Разглашение: Некоторые ссылки на этом сайте являются партнерскими. Это означает, что если вы нажмете на одну из ссылок и купите товар, я могу получить комиссию. Однако все мнения принадлежат мне.
Виртуальные машины Windows отлично подходят для пользователей Linux, поскольку они могут в полной мере взаимодействовать с приложениями Windows.
И в отличие от перезагрузки вашей системы каждый раз, когда вы хотите сменить операционную систему, установка Virtual Manager позволяет (и легко) запускать виртуальные устройства Windows поверх любого существующего дистрибутива без больших простоев или проблем со стабильностью из-за его интеграции.
Конечно, многие дистрибутивы поставляются готовыми «из коробки», поэтому нет необходимости искать что-то еще.
Если эта конкретная задача никого не беспокоит, но они по-прежнему предпочитают что-то более индивидуальное, то, возможно, использование другого программного обеспечения может лучше удовлетворить их потребности.
Список 5 лучших виртуальных машин для Linux-
Есть несколько различных вариантов, когда речь идет о виртуальных машинах для Linux. Вот список некоторых из лучших вариантов:
1. VirtualBox
VirtualBox имеет широкий спектр функций, включая поддержку нескольких гостевых операционные системы, графическое ускорение и сетевые параметры.
Особенности
1. Модульность
Это позволяет легко управлять им сразу из нескольких интерфейсов: например, вы можете запускать, приостанавливать и возобновлять виртуальные машины из графического пользовательского интерфейса (GUI) или из командной строки, или вы можете управлять ими удаленно через веб-сервисы.
2. Виртуализация различных ОС
Вы можете запустить Windows, Linux, Solaris и другие операционные системы одновременно на одном компьютере — путем создания так называемых «виртуальных машин» поверх вашей существующей ОС.
Каждая виртуальная машина имеет собственное виртуальное оборудование, включая ЦП, память, жесткие диски, приводы CD/DVD-ROM, аудиоадаптеры и сетевые карты.
3. Поддержка 64-битных гостевых операционных систем.
С VirtualBox вы можете устанавливать и запускать 64-битные гостевые операционные системы даже на 32-битной операционной системе хоста. 64-разрядные гостевые системы получат полную поддержку функций аппаратной виртуализации, таких как аппаратная виртуализация ЦП и виртуализация ввода-вывода MMU.
4. Снимки
Вы можете делать снимки виртуальных машин в любое время. Моментальный снимок — это сохраненное состояние виртуальной машины в определенный момент времени.
Делать снимки полезно для различных целей: например, вы можете использовать их, чтобы опробовать новое программное обеспечение или поэкспериментировать с настройками, а затем просто вернуться к предыдущему снимку, если что-то пойдет не так.
2. Проигрыватель VMware
VMware Player это бесплатное программное обеспечение для виртуализации от VMware. Его можно использовать в операционных системах Windows и Linux. VMware Player имеет многие из тех же функций, что и VirtualBox, включая поддержку нескольких гостевых операционных систем и ускорение графики.
Особенности
Поддержка нескольких операционных систем:
VMware Player можно использовать для запуска нескольких операционных систем на одном компьютере. Сюда входит поддержка популярных гостевых операционных систем, таких как Windows, Linux и macOS.
Простая установка и настройка:
VMware Player прост в установке и не требует настройки. После установки VMware Player можно использовать для запуска гостевых операционных систем «из коробки».
Поддержка популярных технологий виртуализации:
VMware Player поддерживает популярные технологии виртуализации, такие как аппаратная виртуализация и 64-разрядные гостевые операционные системы.
Бесплатно для личного использования:
VMware Player бесплатен для личного использования. Для использования VMware Player в бизнес-среде требуется коммерческая лицензия.
3. КВМ
KVM — это бесплатное программное обеспечение для виртуализации с открытым исходным кодом от Red Hat. Его можно использовать в операционных системах Linux. KVM имеет широкий спектр функций, включая поддержку нескольких гостевых операционных систем, графическое ускорение и сетевые параметры.
Особенности
Поддержка нескольких процессоров:
KVM может использовать несколько процессоров или ядер, что позволяет создавать виртуальные машины с высокой степенью масштабируемости.
Поддержка нескольких операционных систем:
KVM поддерживает широкий спектр операционных систем, что делает его универсальным решением для виртуализации.
Простота использования:
KVM прост в настройке и использовании, им можно управлять через веб-интерфейс.
Высокая производительность:
KVM обеспечивает практически естественную производительность, что делает его идеальным для ресурсоемких задач.
Масштабируемость:
KVM можно легко увеличивать или уменьшать в соответствии с меняющимися потребностями.
4. Зен
Xen — это бесплатное программное обеспечение для виртуализации с открытым исходным кодом от Citrix. Его можно использовать в операционных системах Linux. Xen имеет широкий спектр функций, включая поддержку нескольких гостевых операционных систем, графическое ускорение и сетевые параметры.
Это гипервизор, то есть он предоставляет среду виртуальной машины, в которой могут работать несколько операционных систем. Xen — это программное обеспечение с открытым исходным кодом, первоначально разработанное Кембриджским университетом.
Особенности
Производительность: Xen использует подход паравиртуализации, который позволяет виртуальным машинам работать непосредственно на оборудовании без необходимости эмуляции. Это приводит к хорошей производительности по сравнению с другими платформами виртуализации.
Масштабируемость:
Xen может масштабироваться для поддержки тысяч виртуальных машин на одном физическом сервере.
Безопасность:
Xen предоставляет ряд функций безопасности, таких как изоляция и управление ресурсами, которые можно использовать для защиты виртуальных машин.
Надежность:
Xen — это стабильная и хорошо протестированная платформа, которая используется уже много лет.
5. КЭМУ
QEMU — это эмулятор процессора, который использует динамическую трансляцию для быстрого выполнения гостевого кода. QEMU имеет два режима работы:
Эмуляция пользовательского режима: В этом режиме QEMU может запускать процессы Linux, скомпилированные для одного ЦП, на другом ЦП. Это позволяет быстро тестировать и отлаживать приложения без необходимости во второй физической компьютерной системе.
Эмуляция системного режима: В этом режиме QEMU эмулирует полную компьютерную систему, включая процессор и различные периферийные устройства. Это используется для запуска целых операционных систем на виртуальных машинах.
Особенности
Одной из наиболее важных особенностей QEMU является поддержка широкого спектра гостевых операционных систем.
QEMU можно использовать для запуска виртуальных машин с различными архитектурами ЦП, включая ARM, x86, PowerPC и другие. Это делает QEMU идеальным инструментом для кроссплатформенной разработки и тестирования.
QEMU также обеспечивает аппаратное ускорение, которое может значительно повысить производительность виртуальных машин. Например, QEMU может использовать расширения ЦП Intel VT-x или AMD-V для повышения производительности виртуальных машин, работающих на процессорах на базе архитектуры x86.
Еще одной важной особенностью QEMU является поддержка сети. QEMU можно использовать для создания виртуальных сетевых сред, которые могут быть полезны для целей тестирования и разработки. QEMU поддерживает широкий спектр сетевых параметров, включая Ethernet, InfiniBand и другие.
Полезное
- Adobe Reader на Chromebook
- Фликстор Обзор
- 10 лучших эмуляторов PS1 для Windows 10
- Сертификация Linux
Для начала вам понадобятся следующие вещи:
- Программное обеспечение виртуальной машины
- Официальный Windows ISO (загрузочный диск или USB)
- ПК или ноутбук с поддержкой виртуализации (вам также понадобится внешний DVD-привод, если ваш ноутбук — ультрабук, или вы можете создать свой
- собственный)
- Достаточное количество оперативной памяти
Итак, первые две вещи вам легко получить, но вам понадобится ПК с виртуализацией.
Как включить виртуализацию в Linux
Чтобы проверить, поддерживает ли ваш Linux-ПК виртуализацию, откройте окно терминала и введите
lscpuЭта команда показывает все, что вам нужно знать о процессоре вашей системы, например модель, архитектуру, кэши и технологию виртуализации.
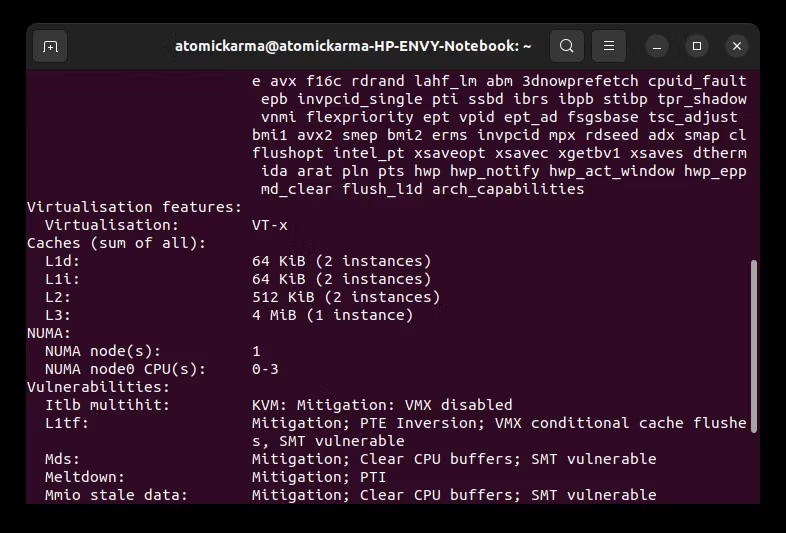
В этом примере ноутбук HP имеет виртуализацию Intel VT-x.
Виртуализация, если она не включена по умолчанию, может быть включена в системном BIOS. Путь к этому будет зависеть от используемого вами оборудования. Для достижения наилучших результатов загрузитесь в BIOS своей системы и найдите ссылки на Intel VT (на ПК с архитектурой Intel) или AMD-V (на ПК с процессором и материнской платой AMD).
Что касается системной оперативной памяти, то, хотя вам может сойти с рук виртуализация в старых операционных системах с 4 ГБ, вам следует начинать с 8 ГБ для достижения наилучших результатов. Ноутбук, используемый для тестирования этого руководства, имеет 12 ГБ ОЗУ.
Выбор программного обеспечения для виртуализации
Хотя QEMU, возможно, является лучшим вариантом виртуальной машины для систем Linux, нам нужно решение, которое может запускать Windows с минимальными усилиями и может быть быстро установлено. Таким образом, для этого руководства мы будем использовать Oracle VirtualBox.
Установите VirtualBox в командной строке. Для систем на базе Debian:
sudo apt <span class="hljs-keyword">install</span> virtualbox Для дистрибутивов на основе RHEL (Fedora, CentOS) используйте:
sudo dnf <span class="hljs-keyword">install</span> virtualboxЕсли вы используете Arch Linux или любой подобный дистрибутив, введите:
sudo pacman -S virtualboxПодождите, пока VirtualBox установится. При желании вы также можете загрузить установщик с сайта Oracle. В нашем руководстве по установке Oracle VirtualBox это объясняется более подробно.
Настройте Windows в Oracle VirtualBox
Установив VirtualBox на ПК с Linux, запустите программное обеспечение.
Oracle VirtualBox можно использовать для запуска любой современной версии Windows. Это руководство подходит для всех, кто хочет установить Windows 10 или 11, но оно также должно работать для Windows XP, Vista, 7 или 8.1. (Некоторые настройки могут отличаться, но все будут работать.)
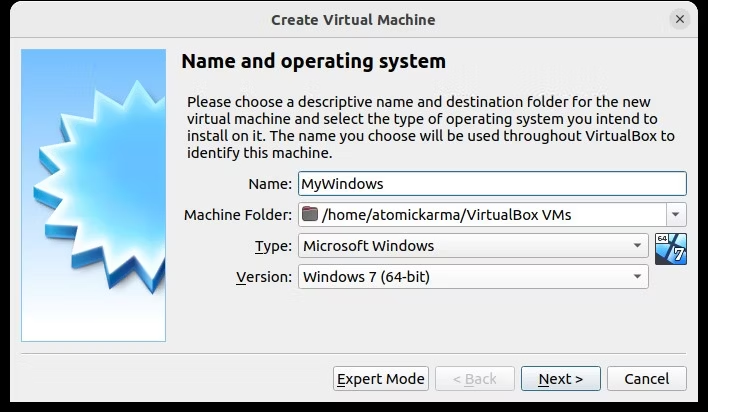
Сначала нажмите «Создать», а затем дайте имя виртуальному устройству. В раскрывающемся меню «Тип» убедитесь, что выбрана Windows, а в поле «Версия» — правильная версия Windows. Вы можете запускать практически все, начиная с Windows 3.1 и заканчивая современными версиями.
Нажмите «Далее», чтобы продолжить, и на следующем экране выберите объем памяти для виртуальной машины. Рекомендуемый размер по умолчанию будет предложен в зависимости от выбранной ОС и аппаратного обеспечения вашего физического компьютера.
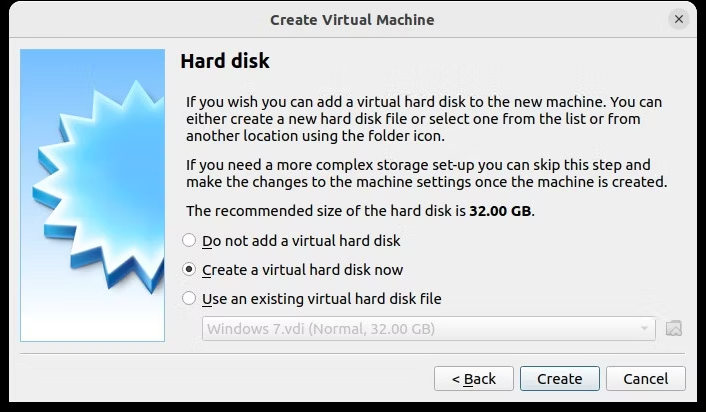
Нажмите «Далее», чтобы создать виртуальный жесткий диск, снова выбрав параметр по умолчанию, если только у вас нет особенно большого объема данных для запуска на виртуальной машине.
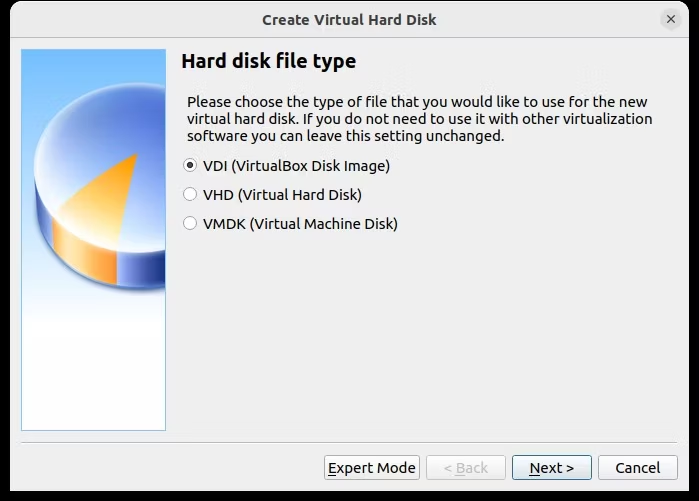
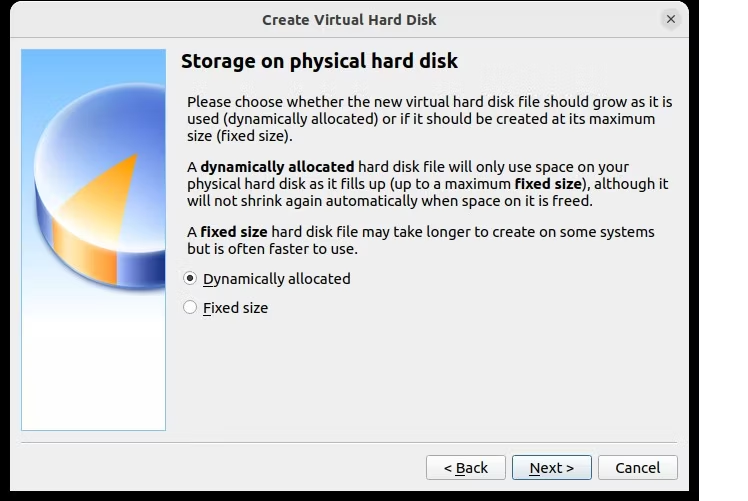
После этого нажмите «Создать», затем выберите нужный тип файла. Если вы просто собираетесь использовать виртуальный жесткий диск с VirtualBox, нажмите «Далее», в противном случае выберите другой формат. Затем вы должны указать, должен ли виртуальный жесткий диск выделяться динамически (т. е. его размер увеличивается по мере необходимости до предварительно выбранного верхнего предела) или фиксированный размер. В большинстве случаев вам понадобится динамический.
Нажмите «Далее», чтобы продолжить, подтвердите (или измените) имя, расположение и размер файла, а затем снова нажмите «Создать», чтобы продолжить.
Установка Windows на Linux
Настроив виртуальную машину — представьте, что это сборка ПК, но с виртуальными компонентами — теперь вы готовы установить Windows. Если вы используете диск или USB-накопитель для доставки ISO, самое время вставить носитель с файлом ISO.
Теперь нажмите зеленую стрелку «Пуск» и выберите расположение исходных данных — установочный диск Windows. Нажмите «Пуск» и подождите, пока виртуальный компьютер загрузит программу установки Windows.
Если вы уже устанавливали Windows раньше, вы должны быть знакомы с этим, если нет, мастер поможет вам в этом процессе.
Как установить виртуальную машину Windows 10 в Linux без диска
Если вы разработчик и ищете способ ненадолго установить Windows 10 в целях тестирования, все вышеперечисленное может показаться непростым делом.
К счастью, есть решение, предоставленное Microsoft. Виртуальные машины от Windows 7 до Windows 10 предоставляются (со сроком действия 90 дней) на портале разработчиков Microsoft Edge. Виртуальную машину отсюда можно легко загрузить и развернуть в VirtualBox.
- Перейдите на страницу виртуальных машин на портале разработчиков Microsoft Edge.
- В разделе «Virtual Machines» выберите ОС, которая соответствует вашим целям (выберите Windows 7, 8.1 и 10).
- В разделе «Выберите платформу ВМ» выберите VirtualBox.
- Нажмите «Download.zip«.
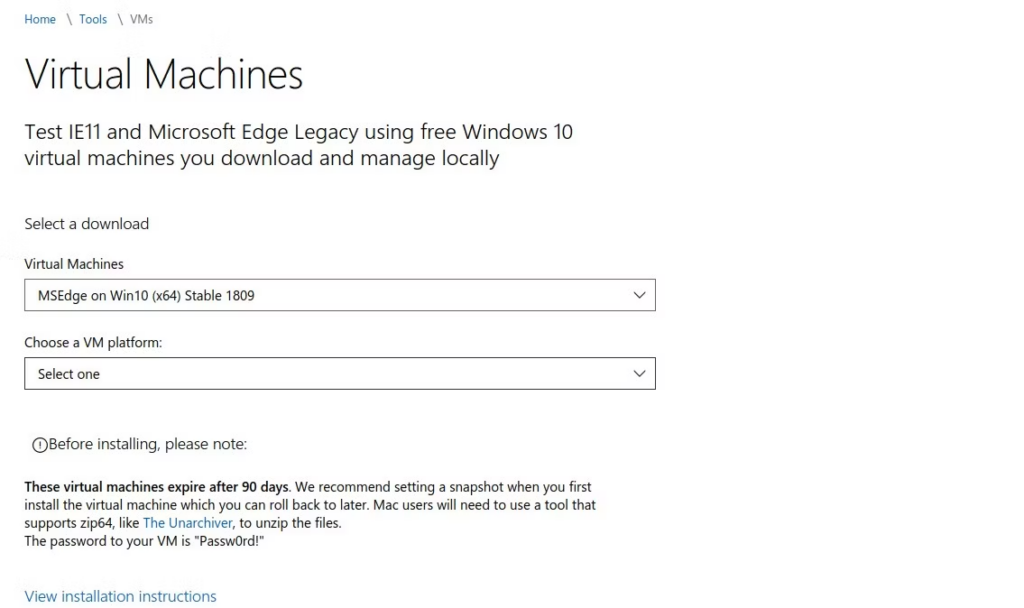
- После загрузки распакуйте загруженный файл
- Откройте Oracle VirtualBox
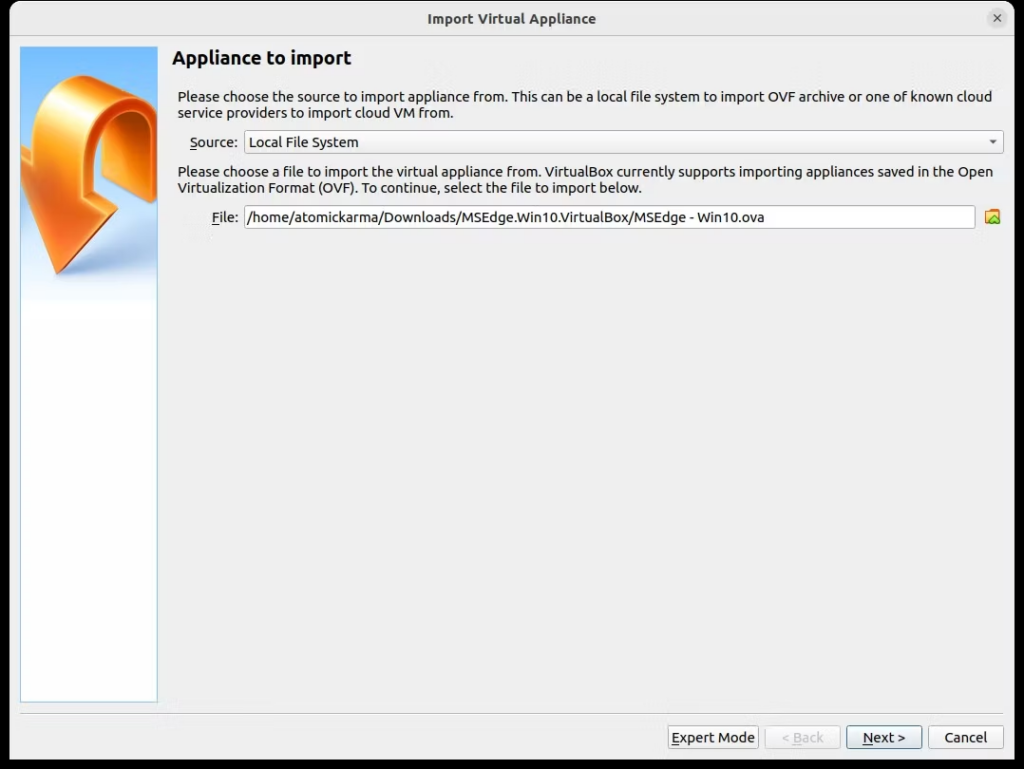
- Выберите File > Import Appliance
- На экране «Импорт виртуального устройства» найдите извлеченный файл Download.zip.
- Нажмите «Далее»
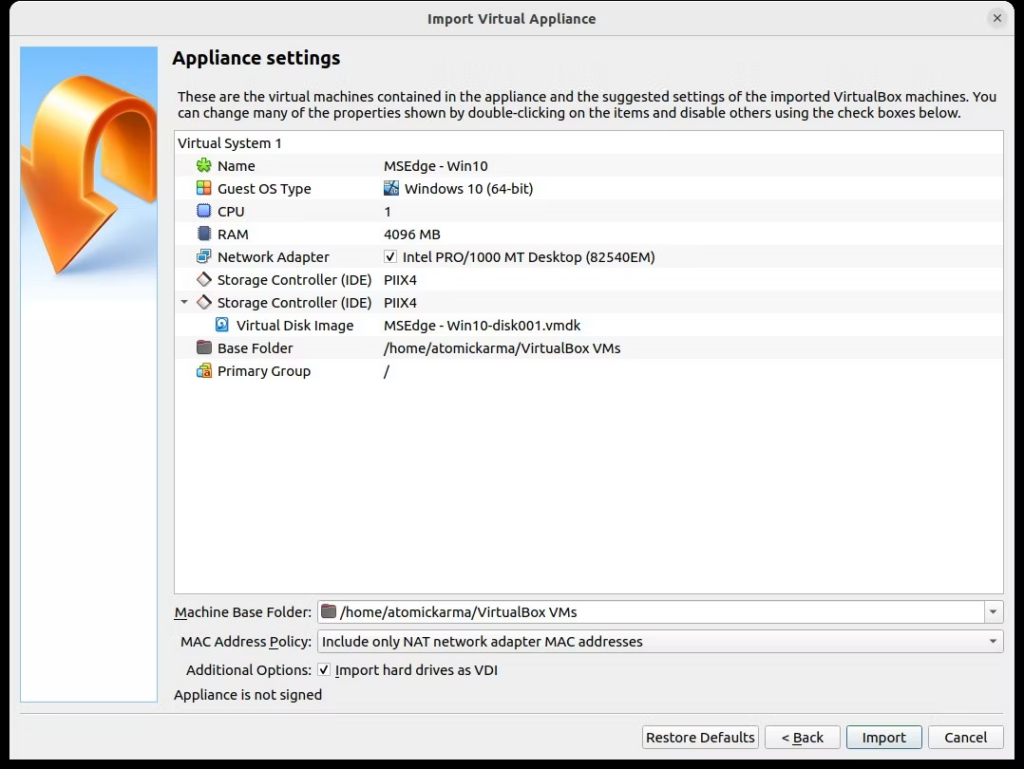
- Подтвердите детали виртуальной машины и предлагаемые настройки, внеся любые изменения, которые вы считаете необходимыми.
- Нажмите Import, чтобы продолжить (длительность импорта будет зависеть от оперативной памяти вашей системы и скорости вашего жесткого диска или твердотельного накопителя).
- После завершения выберите новую виртуальную машину и нажмите Start.
Чтобы войти в виртуальную машину Windows, используйте имя пользователя/пароль по умолчанию IEUser/Passw0rd!
Как упоминалось ранее, стоит создать снимок виртуальной машины после настройки, чтобы было легко вернуться к ней, если что-то пойдет не так.
Следует отметить одну вещь: вам может потребоваться настроить параметры виртуальной машины, чтобы это работало правильно. В собственных рекомендациях Microsoft указано, что вы должны использовать следующие объемы оперативной памяти:
- Windows XP images: 256 – 512MB
- Windows Vista images: 512 – 1024MB
- Windows 7 images: 1024 – 2048MB
- Windows 8 images: 1024 – 2048MB
- Windows 10 images: 1024 – 2048MB
Итак, если загруженный образ виртуальной машины не работает должным образом, отрегулируйте объем ОЗУ, как описано выше. Как правило, ошибайтесь в сторону максимума, а не минимума оперативной памяти.
Запустите Windows и установите программное обеспечение!
Если вы зашли так далеко, все готово. Вы должны иметь возможность загрузиться в Windows и установить программное обеспечение либо с DVD (благодаря инструментам VirtualBox), либо путем загрузки и установки.
Все ваши обычные приложения Windows должны работать как обычно, ограничиваясь только аппаратным обеспечением вашего хост-компьютера — физического ПК, на который вы установили VirtualBox. Использование виртуальной машины — это, вероятно, лучший способ получить приложения и игры для Windows, если вам не подходят «Бутылки и вино».
Наличие виртуальной машины Windows, которую вы можете легко включать и выключать по своему усмотрению, продолжая при этом выполнять свои ежедневные вычисления в Linux, является огромным преимуществом. Если вам нужно запускать программное обеспечение Windows и иметь оборудование для поддержки виртуализации, то это отличное решение.
Although it’s hard for us Linux fanatics to delve into the world of Windows, we all need to embrace Windows from time to time for some specific tasks. Despite all its rewards, Linux is still not a household name among regular computer users, and the chances are that most of your non-technical friends use Windows as their primary system. So, if you want to share some standard software or play the latest games, Windows is still the way to go. However, we Linux folks can’t shift to Windows permanently and overlook the flexibility Linux has been affording us over the years. Luckily, a comprehensive set of powerful Windows emulators for Linux exists to make our life more comfortable and allow us to benefit both systems concurrently.
Best Windows Emulators for Linux

We’ve selected a compelling set of robust Windows emulators for Linux that will allow you to utilize some exceptional but Windows-specific software. If you’re a die-hard gamer, stop worrying, as we’ve also outlined some great methods that will enable you to run your favorite games from your Linux machine seamlessly.
Although the title emphasizes Linux Windows emulator, think of the below picks as workarounds that let you run Windows programs in Linux instead.
1. Wine
Wine is the de-facto Windows emulator for Linux users who want to run Windows applications, software, and games in their Unix systems effortlessly. In its fourth major release, Wine allows you to run your favorite Windows-only programs without any extra hassle.
It’s very easy to install Wine on virtually every POSIX-compliant operating system, including Linux, macOS, & BSD. Moreover, Wine supports many modern-day applications out of the box, thus eliminating the need to tweak them inside your Linux environment.
Features of Wine
- Wine comes with pre-built support for the X-11 window system and allows users to stream their display on remote X terminals.
- Wine supports DirectX (up to version 11) based games and applications out of the box and Windows MultiMedia (WinMM) layers.
- You can interface Windows programs with your Linux system devices, such as sound devices, keyboards, modems, serial devices, ASPI scanners, and such, very easily.
- Wine Linux has excellent API coverage, making it a viable choice for running everyday Windows programs effortlessly.
Get Wine
2. VMware Workstation
VMware is a powerful virtualization platform enabling Linux users to run Windows applications seamlessly inside their machines. You can think of VMware as software that allows you to run an operating system inside another operating system.
This is a very popular Linux Windows emulator among Linux enthusiasts who need to run Windows-based applications regularly. Although proprietary, VMware is arguably among the best Windows emulators for Linux you can use.
Features of VMware Workstation
- VMware Workstation allows users to run multiple instances of Windows operating systems on Linux machines.
- It is paid software, but you can utilize the VMware Workstation Player, its free version, to run Windows programs.
- VMware Workstation allows your system to share up to 3 GB of shared video memory and supports OpenGL out of the box.
- This Linux Windows emulator supports DirectX 10.1, 4K resolution, Wayland protocol, SSH login, Virtual networking, and many more.
Get VMware Workstation
3. CrossOver Linux
CrossOver Linux is, without any doubt, one of the best Windows emulators for Linux you can use on any Linux machine. It is, in effect, a Microsoft Windows compatibility layer that enables Linux users to run their favorite Windows apps inside their Linux system.
CrossOver Linux is based on Wine and packs a select set of widely used Microsoft Windows applications. It integrates seamlessly well with modern GNOME and KDE-based Linux distributions.
Features of CrossOver Linux
- Installing standard Windows applications is much easier in CrossOver Linux than in other ordinary Linux Windows emulators.
- CrossOver Linux doesn’t require you to buy a Windows license like most Windows emulators for Linux require.
- Applications run from CrossOver Linux are faster because they do not depend on virtual machines.
- CrossOver Linux offers Bottles, a unique feature that allows separate Windows environments to be packaged and self-contained with user-selected programs.
Get CrossOver Linux
4. QEMU
QEMU is a robust virtual machine emulator and hardware visualizer that can run Windows programs directly inside a Linux system. It can act in different ways, and you’ll be primarily using it as a full system emulator for running a Windows system inside Linux.
You can then install applications developed for Windows in your Linux system. It is maintained very well and takes care of bugs and errors faster than most Windows emulators for Linux.
Features of QEMU
- QEMU can save the current state of installed Windows systems alongside the running apps and restore them accurately.
- Users can access and utilize their Linux system’s peripherals, including hard disks, CD-ROM drives, network cards, audio interfaces, and USB devices, directly from QEMU.
- QEMU is written in the C programming language and is faster than most Windows emulators for Linux.
- It comes out with a GNU GPL license, allowing users to tweak the emulator as required.
Get QEMU
5. VirtualBox
VirtualBox is a free hypervisor that can act as a compelling Windows emulator for Linux. A hypervisor is a virtualization platform that allows users to install and run an operating system inside from another. So, Linux users can install VirtualBox and utilize it for running Microsoft Windows applications in their Linux system.
Although many people don’t like the notion of using a virtual machine as their Linux Windows emulator, as of now, it is the best method if you want all the functionalities of a working Windows system.
Features of VirtualBox
- VirtualBox is written in C, C++, and x86 assembly language, thus offering faster performance than most contemporary Windows emulators for Linux.
- It is maintained by Oracle, which updates it very frequently and patches bugs pretty fast.
- Corporations widely use VirtualBox to power resource-intensive clouds and for testing software.
- Oracle has made the source public, and thus VirtualBox can be modified by open-source enthusiasts as per their requirements.
Get VirtualBox
6. PlayOnLinux
PlayOnLinux is an impressive graphical frontend built on top of the Wine compatibility layer for Linux. It aims to make it easier for users to run their favorite Windows applications such as video games, Microsoft Office, Microsoft Internet Explorer, and Quicken, as well as many other applications directly inside their Linux computer.
PlayOnLinux removes many of the redundancies you’d have to face otherwise when installing these and provides an easy-to-deal solution for every Linux user.
Features of PlayOnLinux
- PlayOnLinux isolates Windows environments and apps, much like CrossOver does with Bottles.
- Users can create flexible bash scripts for automating their Windows apps’ configuration in this Windows emulator for Linux.
- It comes under an open-source GNU GPL license which allows Linux users to modify the source without requiring explicit permission.
- PlayOnLinux is written in the Python programming language and is thus easy to understand and customize.
Get PlayOnLinux
7. Lutris
Lutris is an exceptionally robust and powerful open source gaming platform built for GNU/Linux. It allows users to play a compelling set of video games available only for Microsoft Windows systems.
It provides a robust interface that enables users to install, configure, and launch Windows-only games acquired from any source. It performs relatively well at playing many games than most Windows emulators for Linux.
Features of Lutris
- Lutris employs robust installation scripts curated by community members to provide an optimal experience of modern Windows games.
- This Linux Windows emulator comes with pre-built support for various games, including games for both Windows and retro gaming consoles.
- Lutris is entirely free to use and provides a top-notch gaming performance matched by only a handful of Windows emulators for Linux.
- Popular games supported by Lutris include The Elder Scrolls, League of Legends, Overwatch, The Witcher 3, Warframe, Battlefield V, and World of Warcraft.
Get Lutris
8. Q4Wine
Q4Wine is not an entirely new Windows emulator for Linux. It is, instead, a Qt4 fork of the popular Wine software. It aims to provide a handy and flexible GUI frontend for Wine, making managing the emulator easier.
If you’re having trouble installing and configuring Wine in your everyday Linux machine, you can easily opt-in for Q4Wine. It offers every functionality Wine offers and binds a compelling user interface that is easy to deal with and enables Windows applications to run flawlessly.
Features of Q4Wine
- Q4Wine allows users to run two different versions of Wine simultaneously.
- Due to its robust user interface, it is very easy to access and control multiple Wine processes with Q4wine.
- Q4wine comes with in-built support for the Wine AppDB browser and FuseISO\Embedded FuseISO mount profiles.
- Thanks to its GNU GPL license, the source can be modified easily to accommodate new features.
Get Q4Wine
9. Steam Play
Steam Play is like a breeze of fresh air for PC gamers who prefer not to switch to Windows entirely from their Linux system. Valve released Steam Play to enable Linux users to access their favorite Windows games directly from their Linux machines, and we can say they did a fair job with it. It supports most titles, but a slight lag in performance can be experienced when playing these games in Linux.
Features of Steam Play
- Users need to install the Steam Beta Client in their Linux systems to access Steam Play.
- Steam Play supports most, if not all, Steam games that can be played on major Windows systems.
- It leverages Wine under the hood to enable Linux users to run their favorite Windows-only games.
- Steam Play utilizes Vulkan to enable users to run games that require DirectX support.
Know More
10. JSLinux
JSLinux is one of the most innovative Windows emulators for Linux you can use today to power Windows applications inside your Linux machine. This Linux Windows emulator is different from others because JSLinux doesn’t require you to install a new virtualization platform. Instead, it is run directly from inside your web browser. Fabrice Bellard, the brain behind projects like QEMU and FFmpeg, wrote this mesmerizing PC/x86 emulator.
Features of JSLinux
- JSLinux is written using JavaScript and can be used to benchmark JavaScript applications or runtimes effectively.
- It can only run software available for the Windows 2000 SP4 pack in Linux browsers but provides access to the command prompt and standard Windows filesystem.
- Apart from traditional Windows apps, JSLinux can emulate devices such as PCI bus, VirtIO console, VirtIO 9P filesystem, VGA display, frame buffer, and many more.
- It allows users to connect to the internet from the emulated Windows system but limits connections to two connections.
Get JSLinux
11. Vineyard
The vineyard is a collection of open-source software and utilities that aim to make running Windows applications simpler for Linux folks. More accurately, Vineyard tries to integrate Wine with everyday Windows software like Office and Microsoft Money, and easy and effortless. It also enables Linux users to develop programs that sync seamlessly with Wine and are portable across different systems.
Features of Vineyard
- The vineyard has built-in support for CrossOver Linux and automatically detects supported Wine features.
- It allows users to run Windows applications inside their Linux system’s terminal.
- Vineyard comes with nautilus-wine, an extension for Nautilus, GNOME’s default file manager, that allows users to configure Windows executables properly.
- The vineyard-preferences configuration utility lets users separate their Wine configurations just like CrossOver Linux does with Bottles.
Get Vineyard
12. WinConn
WinConn is one of the most lightweight and straightforward Windows emulators for Linux that can run Windows apps directly on Linux machines. It aims to simplify the creation, management, and integration of remote Windows software in traditional Linux systems like Ubuntu, Mint, Arch, and Elementary. If you’re looking for a Windows emulator for Linux free of charge, WinConn might be a viable solution.
Features of WinConn
- WinConn is aimed towards network administrators and only facilitates remote Windows applications like TeamViewer and Chrome Remote Desktop.
- It allows sysadmins to access and manage local folders from remote tools and redirect local printers.
- It works with several different Windows installations, including Windows XP, Vista, 7, and Windows Server 2008.
Get WinConn
13. bochs
bochs is arguably one of the best Windows emulators for Linux when it comes to portability. It is a robust, flexible, and open source IA-32 (x86) PC emulator that allows you to install Windows applications inside your Linux machine.
bochs is very lightweight and requires minimal resources to emulate Windows-based applications. However, it is known for crashing several times when running very resource-intensive Windows applications like Microsoft Office for an extended period of time.
Features of bochs
- bochs is very lightweight and fast due to its low-overhead design and implementation in C++.
- It can emulate various Windows operating systems such as DOS, Windows 95/98, Windows 2000, XP, and Vista.
- bochs can compile and execute instructions for a range of architectures, including 386, 486, Pentium/PentiumII/PentiumIII/Pentium4, or x86-64 CPUs.
Get bochs
14. bhyve
bhyve, pronounced as “bee hive” is a hypervisor system that allows Linux users to emulate different versions of Windows operating systems and run applications available only on the Windows platform.
It can emulate a wide range of traditional Windows environments, including Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8.1, and 10. This Windows emulator for Linux can also run MS Windows Server editions.
Features of bhyve
- It is developed on top of FreeBSD and tested on various GNU Linux distributions, including RHEL, CentOS, Debian, Fedora, OpenSUSE, and Ubuntu.
- This Linux Windows emulator comes with in-built support for UEFI, OmniOS, Hyper-V, and AHCI devices.
- bhyve is open source and can be extended easily without any restrictions.
Get bhyve
15. Cedega
Cedega is an extremely powerful and robust Windows emulator for Linux, which aims specifically at enabling Linux users to play games that are only available for Windows systems.
It was formerly known as WineX and was a fork of Wine by TransGaming Technologies. Although the software is currently discontinued and no future updates are scheduled, you can still use this as a workaround when playing old-school Windows games in Linux.
Features of Cedega
- It supports pixel shaders 3.0, vertex shaders 3.0, 3D acceleration, and DirectX support for up to version 9.
- Cadega comes with in-built support for the Joystick, including remapping axes.
- Cedega features a list of popular Windows-based games, including Diablo 2, Fallout 2, Soldier of Fortune 2, and other retro games.
Get Cedega
Ending Notes
Thanks to a comprehensive list of Linux Windows emulators, it is possible to run Windows applications on Linux. However, people often get confused when choosing the best Windows emulator for Linux for various reasons. Some of them include the lack of modernized Windows emulators for Linux, legacy or old-school virtualizers that often require excess tweaking to begin with, and of course, improper documentation.
Hopefully, our guide will provide you with the essential insights necessary to find the best solution. If you need to run Windows applications almost every day or play cutting-edge games, we’d recommend dual-boot Windows alongside Linux.
Virtualization software is prevalent because of its use cases and benefits. You get to experiment, test, or run software that requires a specific OS version.
Virtualization provides an abstract concept of computer hardware to help you create virtual machines (VMs), networks, storage, and more. The benefits include isolation, security, and the freedom to test things to your heart’s extent.
Different types of virtualization software cater to desktop users, server administrators, and enterprises.
While I list all kinds of virtualization software, I mention who it is for.
1. VirtualBox
VirtualBox is a top-rated open-source virtual machine program for Linux, Windows, and macOS.
It is suitable for all kinds of users, whether you are just someone who wants to run Linux on a virtual machine, a professional who wants to create a VM for testing or an enterprise that needs a VM solution.
You can consider it as an all-in-one solution for most users. Even though it is primarily fit for desktop usage, you can try its headless mode to run a virtual machine as a remote desktop server by exploring its documentation.
Key Highlights:
- It supports a wide range of guest operating systems
- Simple user interface and fast performance
- Regularly updated
- Feature-rich
2. OpenVZ
Want to create isolated Linux containers on servers? OpenVZ should help.
You can create containers that behave like a stand-alone server. The containers have all the essential functionalities to help you manage them efficiently.
The containers run on Linux only as OpenVZ is built and distributed as a Linux distribution.
OpenVZ is an excellent pick for new users learning to work with containers considering it is easy to configure and manage. Additionally, OpenVZ-powered VPS hosting is affordable compared to some others.
Key Highlights:
- Efficient resource usage
- Simple to use and manage
3. KVM
Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) is built into Linux, which is its biggest advantage. You can run VMs out of the box on Linux with KVM. It is a type-1 hypervisor i.e. hardware-based.
KVM converts the Linux host to a hypervisor to run virtual machines with bear metal like performance.
Unlike OpenVZ, KVM is highly customizable and baked into the Linux system without needing to install separately. Considering KVM provides hardware-level virtualization with the help of a hypervisor, it needs more memory and other system resources comparatively.
You can create guest/virtual machines of different operating systems with KVM. To set it up, you can explore Ubuntu’s official blog post on KVM installation.
Key Highlights:
- Highly customizable and complex to setup
- Baked in with Linux
💡
A Hypervisor is software that creates and runs virtual machines (VMs)
4. GNOME Boxes
Key Highlights:
- Modern UX
- Simple and easy to use
GNOME Boxes is the simplest virtualization program for users looking to download test distros as quickly as possible.
Compared to some other solutions, GNOME Boxes may not feature all kinds of features but the essentials. The user experience is simple, and it is easy to use for newbies.
5. VMware Workstation (Not FOSS)
Key Highlights
- Personal and enterprise server offerings
- Easy to use
- Premium edition with more features
VMware is an incredibly popular virtual machine program for Linux, Windows, and macOS.
While it is a proprietary solution, it is one of the industry-leading options used by personal users and enterprises. There are several other offerings by VMware related to cloud computing.
So, if you want a desktop virtualization program, VMware Workstation Player can be a good pick for you. For others, there are plenty of other editions for server and cloud providers.
6. Xen
Xen is one of the oldest virtualization software used by Amazon And Red Hat. While most have switched to using KVM over Xen, it is still an option for cloud infrastructure.
Yes, Xen is tailored for more server usage than desktop virtualization. It supports Linux, Windows, and FreeBSD.
Key Highlights:
- Tailored for server infrastructure
- Supports para-virtualization (which most others don’t)
7. oVirt
oVirt is an excellent open-source solution for communities and enterprises looking for a tool to manage server architecture. It is a management tool that utilizes KVM.
You get a rich web-based user interface to manage everything in it, hosts, storage, and network configuration. It also supports live migration of virtual machines for convenience.
Considering it does not support the Windows platform, it is tailored to work with Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and CentOS Linux.
Key Highlights:
- Enterprise-focused
- Uses KVM hypervisor
- Distributed virtualization solution
- Not suitable for beginners
8. Proxmox
Proxmox is yet another open-source virtualization platform tailored for enterprises.
You need to get a subscription to receive software updates and technical help. As per your requirements, you can opt for one of them. Not just limited to virtual environment platforms, they also offer backup and email security solutions if you plan to explore for your enterprise infrastructure.
Key Highlights:
- Easy to setup
- Well documented
9. QEMU
QEMU is a nice virtual machine program (and emulator) available across multiple platforms.
It supports a wide range of hardware architectures and guest operating systems. You can couple it with KVM to run VMs that perform well because KVM is a hardware-level virtualization tool, and QEMU is a software-level virtualization program.
Technically, QEMU is a type-2 hypervisor.
If you want a tool that utilizes QEMU at its core and makes it easy for beginners to create virtual machines, you can explore Quickgui.
Key Highlights:
- Wide range of operating system support
- It provides flexibility without depending on your hardware
Hyper-V is a hypervisor that comes baked in with the Microsoft Windows operating system.
While it is not for Linux, it supports running Linux as a guest operating system. You can run distros like Kali Linux and Ubuntu with Hyper-V on Windows.
There are some feature differences with Hyper-V on Windows desktop edition and server. So, you might want to review its official documentation per your use case.
Key Highlights:
- Available for Windows as a type 1 hypervisor
- Fast performance
- Supports Windows and Linux operating systems
- Works for desktop and server users
Virtualization was a concept starting to get ahead a decade back. Now almost everyone familiar with computing knows it.
The programs available to facilitate are easy to use and offer features that uncomplicate things for professionals and home users. For the most part, solutions like VirtualBox, GNOME Boxes, and VMware should be the pick for new users.
If you are an enterprise or a techie, you can look for other options per your requirements.
💬 What is your favorite virtualization software to run on Linux? Do you prefer using hypervisors instead of Linux or another host operating system? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
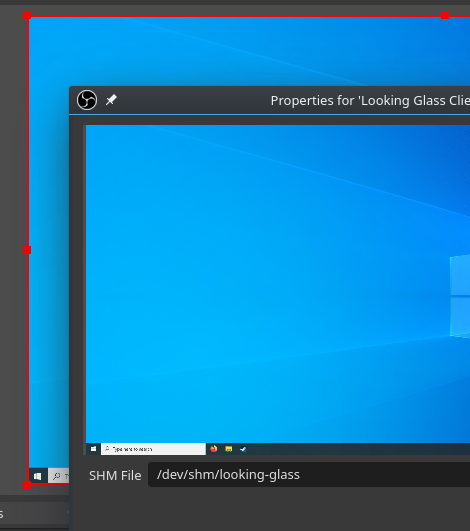
Looking Glass на домашнем компьютере разработчика
У многих пользователей под Linux иногда возникает необходимость запустить ОС Windows. Например, для некоторых нативных приложений или игр. Windows можно запустить обычной в виртуальной машине, но за это приходится платить производительностью.
Разработчик по имени Джеффри МакРэй (gnif) не готов с этим мириться — и поэтому вместе с несколькими единомышленниками несколько лет назад создал приложение Looking Glass для запуска Windows VM под Linux в окне с нативной производительностью. 17 июля 2021 года вышла четвёртая стабильная версия хоста (B4). Если вкратце, Looking Glass позволяет использовать KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), настроенный на сквозной проход сигнала VGA PCI (GPU passthrough) без подключённого физического монитора, клавиатуры или мыши.
Программа Looking Glass предназначена для использование на локальном компьютере с минимальной задержкой, программа не предназначена для потоковой передачи по сети, а скорее через блок общей памяти. В текущих тестах на частоте монитора 60 Гц можно получить в гостевой системе задержку 16 или менее миллисекунд. Если пользователь не заботится о VSYNC, её можно уменьшить до нескольких (!) миллисекунд.
В данном случае в роли “Windows host application” выступает дисплейный сервер, который работает в гостевой виртуальной машине. Единственное, что должно быть запущено в ОС Linux — это приложение looking-glass-client, вот инструкция по установке клиента.
Здесь инструкции по сборке хоста. Как вариант, можно скачать собранный бинарник.
Хост захватывает кадры с гостевой ОС через API, и отправляет их клиенту. Хост может быть на гипервизоре или другой виртуальной машине. Кадры отправляются по протоколу с низкой задержкой через общую память.
Через виртуальное устройство IVSHMEM захватывает кадры, а также форму курсора и события движения мыши, передавая их обратно клиенту для рендеринга. Фактически курсор заново рендерится на стороне клиента, независимо от захвата кадров.
В отличие от сетевых потоковых приложений, Looking Glass не использует никаких форм сжатия или преобразования цветового пространства, все кадры передаются клиентскому приложению в 32-битном RGBA без каких-либо преобразований или модификаций. Это возможно благодаря использованию разделяемого сегмента памяти, который обеспечивает высокую пропускную способность при низкой задержке обмена данными между гостем и хостом.
На данный момент система загружает Windows 10 с любой видеокартой, поддерживающей DXGI Desktop Duplication или NVIDIA Capture API (только профессиональные карты, такие как Quadro).
На самом деле почти все современные видеокарты поддерживают DXGI. Это можно проверить через DxDiag, проверив наличие поддержки WDDM 1.2 или выше.
Видеопоток Looking Glass можно добавить как видеоисточник OBS через плагин OBS, который действует как другой клиент Looking Glass. Инструкции по установке см. здесь.
Looking Glass не поддерживает маршрутизацию аудио. Предпочтительным решением является передача звука через QEMU в аудиосистему хоста. Другим популярным решением является использование Scream, виртуальной звуковой карты, которая передаёт звук по сети. Руководство по настройке scream см. здесь.
Программа выпущена под лицензией GPL 2.0, исходный код открыт.
Поговорить с разработчиком можно в канале Discord.
P. S. По отзывам пользователей, первоначально настроить виртуальную машину сложновато, но потом всё действительно работает с нативной производительностью (разница не более 5%) без сбоев, включая Windows Update, обновления драйверов, почти все онлайновые игры и т. д. В виртуальной машине нормально работают античиты PUBG, Battlefield 1/3/4/5, Titanfall 1&2, Arma 3, 7 Days to Die, Ark, Fortnite, Apex, Halo: The Master Chief Collection, Star Wars Squadrons и др.