PostgreSQL — это бесплатная объектно-реляционная СУБД с мощным функционалом, который позволяет конкурировать с платными базами данных, такими как Microsoft SQL, Oracle. PostgreSQL поддерживает пользовательские данные, функции, операции, домены и индексы. В данной статье мы рассмотрим установку и краткий обзор по управлению базой данных PostgreSQL. Мы установим СУБД PostgreSQL в Windows 10, создадим новую базу, добавим в неё таблицы и настроим доступа для пользователей. Также мы рассмотрим основы управления PostgreSQL с помощью SQL shell и визуальной системы управления PgAdmin. Надеюсь эта статья станет хорошей отправной точкой для обучения работы с PostgreSQL и использованию ее в разработке и тестовых проектах.
Содержание:
- Установка PostgreSQL 11 в Windows 10
- Доступ к PostgreSQL по сети, правила файерволла
- Утилиты управления PostgreSQL через командную строку
- PgAdmin: Визуальный редактор для PostgresSQL
- Query Tool: использование SQL запросов в PostgreSQL
Установка PostgreSQL 11 в Windows 10
Для установки PostgreSQL перейдите на сайт https://www.postgresql.org и скачайте последнюю версию дистрибутива для Windows, на сегодняшний день это версия PostgreSQL 11 (в 11 версии PostgreSQL поддерживаются только 64-х битные редакции Windows). После загрузки запустите инсталлятор.
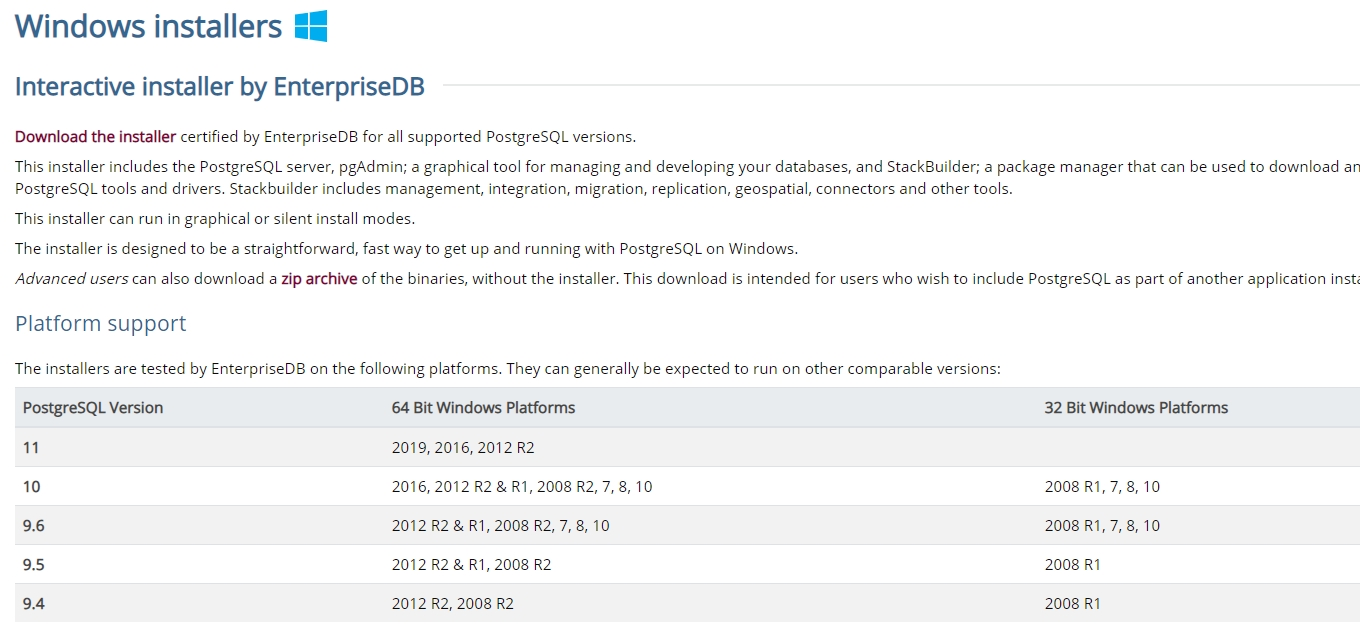
В процессе установки установите галочки на пунктах:
- PostgreSQL Server – сам сервер СУБД
- PgAdmin 4 – визуальный редактор SQL
- Stack Builder – дополнительные инструменты для разработки (возможно вам они понадобятся в будущем)
- Command Line Tools – инструменты командной строки
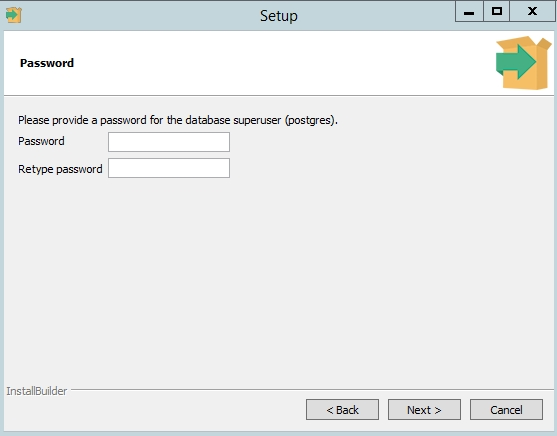
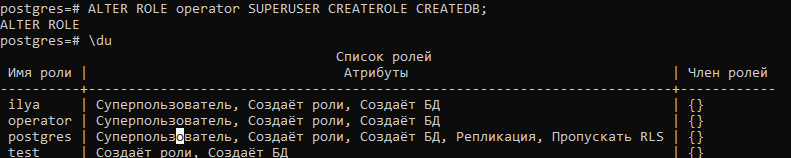
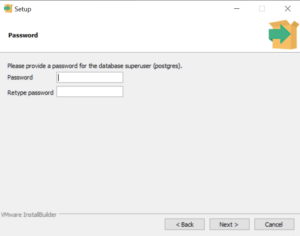
Установите пароль для пользователя postgres (он создается по умолчанию и имеет права суперпользователя).
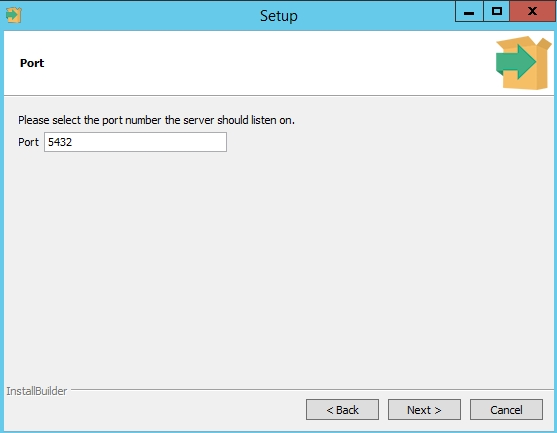
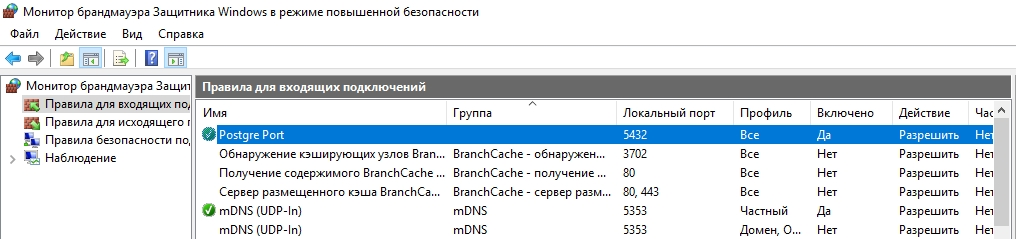
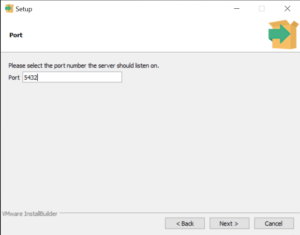
По умолчание СУБД слушает на порту 5432, который нужно будет добавить в исключения в правилах фаерволла.
Нажимаете Далее, Далее, на этом установка PostgreSQL завершена.
Доступ к PostgreSQL по сети, правила файерволла
Чтобы разрешить сетевой доступ к вашему экземпляру PostgreSQL с других компьютеров, вам нужно создать правила в файерволе. Вы можете создать правило через командную строку или PowerShell.
Запустите командную строку от имени администратора. Введите команду:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Postgre Port" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=5432
- Где rule name – имя правила
- Localport – разрешенный порт
Либо вы можете создать правило, разрешающее TCP/IP доступ к экземпляру PostgreSQL на порту 5432 с помощью PowerShell:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name 'POSTGRESQL-In-TCP' -DisplayName 'PostgreSQL (TCP-In)' -Direction Inbound -Enabled True -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 5432
После применения команды в брандмауэре Windows появится новое разрешающее правило для порта Postgres.
Совет. Для изменения порта в установленной PostgreSQL отредактируйте файл postgresql.conf по пути C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\11\data.
Измените значение в пункте
port = 5432
. Перезапустите службу сервера postgresql-x64-11 после изменений. Можно перезапустить службу с помощью PowerShell:
Restart-Service -Name postgresql-x64-11
Более подробно о настройке параметров в конфигурационном файле postgresql.conf с помощью тюнеров смотрите в статье.
Утилиты управления PostgreSQL через командную строку
Рассмотрим управление и основные операции, которые можно выполнять с PostgreSQL через командную строку с помощью нескольких утилит. Основные инструменты управления PostgreSQL находятся в папке bin, потому все команды будем выполнять из данного каталога.
- Запустите командную строку.
Совет. Перед запуском СУБД, смените кодировку для нормального отображения в русской Windows 10. В командной строке выполните:
chcp 1251 - Перейдите в каталог bin выполнив команду:
CD C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\11\bin
Основные команды PostgreSQL:
PgAdmin: Визуальный редактор для PostgresSQL
Редактор PgAdmin служит для упрощения управления базой данных PostgresSQL в понятном визуальном режиме.
По умолчанию все созданные базы хранятся в каталоге base по пути C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\11\data\base.
Для каждой БД существует подкаталог внутри PGDATA/base, названный по OID базы данных в pg_database. Этот подкаталог по умолчанию является местом хранения файлов базы данных; в частности, там хранятся её системные каталоги. Каждая таблица и индекс хранятся в отдельном файле.
Для резервного копирования и восстановления лучше использовать инструмент Backup в панели инструментов Tools. Для автоматизации бэкапа PostgreSQL из командной строки используйте утилиту pg_dump.exe.
Query Tool: использование SQL запросов в PostgreSQL
Для написания SQL запросов в удобном графическом редакторе используется встроенный в pgAdmin инструмент Query Tool. Например, вы хотите создать новую таблицу в базе данных через инструмент Query Tool.
- Выберите базу данных, в панели Tools откройте Query Tool
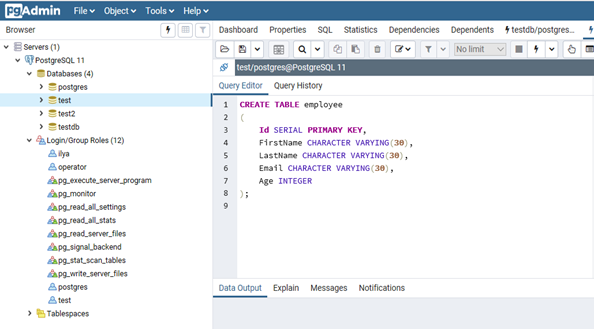
- Создадим таблицу сотрудников:
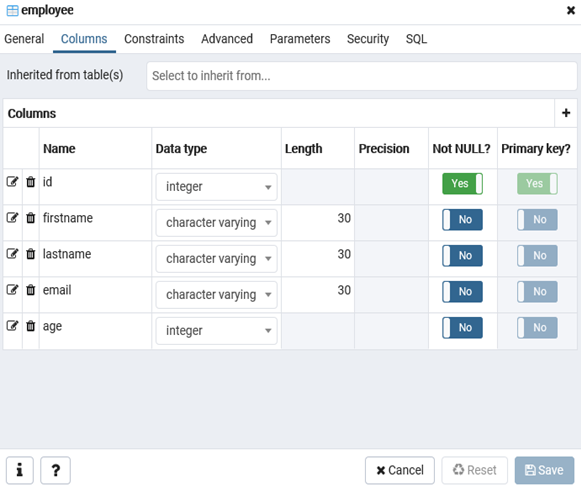
CREATE TABLE employee
(
Id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName CHARACTER VARYING(30),
LastName CHARACTER VARYING(30),
Email CHARACTER VARYING(30),
Age INTEGER
);
Id — номер сотрудника, которому присвоен ключ SERIAL. Данная строка будет хранить числовое значение 1, 2, 3 и т.д., которое для каждой новой строки будет автоматически увеличиваться на единицу. В следующих строках записаны имя, фамилия сотрудника и его электронный адрес, которые имеют тип CHARACTER VARYING(30), то есть представляют строку длиной не более 30 символов. В строке — Age записан возраст, имеет тип INTEGER, т.к. хранит числа.
После того, как написали код SQL запроса в Query Tool, нажмите клавишу F5 и в базе будет создана новая таблица employee.
Для заполнения полей в свойствах таблицы выберите таблицу employee в разделе Schemas -> Tables. Откройте меню Object инструмент View/Edit Data.
Здесь вы можете заполнить данные в таблице.
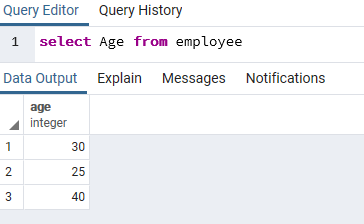
После заполнения данных выполним инструментом Query простой запрос на выборку:
select Age from employee;
PostgreSQL — система управления базами данных с открытым исходным кодом, которая объединяет возможности объектно-ориентированных и реляционных подходов к хранению данных. Она обладает высокой мощностью и расширяемостью, а также поддерживает множество функций и возможностей. PostgreSQL поддерживает множество функций, включая поддержку транзакций, поддержку хранимых процедур и триггеров, полнотекстовый поиск, геопространственные данные, JSON и многое другое. PostgreSQL также обеспечивает высокую производительность и надежность, благодаря своей архитектуре и технологиям многопоточности. Установка PostgreSQL не является сложной задачей и следуя приведенным ниже шагам вы сможете успешно установить её самостоятельно.
Загрузка установочного дистрибутива
Первым шагом в установке PostgreSQL является загрузка установочного файла. Вы можете загрузить установочный файл с официального сайта «www.postgresql.org/download/windows», выбрав соответствующую версию для вашей операционной системы.
Запуск установки
После загрузки установочного файла запустите его. При запуске установки вы увидите окно приветствия, где нужно нажать кнопку «Next».
Выбор места установки приложения
На следующем экране вы должны выбрать директорию, в которую будет установлен PostgreSQL. По умолчанию директория установки – “C:\Program Files\PostgreSQL\”, но вы можете изменить ее на любую другую директорию.
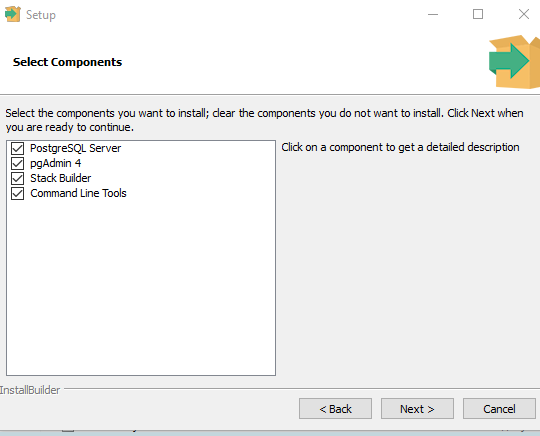
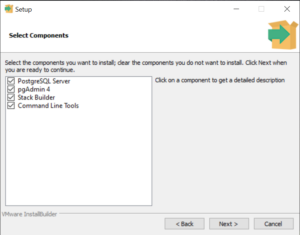
Выбор компонентов
На следующем экране вы можете выбрать компоненты, которые вы хотите установить. По умолчанию выбраны все компоненты, но можно изменить этот выбор в соответствии с вашими потребностями. В данном случае выберем базовые компоненты:
- непосредственно саму СУБД;
- графическую утилиту администрирования pgAdmin 4;
- утилиты администрирования через командную строку.
Установка параметров
На следующем экране нужно ввести пароль для учетной записи по умолчанию PostgreSQL. Этот пароль будет использоваться для доступа к базе данных PostgreSQL.
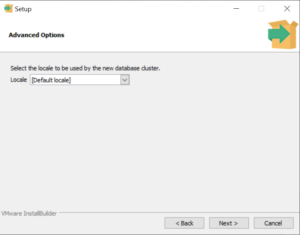
Кроме пароля инсталлятор спросит, на каком порту будет работать приложение, а также локаль, всё оставим по умолчанию :
Запуск установки
После того как вы ввели все необходимые параметры, нажмите кнопку «Next». Установка PostgreSQL может занять некоторое время, в зависимости от технических характеристик сервера.
Завершение установки
После завершения установки вы увидите окно с сообщением об успешной установке PostgreSQL. Нажмите кнопку «Finish», чтобы закрыть установщик.
Проверка работоспособности
После успешной установки PostgreSQL можно проверить работу базы данных, запустив графическую утилиту PgAdmin 4. Выбираем из списка наш сервер и вводим пароль от пользователя администратор, который придумали ранее при установке:
Если все настроено правильно, вы увидите список объектов на локальном сервере. Теперь можно сделать SQL-запрос для вывода установленной версии. Для этого правой кнопкой мыши кликнем по БД postgres и выберем инструмент «Query Tool».
В правой части экрана в поле «Query» вводим:
SELECT version();
И нажимаем «Run». В результате получим примерно как на скрине ниже:
Это позволит убедиться, что база данных работает корректно и готова к использованию в ваших проектах и приложениях.
Заключение
Придерживаясь указанных инструкций, вы легко установите PostgreSQL и сможете использовать его для своих проектов и приложений. Не забывайте регулярно обновлять PostgreSQL и следить за безопасностью вашей базы данных.
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
Before You Start
Before you start, you should confirm that you don’t already have psql installed. In fact, if you’ve ever installed Postgres or TimescaleDB before, you likely already have psql installed.
psql --versionInstall on MacOS Using Homebrew
First, install the Brew Package Manager.
Second, update brew. From your command line, run the following commands:
brew doctor
brew update
brew install libpqFinally, symlink psql (and other libpq tools) into /usr/local/bin:
brew link --force libpqInstall on Ubuntu 16.04,18.04 and Debian 9,10
Install on Ubuntu and Debian using the apt package manager:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install postgresql-clientNote: This only installs the psql client and not the PostgreSQL database.
Install Windows 10
We recommend using the installer from PostgreSQL.org.
Last Step: Connect to Your PostgreSQL Server
Let’s confirm that psql is installed:
psql --versionNow, in order to connect to your PostgreSQL server, we’ll need the following connection params:
- Hostname
- Port
- Username
- Password
- Database name
There are two ways to use these params.
Option 1:
psql -h [HOSTNAME] -p [PORT] -U [USERNAME] -W -d [DATABASENAME]Once you run that command, the prompt will ask you for your password. (Which we specified with the -W flag.)
Option 2:
psql postgres://[USERNAME]:[PASSWORD]@[HOSTNAME]:[PORT]/[DATABASENAME]?sslmode=requireAnd this is how they look in the Timescale UI:
Congrats! Now you have connected via psql.
If you haven’t yet, you can head over to our documentation page and find out more about TimescaleDB, our open-source extension that makes PostgreSQL scalable.
Ingest and query in milliseconds, even at terabyte scale.
Установка и настройка postgresql на windows
Установка postgresql, настройка БД и ролей
1. Скачайте и установите postgresql (https://www.postgresql.org/download/windows/open in new window)
Запустите установщик
Нажмите «Next»
Выбираем директорию установки
Next
Выбираем компоненты для установки (выделить все)
Next
Установить место хранения базы данных
Next
Ввести пароль для пользователя postgres
Next
Порт по умолчанию 5432
Next
Установить локаль по умолчанию Russian, Russia
Next
Проверить все настройки, после чего нажать Next
Next
2. Запуск и настройка postgresql
Первоначально необходимо изменить конфигурационные файлы postgresql.conf и pg_hba.conf в директории, куда установлена база данных
postgresql.conf:
изменить
listen_addresses = ‘*’
Остальные настройки можно оставить по-умолчанию, либо изменить исходя из комплектации сервера
pg_hba_conf:
меняем права на доступ пользователей к базе:
IPv4 local connections:
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::0/0 md5
Это означает, что все пользователи со всех адресов могут подключиться к любой базе данных используя логин и пароль.
Сохраняем, перезапускаем службу postgresql:
нажимаем комбинацию Win+R
Вводим services.msc
Ищем службу и нажимаем «перезапустить»
После этого запускаем меню пуск — postgresql 11 — SQL bash (psql)
Все значения по-умолчанию, просто нажимаем enter, вводим пароль для пользователя postgres
Создаем базу данных:
create database demo_01;
Сразу создаем в базе схему stack
\c demo_01
create schema stack;
Создаем пользователей db_owner и SA, необходимых для работы базы данных и даем им все необходимые права суперюзера
create role db_owner;
create role «SA» with password ‘12345678’;
alter role «SA» superuser;
alter role «SA» createdb;
alter role «SA» createrole;
alter role «SA» replication;
alter role «SA» login;
аналогично для db_owner (без login)
После этого даем всем пользователям права на созданную базу данных
grant all privileges on database demo_01 to «SA»;
grant all privileges on database demo_01 to db_owner;
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to install PostgreSQL 14.7 on Windows 10.
The process is straightforward and consists of the following steps:
- Install PostgreSQL
- Configure Environment Variables
- Verify the Installation
- Download the Northwind PostgreSQL SQL file
- Create a New PostgreSQL Database
- Import the Northwind SQL file
- Verify the Northwind database installation
- Connect to the Database Using Jupyter Notebook
Prerequisites
- A computer running Windows 10
- Internet connection
- Download the official PostgreSQL 14.7 at https://get.enterprisedb.com/postgresql/postgresql-14.7-2-windows-x64.exe
- Save the installer executable to your computer and run the installer.
Note: We recommend version 14.7 because it is commonly used. There are newer versions available, but their features vary substantially!
Step 1: Install PostgreSQL
We’re about to initiate a vital part of this project — installing and configuring PostgreSQL.
Throughout this process, you’ll define critical settings like the installation directory, components, data directory, and the initial ‘postgres’ user password. This password grants administrative access to your PostgreSQL system. Additionally, you’ll choose the default port for connections and the database cluster locale.
Each choice affects your system’s operation, file storage, available tools, and security. We’re here to guide you through each decision to ensure optimal system functioning.
-
In the PostgreSQL Setup Wizard, click Next to begin the installation process.
-
Accept the default installation directory or choose a different directory by clicking Browse. Click Next to continue.
-
Choose the components you want to install (e.g., PostgreSQL Server, pgAdmin 4 (optional), Stack Builder (optional), Command Line Tools),no characters will appear on the screen as you type your password and click Next.
-
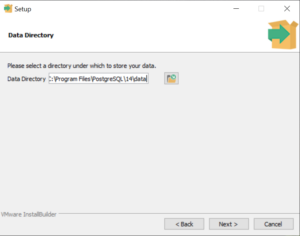
Select the data directory for storing your databases and click Next.
-
Set a password for the PostgreSQL “postgres” user and click Next.
-
There will be some points where you’re asked to enter a password in the command prompt. It’s important to note that for security reasons, as you type your password, no characters will appear on the screen. This standard security feature is designed to prevent anyone from looking over your shoulder and seeing your password. So, when you’re prompted for your password, don’t be alarmed if you don’t see any response on the screen as you type. Enter your password and press ‘Enter’. Most systems will allow you to re-enter the password if you make a mistake.
-
Remember, it’s crucial to remember the password you set during the installation, as you’ll need it to connect to your PostgreSQL databases in the future.
-
-
Choose the default port number (5432) or specify a different port, then click Next.
-
Select the locale to be used by the new database cluster and click Next.
-
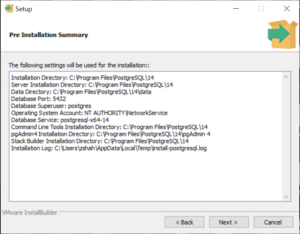
Review the installation settings and click Next to start the installation process. The installation may take a few minutes.
-
Once the installation is complete, click Finish to close the Setup Wizard.
Step 2: Configure Environment Variables
Next, we’re going to configure environment variables on your Windows system. Why are we doing this? Well, environment variables are a powerful feature of operating systems that allow us to specify values — like directory locations — that can be used by multiple applications. In our case, we need to ensure that our system can locate the PostgreSQL executable files stored in the «bin» folder of the PostgreSQL directory.
By adding the PostgreSQL «bin» folder path to the system’s PATH environment variable, we’re telling our operating system where to find these executables. This means you’ll be able to run PostgreSQL commands directly from the command line, no matter what directory you’re in, because the system will know where to find the necessary files. This makes working with PostgreSQL more convenient and opens up the possibility of running scripts that interact with PostgreSQL.
Now, let’s get started with the steps to configure your environment variables on Windows!
-
On the Windows taskbar, right-click the Windows icon and select System.
-
Click on Advanced system settings in the left pane.
-
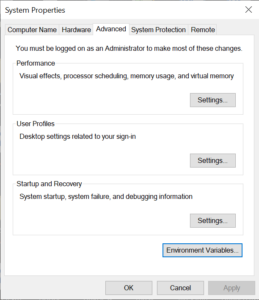
In the System Properties dialog, click on the Environment Variables button.
-
Under the System Variables section, scroll down and find the Path variable. Click on it to select it, then click the Edit button.
-
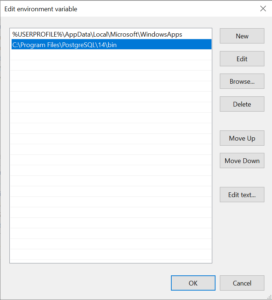
In the Edit environment variable dialog, click the New button and add the path to the PostgreSQL bin folder, typically
C:\\Program Files\\PostgreSQL\\14\\bin. -
Click OK to close the «Edit environment variable» dialog, then click OK again to close the «Environment Variables» dialog, and finally click OK to close the «System Properties» dialog.
Step 3: Verify the Installation
After going through the installation and configuration process, it’s essential to verify that PostgreSQL is correctly installed and accessible. This gives us the assurance that the software is properly set up and ready to use, which can save us from troubleshooting issues later when we start interacting with databases.
If something went wrong during installation, this verification process will help you spot the problem early before creating or managing databases.
Now, let’s go through the steps to verify your PostgreSQL installation.
- Open the Command Prompt by pressing Win + R, typing cmd, and pressing Enter.
- Type
psql --versionand press Enter. You should see the PostgreSQL version number you installed if the installation was successful. - To connect to the PostgreSQL server, type
psql -U postgresand press Enter. - When prompted, enter the password you set for the postgres user during installation. You should now see the postgres=# prompt, indicating you are connected to the PostgreSQL server.
Step 4: Download the Northwind PostgreSQL SQL File
Now, we’re going to introduce you to the Northwind database and help you download it. The Northwind database is a sample database originally provided by Microsoft for its Access Database Management System. It’s based on a fictitious company named «Northwind Traders,» and it contains data on their customers, orders, products, suppliers, and other aspects of the business. In our case, we’ll be working with a version of Northwind that has been adapted for PostgreSQL.
The following steps will guide you on how to download this PostgreSQL-compatible version of the Northwind database from GitHub to your local machine. Let’s get started:
First, you need to download a version of the Northwind database that’s compatible with PostgreSQL. You can find an adapted version on GitHub. To download the SQL file, follow these steps:
-
Open your Terminal application.
-
Create a new directory for the Northwind database and navigate to it:
mkdir northwind && cd northwind -
Download the Northwind PostgreSQL SQL file using curl:
curl -O <https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pthom/northwind_psql/master/northwind.sql>This will download the
northwind.sqlfile to thenorthwinddirectory you created.
Step 5: Create a New PostgreSQL Database
Now that we’ve downloaded the Northwind SQL file, it’s time to prepare our PostgreSQL server to host this data. The next steps will guide you in creating a new database on your PostgreSQL server, a crucial prerequisite before importing the Northwind SQL file.
Creating a dedicated database for the Northwind data is good practice as it isolates these data from other databases in your PostgreSQL server, facilitating better organization and management of your data. These steps involve connecting to the PostgreSQL server as the postgres user, creating the northwind database, and then exiting the PostgreSQL command-line interface.
Let’s proceed with creating your new database:
-
Connect to the PostgreSQL server as the
postgresuser:psql -U postgres -
Create a new database called
northwind:postgres-# CREATE DATABASE northwind; -
Exit the
psqlcommand-line interface:postgres-# \\q
Step 6: Import the Northwind SQL File
We’re now ready to import the Northwind SQL file into our newly created northwind database. This step is crucial as it populates our database with the data from the Northwind SQL file, which we will use for our PostgreSQL learning journey.
These instructions guide you through the process of ensuring you’re in the correct directory in your Terminal and executing the command to import the SQL file. This command will connect to the PostgreSQL server, target the northwind database, and run the SQL commands contained in the northwind.sql file.
Let’s move ahead and breathe life into our northwind database with the data it needs!
With the northwind database created, you can import the Northwind SQL file using psql. Follow these steps:
- In your Terminal, ensure you’re in the
northwinddirectory where you downloaded thenorthwind.sqlfile. -
Run the following command to import the Northwind SQL file into the
northwinddatabase:psql -U postgres -d northwind -f northwind.sqlThis command connects to the PostgreSQL server as the
postgresuser, selects thenorthwinddatabase, and executes the SQL commands in thenorthwind.sqlfile.
Step 7: Verify the Northwind Database Installation
You’ve successfully created your northwind database and imported the Northwind SQL file. Next, we must ensure everything was installed correctly, and our database is ready for use.
These upcoming steps will guide you on connecting to your northwind database, listing its tables, running a sample query, and finally, exiting the command-line interface. Checking the tables and running a sample query will give you a sneak peek into the data you now have and verify that the data was imported correctly. This means we can ensure everything is in order before diving into more complex operations and analyses.
To verify that the Northwind database has been installed correctly, follow these steps:
-
Connect to the
northwinddatabase usingpsql:psql -U postgres -d northwind -
List the tables in the Northwind database:
postgres-# \\dtYou should see a list of Northwind tables: categories, customers, employees, orders, and more.
-
Run a sample query to ensure the data has been imported correctly. For example, you can query the
customerstable:postgres-# SELECT * FROM customers LIMIT 5;This should return the first five rows from the
customerstable. -
Exit the
psqlcommand-line interface:postgres-# \\q
Congratulations! You’ve successfully installed the Northwind database in PostgreSQL using an SQL file and psql.
Step 8: Connect to the Database Using Jupyter Notebook
As we wrap up our installation, we will now introduce Jupyter Notebook as one of the tools available for executing SQL queries and analyzing the Northwind database. Jupyter Notebook offers a convenient and interactive platform that simplifies the visualization and sharing of query results, but it’s important to note that it is an optional step. You can also access Postgres through other means. However, we highly recommend using Jupyter Notebook for its numerous benefits and enhanced user experience.
To set up the necessary tools and establish a connection to the Northwind database, here is an overview of what each step will do:
-
!pip install ipython-sql: This command installs theipython-sqlpackage. This package enables you to write SQL queries directly in your Jupyter Notebook, making it easier to execute and visualize the results of your queries within the notebook environment. -
%load_ext sql: This magic command loads thesqlextension for IPython. By loading this extension, you can use the SQL magic commands, such as%sqland%%sql, to run SQL queries directly in the Jupyter Notebook cells. -
%sql postgresql://postgres@localhost:5432/northwind: This command establishes a connection to the Northwind database using the PostgreSQL database system. The connection string has the following format:postgresql://username@hostname:port/database_nameIn this case,
usernameispostgres,hostnameislocalhost,portis5432, anddatabase_nameisnorthwind. The%sqlmagic command allows you to run a single-line SQL query in the Jupyter Notebook. -
Copy the following text into a code cell in the Jupyter Notebook:
!pip install ipython-sql
%load_ext sql
%sql postgresql://postgres@localhost:5432/northwindOn Windows you may need to try the following command because you need to provide the password you set for the “postgres” user during installation:
%sql postgresql://postgres:{password}@localhost:5432/northwindBear in mind that it’s considered best practice not to include sensitive information like passwords directly in files that could be shared or accidentally exposed. Instead, you can store your password securely using environment variables or a password management system (we’ll link to some resources at the end of this guide if you are interested in doing this).
-
Run the cell by either:
- Clicking the «Run» button on the menu bar.
- Using the keyboard shortcut:
Shift + EnterorCtrl + Enter.
-
Upon successful connection, you should see an output similar to the following:
'Connected: postgres@northwind'This output confirms that you are now connected to the Northwind database, and you can proceed with the guided project in your Jupyter Notebook environment.
Once you execute these commands, you’ll be connected to the Northwind database, and you can start writing SQL queries in your Jupyter Notebook using the %sql or %%sql magic commands.
Next Steps
Based on what you’ve accomplished, here are some potential next steps to continue your learning journey:
- Deepen Your SQL Knowledge:
- Try formulating more complex queries on the Northwind database to improve your SQL skills. These could include joins, subqueries, and aggregations.
- Understand the design of the Northwind database: inspect the tables, their relationships, and how data is structured.
- Experiment with Database Management:
- Learn how to backup and restore databases in PostgreSQL. Try creating a backup of your Northwind database.
- Explore different ways to optimize your PostgreSQL database performance like indexing and query optimization.
- Integration with Python:
- Learn how to use
psycopg2, a popular PostgreSQL adapter for Python, to interact with your database programmatically. - Experiment with ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) libraries like
SQLAlchemyto manage your database using Python.
- Learn how to use
- Security and Best Practices:
- Learn about database security principles and apply them to your PostgreSQL setup.
- Understand best practices for storing sensitive information, like using
.envfiles for environment variables. - For more guidance on securely storing passwords, you might find the following resources helpful:
- Using Environment Variables in Python
- Python Secret Module