В Windows 11 и Windows 10 клиент для Telnet протокола присутствует, но отключен по умолчанию. При необходимости его можно включить одним из способов, описанных далее.
Компоненты Windows
Клиент Telnet — один из дополнительных компонентов Windows, который может быть включен, как и другие такие компоненты:
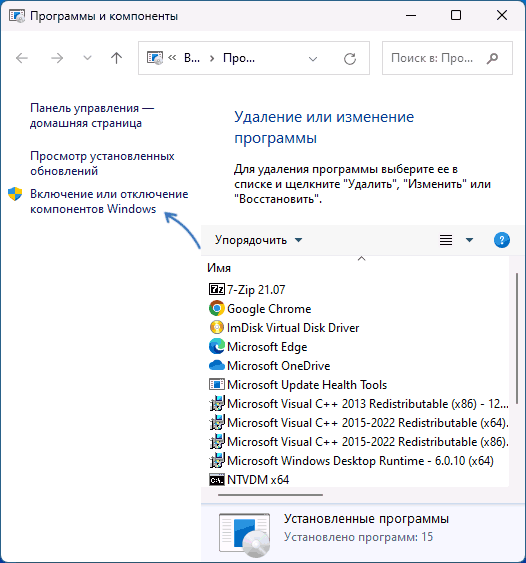
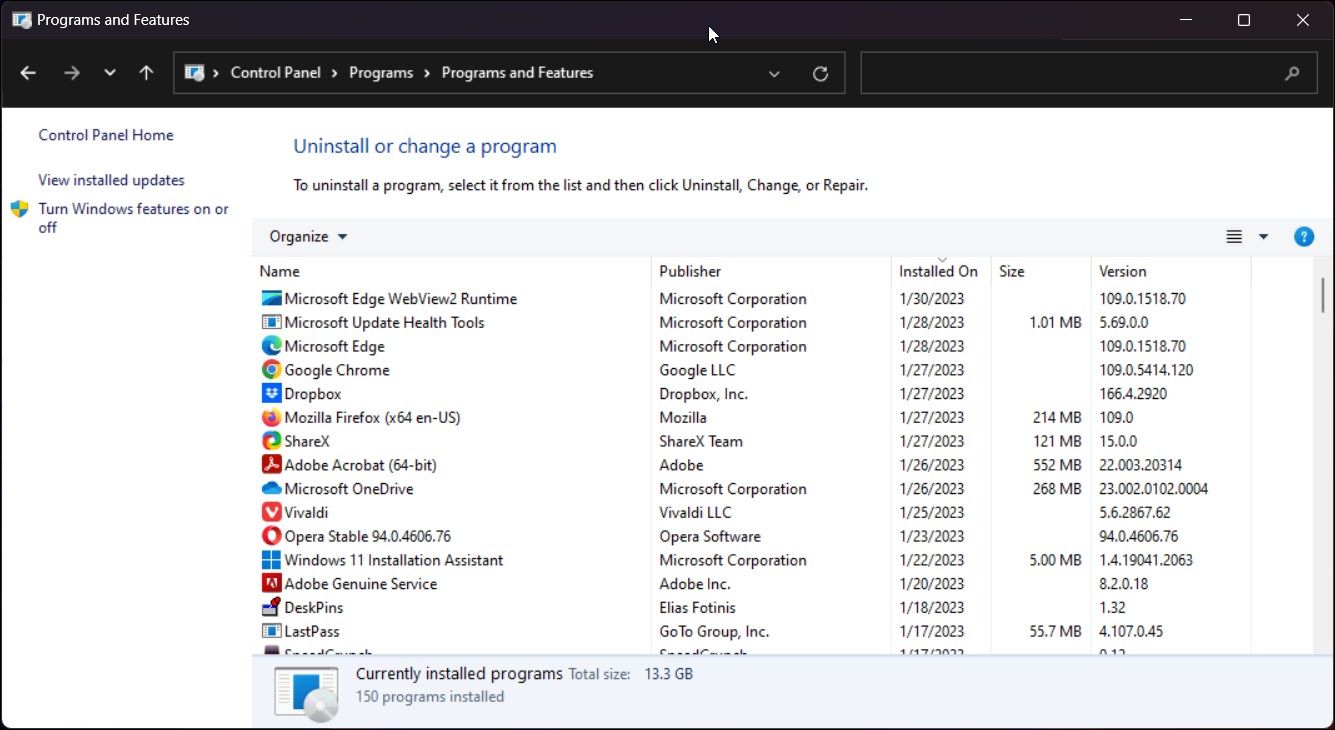
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре (либо нажмите правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке «Пуск» и выберите пункт «Выполнить»), введите appwiz.cpl и нажмите Enter.
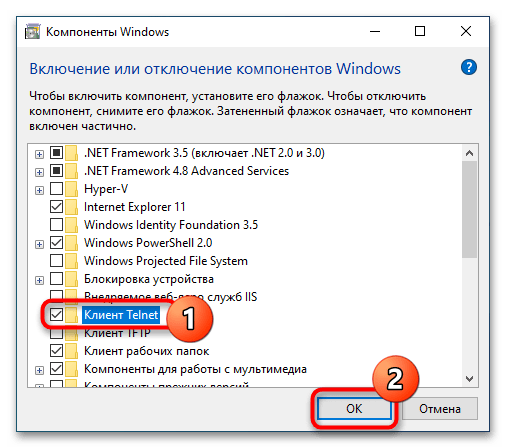
- В открывшемся окне в панели слева нажмите по пункту «Включение или отключение компонентов Windows».
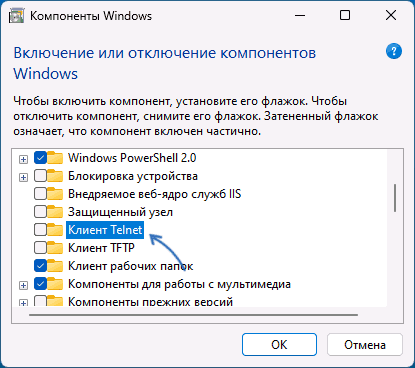
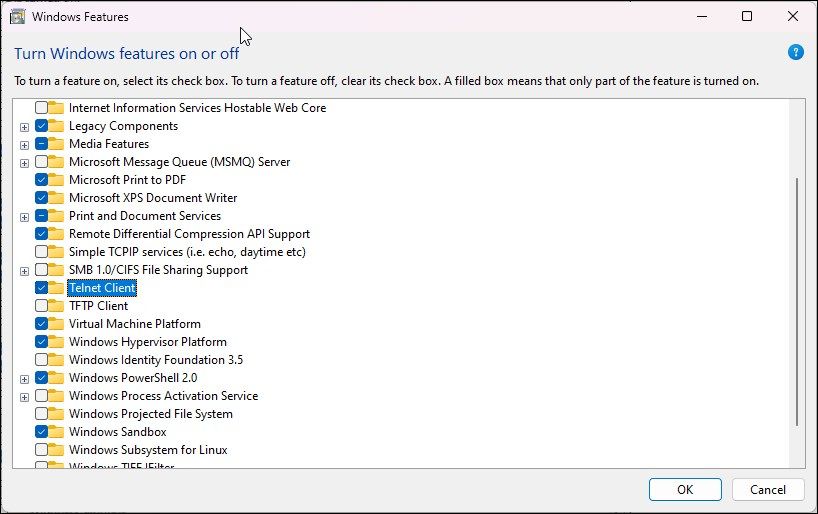
- Отметьте «Клиент Telnet» в списке доступных компонентов и нажмите «Ок».
Останется дождаться, когда клиент Telnet будет установлен.
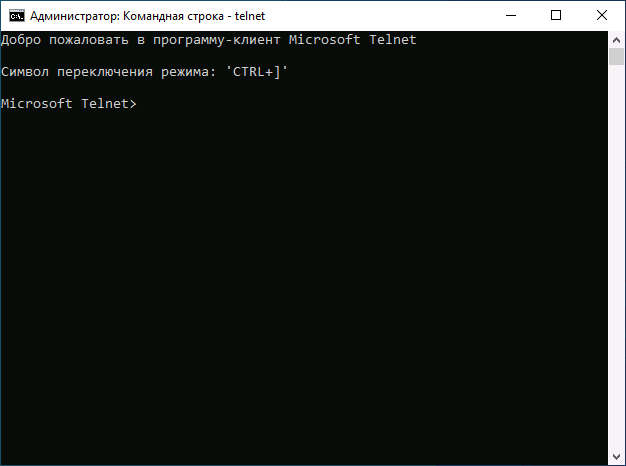
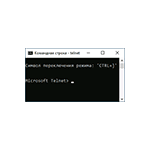
Для начала использования достаточно будет запустить командную строку, ввести команду telnet и нажать Enter.
Командная строка
Вы можете включить Telnet в командной строке, установив компонент с помощью DISM:
- Запустите командную строку от имени администратора.
- Введите команду
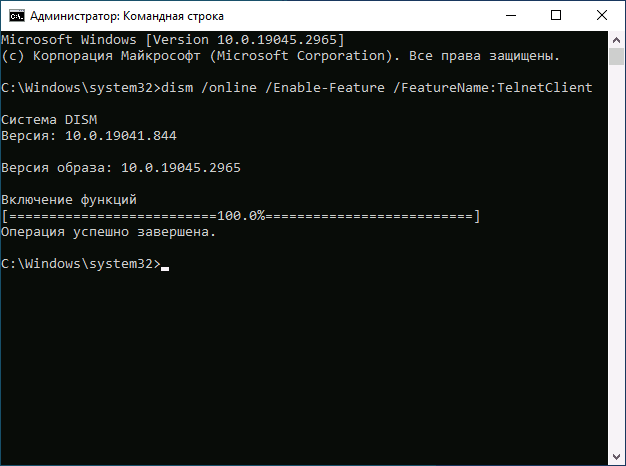
dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
и нажмите Enter.
- Дождитесь завершения установки компонента.
Windows PowerShell
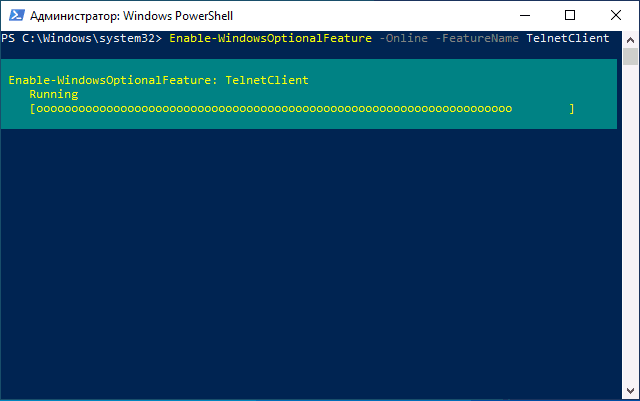
Включить компонент можно и в PowerShell: запустите Windows PowerShell или Терминал Windows от имени администратора, сделать это можно в контекстном меню кнопки «Пуск», после чего введите команду:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName TelnetClient
и нажмите Enter. Через короткое время клиент Telnet будет установлен на вашем компьютере.
Завершая статью, поинтересуюсь: для какой цели вам потребовался именно Telnet клиент в наше время SSH, шифрования и защищенных протоколов? Будет отлично, если вы сможете поделиться этим в комментариях.
Содержание
- Способ 1: «Программы и компоненты»
- Способ 2: «Командная строка / «Windows PowerShell»»
- Вопросы и ответы
В настоящее время протокол Telnet является устаревшим. Использовать его для удаленного управления компьютером небезопасно, поскольку весь трафик передается в незашифрованном виде. В современных версиях Windows вместо протокола Telnet рекомендуется использовать защищенный протокол SSH.
Способ 1: «Программы и компоненты»
Это самый простой и очевидный способ задействовать компонент «Telnet», предназначенный для удаленного управления компьютером. Чтобы открыть оснастку «Программы и компоненты», сделайте следующее:
- Вызовите нажатием Win + R окошко быстрого выполнения команд, вставьте в него команду
optionalfeaturesи нажмите клавишу ввода. Также открыть оснастку можно через приложение «Параметры», перейдя в раздел «Приложения и возможности» → «Дополнительные компоненты» → «Другие компоненты Windows». - Отыщите в открывшемся окне оснастки пункт «Клиент Telnet», отметьте его флажком и нажмите кнопку «OK».
- Windows 10 выполнит поиск необходимых файлов и установит их.
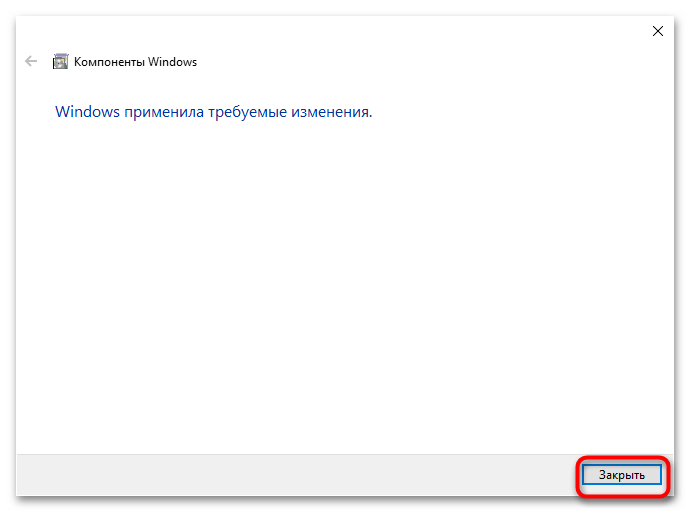
Если Windows попросит перезагрузить компьютер, дайте согласие на перезагрузку.
Способ 2: «Командная строка / «Windows PowerShell»»
Для включения устаревшего клиента «Telnet» можно задействовать классическую «Командную строку» либо же консоль «PowerShell».
- Запустите ту или иную консоль от имени администратора любым удобным вам способом. Например, из контекстного меню кнопки «Пуск».
- Вставьте или введите в консоль команду
dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClientи нажмите клавишу ввода.
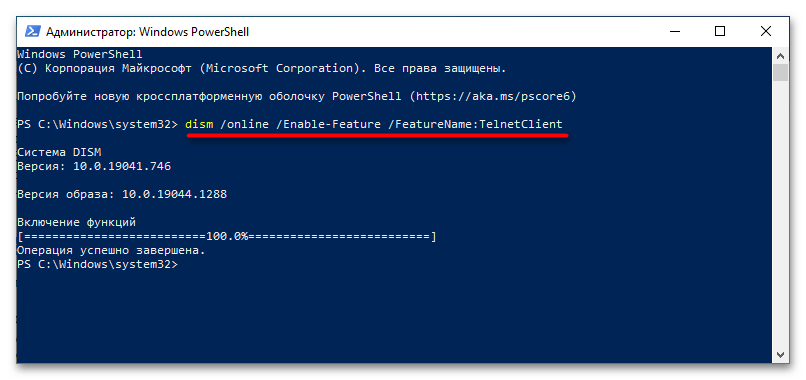
В случае удачного включения компонента команда вернет сообщение «Операция успешно завершена».
Еще статьи по данной теме:
Помогла ли Вам статья?
В данной статье показаны действия, с помощью которых можно включить компонент Telnet Client в операционной системе Windows 10, Windows 8.1 и Windows 7.
Telnet (teletype network) — сетевой протокол с помощью которого можно удаленно (через интернет или локальную сеть) подключиться и управлять различными сетевыми устройствами, например удаленные компьютеры, серверы, роутеры и другие устройства.
По умолчанию компонент Telnet Client в операционных системах Windows 10, Windows 8.1 и Windows 7 отключён, но при необходимости можно легко включить его используя любой из способов, которые представлены далее в этой инструкции.
Содержание
- Включение Telnet Client в окне «Компоненты Windows»
- Активация в командной строке
- Включение через Windows PowerShell
Включение Telnet Client в окне «Компоненты Windows»
Чтобы включить компонент Telnet Client, нажмите сочетание клавиш + R, в открывшемся окне Выполнить введите (скопируйте и вставьте) OptionalFeatures и нажмите клавишу Enter↵.
В открывшемся окне «Компоненты Windows» установите флажок компонента Telnet Client и нажмите кнопку OK.
Через непродолжительное время Windows применит требуемые изменения и компонент Telnet Client будет включен.
Активация в командной строке
Вы можете включить или отключить компонент Telnet Client в командной строке используя DISM
Чтобы включить компонент Telnet Client, запустите командную строку от имени администратора и выполните следующую команду:
Dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
Чтобы отключить компонент Telnet Client, запустите командную строку от имени администратора и выполните следующую команду:
Dism /online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
Включение через Windows PowerShell
Также включить или отключить компонент Telnet Client можно в консоли PowerShell
Чтобы включить компонент Telnet Client, откройте консоль Windows PowerShell от имени администратора и выполните следующую команду:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature –FeatureName «TelnetClient» -Online
Чтобы отключить компонент Telnet Client, откройте консоль Windows PowerShell от имени администратора и выполните следующую команду:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature –FeatureName «TelnetClient» -Online
После включения компонента Telnet Client можно использовать утилиту telnet для выполнения необходимых задач.
Если компонент Telnet Client отключен, то при вводе команды telnet в консоли командной строки вы увидите сообщение о том что:
«telnet» не является внутренней или внешней
командой, исполняемой программой или пакетным файлом.
Используя рассмотренные выше действия, можно включить или отключить компонент Telnet Client в операционной системе Windows 10, Windows 8.1 и Windows 7
The Telnet protocol is capable of remotely managing network devices or computers over LAN or WAN. It is still popular today because it was one of the first protocols used with the launch of the Internet in 1969.
What is Telnet?
Telnet is an abbreviation of “teletype network”, “terminal network” or “telecommunications network”.
TELecommunication NETwork is one of the oldest protocols on the Internet, extends to the time of ARPANET and is used to connect to a remote computer over the Network so that the client computer acts as a terminal connected to the remote computer.
All it takes is a Telnet client. Using pre-web computing terminology, we can say that a client is actually a teleprocessor terminal emulation program adapted to the Internet system, that is, the TCP / IP protocol.
Introduction to the Protocol
Telnet is a standard Internet protocol that allows terminals and applications to connect to the Internet. The protocol provides basic rules that allow a client (a system consisting of a screen and keyboard) to connect with a command interpreter (on the server-side). It is implemented over a TCP connection to send data in an 8-bit encoded ASCII format with verification sequences between them. Thus, it provides an easy-to-implement 8-bit coded, bidirectional (half-duplex) communication system.
This protocol is used to configure remote hosts. So, for example, you use Serial Cable to initially configure a Cisco Router, and then you can configure this protocol remotely from the local or remote network without being next to this device.
Telnet protocol is based on three basic concepts:
- Virtual Network Terminal (NVT) paradigm.
- The principle of options negotiated.
- The trading rules.
This is a basic protocol to which other protocols of the TCP/IP set (FTP, SMTP, POP3, etc.) are implemented. It does not mention authentication because it is completely separate from the applications that use it. Also, it is not a secure data transfer protocol because the data it transmits travels over the network as unencrypted text. Port 23 is assigned to this protocol when it is used to connect the remote host to a computer running as a server.
Apart from the associated options and negotiation rules, these protocol features are essential. Data transmission consists of only byte transmission in the TCP stream. When byte 255 is transmitted, the next byte should be interpreted as a command. Therefore, byte 255 is called IAC (Interpret as Command).
The basic features of the Telnet protocol are available in RFC 854.
How Does It Work?
To use Telnet, it is very important to note that its client has two ways to work: Command mode and normal use mode. Command mode allows you to use a series of commands that affect the operating mode, including connection and disconnection.
These commands include:
- CLOSE: Closes the Telnet connection to the remote computer and returns to command mode (if started in command mode) or closes the application.
- QUIT: Sign out of the Telnet session. If you are connected to a remote computer, this command closes the connection and then the application.
- SET ECHO: If we cannot see what we are writing or, on the contrary, we double it, this command corrects the situation.
- OPEN: This command establishes a connection to a remote computer.
In normal mode, our equipment behaves like the keyboard of the computer we connect to. Each keystroke is sent to the remote device, and what we see on the screen is the echo that the remote equipment actually sends to us in response to this signal.
When you are in normal mode and want to go into command mode (for example, to end the session using QUIT), you must send the escape character. In turn, we are in command mode and if we press CR or Enter, we exit the mode and return to normal mode.
Telnet only serves terminal mode, i.e. without graphics access, but it is a very useful tool for remotely correcting errors without having to be physically in the same place as the machine they own. In addition, personal data on machines accessible by the Internet were used to consult data such as bibliographic information remotely.
Apart from these uses, in general, Telnet was used to log in with a UNIX machine (and it can still be used in the SSH variant today), so multiple users who have an account on the machine, connect, login and work using this machine. It is a very usual way of working with UNIX systems.
Details
Given the above, the first action for Telnet on a remote system would be to connect (“Login”). The client program initiates a negotiation with the host that we want to access the negotiation involving the creation of certain methods and features of the transmission/service to be used. For this, it is necessary to provide the customer with a few initial data that you need to know:
- Name: Refers to the server’s IP Address numerically or URL form. For example 192.168.0.1.
- Port Number: Specifies the service you want to access on the server. An address with an additional port number allows access to not only the remote computer but also to a particular service or program within it. Unless otherwise stated, the default number is 23 (normally used to connect to a user access account). During connection, the number can be added after the name or in a separate box, depending on the program.
- Terminal Type: Terminal identification is a contract used by both the client machine and the server with reference to the specific features and queues to be used. In this way, a virtual terminal is used regardless of what the physically used terminal actually is. From the customer’s point of view, identification should be done in two parts.
- a: It is shown to the client program, which acts as a particular type of virtual terminal.
In MS Telnet v.1.0, this is done in Terminal Preferences Emulation. You can choose two types: 52 and 100 / ANSI.
- b: Sets what type of terminal we will use on the server. This is a string of characters that is sent to the host during the connection negotiation.
In MS Telnet v.1.0, it is specified in the Connect, Remote system, Terminal type section. The available options are typical character strings (the most standard is VT100) that a host expects during this call.
- Login: In some services, login and password are not required because the server does not require them for that service.
- Password: The password that authenticates the user. You can enter your own e-mail address for general services that accept guests (visiting users).
- Log-Off: The last step at the end of a session on a remote system is to log out before physical connection is interrupted, so as not to leave a session open indefinitely on the host computer (it always consumes system resources). The concrete form depends on the system. There are no fixed rules, but on some systems, at the entrance, along with a welcome message, the appropriate word for disconnection is indicated. Usually, it is one of the following:
BYE, LOGOFF, LOGOUT, QUIT, END, EXIT, STOP. CLOSE first, the escape sequence comes. ABORT, escape sequence before (Use as a last resort).
Both Unix and Windows have their own clients: Telnet.exe. In the case of Windows, you can find it in the C: \ Windows directory. This program has Telnet.chm, a good help file with all the details necessary for its operation.
The usual thing is that it involves connecting with large computers (hosts, hosts, servers, etc.), at companies, universities, research centers and similar sites (usually Unix machines). Therefore, it is not a problem to connect to the neighbor’s computer over the Internet (there are other types of tools for this). The reason for the connection is not Web services, from a researcher who wants to continue the workday away from home, to a user who only requests service on a host that can be accessed this way.
The first idea to consider is not to connect to a PC, as we said, but to huge machines with dozens, sometimes hundreds of users. For security reasons, nobody can access these systems. The process is done by granting a right (access account) issued by the system administrator, which expresses a wide range of conditions.
For example, the dates and times we can connect; directories we can visit/use; if we can register for them or just read; how much information we can save. To identify each user with an account opened in the system, a name (nickname) identifying the user or service and an access key (password) that authenticates are used.
It is important to know how to work with Telnet on a remote computer, after communication. There is no point in connecting to a remote machine without knowing the Operating System and the application program we should use to a minimum.
Security
For security reasons, there are three main reasons why Telnet is not recommended for modern systems:
- Telnet General Purpose Domains have several vulnerabilities that have been discovered over the years and still exist.
- Telnet does not encrypt data (including passwords) sent over the connection by default, so it’s easy to interfere and save communications and use the password for malicious purposes later.
- Telnet does not have an authentication scheme that allows communication between two desired hosts and is not interrupted.
SSH Issues
The biggest problem is security, as all the usernames and passwords required to enter the machines browse the Internet in Plain Text (unencrypted text strings). This makes it easy for anyone who spies on network traffic to get usernames and passwords so they can access all these machines. Therefore, SSH appeared almost a few years ago when it emerged and became popular as an encrypted version of Telnet – at the moment all protocol communications can be encrypted during session setup.
Where Not Used?
Telnet should not be used in environments where security is important, for example on the public internet, because sessions are not encrypted.
This means that anyone who has access to any Router, Switch, or Gateway on the Network between two hosts using Telnet can capture packets passing close by and easily get connection and password information with any of the few common ones, such as TCPDump and Wireshark.
These flaws resulted in the rapid abandonment and depreciation of the Telnet protocol in favor of a safer and functional protocol called SSH launched in 1995. SSH provides all the functionality available in Telnet and strong encryption is added to prevent data sensitivity.
Computer security experts such as the SANS Institute and members of the comp.os.linux.security newsgroup recommends stopping Telnet usage for remote connections under all normal conditions.
When Telnet was first developed in 1969, the majority of Internet computer users were in the computer services of academic institutions or large private and government research facilities. Security was not a cause for concern in this environment, and only after the explosion of the 90’s bandwidth was a cause for concern. It may not be recommended to use Telnet in networks with an Internet connection, by multiplying the number of people with Internet access and by the number of people trying to break other people’s servers.
Nowadays
Today, this protocol is also used to access BBSs that was initially only accessible via a modem via a telephone line. To access BBS over Telnet, the Client must support ANSI graphics and file transfer protocols. ANSI charts are widely used among BBS. With file transfer protocols (the most common and best employee is ZModem), you can send and receive files from the BBS, whether it’s a program, a game, or a BBS (local mail, mail from FidoNet).
Some Telnet clients; (Supporting ANSI graphics and file transfer protocols such as Zmodem and others) mTelnet !, NetRunner, Putty, Zoc.
You can configure all network devices using the TCP/IP protocol with this protocol. In addition, a user name and password are required when connecting to a remote device.
When you transfer data with this protocol, it is an unsafe protocol because of your data sends as Clear Text. Instead of using Telnet over the network, SSH protocol is preferred.
How to Use It?
To use telnet, it must first be enabled on a host to be managed. After you enable it, you can easily connect to your remote host via the TCP 23 port with Command Prompt (CMD).
There are two different structures to use/configure the Telnet protocol. These; Server and Client. If you configure a server, you must install or activate the Client service to connect to it remotely.
After the definition of Telnet, now let’s examine how to use Telnet in Windows 10.
In this article, after enabling Telnet Client, we will provide a connection to the active Telnet Server on the ADSL Router.
How to Enable Telnet on Windows 10
You can easily enable and use it on Microsoft Win XP, Vista, 7, 8, 8.1, and 10 operating systems.
Follow the steps below to activate/install the Telnet Client.
Step 1
Right-click on the Start menu, and then click Programs and Features.
Step 2
In the Programs and Features, click Turn Windows features on or off.
Step 3
When the Windows features open or close window opens, select the Telnet Client option.
Step 4
After selecting the Client option, press the OK button.
Step 5
Applying changes to your system …
Step 6
After installing the service, click on the Close button.
Step 7
Open the Run by pressing the Windows Key + R together, type “cmd” and press the Enter key. After running the CMD prompt, type “telnet” at the command prompt and press Enter to start this service.
Step 8
After you see the welcome message, you can see that it works successfully.
Step 9
Now, type O (o) at the CMD prompt to connect to the ADSL Router on the local area network and press Enter.
Step 10
Type your default gateway IP address to access the ADSL Modem and press Enter.
Step 11
When you look at the image below, you can see a successful connection to an ADSL router using CMD.
How to Enable it using CMD
Another way to enable this service is to use the CMD command prompt. You can enable or disable it by using the CMD command prompt.
The DISM command is used on the CMD to activate the client. Execute the command below to install Telnet with CMD on the Windows operating system.
dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
How to Disable it using CMD
Use the following command to disable/remove Telnet.
dism /online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
How to Use it on PC ⇒ Video
You can watch the video below to configure the teletype network on your computer and also subscribe to our YouTube channel to support us.
Final Word
In this article, we have defined the Telnet protocol used to manage remote devices in Windows operating systems and then enabled it. Thanks for following us!
Related Articles
♦ How to Install Net Framework 3.5
♦ How to Activate Windows Photo Viewer
♦ How to Use Ping in CMD
♦ How to Use Windows Experience Index Software
♦ Windows 10 Brightness Not Working
Here’s how to get Telnet up and running on Windows 10 and 11.
Despite the vulnerability issues, Telnet is still used as a client-server protocol by Windows users. It is primarily used for initial network hardware configuration, remote access, port testing and forwarding, and other tasks that don’t involve sensitive information transfer.
You can enable Telnet on Windows 10 and 11 computers via Command Prompt or the Graphics User Interface (GUI) tool. Here we show you the many ways to enable Telnet on your Windows computer.
1. Enable Telnet on Windows Using Control Panel
You can enable Telnet Client using the Classic Control Panel. Since it is an optional feature, you can enable it using the Windows Optional Feature dialog. You can use it add or remove other users’ optional features on Windows.
To enable Telnet Client using Control Panel:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type control and click OK to open Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, Click on Uninstall a Program under Programs and Features.
- In the left pane, click on the Turn Windows feature on or off.
- In the Windows Features dialog, scroll down and select Telnet Client.
- Click OK and wait for the feature to install. Once installed, restart your PC to apply the changes and enable the feature.
If you need to disable Telnet:
- Open the Windows Features dialog and unselect Telnet Client.
- Click OK and wait for the feature to uninstall.
- Click on Restart now to reboot your PC and apply the changes.
2. Enable Telnet Client Using Windows PowerShell
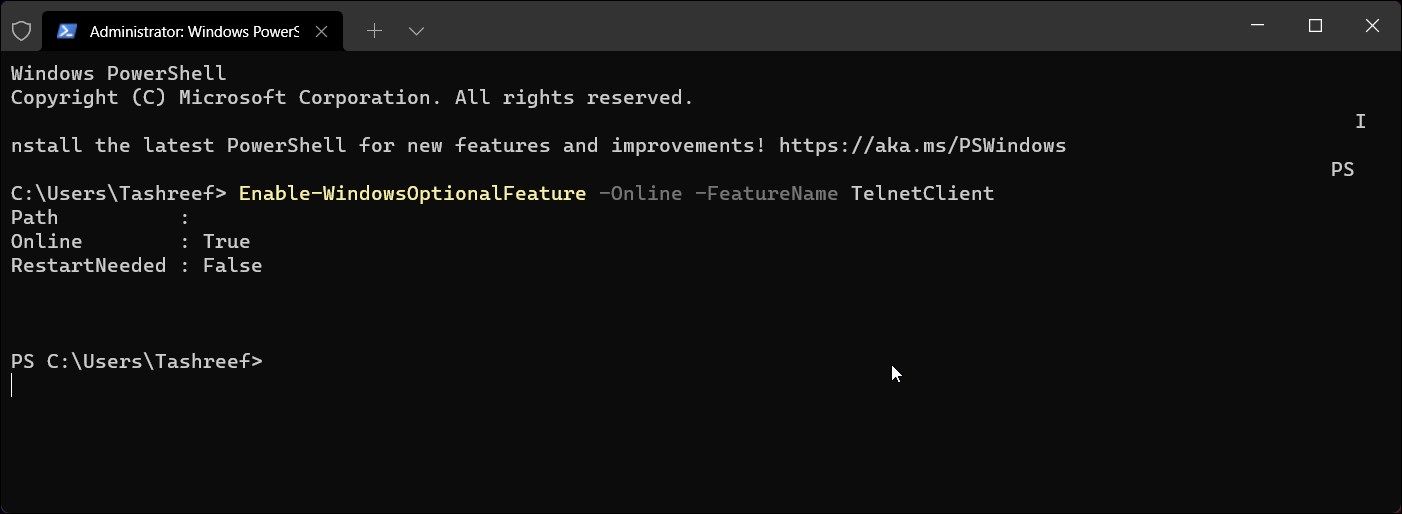
You can use the Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature cmdlet to enable Telnet Client using Windows PowerShell. Useful if you are unable to turn on the feature using the Windows Features dialog and it is also faster than the GUI method.
To enable Telnet using Windows PowerShell:
- Press Win + X to open the WinX menu.
- Click on Windows Terminal(Admin) and click Yes to open the terminal app as administrator. If you are using Windows 10, type PowerShell in Windows Search and open Windows PowerShell administrator.
- In the PowerShell window, type the following command and press Enter to enable Telnet:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName TelnetClient - This process may take several minutes, so wait for it to complete and return a status report. If successful, you’ll see the result as Online:True.
- If you want to disable Telnet Client, use the following command instead:
Disable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName TelnetClient - Close PowerShell and restart your PC.
3. Install Telnet Client Using Command Prompt
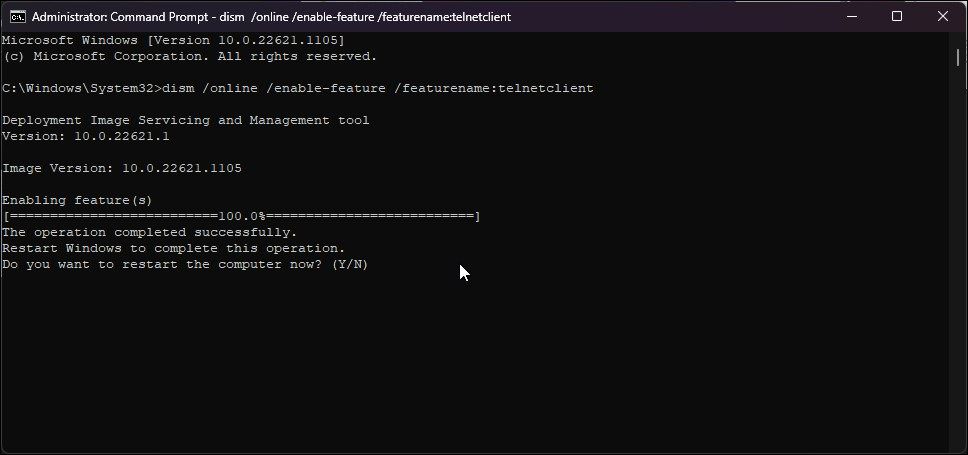
If you prefer Command Prompt over PowerShell, you can use the DISM /Online command to enable the optional features on your Windows 11 computer.
Follow these steps to install Telnet using Command Prompt:
- Press the Win key and type cmd.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient - Command Prompt will start enabling the feature and display the operation completed successfully message.
- If you need to disable Telnet, type the following command and press Enter:
dism /Online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient - Wait for the success message.
- Type exit and press Enter to close Command Prompt.
How to Check the Telnet Client Status on Your PC
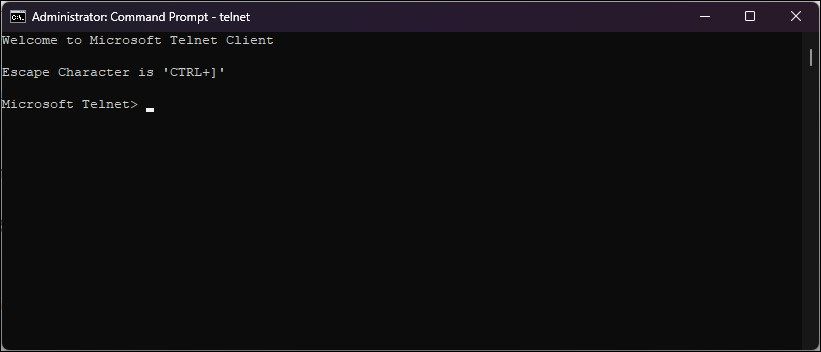
You can check if the Telnet client is enabled on your PC using a Command Prompt command. When enabled, the Telnet command will open a new CMD to connect to remote servers and perform other tasks.
- Launch Command Prompt as administrator (see how to run the Command Prompt as an administrator for in-depth steps).
- In the Command Prompt window, type Telnet and press Enter.
- A new CMD with Microsoft Telnet will open.
All the Ways to Enable Telnet On Your Windows 11 Computer
Telnet is a built-in remote access utility that you can use to troubleshoot firewall and network issues. While it is still part of Windows, system administrators now prefer the more secure SSH protocol to access computers over an unsecured network.
The major disadvantage of Telnet is that it is not secure and prone to a man-in-the-middle attack. If not for particular situations, switch to a more secure network protocol such as SSH and Mosh with better password and public key authentication.