Шелл скрипты или .SH файлы похожи на командные файлы Windows, которые могут выполняться в Linux или Unix.
В Windows 10 можно запустить файл .sh или скрипт оболочки, используя подсистему Windows для Linux.
В этом руководстве мы покажем вам, как запустить файл скрипта оболочки в Windows 10.
Содержание
- Как запустить файл .sh или скрипт шелла в Windows 10
- 1] Выполнить файл скрипта оболочки, используя WSL
- 2] Выполнить скрипт оболочки, используя Ubuntu в Windows 10
Как запустить файл .sh или скрипт шелла в Windows 10
Bash – это оболочка и командный язык Unix, который может запускать файлы скрипты .sh.
Вам не нужно устанавливать Ubuntu или любые другие дистрибутивы Linux, если ваши скрипты не нуждаются в поддержке реального ядра Linux.
Мы поделимся обоими методами.
- Выполнить файл скрипт оболочки, используя WSL
- Выполнить скрипт оболочки с помощью Ubuntu в Windows 10
1] Выполнить файл скрипта оболочки, используя WSL
Установите WSL или Windows Subsystem для Linux
Перейдите в Настройки> Обновление и безопасность> Для разработчиков.
Проверьте переключатель режима разработчика.
Поищите «Функции Windows», выберите «Включить или отключить функции Windows».
Прокрутите, чтобы найти WSL, установите флажок и установите его.
После этого необходимо перезагрузить компьютер, чтобы завершить установку запрошенных изменений.
Нажмите Перезагрузить сейчас.
BASH отныне будет доступен в командной строке и PowerShell.
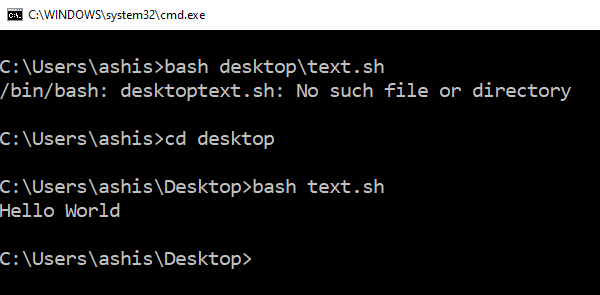
Выполнить файлы скриптов оболочки
- Откройте командную строку и перейдите в папку, где доступен файл скрипта
- Введите Bash script-filename.sh и нажмите клавишу Enter.
- Система выполнит скрипт, и в зависимости от файла вы должны увидеть вывод.
На платформе Linux вы обычно используете SH, но здесь вам нужно использовать BASH.
Тем не менее, BASH в Windows имеет свои ограничения, поэтому, если вы хотите выполнить их в среде Linux, вам нужно установить Ubuntu или что-то подобное.
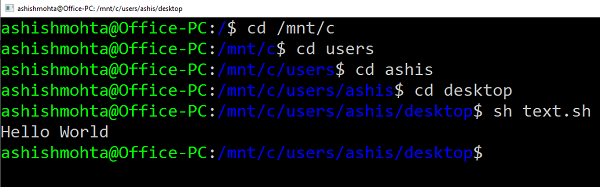
2] Выполнить скрипт оболочки, используя Ubuntu в Windows 10
Убедитесь, что у вас установлена Ubuntu или любой другой дистрибутив Linux.
Ubuntu смонтирует или сделает все ваши каталоги Windows доступными в /mnt.
Таким образом, диск C доступен по адресу /mnt/C.
Таким образом рабочий стол будет доступен по адресу /mnt/c/users/<username>/desktop.
Теперь следуйте этим шагам
- В командной строке введите Bash, и система запустит приглашение дистрибутива.
- Перейдите в папку с помощью команды «cd» , где доступны скрипты.
- Введите «sh script.sh» и нажмите Enter
Система выполнит скрипт
Поскольку Linux теперь доступен в Windows, вам не нужно использовать какие-либо сторонние приложения, такие как Cygwin.
WSL должно быть достаточно для большинства скриптов, чтобы помочь вам запустить эти самые крипты оболочки в Windows 10.
How can I run .sh on Windows 7 Command Prompt? I always get this error when I try to run this line in it,
app/build/build.sh
error,
'app' is not recognized...
or,
bash app/build/build.sh
error,
'bash' is not recognized...
Any ideas what have I missed?
Here the screen grab,
asked Oct 23, 2014 at 6:59
1
Install GIT. During installation of GIT, add GIT Bash to windows context menu by selecting its option. After installation right click in your folder select GIT Bash Here (see attached pic) and use your sh command like for example:
sh test.sh
answered May 27, 2016 at 8:15
Faisal MqFaisal Mq
5,0264 gold badges35 silver badges39 bronze badges
4
The error message indicates that you have not installed bash, or it is not in your PATH.
The top Google hit is http://win-bash.sourceforge.net/ but you also need to understand that most Bash scripts expect a Unix-like environment; so just installing Bash is probably unlikely to allow you to run a script you found on the net, unless it was specifically designed for this particular usage scenario. The usual solution to that is https://www.cygwin.com/ but there are many possible alternatives, depending on what exactly it is that you want to accomplish.
If Windows is not central to your usage scenario, installing a free OS (perhaps virtualized) might be the simplest way forward.
The second error message is due to the fact that Windows nominally accepts forward slash as a directory separator, but in this context, it is being interpreted as a switch separator. In other words, Windows parses your command line as app /build /build.sh (or, to paraphrase with Unix option conventions, app --build --build.sh). You could try app\build\build.sh but it is unlikely to work, because of the circumstances outlined above.
answered Oct 23, 2014 at 7:33
tripleeetripleee
176k34 gold badges275 silver badges318 bronze badges
1
The most common way to run a .sh file is using the sh command:
C:\>sh my-script-test.sh
other good option is installing CygWin
in Windows the home is located in:
C:\cygwin64\home\[user]
for example i execute my my-script-test.sh file using the bash command as:
jorgesys@INT024P ~$ bash /home/[user]/my-script-test.sh
answered Jun 9, 2015 at 23:09
JorgesysJorgesys
124k23 gold badges334 silver badges271 bronze badges
6
you can use also cmder
Cmder is a software package created out of pure frustration over the absence of nice console emulators on Windows. It is based on amazing software, and spiced up with the Monokai color scheme and a custom prompt layout, looking sexy from the start
cmder.net
answered Oct 18, 2016 at 17:05
vipmaavipmaa
1,04216 silver badges25 bronze badges
1
Install the GitBash tool in the Windows OS. Set the below Path in the environment variables of System for the Git installation.
<Program Files in C:\>\Git\bin
<Program Files in C:\>\Git\usr\bin
Type ‘sh‘ in cmd window to redirect into Bourne shell and run your commands in terminal.
answered Aug 21, 2020 at 19:36
TechRookieTechRookie
1712 silver badges4 bronze badges
1
On Windows 10 Anniversary Update, it’s even easier to run shell commands in/with bash on ubuntu on windows
I was trying to set my region for my x-wrt r7000 netgear router, I found the following worked for me, using bash on ubuntu on windows, you do have to enable subsystem found in windows features, and dev mode on
ssh [email protected] < /mnt/c/ccode-eu.sh
answered Aug 25, 2016 at 21:10
SignedAdamSignedAdam
711 silver badge1 bronze badge
1
Personally I used this batch file, but it does require CygWin installed (64-bit as shown).
Just associate the file type .SH with this batchfile (ExecSH.BAT in my case) and you can double-click on the .SH and it runs.
@echo off
setlocal
if not exist "%~dpn1.sh" echo Script "%~dpn1.sh" not found & goto :eof
set _CYGBIN=C:\cygwin64\bin
if not exist "%_CYGBIN%" echo Couldn't find Cygwin at "%_CYGBIN%" & goto :eof
:: Resolve ___.sh to /cygdrive based *nix path and store in %_CYGSCRIPT%
for /f "delims=" %%A in ('%_CYGBIN%\cygpath.exe "%~dpn1.sh"') do set _CYGSCRIPT=%%A
for /f "delims=" %%A in ('%_CYGBIN%\cygpath.exe "%CD%"') do set _CYGPATH=%%A
:: Throw away temporary env vars and invoke script, passing any args that were passed to us
endlocal & %_CYGBIN%\mintty.exe -e /bin/bash -l -c 'cd %_CYGPATH%; %_CYGSCRIPT% %*'
Based on this original work.
answered Feb 21, 2017 at 12:23
AnonymouseAnonymouse
9359 silver badges20 bronze badges
just install git and by «bash <name.sh>» run your .sh file.
answered Apr 3, 2021 at 8:51
I use Windows 10 Bash shell aka Linux Subsystem aka Ubuntu in Windows 10 as guided here
answered Apr 9, 2020 at 6:20
Nam G VUNam G VU
33.4k69 gold badges234 silver badges374 bronze badges
Have you tried cding to the root directory where your .sh is located in order to execute it from there, instead of writing down a path to the file as you showed in your question?
Like so:
$ cd app/build
$ build.sh
answered May 28, 2021 at 6:59
D4V1DD4V1D
5,8053 gold badges31 silver badges65 bronze badges
Are you interested in working with shell scripts on Windows? Thanks to a recent addition by Microsoft, you can now use Windows Subsystem for Linux to make this happen.
Once you enable shell scripts in Windows 10, you can start creating shell scripts of your own. Shell scripts are great for automating simple tasks. You can also work on open-source Linux-based projects if that’s an area of interest to you. Finally, you’ll learn how to execute shell scripts on Windows 10. Continue reading to learn more.
What is Linux?
Linux is an open-source operating system that is highly popular among computer enthusiasts. Linux competes with other computer operating systems like Microsoft’s Windows, Apple’s macOS, and mobile operating systems like Android and iOS.
The Linux operating system was originally developed by Linus Torvalds back in 1991. The Linux kernel was designed as a Unix-like operating system. Unix was an early operating system created by Bell Labs in 1969. Today, modern Linux distributions are still Unix-like, meaning they retain the basic structure and properties that Unix had. An example of a non-Unix operating system would be Microsoft Windows.
The top Linux distributions have changed over the years, but as of 2022, Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Fedora, and Red Hat rank as the top 5 most popular options.
What is Bash?
When Linus Torvalds created Linux, he included a Unix shell called Bash. Bash had been created just two years before, in 1989 by Brian Fox. Bash has been the longtime default for Linux and was also the default for Apple macOS until it was replaced by Z shell in 2019.
Until 2016, Windows users could not use the Linux kernel or Bash at all. Windows first introduced the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) beta with Windows 10 version 1607 update. About a year later, in October 2017, WSL was fully released in Windows 10 version 1709. Microsoft developed WSL for hobbyists and developers who want to work on open-source Linux-based projects.
It’s important to note that WSL is not preinstalled on Windows 10. If you would like access to create and run shell scripts on Windows 10, you will need to manually install WSL or join the Windows insider program.
What is a shell script?
A Shell script is a type of script that cannot be run without a Unix shell. Further, a shell script is a series of commands that are executed line by line by the command line.
You can use shell scripts to automate processes and avoid repetitive tasks. Instead of manually completing each step in a series, you can execute a script, and the command line will handle the rest.
For example, if you find yourself regularly stopping processes that are hogging your CPU, you can automate this process with a script. When you execute the script, it may be designed to find a set of processes using CPU resources and request to kill them.
Enabling shell scripts in Windows 10
- Click on the Start (Windows) button and enter “Control Panel” into the search bar. Click Open on the Control Panel result on the right-hand side.

- Within the Control Panel window, find and click on Programs.

- Now, from the Programs window, find Click Turn Windows features on or off underneath the Programs and Features header.

- In the Windows Features window, scroll to the very bottom of the window. Check the Windows Subsystem for Linux option. Then click OK.

- Windows will automatically install the necessary files. When the installation is complete, select Restart Now.

- When your computer restarts, you need to install Ubuntu from the Microsoft store.

- After installation, make sure you open Ubuntu and see it up. You are now ready to use scripts on your Windows 10 machine.
If you encounter any issues with Ubuntu or bash commands not working correctly, you may want to check that Virtualization is turned on in your BIOS. The most updated WSL version, WSL 2, runs the Linux kernel using virtualization technology. This means a virtual machine needs to be able to run on your system.
Now that Windows Subsystem for Linux and Ubuntu has been installed, you are ready to start creating shell scripts in Windows 10. You may be tempted to write bash scripts with Notepad, but this is not recommended. Because Notepad is designed for Windows/DOS systems, the line endings will differ from those that are found at the end of Unix/Linux line endings.
Text editors for shell scripts
You should use software that is designed to convert to Unix/OSX end-of-line characters. The best open-source software available for this is Notepad++. Amazingly, Notepad++ is lovingly maintained and developed by a single individual, Don Ho.
If you try Notepad++ and don’t like it, you can try another fan favorite, nano. Nano is a text editor for Unix/Linux systems. You can easily create shell scripts that will run in bash, using nano. Download nano to get started.
Example shell scripts
Let’s look at some basic shell scripts, so you can learn more about what you are going to be coding and see how some formatting and syntax work.
1. Hello World!
echo "Hello World!"This script will print out the infamous Hello World! Notice that echo can be used as a print command when not combined with any other modifiers. It will print the string on a new line. If you add the -n modifier, the output will print on the same line.
2. Sum two numbers
If you want to do some basic arithmetic, you might have a script that looks like:
# Add two numbers together
((sum=25+35))
# Print the sum of the numbers
echo $sum
Note that the # symbol is used to make comments that are not expressed. The output of this script will print the sum of 25+35, which is 60.
3. Take user input
The following script will ask for the user’s name and then use the read command to take the user’s input. Then the user’s name is passed into the following expression, ultimately welcoming you to Windows Subsystem for Linux.
echo "What is your name?"
read name
echo "Welcome $name to Windows Subsystem for Linux."
Write basic shell scripts in Windows 10
Continue reading to learn how to write basic shell scripts in Windows 10 using Notepad++.
- Click the Start button and search for “Notepad++” and click Run as administrator on the right-hand side.

- Now you can create your script.

- Once your script is complete, you need to use the EOL Conversion option available in Notepad++. Click Edit and locate EOL Conversion from the dropdown menu. Hover over this option and then select UNIX/OSX Format from the next dropdown menu.

- Now select File and then Save As. Make sure to name your file something you will recognize and add .sh to make it a shell script file.
- Once the shell script is saved, continue to the next section to learn how to run your own shell scripts.
How to run shell scripts (.sh files) on Windows 10
You’ve created your first shell scripts, and it’s time to execute the sh file. Remember that when using WSL, you can only use Linux commands and utilities. Windows 10 programs will not work in bash scripts. To execute a script file, follow these step-by-step instructions:
- Click on the Start (Windows) button and enter “Command Prompt” into the search bar. Click Run as administrator on the Command Prompt result on the right-hand side.
- Navigate to the folder where the script file is saved. You move around in the command prompt using the cd command. For example, if you want to access the Documents folder, you would enter the following and press Enter:
cd C:\Users\Username\OneDrive\Documents
Note: Username would be the username that you set up for yourself when you registered your computer.

- Now enter bash file-name.sh, where file-name is the whatever you’ve named your script file.
bash file-name.sh
The script will execute, and if there are any outputs or print statements included in the script, the output will be returned.
Bash scripts running on Windows 10
You’ve made it far and learned a ton of information in one go. Command-line utilities, different operating systems, and learning to write and execute shell scripts can be difficult topics. In fact, these topics will take time to master. You have a ton of learning to do for scripting, but resources are available to help you all over the internet.
Within this guide, you learned the basics of Linux and Bash. You learned what shell scripts are and that you need to specifically enable Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) to use them. You learned how to create shell scripts using Notepad++ and how to execute the scripts in bash. Enjoy experimenting!
- To run shell scripts on Windows, you must enable WSL and Virtual Machine Platform, install a WSL distro, and use “Bash Script.sh” to execute it.
- Alternatively, use third-party tools like Cygwin, Cmder to run Linux commands on top of Windows OS.
If you have worked with Linux distributions and repositories, you would know what shell scripts are. To run shell scripts on top of a Windows computer can be challenging, as the process is not quite straightforward.
Shell scripts are a piece of code written in plain text but have the “.SH” file extension. These are usually used to automate tasks and execute Linux or Unix packages. These are written in Bash and start with “#! /bin/sh“.
You do not need to install a Linux or Unix distribution alongside your Windows operating system to run a shell script. In this article, we’ll show you how to run a shell script on a Windows PC.
On This Page
What are Shell (.SH) Files
The Linux/Unix operating system uses shell or .SH script files to perform certain tasks. In comparison, it can be substituted by Windows batch files for the Windows operating systems, which are used to execute commands on a computer.
The Batch language is a simple and interpreted programming language, unlike C++ or C#. However, you do not have to translate a shell script file to batch to perform similar tasks on a Windows computer, as you do on a Linux PC.
There are different methods to run the same .SH file on a Windows computer as on a Linux system. Let us show you how to run a shell file on a Windows PC.
Run Shell Script (.SH) File on Windows
There are both native and third-party methods to run shell files on a Windows computer. You can use Cygwin, or a third-party tool of your choice, to run a shell script on Windows OS. Alternatively, you can install the Windows Subsystem for Linux feature on Windows and then execute the shell script file through it.
Below you’ll find the methods to run the file using both methods.
Run Shell Script File using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
This section has been divided into 3 steps to make the process easier to understand. You must do the following 3 things to run a shell script file in the given order:
- Install WSL
- Install a Linux distro
- Run the shell script file
Note: If you are performing these steps on a Virtual Machine, then you will need to enable Nested Virtualization.
Install WSL
Use the following steps to install WSL on your computer:
-
Press the Windows Key + R shortcut keys to open the Run Command box.
-
Type in “optionalfeatures” and press Enter.
Open the Optional Features applet -
Select “Windows Subsystem for Linux” and “Virtual Machine Platform,” and then click Ok.
Enable WSL and Virtual Machine Platform The wizard will now install WSL.
-
When the installation is completed, click “Restart now.”
Restart computer
Once the computer restarts, it is time to install a Linux distro.
Install a Linux Distribution
Use the following steps to install a Linux distribution:
-
When it restarts, press Windows Key + R again to open Run.
-
Type in “cmd” and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to run Command Prompt as administrator.
-
Run the following command to obtain a list of available Linux distros:
wsl --list --onlineGet list of all available Linux distros in Command Prompt Note down the name of the distro you want to install.
-
Use the following command to install the preferred distro while substituting its name:
wsl --install -d [DistributionName]Install a Linux distro in WSL The distro will now begin to download and install.
-
Set up a username and password.
Set up username and password -
Restart the computer.
Now, the next step is to simply run the shell script file.
Run the Shell Script File
Follow the simple steps below to run the shell script file on a Windows PC:
-
Press the Windows Key + R again to open Run.
-
Type in “cmd” and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to run Command Prompt as administrator.
-
Use the CD cmdlet to change the directory to the location of the shell script file.
CD [PathToShellScriptFile]Change directory to the shell script file location -
Now, use the following command to run the shell script file while substituting [ShellFileName] with the complete and correct name of the shell file:
Bash [ShellFileName].shRun the shell script file using Windows Subsystem for Linux
This is how you run a shell script (.SH) file on a Windows computer using WSL.
If this seems like a lengthy process for you, then you can also use the alternative method given below.
Run Shell Script File using Third-Party Tools
You can also run a shell script file on a Windows computer using a third-party tool. In the steps below, we have used Cygwin.
Follow these steps to run a .SH file on a Windows PC:
-
First, download and install Cygwin from their official website.
-
Once installed, run the Cygwin app.
-
In the Cygwin terminal, use the
CDcommand to change the directory to the shell script file location.Note: In Cygwin, the syntax to change the directory is different from Command Prompt or PowerShell. Use the following command syntax and example in the image to change your directory in Cygwin.
CD /cygdrive/[driveLetter]/[Subfolder1]/[Subfolder2]Change directory to the shell script file location in Cygwin -
Now, make the shell script file executable through this command:
chmod +x [ShellFileName].shMake the shell script file executable -
Now, use the following syntax to run the shell script file:
./[ShellFileName].shRun shell script file on Windows using Cygwin
These are the two methods to run shell script files (.SH) on a Windows PC. Of course, there are many other third-party tools available that allow you to run Linux and Unix files on a Windows computer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to create a shell script (.SH) file?
I you know what you want to write inside the shell script file, all you need to do is follow these simple rules:
– Create a new notepad file
– Start the script with “#! /bin/sh”
– Write the code below it
– Save the file with a “.sh” extension
– To run the script, type “bash [FileName].sh” after navigating to the folder.
Can I run shell scripts on Windows?
Yes, shell script files can be executed on a Windows computer using Windows Subsystem for Linux, or third-party tools like Cygwin, kiTTY, ConEmu, Cmder, etc.
Why use shell scripts on Windows?
Shell scripts are used to perform repetitive tasks to save time and resources. They are also used to automate tasks. With the WSL feature, Microsoft has opened doors to natively run shell scripts on Windows operating systems.
When I am trying to execute a file(name.sh) in the command line by the command ./name.sh , I am getting the error that:
«.» is not recognized as an internal
or external command, operable or batch
file
please help me execute the .sh file
Broam
3,98418 silver badges20 bronze badges
asked Mar 15, 2010 at 7:34
0
You’re on Windows CMD.EXE (from the error message). It uses a different syntax to execute commands. You’ll need to use sh name.sh, assuming that you’ve got Cygwin or similar installed.
To clarify, Windows does not have a built-in utility to support .sh files. To run such, you’ll need to install a third-party tool such as Cygwin.
Rich Homolka
31.1k6 gold badges55 silver badges80 bronze badges
answered Mar 15, 2010 at 7:58
Roger LipscombeRoger Lipscombe
2,2733 gold badges22 silver badges34 bronze badges
3
My solution:
-
Download and install .git for Windows
-
Right click desktop and say «git bash here»
-
Execute your script like in unix
-
Done!
Caution: Many commands won’t work on windows! But still, a lot of the basic stuff will work.
If you need that script regularly you may want to create a shortcut (on your desktop e.g.):
-
Create a Shortcut to
mintty.exeon your desktop -
Edit properties of the shortcut and change the target (keep the path):
-
C:\Program Files\Git\usr\bin\mintty.exe" -h always /bin/bash -l -e 'D:\folder\script.sh'
answered Apr 9, 2017 at 18:58
2
You are trying to run a Linux command at the Windows Command Prompt.
On Linux the forward slash is a path separater. On Windows the backslash is a path separator and the forward slash generally indicates an argument.
Therefore, Windows thinks you are trying to run a command called «.» and parsing it the argument «/name.sh». The correct convention would be «.\name.sh». Additionally Windows will automatically search the current directory for your command so you could just type «name.sh».
The next problem you will face is that Windows does not know what a sh script is, again this is a Linux thing. You could solve this by installing Cygwin if you really want or need to run a sh script.
However, judging by one of your previous comments you could just as well rename the script to name.bat and delete the «#!/bin/sh» line. Now you have a Batch file which Windows should understand. You can read more about batch files here.
answered Mar 15, 2010 at 13:48
Martin FidoMartin Fido
3112 silver badges3 bronze badges
Alternatively you could turn to the dark side and install Linux. From the prompt:
sh runide.sh
or
sudo sh runide.sh
Your program will run and you will have a better system as well.
Gaff
18.6k15 gold badges57 silver badges68 bronze badges
answered Nov 18, 2010 at 15:46
stevesteve
1371 silver badge2 bronze badges
2
You’re trying to run your car on orange juice instead of gasoline. Windows shares similar commands stored in .bat or .cmd files with Unix/Linux/zOS Unix Subsystem/*ix shell scripts as these two families of operating systems share a common ancestor the DEC PDP-x machines.
If you want instant gratification, you will need to install an environment that provides a «sh.exe» program or «csh.exe» or «bash.exe» program (tsh.exe anyone?)
Alternatively, if you know Unix script commands, very well, and you know Windows .cmd and .bat file commands, very well, you can translate the .sh file into a .bat or .cmd file. Even so, you will often encounter more Unix-styled programs that have no equivalent under Windows—grep, sed, vi, emacs, etc. Thus, the call to install CygWin (no minimalist)—just to get the shell and Unix tools. Put it on a flash-drive, for these special occasions.
answered Aug 16, 2011 at 22:52
J.M.J.M.
511 silver badge1 bronze badge
Someone said something about MS-DOS using / for commands and \ for paths. This is slightly misleading. Look at my example:
C:\myfoo\foo\>cd../..
C:\myfoo\foo\>cd..\..
Has no difference in effect. Yes, it is not true for all operations – the actual answer is simply No, or without Cygwin or SSHD you can’t.
I only know because I stupidly spent half a day trying to figure out what if then fi and eval, exec do with -Djava.something when called.
slhck
224k71 gold badges607 silver badges594 bronze badges
answered May 28, 2012 at 23:19
This is an old thread but for those running Windows 10. Just open windows features from the control panel ‘Turn Windows Features on or Off’
Choose the feature ‘Windows Subsystem for Linux’.
After installing, you have ‘Bash’ and you even can configure native Linux servers within bash.
And of course,
the sh command, within bash, works too.
answered May 1, 2018 at 16:06
I found a different and easy solution, called UnixUtil.
Download and unzip it to C: drive. Set the environment variable path to include C:\UnixUtils\usr\local\wbin.
This is important. DO NOT set path to C:\UnixUtils\bin
Canadian Luke
24.3k39 gold badges118 silver badges171 bronze badges
answered May 13, 2014 at 22:05
For completeness I want to mention a new “Windows Subsystem for Linux” feature for Windows 10. The details are described in http://www.howtogeek.com/249966/how-to-install-and-use-the-linux-bash-shell-on-windows-10/
Note, that it requires activate the “Developer Mode” switch and
enable the “Windows Subsystem for Linux (Beta)” option.
For myself I found that Git for Windows installation (that I am using anyway) is sufficient.
answered Dec 27, 2016 at 10:39
It’s possible that the problem is actually within the file name.sh — you are trying to use the . command but it is attempting to run a kind of shell (e.g., csh, I think) in which that’s not a valid command.
So: does name.sh start with the correct #!/bin/sh (if you are actually trying to run sh)?
answered Mar 15, 2010 at 7:55
1
ok, there’s a LOT wrong with that — drop the #!/bin/sh, and change the extention to bat, and it might work with a few more fixes. Then you can just invoke it by its filename as well.
The syntax of a unix shell script, and a windows batch file arn’t too similar. cygwin, or a load of messing around with unxutils might make something that would work in both, but unless you’re ABSOLUTELY sure the environment is always the same, it isn’t worth the headache
answered Mar 15, 2010 at 13:46
Journeyman Geek♦Journeyman Geek
128k52 gold badges263 silver badges433 bronze badges
3
If you have a Linux box in your home (or work) and plugged to the same network, and this network is safe, this might do the trick:
- Make a folder share on Windows (pretty easy, but make sure the network is safe from intruders).
- Mount it in Linux with
mount //WinMachine/Share LinuxFolder(IIRC, and requires Samba). - Using something like PuTTY, log in remotely to that Linux box.
- Run your command in the mounted folder.
answered Aug 31, 2012 at 15:16
Camilo MartinCamilo Martin
2,6044 gold badges32 silver badges41 bronze badges
To run the shell script from the windows.
First use the command : dos2unix
then you can use your normal command :
sh runide.sh
This will work out.
answered Nov 23, 2015 at 11:57
2
Although the existing answers here were correct at the time, Windows 10 does now optionally include a modified version of Ubuntu running a full bash shell.
Once made executable, scripts can be run in the usual way from within bash, eg:
chmod +x myscript.sh
./myscript.sh
If you want to run a script directly from the Windows you could create a shortcut in the same directory and set the ‘Target’ to something like:
C:\Windows\System32\bash.exe -c "./myscript.sh"
If the path of your script is relative to the location of the shortcut (like the example above) ensure the ‘Start in’ field is also blank.
answered Aug 25, 2016 at 7:34
MolombyMolomby
1,8151 gold badge17 silver badges15 bronze badges