From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Original Windows logo from 1985
Current Windows logo (introduced in 2021)
Microsoft Windows is a computer operating system developed by Microsoft. It was first launched in 1985 as a graphical operating system built on MS-DOS. The initial version was followed by several subsequent releases, and by the early 1990s, the Windows line had split into two separate lines of releases: Windows 9x for consumers and Windows NT for businesses and enterprises. In the following years, several further variants of Windows would be released: Windows CE in 1996 for embedded systems; Pocket PC in 2000 (renamed to Windows Mobile in 2003 and Windows Phone in 2010) for personal digital assistants and, later, smartphones; Windows Holographic in 2016 for AR/VR headsets; and several other editions.
Personal computer versions[edit]
A «personal computer» version of Windows is considered to be a version that end-users or OEMs can install on personal computers, including desktop computers, laptops, and workstations.
The first five versions of Windows–Windows 1.0, Windows 2.0, Windows 2.1, Windows 3.0, and Windows 3.1–were all based on MS-DOS, and were aimed at both consumers and businesses. However, Windows 3.1 had two separate successors, splitting the Windows line in two: the consumer-focused «Windows 9x» line, consisting of Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me; and the professional Windows NT line, comprising Windows NT 3.1, Windows NT 3.5, Windows NT 3.51, Windows NT 4.0, and Windows 2000. These two lines were reunited into a single line with the NT-based Windows XP; this Windows release succeeded both Windows Me and Windows 2000 and had separate editions for consumer and professional use. Since Windows XP, multiple further versions of Windows have been released, the most recent of which is Windows 11.
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version | Editions | Build number | Architecture | End of support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 1.01 | Interface Manager | 1985-11-20 | 1.01 | — | — | x86-16 | 2001-12-31 |
| Windows 1.02 | — | 1986-05-14 | 1.02 | — | — | ||
| Windows 1.03 | — | 1986-08-21 | 1.03 | — | — | ||
| Windows 1.04 | — | 1987-04-10 | 1.04 | — | — | ||
| Windows 2.01 | — | 1987-12-09 | 2.01 | — | — | x86-16, IA-32 | |
| Windows 2.03 | — | 1987-12-09 | 2.03 | — | — | ||
| Windows 2.1 | — | 1988-05-27 | 2.10 | — | — | ||
| Windows 2.11 | — | 1989-03-13 | 2.11 | — | — | ||
| Windows 3.0 | — | 1990-05-22 | 3.00 |
|
— | ||
| Windows 3.1 | — | 1992-04-06 | 3.10 |
|
103 | ||
| Sparta[a] | 1992-10-31 |
|
102 | IA-32 | |||
| Windows NT 3.1 | Razzle[1] | 1993-07-27 | NT 3.1 |
|
528 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS | 2000-12-31 |
| Windows 3.11 | — | 1993-11-08 | 3.11 |
|
? | x86-16, IA-32 | 2001-12-31 |
| Snowball |
|
300 | IA-32 | ||||
| Windows 3.2 | — | 1993-11-22 | 3.2 |
|
153 | x86-16, IA-32 | |
| Windows NT 3.5 | Daytona | 1994-09-21 | NT 3.5 |
|
807 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-30 | NT 3.51 |
|
1057 | |||
| Windows 95 | Chicago | 1995-08-24 | 4.00 |
|
950 | IA-32 | |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Shell Update Release | 1996-08-24 | NT 4.0 |
|
1381 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | 2004-06-30 |
| Windows 98 | Memphis[b] | 1998-06-25 | 4.10 |
|
1998 | IA-32 | 2006-07-11 |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | — | 1999-05-05 |
|
2222A | |||
| Windows 2000 | Windows NT 5.0 | 2000-02-17 | NT 5.0 |
|
2195 | IA-32 | 2010-07-13 |
| Windows Me | Millennium | 2000-09-14 | 4.90 |
|
3000 | IA-32 | 2006-07-11 |
| Windows XP | Whistler | 2001-10-25 | NT 5.1 |
|
2600 | IA-32 | 2014-04-08 |
|
Itanium | ||||||
| Freestyle | 2002-10-29 |
|
IA-32 | ||||
| Harmony | 2003-09-30 |
|
|||||
| Symphony | 2004-10-12 |
|
2700 | ||||
| Emerald | 2005-10-14 |
|
2710 | ||||
| Anvil | 2005-04-25 | NT 5.2 |
|
3790 | x86-64 | ||
| Windows Vista | Longhorn[3] | 2007-01-30 | NT 6.0 |
|
6002[c] | IA-32, x86-64 | 2017-04-11 |
| Windows 7 | Windows 7[4] | 2009-10-22 | NT 6.1 |
|
7601[d] | IA-32, x86-64 | 2020-01-14 |
| Windows 8 | Windows 8 | 2012-10-26 | NT 6.2 |
|
9200 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2016-01-12 |
| Windows 8.1 | Blue[5] | 2013-10-17 | NT 6.3 |
|
9600 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2023-01-10 |
| 2014-05-23[e] |
|
||||||
| Windows 10 version 1507 | Threshold[6][f] | 2015-07-29 | NT 10.0[g][h] |
|
10240 | IA-32, x86-64 | 2025-10-14[8][m] |
| Windows 10 version 1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015-11-10 | 1511 | 10586 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1607 | Redstone 1[9] | 2016-08-02 | 1607 | 14393 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1703 | Redstone 2[10] | 2017-04-05 | 1703 | 15063 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1709 | Redstone 3[11] | 2017-10-17 | 1709 | 16299 | IA-32, x86-64, ARM64 | ||
| Windows 10 version 1803 | Redstone 4 | 2018-04-30 | 1803 | 17134 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1809 | Redstone 5[12] | 2018-11-13 | 1809 | 17763 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1903 | 19H1[13] | 2019-05-21 | 1903 | 18362 | |||
| Windows 10 version 1909 | Vanadium[n][15] | 2019-11-12 | 1909 | 18363 | |||
| Windows 10 version 2004 | Vibranium[15][16][o] | 2020-05-27 | 2004 | 19041 | |||
| Windows 10 version 20H2 | 2020-10-20 | 20H2 | 19042 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 21H1 | 2021-05-18 | 21H1 | 19043 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 21H2 | 2021-11-16 | 21H2 | 19044 | ||||
| Windows 10 version 22H2 | 2022-10-18 | 22H2 | 19045 | ||||
| Windows 11 version 21H2 | Sun Valley[p] | 2021-10-05 | 21H2 |
|
22000 | x86-64, ARM64 | 2023-10-10[q] |
| Windows 11 version 22H2 | Sun Valley 2 | 2022-09-20 | 22H2 | 22621 | 2024-10-08[q] |
Mobile versions[edit]
Mobile versions refer to versions of Windows that can run on smartphones or personal digital assistants.
Pocket PC 2000 logo
Windows Phone 7 logo
Windows Phone 8 logo
Windows Phone 8.1 logo
Logo used for Windows 10 and Windows 10 Mobile
| Name | Codename | Architecture | Release date |
Version Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pocket PC 2000 | Rapier | ARMv4, MIPS, SH-3 | 2000-04-19 | CE 3.0 |
| Pocket PC 2002 | Merlin | ARMv4 | 2001-10-04 | |
| Windows Mobile 2003 | Ozone | ARMv5 | 2003-06-23 | CE 4.x |
| Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | 2004-03-24 | ||
| Windows Mobile 5.0 | Magneto | 2005-05-09 | CE 5.0 | |
| Windows Mobile 6.0 | Crossbow | 2007-02-12 | ||
| Windows Mobile 6.1 | — | 2008-04-01 | CE 5.2 | |
| Windows Mobile 6.1.4 | 6 on 6 | 2008-11-11[18] | ||
| Windows Mobile 6.5 | Titanium | 2009-05-11 | CE 6.0 | |
| Windows Phone 7[r] | — | ARMv7 | 2010-10-29 | |
| Windows Phone 7.5 | Mango | 2011-09-27 | ||
| Windows Phone 7.8 | — | 2013-02-01 | ||
| Windows Phone 8 | Apollo | 2012-10-29 | NT 6.2 | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Blue | 2014-04-14 | NT 6.3 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015-11-12 | 1511 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1607 | Redstone 1 | 2016-08-16 | 1607 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1703 | Redstone 2 | 2017-04-24 | 1703 | |
| Windows 10 Mobile, version 1709 | feature2[19] | 2017-10-24 | 1709 |
Server versions[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version number | Editions | Build number | Architecture | End of support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT 3.1 | Razzle | 1993-07-27 | NT 3.1 |
|
528 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS | 2000-12-31 |
| Windows NT 3.5 | Daytona | 1994-09-20 | NT 3.5 |
|
807 | IA-32, Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC | 2001-12-31 |
| Windows NT 3.51 | 1995-05-29 | NT 3.51 |
|
1057 | 2001-12-31 | ||
| Windows NT 4.0 | Shell Update Release | 1996-07-29 | NT 4.0 |
|
1381 | 2004-12-31 | |
| Windows 2000 | NT 5.0 | 2000-02-17 | NT 5.0 |
|
2195 | IA-32 | 2010-07-13 |
| Windows Server 2003 | Whistler Server | 2003-04-24 | NT 5.2 |
|
3790 | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium | 2015-07-14 |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 | Whistler Server | 2005-12-06 | 2015-07-14 | ||||
| Windows Server 2008 | Longhorn Server | 2008-02-27 | NT 6.0 |
|
6002[c] | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium | 2020-01-14 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Windows Server 7 | 2009-10-22 | NT 6.1 | 7601[d] | x86-64, Itanium | 2020-01-14 | |
| Windows Server 2012 | Windows Server 8 | 2012-09-04 | NT 6.2 |
|
9200 | x86-64 | 2023-10-10 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows Server Blue | 2013-10-17 | NT 6.3 | 9600 | 2023-10-10 | ||
| Windows Server 2016 | — | 2016-10-12 | 1607[20] |
|
14393 | 2027-01-12 | |
| Windows Server, version 1709[21] | — | 2017-10-17 | 1709 | 16299 | 2019-04-09 | ||
| Windows Server, version 1803[22] | — | 2018-04-30 | 1803 | 17134 | 2019-11-12 | ||
| Windows Server, version 1809 | — | 2018-11-13[23] | 1809 | 17763 | 2020-11-10 | ||
| Windows Server 2019[20] | — | 2029-01-09[20] | |||||
| Windows Server, version 1903[20] | — | 2019-05-21 | 1903 | 18362 | 2020-12-08[20] | ||
| Windows Server, version 1909[20] | — | 2019-11-12 | 1909 | 18363 | 2021-05-11[20] | ||
| Windows Server, version 2004[24] | — | 2020-06-26 | 2004 | 19041 | 2021-12-14[20] | ||
| Windows Server, version 20H2[24] | — | 2020-10-20 | 20H2 | 19042 | 2022-08-09[20] | ||
| Windows Server 2022 | — | 2021-08-18 | 21H2[25] | 20348 | 2031-10-14[20] |
High-performance computing (HPC) servers[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | — | 2006-06-09 | Windows Server 2003 R2 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 | Socrates | 2008-09-22 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | — | 2010-09-20 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows Essential Business Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Essential Business Server 2008 | Centro | 2008-09-15 | 2020-01-14 | 5700 | Windows Server 2008 |
Windows Home Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Home Server | Quattro | 2007-11-04 | 2013-01-08 | Windows Server 2003 R2 |
| Windows Home Server 2011 | Vail | 2011-04-06 | 2016-04-12 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows MultiPoint Server[edit]
Windows MultiPoint Server was an operating system based on Windows Server. It was succeeded by the MultiPoint Services role in Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server version 1709. It was no longer being developed in Windows Server version 1803 and later versions.
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 | Solution Server | 2010-02-24 | 2020-07-14 | NT 6.1 | 537 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2011 | WMS 2 | 2011-05-12 | 2021-07-13 | 1600 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 | |
| Windows MultiPoint Server 2012 | WMS 3 | 2012-10-30 | 2023-10-10 | NT 6.2 | 2506 | Windows Server 2012 |
Windows Small Business Server[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | End-of-support date | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Business Server 2000 | — | 2001-02-21 | 2010-07-13 | 1343 | Windows 2000 Server |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 | Bobcat | 2003-10-09 | 2015-07-14 | 2893 | Windows Server 2003 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 | Cougar | 2008-08-21 | 2020-01-14 | 5601 | Windows Server 2008 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard | Windows Small Business Server 7 | 2010-12-13 | 2020-01-14 | 7900 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
| Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials | Colorado | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-05 | 8800 |
Device versions[edit]
ARM-based tablets[edit]
Windows RT logo
The Surface RT (shown with keyboard cover attached) was the flagship Windows RT device upon its release.
In 2012 and 2013, Microsoft released versions of Windows specially designed to run on ARM-based tablets; these versions of Windows, named «Windows RT» and «Windows RT 8.1,» were based on Windows 8 and Windows 8.1, respectively. Upon the release of Windows 10 in 2015, the ARM-specific version for large tablets was discontinued; large tablets (such as the Surface Pro 4) were only released with x86 processors and could run the full version of Windows 10. Windows 10 Mobile had the ability to be installed on smaller tablets (up to nine inches);[26] however, very few such tablets were released, and Windows 10 Mobile primarily ended up only running on smartphones until its discontinuation. In 2017, the full version of Windows 10 gained the ability to run on ARM, thus rendering a specific version of Windows for ARM-based tablets unnecessary.
| Name | Release date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows RT | 2012-10-26 | NT 6.2 | 9200 | Windows 8 |
| Windows RT 8.1 | 2013-10-18 | NT 6.3 | 9600 | Windows 8.1 |
Mixed reality and virtual reality headsets[edit]
| Name | Build number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1607[27] | 14393 |
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1803[27] | 17134 |
| Windows 10 Holographic, version 1809[27] | 17763 |
| Windows Holographic, version 1903[28] | 18362 |
| Windows Holographic, version 2004[28] | 19041 |
| Windows Holographic, version 20H2[28] | 19041 |
| Windows Holographic, version 21H1[28] | 20346 |
| Windows Holographic, version 21H2[28] | 20348 |
| Windows Holographic, version 22H1[28] | 20348 |
Surface Hub[edit]
Microsoft originally announced the Surface Hub, an interactive whiteboard, in January 2015. The Surface Hub family of devices runs a custom variant of Windows 10 known as Windows 10 Team.
| Name | Build number |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 Team, version 1511[29] | 10586 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 1607[29] | 14393 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 1703[29] | 15063 |
| Windows 10 Team, version 20H2[29] | 19042 |
Windows XP-based tablets[edit]
Two versions of Windows XP were released that were optimized for tablets. Beginning with Windows Vista, all tablet-specific components were included in the main version of the operating system.
| Name | Codename | Release date | Version number | Build number | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows XP Tablet PC Edition | — | 2002-11-07 | NT 5.1 | 2600 | Windows XP |
| Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005 | Lonestar | 2004-08 | NT 5.1 | 2600 | Windows XP |
Embedded versions[edit]
Windows Embedded Compact[edit]
| Name | Codename(s) | Release date |
|---|---|---|
| Windows CE 1.0 | Pegasus; Alder | 1996-11-16 |
| Windows CE 2.0 | Jupiter; Birch | 1997-09-29 |
| Windows CE 2.1 | — | 1998-07 |
| Windows CE 2.11 | — | 1998-10 |
| Windows CE 2.12 | — | 1999 |
| Windows CE 3.0 | Cedar; Galileo | 2000 |
| Windows CE 4.0 | Talisker | 2002-01-07 |
| Windows CE 4.1 | Jameson | 2002-07-30 |
| Windows CE 4.2 | McKendric | 2003-04-23 |
| Windows CE 5.0 | Macallan | 2004-07-09 |
| Windows Embedded CE 6.0 | Yamakazi | 2006-11-01 |
| Windows Embedded Compact 7 | Chelan | 2011-03-01 |
| Windows Embedded Compact 2013 | — | 2013-06-13 |
Windows Embedded Standard[edit]
| Name | Codename | Release date | Based on |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows NT Embedded 4.0 | Impala | 1999-08-30 | Windows NT 4.0 Workstation |
| Windows XP Embedded | Mantis | 2001-11-28 | Windows XP Professional |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | — | 2008-12-14 | Windows XP Service Pack 3 |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 | Quebec | 2010 | Windows 7 |
| Windows Embedded 8 | — | 2013 | Windows 8 |
| Windows Embedded 8.1 | — | 2013 | Windows 8.1 |
Other embedded versions[edit]
- Windows Embedded Industry
- Windows Embedded Automotive
Cancelled versions[edit]
Cancelled personal computer versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Version | Latest known build number | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cairo | — | 1996 | NT 4.0 | 1175 | Originally announced at the 1991 Microsoft Professional Developers Conference, Cairo was the codename of a project whose charter was to build technologies for a next-generation operating system that would fulfill Bill Gates’s vision of «information at your fingertips».[30] Cairo never shipped, although portions of its technologies have since appeared in other products. |
| Nashville[t] | Windows 96 | 1996 | 4.1 | 999 | Nashville was an operating system planned to have been released between Windows 95 and Windows 98, presumably under the «Windows 96» moniker. |
| Neptune | — | Early 2000 | NT 5.50 | 5111 | Neptune, based on the Windows 2000 codebase, was planned to be the first version of Microsoft Windows NT to have a consumer edition variant. A version was sent out to testers but was never released.[31] The teams working on Neptune and Odyssey eventually combined to work on Windows XP. |
| Odyssey | — | Early 2000 | NT 6.0[32] | — | Odyssey was planned to be the successor of Windows 2000. The teams working on Neptune and Odyssey eventually combined to work on Windows XP. |
| Triton | — | Early 2000 | — | — | Triton was planned to be the successor of Windows Neptune and had been scheduled to be released in March 2001. |
| Blackcomb | — | 2006-01 | — | — | Blackcomb was originally planned to be a release of Windows following Windows XP. However, due to the large feature scope planned for Blackcomb, a smaller release codenamed «Longhorn» was planned first, and Blackcomb was delayed to 2003/2004. Both projects faced delays; Longhorn would go on to be released to consumers as «Windows Vista» in January 2007, while development on Blackcomb continued until the Blackcomb project was renamed «Vienna» in early 2006. |
| Vienna | — | 2007-07[u] | — | — | Vienna replaced Blackcomb and was intended as Windows Vista’s successor. Vienna was eventually cancelled in favor of a new project codenamed «Windows 7» (which went on to be released in 2009 with the same name). |
| Polaris | — | 2018 | — | 16299 | Cancelled in favor of Santorini |
| Santorini[v] | Windows 10X | 2021-05-18[w][34] | 21H1 | 20279 | Microsoft had been reported as working on a new «lite» version of Windows as early as December 2018.[35] Such a version was officially announced under the name «Windows 10X» at an event in October 2019; the operating system was intended to first launch on dual-screen devices. In May 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would instead be launching on single-screen PCs, such as laptops and 2-in-1 devices, first.[36] However, on May 18, 2021, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would not be launching (at least not in 2021); many of its features were instead rolled into Windows 11. |
Cancelled mobile versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photon | Windows Mobile 7 | September 2008[37] | Originally a successor of Windows Mobile, it had been scrapped for Windows Phone 7[38][39] |
| Phoenix | — | Early 2017 | Cancelled when Microsoft «wound down» its phone efforts.[40] |
| Andromeda | — | Mid-2018 | Much of the work that was put into Andromeda was migrated into Santorini. The Surface Duo, a dual-screen Android-powered smartphone launched by Microsoft in 2020, was loosely based on the prototype hardware that had been used to test Andromeda.[41] |
Cancelled server versions[edit]
| Codename | Intended name | Discontinuation | Latest known build number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cascades | Windows Essential Business Server 2008 R2 | April 7, 2010[w] | 7224 |
See also[edit]
- List of Microsoft operating systems
- Microsoft Windows version history
- Windows 10 version history
- Windows 11 version history
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- List of Microsoft codenames
Notes[edit]
- ^ Originally codenamed Winball
- ^ Has also been called ChiCairo and London.[2]
- ^ a b Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 originally had the build number 6000 when they were first released; the build number was increased by one with each of the two subsequent Service Packs.
- ^ a b Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 originally had the build number 7600 when they were first released; the build number was increased to 7601 with the release of Service Pack 1.
- ^ Announcement date
- ^ Retroactively referred to as Threshold 1
- ^ Early preview builds of Windows 10 had the version number NT 6.4.[7]
- ^ Retroactively referred to as version 1507
- ^ Windows 10 Pro for Workstations became a Windows 10 edition starting with version 1709. Prior versions of Windows 10 do not include this as an edition.
- ^ Windows 10 versions 1507 and 1511 do not include a «Windows 10 Pro Education» edition; that edition was only added with version 1607.
- ^ Windows 10 S is only available in version 1703 and 1709.
- ^ Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC is only available for versions 1507, 1607, 1809, and 21H2. It had originally been named Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB in version 1507.
- ^ October 14, 2025 is the general end-of-support date for Windows 10. Specific versions and editions of Windows 10 have different end of support dates; see Windows 10 version history for a breakdown of dates by version and edition.
- ^ Originally codenamed 19H2[14]
- ^ Vibranium was the codename for Windows 10 version 2004. During the 20H2, 21H1, and 21H2 development cycles, builds were compiled under the codenames Manganese, Iron, and Cobalt, respectively. However, the versions of 20H2 and 21H1 that were released were built on top of version 2004 instead of these new builds. Windows 10 version 21H2 was similarly built on top of the Vibranium/2004 codebase instead of the Cobalt codebase; Cobalt builds were instead used as the base for the first version of Windows 11 (which had a core based on Cobalt in addition to a UI codenamed Sun Valley, and which also carries the version 21H2).
- ^ The core of Windows 11 version 21H2 is codenamed Cobalt;[17] the «Sun Valley» codename refers to the UI layer of Windows 11 version 21H2 and is commonly used to address Windows 11 version 21H2 as a whole.
- ^ a b The end-of-support date listed in the table refers to Home and Pro editions. The date for other editions, such as Education and Enterprise, may differ.
- ^ Originally named «Windows Phone 7 Series»
- ^ Between versions 1709 and 20H2 of Windows Server, the «Windows Server Essentials» edition of Windows Server was only included in Windows Server 2019.
- ^ Nashville was originally codenamed Cleveland.
- ^ July 2007 is when it was reported that the Vista’s successor was codenamed «7», rather than «Vienna», indicating that Vienna’s discontinuation had occurred by then. However, Vienna may have been cancelled prior to then.
- ^ While Santorini was the general codename for Windows 10X, Centaurus was the specific codename for Windows 10X on foldable PCs and Pegasus was the codename for Windows 10X on «traditional» PCs (such as laptops or 2-in-1 computers).[33]
- ^ a b Date refers to when the cancellation of the operating system was announced. The decision for the operating system to be cancelled may have occurred prior to then.
References[edit]
- ^ «Random internal Windows terminology:IDW, Razzle, and their forgotten partners IDS and Dazzle». The Old New Thing. 2018-12-24. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- ^ «Systems Release Strategy — Draft:10/10/93» (PDF). Slated Antitrust. November 10, 1993.
- ^ Martens, China (July 22, 2005). «Update:Microsoft’s Longhorn becomes Windows Vista». IDG Communications, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Microsoft Corp. has announced the official name for its upcoming operating system, previously known under the code name Longhorn. The operating system, now due out in 2006, will be called Windows Vista
- ^ «What was the code name for Windows 7?». The Old New Thing. 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2021-05-09.
The code name for Windows 7 was… Windows 7.
- ^ O’Brien, Terrence. «Microsoft drops the Blue codename, confirms Windows 8.1 will be a free upgrade available later this year». Engadget. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
One of the worst kept secrets rattling around Microsoft’s campus is Windows Blue, the forthcoming update to Windows 8 that addresses users’ bugbears about the OS. Now, Microsoft is officially rechristening the platform, and with a more staid name: Windows 8.1.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft to share Windows Threshold plans at Build 2014 show: Report». ZDNet. ZDNET. Retrieved 7 April 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Windows 10 won’t be Windows 6.4». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
Windows 10 Technical Preview builds are currently identified as Windows NT 6.4, but future builds will include the change
- ^ Warren, Tom. «Microsoft to end Windows 10 support on October 14th, 2025». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ^ Tkachenko, Sergey. «What’s new in Windows 10 version 1607 Anniversary Update». Winaero. Retrieved 30 April 2023.
Windows 10 version 1607, code named «Redstone 1», was released in August 2016.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (August 4, 2016). «Microsoft confirms two major updates planned for Windows 10 in 2017». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Windows Central understands that the first major update for 2017 (codenamed Redstone 2) will release in the early part of 2017.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (August 4, 2016). «Microsoft confirms two major updates planned for Windows 10 in 2017». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
The second major update scheduled for 2017 is codenamed «Redstone 3»
- ^ Woods, Rich. «Windows 10 Redstone 5 is officially version 1809». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Redstone 5 is now officially Windows 10 version 1809.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
Windows 10’s next major update is codenamed 19H1.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
This means the next Windows 10 update, previously codenamed 19H2, will be called Vanadium (comes after Titanium/19H1).
- ^ a b Brown, Matt (October 31, 2018). «Next Windows 10 updates reportedly codenamed ‘Vanadium’ and ‘Vibranium’«. Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ Hassan, Mehedi (October 31, 2018). «Windows 10’s Next Major Updates Will Be Codenamed Vanadium, Vibranium». Thurrott. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ Parmar, Mayank (3 September 2021). «Windows 11 Build 22449 is now available with new loading animation». Windows Latest. Retrieved 4 September 2021.
Windows 11 version 21H2 (shipping on October 5)=Cobalt (Co).
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft starts rolling out IE 6 for Windows Mobile». ZDNET. ZDNET. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
The new IE 6 bits were released on November 11 as part of the Windows Mobile 6.1.4 release from Microsoft’s Download Center Web site.
- ^ Woods, Rich. «It’s finally dead: Windows 10 Mobile is no longer supported after today». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
Windows 10 feature2 ended up being version 1709, and it was the final feature update for Windows 10 Mobile.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Gerend, Jason. «Windows Server release information». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ «What’s New in Windows Server version 1709». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ «Windows Server, version 1803 end of servicing on November 12, 2019». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ Woods, Rich. «Microsoft re-releases Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ a b Gerend, Jason. «Windows Server servicing channels». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- ^ Sharma, Mayank. «Microsoft has snuck out its Windows Server 2022 release». TechRadar. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
Windows Server 2022 identifies itself as version 21H2
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo. «Microsoft ups allowable Windows 10 Mobile screen size to nearly nine inches». ZDNET. ZDNET. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ a b c «HoloLens 1st (gen) release notes». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f «HoloLens 2 release notes». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ a b c d «Surface Hub update history». Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- ^ Bill Gates (1994-11-14). «Information At Your Fingertips, 1994 Comdex Keynote». Archived from the original on 2007-11-10. Retrieved 2008-01-02.
- ^ «Microsoft combines Neptune, Odyssey into Whistler». CNN. January 27, 2000. Archived from the original on September 1, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2010.
- ^ «Windows Odyssey». Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Knowing that Neptune is 5.50, it’s only logical to conclude Odyssey was to be 6.0
- ^ Bowden, Zac (October 30, 2019). «Windows Core OS:The complete guide». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Vox Media, LLC. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Sams, Brad (December 3, 2018). «What is Windows Lite? It’s Microsoft’s Chrome OS Killer». Petri. BWW Media Group. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (May 4, 2020). «Windows 10X will now launch first on single-screen PCs». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Litvinenko, Yuri. «Microsoft’s Project Photon:A Stunted Effort to Rebuild Windows Mobile». Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Checking reports against each other provides the grounds to assume Microsoft kept working on Photon till September 2008.
- ^ «Windows Mobile 7 vs Windows Phone 7». Popular Pages at brighthub.com. May 20, 2011. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ «Revealed:Original Windows Mobile 7 UI». neowin.net. February 20, 2010. Retrieved December 15, 2016.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (September 18, 2020). «Project Andromeda:The secret history of Windows on Surface Duo». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
Microsoft had originally planned to ship CShell on Windows 10 Mobile under the codename Pheonix [sic], but that plan very quickly went away once the company decided to wind down its existing phone efforts in early 2017.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (September 18, 2020). «Project Andromeda:The secret history of Windows on Surface Duo». Windows Central. Future US, Inc. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
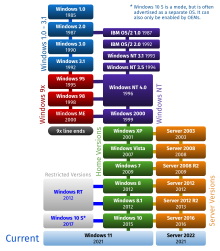
The Windows operating system versions can confuse people since there are a lot of them. Find out which version was released when, and what the major changes were offered.
The Windows operating system has been around since 1985 when Windows 1.01 was first launched to the public. It has since come a long way and has now evolved into Windows 11 (the current latest Windows OS).
Not only that, but each Windows also had sub-variations of these versions, which were introduced with major bi-annual feature updates. Microsoft has now shifted to annual feature releases. For example, Windows 10 has versions 21H2, 21H1, and many others, while Windows 11 has 21H2, 22H2, and 23H2.
This post lists the complete timeline and highlights the significant details of each Windows version released from the beginning of time.
Windows Timeline
The image below is an illustration of the different Windows versions and their release point in time.
Windows History
The table below briefly describes the important aspects of each of the Windows operating systems along with some other useful information.
| Name | Codename | Release year | Version | Editions | Currently Supported | Details |
| Windows 1.01 | Interface Manager | 1985 | 1.01 | – | No | The first client Windows OS introduced the MS-DOS Executive |
| Windows 1.02 | – | 1986 | 1.02 | – | No | – |
| Windows 1.03 | – | 1986 | 1.03 | – | No | 2 moderately-different versions exist with a difference in the USER.EXE file |
| Windows 1.04 | – | 1987 | 1.04 | – | No | Additional support for IBM drivers |
| Windows 2.01 | – | 1987 | 2.01 | No | Introduced overlapping, resizable windows and could run multiple DOS applications simultaneously | |
| Windows 2.03 | – | 1987 | 2.03 | – | No | Introduced 386 enhanced mode, which allows Windows to use memory beyond 640k |
| Windows 2.1 | – | 1988 | 2.1 | – | No | Required hard disk drives to take advantage of some Intel processors |
| Windows 2.11 | – | 1989 | 2.11 | – | No | AppleTalk support and faster printing with updated printer drivers |
| Windows 3.0 | – | 1990 | 3.0 | – | No | A new, colorful user interface introduced |
| Windows 3.1 | – | 1992 | 3.1 | – | No | More stable and faster |
| Windows 3.1 | Winball / Sparta | 1992 | 3.1 | Windows for Workgroups | No | Includes native networking support and introduced the Hearts card game |
| Windows NT 3.1 | Razzle | 1993 | NT 3.1 | – | No | The first OS with 32-bit architecture |
| Windows 3.11 | – | 1993 | 3.11 | – | No | Mostly containing bug fixes and improvements; no major new features |
| Windows 3.11 | Snowball | 1993 | 3.11 | Windows for Workgroups | No | Mostly focused on 32-bit networking: 32-bit file access and 32-bit full network redirectors |
| Windows 3.2 | – | 1993 | 3.2 | – | No | Focused on Simplified Chinese language |
| Windows NT 3.5 | Daytona | 1994 | NT 3.5 | Windows NT 3.5 Workstation | No | Included Winsock and TCP/IP support |
| Windows NT 3.51 | Daytona | 1995 | NT 3.51 | Windows NT 3.51 Workstation | No | Provides client/server support for interoperating with Windows 95 |
| Windows 95 | Chicago | 1995 | 4.00 | – | No | Drastically improved GUI and plug-and-play capabilities |
| Windows NT 4.0 | Shell Update Release | 1996 | NT 4.0 | Windows NT 4.0 Workstation | No | Introduced the concept of system policies |
| Windows 98 | Memphis | 1998 | 4.10 | – | No | Major cosmetic UI upgrades, highly web integrated |
| Windows 98 Second Edition (SE) | – | 1999 | 4.10 | – | No | Mostly included bug fixes and minor improvements. IE 4.0 was replaced with IE 5.0 |
| Windows 2000 | Windows NT 5.0 | 2000 | NT 5.0 | Windows 2000 Professional | No | Introduced NTFS 3.0, Encrypting File System, basic and dynamic disk storage |
| Windows ME | Millennium | 2000 | 4.90 | – | No | Initially included IE 5.5, Windows Movie Maker. Designed for home users |
| Windows XP | Whistler | 2001 | NT 5.1 | Starter, Home, professional, 64-Bit Edition | No | Increased performance and stability, intuitive UI, improved hardware support, expanded multimedia capabilities |
| Windows XP | Freestyle | 2002 | NT 5.1 | Media Center Edition | No | Inclusion of the Windows Media Center |
| Windows XP | Harmony | 2003 | NT 5.1 | Media Center Edition 2004 | No | Windows XP Service Pack 2 upgrades earlier versions of MCE to this one |
| Windows XP | Symphony | 2004 | NT 5.1 | Media Center Edition 2005 | No | Includes support for Media Center Extenders, and CD/DVD-Video burning support |
| Windows XP | Emerald | 2005 | NT 5.1 | Media Center Edition 2005 Update Rollup 2 | No | Adds support for the Xbox 360 as a media center extender, DVB-T broadcasts, and two ATSC tuner cards |
| Windows XP | Anvil | 2005 | NT 5.2 | Professional x64 Edition | No | – |
| Windows Vista | Longhorn | 2007 | NT 6.0 | Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Business, Enterprise, Ultimate | No | Updated GUI, Windows Search, redesigned networking, audio, print, and display sub-systems |
| Windows 7 | – | 2009 | NT 6.1 | Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Business, Enterprise, Ultimate | No | Touch and handwriting recognition improvements, support for virtual hard disks, improved multi-core processor performance, improved boot performance, DirectAccess, and kernel improvements |
| Windows 8 | – | 2012 | NT 6.2 | Professional, Enterprise | No | Major changes to the UI, optimized for tablets, touch-optimized Windows shell |
| Windows 8.1 | Blue | 2013 | NT 6.3 | Professional, Enterprise | Yes | additional customization options for Start menu, Start button on the desktop restored, ability to snap up to four apps on display, ability to boot directly to desktop |
| Windows 8.1 | Blue | 2014 | NT 6.3 | Windows 8.1 with Bing | Yes | Bing-based unified search system was added |
| Windows 10 v1507 | Threshold | 2015 | NT 10.0 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Significant changes to the UI and OS functionality, offered in various editions |
| Windows 10 v1511 | Threshold 2 | 2015 | 1511 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Preinstalled Skype, Microsoft Edge synchronization capability, tab previews in Edge |
| Windows 10 v1607 | Redstone 1 | 2016 | 1607 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Visual and functional improvements |
| Windows 10 v1703 | Redstone 2 | 2017 | 1703 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Visual and functional improvements |
| Windows 10 v1709 | Redstone 3 | 2017 | 1709 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Visual and functional improvements |
| Windows 10 v1803 | Redstone 4 | 2018 | 1803 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Visual and functional improvements |
| Windows 10 v1809 | Redstone 5 | 2018 | 1809 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Visual and functional improvements |
| Windows 10 v1903 | Vanadium | 2019 | 1903 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Light theme introduced, separate Search and Cortana, Windows Sandbox, recommended troubleshooting tips |
| Windows 10 v1909 | Vibranium | 2019 | 1909 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Create events from Calendar flyout, improved notification management, OneDrive integration with File Explorer search |
| Windows 10 v2004 | Vibranium | 2020 | 2004 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Better Your Phone experience, DirectX 12 Ultimate, WSL 2 |
| Windows 10 v20H2 | – | 2020 | 20H2 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | Chromium-based Microsoft Edge, theme-aware Start menu tiles, and other improvements |
| Windows 10 v21H1 | – | 2021 | 21H1 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | No | News and Interests in taskbar, improvements to Windows Defender (now Windows Security) |
| Windows 10 v21H2 | – | 2021 | 21H2 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | Yes (Extended) | Support for Wi-Fi 6E, new simplified passwordless deployment modes for Windows Hello for Business |
| Windows 11 v21H2 | Sun Valley | 2021 | 21H2 | Home, Pro, Education, Pro Education, Pro for Workstations, Enterprise, SE | Yes | Major UI changes, modern look, widgets included, integrated Microsoft Teams, redesigned taskbar, updated backgrounds |
| Windows 10 2022 Update | – | 2022 | 22H2 | Home, Pro, Education, Enterprise, Pro for Workstations, Pro Education, S, Enterprise LTSC | Yes | Changes to servicing schedules, minor UI changes, TLS 1.0 and 1.1 will be disabled by default, ability to consent to receiving urgent notifications when Focus Assist is on |
| Windows 11 2022 Update | Sun Valley 2 | 2022 | 22H2 | Home, Pro, Education, Pro Education, Pro for Workstations, Enterprise, SE | Yes | Spotlight for Desktop, new Media Player, UI improvements, live captions, improved Narrator and Voice Access, Windows Subsystem for Android |
| Windows 11 2023 Update | Sun Valley 3 | 23H2 | Home, Pro, Education, Pro Education, Pro for Workstations, Enterprise, SE | Yes | Windows AI Copilot, dynamic lighting, hide the date and time on Taskbar, native support for new formats including 7-zip, RAR, gz, Backup and restore apps, taskbar regrouping, improved volume mixer, improved sharing experience |
The table above depicts all the significant changes as well as the release details of individual Windows versions since Microsoft first launched the operating system back in 1985. To learn more about the support for each version, refer to the End of Life page.
Let us now categorize these operating systems so that their hierarchy is easier to understand.
Note: The “X” in the table denotes an empty integer as part of the complete Windows version.
| Sr. No. | DOS-based | Windows 9X | Windows NT |
| 1 | Windows 1.0X | Windows 95 | NT 3.1 |
| 2 | Windows 2.0X | Windows 98 | NT 3.5 |
| 3 | Windows 1.2X | Windows ME | NT 3.51 |
| 4 | Windows 3.0 | NT 4.0 | |
| 5 | Windows 3.1X | 2000 | |
| 6 | XP | ||
| 7 | Vista | ||
| 8 | Windows 7 | ||
| 9 | Windows 8 | ||
| 10 | Windows 8.1 | ||
| 11 | Windows 10 | ||
| 12 | Windows 11 |
Closing Words
Microsoft has made functional, cosmetic, and infrastructural changes to the Windows operating system since it was first released. They have been working on making it the top OS for consumers, continuously enhancing the user experience through feedback and testing through the Insider program.
That said, we hope that the images and tables above reduce the complication of understanding the Windows hierarchy.

Usman Khurshid|October 6, 2023
While leaks may suggest Microsoft is gearing up for the next version of Windows 12 as a subscription model, the current licenses will remain intact and valid for the next…
View post

Usman Khurshid|October 3, 2023
While it’s advisable to keep your essential Microsoft Store apps updated for security and performance reasons, there are situations where automatic updates can be bothersome. Here’s how you can disable…
View post

Subhan Zafar|September 28, 2023
Confused about all the different Windows updates and what they mean? Here is what you need to know.
View post


Данная статья представляет краткий обзор всех версий операционной системы Windows.
Версия Вашей системы: Windows 7
Версии для настольных компьютеров
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows 1 | 1985 | Не поддерживается Не используется |
 |
Windows 2 | 1987 | |
 |
Windows 3 | 1990 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.1 | 1993 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows 95 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 98 | 1998 | |
 |
Windows Millenium | 2000 | |
 |
Windows 2000 (NT 5.0) | 2000 | |
 |
Windows XP (NT 5.1) | 2001 | Не поддерживается Встречается редко |
 |
Windows Vista (NT 6.0) | 2006 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 7 (NT 6.1) | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока используется |
 |
Windows 8 (NT 6.2) | 2012 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 8.1 (NT 6.3) | 2013 | Поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 10 (NT 10) | 2015 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows 11 (NT 10) | 2021 | Поддерживается Начинает применяться |
Серверные Windows
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server | 1993 | Не поддерживается Как правило, не используется |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Server | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 Server | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 Server | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 2000 Server | 2000 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 | 2003 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 | 2008 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока еще используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 | 2012 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013 | |
 |
Windows Server 2016 | 2016 | |
 |
Windows Server 2019 | 2018 | |
 |
Windows Server 2022 | 2021 | Начало использования |
Все версии Windows по линейкам + хронология
| Линейка | Годы | Перечисление версий |
|---|---|---|
| 16 бит | 1985 — 1995 | Windows 1 / 2 / 3 |
| 32 бита (9x) |
1995 — 2001 | Windows 95 / 98 / ME |
| NT (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Workstation / 2000 / XP / Vista / 7 / 8 / 8.1 / 10 |
| NT Servers (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Server / 2000 Server / 2003 / 2003 R2 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2012 / 2012 R2 / 2016 / 2019 / 2022 |
История успеха
Данная история успеха отражает частоту использования системы; количество глюков, с которыми столкнулись пользователи; отзывы.
 |
Windows 1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 2 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows 3 | Успех |
 |
Windows 95 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 98 | Успех |
 |
Windows Millenium | Провал |
 |
Windows 2000 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows XP | Большой успех |
 |
Windows Vista | Провал |
 |
Windows 7 | Успех |
 |
Windows 8 | Провал |
 |
Windows 8.1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 10 | Успех |
 |
Windows 11 | Нейтрально |
* несмотря на провал некоторых версий операционной системы, они несли новые функции, которые перешли в уже успешные версии. Например, в миллениум появились красивые иконки и окна, которые перешли в Windows 2000. Поэтому провал не стоит оценивать, как неудачную работу.
 Windows 1
Windows 1
Годы поддержки: 1985 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
До Windows 1 был MS-DOS, поэтому самое главное новшество — графический интерфейс и возможность управления при помощи мыши.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 2
Windows 2
Годы поддержки: 1989 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Возможность использования сочетания клавиш.
- Появились перекрывающиеся окна.
- Возможность увеличить и уменьшить окно.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 3
Windows 3
Годы поддержки: 1990 — 2008. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первый (от Microsoft) удобный для пользователя интерфейс.
- Появление диспетчера программ.
- Появление мультимедийных возможностей.
- Поддержка сети (с 3.1).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 8086/8088 | 80486DX 33 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 640 Кбайт | 4 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 6,5 Мб | 60 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.1
Windows NT 3.1
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первая система на базе ядра NT.
- Поддержка файловой системы NTFS.
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера и клиента DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows 95
Windows 95
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 80386 DX | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 4 Мб | 8 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 50 Мб | 100 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 98
Windows 98
Годы поддержки: 1998 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486DX 66 МГц | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows Millenium
Windows Millenium
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 150 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows 2000
Windows 2000
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows XP
Windows XP
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Редакции: XP, XP Professional
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | от 1,5 Гб |
 Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Годы поддержки: 2006 — 2017. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Premium), Бизнес (Business), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 800 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 20 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows 7
Windows 7
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Home Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Home Premium), Профессиональная (Professional), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8
Windows 8
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2016. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 10
Windows 10
Годы поддержки: 2015 — 2025. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания
- Домашняя (Home). Для большинства домашних компьютеров. Нет возможности настроить удаленный рабочий стол для того, чтобы к систему можно было подключиться удаленно; нет возможности использования групповых политик и присоединения к домену.
- Профессиональная (Pro). Содержит все функции домашней версии + возможность присоединения к домену, использования групповых политик, возможность подключения к компьютеру с использованием удаленного рабочего стола.
- Корпоративная (Enterprise). Урезаны некоторые функции домашней версии. Есть все дополнительные функции версии Pro + DirectAccess, AppLocker.
- S. Является урезанной версией; предустановлена на некоторые устройства. Не поддерживает стандартную установку приложений — возможна установка только из магазина Windows.
Что нового
Windows 10 претерпевает сильные изменения с выходом новых билдов. Поэтому нововведения будем рассматривать исходя из этого.
Билд 1507 (ноябрь 2015):
- Улучшенная производительность.
- Новый встроенный браузер Microsoft Edge.
- Автоматическое сжимание соседнего окна, при прижимании активного окна в одной из сторон рабочего стола.
- «Все приложения» в «Пуск» поддерживают отображение в 2048 элементов (раньше только 512).
- Принудительная установка обновлений.
- Использование виртуального голосового помощника Кортана.
- Обновленный меню пуск — представляет из себя гибрид предыдущих версий и Windows 8 (вернулся старый вариант раскрытия, а в правой части появились плитки).
- Возможность создания нескольких рабочих столов.
- Отказ от плиточной системы Windows 8.
1607 (август 2016):
- Возможность рукописного ввода (Windows Ink).
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры.
- Синхронизация с мобильного устройства уведомлений.
- Изменение меню параметров системы.
1703 (апрель 2017):
- Встроенная поддержка шлемов виртуальной реальности.
- Игровой режим
- По умолчанию предлагается командная строка в Powershell.
- Доступ к классической панели управления скрыт из контекстного меню. Теперь его можно вызвать командой control.
- Улучшение работы встроенного антивируса.
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры для Active Directory.
- Возможность создавать скриншот с выделением области с помощью сочетания клавиш Win + Shaft + S.
- Поддержка шрифта Брайля.
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи.
1709 (октябрь 2017):
- Возможность работы Cortana на одном устройстве и окончание работы на другом.
- Отключение протокола SMBv1. Включить можно вручную.
- Появление панели «Люди».
- Информация о GPU в диспетчере задач.
- Полноэкранный режим Microsoft Edge
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи (функция Power Throttling).
- Появление панели эмодзи.
- Выборочная синхронизация OneDrive.
- Исправление проблемы торможения в играх.
1803 (апрель 2018):
- Возможность восстановить пароль с помощью контрольных вопросов.
1809 (октябрь 2018):
- Темная тема для проводника.
- Возможность получения доступа к сообщениям с телефона (функция «Ваш телефон»).
1903 (май 2019):
- Изолированный рабочий стол для безопасного запуска приложений.
1909 (ноябрь 2019):
- Универсальный поиск в Проводнике.
- Улучшение производительности.
2004 (май 2020):
- Функция «Загрузка из облака» для переустановки Windows 10.
- Регулирование пропускной способности для обновлений Windows.
- Отображение температуры видеоядра в Диспетчере задач.
- Возможность удаления Блокнот, Paint, WordPad.
- Возможность использование Windows без пароля.
* данный список содержит часть нововведений. Полный список на странице в Википедии.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: только 64 бита.
Основные издания: Домашняя (Home), Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise).
Дополнительные издания: для обучения (Education), для облаков (Cloud).
Системные требования
| Процессор | 2 ядра, 1 ГГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 64 Гб |
| БИОС (прошивка) | UEFI |
| Видеоадаптер | Совместимый с DirectX 12 / WDDM 2.x |
| Интернет | Для Home необходим вход под учетной записью Microsoft. |
 Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Server
Windows NT 3.5 Server
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Server
Windows NT 3.51 Server
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Server
Windows NT 4.0 Server
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 2000 Server
Windows 2000 Server
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Advanced Server и Datacenter Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Годы поддержки: 2003 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Web, Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003 R2
Windows Server 2003 R2
Годы поддержки: 2005 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008
Годы поддержки: 2008 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Storage, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц | |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб | ||
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Small Business, Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2012 R2
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2016
Годы поддержки: 2016 — 2026. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Лицензирование на физические ядра процессора (минимум 16).
- Новый режим установки — Nano.
- Появление контейнерной виртуализации.
- OpenGL и OpenCL для RDP.
- Шифрование виртуальных машин и внутреннего сетевого трафика.
- Блочная репликация файловых хранилищ.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
Более подробно в обзоре Windows Server 2016.
 Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019
Годы поддержки: 2018 — 2029. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность — встроенные технологии Defender ATP и Defender Exploit Guard.
- Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL) — контейнеры для поддержки приложений Linux.
- Для построения кластера с четным количеством узлов в качестве диска-свидетеля может выступать USB-диск.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) |
4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность.
- Больше возможностей для работы с облаками, особенно, Microsoft Azure.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) Поддержка ECC |
4 Гб
Поддержка ECC |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
| Сетевой адаптер | 1 гигабит в секунду |
Are you researching the history of Microsoft Windows versions? This article contains a complete list of all Microsoft Windows Versions and the date of release.
Windows is a Microsoft operating system, the de-facto standard perfect for home, educational, and business computers.
MS Windows is a GUI-based OS that was introduced in November 1985 and ever since then, it has been released in several versions since then, as shown in the table below.
Microsoft company started with the partnership of Bill Gates and Paul Allen in the year 1975.
Bill Gates and Paul Allen co-developed Xenix which is a version of Unix. The Microsoft company was incorporated in the year 1981.
In the world today, Windows is the most used operating system for PC. And it is used by several brands to power their hardware.
The major advantage Windows has over most other operating systems is simplicity and flexibility.
Among other OS Microsoft Windows has the most friendly user interface. So many developers have developed amazing software out there for different purposes free of charge.
As new versions of Windows is being released, the operating system is getting more secure, and its loopholes and vulnerability are all being fixed.
We have seen the Windows version change from one to another. Below is the list of all the versions.
Microsoft Windows Versions, Editions, and Release Date
| NAME | RELEASE DATE | EDITION |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 11 | October 5, 2021 |
|
| Windows 10 | 29 July 2015 |
|
| Windows 8.1 | 17 October 2013 |
|
| Windows 8 | 26 October 2012 |
|
| Windows 7 | 22 October 2009 |
|
| Windows Vista | 30 January 2007 |
|
| Windows XP Professional x64 | 25 April 2005 | N/A |
| Windows XP | 25 October 2001 |
|
| Windows ME | 14 September 2000 | N/A |
| Windows 2000 | 17 February 2000 | Professional |
| Windows 98 | 25 June 1998 |
|
| Windows NT 4.0 | 24 August 1996 | Windows NT 4.0 Workstation |
| Windows 95 | 24 August 1995 |
|
| Windows NT 3.51 | 30 May 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 Workstation |
| Windows NT 3.5 | 21 September 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 Workstation |
| Windows 3.2 | 22 November 1993 | Simplified Chinese only |
| Windows for Workgroups 3.11 | November 1993 | N/A |
| Windows NT 3.1 | 27 July 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 |
| Windows 3.1 | April 1992 |
|
| Windows 3.0 | 22 May 1990 | N/A |
| Windows 2.11 | 13 March 1989 |
|
| Windows 2.10 | 27 May 1988 |
|
| Windows 2.03 | 9 December 1987 | N/A |
| Windows 1.04 | April 1987 | N/A |
| Windows 1.03 | August 1986 | N/A |
| Windows 1.02 | May 1986 | N/A |
| Windows 1.01 | 20 November 1985 | N/A |
Breakdown of Microsoft Windows Versions
Windows 1.0 – The Beginning
Released in November 1985, Windows 1.0 marked Microsoft’s first attempt at a graphical user interface for IBM-compatible PCs.
It introduced the concept of overlapping windows and icons, laying the foundation for future versions.
Windows 3.1 – The Rise of Graphical Interfaces
Windows 3.1, launched in April 1992, was a significant improvement, providing better stability and enhanced graphics.
It became immensely popular among users and developers.
Windows 95 – A Game-Changer
Windows 95, unveiled in August 1995, was a game-changer.
Its user-friendly interface, Start menu, and support for plug-and-play hardware made it a massive success.
Windows 98 – Enhancing the User Experience
Building on the success of Windows 95, Windows 98 arrived in June 1998.
It brought improvements in speed, stability, and support for USB devices.
Windows 2000 – A Leap in Stability
In February 2000, Windows 2000 was introduced as a business-oriented operating system.
It offered improved security, stability, and support for larger networks.
Windows XP – A Worldwide Favorite
Windows XP, released in October 2001, became a worldwide favorite.
Its user-friendly interface and robustness made it a staple in homes and businesses for years.
Windows Vista – The Ambitious Overhaul
While Windows Vista, launched in January 2007, faced mixed reviews, it aimed for a more secure and visually appealing experience.
However, it was later succeeded by a more popular version.
Windows 7 – A Return to Glory
Windows 7, released in October 2009, won back the hearts of users with its stability and enhanced features. It became the go-to choice for many.
Windows 8 – A Touch of Modernity
Windows 8, introduced in October 2012, brought a touch-centric approach to computing.
Its tile-based Start screen was a significant departure from previous versions.
Windows 10 – The Last of Its Kind
Windows 10, launched in July 2015, was touted as the “last” version of Windows.
It introduced regular updates rather than entirely new versions, focusing on continuous improvements.
Microsoft Windows 11 – A New Era
It took Microsoft a solid 6 years to release Windows 11 which was referred to as the Next Generation Windows OS.
After Microsoft released Windows 10 on 29 July 2015, six years later on October 5, 2021, the Windows 11 was released with lots of amazing features.
The new features in Microsoft Windows 11 include; Gaming in Auto HDR, Apps for Android, A New and Better Look, Widgets for Windows, Tablet Mode, and lots more.
Also, there are features present in Windows 10 but deprecated or/and removed in Windows 11.
The most amazing thing Microsoft did about the Windows 11 operating system is allowing Windows 10 users to easily upgrade to windows 11 without having glitches.
This is possible as long as the upgrading hardware meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11.
Windows Editions
Throughout its history, Windows has seen various editions tailored to different user needs, such as Home, Pro, Enterprise, and more. Each edition offers unique features and capabilities.
Advantages of Windows Operating System
- It is comparatively easy, especially when you compare it with other available OS.
- No special training is required to understand how to operate the Windows operating system.
- Windows operating system has wide support for games.
- Windows can run smoothly on most processors.
- The collection of software programs, applications, and games is relatively much more on Windows.
- The recent versions of the Windows operating system come with its own security, known as Windows Defender.
Languages Available in Windows
- Arabic (Saudi Arabia)
- Bulgarian (Bulgaria)
- Chinese (Taiwan)
- Chinese (PRC)
- Croatian (Croatia)
- Czech (Czech Republic)
- Danish (Denmark)
- Dutch (Netherlands)
- English (United States)
- English (United Kingdom)
- Estonian (Estonia)
- Finnish (Finland)
- French (Canada)
- French (France)
- German (Germany)
- Greek (Greece)
- Hebrew (Israel)
- Hungarian (Hungary)
- Italian (Italy)
- Japanese (Japan)
- Korean (Korea)
- Lithuanian (Lithuania)
- Latvian (Latvia)
- Norwegian, Bokmål (Norway)
- Polish (Poland)
- Portuguese (Portugal)
- Portuguese (Brazil)
- Romanian (Romania)
- Russian (Russia)
- Serbian (Latin, Serbia)
- Slovenian (Slovenia)
- Slovak (Slovakia)
- Spanish (Mexico)
- Spanish (Spain)
- Swedish (Sweden)
- Turkish (Turkey)
- Thai (Thailand)
- Ukrainian (Ukraine)
Conclusion
Microsoft Windows has come a long way from its humble beginnings, evolving into a versatile and ubiquitous operating system.
Its versions and editions have catered to the changing needs of users, making it a cornerstone of the digital age.
For the most up-to-date information on Microsoft Windows versions and editions, please refer to the official Microsoft website.
FAQs on Microsoft Windows Versions
- What is the latest version of Windows? As at the date this post was late updated Windows 11 is the latest version of Windows. However, newer versions will be released in the future.
- Can I still use older versions of Windows? Yes, you can use older versions of Windows, but Microsoft may no longer provide security updates and support for some of them. It’s advisable to use a supported version for security reasons.
- What are the key differences between Windows editions? The differences between Windows editions often include features such as advanced security options, domain connectivity, and remote desktop capabilities. The specific features vary between editions.
- How can I upgrade to a newer version of Windows? You can upgrade to a newer version of Windows through the official Microsoft website or using the Windows Update feature in your current operating system.
- Is Windows the most widely used operating system globally? Yes, Windows has been one of the most widely used operating systems worldwide for personal computers, although the popularity of other operating systems like macOS and Linux has also grown over the years.
I hope this article was helpful. Make use of the share button below to share with friends today!
RELATED ARTICLES
- How To Fix Sound Issue In Windows 10 – Audio Problem
- List of Android Version Names and Release Date
- List of all Keyboard and Windows Shortcut Keys
- How To Protect Computer from Virus Attack
124
124 people found this article helpful
Guide to Windows version numbers and major Windows builds
Updated on September 20, 2022
Each Microsoft Windows operating system has a familiar name, such as Windows 11 or Windows Vista, but behind each common name is an actual Windows version number1.
Windows Version Numbers
Below is a list of major Windows versions and their associated version numbers:
| Reference Table for Windows Version Numbers | ||
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Version Details | Version Number |
| Windows 11 | Windows 11 (22H2) | 10.0.22621 |
| Windows 11 (21H2) | 10.0.22000 | |
| Windows 10 | Windows 10 (21H2) | 10.0.19044 |
| Windows 10 (21H1) | 10.0.19043 | |
| Windows 10 (20H2) | 10.0.19042 | |
| Windows 10 (2004) | 10.0.19041 | |
| Windows 10 (1909) | 10.0.18363 | |
| Windows 10 (1903) | 10.0.18362 | |
| Windows 10 (1809) | 10.0.17763 | |
| Windows 10 (1803) | 10.0.17134 | |
| Windows 10 (1709) | 10.0.16299 | |
| Windows 10 (1703) | 10.0.15063 | |
| Windows 10 (1607) | 10.0.14393 | |
| Windows 10 (1511) | 10.0.10586 | |
| Windows 10 | 10.0.10240 | |
| Windows 8 | Windows 8.1 (Update 1) | 6.3.9600 |
| Windows 8.1 | 6.3.9200 | |
| Windows 8 | 6.2.9200 | |
| Windows 7 | Windows 7 SP1 | 6.1.7601 |
| Windows 7 | 6.1.7600 | |
| Windows Vista | Windows Vista SP2 | 6.0.6002 |
| Windows Vista SP1 | 6.0.6001 | |
| Windows Vista | 6.0.6000 | |
| Windows XP | Windows XP2 | 5.1.26003 |
[1] More specific than a version number, at least in Windows, is a build number, often indicating exactly what major update or service pack has been applied to that Windows version. This is the last number shown in the version number column, like 7600 for Windows 7. Some sources note the build number in parenthesis, like 6.1 (7600).
[2] Windows XP Professional 64-bit had its own version number of 5.2. As far as we know, that’s the only time Microsoft has designated a special version number for a specific edition and architecture-type of a Windows operating system.
[3] Service pack updates to Windows XP did update the build number but in a very minor and long-winded way. For example, Windows XP with SP3 and other small updates is listed as having a version number of 5.1 (Build 2600.xpsp_sp3_qfe.130704-0421 : Service Pack 3).
How to Update Windows
To update Windows to the newest build number, use Windows Update. The built-in Windows Update utility is the easiest way to check for and install Windows updates.
If you haven’t set up your version of Windows to install updates automatically, you can change the Windows Update settings so that new updates are downloaded and applied automatically. It’s the simplest way to keep Windows updated to the latest version number.
Major Changes in Windows 10
Microsoft introduced several changes to the Windows operating system with Windows 10. These are some of the most significant differences between Windows 10 and Windows 8 (and older versions of Windows):
- Cortana comes built-in to Windows 10
- Microsoft Edge is pre-installed as a replacement browser for Internet Explorer
- Brand-new versions of Mail, Calendar, Maps, and Photos
- Expanded notifications are available through Windows Action Center
- User interface that works well with both touch screen displays and traditional monitors that use a keyboard and mouse
- Windows 10’s Start menu replaces the full-screen Windows 8 Start Screen
- Microsoft Paint 3D replaces Microsoft Paint
- Share files wirelessly with other PCs using Windows Nearby Sharing
- Set quiet hours by blocking notifications with Windows Focus Assist
- Windows Hello lets you log in to Windows 10, apps, and websites with your face
- Play Xbox One games on your Windows computer
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe