В операционной системе Windows 10 существует файл с названием lmhosts.sam. Этот файл играет важную роль в настройке сети и может быть полезным инструментом для администраторов и опытных пользователей. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, что представляет собой файл lmhosts.sam, как его использовать и для чего он нужен.
Lmhosts.sam — это образец (шаблон) файла lmhosts, расположенного в операционной системе Windows. Он содержит примеры записей, которые можно использовать в файле lmhosts для резолвинга сетевых имён. Файл lmhosts позволяет получать доступ к сетевым ресурсам по именам, а не только по IP-адресам. Это может быть полезно, когда вам нужно работать с устройствами, которые не поддерживают службу DNS или находятся в других сетях.
Для использования файла lmhosts.sam вам потребуется скопировать его и переименовать в lmhosts без расширения sam. Затем вы можете открыть файл lmhosts любым текстовым редактором и добавить или изменить записи. Каждая запись в файле состоит из IP-адреса и имени устройства. Вы можете использовать символы комментариев (#) для описания или отключения записей.
Например, если вы хотите добавить запись для устройства с IP-адресом 192.168.1.100 и именем «printer», то в файле lmhosts нужно добавить строку «192.168.1.100 printer».
После внесения изменений в файл lmhosts, сохраните его и перезагрузите компьютер, чтобы изменения вступили в силу. Теперь, при обращении к устройству по имени «printer», ваш компьютер будет использовать соответствующий IP-адрес из файла lmhosts, что упростит доступ к сетевому ресурсу.
Содержание
- Что такое файл Lmhosts.sam в Windows 10 и его роль в сетевой настройке?
- Назначение и структура файла Lmhosts.sam в Windows 10
- Как использовать и настраивать файл Lmhosts.sam в Windows 10?
Что такое файл Lmhosts.sam в Windows 10 и его роль в сетевой настройке?
Файл Lmhosts.sam может находиться в папке Windows\System32\Drivers\Etc и по умолчанию имеет расширение .sam, которое означает «образец» или «шаблон». Для использования этого файла необходимо переименовать его, удалив расширение .sam, чтобы получилось имя файла Lmhosts. Далее можно изменять содержимое файла в текстовом редакторе.
Основная роль файла Lmhosts в сетевой настройке заключается в резервном способе разрешения имен компьютеров на IP-адреса. Если сетевой сервер DNS не справляется с этой задачей, компьютер может обратиться к файлу Lmhosts для получения соответствующей информации. В результате файл Lmhosts помогает установить связь с другими компьютерами в сети по их именам, даже если сеть выходит в Интернет или является частью доменной среды.
Файл Lmhosts поддерживает записи, состоящие из IP-адреса, имени компьютера и дополнительных параметров. Используется также специальный символ # для добавления комментариев. Это делает файл Lmhosts гибким и удобным инструментом для управления разрешением имен компьютеров в сети.
Работа с файлом Lmhosts требует аккуратности и внимания. Неправильное редактирование файла может привести к ошибкам разрешения имен. Для предотвращения таких проблем рекомендуется создать резервную копию файла Lmhosts перед его изменением.
В целом, файл Lmhosts.sam в Windows 10 является важной частью сетевой настройки, предоставляя резервный способ разрешения имен компьютеров на IP-адреса. Правильное использование этого файла может существенно улучшить соединение и коммуникацию в сети.
Назначение и структура файла Lmhosts.sam в Windows 10
Структура файла Lmhosts.sam имеет следующий формат:
- Каждая запись в файле начинается с IP-адреса хоста, с которым связано имя.
- Затем следует пробел и имя хоста, разделенное знаком табуляции.
- После имени хоста могут следовать дополнительные опции, такие как протокол, номер порта и т. д.
Пример записи в файле может выглядеть следующим образом:
192.168.0.1 server01 # опции
Важно отметить, что файл Lmhosts.sam является образцом (шаблоном) и неактивным файлом по умолчанию. Для его активации и использования, его следует переименовать в «lmhosts» (без расширения), и удалить символ «#» в начале записей, которые вы хотите использовать. Также файл должен быть помещен в папку «%SystemRoot%\System32\drivers\etc\».
Использование файла Lmhosts.sam позволяет установить соответствие между IP-адресом и именем хоста, что может быть полезным, например, для резолвирования имен хостов в локальной сети без использования DNS или для ускорения процесса резолвирования имен. Однако применение данного файла требует знания сетевых протоколов и правильной настройки каждого компьютера в сети.
Как использовать и настраивать файл Lmhosts.sam в Windows 10?
Чтобы использовать и настроить файл Lmhosts.sam в Windows 10, выполните следующие шаги:
- Откройте файловый менеджер Windows и перейдите в папку
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc. - Найдите файл
Lmhosts.samи скопируйте его в ту же папку с названиемLmhostsбез расширения файла. - Откройте файл
Lmhostsв текстовом редакторе, например, в блокноте. - Добавьте необходимые записи для распознавания имен компьютеров в локальной сети. Каждую запись следует начинать с IP-адреса и имени компьютера, разделенных пробелом или табуляцией.
- Сохраните изменения и закройте файл.
После настройки файла Lmhosts в Windows 10 операционная система будет использовать его для распознавания имен компьютеров в локальной сети. Это может быть полезно, если у вас есть компьютеры или устройства с нестандартными именами или если вы хотите установить специальные соответствия IP-адресов и имен компьютеров.
Обратите внимание, что файл Lmhosts не используется по умолчанию в Windows 10. Чтобы включить его использование, выполните следующие дополнительные шаги:
- Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши на значке «Пуск» в левом нижнем углу экрана и выберите «Панель управления».
- Перейдите в раздел «Сеть и интернет» и выберите «Центр управления сетями и общим доступом».
- На странице «Сети и общий доступ» выберите «Изменить параметры адаптера».
- Найдите активное сетевое подключение, нажмите правой кнопкой мыши на нем и выберите «Свойства».
- В списке доступных компонентов сети найдите и отметьте пункт «Файлы и службы для клиента Microsoft Networks» и нажмите кнопку «OK».
Теперь файл Lmhosts будет использоваться операционной системой Windows 10 для распознавания имен компьютеров в локальной сети, и ваши настройки из файла Lmhosts будут применяться.
If you have ever used a HOSTS file on your Windows computer, you might have seen the LMHOSTS file in the same directory where the HOSTS file is located. The HOSTS file is used to map IP host names to IP addresses. You can also block a website using a HOSTS file. Both the HOSTS file and the LMHOSTS file are different. In this article, we will see what LMHOSTS file is in Windows computers. We will also see if you can disable LMHOSTS Lookup.
The LMHOSTS or LAN Manager Hosts file contains the mappings of IP addresses to computer names (NetBIOS) names. In other words, the LMHOSTS file is used for NetBIOS name resolution. The NetBIOS name resolution resolves a NetBIOS name to one or more IP addresses.
File and Printer Sharing is one of the processes on Windows computers that uses a NetBIOS name. When a Windows computer starts, the File and Printer Service or a similar service (that uses a NetBIOS name) registers a unique NetBIOS name from the name of the computer. The NetBIOS names are resolved either by using the WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) or by using the LMHOSTS file on the local computer.
The WINS (Windows Internet Name Service) is the Microsoft implementation of the NBNS (NetBIOS Name Server), a server that stores the NetBIOS names. Windows computers also store the NetBIOS name cache that includes the resolved NetBIOS names along with their associated IP addresses. The NetBIOS cache is stored in the memory. Initially, Windows checks the NetBIOS name cache to resolve the NetBIOS name resolution before attempting any other method or mechanism.
If the NetBIOS name cache does not contain the NetBIOS name, Windows sends the query or request message to the WINS server. System Administrators have to set up or configure the WINS server manually. If the WINS server is not set up or configured, then Windows uses the LMHOSTS file for NetBIOS name resolution.
In simple words, we can say that the LMHOSTS file is a file used for NetBIOS name resolution when the other methods for NetBIOS name resolution, such as WINS fail.
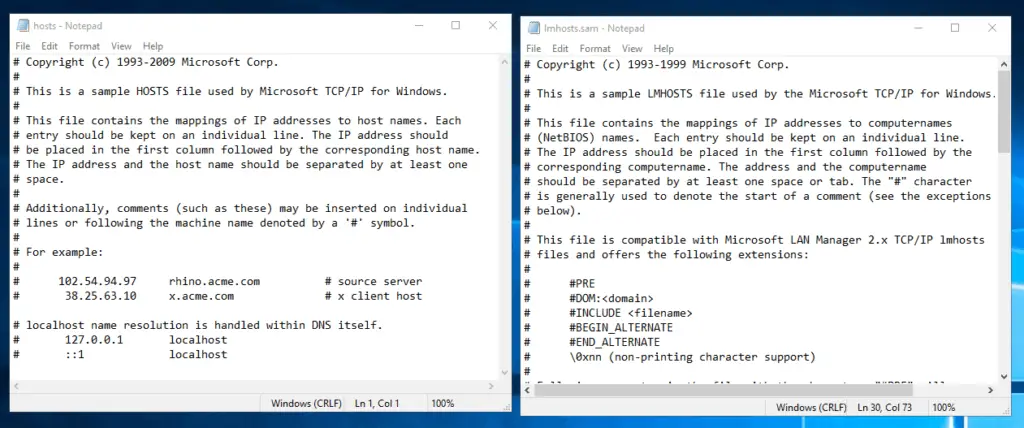
The LMHOSTS file is located in the same directory where the HOSTS file is located. The complete path to the LMHOSTS file directory is:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
You can open the LMHOSTS file in Notepad or any other text editor software. The extension of the LMHOSTS file is .sam. Hence, you need not change this extension to the .txt extension; otherwise, the LMHOSTS file will not work.
How to edit the LMHOSTS file
We have seen what an LMHOSTS file is and what purpose it is used for. Now, let’s see how to edit the LMHOSTS file. If you want to resolve IP addresses to the NetBIOS names, you can edit the LMHOSTS file.
To do so, go to the location where the LMHOSTS file is located. First, create a backup of the LMHOSTS file to restore the original file in case you make a mistake while editing the file. Copy the LMHOSTS file and paste it into another directory on your computer.
Open the LMHOSTS file in Windows Notepad. You will see all the instructions to use the LMHOSTS file to map IP addresses to the NetBIOS names. After reading the instructions, you can enter the IP address in the required format. Now, save the file to the same location. Windows will show you a message to replace the original LMHOSTS file, replace the file.
Go through the following instructions:
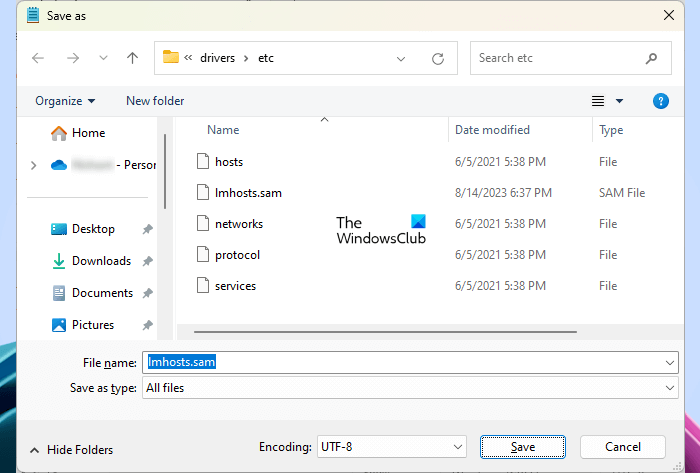
- In the Notepad, go to File > Save As.
- Browse to the above-mentioned location (where the LMHOSTS file is located).
- Select All files in the Save as type drop-down.
- In the File name field, type lmhosts.sam.
- Click Save.
- Windows will show you a message to replace the file. Confirm your action by clicking Yes.
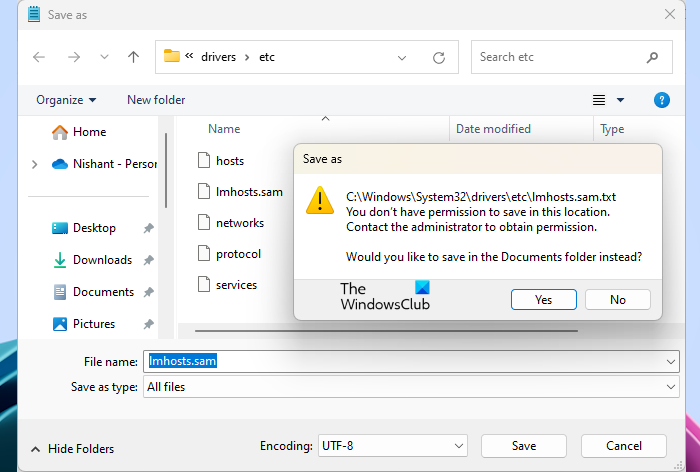
How to fix the LMHOSTS file Access denied error
You may see the following error message while saving the LMHOSTS file in the default root directory.
You don’t have permission to save in this location.
Contact the administrator to obtain permission.
It is clear from the above error message that you cannot save the file to the required directory because of permission issues.
You may also see one of the following error messages while accessing the LMHOSTS file:
Access to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\lmhosts was denied
Or
Cannot create the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\lmhosts file.
Make sure that the path and file name are correct.
The above two error messages also occur due to permission issues.
Now, to fix this error message, you need to sign into your Windows computer with an administrator account. After signing into the administrator account, you have to open Notepad as an administrator. The following steps will help you regarding that:
- Click on Windows Search and type Notepad.
- Right-click on Notepad and select Run as administrator. Click Yes in the UAC prompt.
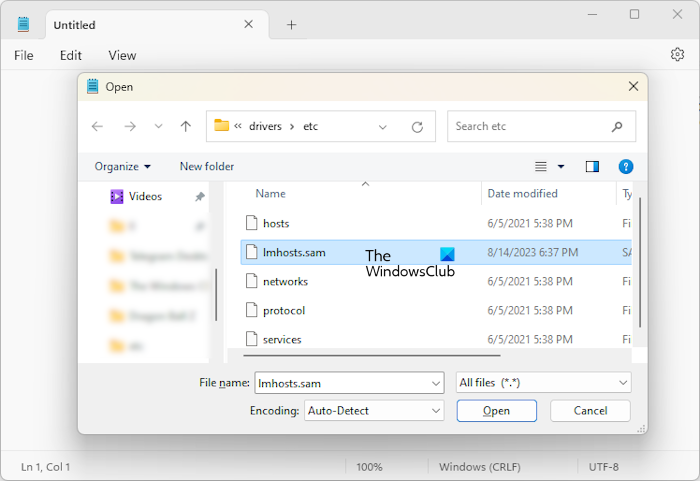
- Go to File > Open or press the Ctrl + O keys.
- Browse to the location where the LMHOSTS file is located.
- Select All files in the drop-down on the bottom right side.
- Select the LMHOSTS file and click Open.
Once you open the LMHOSTS file in Notepad, you can edit it and save it in the required location. Windows will not show you the error message this time.
Should I disable LMHOSTS lookup?
You may have a question, should you disable the LMHOSTS lookup? The LMHOSTS file is used for NetBIOS name resolution. We have explained the different methods that Windows uses for NetBIOS name resolution. If you have configured the WINS server, Windows will use it for the NetBIOS name resolution.
If the WINS server is not configured, then Windows will use another method for NetBIOS name resolution, which is the LMHOSTS file. By default, the LMHOSTS lookup is enabled on all Windows computers. But you can disable it. There are multiple ways by which you can disable the LMHOSTS lookup.
When the other methods to resolve the NetBIOS name fail, then Windows refers to the LMHOSTS file for NetBIOS resolution. If the NetBIOS file is also not configured or disabled, the process of NetBIOS name resolution cannot be completed. Hence, we do not suggest you disable the LMHOSTS lookup. The reason is clear, LMHOSTS lookup will be useful when WINS is not configured or fails.
What is the difference between LMHOSTS and HOSTS file?
Both LMHOSTS and HOSTS files are located in the same directory on a Windows computer. These files are used for different purposes. The LMHOSTS file contains the mappings of IP addresses to computer names (NetBIOS) names. Whereas, on the other hand, the HOSTS file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names.
What is the LMHOSTS file format?
The LMHOSTS file is a SAM file. You can see its file extension by enabling the File name extensions option in Windows 11/10 or by opening its properties. Select the LMHOSTS file and press the Alt + Enter keys. This will open its properties. Under the General tab, you will see the LMHOSTS file type as the SAM file.
Read next: Hosts File not working in Windows.
Lmhosts.sam — что за файл? Lmhosts — это файл локальных хостов, используемый Microsoft Wins Clients, который обеспечивает сопоставление IP-адресов с именами компьютеров NT (имена NetBIOS). Содержание Lmhosts.sam меняется, если пользователь не может получить доступ или испытывает трудности с DNS-сервером.
Одна из мер безопасности, предпринятых Microsoft для защиты Windows Vista и Windows 7 от вредоносных программ, заключалась в том, что было труднее редактировать файлы lmhosts и hosts. В старых версиях операционной системы вредоносный код мог изменить эти файлы, что приводило к заражению ПК. Многие начинающие пользователи задаются вопросом: «Lmhosts.sam — что это?». Постараемся ответить на него.
Файл lmhosts.sam — что это такое и что он делает?
lmhosts представляет собой текстовый файл, который сопоставляет адреса интернет-протокола (IP) с именами удаленных серверов NetBIOS, с которыми пользователь связывается по протоколу TCP/IP. Файл lmhosts находится в папке %SystemRoot%\System32\drivers\etc. Файл hosts содержит IP-адрес для сопоставлений имен доменов для TCP/IP. Имена доменов и имена NetBIOS должны быть одинаковыми, но поскольку их можно настроить в двух разных местах, могут возникнуть конфликты. Поэтому IP-сопоставления должны храниться в файле lmhosts, так как изначально именно этот файл
Windows проверяет при разрешении любого имени, будь то NetBIOS или Domain.
Как найти и отредактировать lmhosts.sam?
Найдите и откройте файл. Поскольку он может находиться в разных местах, обычно проще всего открыть поиск в Windows и выполнить поиск файла lmhosts.sam.
Для пользователей, которые вручную ищут местонахождение файла, ниже приведен список версий Microsoft Windows и расположение файла lmhosts:
- XP, Vista, 7 и 8 — C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\Etc;
- 2000 — C:\WINNT\System32\Drivers\Etc;
- 98 и ME — C:\Windows\.
После того, как файл был найден, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по иконке и выберите «Открыть с …», в ответ на приглашение выберите «Выбрать программу из списка» и нажмите ОК. В списке программ, используемых для открытия файла, прокрутите список и в нижней части перечня выделите WordPad или предпочтительный текстовый редактор и нажмите кнопку ОК.
Lmhosts.sam — что за файл?
По умолчанию файл lmhosts уже содержит данные, такие как комментарии и примеры, похожие на приведенные ниже:
- 127.0.0.1 localhost # — пример локального хоста;
- 4.7.5.3 example # — пример поддельного IP-адреса и имени.
В приведенных выше двух строках есть IP-адрес, имя NetBIOS и примечание # для этой строки. Localhost и example — это имена NetBIOS.
Если вы используете Windows Vista, 7 или 8 dthcb., вы можете получить ошибку «отказано в доступе» при попытке сохранить изменения в файле lmhost. Эта ошибка возникает, когда ваш текстовый редактор не имеет прав администратора. Чтобы решить эту проблему, запустите «Блокнот» или WordPad в качестве администратора.
Файл lmhosts.sam — что это? LMHosts предназначен специально для сетей на базе Microsoft. Если вы связываете DNS с файлом hosts, LMhosts эквивалентен WINS. Это позволяет понять, кто является контроллером домена и какой домен просматривается.
Инструкция для пользователя
Создание и редактирование записей в Lmhosts.sam — что это? Используйте следующие правила для работы с данными в этом файле:
- Запись состоит из IP-адреса компьютера, за которым следует по крайней мере одна вкладка и имя NetBIOS компьютера.
- Вы не можете добавить запись LMHOSTS для компьютера, который является клиентом DHCP, потому что IP-адреса DHCP-клиентов изменяются динамически. Чтобы избежать проблем, убедитесь, что компьютеры, имена которых введены в файлы LMHOSTS, настроены на статические IP-адреса.
- Каждая запись должна быть отдельной строкой.
- Имена NetBIOS могут содержать символы верхнего и нижнего регистра и специальные символы.
- Каждое имя NetBIOS имеет длину 16 байт. Определяемая пользователем часть имени NetBIOS — это первые 15 символов. По умолчанию 16-й символ устанавливается для идентификации службы сетевого клиента, которая зарегистрировала это имя.
Наиболее знакомым примером имени NetBIOS является имя компьютера на любом компьютере под управлением Windows. Когда компьютер запущен, запускаются службы Microsoft Network Client и регистрируются их имена, которые состоят из имени компьютера плюс уникальный 16-й символ. Например, имя <имя_компьютера [0x00]> является службой Microsoft Workstation; имя <имя_компьютера [0x20]> — это служба Microsoft Server. Как вы можете видеть, единственная разница между этими двумя именами — это 16-й символ, который позволяет однозначно идентифицировать каждую из сетевых клиентских служб, запущенных на компьютере.
The LMHOSTS (LAN Manager Hosts) file is used to enable Domain Name Resolution under Windows when other methods, such as WINS, fail. It is used in conjunction with workgroups and domains. If you are looking for a simple, general mechanism for the local specification of IP addresses for specific hostnames (server names), use the HOSTS file, not the LMHOSTS file.
The file, if it exists, is read as the LMHOSTS setting file. A sample file (lmhosts.sam) is provided. It contains documentation for manually configuring the file.
File locations
Edit
Windows 95, 98, Millennium Edition
- The file is located in %windir%, and a sample file (lmhosts.sam) is installed here. Note that %windir% is an environment variable pointing to the Windows installation directory, usually C:\Windows.
Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 10, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016+
- The file is located in %windir%\system32\drivers\etc\, and a sample file (lmhosts.sam) is installed here. Note that %windir% is an environment variable pointing to the Windows installation directory, usually C:\Windows.
See also
Edit
- HOSTS file
- NetBIOS
External links
Edit
- Domain Browsing with TCP/IP and LMHOSTS Files
- LMHOSTS File Information and Predefined Keywords Microsoft knowledgebase article
- Using LMHOSTS Files on Windows NT
What is Lmhosts? What is it for?
LMHOSTS is an ASCII file used to enable Domain Name Resolution under Windows Operating Systems when other methods, such as WINS, fail.

Lmhosts stands for LAN (Local Area Network) Manager Hosts.
After installing Windows, a file called Lmhosts.sam is created in C:\Windows\system32\drivers\etc. This file is just a sample which also contains a set of instruction on how to use this resolution method. The extension .sam means sample.
When using this file for name resolution, you should edit open the Lmhosts.sam with Notepad (or another text editor) and save it without the .sam extension (keep the same name and the exact same location).
In this article
- Lmhosts file location
- Creating and Editing an Lmhosts file
- Lmhosts sample file transcription
- Difference between Lmhosts and host files
- Troubleshooting: Can’t save the Lmhosts file
Note that Windows Server automatically resolves NetBIOS names for computers in a TCP/IP local network, so you don’t really need LMHOSTS. However, you can use an LMHOSTS file to resolve IP addresses of computers on other networks to which your network is connected by a gateway when a WINS server isn’t available.
Lmhosts file location
The file is located in %windir%\system32\drivers\etc\, and the sample file (lmhosts.sam) is located here. The %windir% is an environment variable pointing to the Windows installation directory, typically C:\Windows.
Using Lmhosts for name resolution
Remember that Lmhosts function is to resolve manually NetBIOS names, not Host names. For resolving manually Host Names you should use the Hosts file. Read the section: Difference between Lmhosts and host files in this article.
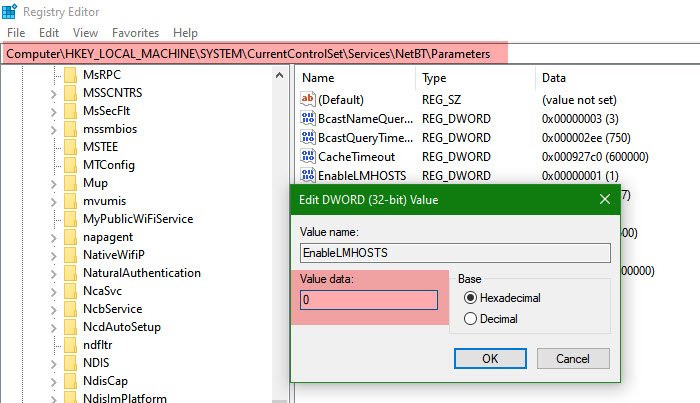
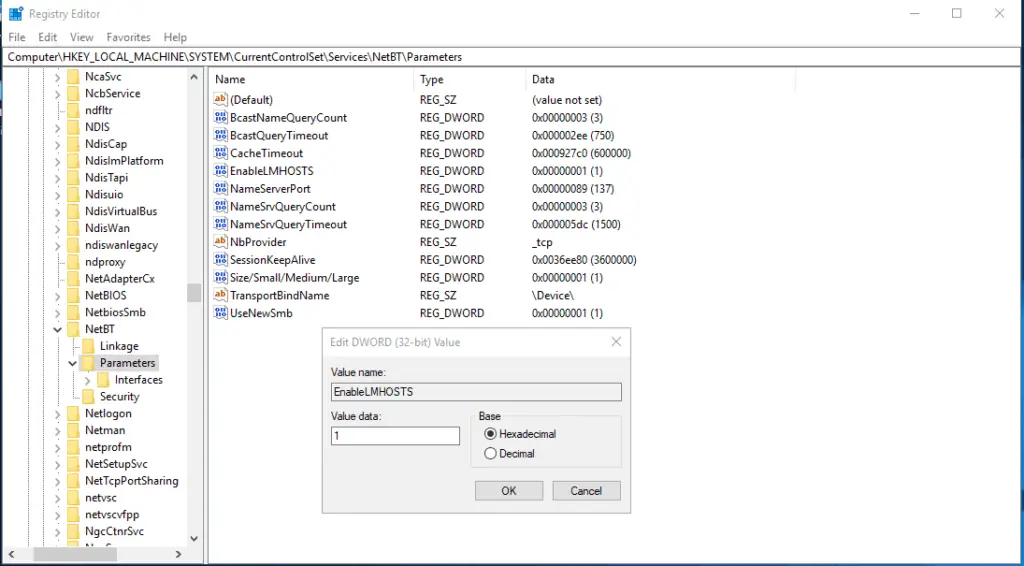
Be sure that the “EnableLMHOSTS” registry key is set to “1”. It normally is. You can find it under:
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\NetBT\Parameters
Creating and Editing an Lmhosts file
How to edit the Lmhosts file?
Any Windows operating system, by default, makes the LMHOSTS.SAM file available, usually in the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc folder. The first thing to do is to copy this file keeping the same name and removing the .SAM extension. Don’t delete the LMHOSTS.SAM. It may be useful in the future.
You should use a simple text editor, like Notepad, to edit the file you created and start making the changes you need.
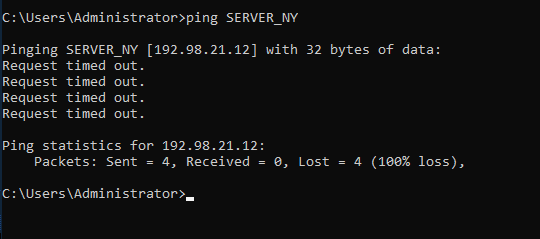
For example, you need your computer to be aware that the server SERVER_NY has the IP address 192.98.21.12. Just add this line:
# Only a comment. Nothing to compute
192.98.21.12 SERVER_NY #This is the New York web server
Save the file (LMHOSTS without the .SAM extension, but in the same folder)
At the command prompt, you can use NET VIEW to check your recent entry.
C:\net view \\SERVER_NY
You can also use the PING command.
C:\ping SERVER_NY
Some important rules:
- Never add a space at the beginning of the line.
- Use # to comment or to temporarily exclude a line.
- NetBIOS names can have a maximum of 15 characters defined by the Administrator, the last character is set by the system (total max of 16 characters). Names larger than that will simply not be read.
- Read the LMHOSTS.SAM file for more instructions. We have the full transcription in the next section of the article.
Lmhosts sample file transcription
Transcription of the instruction included in Lmhosts.sam file:
Copyright (c) 1993-1999 Microsoft Corp.
This is a sample LMHOSTS file used by the Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to computernames (NetBIOS) names. Each entry should be kept on an individual line.
The IP address should be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding computername. The address and the computername should be separated by at least one space or tab. The “#” character is generally used to denote the start of a comment (see the exceptions below).
This file is compatible with Microsoft LAN Manager 2.x TCP/IP lmhosts files and offers the following extensions:
#PRE
#DOM:<domain>
#INCLUDE <filename>
#BEGIN_ALTERNATE
#END_ALTERNATE
\0xnn (non-printing character support)
Following any entry in the file with the characters “#PRE” will cause the entry to be preloaded into the name cache. By default, entries are not preloaded, but are parsed only after dynamic name resolution fails.
Following an entry with the “#DOM:<domain>” tag will associate the entry with the domain specified by <domain>. This affects how the browser and logon services behave in TCP/IP environments. To preload the host name associated with #DOM entry, it is necessary to also add a #PRE to the line. The <domain> is always preloaded although it will not be shown when the name cache is viewed.
Specifying “#INCLUDE <filename>” will force the RFC NetBIOS (NBT) software to seek the specified <filename> and parse it as if it were local. <filename> is generally a UNC-based name, allowing a centralized lmhosts file to be maintained on a server.
It is ALWAYS necessary to provide a mapping for the IP address of the server prior to the #INCLUDE. This mapping must use the #PRE directive.
In addtion the share “public” in the example below must be in the LanManServer list of “NullSessionShares” in order for client machines to be able to read the lmhosts file successfully. This key is under \machine\system\currentcontrolset\services\lanmanserver\parameters\nullsessionshares
in the registry. Simply add “public” to the list found there.
The #BEGIN_ and #END_ALTERNATE keywords allow multiple #INCLUDE statements to be grouped together. Any single successful include will cause the group to succeed.
Finally, non-printing characters can be embedded in mappings by first surrounding the NetBIOS name in quotations, then using the \0xnn notation to specify a hex value for a non-printing character.
The following example illustrates all of these extensions:
102.54.94.97 rhino #PRE #DOM:networking #net group’s DC
102.54.94.102 “appname \0x14” #special app server
102.54.94.123 popular #PRE #source server
102.54.94.117 localsrv #PRE #needed for the include
#BEGIN_ALTERNATE
#INCLUDE \\localsrv\public\lmhosts
#INCLUDE \\rhino\public\lmhosts
#END_ALTERNATE
In the above example, the “appname” server contains a special character in its name, the “popular” and “localsrv” server names are preloaded, and the “rhino” server name is specified so it can be used to later #INCLUDE a centrally maintained lmhosts file if the “localsrv” system is unavailable.
Note that the whole file is parsed including comments on each lookup, so keeping the number of comments to a minimum will improve performance.
Therefore it is not advisable to simply add lmhosts file entries onto the end of this file.
Difference between Lmhosts and host files
An LMHOSTS file specifies the NetBIOS computer name and IP address mappings. A HOSTS file specifies the DNS name and IP address.
On a local computer, the HOSTS file (used by Windows Sockets applications to find TCP/IP host names) and LMHOSTS file (used by NetBIOS over TCP/IP to find NetBIOS computer names) can both be used to list known IP addresses, mapped with corresponding computer names.
LMHOSTS is used for name resolution in Windows for internetworks where WINS is not available.
The HOSTS file is used as a local DNS equivalent to resolve host names to IP addresses.
The LMHOSTS file is used as a local WINS equivalent to resolve NetBIOS computer names to IP addresses.
Each of these files is also known as a host table. Sample versions of LMHOSTS (called LMHOSTS.SAM) and HOSTS files are added to the Windows directory when you install Windows 95 with TCP/IP support. These files can be edited using any ASCII editor, such as WordPad or Edit. To take advantage of HOSTS or LMHOSTS, DNS must be enabled on the computer. For information about setting up and using HOSTS and LMHOSTS files, see Appendix G, “HOSTS and LMHOSTS Files for Windows 95.”
Troubleshooting: Can’t save the Lmhosts file
If you’re trying to save changes made to a Lmhosts file you may receive an error message like this:
Access to C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\ hosts was denied
Or
Cannot create the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts file.
Make sure that the path and file name are correct.
This issue can occur even if you log on by using an account that has administrative privileges.
To bypass this issue, go to Notepad (Start->All Programs->Accessories), right-click Notepad and click Run as administrator.
From the Notepad File menu, open the Lmhosts file (usually in C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\ folder) and make the changes you need to do. Click Save from the File menu and that’s it.