- Unsupported Linux distributions and Unix-like operating systems
- Microsoft Windows
You can install GitLab on several cloud providers,
or use one of the following methods.
| Installation method | Description | When to choose |
|---|---|---|
| Linux package (previously known as Omnibus GitLab) | The official deb and rpm packages. The Linux package has GitLab and dependent components, including PostgreSQL, Redis, and Sidekiq. |
Use if you want the most mature, scalable method. This version is also used on GitLab.com. — For additional flexibility and resilience, see the reference architecture documentation. — Review the system requirements. — View the list of supported Linux operating systems. |
| Helm chart | A chart for installing a cloud-native version of GitLab and its components on Kubernetes. | Use if your infrastructure is on Kubernetes and you’re familiar with how it works. Management, observability, and some concepts are different than traditional deployments. — Administration and troubleshooting requires Kubernetes knowledge. — It can be more expensive for smaller installations. The default installation requires more resources than a single node Linux package deployment, because most services are deployed in a redundant fashion. |
| Docker | The GitLab packages in a Docker container. | Use if you’re familiar with Docker. |
| Source | GitLab and its components from scratch. | Use if none of the previous methods are available for your platform. Can use for unsupported systems like *BSD. |
| GitLab Environment Toolkit (GET) | A set of opinionated Terraform and Ansible scripts. | Use to deploy a reference architecture on selected major cloud providers. Has some limitations and manual setup for production environments. |
| GitLab Operator | An installation and management method that follows the Kubernetes Operator pattern. | Use to run GitLab in an OpenShift environment. |
Unsupported Linux distributions and Unix-like operating systems
- Arch Linux
- Fedora
- FreeBSD
- Gentoo
- macOS
Installation of GitLab on these operating systems is possible, but not supported.
See the installation guides for more information.
See OS versions that are no longer supported
for a list of supported and unsupported OS versions for Linux package installations as well as the last support GitLab version for that OS.
Microsoft Windows
GitLab is developed for Linux-based operating systems.
It does not run on Microsoft Windows, and we have no plans to support it in the near future. For the latest development status, view this issue.
Consider using a virtual machine to run GitLab.
GitLab — это платформа управления исходными кодами, которая предоставляет командам разработчиков возможность совместной работы и контроля версий. Установка и настройка GitLab на Windows может показаться сложным заданием для начинающих пользователей. В данной статье мы рассмотрим поэтапный процесс установки и настройки GitLab на операционной системе Windows, чтобы помочь вам начать использовать этот мощный инструмент в вашем проекте.
Шаг 1: Установка необходимых компонентов
Перед установкой GitLab на Windows вам необходимо убедиться, что у вас установлены следующие компоненты: Git Bash, Ruby и GitLab Runner. Git Bash позволяет работать с Git из командной строки, Ruby — язык программирования, а GitLab Runner используется для запуска автоматизированных процессов компиляции и тестирования кода. Вы можете скачать и установить эти компоненты с официальных сайтов.
Шаг 2: Установка и настройка GitLab
После установки необходимых компонентов вы готовы перейти к установке и настройке GitLab. Скачайте установщик GitLab с официального сайта и запустите его. Установщик предложит вам выбрать компоненты для установки и путь установки. Рекомендуется выбрать все компоненты по умолчанию и оставить путь установки без изменений.
Примечание: В процессе установки GitLab может потребоваться установка и настройка базы данных PostgreSQL. При возникновении проблем с настройкой базы данных, рекомендуется воспользоваться руководством по установке и настройке PostgreSQL.
После завершения установки GitLab вы можете открыть его веб-интерфейс, перейдя по адресу http://localhost в вашем веб-браузере. Вам будет предложено создать учетную запись администратора GitLab и настроить его параметры.
Поздравляем! Вы успешно установили и настроили GitLab на Windows. Теперь вы готовы начать работу с этим инструментом и использовать его для совместной работы над вашими проектами.
Если вы хотите использовать GitLab на своем компьютере под управлением ОС Windows, вам потребуется следовать нескольким простым шагам для установки и настройки.
- Поехали на официальный сайт GitLab и скачайте установщик для Windows.
- Запустите загруженный файл и следуйте инструкциям мастера установки.
- Выберите путь для установки GitLab, предпочтительно на системный диск C:.
- Настройте имя пользователя и пароль для учетной записи администратора GitLab.
- Выберите один из доступных портов для веб-интерфейса GitLab.
- Продолжайте установку, следуя инструкциям мастера.
- После завершения установки запустите командную строку Git Bash.
- Введите команду
git labи дождитесь появления сообщения об успешном запуске GitLab. - Откройте веб-браузер и введите адрес
localhost:выбранный_порт, чтобы получить доступ к веб-интерфейсу GitLab. - Войдите в систему, используя имя пользователя и пароль, указанные во время установки.
Теперь вы успешно установили и настроили GitLab на своем компьютере под управлением ОС Windows. Можете начинать использовать его для управления своими репозиториями, контроля версий и совместной работы с командой разработчиков.
Установка GitLab
Перед началом установки GitLab на Windows необходимо выполнить следующие шаги:
- Установите и настройте все необходимые предварительные требования. К ним относятся Ruby, Redis и MySQL.
- Убедитесь, что ваша операционная система подходит для установки GitLab.
- Создайте учетную запись пользователя GitLab и настройте его пароль.
После выполнения этих шагов можно приступить к самой установке GitLab. Для этого потребуется выполнить следующие действия:
| Шаг | Описание |
|---|---|
| 1 | Скачайте установщик GitLab для Windows с официального сайта. |
| 2 | Запустите установщик и следуйте инструкциям на экране. Укажите путь к установочной директории. |
| 3 | Подождите, пока процесс установки будет завершен. Это может занять некоторое время. |
| 4 | После успешной установки GitLab, запустите службу GitLab. |
| 5 | Откройте веб-браузер и введите адрес «localhost» или «127.0.0.1». |
| 6 | В появившемся окне зарегистрируйте нового пользователя и создайте проект. |
Поздравляю! GitLab успешно установлен на вашей операционной системе Windows. Теперь вы можете начать использовать GitLab для управления своими проектами и репозиториями.
Шаг 1 — Загрузка установочного файла
1. Откройте веб-браузер и перейдите на официальный сайт GitLab по адресу https://about.gitlab.com/.
2. На главной странице найдите раздел «Get started with GitLab» и кликните на кнопку «Free trial».
3. Вас перенаправят на страницу с различными вариантами установки. Найдите раздел «Self-managed installations» и выберите «Install GitLab for your infrastructure».
4. Появится страница с подробной информацией о GitLab и различных вариантах установки. В разделе «Self-managed» выберите «Install GitLab on your own server» и кликните на кнопку «Install GitLab».
5. Загрузится страница с подробными инструкциями по установке GitLab на различные операционные системы. Прокрутите страницу вниз до раздела «Windows» и найдите ссылку «Download for Windows». Кликните на эту ссылку.
6. Выберите место, куда хотите сохранить установочный файл, и нажмите кнопку «Сохранить».
Теперь у вас есть установочный файл GitLab, и вы готовы перейти к следующему шагу установки и настройки.
Шаг 2 — Запуск установки
После успешной загрузки GitLab, найдите загруженный установочный файл и дважды щелкните по нему, чтобы запустить процесс установки.
Откроется окно приветствия, где вам следует прочитать и принять лицензионное соглашение. Убедитесь, что вы внимательно изучили условия лицензии перед продолжением установки.
Затем вам будет предложено выбрать путь установки GitLab на вашем компьютере. По умолчанию путь будет установлен на C:\gitlab, но вы можете выбрать другую директорию, если это необходимо. Если вы хотите сохранить настройки по умолчанию, просто нажмите кнопку «Далее».
После выбора пути установки будет предложено выбрать опции установки. Установите флажок напротив каждой опции, которую вы хотите включить, и нажмите кнопку «Далее». Некоторые из этих опций включают установку GitLab Shell, Redis и PostgreSQL. Установка этих компонентов обеспечит полноценную работу GitLab.
Когда вы закончите выбор опций, нажмите кнопку «Установить». Процесс установки может занять некоторое время, будьте терпеливы.
По завершении установки будет открыто окно с информацией об успешной установке GitLab. Нажмите кнопку «Готово», чтобы закрыть окно установки и перейти к настройке GitLab.
Теперь вы готовы перейти к следующему шагу, где мы рассмотрим настройку GitLab на вашем компьютере.
Шаг 3 — Выбор директории установки
После того, как вы скачали исполняемый файл установщика для GitLab на Windows, необходимо выбрать директорию, в которую будет произведена установка.
Рекомендуется выбирать директорию без пробелов и русских букв. Вероятно, установочная программа предложит вам директорию по умолчанию, например, C:\GitLab. Вы можете оставить этот путь или выбрать другую папку, в которую будет установлен GitLab.
Помните, что выбранная вами директория должна иметь достаточно свободного места для установки GitLab и всех его компонентов.
После выбора директории, нажмите на кнопку «Установить», и установка GitLab начнется.
| Директория | Описание |
|---|---|
C:\GitLab |
Директория по умолчанию |
D:\GitLab |
Другая директория для установки |
В следующем шаге мы рассмотрим настройку GitLab после его установки.
Настройка GitLab
Для начала настройки GitLab на Windows вам потребуется выполнить несколько шагов:
- Установите GitLab на свой компьютер, следуя инструкциям в предыдущем разделе.
- Запустите GitLab и откройте его в веб-браузере по адресу http://localhost.
- Первоначальная настройка GitLab будет выполнена на странице «root password» (пароль администратора). Введите сложный пароль, который будет использоваться для входа в систему.
- Продолжайте выполнение настройки GitLab, следуя инструкциям на странице. Вы можете настроить различные параметры, такие как название вашей организации и адрес электронной почты администратора.
- Завершите настройку GitLab и сохраните все изменения.
Теперь ваша установка GitLab на Windows готова к использованию. Вы можете создавать репозитории, добавлять участников и управлять проектами через веб-интерфейс GitLab.
Важно помнить, что для обеспечения безопасности вам необходимо регулярно обновлять и проверять настройки GitLab, а также следить за новыми версиями программного обеспечения и выпускать соответствующие обновления.
Шаг 1 — Открытие GitLab в веб-браузере
После успешной установки GitLab на вашей системе Windows, вы можете открыть GitLab в любом веб-браузере по адресу http://localhost. Этот адрес указывает на локальный сервер, на котором работает GitLab.
Открыв страницу веб-браузера, вы увидите экран входа GitLab. Если вы впервые запускаете GitLab, вам потребуется создать новую учетную запись администратора. Введите имя пользователя, пароль и адрес электронной почты, а затем нажмите кнопку «Create account» (Создать учетную запись).
Если вы уже создали учетную запись администратора или другую учетную запись пользователей, вы можете войти на свою учетную запись, введя свои учетные данные в соответствующие поля и нажав кнопку «Sign in» (Войти).
После входа в GitLab вы будете перенаправлены на главную страницу, где вы сможете управлять своими проектами, просматривать репозитории и выполнять другие действия, связанные с управлением кодом и командной работой с использованием GitLab.
Шаг 2 — Создание нового пользователя
После установки GitLab на Windows вы можете создать нового пользователя, чтобы получить доступ к панели администрирования и настроить репозитории.
Чтобы создать нового пользователя, откройте веб-браузер и введите адрес вашего GitLab-сервера. Затем нажмите на кнопку «Регистрация» или «Создать новый аккаунт».
На странице регистрации вам будет предложено указать следующую информацию:
- Имя пользователя: введите уникальное имя пользователя, которое вы будете использовать для входа в систему.
- Электронная почта: введите вашу электронную почту, которая будет использоваться для связи и уведомлений.
- Пароль: введите надежный пароль для защиты вашей учетной записи.
- Подтверждение пароля: введите пароль еще раз для подтверждения.
После заполнения всех полей нажмите кнопку «Зарегистрироваться» или «Создать аккаунт».
После успешной регистрации вы будете перенаправлены на страницу вашей учетной записи, где вы сможете настраивать свои репозитории и управлять вашими проектами.
Видео:
Регистрация на GitLab и GitHub. 2.2. Курс «Git для начинающих»
Ledger Nano S Plus Обзор 2023: Включение, настройка, отправка, получение крипты, Ledger Live
Установка GIT (ОС Windows)
In the last article, we saw the various parts of GitLab, its architecture and how GitLab works. If you haven’t already, I suggest reading the previous article first before reading this one. Here is the link
GitLab, A Complete Beginner’s Guide!
In this article lets look at how to set it up locally on your Windows PC, so that you can have your very own GitLab setup running right at your home or organization!
If you are using Mac or Linux, you can follow the links below.
Complete Guide To Setting Up GitLab Locally On Mac.
Complete Guide To Setting Up GitLab Locally On Linux PC..!!
So let’s begin!
Things you will need
All you need are a computer running Windows OS with enough resources (CPU, memory, and disk space) for running the GitLab Server and GitLab Runner. How much resources is enough depends on how much performance you need, the more you have the better it is!
You can also set it up on the cloud over at Gitlab.com, but
- the free plans have some limitations in terms of processing power and hard disk space.
- Also doing it locally gives you more control over the setup and
- it will also be an opportunity to learn you more about GitLab
Hence I suggest taking this route of a local installation.
If you are part of a larger organization, and you wish to install it on the cloud, then you can always take a look at the paid plans of GitLab here link
Approach to install GitLab on Windows
Okay, let’s get back to the task in hand.
As we saw in the previous article GitLab consists of 2 parts.
- GitLab Server and
- GitLab Runner
Also, we have learned in the previous article that it is preferable to set the GitLab server and runners on separate computers. But I am going for a home set up, so I will be setting them both upon the same Windows computer.
The GitLab Server relies heavily on Linux technologies and hence it cannot be installed in our Windows PC natively. If you do some research, there are ways you can do it through the Linux subsystem in windows, but we are not going to take that approach.
The
problem with these workarounds are
- The installation process is a bit complicated and is not recommended for beginners.
- They are only guaranteed to work on a version to version basis. What I mean by that is you need to have a particular version of Windows and a particular version of GitLab for everything to run smoothly. If you update your Windows or if you wish to upgrade your GitLab then you might break your GtiLab set up. Since both Windows and GitLab updates come frequently, it is not such a good idea to waste time trying to fix things every few months.
- It is unofficial and hence support for future versions cannot be guaranteed.
- These unofficial methods will bring their own limitations as opposed to running natively on Linux
Due to these above reasons, we are going to go for a more stable approach of installing the GitLab server in a virtual environment. We will also see in this article the ways to make it run as smoothly and efficiently as possible while making sure it consumes as few resources as possible.
So this
is what we are going to do
- Install the GitLab Server on a Virtual Box running Ubuntu server
- Install GitLab runner natively on Windows.
This approach takes away the cons of using unofficial hacks, as it will work on all versions of you Windows and GitLab and you don’t need to worry too much while updating your software either!
By following the step by step guide shown below you should be able to set everything up and running in an hour or 2 (depending upon how good your internet connection is, it can take longer!)
GitLab Installation Process
STEP#1: Download and install VirtualBox
You can download and install VirtualBox from this link
Just click on the Windows hosts and the download should start automatically. The installation process is pretty straightforward, you can just accept the default options and click through to complete the process.
Once the installation is completed you can open VirtualBox from the Start menu in Windows.
STEP#2: Install Ubuntu Server as a Virtual Machine in your Windows PC.
The next step is to get a Linux distro to install our GitLab server. For this purpose, I recommend Ubuntu Server. I chose this particular distro for 2 reasons.
- Ubuntu is known for its stability.
- GitLab Server software has support for Ubuntu
- The server edition is chosen so that it will consume fewer resources on your computer.
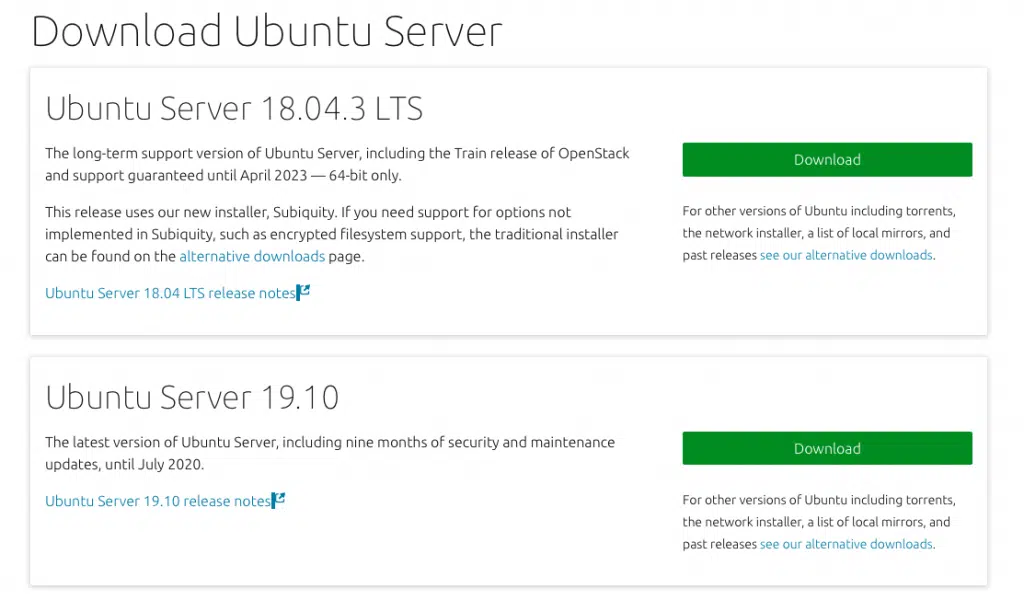
For this first, you need the Ubuntu Server image. You can download it from this link.
Ubuntu usually offers 2 sets of packages for us to choose from.
- Long term support version: Has a support period of 5 years
- Latest Version: has all the latest features.
I suggest you go for the LTS one, but then the latest version should also work just fine. So click on a “Download” button and your download should start automatically. It will take some time to complete as the iso is around 900MB.
Once the download is complete you can proceed to the installation process on VirtualBox.
STEP#3: Install Ubuntu Server on VirtualBox
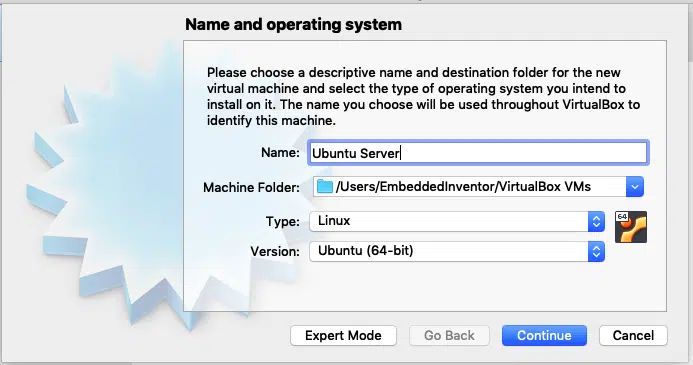
Open VirtualBox Application and click on the “New” button
A window like this should pop up
Give your virtual machine a name and choose Linux for type and ubuntu 64 bit for version and click “Continue”.
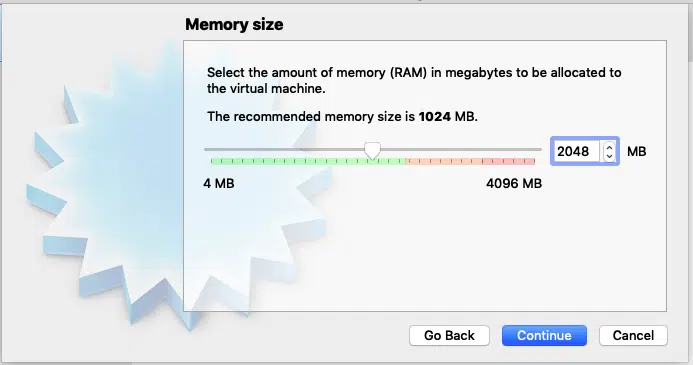
The next screen usually asks for RAM. GitLab recommends 8GB for a GitLab system with 100 users, I suggest a minimum of 2GB RAM for a home set up, you can give more if you can, just make sure you don’t allot more than 50% of your total available RAM.
Once you have allocated RAM space, Click “Continue” to the next page.
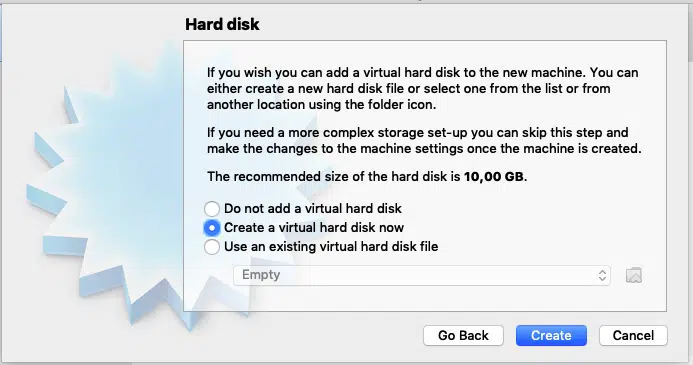
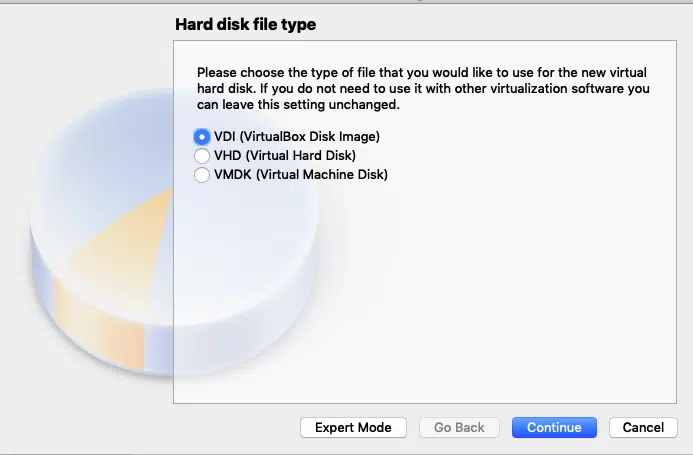
Next, you will be prompted for hard disk. Make sure “Create a virtual hard disk now” is selected and click “Create”
Accept
the default “VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image)” and click
“Continue”
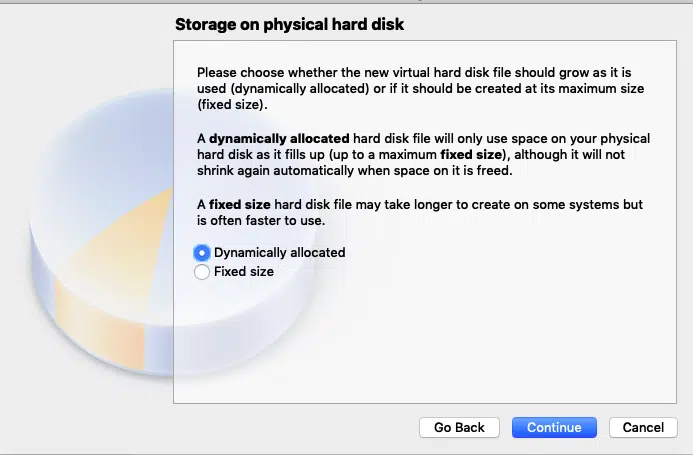
Accept “Dynamically Allocated” and Press continue. This option allocates hard disk space to the virtual machine on the run, so that as you use the more space, more will be allocated.
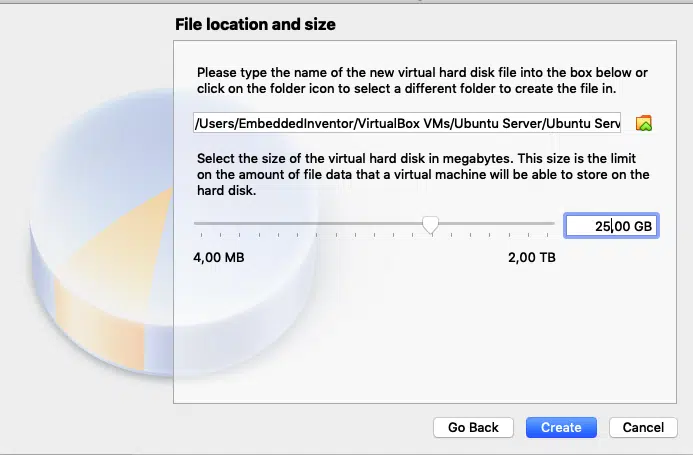
I suggest you allocate at least 25GB of space to the virtual machine, you can allot more if you can. Once you have chosen the disk space click create
Once you have done this, you should be taken back to the main window of VirtualBox and you should see the virtual machine you just created on the left pane of the window as shown in the screenshot below.
Next click on the “Settings”
And click on storage -> empty -> disk icon -> “Choose a disk file”
Select the ubuntu server iso image you have just downloaded and press ok. This is equivalent to inserting the Ubuntu disk in a real machine.
Next, go to settings->Network and choose “Bridged Adapter” in the “Attached to:” drop-down menu and press “OK”
I have explained the reason behind using these network settings in detail in this article, you can go ahead and read that if you are into computer networks.
The short explanation is, we will not be able to access the GitLab server from our other machines on the network unless we choose this option.
That’s it, the configuration is done!
You can now go ahead and click the start button!
Now the installation process will start. Since we have chosen to go with “Ubuntu server” in order to minimize the resource consumption (so that GitLab can take up as many resources as it needs) we don’t get a fancy Graphical UI, like in the desktop version of Ubuntu. You need to navigate the menus during installation only using Keyboard (tab, enter and arrow keys) since the Ubuntu server doesn’t come with mouse support. So go through the process and get it done.
STEP#4: Get the IP address of your ubuntu server
Okay now
once you got the Ubuntu server up and running, you need to find its IP address
and make a note of it.
To do that, use the “ifconfig” command on your Ubuntu server’s terminal
STEP#5: Download and install GitLab server
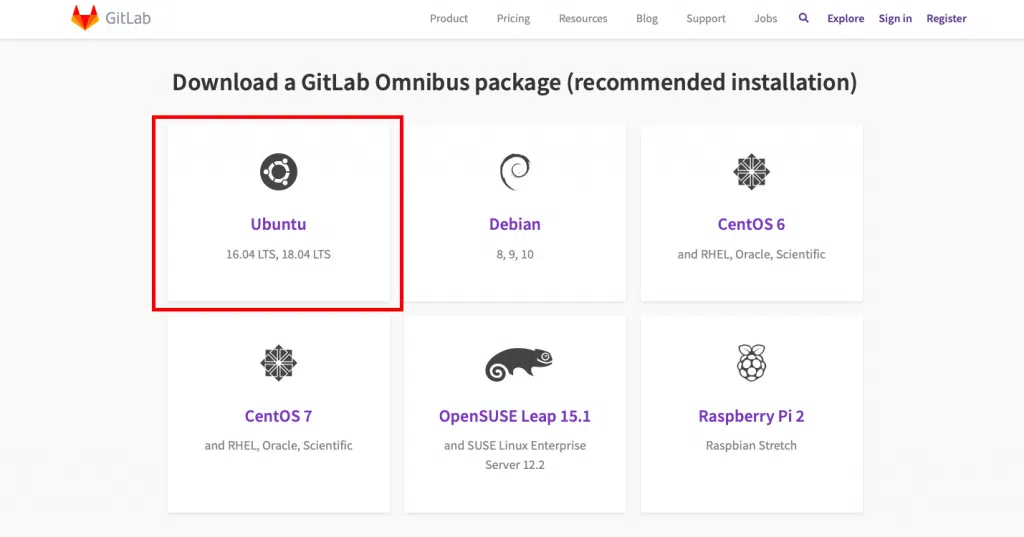
To download GitLab server, go to the official link on the Gitlab’s Website
As you can see GitLab official supports several Linux distros, even a Raspberry Pi 2’s Raspbian! We are interested in Ubuntu, so click on the Omnibus Ubuntu Link on as shown in the screenshot above.
Once you click on Ubuntu, the commands you need to enter to install GitLab server will be shown to you.
I am not showing each instruction here since GitLab updates the information presented on their website all the time and that can make this section of the article outdated. Just follow the step by step instructions given in the link to install the GitLab Server on your VM.
Just type in the commands shown there on you Ubuntu server’s terminal one by one to get GitLab Server installed.
A couple of tips on the GitLab installation instructions
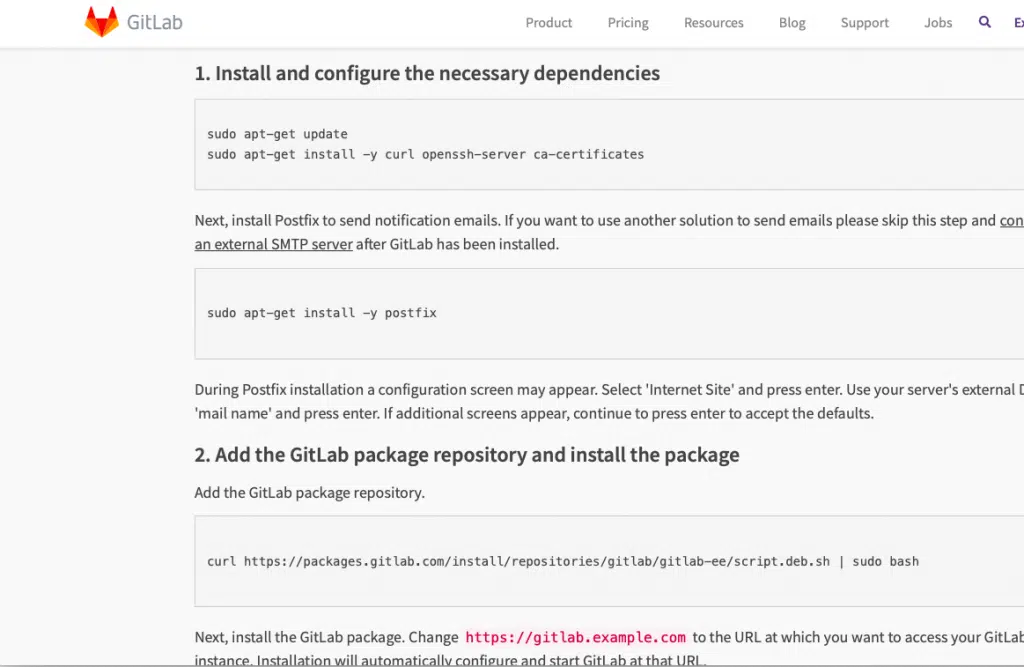
Tip#1
In the postfix installation step (step 1 last command on the GitLab website)
sudo apt-get install -y postfix
you can skip the mail option by choosing the “no configuration” option as shown in the screenshot below.
Tip#2
In the last command of step 2 at GitLab website
sudo EXTERNAL_URL="https://gitlab.example.com" apt-get install gitlab-ee
Make sure you replace the URL with the IP address of the VM that we have made a note of in Step 5 above like this
sudo EXTERNAL_URL="192.168.0.116" apt-get install gitlab-ee
Or to be more precise just place the VM’s IP address that we obtained in Step#4 in its appropriate place
sudo EXTERNAL_URL=”<Your VM’s IP address>” apt-get install gitlab-ee
This step will take a while, so be patient. In my machine it took 4 minutes 48 seconds as shown in the screenshot below, yours can vary depending on the processing power it has.
Once done it will show u something like in the screenshot below.
Once it’s done, you can go ahead to your favorite browser and type in the IP address of your VM and check if the installation has succeeded.
And voila! GitLab server installation has succeeded!
Go ahead and follow the onscreen instructions to set up your password, accounts and everything else!
STEP#6: Download GitLab runners
Before installing GitLab runners you need to install Git on your Windows PC. You can download the latest version of Git in this link.
Now that we have set up the Gitlab server and Git, the next step is to set up the GitLab runner!
At the time of writing this article, the installation process goes like this:
Make a folder on your computer and go to either this link for 32bit version or this link for 64bit version to download the binaries and put them in the folder you created
For getting the most up to date instruction, I am gonna ask you to follow the process given in the GitLab website
STEP#7: Connect the GitLab server to the GitLab runner
GitLab
calls this process of connecting the Server to Runner as “Registering the
GitLab Runner to the Server”
You can follow the instructions for Windows in this link to do the same.
Scroll down to the windows section and you will see something similar to this
Step# 7.1: Start the registration process
To enter these commands you need to open a command prompt with administrator privileges. For this just type cmd on the search menu, right-click on Command prompt and choose run as administrator
After that, just go to the folder to which you have downloaded the Gitlab Runner to and copy the path to that folder
Next, go back to the command line and give the following command
cd <path you copied>
Run the following command to start the registration process
gitlab-runner-windows-amd64.exe register
As shown in the screenshots above, enter your Virtual Machine’s IP address when prompted. Make sure you add “http://” before the IP address.
Once the IP address is entered, the next prompt appears asking you to enter a token, so let’s first go get a token from our GitLab server.
Step#7.2: Obtain token from GitLab Server
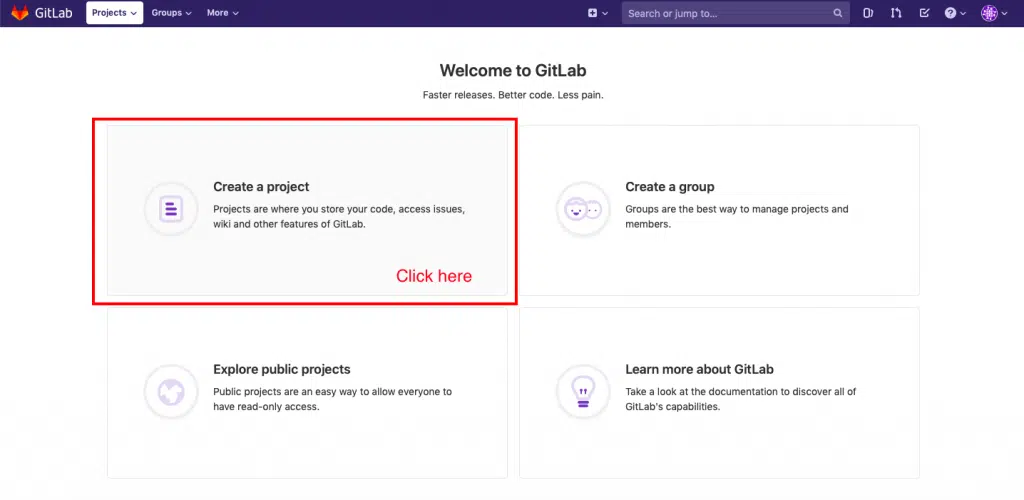
Go to your browser and enter the GitLab Server’s IP address. Once you have logged in you can create your first project by clicking on the respective pane as shown in the screenshot below.
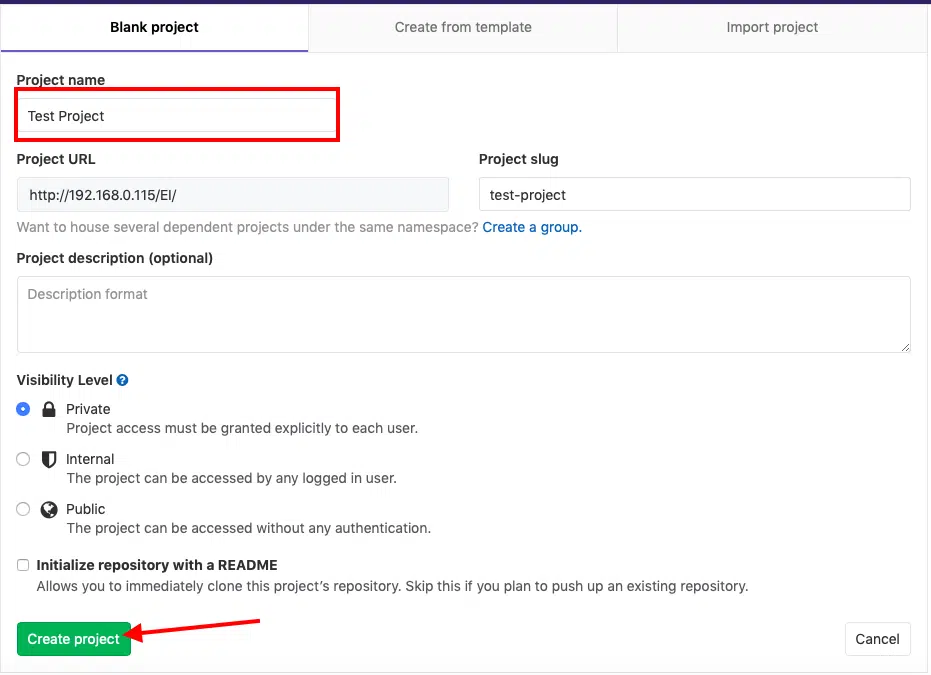
Just give the project a name and click on the create project button. The other field should get populated automatically.
Once you click the button as shown in the screenshot above, you will be taken to your project page.
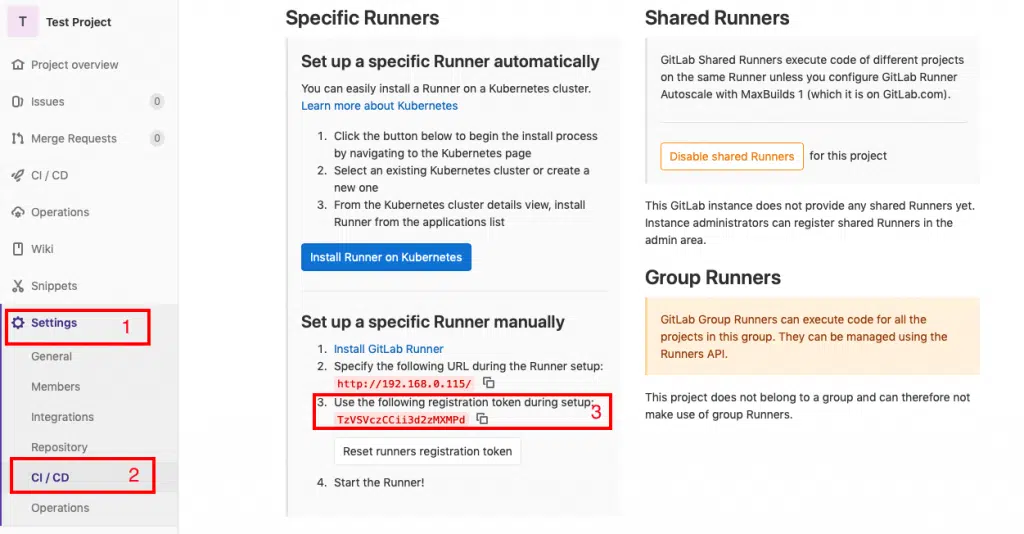
From there just click on Settings->CI/CD and scroll down a bit and click the “Expand” button next to “Runners” and you will find the token you need as shown in the screenshot below.
This token basically connects your project on the GitLab Server to the GitLab runner.
Step#7.3: Enter the token
Now that we have the token let’s enter it on the Command prompt
Once
entering the token, you will be prompted to give the runner a description, go
ahead and do that.
After that, you will be asked to enter some tags.
What are tags? Why are they needed for GitLab runners?
The
better term for tags can be capabilities.
Consider
this scenario.
Assume you are working in a large team of 1000 developers, who are doing say 50 different projects and your GitLab system has 100 different runners set up with several capabilities to do specific tasks. Some projects may need C compilers, while others may need python interpreters.
Now in order to connect a given project with a free-runner, we need some sort of parameter to tell the GitLab server that this particular free runner is capable of running the scripts needed for that particular job.
This is where tags come into the picture. By giving tags like “C” or “Python” a single runner can be connected to multiple projects and a single project can execute its jobs on several runners to ensure the best possible performance.
Using
these tags the Gitlab server can find a runner with the specific capability to
use for a given job. So give some suitable tags that will imply the
capabilities of your runner.
Once that is done, you will be prompted to enter “executor”.
Executors are programs that run our CI/CD scripts. Type shell and press enter
This will end the registration process the Runner to the server
Once registered you can start the GitLab runner as a Service (background task) by issuing the commands
gitlab-runner-windows-amd64.exe install gitlab-runner-windows-amd64.exe start
As you can see in the screenshot below, in the task manager app we can see that our gitlab-runner service is running!
Test to see if everything works
By following the 7 steps above, you should have a set up with GitLab Server and Runner running on your system. Its time to test and see if everything works the way it is supposed to work!
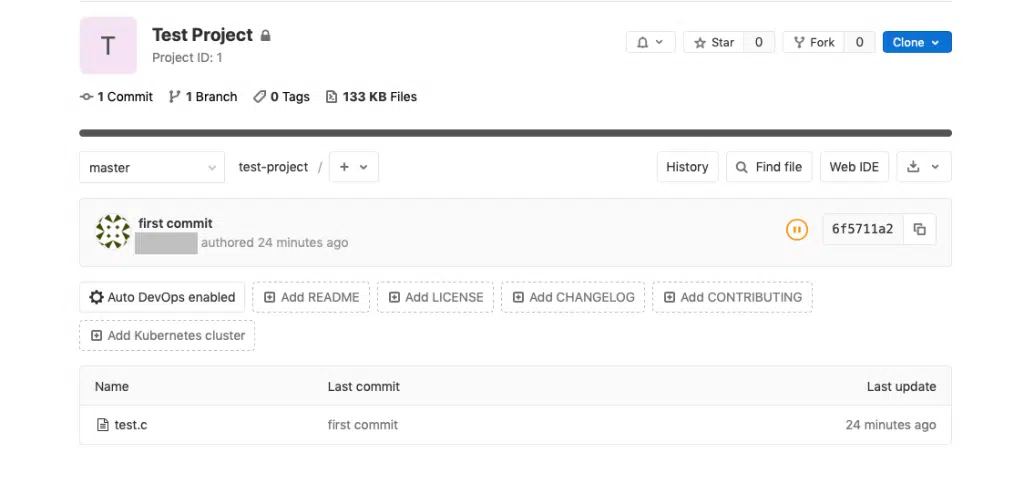
First, let’s test the GitLab server by creating a repo and pushing it to the server.
Testing GitLab Server
STEP#1: Make a test git repo
Let’s make a simple git repo on a new folder on our Desktop and push it to the GitLab server.
So open your Git-Bash app, which got installed as you were installing git.
Once opened type in the following commands
cd cd Desktop mkdir test_project cd test_project touch test.c
The above lines of command are just the fancy way of creating a folder named test_project on your Desktop and a file named test.c inside it. You can also do it through the Graphical User Interface if you want to.
So next, please open the C file using your favorite text editor and type in a simple program for testing, something like the following.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Hello Embedded Inventors!");
return 0;
}
Next, let’s initialize a git repository on our test_project folder. So go back to the terminal cd into the test_project folder and type in the following command
You should receive a reply saying “Initialized empty Git repository”
STEP#2: Push it to the server
Now that we have our git repo ready, let’s push it to our git server. To do that login to your GitLab and go to the project we created earlier. There GitLab shows us the commands needed to push our repo to the server.
First, let’s configure our name and email on the git repository to the ones set on the GitLab server
So enter
the following command.
git config --global user.name "<enter your name here>" git config --global user.email "<enter your email here>"
Next, we need to connect our server and our repository. To do that just enter the following commands
git remote add origin <your project URL>.git
In my case it is
git remote add origin http://192.168.0.115/EI/test-project.git
To find your project URL, just copy the address bar of your browser while you are on your project’s page in GitLab
Then add our test.c file and commit the changes using the following commands
git add . git commit -m"first commit"
Then push
your git repo onto the GitLab using the command
git push -u origin master
You will be prompted to enter the user name and password of your GitLab account, once done go to your browser and just refresh the page and you should be able to see your test project page in GitLab!
Testing GitLab Runner
STEP#3: Make a simple bash script to build the test.c
file
Create a bash script on your project folder
cd cd Desktop/test_project touch build.ps1
Edit it so that it looks something like this
gcc test.c -o test echo "Build completed"
STEP#4: Create and edit .gitlab_ci.yml to run the
above script
What is .gitlab-ci.yml and why it is needed? This is the file that contains the instructions for the GitLab runners to execute the CI/CD tasks. It should be present in the project’s root folder. It can be used to test if a commit builds correctly, passes some unit tests and if it needs packaging and deployment.
You can
learn more about how to configure it from the official quick start tutorial
here
For the
purpose of testing our installation let’s create a file named .gitlab-ci.yml in
the test_project folder and put the following lines in there.
Make sure you are in the right directory
cd cd Desktop/test_project
Create the file using the command
Open it with your favorite text editor and type the following lines into it.
build:
script:
- powershell -File build.ps1
tags:
- test
The last line tells the GitLab server to use the GitLab runner with the tag named “test”. If you gave your GitLab runner installation a different tag, make sure you make the appropriate change to the above lines.
Also,
make sure you use spaces instead of tabs at the beginning of the above lines.
Now add it to the git repository and push it to the Gitlab server
git add . git commit -m"gitlab yml added" git push
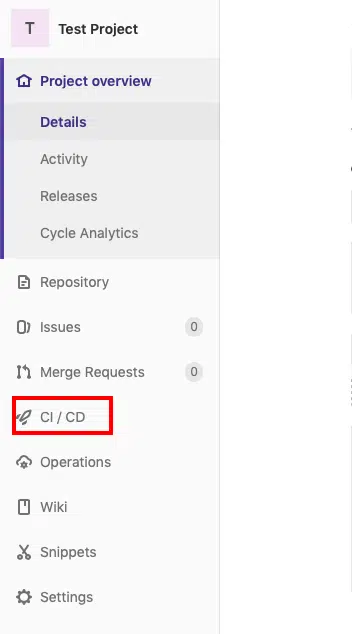
Now let’s get back to our GitLab server’s URL and see if it worked. Go to the project page and click on CI/CD
You will
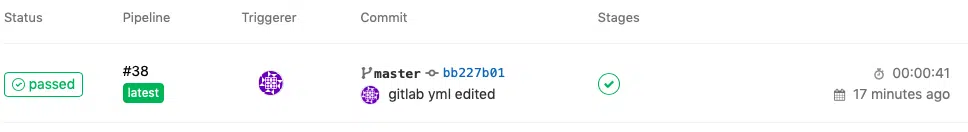
be taken to the pipeline page which shows the result of your latest commit.
It will
take a minute or so before it completes the pipeline and as you can see in the
screenshot above, mine took 41 seconds to complete and the status is
“passed”
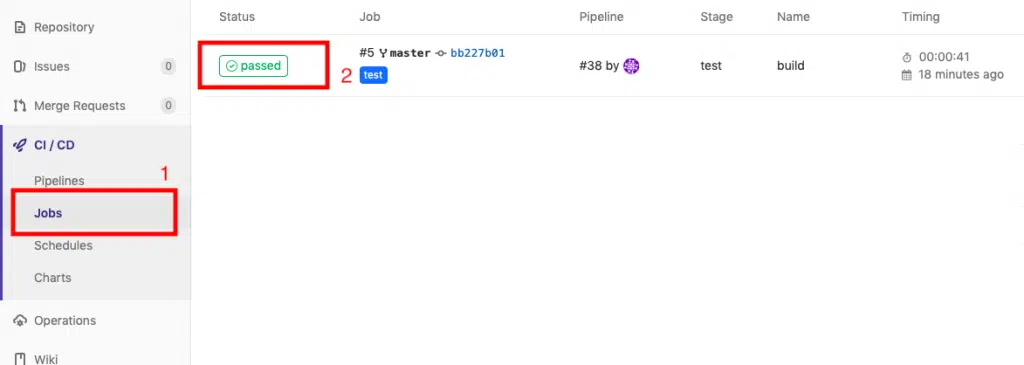
If you
click on “jobs” under the CI/CD menu, you will be taken to another
page which shows you more information about the execution of our yml file
Next click on “passed” as shown in the screenshot above, this will take you to another page which will look something like this.
As you can see, our build.ps1 gets executed by the GitLab runner and it succeeds to compile our project.
And with that, I will conclude this tutorial!
I leave the rest to you to play, explore, experiment and learn GitLab!
I hope you guys enjoyed this article and learned something useful.
You can email us or contact us through this link if you have any questions or suggestions.
If you liked the post, feel free to share this post with your friends and colleagues!
GitLab — мощная платформа для управления репозиториями Git, которая позволяет организовать совместную работу над проектами с помощью инструментов контроля версий. Однако, перед тем, как начать использовать GitLab, необходимо его установить. Есть несколько способов установки GitLab на Windows, и в этой статье мы расскажем вам о самом простом и надежном из них.
Шаг 1: Скачайте и установите Git for Windows
Первым делом необходимо установить Git на ваш компьютер. Вам потребуется установочный файл, который можно скачать с официального сайта Git по ссылке www.git-scm.com. Пройдите по указанной ссылке и нажмите на кнопку «Download». После завершения загрузки установите Git, следуя подсказкам инсталлятора.
Примечание: Установочный файл для Git доступен только для 64-битных версий Windows.
Шаг 2: Скачайте и установите Docker Desktop
Для удобной установки GitLab на Windows, мы рекомендуем использовать Docker — инструмент для создания и управления контейнерами. Docker Desktop можно скачать с официального сайта Docker по ссылке www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop. Найдите для вашей операционной системы кнопку «Download» и скачайте установочный файл. Запустите его и следуйте инструкциям для установки Docker на ваш компьютер.
Шаг 3: Скачайте и установите GitLab Community Edition
После установки Git и Docker Desktop, вы готовы перейти к установке GitLab. Для этого вам понадобится установить Docker-образ GitLab Community Edition. Откройте командную строку или терминал и введите следующую команду:
docker pull gitlab/gitlab-ce
Когда Docker загрузит образ GitLab Community Edition, вы будете готовы к запуску GitLab на своем компьютере. Далее вам потребуется настроить контейнер GitLab, что будет предметом следующей статьи.
Содержание
- Как установить GitLab на Windows
- Загрузка и установка Git
- Установка и запуск PostgreSQL
- Установка Ruby и RubyGems
- Установка GitLab
Как установить GitLab на Windows
GitLab представляет собой платформу для управления исходным кодом, которая позволяет командам программистов эффективно сотрудничать в создании и разработке проектов. В этом руководстве мы рассмотрим пошаговую процедуру установки GitLab на операционную систему Windows.
- Скачайте установочный файл GitLab с официального сайта по адресу https://about.gitlab.com/install/#windows.
- Запустите установочный файл GitLab.
- Выберите путь установки GitLab на вашем компьютере.
- Нажмите «Установить», чтобы начать процесс установки.
- Дождитесь завершения установки GitLab на вашем компьютере.
- После завершения установки, запустите GitLab и выполните необходимую настройку.
- Откройте веб-браузер и перейдите по адресу «http://localhost:8080», чтобы проверить работу GitLab.
- Войдите в систему GitLab, используя учетные данные, созданные в процессе установки.
Теперь у вас установлен и готов к использованию GitLab на вашем компьютере под управлением операционной системы Windows. Не забудьте изучить дополнительные инструкции по использованию GitLab, чтобы узнать о его возможностях и функциях.
Загрузка и установка Git
Для установки Git на Windows вам понадобится скачать исполняемый файл установщика с официального сайта Git.
- Откройте браузер и перейдите на страницу загрузки Git по адресу: https://git-scm.com/downloads.
- На этой странице вы увидите список доступных версий Git для различных операционных систем. Вам нужно выбрать версию для Windows и нажать на соответствующую ссылку загрузки.
- Когда загрузка завершится, найдите скачанный файл установщика в папке загрузок на вашем компьютере и запустите его.
- В процессе установки вам будут предложены различные параметры для настройки Git. Оставьте их по умолчанию или настройте по своему усмотрению.
- После завершения установки Git проверьте, что он успешно установлен, открыв командную строку (нажмите Win + R и введите «cmd», затем нажмите Enter) и введите команду «git —version». Если вы видите версию Git, значит он был успешно установлен.
Поздравляю! Теперь у вас установлен Git, и вы готовы перейти к установке GitLab.
Установка и запуск PostgreSQL
- Перейдите на официальный веб-сайт PostgreSQL по адресу https://www.postgresql.org/download/windows/.
- Выберите нужную версию PostgreSQL, в зависимости от вашей операционной системы Windows.
- Загрузите установочный пакет PostgreSQL.
- Запустите загруженный установочный файл и следуйте инструкциям мастера установки.
- На странице выбора компонентов установки, убедитесь, что выбраны все компоненты, необходимые для функционирования PostgreSQL.
- На странице выбора расположения установки, выберите путь, куда будет установлена PostgreSQL.
- На странице выбора пароля для суперпользователя (пользователя «postgres»), введите и подтвердите пароль и запомните его.
- После завершения установки, PostgreSQL будет автоматически запущен в качестве службы.
- Для проверки успешной установки и запуска PostgreSQL, откройте командную строку Windows и выполните следующую команду:
psql -U postgres. Если вы видите приглашение командной строки PostgreSQL, значит установка прошла успешно.
Поздравляю! Теперь у вас установлена и запущена PostgreSQL на вашей операционной системе Windows. Вы можете начать использовать PostgreSQL для создания, управления и обработки баз данных.
Установка Ruby и RubyGems
Прежде чем установить GitLab на Windows, необходимо установить Ruby и RubyGems.
Шаги для установки Ruby и RubyGems:
- Перейдите на официальный сайт Ruby (https://www.ruby-lang.org/en/downloads/) и скачайте установочный файл Ruby для Windows.
- Запустите скачанный установочный файл и следуйте инструкциям мастера установки.
- Выберите путь установки Ruby (рекомендуется использовать значение по умолчанию) и установите Ruby на ваш компьютер.
- После установки Ruby, откройте командную строку и введите команду «ruby -v», чтобы убедиться, что Ruby успешно установлен.
- Перейдите на официальный сайт RubyGems (https://rubygems.org/pages/download) и скачайте последнюю версию RubyGems.
- Распакуйте скачанный архив RubyGems и откройте командную строку в папке с распакованными файлами.
- Введите команду «ruby setup.rb» для установки RubyGems.
- После установки RubyGems, введите команду «gem -v», чтобы убедиться, что RubyGems успешно установлен.
Поздравляю! Теперь у вас установлены Ruby и RubyGems, и вы готовы приступить к установке GitLab на Windows.
Установка GitLab
Для установки GitLab на операционную систему Windows требуется выполнить следующие шаги:
| Шаг 1: | Скачайте установочный файл GitLab с официального сайта. |
| Шаг 2: | Запустите установочный файл и следуйте инструкциям мастера установки. |
| Шаг 3: | Выберите путь установки GitLab на вашем компьютере. |
| Шаг 4: | Выберите компоненты, которые вы хотите установить (по умолчанию выбраны все необходимые компоненты). |
| Шаг 5: | Выберите пункт «Local user account» для создания нового аккаунта пользователя GitLab или «Domain user account» для использования существующего аккаунта пользователя. |
| Шаг 6: | Введите имя пользователя и пароль для нового аккаунта пользователя GitLab (если применимо) и нажмите «Next». |
| Шаг 7: | Настройте порты, на которых будет работать GitLab, и нажмите «Next». |
| Шаг 8: | Выберите пункт «Install GitLab now» для начала установки или «Customize» (настраиваете настройки перед установкой) и нажмите «Next». |
| Шаг 9: | Нажмите «Install» и дождитесь завершения установки GitLab. |
| Шаг 10: | После завершения установки нажмите «Finish» и перезагрузите компьютер для применения изменений. |
После выполнения этих шагов у вас будет установлен GitLab на вашем компьютере с операционной системой Windows.
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests…
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up