Перейти к содержимому
Управлять процессами в Windows можно не только через UI («Менеджер задач»), но и через командную строку. К тому же командная строка предоставляет больше контроля над данными действиями.
Для вывода списка запущенных процессов нужно ввести команду:
tasklist
Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage ========================= ======== ================ =========== ============ System Idle Process 0 Services 0 4 K System 4 Services 0 4 124 K smss.exe 348 Services 0 336 K csrss.exe 480 Services 0 2 780 K wininit.exe 552 Services 0 572 K csrss.exe 568 Console 1 9 260 K winlogon.exe 616 Console 1 2 736 K services.exe 640 Services 0 9 284 K lsass.exe 660 Services 0 16 464 K explorer.exe 27736 Console 1 125 660 K
«Убить» процесс можно как по его имени, так и по PID:
>Taskkill /IM explorer.exe /F
>Taskkill /PID 27736 /F
Флаг /F указывает, что завершить процесс нужно принудительно. Без данного флага, в некоторых случаях, процесс может не «убиться» (к примеру, это актуально как раз для процесса explorer.exe).
Multitasking with many apps and programs in the background can become difficult to manage and kill the processes running in the background using just the Task Manager or even with tools like Microsoft Process Explorer. However, another way to kill tasks and processes is from the command line in Windows.
However, you can open the Task Manager, right-click the process, and then click “End Task” to kill off the process. You can also terminate a specific process from the Details tab in the Task Manager. Sometimes you encounter issues with the Task Manager itself. For times like these, you may need to kill a process using the command line, which includes both the Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell.
In this article, we show you multiple ways to kill a process in Windows using Command Line.
This Page Covers
Why use the command line to terminate a process?
Although a normal user will not require killing processes using the command line, there are several use cases where command line tools are much better than their visual counterparts like the task manager. The following command line tools can be used in the following scenarios:
- Troubleshooting: Some processes are simply stubborn. They just stop responding and refuse to die. In such a condition, killing them forcefully using the command line is an easier and safer option.
- System administration: If you are a sysadmin, you should be a fan of command line utilities. These tools save a lot of work and time. You can run these commands remotely throughout your network to troubleshoot systems remotely.
- Script Automation: If you are a developer and need to start or stop processes in Windows, you will need these command line tools for automation.
- Virus prevention: If your system gets infected with viruses, it will simply not let you kill the compromised processes, as they will respawn upon kill. In this case, you can automate a monitoring process where the process is killed as soon as it starts.
There are several other use cases, but these are the most common ones.
How to Kill a Process from Command Prompt
You can kill the process in cmd using the taskkill command. However, you must either know its Process Identifier (PID) or the name of the process before you can end it.
To view and list the tasks and processes currently running on your computer, run the following command in an elevated Command Prompt:
TasklistNote either the name under the Image name column or the PID number of the task you want to kill. These will be used in the cmdlets to kill the respective process.
Once you have either the name or the PID of the task, use either of the following cmdlets to kill the process:
-
Kill task using process name in Command Prompt:
Replace [ProcessName] with the name of the process.
taskkill /IM "[ProcessName]" /FKill process from Command Prompt using process name -
Kill task using PID in Command Prompt:
Replace [PID] with the Process ID.
taskkill /F /PID [PID]Kill process from Command Prompt using a process ID
If you are using earlier versions of Windows, like Windows 7, Windows Vista or even Windows XP, you can use tskill command, which is similar to taskkill but limited in functionality. You just need to provide the process ID to kill a task using tskill command:
tskill process-idReplace process-id with the actual process ID. For example,
tskill 1234How to Kill a Process from Windows PowerShell
Similar to the Command Prompt, you can also kill processes using PowerShell. But first, we must get the name or the process ID for the process to kill.
To obtain a list of the running processes in PowerShell, run the following command in PowerShell with elevated privileges:
Get-ProcessFrom here, note down the process name or the PID (in the ID column) of the process that you want to kill, and then use it in the following commands:
Note: Unlike the Command Prompt, Windows PowerShell shows no output once a process is killed.
-
Kill task using process name in PowerShell:
Replace [ProcessName] with the name of the process.
Stop-Process -Name "[ProcessName]" -ForceKill process from PowerShell using process name -
Kill task using PID in PowerShell:
Replace [PID] with the Process ID.
Stop-Process -ID [PID] -ForceKill process from PowerShell using a process ID
How to Kill a Process using WMIC
Windows Management Instrumentation Command-Line (WMIC) is a useful command line tool to perform administrative tasks especially for sysadmins and power users. You can terminate the process using wmic command.
Please note all the below mentioned commands will only work if you open Command Prompt, PowerShell or Terminal as an administrator.
wmic process where "ProcessId='process-id'" deleteReplace process-id with the actual process ID. For example,
wmic process where "ProcessId='1234'" deleteYou can also terminate the process using its name:
wmic process where "name='process-name'" deleteReplace process-name with the actual process name. For example,
wmic process where "name='Skype.exe'" deleteIf there are multiple processes by the same name, this command will kill all of them. For example, the above mentioned command will delete all instances with the name Skype.exe.
How to Kill a Process using SysInternals PsKills
PsKill is a tiny tool that comes with the PsTools Suite by SysInternals. This is a command-line tool used to kill processes, both locally and remotely on other computers on the network.
Although it was designed for WindowsNT and Windows 2000 that did not include the other command-line tools (Killtask and Stop-Process), PsKill can still be used to end processes.
Learn how to manage processes and services on remote computers.
Use the following steps to download and use PsKill to kill tasks using the command line on a Windows computer:
-
Start by downloading PsTools.
Download PSTools -
Extract the contents of the PsTool file.
Extract PsTools -
Launch an elevated Command Prompt and then use the
CDcmdlet to change your directory to the extracted PsTools folder.CD [PathToPsTools]Change directory to PsTools folder -
Run the following command to list all the running processes:
PsListList all running processes using PsList Note down the name of the process that you want to kill.
-
Now use the following command to kill a process using its name:
PsKill.exe [ProcessName]Kill process using PsKill
As you can see from the image above, the respective process will be killed, and the associated service or program will be terminated.
Ending Thoughts
Even without the use of the Task Manager, there are multiple ways of killing a task or a process directly from the command line. You can even use these commands in scripts to end a Windows process.
On top of that, you can choose whether to kill a process using its name or its PID. Either way, Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell can be used with both native and external commands for this purpose. Not only that, but you can also use these commands in Windows Terminal for the same purpose.
If you are a sysadmin who wants quick and convenient methods to kill running processes, the given command line methods just might be the most convenient way of accomplishing it.
We use the taskkill command to terminate applications and processes in the Windows command prompt. Running taskkill is the same as using the End task button in the Windows Task Manager.
With taskkill, we kill one or more processes based on the process ID (PID) or name (image name). The syntax of this command is as follows:
taskkill /pid PID
taskkill /im nameYou can use the tasklist command to find the PID or image name of a Windows process.
The /F option tells Windows to force kill the process:
taskkill /f /im notepad.exeKill a Process by PID
In the following example, we run the taskkill command to terminate a process with a PID of 1000:
taskkill /f /pid 3688The multiple processes can be terminated at once, as shown in the following example:
taskkill /pid 3688 /pid 4248 /pid 4258Kill a Process by Name
To kill a process by its name, we use the /IM option. In the following example, we run the taskkill command to terminate the notepad.exe process:
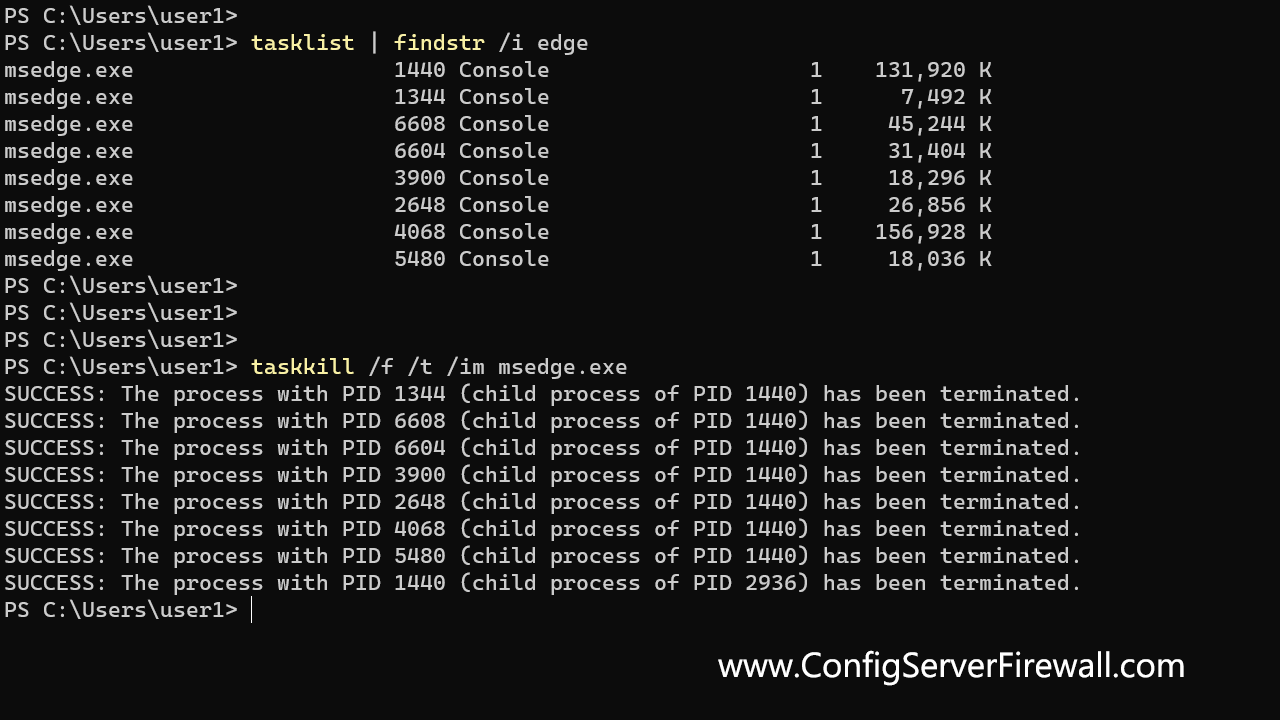
taskkill /im notepad.exeThe /t option tells Windows to terminate the specified process and all child processes. In the following example, we force kill Microsoft Edge and its child processes:
taskkill /f /t /im msedge.exeCommand Options
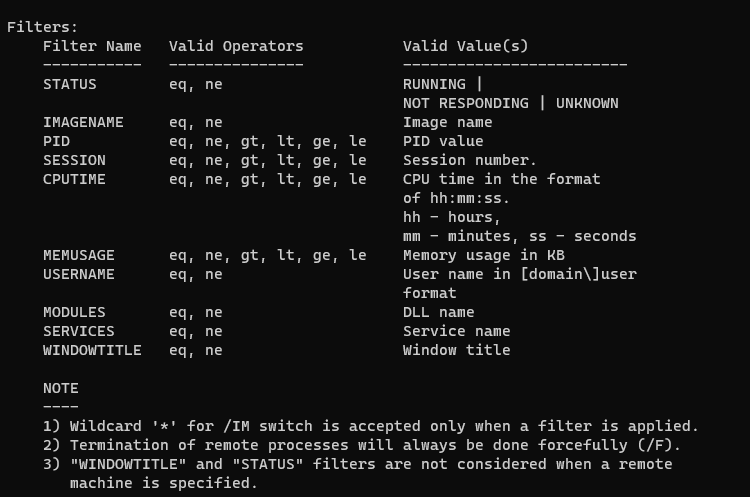
| /S | Specifies the IP Address or name of the remote system to connect to. |
| /U | Specifies the name of the Windows user under which the command should execute. |
| /P | Password for the user. Prompts for input if omitted. |
| /FI | This option is to apply filters (see examples below). |
| /PID | Specifies the PID of the process to be terminated. |
| /IM | Specifies the image name of the process to be terminated. |
| /T | Terminates the specified process and its child processes (end all tasks). |
| /F | Forcefully kill a process. |
Examples
Terminate a process with a PID of 4000:
taskkill /pid 4000Terminate spoolsv.exe (which is the Print Spooler service on Windows):
taskkill /im spoolsv.exeUsing /f and /t options to forcefully terminate the entire process tree of the Microsoft Edge browser:
taskkill /f /t /im msedge.exeForce kill any process that starts with the name note:
taskkill /f /t /im note*In the following example, we terminate all processes that are not responding by using a filter:
taskkill /f /fi "status eq not responding"In the above example, eq stands for equal. You can use the following filters with the /fi option.
Run taskkill command on a remote computer:
taskkill /s 192.168.1.100 /u robst /pid 5936In the above example, the process with PID 5936 will be terminated on a remote computer with an IP address of 192.168.1.100.
Note that the Windows Firewall must be configured on the remote computer to allow the taskkill command. Click the link below for instructions on how to do it.
How to allow tasklist and taskkill commands from Windows Firewall
All right, here’s the end of this tutorial. While working on the CMD, you can run taskkill /? to display the help page, command options, and filters of the tasklist command.
The PowerShell equivalent to the taskkill is the Stop-Process cmdlet. But you can always use taskkill in PowerShell as well.
Многие пользователи умеют завершать процессы через «Диспетчер задач». Но, далеко не все знают, что ту же процедуру можно выполнить и с помощью командной строки. В большинстве случаев это не так удобно, как через «Диспетчер задач», но в некоторых ситуациях без этого не обойтись.
Завершение процессов через командную строку позволяет быстро закрыть большое количество похожих программ или программ, которые были запущены определенным пользователем на удаленном компьютере.
Как посмотреть запущенные процессы через командную строку
Для того чтобы посмотреть запущенные процессы через командную строку на Windows 7 или Windows 10 нужно использовать команду «tasklist». Данная команда позволяет получить подробную информацию о всех запущенных процессах на локальном или удаленном компьютере. Подробную информацию о данной команде, ее синтаксисе и используемых параметрах можно получить здесь.
tasklist
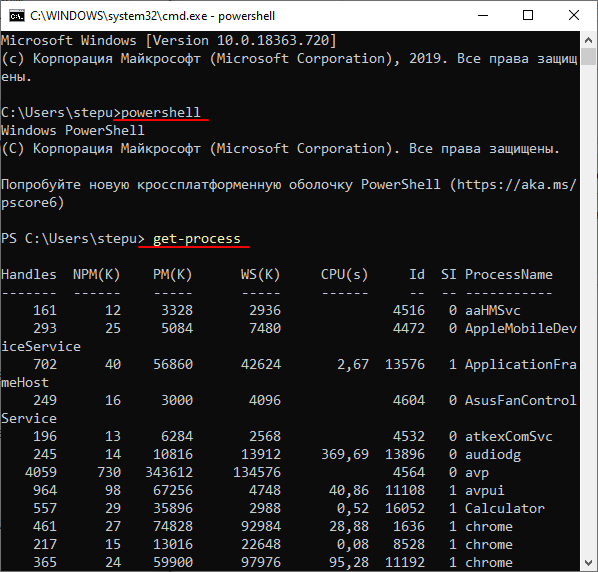
Также для просмотра запущенных процессов в командной строке можно использовать возможности PowerShell. Для этого нужно сначала выполнить команду «powershell», для того чтобы перейти в режим PowerShell, и потом выполнить команду «get-process». Более подробную информацию о команде «get-process», ее синтаксисе и параметрам можно получить здесь.
powershell get-process
Обе эти команды выводят в командную строку подробную информацию о запущенных процессах, включая их названия, идентификаторы и потребляемую память.
Как завершить запущенный процесс через командную строку

Основными параметрами команды «taskkill» являются:
- /PID
Завершение по идентификатору (PID); - /IM
Завершение по названию (можно использовать знак подстановки *); - /T
Завершение всех дочерних процессов; - /F
Принудительное завершение процесса;
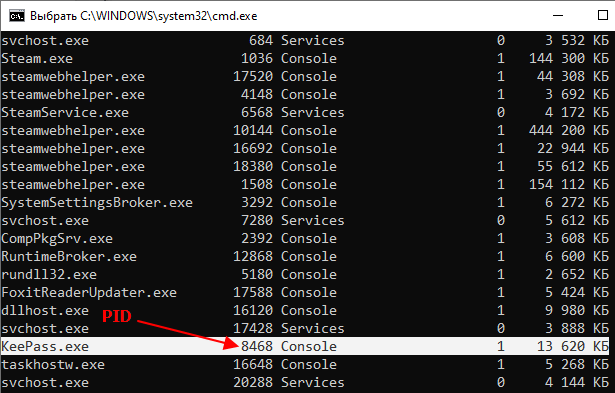
Чтобы завершить процесс используя идентификатор нужно выполнить команду «tasklist», найти нужный процесс и узнать его PID.
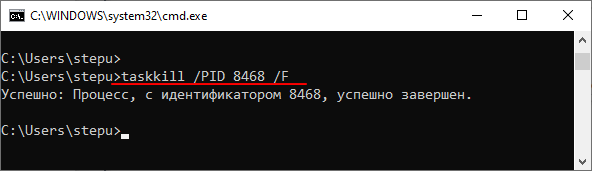
После этого нужно выполнить команду «taskkill» указав PID процесса. Также обычно используют параметр «/F» для принудительного завершения работы программы. Без параметра «/F» программа может не закрыться, если у нее есть несохраненные данные. В результате команда буде выглядеть примерно так:
taskkill /PID 8468 /F
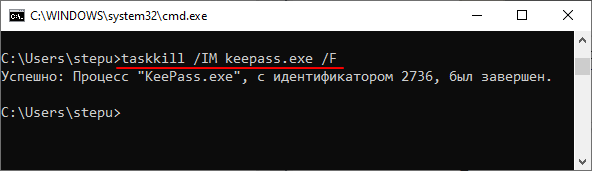
Также программу можно завершить по названию процесса. Для этого нужно ввести команду «taskkill» указав название процесса с помощью параметра «/IM» и при необходимости использовав параметр «/F» для принудительного завершения. Например, для того чтобы закрыть программу «keepass.exe» нужно выполнить следующее:
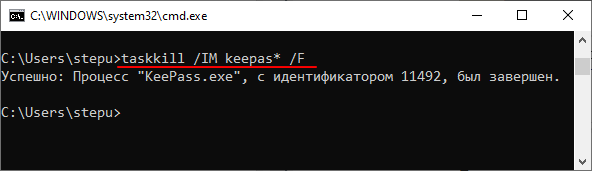
taskkill /IM keepass.exe /F
Также нужно отметить, что параметр «/IM» позволяет использовать знак подстановки (*). Поэтому не обязательно вводить полное название процесса. Вместо этого вы можете выполнить:
taskkill /IM keepas* /F
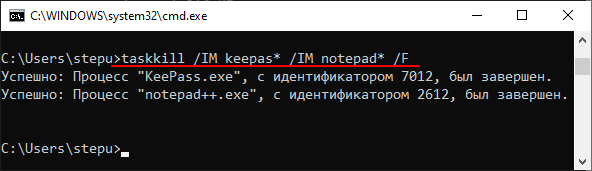
При необходимости можно завершать сразу несколько процессов, для этого достаточно указать несколько параметров «/PID» или «/IM». Например, для того чтобы принудительно закрыть сразу две программы (Keepass и Notepad++) нужно выполнить следующую команду:
taskkill /IM keepas* /IM notepad* /F
Обратите внимание, завершение процессов с помощью команды «taskkill» зависит от уровня прав пользователя. Если у вас нет достаточных прав, то завершить работу программы не удастся.
Посмотрите также:
- Как поставить высокий приоритет программе в Windows 11 и Windows 10
- Выключение компьютера через командную строку
- Как перезагрузить компьютер через командную строку
- Как вызвать командную строку в Windows 7
- Как поменять дату в Windows 7
Автор
Александр Степушин
Создатель сайта comp-security.net, автор более 2000 статей о ремонте компьютеров, работе с программами, настройке операционных систем.
Остались вопросы?
Задайте вопрос в комментариях под статьей или на странице
«Задать вопрос»
и вы обязательно получите ответ.
If a program stops responding or behaves unexpectedly and does not even allow you to close it, then you can kill its process to forcefully close the program. Traditionally, Windows allows users to do so through Task Manager and Command Prompt. In addition, you can also use PowerShell.
3 Ways To Kill A Process In Windows 10 Method 1: Use End Task in Task Manager Method 2: Use Taskkill in Command Prompt Method 3: Use Stop Process in Windows Powershell
Method 1: Use End Task in Task Manager
Terminating a process from Task Manager is the most traditional and straightforward approach. Here, you can observe system resources utilized by each process, and check computer performance. The processes can be sorted based on their names, CPU consumption, Disk/Memory usage, PID, etc. to narrow down the list as per your convenience. Here’s how to kill a process using Task Manager:
-
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys together to open Task Manager.
-
If reqd, click on More Details to view all the processes running on your system currently.
-
Right-click the process which you want to terminate and click on End task, as shown. We have shown Google Chrome as an example.
Also Read: Kill Resource Intensive Processes with Windows Task Manager (GUIDE)
Method 2: Use Taskkill in Command Prompt
While terminating processes from Task Manager is a cakewalk, you have to admit that it is pretty lackluster. The disadvantages of using Task Manager are:
It does not allow you to terminate multiple processes simultaneously. You cannot end apps running with administrative privileges.
Hence, you can use Command Prompt instead.
Note: To terminate a process running with administrative rights, you will need to launch Command Prompt as administrator.
-
In the Windows search bar, type cmd and click on Run as administrator as shown.
-
Type tasklist and press Enter key to get the list of all running processes.
Option 1: Kill Individual Processes
3A. Type taskkill/IM Image Name command to terminate a process using its Image Name and hit Enter.
For example: To terminate notepad process, run taskkill/IM notepad.exe command, as shown.
3B. Type taskkill/PID PID number to terminate a process using its PID number and press Enter key to execute.
For example: To terminate notepad using its PID number, type taskkill/PID 11228 as depicted below.
Option 2: Kill Multiple Processes
4A. Run taskkill/IM Image Name1/IM Image Name2 to kill multiple processes, at once, using their respective Image Names.
Note: Image Name1 will be replaced with the first process Image Name (e.g. chrome.exe) and so do the Image Name2 with the second process Image Name (e.g. notepad.exe).
4B. Similarly, execute taskkill/PID PID num1/PID PID num2 command to kill multiple processes using their respective PID numbers.
Note: num1 is for the first process PID (e.g. 13844) and num2 is for the second process PID (e.g. 14920) and so on.
Option 3: Kill A Process Forcefully
5. Simply, add /F in the above commands to kill a process forcefully.
To learn more about Taskkill, type taskkill /? in Command Prompt and hit Enter to execute. Alternately, read about Taskkill in Microsoft docs here.
Also Read: Fix Command Prompt Appears then Disappears on Windows 10
Method 3: Use Stop Process in Windows Powershell
Likewise, you can use the tasklist command in PowerShell to attain a list of all running processes. Although to terminate a process, you will need to use the Stop-Process command syntax. Here’s how to kill a process via Powershell:
-
Press Windows + X keys together to bring up the Power User Menu.
-
Here, click on Windows PowerShell (Admin), as shown.
-
Type the tasklist command and press Enter to get a list of all processes.
Option 1: Using Image Name
3A. Type Stop-Process -Name Image Name command to terminate a process using its Image Name and hit Enter.
For example: Stop-Process -Name Notepad) as highlighted.
Option 2: Using PID
3B. Type Stop-Process -Id processID to terminate a process using its PID and press Enter key.
For example: run Stop-Process -Id 7956 to end task for Notepad.
Option 3: Forceful Termination
4. Add -Force with the above commands to forcefully close a process.
Q1. How do I force to kill a process in Windows?
Ans. To force kill a process in Windows, execute the command taskkill /IM Process Name /F in Command Prompt or, execute Stop-Process -Name ApplicationName -Force command in Windows Powershell.
Q2. How do I kill all processes in Windows?
Ans. Processes of the same application are clustered under a common header in the Task Manager. So to kill all its processes, simply terminate the cluster head. If you wish to terminate all background processes, then follow our article to disable background apps. You can also consider performing a clean boot.
Recommended:
How to Fix PC Won’t POST 8 Ways to Fix Windows 10 Installation Stuck How to Fix Git Merge Error
We hope that you learnt how to kill a process on Windows 10 PC. If you have any queries/suggestions regarding this article, then feel free to drop them in the comments section.