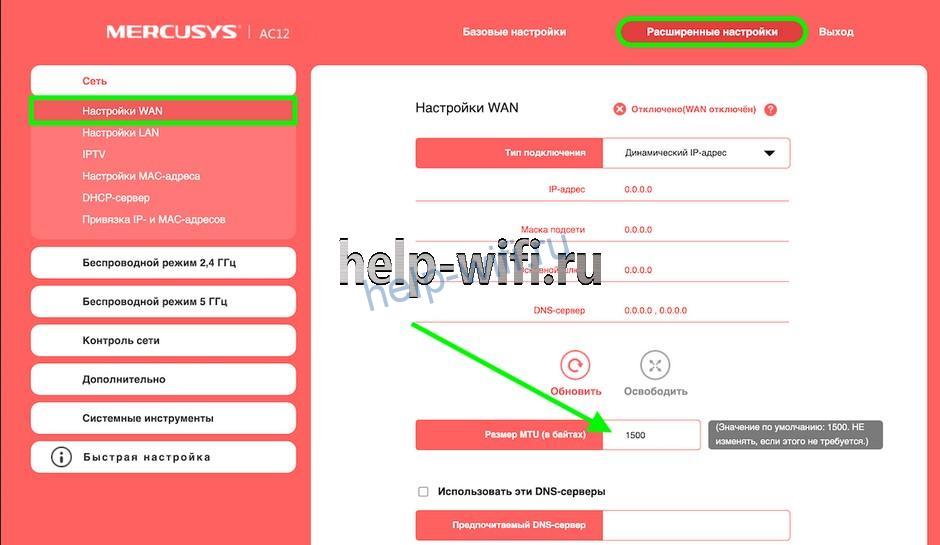
Mercusys
Откройте меню «Расширенные настройки», перейдите в пункт «Настройки WAN».
Настройка на компьютере
Поменять MTU в Windows 7, 10 можно за несколько минут.
Пошагово процесс выглядит так:
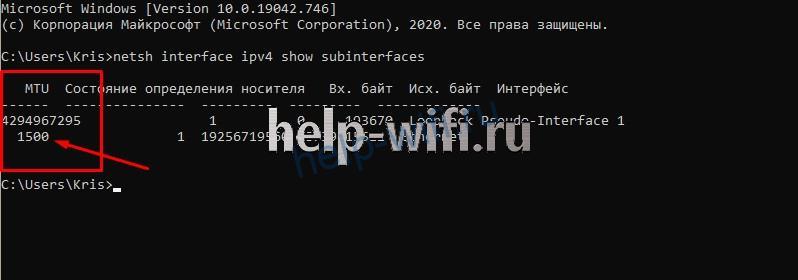
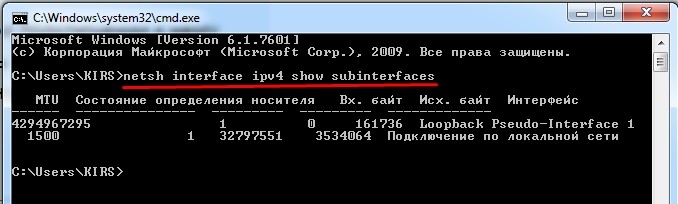
- Определите текущую величину МТУ. Запустите командную строку. Введите команду «netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces». На экране появится таблица, в которой видно, что значение параметра 1500.
- Установите новое значение максимального размера передаваемых пакетов. Для этого введите команду «netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface “Ethernet” mtu=1300 store=persistent», где 1300 – новая величина передаваемого блока данных.
- Проверить ввод новых настроек. Необходимо снова ввести команду «netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces». Проверка считается успешной, если значение изменилось на 1300. Если значение осталось прежним, то снова введите команду из пункта 2.
После сохранения этих настроек с компьютера будут отправляться пакеты, максимальный размер которых ограничен на IP-уровне 1300 байтами. Но на MAC-уровне их величина будет равна 1314 байт. Отправка пакетов данных большего размера осуществляться не будет.
В ОС семейства Linux тоже можно изменить МТУ. Для этого запустите консоль комбинацией Ctrl+Alt+F1.
Дальнейший порядок действий:
- Определите величину МТУ с помощью команды ip link.
- Установите новое значение максимального передаваемого блока данных с помощью команды «ip link set dev eth0 mtu 1200», где 1200 – нужный размер МТУ.
С помощью команды происходит временная замена значения максимальной величины передаваемых пакетов на 1200. После перезагрузки восстановится значение по умолчанию. Для того, чтобы сделать новую величину постоянной, отредактируйте файл /etc/network/interfaces. К описанию нужного интерфейса (eth0) добавьте отдельной строкой mtu 1200.
После сохранения настроек выполните команду ifdown $eth0 && ifup $eth0, где eth0 – наименование интерфейса.
Что будет, если установить некорректное значение
Если на маршрутизаторе поменять значение МТУ на некорректное, возникнут проблемы с интернетом. При маленьком размере пакетов во время загрузки некоторых сайтов будут появляться ошибки, увеличится пинг. Установить значение МТУ больше стандартного не позволит прошивка роутера. Ограничение на максимальный размер пакета данных есть во всех современных модемах и маршрутизаторах.
Если пользователь все-таки сможет установить большой размер параметра, интернет работать не будет.
Роутер для раздачи проводного интернета по Wi-Fi установлен практически в каждой современной квартире. Чаще всего пользователи настраивают маршрутизатор единожды, используя помощник по автоматической настройке, после чего не изменяя опции устройства. Подобная позиция не всегда правильная, и зачастую автоматическая настройка Wi-Fi роутера не позволяет добиться максимально качественного соединения с интернетом. Одной из опций в настройках маршрутизатора, которой пользователи не уделяют должного внимания, является MTU. В рамках данной статьи рассмотрим, что такое MTU в настройках роутера, и какое значение нужно выставить для оптимальной работы интернета.
Что такое MTU в настройках роутера

Если не вдаваться в подробности, то можно сказать, что параметр MTU отвечает за качество передачи информации от провайдера к компьютеру пользователя. При этом под качеством понимается не только исключение вероятности потери данных при передаче, но и скорость.
Почему нужно ограничить размер MTU в настройках роутера
В большинстве современных роутеров размер передаваемых MTU определяется автоматически, и делается это не всегда правильно. Пользователям, которые заботятся о качестве и скорости соединения, рекомендуется самостоятельно ограничить размер MTU, определив его оптимальное значение и установив его в настройках маршрутизатора.
Благодаря правильно выставленным настройкам MTU удается:
- Расширить канал передачи, за счет чего им одновременно смогут пользоваться различные службы, программы, процессы и так далее;
- Избавить канал от лишней нагрузки, что увеличит скорость передачи данных;
- Снизить практически до нуля шанс получения «испорченных пакетов» с данными при передаче по сети.
В целом, при правильно выставленных ограничениях MTU удается рационально использовать предлагаемый провайдером канал связи, с минимальным риском потери информации.
Правильная настройка MTU необходима, если имеются проблемы с интернетом на компьютере, например: долго загружаются сайты, высокий пинг при подключении к сторонним серверам, загрузка файлов из интернета время от времени беспричинно обрывается и возникают другие проблемы.
Какое значение MTU нужно выставить
Чтобы определить оптимальное значение MTU, нужно провести тестирование сети, что можно сделать с компьютера под управлением Windows. В ходе тестирования потребуется определить, как много времени уходит для передачи и возврата пакета с данными от используемого компьютера до сервера. При этом в ходе теста нужно будет варьировать количество байт информации, содержащейся в пакете. Снижать число байт потребуется до того момента, пока не удастся полностью исключить фрагментацию пакета.
Выполните тестирование сети следующим образом:
- Запустите командную строку Windows от имени администратора;
- Далее введите тестовую команду, например, для отправки запроса на сервер нашего сайта okeygeek. Выглядеть команда будет следующим образом:
Ping www.okeygeek.ru –f –l xxxx
В данной команде заменит XXXX на значение MTU. Как было отмечено выше, данное значение необходимо варьировать, в поиске идеального. Рекомендуем начать с MTU в 1500, то есть первой командой будет:
Ping www.okeygeek.ru –f –l 1500
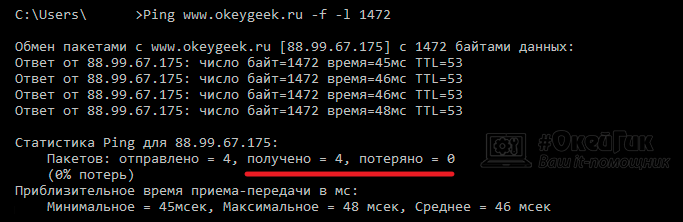
- После выполнения команды, в строке отобразится результат. Будет указано, какое количество пакетов отправлено, получено и потеряно. Нужно добиться, чтобы потеряно было не более 10% пакетов.
- Путем подбора определите оптимальное значение MTU, в нашем случае оно равно 1472 байтам.
Обратите внимание: Чаще всего оптимальное значение MTU находится в пределах от 1500 до 1400 байт.
Определившись с оптимальным значением MTU, нужно изменить данную опцию в настройках роутера, установив определенное количество байт, но с небольшим изменением. Дело в том, что конечная величина MTU будет отличаться от определенной в прошлом шаге, поскольку потребуются дополнительные байты для формирования пакета, которые уйдут на его заголовок и запрос.
В среднем, на заголовок и запрос требуется 28 байт. Соответственно, идеальное значение в рассматриваемом случае будет:
1472 байта + 28 байт = 1500 байт
Значение 1500 потребуется прописывать в настройках роутера.
Важно отметить, что максимально допустимые значения напрямую зависят от протокола передачи данных, который используется:
- PPPoE – 1420 байт;
- Dynamic/Static IP – 1500 байт;
- L2TP – 1460 байт.
Значение, определенное выше в ходе расчетов, не должно превышать максимально допустимое. Если оно его превышает, возникнут еще более серьезные проблемы с работой интернета.
(425 голос., средний: 4,50 из 5)
Загрузка…
In computer networking, the maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the size of the largest protocol data unit (PDU) that can be communicated in a single network layer transaction.[1] The MTU relates to, but is not identical to the maximum frame size that can be transported on the data link layer, e.g., Ethernet frame.
Larger MTU is associated with reduced overhead. Smaller MTU values can reduce network delay. In many cases, MTU is dependent on underlying network capabilities and must be adjusted manually or automatically so as to not exceed these capabilities. MTU parameters may appear in association with a communications interface or standard. Some systems may decide MTU at connect time, e.g. using Path MTU Discovery.
Applicability
Edit
MTUs apply to communications protocols and network layers. The MTU is specified in terms of bytes or octets of the largest PDU that the layer can pass onwards. MTU parameters usually appear in association with a communications interface (NIC, serial port, etc.). Standards (Ethernet, for example) can fix the size of an MTU; or systems (such as point-to-point serial links) may decide MTU at connect time.
Underlying data link and physical layers usually add overhead to the network layer data to be transported, so for a given maximum frame size of a medium, one needs to subtract the amount of overhead to calculate that medium’s MTU. For example, with Ethernet, the maximum frame size is 1518 bytes, 18 bytes of which are overhead (header and frame check sequence), resulting in an MTU of 1500 bytes.
Tradeoffs
Edit
A larger MTU brings greater efficiency because each network packet carries more user data while protocol overheads, such as headers or underlying per-packet delays, remain fixed; the resulting higher efficiency means an improvement in bulk protocol throughput. A larger MTU also requires processing of fewer packets for the same amount of data. In some systems, per-packet-processing can be a critical performance limitation.
However, this gain is not without a downside. Large packets occupy a slow link for more time than a smaller packet, causing greater delays to subsequent packets, and increasing network delay and delay variation. For example, a 1500-byte packet, the largest allowed by Ethernet at the network layer, ties up a 14.4k modem for about one second.
Large packets are also problematic in the presence of communications errors. If no forward error correction is used, corruption of a single bit in a packet requires that the entire packet be retransmitted, which can be costly. At a given bit error rate, larger packets are more susceptible to corruption. Their greater payload makes retransmissions of larger packets take longer. Despite the negative effects on retransmission duration, large packets can still have a net positive effect on end-to-end TCP performance.[2]
Internet protocol
Edit
The Internet protocol suite was designed to work over many different networking technologies, each of which may use packets of different sizes. While a host will know the MTU of its own interface and possibly that of its peers (from initial handshakes), it will not initially know the lowest MTU in a chain of links to other peers. Another potential problem is that higher-level protocols may create packets larger than even the local link supports.
IPv4 allows fragmentation which divides the datagram into pieces, each small enough to accommodate a specified MTU limitation. This fragmentation process takes place at the internet layer. The fragmented packets are marked so that the IP layer of the destination host knows it should reassemble the packets into the original datagram.
All fragments of a packet must arrive for the packet to be considered received. If the network drops any fragment, the entire packet is lost.
When the number of packets that must be fragmented or the number of fragments is great, fragmentation can cause unreasonable or unnecessary overhead. For example, various tunneling situations may exceed the MTU by very little as they add just a header’s worth of data. The addition is small, but each packet now has to be sent in two fragments, the second of which carries very little payload. The same amount of payload is being moved, but every intermediate router has to forward twice as many packets.
The Internet Protocol requires that hosts must be able to process IP datagrams of at least 576 bytes (for IPv4) or 1280 bytes (for IPv6). However, this does not preclude link layers with an MTU smaller than this minimum MTU from conveying IP data. For example, according to IPv6’s specification, if a particular link layer cannot deliver an IP datagram of 1280 bytes in a single frame, then the link layer must provide its own fragmentation and reassembly mechanism, separate from the IP fragmentation mechanism, to ensure that a 1280-byte IP datagram can be delivered, intact, to the IP layer.
MTUs for common media
Edit
In the context of Internet Protocol, MTU refers to the maximum size of an IP packet that can be transmitted without fragmentation over a given medium. The size of an IP packet includes IP headers but excludes headers from the link layer. In the case of an Ethernet frame this adds an overhead of 18 bytes, or 22 bytes with an IEEE 802.1Q tag for VLAN tagging or class of service.
The MTU should not be confused with the minimum datagram size that all hosts must be prepared to accept. This is 576 bytes for IPv4[3] and of 1280 bytes for IPv6.[4]
| Media for IP transport | Maximum transmission unit (bytes) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Internet IPv4 path MTU | At least 68,[5] max of 64 KiB[6] | Systems may use Path MTU Discovery[7] to find the actual path MTU. Routing from larger MTU to smaller MTU causes IP fragmentation. |
| Internet IPv6 path MTU | At least 1280,[8] max of 64 KiB, but up to 4 GiB with optional jumbogram[9] | Systems must use Path MTU Discovery[10] to find the actual path MTU. |
| X.25 | Minimal 576 (sending) or 1600 (receiving)[11] | |
| Ethernet v2 | 1500[12] | Nearly all IP over Ethernet implementations use the Ethernet II frame format. |
| Ethernet with LLC and SNAP | 1492[13] | |
| Ethernet jumbo frames | 1501 – 9202[14] or more[15] | The limit varies by vendor. For correct interoperation, frames should be no larger than the maximum frame size supported by any device on the network segment.[16] Jumbo frames are usually only seen in special-purpose networks. |
| PPPoE v2 | 1492[17] | Ethernet II MTU (1500) less PPPoE header (8) |
| DS-Lite over PPPoE | 1452 | Ethernet II MTU (1500) less PPPoE header (8) and IPv6 header (40) |
| PPPoE jumbo frames | 1493 – 9190 or more[18] | Ethernet Jumbo Frame MTU (1501 — 9198) less PPPoE header (8) |
| IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi (WLAN) | 2304[19] | The maximum MSDU size is 2304 before encryption. WEP will add 8 bytes, WPA-TKIP 20 bytes, and WPA2-CCMP 16 bytes. |
| Token Ring (802.5) | 4464 | |
| FDDI | 4352[7] |
Ethernet maximum frame size
Edit
The IP MTU and Ethernet maximum frame size are configured separately. In Ethernet switch configuration, MTU may refer to Ethernet maximum frame size. In Ethernet-based routers, MTU normally refers to the IP MTU. If jumbo frames are allowed in a network, the IP MTU should also be adjusted upwards to take advantage of this.
Since the IP packet is carried by an Ethernet frame, the Ethernet frame has to be larger than the IP packet. With the normal untagged Ethernet frame overhead of 18 bytes, the Ethernet maximum frame size is 1518 bytes. If a 1500 byte IP packet is to be carried over a tagged Ethernet connection, the Ethernet frame maximum size needs to be 1522 due to the larger size of an 802.1Q tagged frame. 802.3ac increases the standard Ethernet maximum frame size to accommodate this.
Path MTU Discovery
Edit
The Internet Protocol defines the path MTU of an Internet transmission path as the smallest MTU supported by any of the hops on the path between a source and destination. Put another way, the path MTU is the largest packet size that can traverse this path without suffering fragmentation.
Path MTU Discovery is a technique for determining the path MTU between two IP hosts, defined for both IPv4[20] and IPv6[21]. It works by sending packets with the DF (don’t fragment) option in the IP header set. Any device along the path whose MTU is smaller than the packet will drop such packets and send back an ICMP Destination Unreachable (Datagram Too Big) message which indicates its MTU. This information allows the source host to reduce its assumed path MTU appropriately. The process repeats until the MTU becomes small enough to traverse the entire path without fragmentation.
Standard Ethernet supports an MTU of 1500 bytes and Ethernet implementation supporting jumbo frames, allow for an MTU up to 9000 bytes. However, border protocols like PPPoE will reduce this. Path MTU Discovery exposes the difference between the MTU seen by Ethernet end-nodes and the Path MTU.
Unfortunately, increasing numbers of networks drop ICMP traffic (for example, to prevent denial-of-service attacks), which prevents path MTU discovery from working. Packetization Layer Path MTU Discovery[22][23] is a Path MTU Discovery technique which responds more robustly to ICMP filtering. In an IP network, the path from the source address to the destination address may change in response to various events (load-balancing, congestion, outages, etc.) and this could result in the path MTU changing (sometimes repeatedly) during a transmission, which may introduce further packet drops before the host finds a new reliable MTU.
A failure of Path MTU Discovery carries the possible result of making some sites behind badly configured firewalls unreachable. A connection with mismatched MTU may work for low-volume data but fail as soon as a host sends a large block of data. For example, with Internet Relay Chat a connecting client might see the initial messages up to and including the initial ping (sent by the server as an anti-spoofing measure), but get no response after that. This is because the large set of welcome messages sent at that point are packets that exceed the path MTU. One can possibly work around this, depending on which part of the network one controls; for example one can change the MSS (maximum segment size) in the initial packet that sets up the TCP connection at one’s firewall.
In other contexts
Edit
MTU is sometimes used to describe the maximum PDU sizes in communication layers other than the network layer.
- Cisco Systems and MikroTik use L2 MTU for the maximum frame size.[24][25]
- Dell/Force10 use MTU for the maximum frame size.[26]
- Hewlett-Packard used just MTU for the maximum frame size including the optional IEEE 802.1Q tag.[27]
- Juniper Networks use several MTU terms: Physical Interface MTU (L3 MTU plus some unspecified protocol overhead), Logical Interface MTU (consistent with IETF MTU) and Maximum MTU (maximum configurable frame size for jumbo frames).[28]
The transmission of a packet on a physical network segment that is larger than the segment’s MTU is known as jabber. This is almost always caused by faulty devices.[29] Network switches and some repeater hubs have a built-in capability to detect when a device is jabbering.[30][31]
References
Edit
- ^ RFC 791. p. 25. doi:10.17487/RFC0791.
- ^ Murray, David; Terry Koziniec; Kevin Lee; Michael Dixon (2012). «Large MTUs and internet performance». 2012 IEEE 13th International Conference on High Performance Switching and Routing. pp. 82–87. doi:10.1109/HPSR.2012.6260832. ISBN 978-1-4577-0833-6. S2CID 232321.
- ^ RFC 791. p. 24. doi:10.17487/RFC0791.
Every internet destination must be able to receive a datagram of 576 octets either in one piece or in fragments to be reassembled.
- ^ RFC 2460. p. 13. doi:10.17487/RFC2460.
- ^ RFC 791. p. 24. doi:10.17487/RFC0791.
Every internet module must be able to forward a datagram of 68 octets without further fragmentation.
- ^ RFC 791. p. 12. doi:10.17487/RFC0791.
Total Length is the length of the datagram, measured in octets, including internet header and data. This field allows the length of a datagram to be up to 65,535 octets.
- ^ a b RFC 1191. doi:10.17487/RFC1191.
- ^ RFC 2460
- ^ RFC 2675, p. 1, «The IPv6 header [IPv6] has a 16-bit Payload Length field and, therefore, supports payloads up to 65,535 octets long. This document specifies an IPv6 hop-by-hop option, called the Jumbo Payload option, that carries a 32-bit length field in order to allow transmission of IPv6 packets with payloads between 65,536 and 4,294,967,295 octets in length. Packets with such long payloads are referred to as ‘jumbograms’.»
- ^ RFC 6145
- ^ RFC 1356
- ^
Network Working Group of the IETF,
RFC 894: A Standard for the Transmission of IP Datagrams over Ethernet Networks,
Page 1,
«The maximum length of the data field of a packet sent over an Ethernet is 1500 octets, thus the maximum length of an IP datagram sent over an Ethernet is 1500 octets.»,
ERRATA - ^ IEEE 802.3[page needed]
- ^ Scott Hogg (2013-03-06), Jumbo Frames, Network World, retrieved 2013-08-05,
Most network devices support a jumbo frame size of 9216 bytes.
- ^ Juniper Networks (2020-03-23), Physical Interface Properties, retrieved 2020-05-01
- ^ Joe St Sauver (2003-02-04). «Practical Issues Associated With 9K MTUs» (PDF). uoregon.edu. p. 67. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
you still need to insure that ALL upstream Ethernet switches, including any switches in your campus core, are ALSO jumbo frame capable
- ^ RFC 2516 with the standard Ethernet MTU of 1500 bytes; extensions exist
- ^ RFC 4638
- ^ 802.11-2012, page 413, section 8.3.2.1
- ^ J. Mogul; S. Deering (November 1990). Path MTU Discovery. Network Working Group. doi:10.17487/RFC1191. RFC 1191. Draft Standard. Obsoletes RFC 1063.
- ^ J. McCann; S. Deering; J. Mogul (July 2017). R. Hinden (ed.). Path MTU Discovery for IP version 6. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8201. STD 87. RFC 8201. Internet Standard. Obsoletes RFC 1981.
- ^ M. Mathis; J. Heffner (March 2007). Packetization Layer Path MTU Discovery. Network Working Group. doi:10.17487/RFC4821. RFC 4821. Proposed Standard. Updated by RFC 8899.
- ^ G. Fairhurst; T. Jones; M. Tüxen; I. Rüngeler; T. Völker (September 2020). Packetization Layer Path MTU Discovery for Datagram Transports. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8899. ISSN 2070-1721. RFC 8899. Proposed Standard. Updates RFC 4821, 4960, 6951, 8085 and 8261.
- ^ «Configure and Verify Maximum Transmission Unit on Cisco Nexus Platforms». Cisco. 2016-11-29. Document ID:118994. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ «MTU in RouterOS». MikroTik. 2022-07-08. Retrieved 2022-09-02.
- ^ «How to configure MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) for Jumbo Frames on Dell Networking Force10 switches». Dell. 2016-06-02. Article ID: HOW10713. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ^ «Jumbo Frames». HP Networking 2910al Switches Management and Configuration Guide. Hewlett-Packard. November 2011. P/N 5998-2874.
- ^ «SRX Series Services Gateways for the Branch Physical Interface Modules Reference: MTU Default and Maximum Values for Physical Interface Modules«. Juniper. 2014-01-03. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ jabber, The Network Encyclopedia, retrieved 2016-07-28
- ^ show interfaces, Juniper Networks, retrieved 2016-07-28
- ^ IEEE 802.3 27.3.1.7 Receive jabber functional requirements
External links
Edit
- Marc Slemko (January 18, 1998). «Path MTU Discovery and Filtering ICMP». Archived from the original on August 9, 2011. Retrieved 2007-09-02.
- Tweaking your MTU / RWin for Orange Broadband Users
- How to set the TCP MSS value using iptables
- mturoute – a console utility for debugging mtu problems
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer networking, the maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the size of the largest protocol data unit (PDU) that can be communicated in a single network layer transaction.[1] The MTU relates to, but is not identical to the maximum frame size that can be transported on the data link layer, e.g., Ethernet frame.
Larger MTU is associated with reduced overhead. Smaller MTU values can reduce network delay. In many cases, MTU is dependent on underlying network capabilities and must be adjusted manually or automatically so as to not exceed these capabilities. MTU parameters may appear in association with a communications interface or standard. Some systems may decide MTU at connect time, e.g. using Path MTU Discovery.
Applicability[edit]
MTUs apply to communications protocols and network layers. The MTU is specified in terms of bytes or octets of the largest PDU that the layer can pass onwards. MTU parameters usually appear in association with a communications interface (NIC, serial port, etc.). Standards (Ethernet, for example) can fix the size of an MTU; or systems (such as point-to-point serial links) may decide MTU at connect time.
Underlying data link and physical layers usually add overhead to the network layer data to be transported, so for a given maximum frame size of a medium, one needs to subtract the amount of overhead to calculate that medium’s MTU. For example, with Ethernet, the maximum frame size is 1518 bytes, 18 bytes of which are overhead (header and frame check sequence), resulting in an MTU of 1500 bytes.
Tradeoffs[edit]
A larger MTU brings greater efficiency because each network packet carries more user data while protocol overheads, such as headers or underlying per-packet delays, remain fixed; the resulting higher efficiency means an improvement in bulk protocol throughput. A larger MTU also requires processing of fewer packets for the same amount of data. In some systems, per-packet-processing can be a critical performance limitation.
However, this gain is not without a downside. Large packets occupy a slow link for more time than a smaller packet, causing greater delays to subsequent packets, and increasing network delay and delay variation. For example, a 1500-byte packet, the largest allowed by Ethernet at the network layer, ties up a 14.4k modem for about one second.
Large packets are also problematic in the presence of communications errors. If no forward error correction is used, corruption of a single bit in a packet requires that the entire packet be retransmitted, which can be costly. At a given bit error rate, larger packets are more susceptible to corruption. Their greater payload makes retransmissions of larger packets take longer. Despite the negative effects on retransmission duration, large packets can still have a net positive effect on end-to-end TCP performance.[2]
Internet protocol[edit]
The Internet protocol suite was designed to work over many different networking technologies, each of which may use packets of different sizes. While a host will know the MTU of its own interface and possibly that of its peers (from initial handshakes), it will not initially know the lowest MTU in a chain of links to other peers. Another potential problem is that higher-level protocols may create packets larger than even the local link supports.
IPv4 allows fragmentation which divides the datagram into pieces, each small enough to accommodate a specified MTU limitation. This fragmentation process takes place at the internet layer. The fragmented packets are marked so that the IP layer of the destination host knows it should reassemble the packets into the original datagram.
All fragments of a packet must arrive for the packet to be considered received. If the network drops any fragment, the entire packet is lost.
When the number of packets that must be fragmented or the number of fragments is great, fragmentation can cause unreasonable or unnecessary overhead. For example, various tunneling situations may exceed the MTU by very little as they add just a header’s worth of data. The addition is small, but each packet now has to be sent in two fragments, the second of which carries very little payload. The same amount of payload is being moved, but every intermediate router has to forward twice as many packets.
The Internet Protocol requires that hosts must be able to process IP datagrams of at least 576 bytes (for IPv4) or 1280 bytes (for IPv6). However, this does not preclude link layers with an MTU smaller than this minimum MTU from conveying IP data. For example, according to IPv6’s specification, if a particular link layer cannot deliver an IP datagram of 1280 bytes in a single frame, then the link layer must provide its own fragmentation and reassembly mechanism, separate from the IP fragmentation mechanism, to ensure that a 1280-byte IP datagram can be delivered, intact, to the IP layer.
MTUs for common media[edit]
In the context of Internet Protocol, MTU refers to the maximum size of an IP packet that can be transmitted without fragmentation over a given medium. The size of an IP packet includes IP headers but excludes headers from the link layer. In the case of an Ethernet frame this adds an overhead of 18 bytes, or 22 bytes with an IEEE 802.1Q tag for VLAN tagging or class of service.
The MTU should not be confused with the minimum datagram size that all hosts must be prepared to accept. This is 576 bytes for IPv4[3] and of 1280 bytes for IPv6.[4]
| Media for IP transport | Maximum transmission unit (bytes) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Internet IPv4 path MTU | At least 68,[5] max of 64 KiB[6] | Systems may use Path MTU Discovery[7] to find the actual path MTU. Routing from larger MTU to smaller MTU causes IP fragmentation. |
| Internet IPv6 path MTU | At least 1280,[8] max of 64 KiB, but up to 4 GiB with optional jumbogram[9] | Systems must use Path MTU Discovery[10] to find the actual path MTU. |
| X.25 | Minimal 576 (sending) or 1600 (receiving)[11] | |
| Ethernet v2 | 1500[12] | Nearly all IP over Ethernet implementations use the Ethernet II frame format. |
| Ethernet with LLC and SNAP | 1492[13] | |
| Ethernet jumbo frames | 1501 – 9202[14] or more[15] | The limit varies by vendor. For correct interoperation, frames should be no larger than the maximum frame size supported by any device on the network segment.[16] Jumbo frames are usually only seen in special-purpose networks. |
| PPPoE v2 | 1492[17] | Ethernet II MTU (1500) less PPPoE header (8) |
| DS-Lite over PPPoE | 1452 | Ethernet II MTU (1500) less PPPoE header (8) and IPv6 header (40) |
| PPPoE jumbo frames | 1493 – 9190 or more[18] | Ethernet Jumbo Frame MTU (1501 — 9198) less PPPoE header (8) |
| IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi (WLAN) | 2304[19] | The maximum MSDU size is 2304 before encryption. WEP will add 8 bytes, WPA-TKIP 20 bytes, and WPA2-CCMP 16 bytes. |
| Token Ring (802.5) | 4464 | |
| FDDI | 4352[7] |
Ethernet maximum frame size[edit]
The IP MTU and Ethernet maximum frame size are configured separately. In Ethernet switch configuration, MTU may refer to Ethernet maximum frame size. In Ethernet-based routers, MTU normally refers to the IP MTU. If jumbo frames are allowed in a network, the IP MTU should also be adjusted upwards to take advantage of this.
Since the IP packet is carried by an Ethernet frame, the Ethernet frame has to be larger than the IP packet. With the normal untagged Ethernet frame overhead of 18 bytes, the Ethernet maximum frame size is 1518 bytes. If a 1500 byte IP packet is to be carried over a tagged Ethernet connection, the Ethernet frame maximum size needs to be 1522 due to the larger size of an 802.1Q tagged frame. 802.3ac increases the standard Ethernet maximum frame size to accommodate this.
Path MTU Discovery[edit]
The Internet Protocol defines the path MTU of an Internet transmission path as the smallest MTU supported by any of the hops on the path between a source and destination. Put another way, the path MTU is the largest packet size that can traverse this path without suffering fragmentation.
Path MTU Discovery is a technique for determining the path MTU between two IP hosts, defined for both IPv4[20] and IPv6[21]. It works by sending packets with the DF (don’t fragment) option in the IP header set. Any device along the path whose MTU is smaller than the packet will drop such packets and send back an ICMP Destination Unreachable (Datagram Too Big) message which indicates its MTU. This information allows the source host to reduce its assumed path MTU appropriately. The process repeats until the MTU becomes small enough to traverse the entire path without fragmentation.
Standard Ethernet supports an MTU of 1500 bytes and Ethernet implementation supporting jumbo frames, allow for an MTU up to 9000 bytes. However, border protocols like PPPoE will reduce this. Path MTU Discovery exposes the difference between the MTU seen by Ethernet end-nodes and the Path MTU.
Unfortunately, increasing numbers of networks drop ICMP traffic (for example, to prevent denial-of-service attacks), which prevents path MTU discovery from working. Packetization Layer Path MTU Discovery[22][23] is a Path MTU Discovery technique which responds more robustly to ICMP filtering. In an IP network, the path from the source address to the destination address may change in response to various events (load-balancing, congestion, outages, etc.) and this could result in the path MTU changing (sometimes repeatedly) during a transmission, which may introduce further packet drops before the host finds a new reliable MTU.
A failure of Path MTU Discovery carries the possible result of making some sites behind badly configured firewalls unreachable. A connection with mismatched MTU may work for low-volume data but fail as soon as a host sends a large block of data. For example, with Internet Relay Chat a connecting client might see the initial messages up to and including the initial ping (sent by the server as an anti-spoofing measure), but get no response after that. This is because the large set of welcome messages sent at that point are packets that exceed the path MTU. One can possibly work around this, depending on which part of the network one controls; for example one can change the MSS (maximum segment size) in the initial packet that sets up the TCP connection at one’s firewall.
In other contexts[edit]
MTU is sometimes used to describe the maximum PDU sizes in communication layers other than the network layer.
- Cisco Systems and MikroTik use L2 MTU for the maximum frame size.[24][25]
- Dell/Force10 use MTU for the maximum frame size.[26]
- Hewlett-Packard used just MTU for the maximum frame size including the optional IEEE 802.1Q tag.[27]
- Juniper Networks use several MTU terms: Physical Interface MTU (L3 MTU plus some unspecified protocol overhead), Logical Interface MTU (consistent with IETF MTU) and Maximum MTU (maximum configurable frame size for jumbo frames).[28]
The transmission of a packet on a physical network segment that is larger than the segment’s MTU is known as jabber. This is almost always caused by faulty devices.[29] Network switches and some repeater hubs have a built-in capability to detect when a device is jabbering.[30][31]
References[edit]
- ^ RFC 791. p. 25. doi:10.17487/RFC0791.
- ^ Murray, David; Terry Koziniec; Kevin Lee; Michael Dixon (2012). «Large MTUs and internet performance». 2012 IEEE 13th International Conference on High Performance Switching and Routing. pp. 82–87. doi:10.1109/HPSR.2012.6260832. ISBN 978-1-4577-0833-6. S2CID 232321.
- ^ RFC 791. p. 24. doi:10.17487/RFC0791.
Every internet destination must be able to receive a datagram of 576 octets either in one piece or in fragments to be reassembled.
- ^ RFC 2460. p. 13. doi:10.17487/RFC2460.
- ^ RFC 791. p. 24. doi:10.17487/RFC0791.
Every internet module must be able to forward a datagram of 68 octets without further fragmentation.
- ^ RFC 791. p. 12. doi:10.17487/RFC0791.
Total Length is the length of the datagram, measured in octets, including internet header and data. This field allows the length of a datagram to be up to 65,535 octets.
- ^ a b RFC 1191. doi:10.17487/RFC1191.
- ^ RFC 2460
- ^ RFC 2675, p. 1, «The IPv6 header [IPv6] has a 16-bit Payload Length field and, therefore, supports payloads up to 65,535 octets long. This document specifies an IPv6 hop-by-hop option, called the Jumbo Payload option, that carries a 32-bit length field in order to allow transmission of IPv6 packets with payloads between 65,536 and 4,294,967,295 octets in length. Packets with such long payloads are referred to as ‘jumbograms’.»
- ^ RFC 6145
- ^ RFC 1356
- ^
Network Working Group of the IETF,
RFC 894: A Standard for the Transmission of IP Datagrams over Ethernet Networks,
Page 1,
«The maximum length of the data field of a packet sent over an Ethernet is 1500 octets, thus the maximum length of an IP datagram sent over an Ethernet is 1500 octets.»,
ERRATA - ^ IEEE 802.3[page needed]
- ^ Scott Hogg (2013-03-06), Jumbo Frames, Network World, retrieved 2013-08-05,
Most network devices support a jumbo frame size of 9216 bytes.
- ^ Juniper Networks (2020-03-23), Physical Interface Properties, retrieved 2020-05-01
- ^ Joe St Sauver (2003-02-04). «Practical Issues Associated With 9K MTUs» (PDF). uoregon.edu. p. 67. Retrieved 2016-12-15.
you still need to insure that ALL upstream Ethernet switches, including any switches in your campus core, are ALSO jumbo frame capable
- ^ RFC 2516 with the standard Ethernet MTU of 1500 bytes; extensions exist
- ^ RFC 4638
- ^ 802.11-2012, page 413, section 8.3.2.1
- ^ J. Mogul; S. Deering (November 1990). Path MTU Discovery. Network Working Group. doi:10.17487/RFC1191. RFC 1191. Draft Standard. Obsoletes RFC 1063.
- ^ J. McCann; S. Deering; J. Mogul (July 2017). R. Hinden (ed.). Path MTU Discovery for IP version 6. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8201. STD 87. RFC 8201. Internet Standard. Obsoletes RFC 1981.
- ^ M. Mathis; J. Heffner (March 2007). Packetization Layer Path MTU Discovery. Network Working Group. doi:10.17487/RFC4821. RFC 4821. Proposed Standard. Updated by RFC 8899.
- ^ G. Fairhurst; T. Jones; M. Tüxen; I. Rüngeler; T. Völker (September 2020). Packetization Layer Path MTU Discovery for Datagram Transports. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC8899. ISSN 2070-1721. RFC 8899. Proposed Standard. Updates RFC 4821, 4960, 6951, 8085 and 8261.
- ^ «Configure and Verify Maximum Transmission Unit on Cisco Nexus Platforms». Cisco. 2016-11-29. Document ID:118994. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ «MTU in RouterOS». MikroTik. 2022-07-08. Retrieved 2022-09-02.
- ^ «How to configure MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) for Jumbo Frames on Dell Networking Force10 switches». Dell. 2016-06-02. Article ID: HOW10713. Retrieved 2017-01-06.
- ^ «Jumbo Frames». HP Networking 2910al Switches Management and Configuration Guide. Hewlett-Packard. November 2011. P/N 5998-2874.
- ^ «SRX Series Services Gateways for the Branch Physical Interface Modules Reference: MTU Default and Maximum Values for Physical Interface Modules«. Juniper. 2014-01-03. Retrieved 2017-01-04.
- ^ jabber, The Network Encyclopedia, retrieved 2016-07-28
- ^ show interfaces, Juniper Networks, retrieved 2016-07-28
- ^ IEEE 802.3 27.3.1.7 Receive jabber functional requirements
External links[edit]
- Marc Slemko (January 18, 1998). «Path MTU Discovery and Filtering ICMP». Archived from the original on August 9, 2011. Retrieved 2007-09-02.
- Tweaking your MTU / RWin for Orange Broadband Users
- How to set the TCP MSS value using iptables
- mturoute – a console utility for debugging mtu problems
Всем привет! Начнем, пожалуй, с вопроса – а что же такое MTU? MTU (от английского Maximum transmission unit) – это максимальный объем в пакете, который может передавать в той или иной сетевой среде. Как вы знаете, все данные передаются определенными пакетами – будь это интернет, Wi-Fi или локальная сеть дома. Все как на почте – почтальон не может переносить больше определенного веса.
Конечно, тут идут и некоторые ограничения. Например, в PPPoE обычно используется 1492 байта. При Ethernet подключении 1500 байта, а в беспроводной сети MTU равен 2304. Если же сетевому устройству нужно передать куда больше информации, то все делится как раз на эти MTU блоки.
Размер MTU зачастую определяется самим отправляющим устройством. MTU в настройках роутера также задается по умолчанию значением заданным разработчиками. Если говорить проще, то происходит следующее:
- Отправляющее устройство режет всю информацию на отдельные MTU куски и отправляет их по каналу связи.
- Принимающее устройство собираем все эти куски в целый кусок, отправленной информации.
Также нужно знать, что в размер MTU входит:
- MSS (Maximum Segment Size) – это основной блок данных.
- Заголовок IP.
- Заголовок ICMP
К чему может привести неправильное значение MTU? Если на роутере, который чаще всего является шлюзом между интернетом и локальной сетью, выставлено неправильное значение, то могут наблюдаться проблемы со связью и интернетом. Например, нельзя зайти на какой-то сайт, некоторые службы в локальной сети перестают работать. Но само значение можно выставить вручную в настройках маршрутизатора.
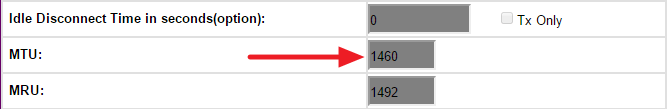
Также вы можете встретить параметр MRU (maximum receive unit) – это максимальный размер пакета, который может принять устройство. Все по аналогии с MTU. Далее я расскажу, как узнать оптимальный размер MTU в вашей сети и как установить это значение в роутере.
ВНИМАНИЕ! Это нужно делать только в том случае, если у вас наблюдаются проблемы с интернетом, сетью или какими-то сетевыми службами. Если у вас все в порядке, то лучше ничего не делать, так как дальнейшие действия могут привести к ухудшению связи.
Содержание
- Определение идеального MTU
- Установка MTU в роутере
- Zyxel Keenetic
- TP-Link
- D-Link
- ASUS
- LinkSys
- Netis
- Tenda
- Задать вопрос автору статьи
Способ достаточно простой – мы будем использовать встроенную утилиту в Windows «ping» с помощью командной строки. Нажмите на клавиши «Win» (находится в нижнем ряду между «Ctrl» и «Alt») и английскую «R».
В окошке введите команду «cmd» и нажмите «ОК». Командную строку также можно запустить через «Пуск», введя в поисковую строку эти три буквы.
Для начала давайте узнаем, какой MTU у нас стоит по умолчанию. Для этого вводим команду:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
Я подключен по Wi-Fi, поэтому у меня стоит стандартное значение 1500. Если же вы подключены к кабелю провайдера напрямую, то эта команда может вам помочь.
Далее мы будем использовать стандартную команду ping с определенными параметрами. Наша задача взять за основу какое-то определенное значение MTU и увеличивать его до тех пор, пока система не сообщит нам, что нам нужно установить параметр фрагментации или разбиения пакета.
Если говорить проще, то мы будем увеличивать пакет до тех пор, пока он проходит по нашему соединению в интернете. Для примера мы будем пинговать всем известный «google.com», но вы можете взять любой другой сайт:
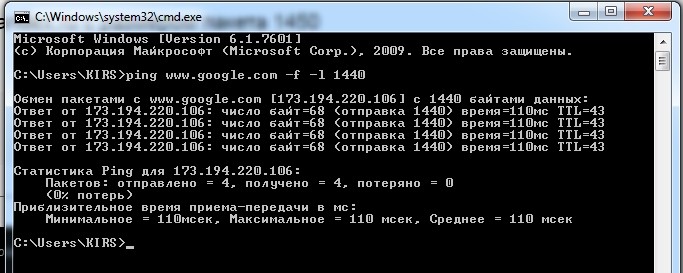
ping www.google.com -f -l 1440
В итоге мы видим, что пакеты с размером в 1440 байтов спокойно отправляются в сеть. Поэтому мы увеличим размер MTU на 1. Немного о команде: значение «-f» – запрещает фрагментировать пакет – это нужно для наших тестов. «-l» (маленькая английская буква «L») – задает размер пакета.
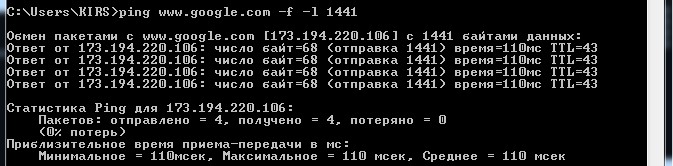
Теперь увеличиваем его на один. Чтобы не прописывать команду постоянно, нажмите на клавиатуре на стрелку вверх, сотрите последнюю цифру и увеличьте её на один:
ping www.google.com -f -l 1441
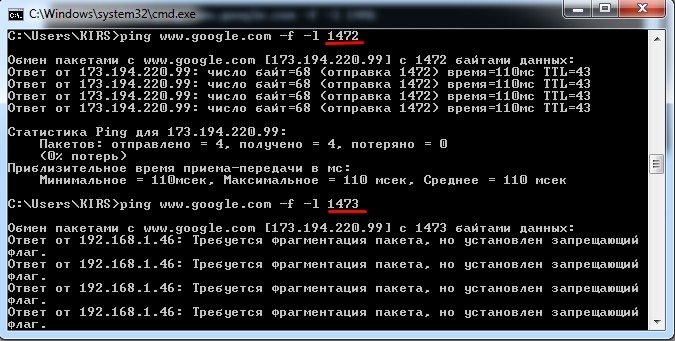
Как видите этот пакет также свободно проходит. В общем проделываем эту процедуру до тех пор, пока вы сами не найдете идеальный параметр для вашей среды. В самом конце вы должны увидеть сообщение:
«Требуется фрагментация пакета, но установлен запрещающий флаг»
В моем случае это 1472, но у вас может быть совершенно другой параметр, так что нужно проводить свои тесты.
Но это не окончательное значение MTU – это мы нашли только MSS. Поэтому к нему нам нужно прибавить IP и ICMP заголовки. Для этого просто прибавляем ещё 28 байта:
1472 + 28 = 1500
Теперь данное значение можно установить в вашем домашнем роутере.
Установка MTU в роутере
Для начала нам нужно зайти в настройки роутера – для этого нужно ввести IP или DNS адрес в адресную строку любого браузера. Можете попробовать популярные адреса:
- 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.0.1
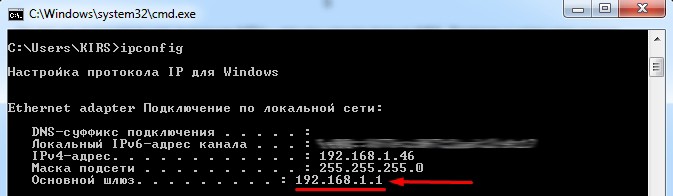
Адрес можно подсмотреть на этикетке под корпусом. Или ввести в консоль команду:
ipconfig
IP маршрутизатора будет в строке 192.168.1.1.
Далее инструкции могут отличаться в зависимости от модели роутера.
Zyxel Keenetic
Новая прошивка
«Проводной» – «Параметры IP и DNS» (или «Аутентификация у провайдера (PPPoE / PPTP / L2TP)»)
Старая прошивка
Переходим в раздел «Интернета» – далее на вкладке «Подключение» выбираем активный коннект к интернету.
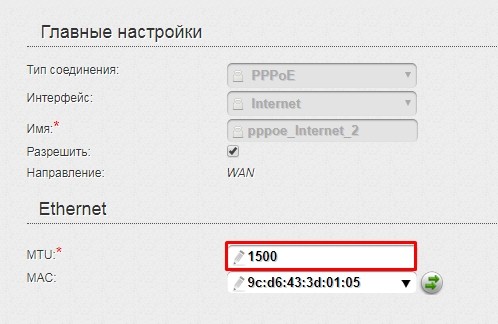
Ищем строку «Размер MTU».
TP-Link
Старая прошивка
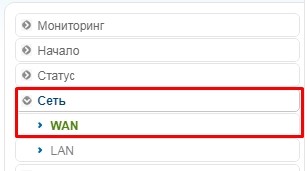
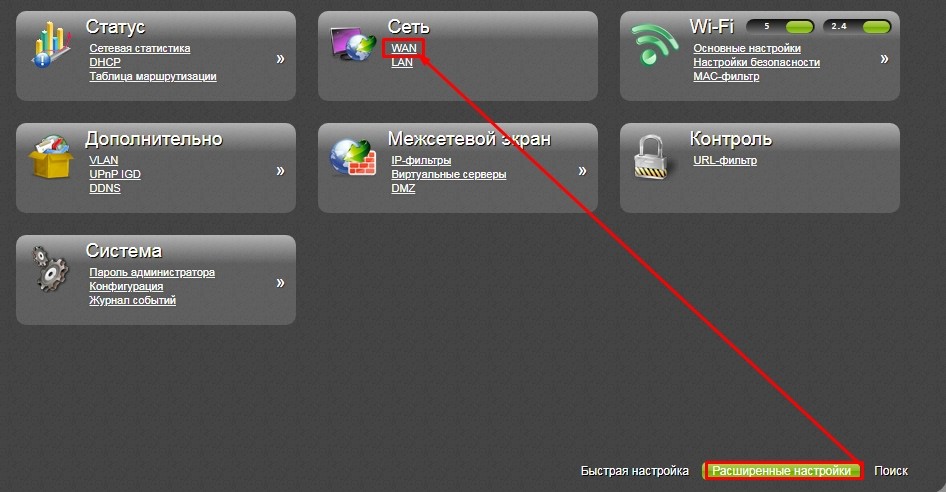
«Сеть» – «WAN».
Новая прошивка
«Дополнительные настройки» – «Сеть» – «Интернет» – «Дополнительные настройки».
D-Link
Классическая прошивка
«Сеть» – «WAN».
Новая прошивка
Из списка выбираем активное подключение (через которое идет интернет).
Далее находим параметр MTU.
ASUS
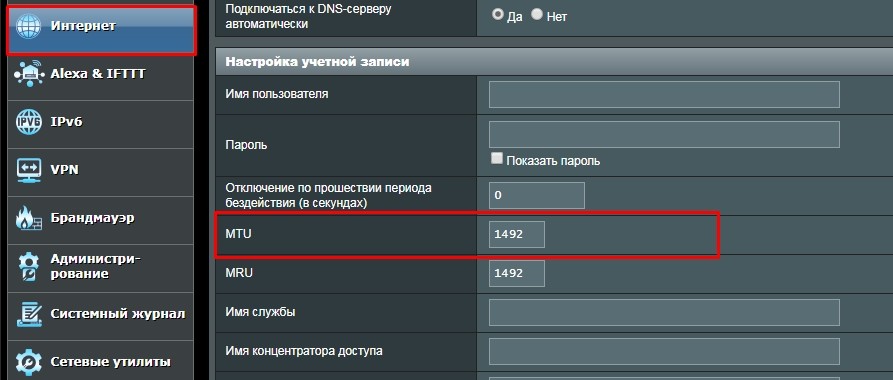
Переходим в раздел «Интернет».
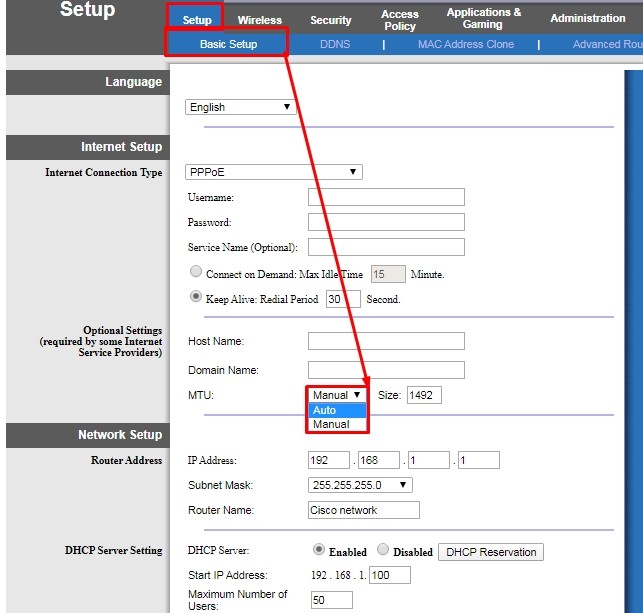
LinkSys
«Setup» – «Basic Setup» – чуть ниже будет строка «MTU». По умолчанию стоит значение «Auto», которое само высчитывает нужное число. Для установки конкретного параметра нужно установить режим «Manual» и вписать найденные через консоль цифры.
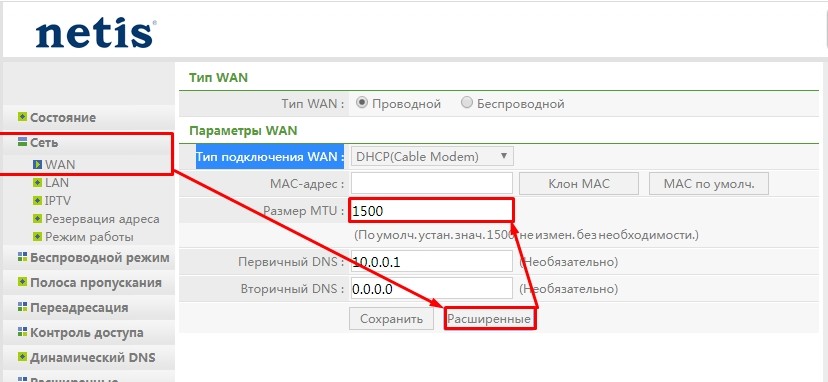
Netis
«Сеть» – «WAN» – нажимаем на кнопку «Расширенные» под вашим подключением.
Tenda
V1-3
«Системные настройки» – «Настройки WAN».
V4
Кликаем на последний раздел «Administration».