После установки гостевой операционной системы Windows на гипервизор KVM мы можем столкнуться с проблемой отсутствия драйверов. Как правило, больше всего неудобств вызывает отсутствие сетевых драйверов. Мы рассмотрим универсальный способ установки драйверов на Windows, который установлен на виртуальную машину KVM.
Предполагается, что наш KVM установлен на операционную систему семейства Linux, например, CentOS или Ubuntu. Все команды в данной инструкции будут выполняться из командной строки.
Загрузка драйверов и их монтирование
Первым делом загрузим ISO образ с набором драйверов и примонтируем его к операционной системе. Для этого заходим на хост виртуализации по SSH и вводим команду:
wget https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/direct-downloads/stable-virtio/virtio-win.iso -P /data/kvm/iso/
* где https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/direct-downloads/stable-virtio/virtio-win.iso — источник файла iso с драйверами KVM; /data/kvm/iso/ — каталог на сервере, в который мы загрузим образ.
* если при вводе команды система выдаст ошибку, необходимо установить wget командой yum install wget или apt-get install wget.
Дожидаемся загрузки файла на сервер, после чего создаем конфигурационный файл для монтирования образа в операционную систему:
vi /etc/libvirt/qemu/guest-virtio-drivers.xml
Добавляем в него следующее:
<disk type=’file’ device=’cdrom’>
<driver name=’qemu’ type=’raw’/>
<source file=’/data/kvm/iso/virtio-win.iso’/>
<target dev=’hdb’ bus=’ide’/>
<readonly/>
<address type=’drive’ controller=’0′ bus=’0′ target=’0′ unit=’1’/>
</disk>
* /data/kvm/iso/virtio-win.iso — путь до файла, который мы загрузили на сервер. В данном файле мы создали описание для монтирования устройства cdrom.
С помощью созданного файла XML мы монтируем ISO образ в CDROM на виртуальной машине:
virsh update-device WIN /etc/libvirt/qemu/guest-virtio-drivers.xml
* где WIN — имя виртуальной машины.
Установка драйверов
Подключаемся к виртуальной машине с помощью VNC. Мы должны увидеть примонтированный CD-ROM с драйверами virtio:
Кликаем правой кнопкой мыши по пуск и выбираем Диспетчер устройств:
* в ранних версиях Windows необходимо кликнуть правой кнопкой мыши по Мой компьютер — Управление — Диспетчер устройств.
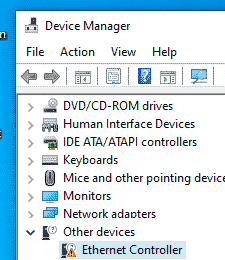
В разделе «Другие устройства» кликаем правой кнопкой мыши по устройству, для которого необходим драйвер и выбираем Обновить драйверы:
В открывшемся окне выбираем Выполнить поиск драйверов на этом компьютере:
… и выбираем наш CD-ROM с драйверами:
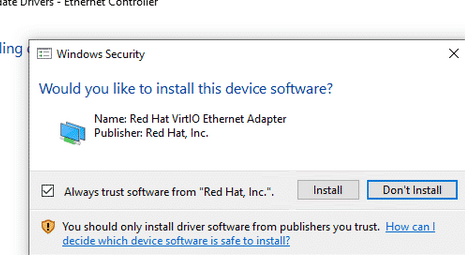
Если система выдаст предупреждение безопасности, кликаем по Установить:
Драйвер установлен. Повторяем процедуру для каждого устройства, для которого система не смогла установить драйвер.
Была ли полезна вам эта инструкция?
Да Нет
Windows VirtIO Drivers
The source for the Windows drivers is hosted in a repository on GIT hub. Anonymous users can clone the repository
git clone git://github.com/virtio-win/kvm-guest-drivers-windows.git
Browse GIT repository online
Binary Drivers
Binary drivers are provided by some Linux distributions including WHQL Certified drivers.
For example the binary drivers for Ubuntu can be found here.
64-bit versions of Windows Vista and newer (this currently includes Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2012) require the drivers to be digitally signed to load.
If your distribution does not provide binary drivers for Windows, you can use the package from the Fedora Project. These drivers are digitally signed, and will work on 64-bit versions of Windows:
Latest VirtIO drivers for Windows from Fedora
Code signing drivers for the Windows 64bit platforms
- Drivers should be signed for Windows 64bit platforms.
- Here are some links how to self sign and install self signed drivers:
- Installing Test-Signed Driver Packages
- How to Release-Sign File System Drivers
Introduction
VirtIO Drivers are paravirtualized drivers for kvm/Linux (see http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Virtio). In short, they enable direct (paravirtualized) access to devices and peripherals for virtual machines using them, instead of slower, emulated, ones.
A quite extended explanation about VirtIO drivers can be found here http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/library/l-virtio.
At the moment these kind of devices are supported:
- block (disks drives), see Paravirtualized Block Drivers for Windows
- network (ethernet cards), see Paravirtualized Network Drivers for Windows
- balloon (dynamic memory management), see Dynamic Memory Management
You can maximize performances by using VirtIO drivers. The availability and status of the VirtIO drivers depends on the guest OS and platform.
Windows OS Support
Windows does not have native support for VirtIO devices included.
But, there is excellent external support through opensource drivers, which are available compiled and signed for Windows:
https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/direct-downloads/archive-virtio/?C=M;O=D
Note that this repository provides not only the most recent, but also many older versions.
Those older versions can still be useful when a Windows VM shows instability or incompatibility with a newer driver version.
The binary drivers are digitally signed by Red Hat, and will work on 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows
Installation
Using the ISO
You can download the latest stable or you can download the most recent build of the ISO.
Normally the drivers are pretty stable, so one should try out the most recent release first.
You can access the ISO in a VM by mounting the ISO with a virtual CD-ROM/DVD drive on that VM.
Wizard Installation
You can use an easy wizard to install all, or a selection, of VirtIO drivers.
- Open the Windows Explorer and navigate to the CD-ROM drive.
- Simply execute (double-click on) virtio-win-gt-x64
- Follow its instructions.
- (Optional) use the virtio-win-guest-tools wizard to install the QEMU Guest Agent and the SPICE agent for an improved remote-viewer experience.
- Reboot VM
Manual Installation
- Open the Windows Explorer and navigate to the CD-ROM drive.
- There you can see that the ISO consists of several directories, each having sub-directories for supported OS version (for example, 2k19, 2k12R2, w7, w8.1, w10, …).
- Balloon
- guest-agent
- NetKVM
- qxl
- vioscsi
- …
- Navigate to the desired driver directories and respective Windows Version
- Right-click on the file with type «Setup Information»
- A context menu opens, select «Install» here.
- Repeat that process for all desired drivers
- Reboot VM.
Downloading the Wizard in the VM
You can also just download the most recent virtio-win-gt-x64.msi or virtio-win-gt-x86.msi from inside the VM, if you have already network access.
Then just execute it and follow the installation process.
Troubleshooting
Try an older version of the drivers first, if that does not help ask in one of our support channels:
https://pve.proxmox.com/wiki/Get_support
Further Reading
https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/creating-windows-virtual-machines-using-virtio-drivers/index.html
http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/WindowsGuestDrivers
The source code of those drivers can be found here: https://github.com/virtio-win/kvm-guest-drivers-windows
http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/WindowsGuestDrivers/Download_Drivers
See also
- Paravirtualized Block Drivers for Windows
- Paravirtualized Network Drivers for Windows
- Dynamic Memory Management
После установки гостевой Windows в виртуальную машину на хосте KVM, нужно добавить корректные драйвера (kvm virtio driver). Без этих драйверов гостевая Windows не сможет определить виртуальные сетевые адаптеры и ряд другого оборудования.
Скачайте актуальную версию ISO образа с драйверами KVM для Windows (около 500 Мб):
$ wget https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/direct-downloads/stable-virtio/virtio-win.iso -P /vm/kvm/iso/
Создайте конфигурационной файл для монтирования iso образа в виртуальную машину:
$ vi /etc/libvirt/qemu/guest-virtio-drivers.xml
Добавьте в него следующую конфигурацию:
<disk type='file' device='cdrom'> <driver name='qemu' type='raw'/> <source file='/vm/kvm/iso/virtio-win.iso'/> <target dev='hdb' bus='ide'/> <readonly/> <address type='drive' controller='0' bus='0' target='0' unit='1'/> </disk>
Чтобы смонтировать ISO образ в виртуальную машину KVM, выполните:
$ virsh update-device test-win1 /etc/libvirt/qemu/guest-virtio-drivers.xml
Подключитесь к консоли виртуальной машины Windows, запустите диспетчер устройств и найдите оборудование Ethernet Controller в секции Other Device. Как вы видите, Windows не нашла драйвер для сетевой карты.
Щелкните по контроллеру правой клавишей и выберите: Update Driver -> Browse my computer for driver software, укажите путь к виртуальному CD диску, в который смонтирован ISO образ.
Подтвердите установку драйвера Red Hat VirtIO Ethernet Adapter.
Аналогичным образом установите все остальные драйвера, для оборудования, которое Windows не смогла обнаружить.
KVM/QEMU Windows guest drivers (virtio-win)
This repository contains KVM/QEMU Windows guest drivers, for both
paravirtual and emulated hardware. The code builds and ships as part
of the virtio-win RPM on Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and the
binaries are also available in the form of distribution-neutral ISO
and VFD images. If all you want is use virtio-win in your Windows
virtual machines, go to the
Fedora virtIO-win documentation
for information on obtaining the binaries.
If you’d like to build virtio-win from sources, clone this repo and
follow the instructions in Building the Drivers.
Note that the drivers you build will be either unsigned or test-signed
with Tools/VirtIOTestCert.cer, which means that Windows will not load
them by default. See Microsoft’s driver signing page
for more information on test-signing.
If you want to build cross-signed binaries (like the ones that ship in
the Fedora RPM), you’ll need your own code-signing certificate.
Cross-signed drivers can be used on all versions of Windows except for
the latest Windows 10 with secure boot enabled. However, systems with
cross-signed drivers will not receive Microsoft support.
If you want to produce Microsoft-signed binaries (fully supported,
like the ones that ship in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux RPM), you’ll
need to submit the drivers to Microsoft along with a set of test
results (so called WHQL process). If you decide to WHQL the drivers,
make sure to base them on commit eb2996de or newer, since the GPL
license used prior to this commit is not compatible with WHQL.
Additionally, we ask that you make a change to the Hardware IDs so
that your drivers will not match devices exposed by the upstream
versions of KVM/QEMU. This is especially important if you plan to
distribute the drivers with Windows Update, see the
Microsoft publishing restrictions for more details.