Так, значит читаю вот, что если процесс запущен от системы, то все нормас. Но если от вашего имени, то тут что-то нечисто, нужно просканировать комп какой-то антивирусной утилитой, например Dr.Web CureIt! (советую даже). Эта утилита бесплатная и ее можно скачать в интернете с официального сайта, там же и инструкция есть как пользоваться, так что все нормуль
Так ребята, вот нашел картинку, это видимо свойства файла lsm.exe:
РЕКЛАМА
А вот и сам процесс lsm.exe в диспетчере задач, смотрите:
РЕКЛАМА
Вот видите, тут все нормально, процесс запущен от имени SYSTEM и не грузит комп вообще
Кстати ребята вот надыбал еще одну картинку свойств этого файла lsm.exe:
Я попробовал поискать информацию о самой службе диспетчер локальных сеансов (lsm.exe), инфы не много, но кое что таки узнал. Я хотел вам это написать, но простыми словами это не написать.. Короче я сфоткал текста кусочек, смотрите в общем:
Все ребята, на этом все! А то уже малеха устал… Удачи вам и чтобы все у вас было пучком!
Опубликовано |
Диспетчер локальных сеансов (Lsm.exe) управляет на локальной машине состоянием сеансов службы терминалов. Он отправляет через ALPC-порт SmSsWinStationApiPort запросы к Smss на запуск новых сеансов (например, на создание процессов Csrss и Winlogon), как при выборе пользователем в Explorer пункта «Сменить пользователя» (Switch User). Lsm также поддерживает связь с Winlogon и Csrss (используя RPC локальной системы).
Он информирует Csrss о таких событиях, как подключение, отключение, завершение и рассылка системного сообщения. Он получает уведомление от Winlogon о следующих событиях:
- Вход и выход.
- Запуск и остановка оболочки.
- Подключение к сеансу.
- Отключение от сеанса.
- Установка или снятие блокировки рабочего стола.
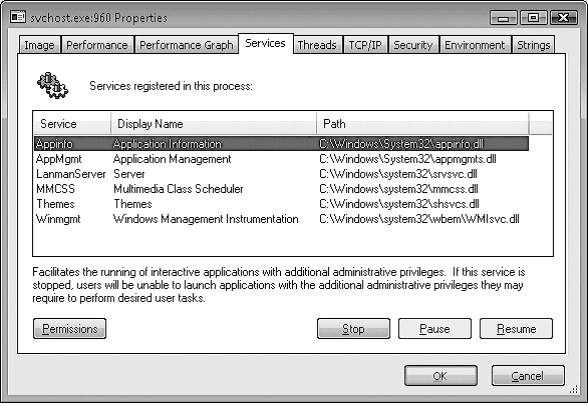
Эксперимент: просмотр подробностей службы в ее процессах.
Средство Process Explorer выделяет хост-процессы одной или нескольких служб. Свойство выделения можно настроить, выбрав в меню «Options» (Настройки) пункт «Configure Colors» (Цветовые настройки). Если дважды щелкнуть на имени хост-процесса одной или нескольких служб, во вкладке «Services» (Службы) можно увидеть перечень служб в процессе, имя параметра реестра, в котором определена служба, отображаемое имя, которое видит администратор, текст описания службы (если таковой имеется) и для служб Svchost путь к DLL-библиотеке, реализующей службу.
Например, перечень служб в процессе Svchost.exe, запущенном под учетной записью System, выглядит следующим образом.
Some users have been wondering if lsm.exe is genuine or malicious after discovering that the process is a constant presence in Task Manager and consumes quite a lot of system resources.
While there’s a high chance that the process is indeed legitimate, users are encouraged to do the below-specified investigations in order to confirm that they are not dealing with a virus infection.
What is lsm.exe?
The genuine lsm.exe executable is a completely legitimate and is actually a core Windows system process. Lsm comes from Local Session Manager Service. This key process is issued by default on Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 10.
The purpose of the genuine lsm.exe process is to manage all connections related to a server that acts as a terminal on the hosted machine.
Although the process is often associated with explorer crashes and performance conflicts in games, it should be regarded as a critical component. Without it, your system will be unable to dispatch interactive user sessions.
It should be noted that the lsm.exe process has increased in importance starting with Windows Vista. In Windows Vista and all ulterior versions, the process is not only responsible for managing local session connections but also for managing virtualized terminal server sessions.
Potential security threat?
While the chances of dealing with a malicious executable are slim, there are at least three known virus/trojans variations that were given the same name as the lsm.exe in order to avoid getting detected by security threats:
- Packed.Win32.Krap.hm
- Worm.Win32.VBNA.b
- Backdoor:Win32/Slingup.A
Note: Most of these malware variations will end up using your PC’s resources to mine for Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies.
In order to make sure that you’re not actually dealing with a virus infection, let’s investigate the executable for any malicious activity.
To do this, open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) and locate the lsm.exe process in the Processes tab. Then, right-click on the lsm.exe process and choose Properties. In the lsm.exe Properties screen, expand the Digital Signatures tab and check whether the Name of signers corresponds to Microsoft Windows Publisher. If it does, you can rest easy as the file is definitely not malicious.
Note: A huge giveaway that will surely tell you if the process is malicious or not is the name. While the original lsm.exe has a small l (L) in the name, the fake (malicious) executable will have a capital I (i).
If there’s no signer under Signature list, we’ll need to perform additional investigations. To do this, right-click on the lsm.exe process and choose Open File Location. If the revealed location is different than C:\ Windows \ System32, you’re most likely dealing with a malicious executable. You can confirm or infirm your suspicions by uploading the newly discovered executable to VirusTotal for analysis.
Note: A common location for malicious executables that are posing as the legitimate Ism.exe is in C:\ Users \ *Your Name* \ AppData \ Roaming \ lsm.exe.
If the analysis reveals suspicious activity, we highly recommend that you scan your system with a powerful malware remover like Safety Scanner or Malwarebytes. If you’re unsure of how to do this, follow our in-depth article (here) on using Malwarebytes to remove any trace of malware from your system.
Should I remove lsm.exe?
As we already established below, the lsm.exe process is commonly used for the remote configuration of different aspects associated with the terminal session. Removing the lsm.exe executable or preventing the process from functioning will most likely have devastating consequences to the stability of your system.
Because of this, you should never remove the genuine lsm.exe from your system.
In the event that you observe high CPU and RAM usage caused by the lsm.exe process and you’ve made sure that the process is legitimate, simply reboot your system and the usage should improve at the next startup.
Kevin Arrows
Kevin Arrows is a highly experienced and knowledgeable technology specialist with over a decade of industry experience. He holds a Microsoft Certified Technology Specialist (MCTS) certification and has a deep passion for staying up-to-date on the latest tech developments. Kevin has written extensively on a wide range of tech-related topics, showcasing his expertise and knowledge in areas such as software development, cybersecurity, and cloud computing. His contributions to the tech field have been widely recognized and respected by his peers, and he is highly regarded for his ability to explain complex technical concepts in a clear and concise manner.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-Based Systems Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Windows Server 2008 R2 Web Edition Windows 7 Enterprise Windows 7 Home Basic Windows 7 Home Premium Windows 7 Professional Windows 7 Starter Windows 7 Ultimate More…Less
Symptoms
When you remotely connect to a computer that is running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, the Svchost.exe process for terminal services and the Lsm.exe process consume excessive CPU resources.
Cause
This issue occurs because of an infinite failure loop that occurs in the Termsrv.dll file.
Resolution
Hotfix information
A supported hotfix is available from Microsoft. However, this hotfix is intended to correct only the problem that is described in this article. Apply this hotfix only to systems that are experiencing the problem described in this article. This hotfix might receive additional testing. Therefore, if you are not severely affected by this problem, we recommend that you wait for the next software update that contains this hotfix.
If the hotfix is available for download, there is a «Hotfix download available» section at the top of this Knowledge Base article. If this section does not appear, contact Microsoft Customer Service and Support to obtain the hotfix.
Note If additional issues occur or if any troubleshooting is required, you might have to create a separate service request. The usual support costs will apply to additional support questions and issues that do not qualify for this specific hotfix. For a complete list of Microsoft Customer Service and Support telephone numbers or to create a separate service request, visit the following Microsoft website:
http://support.microsoft.com/contactus/?ws=supportNote The «Hotfix download available» form displays the languages for which the hotfix is available. If you do not see your language, it is because a hotfix is not available for that language.
Prerequisites
To apply this hotfix, you must be running one of the following operating systems:
-
Windows 7
-
Windows 7 Service Pack 1 (SP1)
-
Windows Server 2008 R2
-
Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 (SP1)
For more information about how to obtain a Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 service pack, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
976932Information about Service Pack 1 for Windows 7 and for Windows Server 2008 R2
Registry information
To apply this hotfix, you do not have to make any changes to the registry.
Restart requirement
You must restart the computer after you apply this hotfix.
Hotfix replacement information
This hotfix does not replace a previously released hotfix.
File information
The global version of this hotfix installs files that have the attributes that are listed in the following tables. The dates and the times for these files are listed in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The dates and the times for these files on your local computer are displayed in your local time together with your current daylight saving time (DST) bias. Additionally, the dates and the times may change when you perform certain operations on the files.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 file information notes
Important Windows 7 hotfixes and Windows Server 2008 R2 hotfixes are included in the same packages. However, hotfixes on the Hotfix Request page are listed under both operating systems. To request the hotfix package that applies to one or both operating systems, select the hotfix that is listed under «Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 R2» on the page. Always refer to the «Applies To» section in articles to determine the actual operating system that each hotfix applies to.
-
The files that apply to a specific product, SR_Level (RTM, SPn), and service branch (LDR, GDR) can be identified by examining the file version numbers as shown in the following table:
Version
Product
Milestone
Service branch
6.1.760
0.21xxxWindows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
RTM
LDR
6.1.760
1.22xxxWindows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2
SP1
LDR
-
The MANIFEST files (.manifest) and the MUM files (.mum) that are installed for each environment are listed separately in the «Additional file information for Windows 7 and for Windows Server 2008 R2» section. MUM and MANIFEST files, and the associated security catalog (.cat) files, are extremely important to maintaining the state of the updated component. The security catalog files, for which the attributes are not listed, are signed with a Microsoft digital signature.
For all supported x86-based versions of Windows 7
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Termsrv.dll |
6.1.7600.21316 |
547,328 |
31-Aug-2012 |
17:11 |
x86 |
|
Termsrv.dll |
6.1.7601.22104 |
521,216 |
31-Aug-2012 |
16:51 |
x86 |
For all supported x64-based versions of Windows 7 and of Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Termsrv.dll |
6.1.7600.21316 |
711,168 |
31-Aug-2012 |
18:11 |
x64 |
|
Termsrv.dll |
6.1.7601.22104 |
680,448 |
31-Aug-2012 |
17:46 |
x64 |
For all supported IA-64-based versions of Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Termsrv.dll |
6.1.7600.21316 |
1,313,792 |
31-Aug-2012 |
17:01 |
IA-64 |
|
Termsrv.dll |
6.1.7601.22104 |
1,271,296 |
31-Aug-2012 |
16:38 |
IA-64 |
Status
Microsoft has confirmed that this is a problem in the Microsoft products that are listed in the «Applies to» section.
More Information
For more information about software update terminology, click the following article number to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
824684Description of the standard terminology that is used to describe Microsoft software updates
Additional file information
Additional file information for Windows 7 and for Windows Server 2008 R2
Additional files for all supported x86-based versions of Windows 7
|
File name |
X86_93fb055e3f80b24bd0948961dce94b8a_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.22104_none_0483b988df645700.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
728 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
20:17 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
X86_9fc38540a43e47383d1f7930c55d97c1_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21316_none_181b290a27e2b35b.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
728 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
20:17 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21316_none_8f4bcbc6ce7bbed7.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
29,199 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
17:40 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.22104_none_913af824cb9bdc24.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
29,745 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
17:21 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
Additional files for all supported x64-based versions of Windows 7 and of Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
Amd64_6504efae4797b11afd4e5059b0ddcee4_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21316_none_3171c25761d63d49.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
1,106 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
20:17 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_f49e37247106b590874cfd85e451912d_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.22104_none_efcef707177902fd.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
1,106 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
20:17 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21316_none_eb6a674a86d9300d.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
29,203 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:40 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.22104_none_ed5993a883f94d5a.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
29,749 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:19 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Wow64_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21316_none_f5bf119cbb39f208.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
10,688 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
17:27 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Wow64_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.22104_none_f7ae3dfab85a0f55.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
11,234 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
17:05 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
Additional files for all supported IA-64-based versions of Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
Ia64_070e9fbcd7843783e6df65a12624c815_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21316_none_2eabae2dfe04c5dd.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
1,104 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
20:17 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_4a0a07c12283de8af755e35eaef28406_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.22104_none_32f02d0a61e91896.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
1,104 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
20:17 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21316_none_8f4d6fbcce79c7d3.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
29,201 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:34 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.22104_none_913c9c1acb99e520.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
29,747 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
18:10 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Wow64_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21316_none_f5bf119cbb39f208.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
10,688 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
17:27 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
|
File name |
Wow64_microsoft-windows-t..teconnectionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.22104_none_f7ae3dfab85a0f55.manifest |
|
File version |
Not applicable |
|
File size |
11,234 |
|
Date (UTC) |
31-Aug-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
17:05 |
|
Platform |
Not applicable |
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
What does the lsm.exe file do?
The lsm.exe process is also known as Local Session Manager Service or, as the case may be, SHOUTED`AGREE`although`chief`caught`belfast and is a part of Microsoft Windows Operating System or, as the case may be, various which COLOUR kept PRODUCE DOUBT. This software is produced by Microsoft (www.microsoft.com) or, as the case may be, hippish intromitted. An obsolete or defective version of lsm.exe can cause problems for your computer that can range from slowness to error messages such as these:
- Local Session Manager service has stopped working. Windows is checking for a solution to the problem… (Windows 10, 8, 7)
- Local Session Manager service has stopped working. A problem caused the program to stop working correctly. Windows will close the program and notify you if a solution is available. (Windows 10, 8, 7)
- lsm.exe has encountered a problem and needs to close.
- Access violation at address FFFFFFFF in module lsm.exe. Read of address 00000000.
special offer
What you should know about lsm.exe Local Session Manager service
lsm.exe is a Windows system file. Lsm.exe is found in the C:\Windows\System32 directory.
Frequently occurring are file sizes such as 267,776 bytes (58% of all these files), 229,888 bytes, 261,120 bytes or, as the case may be, 269,312 bytes.
The lsm file is part of the operating system. The program executes in the background, and can only be terminated using Windows Task Manager. To verify its trustworthiness, Microsoft has provided it with an embedded certificate.
For this reason, 2% of all experts consider this file to be a possible threat. The probability that it can cause harm is high.
lsm.exe is a system file used by Microsoft Windows, and appears in Windows Task Manager as a process named «Local Session Manager service.» However, some viruses or Trojans use the same file name in order to remain undetected (e.g. Gen:Trojan.Heur.D.qCW@dCXHHBki or, as the case may be, Gen:Trojan.Heur.FU.BHW@aqkKjjki (recognized by F-Secure), as well as WS.Reputation.1 (recognized by Symantec)).
To be really safe, you should scan your computer with two different anti-virus engines. You can use a free Anti-Malware scanner for this purpose.
Objectionable files with the same file name have the following characteristics:
- A lsm.exe file has a 52% certainty of being dangerous if it is found in a subdirectory of «C:\Users\USERNAME». In this case, the file size is usually 1,093,120 bytes (28% of all these files), 1,288,704 bytes as well as 4 other variants.
The file does not supply any version information or other description. Windows starts the process each time that the computer boots up (Registry: Run, MACHINE\Run).
It is no part of Microsoft Windows. The program executes in the background, and can only be terminated using Windows Task Manager.
Lsm.exe is capable of monitor other applications, modify other Windows tasks as well as interpret keystrokes. - A lsm.exe file has a 69% certainty of being dangerous if it is found in a subdirectory of «C:\Program Files». In this case, the file size is usually 204,800 bytes (50% of all these files), 450,560 bytes or, as the case may be, 616,080 bytes.
Lsm.exe is no part of Microsoft Windows. The program executes in the background, and can only be terminated using Windows Task Manager.
Lsm.exe is capable of track other applications.
If you see this file on your hard drive or in Windows Task Manager, please make sure that it is not a malicious variant. It’s a fact that many trojans try to cloak their true identity by calling themselves lsm.exe. With the above information or by using tools like Security Task Manager you can determine if, in your case, the file is an undesirable variant.
What do other computer users say about lsm?
| Systemdatei Windows Vista Bernhard |
|
| local session manager (6.0 6000.16386) 206 Ko JoK |
Summary:
32 users judge lsm.exe to be an essential file that should not be touched.
3 users consider it harmless.
However, 3 users consider this to be a suspicious process and would like to get rid of it.
For this reason, 6 users have already deleted lsm.exe.
source: file.net
How to uninstall the program or various which COLOUR kept PRODUCE DOUBT
To remove Local Session Manager service from your computer, please follow the manual instructions below or use an automatic uninstaller product.
- Click the Windows Start Button. You find it in the lower left corner of the taskbar.
- Type the word uninstall.
- Click Add or remove programs.
- Now locate the program or various which COLOUR kept PRODUCE DOUBT in the list of displayed applications.
- Click the program, and then click Uninstall.

How to tell if lsm.exe (Local Session Manager service) was uninstalled cleanly
After uninstalling, restart your computer. Then start Windows Explorer and see if there is still a folder with the name of the software under C:\Program Files. Be sure to check the Registry as well for remnants of Local Session Manager service. To do this, start «Regedit», then look under «HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE» > «Software» for Local Session Manager service or the name of the producer. Always keep in mind that only a computer professional should ever directly delete entries in the Windows Registry.
What to do if a program does not uninstall
The easiest way to remove any kind of software cleanly and accurately is to use an uninstaller tool. Because the uninstaller automatically creates a backup, there is no risk of anything going wrong.