When you try to import a module in a Python file, Python tries to resolve this module in several ways. Sometimes, Python throws the ModuleNotFoundError afterward. What does this error mean in Python?
As the name implies, this error occurs when you’re trying to access or use a module that cannot be found. In the case of the title, the «module named Python» cannot be found.
Python here can be any module. Here’s an error when I try to import a numpys module that cannot be found:
import numpys as np
Here’s what the error looks like:
Here are a few reasons why a module may not be found:
- you do not have the module you tried importing installed on your computer
- you spelled a module incorrectly (which still links back to the previous point, that the misspelled module is not installed)…for example, spelling
numpyasnumpysduring import - you use an incorrect casing for a module (which still links back to the first point)…for example, spelling
numpyasNumPyduring import will throw the module not found error as both modules are «not the same» - you are importing a module using the wrong path
How to fix the ModuleNotFoundError in Python
As I mentioned in the previous section, there are a couple of reasons a module may not be found. Here are some solutions.
1. Make sure imported modules are installed
Take for example, numpy. You use this module in your code in a file called «test.py» like this:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(arr)
If you try to run this code with python test.py and you get this error:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named "numpy"
Then it’s most likely possible that the numpy module is not installed on your device. You can install the module like this:
python -m pip install numpy
When installed, the previous code will work correctly and you get the result printed in your terminal:
[1, 2, 3]
2. Make sure modules are spelled correctly
In some cases, you may have installed the module you need, but trying to use it still throws the ModuleNotFound error. In such cases, it could be that you spelled it incorrectly. Take, for example, this code:
import nompy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(arr)
Here, you have installed numpy but running the above code throws this error:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named "nompy"
This error comes as a result of the misspelled numpy module as nompy (with the letter o instead of u). You can fix this error by spelling the module correctly.
3. Make sure modules are in the right casing
Similar to the misspelling issue for module not found errors, it could also be that you are spelling the module correctly, but in the wrong casing. Here’s an example:
import Numpy as np
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3])
print(arr)
For this code, you have numpy installed but running the above code will throw this error:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'Numpy'
Due to casing differences, numpy and Numpy are different modules. You can fix this error by spelling the module in the right casing.
4. Make sure you use the right paths
In Python, you can import modules from other files using absolute or relative paths. For this example, I’ll focus on absolute paths.
When you try to access a module from the wrong path, you will also get the module not found here. Here’s an example:
Let’s say you have a project folder called test. In it, you have two folders demoA and demoB.
demoA has an __init__.py file (to show it’s a Python package) and a test1.py module.
demoA also has an __init__.py file and a test2.py module.
Here’s the structure:
└── test
├── demoA
├── __init__.py
│ ├── test1.py
└── demoB
├── __init__.py
├── test2.py
Here are the contents of test1.py:
def hello():
print("hello")
And let’s say you want to use this declared hello function in test2.py. The following code will throw a module not found error:
import demoA.test as test1
test1.hello()
This code will throw the following error:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'demoA.test'
The reason for this is that we have used the wrong path to access the test1 module. The right path should be demoA.test1. When you correct that, the code works:
import demoA.test1 as test1
test1.hello()
# hello
Wrapping up
For resolving an imported module, Python checks places like the inbuilt library, installed modules, and modules in the current project. If it’s unable to resolve that module, it throws the ModuleNotFoundError.
Sometimes you do not have that module installed, so you have to install it. Sometimes it’s a misspelled module, or the naming with the wrong casing, or a wrong path. In this article, I’ve shown four possible ways of fixing this error if you experience it.
I hope you learned from it 
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
В Python может быть несколько причин возникновения ошибки ModuleNotFoundError: No module named ...:
- Модуль Python не установлен.
- Есть конфликт в названиях пакета и модуля.
- Есть конфликт зависимости модулей Python.
Рассмотрим варианты их решения.
Модуль не установлен
В первую очередь нужно проверить, установлен ли модуль. Для использования модуля в программе его нужно установить. Например, если попробовать использовать numpy без установки с помощью pip install будет следующая ошибка:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'numpy'Для установки нужного модуля используйте следующую команду:
pip install numpy
# или
pip3 install numpyИли вот эту если используете Anaconda:
conda install numpyУчтите, что может быть несколько экземпляров Python (или виртуальных сред) в системе. Модуль нужно устанавливать в определенный экземпляр.
Конфликт имен библиотеки и модуля
Еще одна причина ошибки No module named — конфликт в названиях пакета и модуля. Предположим, есть следующая структура проекта Python:
demo-project
└───utils
__init__.py
string_utils.py
utils.pyЕсли использовать следующую инструкцию импорта файла utils.py, то Python вернет ошибку ModuleNotFoundError.
>>> import utils.string_utils
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\demo-project\utils\utils.py", line 1, in
import utils.string_utils
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'utils.string_utils';
'utils' is not a package
В сообщении об ошибке сказано, что «utils is not a package». utils — это имя пакета, но это также и имя модуля. Это приводит к конфликту, когда имя модуля перекрывает имя пакета/библиотеки. Для его разрешения нужно переименовать файл utils.py.
Иногда может существовать конфликт модулей Python, который и приводит к ошибке No module named.
Следующее сообщение явно указывает, что _numpy_compat.py в библиотеке scipy пытается импортировать модуль numpy.testing.nosetester.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\demo-project\venv\
Lib\site-packages\
scipy\_lib\_numpy_compat.py", line 10, in
from numpy.testing.nosetester import import_nose
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'numpy.testing.nosetester'Ошибка ModuleNotFoundError возникает из-за того, что модуль numpy.testing.nosetester удален из библиотеки в версии 1.18. Для решения этой проблемы нужно обновить numpy и scipy до последних версий.
pip install numpy --upgrade
pip install scipy --upgrade Что означает ошибка ModuleNotFoundError: No module named
Python ругается, что не может найти нужный модуль
Python ругается, что не может найти нужный модуль
Ситуация: мы решили заняться бигдатой и обработать большой массив данных на Python. Чтобы было проще, мы используем уже готовые решения и находим нужный нам код в интернете, например такой:
import numpy as np
x = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
nums = np.array([2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
type(nums)
zeros = np.zeros((5, 4))
lin = np.linspace(1, 10, 20)Копируем, вставляем в редактор кода и запускаем, чтобы разобраться, как что работает. Но вместо обработки данных Python выдаёт ошибку:
❌ModuleNotFoundError: No module named numpy
Странно, но этот код точно правильный: мы его взяли из блога разработчика и, по комментариям, у всех всё работает. Откуда тогда ошибка?
Что это значит: Python пытается подключить библиотеку, которую мы указали, но не может её найти у себя.
Когда встречается: когда библиотеки нет или мы неправильно написали её название.
Что делать с ошибкой ModuleNotFoundError: No module named
Самый простой способ исправить эту ошибку — установить библиотеку, которую мы хотим подключить в проект. Для установки Python-библиотек используют штатную команду pip или pip3, которая работает так: pip install <имя_библиотеки>. В нашем случае Python говорит, что он не может подключить библиотеку Numpy, поэтому пишем в командной строке такое:
pip install numpy
Это нужно написать не в командной строке Python, а в командной строке операционной системы. Тогда компьютер скачает эту библиотеку, установит, привяжет к Python и будет ругаться на строчку в коде import numpy.
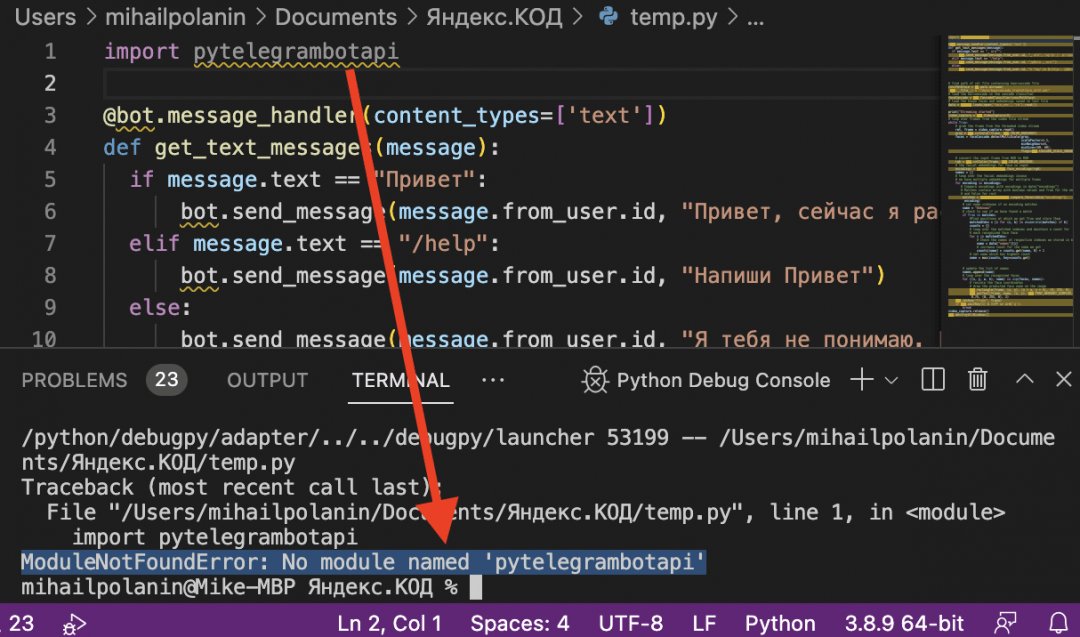
Ещё бывает такое, что библиотека называется иначе, чем указано в команде pip install. Например, для работы с телеграм-ботами нужна библиотека telebot, а для её установки надо написать pip install pytelegrambotapi. Если попробовать подключить библиотеку с этим же названием, то тоже получим ошибку:
А иногда такая ошибка — это просто невнимательность: пропущенная буква в названии библиотеки или опечатка. Исправляем и работаем дальше.
The ModuleNotFoundError: No module named error occurs when Python cannot find the module you are trying to import. This can happen for a few reasons:
- Incorrect Module Name
- Incorrect Module Path
- File Extension Mismatch
- Missing Library Installation
- Unsupported Module
- Python 2 vs. Python 3
- Pip Version Mismatch
- Incorrect PYTHONPATH
In this article, We’ll discuss the reasons and the solutions for the ModuleNotFoundError error.
1. Incorrect Module Name:
One of the most common reasons for the «ModuleNotFoundError» is an incorrect module name.
For example, attempting to import the «os» module with a misspelled name like «oss» will result in an error:
>>> import oss
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'oss'To resolve this, ensure that you use the correct module name:
>>> import os
>>> 2. Incorrect Module Path:
The second reason for this error is an incorrect module path. You’ll encounter the error if you’re trying to import a module that’s not in the same directory or not in the PYTHONPATH. For example:
Project structure:
core.py
folder_1
---my_module.py
import my_module # Bad
import folder_1.my_module # Good
3. File Extension Mismatch:
If your module’s file extension differs from what Python expects (like.py.bin instead of.py), it may not be recognized as a proper module by Python. Make sure the file extension is .py.
Here is the structure:
project_directory/
├── my_module.txt
└── main.pyNow, let’s say you want to import and use my_module in your main.py script:
# main.py
import my_module
result = my_module.some_function()
print(result)
When you run main.py, you’ll get an «ImportError: No module named 'my_module‘» error because Python wants the module to have an a.py extension, not an a.txt extension.
4. Missing Library Installation:
If you attempt to import a library module not installed in your Python environment, you’ll get the «ModuleNotFoundError.» Install the necessary libraries using a package manager like «pip.» For example:
>>> from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'bs4'Now, let’s install the library and try to re-import it:
pip install beautifulsoup4
Collecting beautifulsoup4
Using cached https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d1/41/e6495bd7d3781cee623ce23ea6ac73282a373088fcd0ddc809a047b18eae/beautifulsoup4-4.9.3-py3-none-any.whl
Requirement already satisfied: soupsieve>1.2; python_version >= "3.0" in /home/py/Desktop/seo_pro/seo_env/lib/python3.6/site-packages (from beautifulsoup4) (1.9.5)
Installing collected packages: beautifulsoup4
Successfully installed beautifulsoup4-4.9.3Re-importing:
>>> from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
>>> As you can see, after installing the package, the program is working.
5. Unsupported Module:
Some Python libraries drop support for specific modules in new updates. You’ll encounter this error if you try to import an unsupported module. Always check the library’s documentation to see if the module is still available.
6. Python 2 vs. Python 3:
As Python 2 is no longer supported, some libraries are exclusive to Python 3. If you’re using Python 2, you may encounter this error when using modules designed for Python 3. Ensure you’re using the correct Python version.
To check your Python version:
python -V
# Python 2.7.18
python3 -V
# Python 3.9.5
In my case, «python3» is the function that lets me use Python 3. So, I’ll run the program with «python3.» If Python3 is not installed on your computer, you should do so on Windows, Mac, or Linux.
7. Pip Version Mismatch:
Even though the mistake is easy, it happens a lot. You used pip3 install to install a Python library, which means it works with Python 3.x.
The solution is straightforward: always use the correct Python interpreter that matches the library’s version.
For example, If you installed the libraries using pip3, run your program using the python3 interpreter. On the other hand, if you used pip to install the libraries, run your program with the standard Python interpreter.
8. Check PYTHONPATH:
Check that the PYTHONPATH environment variable is properly set to include the paths to the directories that hold your Python modules. This ensures that when you attempt to import your modules, Python can find them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when facing the «ModuleNotFoundError: No module named» error:
- Verify the module name.
- Ensure the correct module path.
- Check File Extension
- Install the required libraries.
- Check if the library supports the module.
- Check PYTHONPATH
- Check Pip Version Mismatch
- Use Python 3 if Python 2 is incompatible.
These steps can resolve the error and ensure your Python code runs smoothly. We hope this article has helped you address this issue effectively.
It happens quite often that someone installs a Python package using pip, but then can’t seem to import it in Python. To understand why this happens, you must know how Windows finds executables to run, and how the Python software is installed. The basics:
- When running a command, Windows searches for an executable in the environment variable PATH. It executes the first one found.
- The Python interpreter,
python.exe, is installed in<PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR>(e.g.C:\Python\3.7). - Python tools such as
pip,pylint,virtualenv,PyCrust, etc., are installed in<PYTHON_INSTALL_DIR>\Scripts. - The Python launcher for Windows,
py.exe, is installed in your Windows system directory (e.g.C:\Windows). pythonandpipcommands use the modules found in the directory their installed in, they do not look at PATH.
So, let’s say you have the following Python versions:
C:\Python\2.7
C:\Python\3.6
C:\Python\3.7
and your PATH environment contains the following directories:
C:\Python\2.7
C:\Python\3.6\Scripts
then, see the following output:
C:\>python -V
Python 2.7.16
C:\>pip -V
pip 19.1.1 from c:\python\3.6\lib\site-packages\pip (python 3.6)
C:\>py -V
Python 3.7.3
So, when running pip, it is possible that the packages are installed in another Python version then the version you’ll get when running python.
To see which versions are (correctly) installed on your system, run py -0p. Example output:
C:\>py -0p
Installed Pythons found by py Launcher for Windows
-3.7-64 C:\Python\3.7-64\python.exe *
-3.7-32 C:\Python\3.7-32\python.exe
-3.6-64 C:\Python\3.6-64\python.exe
-2.7-64 C:\Python\2.7-64\python.exe
-2.7-32 C:\Python\2.7-32\python.exe
General solution (for Windows)
The best thing is not to rely on your system PATH. Use the py launcher to select the version you want. To run the pip module corresponding to the Python version you want to use, start pip as a module instead of executable.
So instead of:
pip install <package>
run:
py -3.6 -m pip install <package>
To see which Python packages you have installed for that Python version, use:
py -3.6 -m pip freeze
Some additional remarks
- Whether a Python installation is added to your PATH or not, is an option during the installation. If it is added, it is added at the beginning of the PATH, so the most recently installed Python version will be selected first.
- The Windows system directory should always be in your PATH, so the
pycommand will always be available, even if you did not add any Python installation to your PATH. - If you double-click on a .py file from Windows Explorer, or type the filename directly as a command in a Command Prompt (e.g.
test.py), then the action is determined from the Windows registry. It is possible that the file will be opened in your IDE, or that it’s executed using a Python interpreter. In that case, it is probably the most recently installed Python version. It’s possible that the commandpython test.py, uses a different Python version than the commandtest.py. - Some installations also include executables named
python2/python3(not on Windows),pip3/pip3.7(also on Windows), etc. This would also allow you to specify which version to use. These would be useful on systems where these binaries exist and are in the path.
![ModuleNotFoundError: no module named Python Error [Fixed]](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/content/images/size/w2000/2022/09/module-not-found-error.png)