MinGW (Minimalist GNU for Windows) is a development environment for Windows that includes a port of the GCC (GNU Compiler Collection) compiler. MinGW is commonly used to build open-source software for Windows. To install MinGW on Windows 10, follow the steps below:
Method 1: Download and Install MinGW
MinGW is a native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), with freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications.
Step 1: Download the MinGW Installer
Go to the MinGW website (https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw-w64/files/mingw-w64/) and click on the «Download» button for the latest version of the MinGW installer.
Step 2: Run the MinGW Installer
After downloading the MinGW installer, run the executable file and follow the installation wizard.
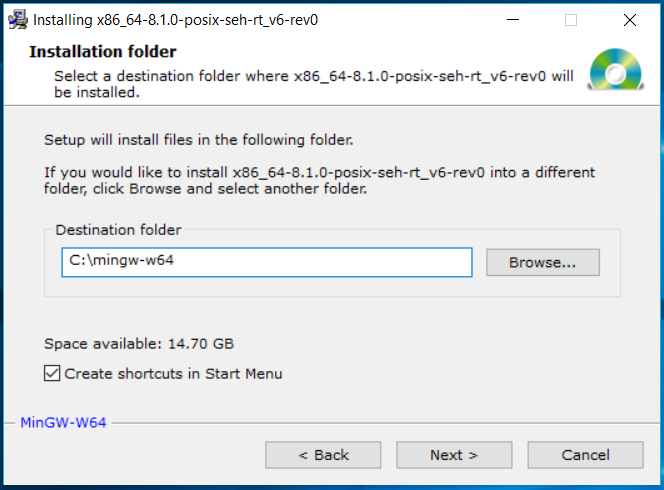
Step 3: Select the Installation Options
During the installation process, you will be prompted to select the installation options. Select the following options:
- Architecture: x86_64
- Threads: posix
- Exception: seh
- Build revision: latest
Step 4: Set the Installation Directory
Set the installation directory to a location of your choice.
Step 5: Add MinGW to the System Path
After the installation is complete, add the MinGW bin directory to the system path by following these steps:
- Open the Start menu and search for «Environment Variables»
- Click on «Edit the system environment variables»
- Click on the «Environment Variables» button
- Under «System Variables», find the «Path» variable and click «Edit»
- Click «New» and add the path to the MinGW bin directory (e.g. «C:\MinGW\bin»)
- Click «OK» to save the changes
Step 6: Verify the Installation
To verify that MinGW is installed correctly, open a command prompt and type the following command:
This should display the version of the GCC compiler that is installed.
Method 2: Add MinGW to the System Path
Step 1: Download MinGW 64
Go to the MinGW-w64 website and download the latest version of MinGW 64 for your system.
Step 2: Install MinGW 64
Run the downloaded installer and follow the instructions. By default, MinGW 64 will be installed in C:\Program Files\mingw-w64\x86_64-8.1.0-posix-seh-rt_v6-rev0. You can change this location if you want.
Step 3: Add MinGW to the System Path
- Open the Start menu and search for «Environment Variables».
- Click on «Edit the system environment variables».
- Click on the «Environment Variables» button.
- Under «System Variables», scroll down and find the «Path» variable. Click on «Edit».
- Click on «New» and add the path to the MinGW 64 bin directory. By default, this is
C:\Program Files\mingw-w64\x86_64-8.1.0-posix-seh-rt_v6-rev0\mingw64\bin. - Click «OK» on all the windows to close them.
Step 4: Verify the Installation
Open a command prompt and type gcc --version. If MinGW 64 is installed correctly, you should see the version information for GCC.
$ gcc --version
gcc (MinGW.org GCC Build-2) 9.2.0Step 5: Use MinGW 64
You can now use MinGW 64 to compile and run C and C++ programs. Here is an example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, world!\n");
return 0;
}Save this code to a file named hello.c. Open a command prompt and navigate to the directory where hello.c is saved. Compile the code with the following command:
This will create an executable file named hello.exe. Run the program with the following command:
You should see the following output:
Method 3: Verify the Installation
Step 1: Download and Install MinGW 64
- Download the MinGW 64 installer from the official website: http://mingw-w64.org/doku.php/download
- Run the installer and select the following options:
- Architecture: x86_64
- Threads: posix
- Exception: seh
- Build revision: latest
- Destination folder: choose a directory of your choice
- Click on «Next» and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Step 2: Verify the Installation
-
Open the Command Prompt by pressing the Windows key + R and typing «cmd» in the Run dialog box.
-
Type the following command to check if MinGW is installed correctly:
If MinGW is installed correctly, you should see the version number of the GCC compiler.
-
Type the following command to check if the MinGW bin directory is added to the system path:
If the MinGW bin directory is added to the system path, you should see the directory path in the output.
-
Type the following command to compile a simple C program:
This will compile the «hello.c» file and create an executable file named «hello.exe».
-
Type the following command to run the executable file:
If the program runs successfully and prints «Hello, World!» to the console, then MinGW is installed correctly and ready to use.
Для работы над заданиями курса в Windows 10 рекомендуется использовать следующее программное окружение:
- Редактор Visual Studio Code
- Инструменты командной строки Git for Windows
- Среда разработки MinGW-w64 (Minimalist GNU for Windows), содержащая компилятор GCC (GNU Compiler Collection)
- Инструменты для сборки проектов CMake
- Система управления пакетами python Miniconda3
Рассмотрим процесс установки и настройки этих инструментов.
Установка VS Code
Установка VS Code не представляет сложностей. Достаточно скачать установочный файл со страницы загрузок и запустить его. Пока это все, что необходимо сделать. После установки остальных программ мы вернемся к настройке VS Code.
Установка и настройка Git for Windows
Скачайте установочный файл Git for Windows со страницы загрузок и запустите его. На момент написания этого текста актуальной версией является 2.28.0. В процессе установки Вам будут заданы вопросы по конфигурации. В большинстве случаев подойдут рекомендуемые варианты.
Если в системе уже установлен редактор VS Code, то его можно выбрать в качестве редактора по умолчанию для Git:
Важным моментом является настройка обработки конца строки в файлах. Чтобы с этим не возникало проблем, необходимо выбрать вариант, который уже отмечен по умолчанию:
Чтобы команды git были доступны во всех терминалах, следует выбрать рекомендуемый вариант для изменения переменной окружения PATH:
Проверьте, что установка завершилась успешно, открыв терминал и исполнив команду git. Результат должен выглядеть так:
> git
usage: git [--version] [--help] [-C <path>] [-c <name>=<value>]
[--exec-path[=<path>]] [--html-path] [--man-path]
[--info-path] [-p | --paginate | -P | --no-pager]
[--no-replace-objects] [--bare] [--git-dir=<path>]
[--work-tree=<path>] [--namespace=<name>]
<command> [<args>]
В качестве терминала в Windows 10 мы рекомендуем использовать PowerShell.
Теперь необходимо задать имя пользователя и адрес электронной почты:
> git config --global user.name "Ivan Petrov"
> git config --global user.email i.petrov@nsu.ru
Git хранит настройки в файле ~\.gitconfig. У автора этот файл выглядит следующим образом:
[user]
email = vit.vorobiev@gmail.com
name = Vitaly Vorobyev
[core]
editor = \"[path-to-vscode]" --wait
На этом первоначальная конфигурация инструментов git завершена. Навык работы с git приходит с практикой. Действия с git, необходимые для выполнения заданий курса, всегда будут подробно описаны. Тем не менее, мы рекомендуем обращаться к документации, чтобы прояснять непонятные моменты.
Установка MinGW-w64
Установочный файл MinGW-w64 mingw-w64-install.exe можно найти на этой странице. При установке не нужно менять настройки по умолчанию, кроме пути установки. Путь установки не должен содержать пробелов, поэтому путь по умолчанию в директории Program Files не подходит.
После завершения установки, в директории mingw32\bin будут расположены различные исполняемые файлы. Среди них нас интересует файл g++.exe, который запускает сборку программ C++. Сделаем так, чтобы этот файл был доступен в любой директории из командной строки. Если этого не сделать, то для использования команды g++ надо будет прописывать полный путь до файла g++.exe.
Откройте меню “Система” в “Панели управления”:
Из меню “Система” перейдите в “Дополнительные параметры системы”:
Выберите “Переменные среды”:
Выберите переменную Path и нажмите кнопку “Изменить…”:
Добавьте в новую строку полный путь до директории mingw32\bin и нажмите кнопку OK.
Чтобы проверить, что настройка выполнена успешно, откройте консоль (не в директории mingw32\bin) и выполните команду g++ --help:
> g++ --help
Usage: g++.exe [options] file...
Ваша система теперь готова к сборке программ на языке C++.
Установка CMake
Скачайте со станицы загрузок установочный файл cmake-3.18.1-win64-x64.msi (на момент написания текста актуальная версия — 3.18.1). Для 32-разрядной системы вместо этого нужно скачать файл cmake-3.18.1-win32-x86.msi. Запустите файл и выполните установку. В ходе установки выберите изменение переменной окружения PATH:
Выполните в консоли команду cmake --help для проверки корректности установки CMake:
> cmake --help
Usage
cmake [options] <path-to-source>
cmake [options] <path-to-existing-build>
cmake [options] -S <path-to-source> -B <path-to-build>
Specify a source directory to (re-)generate a build system for it in
the current working directory. Specify an existing build directory to
re-generate its build system.
Код большинства заданий по C++ этого курса будет компилироваться с помощью CMake. Эта система значительно упрощает процесс сборки C++ проектов, особенно если они состоят из многих файлов.
Установка Miniconda3
Система Windows (в отличие от Linux) не имеет установленного по умолчанию интерпретатора python. Менеджер пакетов python Anaconda и его минимальная сборка Miniconda позволят нам установить в системы все необходимые инструменты для работы с python. Загрузите со страницы загрузки установочный файл Miniconda3 Windows 64-bit или Miniconda3 Windows 32-bit, в зависимости от разрядности системы. При установке отметьте галочку для добавления необходимых записей в переменную окружения PATH, несмотря на то что это действие не рекомендуется установщиком:
Убедитесь в том, что установка выполнена успешно, выполнив в консоли следующую команду:
>conda --help
usage: conda-script.py [-h] [-V] command ...
conda is a tool for managing and deploying applications, environments and packages.
Выполните инициализацию (необходимо выполнить один раз):
Создайте окружение для работы с заданиями этого курса:
>conda create -n nsu python=3
Conda вычислит набор пакетов, которые необходимо установить в новом окружении, и попросит подтвердить создание окружения:
После установки активируйте новое окружение и запустите консоль python:
>conda activate nsu
(nsu) >python
Python 3.8.5 (default, Aug 5 2020, 09:44:06) [MSC v.1916 64 bit (AMD64)] :: Anaconda, Inc. on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>>
Ваша система теперь готова для работы с заданиями курса “Программирование на C++ и python”. Нам осталось настроить редактор VS Code для максимально удобной работы.
Настройка VS Code
Установите следующие расширения VS Code:
- C/C++ for Visual Studio Code
- CMake Tools
- Python
Выбор интерпретатора python
При начале работы с кодом python (при открытии файла с расширением .py) VS Code предложит выбрать интерпретатор python, который будет использоваться для подсветки кода, проверки синтаксиса и вывода подсказок:
Можете, например, выбрать интерпретатор из недавно созданного окружения nsu.
Создадим файл test.py, содержащий одну строку:
Исполнить этот скрипт можно, открыв консоль в VS Code с помощью сочетания клавиш Ctrl+J и набрав в ней
В правом верхнем углу окна находится кнопка с зеленым треугольником ▷, нажатие на которую приводит к тому же результату:
Настройка работы с GCC
Создайте файл test.cpp, содержащий следующий код:
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::cout << "Hello, world!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Скомпилируем его с помощью компилятора GCC и командной строки. Откройте консоль в VS Code (Ctrl+J) и исполните команду
Компилятор создал исполняемый файл a.exe. Запустите его:
Работает. Настроим теперь VS Code для автоматизации этого действия. Выберите в меню пункт Terminal -> Configure Default Build Task...:
Выберите из выпавшего списка пункт g++.exe. В результате будет сгенерирован файл .vscode/tasks.json подобный такому:
{
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "C/C++: cpp.exe build active file",
"command": "D:\\mingw\\mingw32\\bin\\g++.exe",
"args": [
"-g",
"${file}",
"-o",
"${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe"
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}"
},
"problemMatcher": [
"$gcc"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
}
}
]
}
Теперь при нажатии клавиш Ctrl+Shift+B или выборе пункта меню Terminal -> Run Build Task будет выполняться компиляция открытого файла. Для файла test.cpp будет создан исполняемый файл test.exe.
Работа с CMake
Откройте новую рабочую директорию VS Code, создайте в ней файл main.cpp, содержащий следующий код:
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::cout << "Hello, world!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
и файл CMakeLists.txt со следующим содержанием:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.0)
add_executable(test main.cpp)
Эти два файла составляют минимальный CMake-проект. Выполним сначала сборку CMake-проекта через консоль: создайте в рабочей директории поддиректорию build, в которой будет осуществляться сборка, и перейдите в неё:
Выполните настройку проекта и запустите сборку:
> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" ..
> cmake --build .
В первой команде мы указали, что сборка будет осуществляться с помощью MinGW и что файлы проекта расположены в родительской директории (путь ..). Вторая команда осуществляет сборку в текущей директории (путь .). В директории build должен появиться исполняемый файл test.exe.
Расширение VS Code для работы с CMake позволяет автоматизировать сборку проекта. Выберите рабочую директорию VS Code (комбинация клавиш Ctrl+K+O), содержащую файлы main.cpp и CMakeLists.txt. Наберите комбинацию клавиш Ctrl+Shift+P и в строке сверху наберите команду >CMake: Configure. Это запустит настройку инструментов CMake. После завершения настройки в нижней части окна появятся инструменты управления сборкой:
Кнопку “Сборка” запускает сборку, а кнопка ▷ — исполняемый файл.
Если автоматическая настройка CMake привела к ошибке, то, вероятно, инициализация CMake выполнилась без параметра -G "MinGW Makefiles". В этом случае выполните эту команду в консоли, как показано выше. Достаточно выполнить это действие один раз, после чего конфигурация этого и других проектов будет выполняться верно.
Работа с git
Покажем как можно работать с git-репозиторием через VS Code. Выполните fork репозитория задания Hello, Classroom на GitHub:
Это действие создает новый репозиторий в Вашем аккаунте. Разрешите автоматическое тестирование решения, нажав на большую зеленую кнопку во вкладке Actions:
Новый репозиторий необходимо клонировать на Вашу локальную систему. Удобнее всего это делать с помощью протокола ssh. Для этого сначала необходимо включить OpenSSH Client, который по умолчанию выключен.
Взаимодействие с GitHub репозиторием будет происходить по протоколу ssh с помощью техники шифрования с открытым ключом. Создать пару из приватного и публичного ключа можно в консоли:
>ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
По умолчанию сгенерированные ключи будут расположены в директории ~\.ssh. Файл с публичным ключом называется id-rsa.pub. Публичный ключ нужно добавить на GitHub. Для этого откройте раздел SSH and GPG keys в меню Settings и нажмите на кнопку New SSH key:
Заполните открывшуюся форму. В поле Key нужно скопировать содержимое файла id-rsa.pub. Проследите, чтобы при копировании не появились лишние переносы строк. Весь ключ должен быть расположен в одной строке.
Теперь мы готовы к клонированию репозитория. Выберите на компьютере директорию, в которой Вы будете работать с заданиями курса и перейдите в неё. Откройте страницу репозитория hello-classroom в Вашем аккаунте GitHub и скопируйте строку для клонирования через ssh:
Выполните в консоли команду git clone:
> git clone git@github.com:fakestud/hello-classroom.git
Cloning into 'hello-classroom'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 15, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (15/15), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (8/8), done.
remote: Total 15 (delta 0), reused 15 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
Receiving objects: 100% (15/15), done
Строка git@github.com:fakestud/hello-classroom.git есть скопированная выше строка. Репозиторий был клонирован в директорию hello-classroom. Выберите её в качестве рабочей директории VS Code. Прочитайте файл README.md, содержащий инструкции по решению задания. После решения задания выполните локальную проверку:
> conda activate nsu
> pip install -r .\requirements.txt
> g++ -std=c++17 main.cpp -o a.out
> test_cmd tests/ .\a.out
Running 1 tests on 4 CPUs...
test1
Command: .\a.out
Success
All 1 tests passed.
Тесты пройдены успешны. Значит, мы готовы к синхронизации репозитория GitHub с нашей локальной версией. В командной строке для этого достаточно выполнить следующие команды:
git add main.cpp
git commit -m "Task solved"
git push -u origin master
Редактор VS Code позволяет выполнить эти действия через графический интерфейс. VS Code отслеживает изменения локальной версии репозитория. Откройте вкладку контроля версий слева и посмотрите на список изменившихся файлов. В нашем случае это должен быть только файл main.cpp. Выполните команду git add, нажав на кнопку +:
Затем команду git commit, нажав на кнопку ✓ и введя комментарий в текстовом поле:
Наконец, выполните команду git push:
Источники
- First-Time Git Setup
- VS Code: User and Workspace Settings
- VS Code: Using GCC with MinGW
- VS Code: Get started with CMake Tools on Linux
- Git in Visual Studio Code
- Must-have плагины и несколько полезностей для С\С++ разработки в VS Code
- Памятка пользователям ssh
I simply want to install MinGW64 to get the 64 bits C compiler. I know there are tons of tutorials on the web but they do not work for me.
-
I went to: https://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw-w64/ and clicked the download button.
-
According to the tutorials i saw there should be an installer but all i got is a folder named ‘mingw-w64-v7.0.0’
inside of it there are those folders:
build-aux
COPYING.MinGW-w64
COPYING.MinGW-w64-runtime
mingw-w64-crt
mingw-w64-doc
mingw-w64-headers
mingw-w64-libraries
mingw-w64-tools
but i found nowhere any kind of executables or installer, what do i do next ?
Note I already have the 32 bits version installed in c:\MinGW, thank you very much for any help as i am getting really frustrated.
asked Jun 29, 2020 at 14:36
2
answered Jun 29, 2020 at 14:55
0
You can get a MinGW-w64 build that requires no installation from http://winlibs.com/, just extract the archive and start using it. The site also explains how to use the compiler from Code::Blocks IDE.
answered Jun 30, 2020 at 18:38
Brecht SandersBrecht Sanders
6,3201 gold badge16 silver badges41 bronze badges
-
First, let’s access the official MinGW website:
mingw.org -
Now let’s go to the downloads tab, which is in the upper left corner:
- On the download page choose option
MingW-W64-builds:
- Now click the direct link to github:
- On the github page, choose the following option:
x86_64-12.2.0-release-posix-seh-rt_v10-rev0.7z
Now you will download the file and unzip it using winrar (or any other file extraction tool).
After unzipping the file, go to the location where you unzipped it
and copy the path of the bin folder:
That done, to windows settings -> system -> about -> advanced system settings.
Click environment variables -> system variables -> path -> edit -> new -> paste the bin folder path you copied earlier.
Okay, now open your terminal (win + r) and type cmd and type the following command g++ --version, if everything went well, the g++ version will appear.
MinGW also called as Minimalistic GNU for Windows is a popular compiler for C and C++ and used for the development of native MS-Windows applications. It does not depend on any 3rd party tools or libraries but relies on the several DLLs provided by Microsoft as components of the operating system. Out of these DLLs, MSVCRT.DLL i.e. Microsoft C runtime library is the primary one. Apart from the system components, the threaded applications must use freely distributable thread support DLL, provided as part of MinGW itself. You may consider using Cygwin for POSIX application deployment.
Below listed are the features and components provided by MinGW. You may also refer MinGW for more details.
- A port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), including C, C++, ADA and Fortran compilers;
- GNU Binutils for Windows (assembler, linker, archive manager)
- A command-line installer, with optional GUI front-end, (mingw-get) for MinGW and MSYS deployment on MS-Windows
- A GUI first-time setup tool (mingw-get-setup), to get you up and running with mingw-get.
In this tutorial, we will install MinGW on windows and write, compile, and execute our Hello World program in C++.
Step 1 — Download MinGW
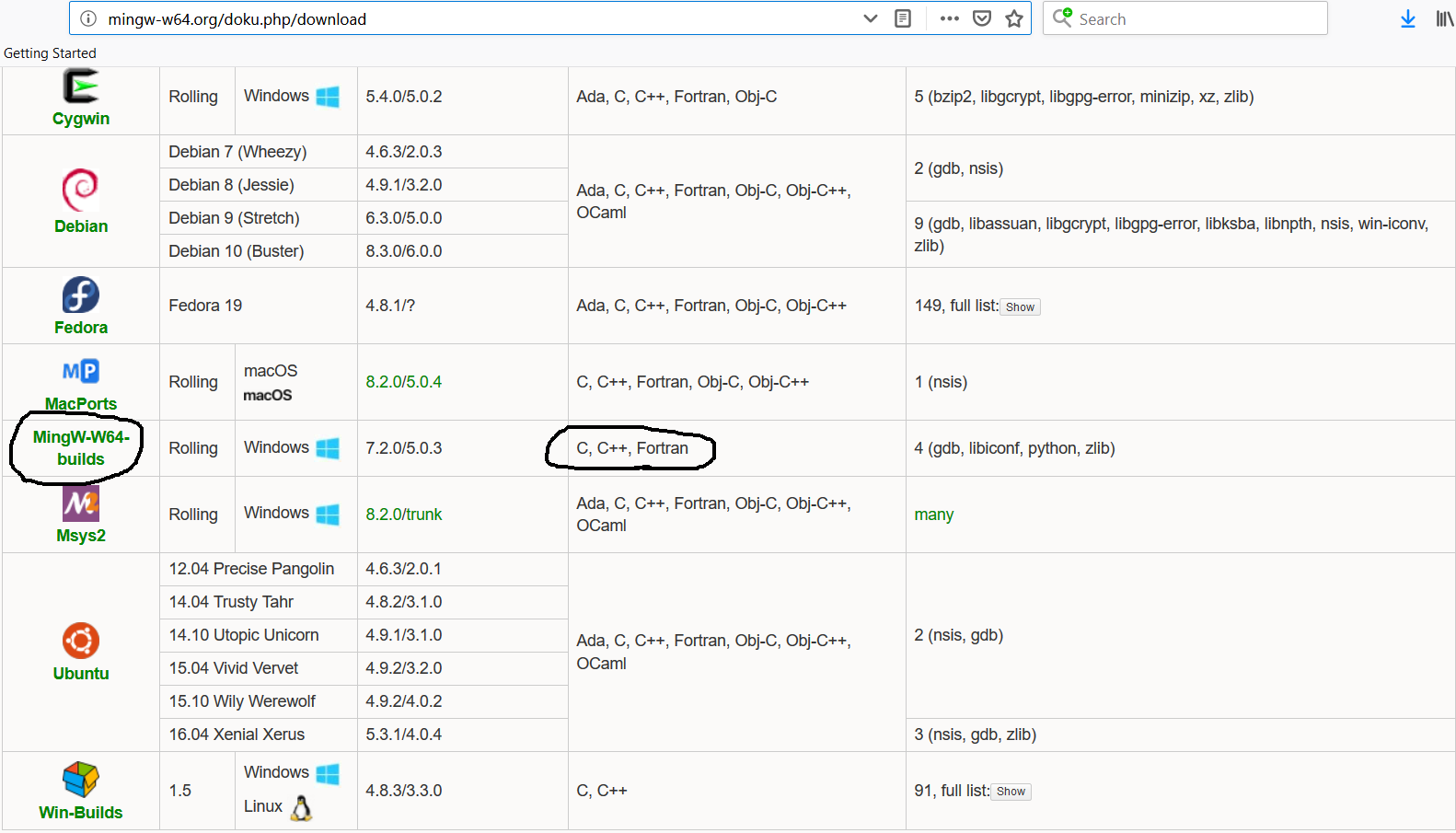
Go to the Download Page to start downloading mingw-w64. It will show various download options as shown in Fig 1.
Fig 1
Download MinGW-W64-builds as highlighted in Fig 1.
You may also download and install MinGW Installation Manager in case you are planning only for the 32-bit compiler. The MinGW-W64 provides both 32-bit and 64-bit compilers.
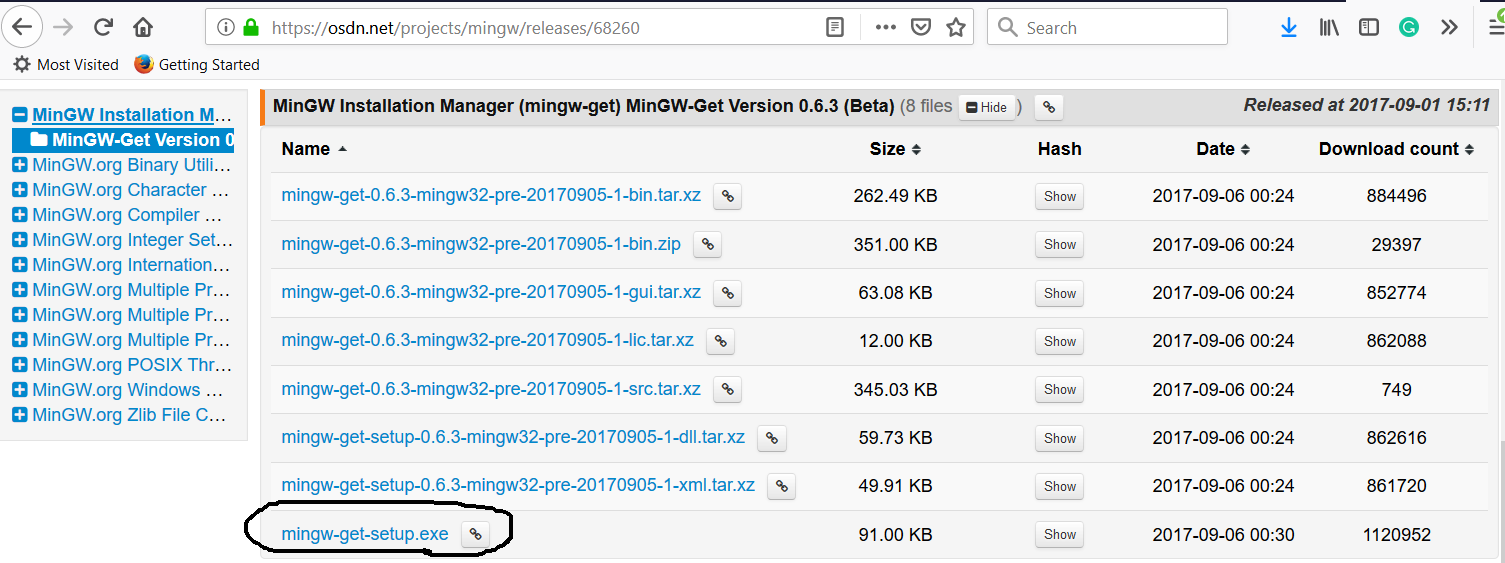
Fig 2
Download MinGW Installation Manager as highlighted in Fig 2.
Step 2 — Install MinGW-W64
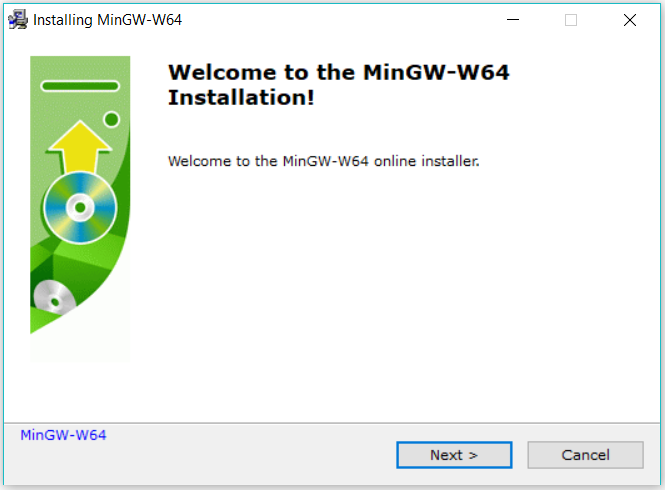
Now execute the MinGW-W64-builds executable downloaded by us in the previous step. It will show the welcome screen as shown in Fig 3.
Fig 3
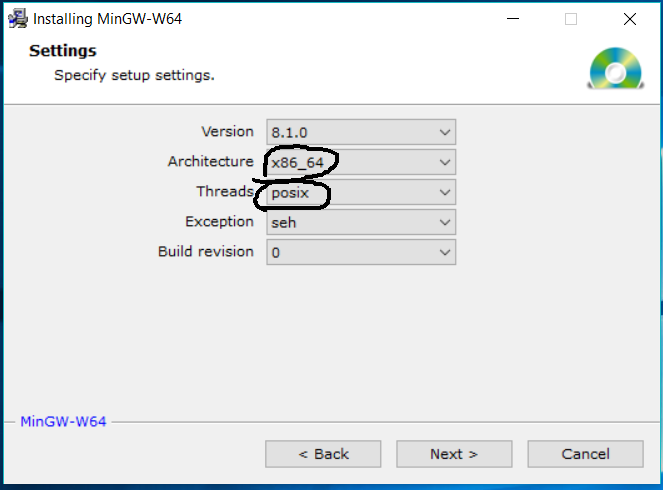
Click on the Next Button to continue with the installation. It will show the settings screen as shown in Fig 4.
Fig 4
Note that I have selected x86_64 architecture in order to support 64-bit instructions. You may continue with i686 for 32-bit instructions. Also, I have selected the posix option of Threads settings for programs involving multithreading. You may select the win32 option based on your needs. Now click on the Next Button to continue with the installation. The next screen asks for the installation path as shown in Fig 5.
Fig 5
Make sure that you provide an installation path without any spaces. Now click on the Next Button to finish the installation.
It might show you error specific to fail to download. I tried a few times and got success in 3rd attempt. You may also continue with manual installation in case it failed multiple times. You can simply download the archive of MinGW-W64 and extract it to the desired location.
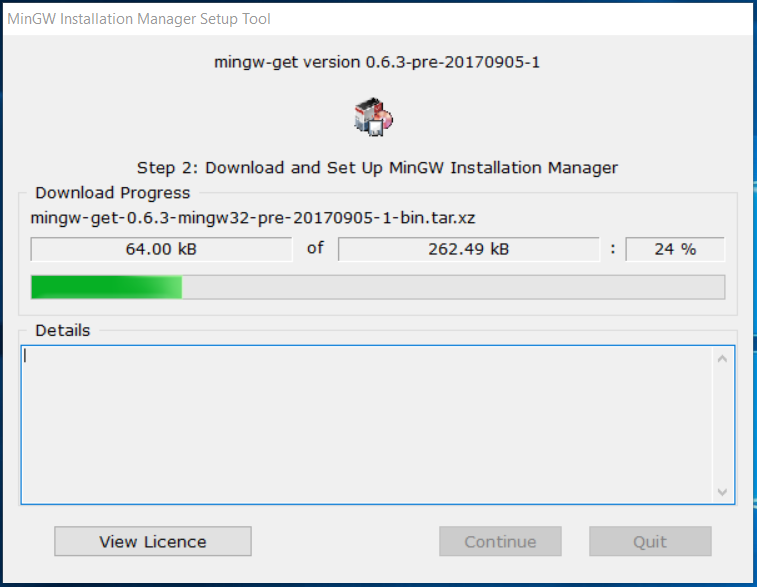
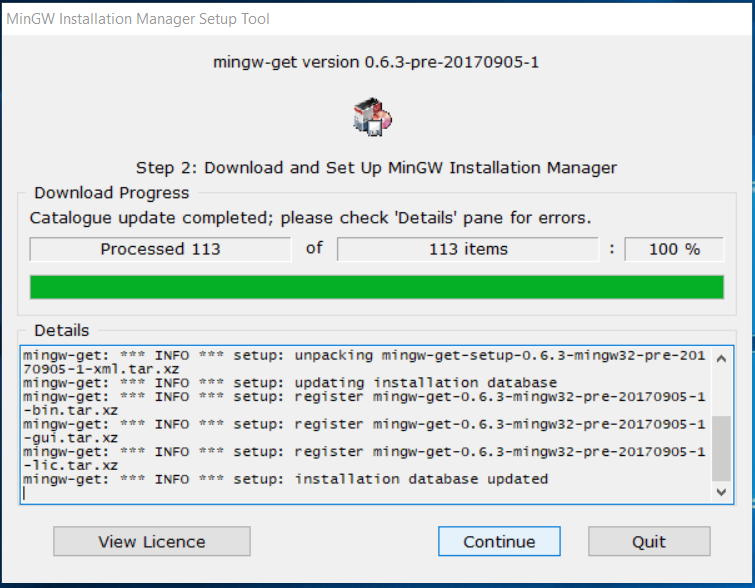
It will show the download progress and status as shown in Fig 6, Fig 7, and Fig 8.
Fig 6
Fig 7
Fig 8
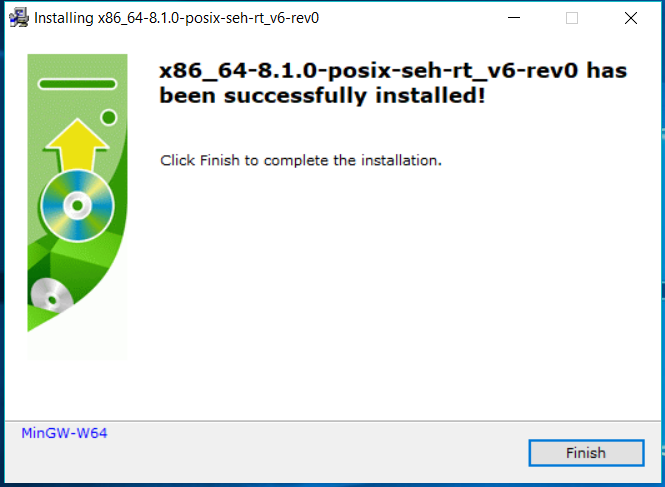
Now click on the Next Button after download completes. It will show the success message as shown in Fig 9.
Fig 9
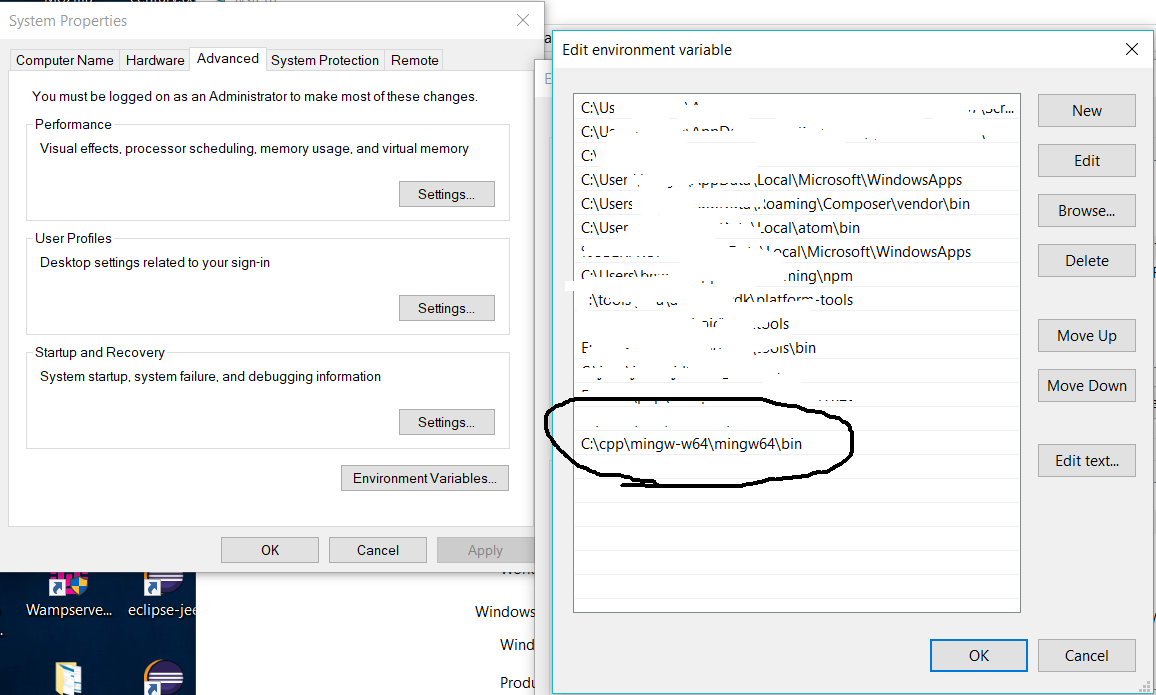
Click on the Finish Button to close the installer. Now add the bind directory of MinGW-W64 to the system path as shown in Fig 10.
Fig 10
Step 3 — Install MinGW
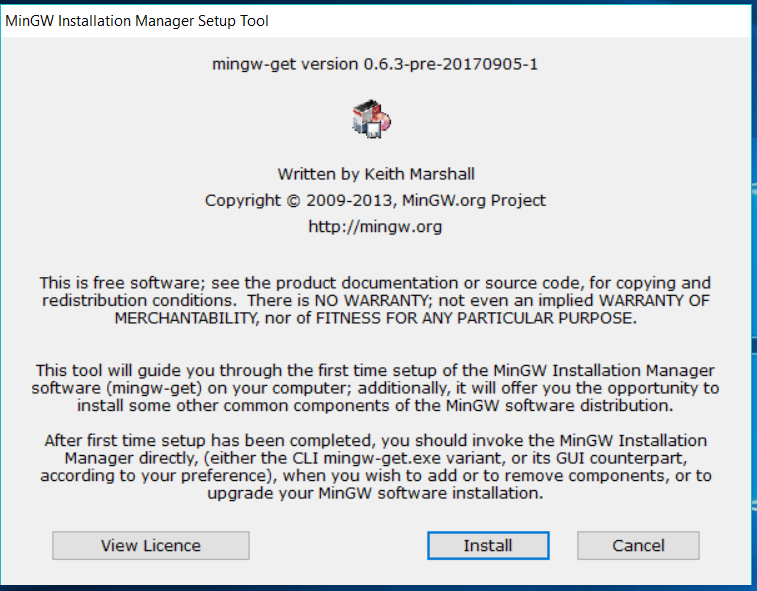
In this step, we will install the MinGW distributed by the official website as shown in Fig 2. Execute the installer downloaded in previous steps. It will show the welcome screen as shown in Fig 11.
Fig 11
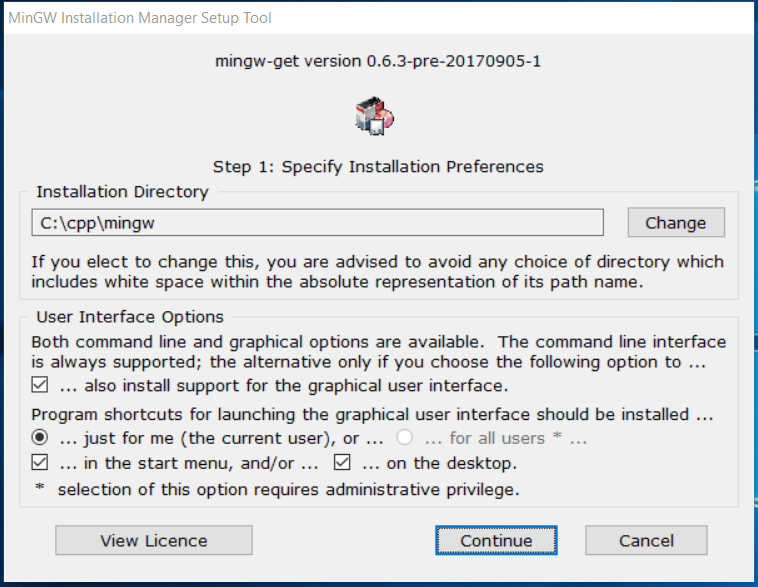
Click on the Install Button to start the installation. It will ask for the installation directory as shown in Fig 12.
Fig 12
Click on the Continue Button to start the installation. It will show the progress as shown in Fig 13 and Fig 14.
Fig 13
Fig 14
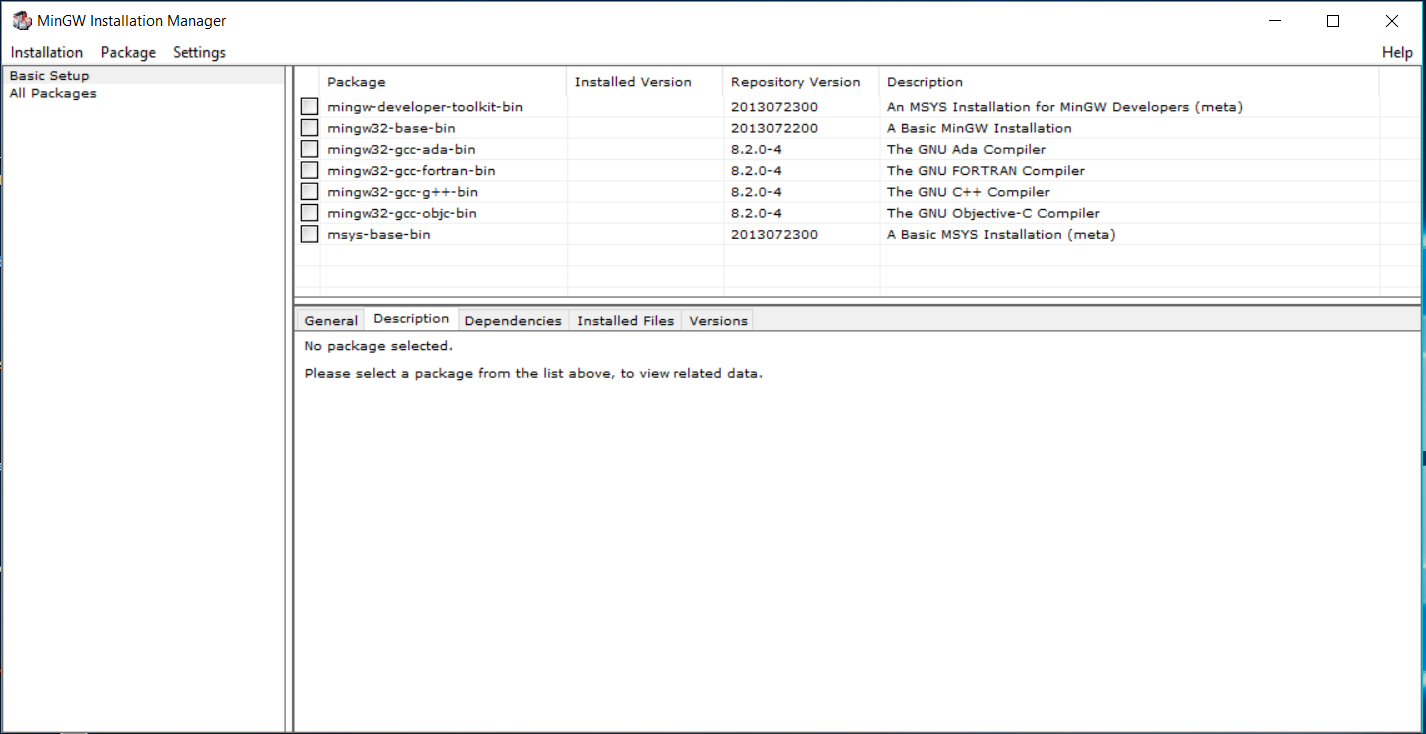
Click on the Continue Button to launch the installation manger as shown in Fig 15.
Fig 15
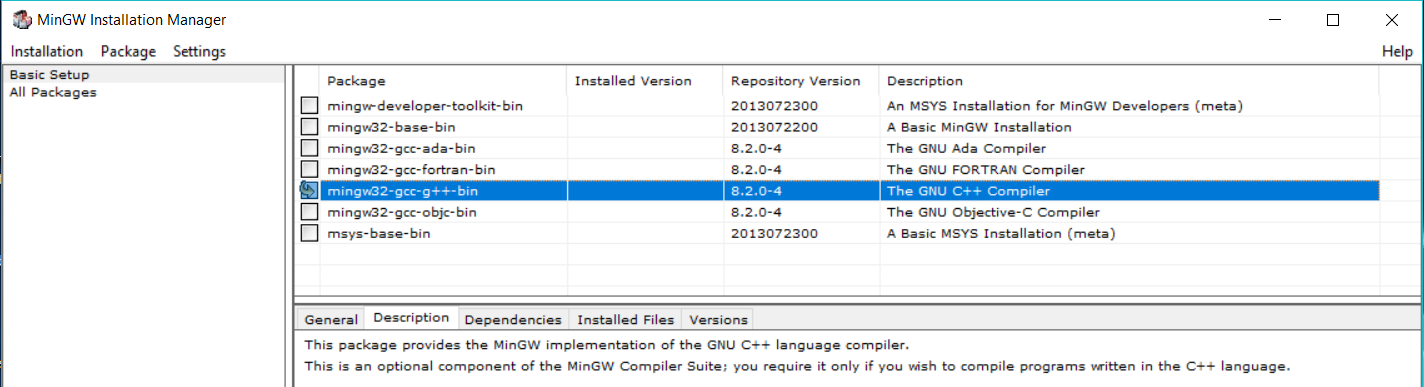
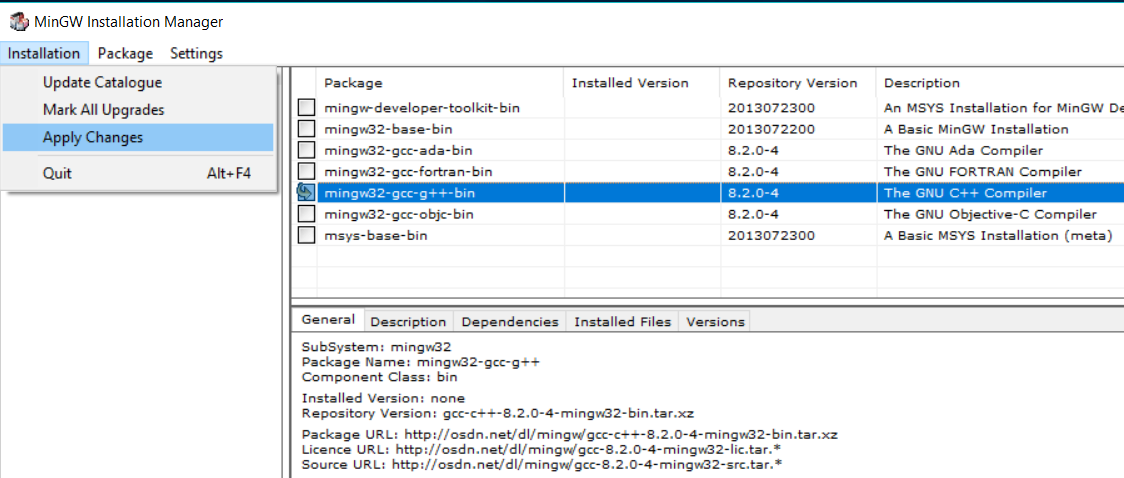
Choose the package GCC as shown in Fig 16.
Fig 16
Click on the Apply Button to apply the changes as shown in Fig 17.
Fig 17
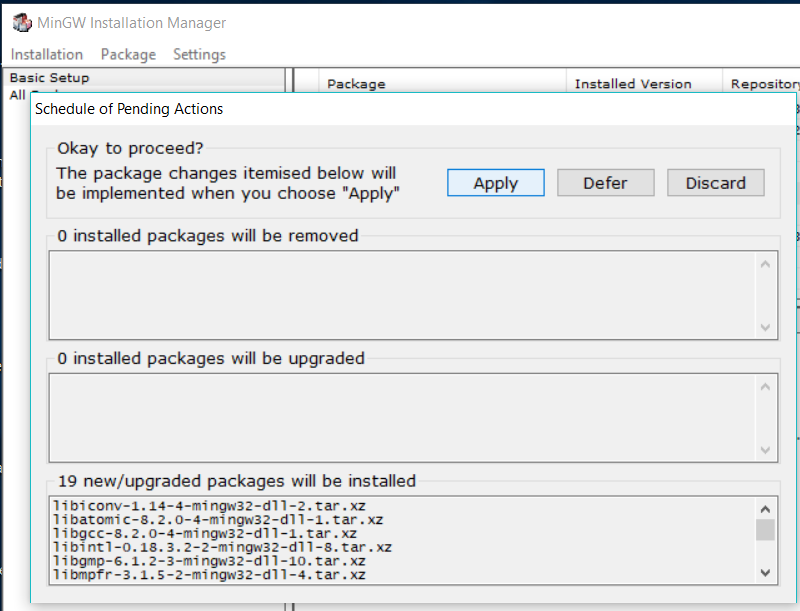
Click on the Apply Changes Button. It will show the confirmation message as shown in Fig 18.
Fig 18
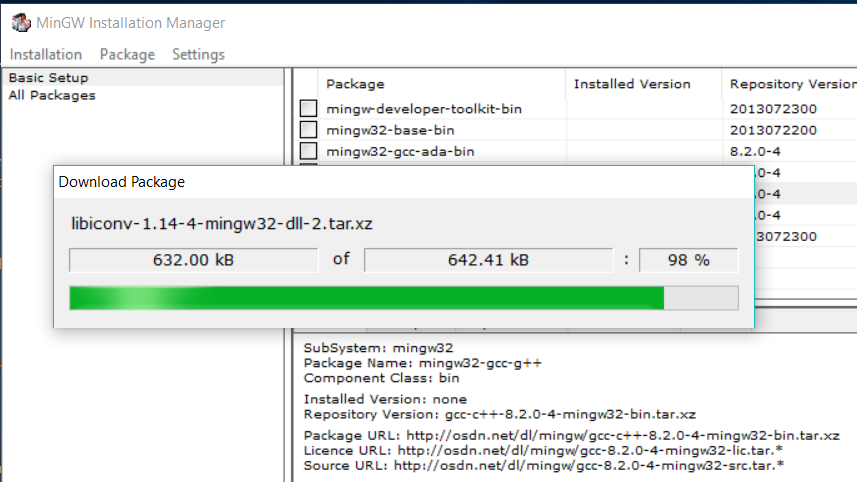
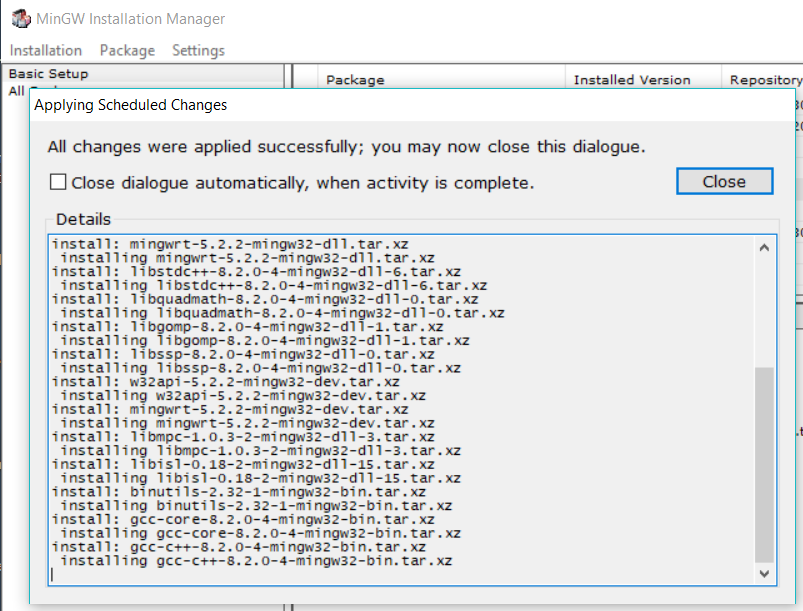
Click on the Apply Button to install GCC. It will show the Package progress as shown in Fig 19 and Fig 20.
Fig 19
Fig 20
Click on the Close Icon and also close the installation manager to complete the installation of the compiler required to compile the programs.
You may add the MinGW path to bin directory which is C:\cpp\mingw\bin in my case to system path as we did for MinGW-W64. Make sure that you keep only one compiler path at a time among MinGW and MinGW-W64.
Step 4 — Getting started with C — Hello World
Write your first C program as shown below and save in a file hello.c.
#include<stdio.h>int main() {
printf( "Hello World" );
}
Compile and execute the program using the command as shown below.
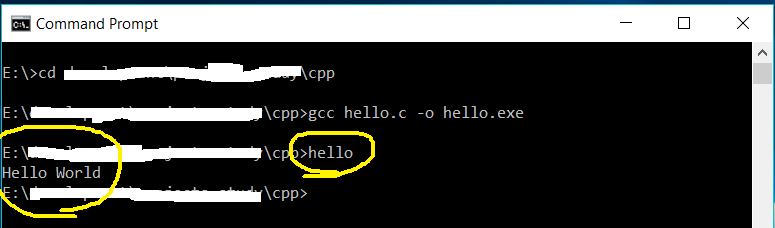
# Compile and make executable
gcc hello.c -o hello.exe
It will compile the program and generate the executable i.e. hello.exe. We can simply type hello to execute the program. It will print Hello World on the console as shown in Fig 21.
Fig 21
Step 5 — Getting started with C++ — Hello World
We can repeat the previous step to write the Hello World program in C++. Write your first C++ program as shown below and save it to hello.cpp.
#include<iostream>using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello World";
return 0;
}
Compile and execute the program using the command as shown below.
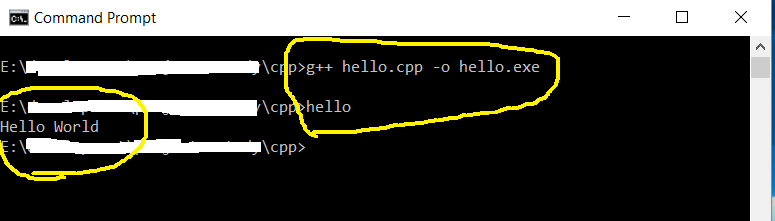
# Compile and make executable
g++ hello.cpp -o hello.exe
It will compile the program and generate the executable i.e. hello.exe. We can simply type hello to execute the program. It will print Hello World on the console as shown in Fig 22.
Fig 22
This is how we can install MinGW and MinGW-W64 and configure the system path to access the executables from the command line. We also wrote our first C and CPP programs, compiled and executed them to print Hello World on the console.