Последнее обновление: 01.01.2023
Установка компилятора
Рассмотрим создание первой простейшей программы на языке Си с помощью компилятора GCC, который на сегодняшний день является одим из
наиболее популярных компиляторов для Cи и который доступен для разных платформ. Более подобному информацию о GCC можно получить на официальном сайте проекта https://gcc.gnu.org/.
Набор компиляторов GCC распространяется в различных версиях. Для Windows одной из наиболее популярных версий является пакет средств для разработки от
некоммерческого проекта MSYS2. Следует отметить, что для MSYS2 требуется 64-битная версия Windows 7 и выше (то есть Vista, XP и более ранние версии не подходят)
Итак, загрузим программу установки MSYS2 с официального сайта MSYS2:
После загрузки запустим программу установки:
На первом шаге установки будет предложено установить каталог для установки. По умолчанию это каталог C:\msys64:
Оставим каталог установки по умолчанию (при желании можно изменить). На следующем шаге устанавливаются настройки для ярлыка для меню Пуск, и затем собственно будет произведена установка.
После завершения установки нам отобразить финальное окно, в котором нажмем на кнопку Завершить
После завершения установки запустится консольное приложение MSYS2.exe. Если по каким-то причинам оно не запустилось,
то в папке установки C:/msys64 надо найти файл usrt_64.exe:
Теперь нам надо установить собственно набор компиляторов GCC. Для этого введем в этом приложении следующую команду:
pacman -S mingw-w64-ucrt-x86_64-gcc
Для управления пакетами MSYS2 использует пакетный менеджер Packman. И данная команда говорит пакетному менелжеру packman установить пакет mingw-w64-ucrt-x86_64-gcc,
который представляет набор компиляторов GCC (название устанавливаемого пакета указывается после параметра -S).
и после завершения установки мы можем приступать к программированию на языке Си. Если мы откроем каталог установки и зайдем в нем в папку C:\msys64\ucrt64\bin,
то найдем там все необходимые файлы компиляторов:
В частности, файл gcc.exe как раз и будет представлять компилятор для языка Си.
Далее для упрощения запуска компилятора мы можем добавить путь к нему в Переменные среды. Для этого можно в окне поиска в Windows ввести «изменение переменных среды текущего пользователя»:
Нам откроется окно Переменныех среды:
И добавим путь к компилятору C:\msys64\ucrt64\bin:
Чтобы убедиться, что набор компиляторов GCC успешно установлен, введем следующую команду:
В этом случае нам должна отобразиться версия компиляторов
Создание первой программы
Итак, компилятор установлен, и теперь мы можем написать первую программу. Для этого потребуется любой текстовый редактор для набора исходного кода.
Можно взять распространенный редактор Visual Studio Code или даже обычный встроенный Блокнот.
Итак, создадим на жестком диске папку для исходных файлов. А в этой папке создадим новый файл, который назовем hello.c.
В моем случае файл hello.c находится в папке C:\c.
Теперь определим в файле hello.c простейший код, который будет выводить строку на консоль:
#include <stdio.h> // подключаем заголовочный файл stdio.h
int main(void) // определяем функцию main
{ // начало функции
printf("Hello METANIT.COM!\n"); // выводим строку на консоль
return 0; // выходим из функции
} // конец функции
Для вывода строки на консоль необходимо подключить нужный функционал. Для этого в начале файла идет строка
#include <stdio.h>
Директива include подключает заголовочный файл stdio.h, который содержит определение функции printf, которая нужна для вывода строки на консоль.
Далее идет определение функции int main(void). Функция main должна присутствовать в любой программе на Си, с нее собственно и начинается
выполнение приложения.
Ключевое слово int в определении функции int main(void) говорит о том, что функция возвращает целое число.
А слово void в скобках указывает, что функция не принимает параметров.
Тело функции main заключено в фигурные скобки {}. В теле функции происходит вывод строки на консоль с помощью функции printf, в которую передается выводимая строка «Hello METANIT.COM!».
В конце осуществляем выход из функции с помощью оператора return. Так как функция должна возвращать целое число, то после return указывается число 0.
Ноль используется в качестве индикатора успешного завершения программы.
После каждого действия в функции ставятся точка с запятой.
Теперь скомпилируем этот файл. Для этого откроем командную строку Windows и вначале с помощью команды cd перейдем к папке с исходным файлом:
Чтобы скомпилировать исходный код, необходимо компилятору gcc передать в качестве параметра файл hello.c:
После этого будет скомпилирован исполняемый файл, который в Windows по умолчанию называется a.exe. И мы можем обратиться к этому файлу
и в этом случае консоль выведет строку «Hello METANIT.COM!», собственно как и прописано в коде.
Стоит отметить, что мы можем переопределить имя компилируемого файла с помощью флага -o и передав ему имя файла, в который будет компилироваться программа.
Например:
В этом случае программа будет компилироваться в файл hello.exe, который мы также запустить.
Чтобы не приходилось вводить две команды: одну для компиляции программы и другую для ее запуска, мы можем объединить команды:
gcc hello.c -o hello.exe & hello
Эта команда сначала компилирует код в файл hello.exe, а потом сразу запускает его.
Загрузить PDF
Загрузить PDF
В этой статье рассказывается, как скомпилировать программу из исходного кода на языке C с помощью компилятора GNU Compiler (GCC) для Linux или Minimalist Gnu (MinGW) для Windows.
-
1
В Unix-системе откройте терминал.
-
2
Введите gcc --version и нажмите ↵ Enter. Отобразится версия компилятора C. Если команда не сработала, скорее всего, GCC не установлен.[1]
- Если компилятор не установлен, почитайте документацию к своему дистрибутиву Linux, чтобы узнать, как скачать соответствующий пакет.
- Если вы компилируете программу, написанную на языке C++, вместо «gcc» введите «g++».
-
3
Перейдите в каталог, в котором хранится исходный код.
- Например, если файл с исходным кодом «main.c» находится в каталоге /usr/wikiHow/source, введите cd /usr/wikiHow/source.
-
4
Введите gcc main.c -o HelloWorld. Замените «main.c» на имя файла с исходным кодом, а «HelloWorld» замените на имя конечной программы. Программа будет скомпилирована.
- Если на экране появились сообщения об ошибках, введите gcc -Wall -o errorlog file1.c, чтобы получить дополнительную информацию. Затем в текущем каталоге откройте файл «errorlog»; для этого введите cat errorlog.
- Чтобы скомпилировать одну программу из нескольких файлов с исходным кодом, введите gcc -o outputfile file1.c file2.c file3.c.
- Чтобы скомпилировать сразу несколько программ из нескольких файлов с исходными кодами, введите gcc -c file1.c file2.c file3.c.
-
5
Запустите скомпилированную программу. Введите &# 46;/HelloWorld, где «HelloWorld» замените именем программы.
Реклама
-
1
Скачайте Minimalist GNU для Windows (MinGW). Эту версию GCC для Windows довольно легко установить. Установочный файл можно скачать на этом сайте.[2]
-
2
Запустите установочный файл MinGW.
- Если файл не запустился автоматически, дважды щелкните по нему в папке для загрузок, а затем нажмите «Установить».
-
3
Задайте параметры установки и нажмите Continue (Далее).
- Рекомендуем установить MinGW в папку по умолчанию, а именно в (C:\MinGW). Если нужно поменять папку, не выбирайте папку, в названии которой присутствуют пробелы, такую как «Program Files».[3]
- Рекомендуем установить MinGW в папку по умолчанию, а именно в (C:\MinGW). Если нужно поменять папку, не выбирайте папку, в названии которой присутствуют пробелы, такую как «Program Files».[3]
-
4
Выберите компиляторы, которые нужно установить.
- На левой панели рекомендуем нажать «Basic Setup» (Обычная установка). Затем на правой панели поставьте флажки рядом со всеми перечисленными компиляторами.
- Более опытные пользователи могут выбрать опцию «All packages» (Все пакеты) и отметить дополнительные компиляторы.
-
5
Откройте меню Installation (Установка). Оно находится в верхнем левом углу MinGW.
-
6
Нажмите Apply Changes (Применить изменения).
-
7
Нажмите Apply (Применить). Компиляторы будут загружены и установлены.
-
8
В путь к MinGW вставьте системные переменные среды. Сделайте следующее:
- Нажмите ⊞ Win+S, чтобы открыть строку поиска, и введите среда.
- В результатах поиска щелкните по «Изменение системных переменных среды».
- Нажмите «Переменные среды».
- Нажмите «Изменить» (под «Пользовательские переменные»).
- Прокрутите вниз информацию в поле «Значение переменной».
- Непосредственно под последней записью введите ;C:\MinGW\bin. Обратите внимание, что если вы установили MinGW в другую папку, введите ;C:\путь-к-папке\bin.
- Дважды нажмите «OK». Еще раз нажмите «OK», чтобы закрыть окно.
-
9
Откройте командную строку в качестве администратора. Для этого:
- Нажмите ⊞ Win+S и введите строка.
- В результатах поиска щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по «Командная строка» и в меню выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
- Нажмите «Да», чтобы разрешить внесение изменений.
-
10
Перейдите в папку, в которой хранится файл с исходным кодом.
- Например, если файл с исходным кодом «helloworld.c» находится в папке C:\Source\Programs, введите cd C:\Source\Programs.
-
11
Введите gcc helloworld.c -o helloworld.exe. Замените «helloworld» на имя файла с исходным кодом и имя программы. По завершении компиляции программы вы вернетесь в командную строку, при этом не будет никаких сообщений об ошибках.[4]
- Любые ошибки программирования должны быть устранены перед компиляцией программы.
-
12
Чтобы запустить программу, введите ее имя. Если программа называется helloworld.exe, введите это имя, чтобы запустить программу.
Реклама
Советы
- Компиляция кода с помощью флага -g приведет к созданию отладочной информации, которая может быть использована соответствующим отладчиком, например, GDB.
- Создайте сборочный файл проекта (make-файл), чтобы упростить компиляцию больших программ.
- Если вы активно используете оптимизацию, помните, что оптимизация по скорости может привести к снижению размера и, иногда, качества (и наоборот).
- При компиляции программы на языке C++ используйте G++ так же, как вы используете GCC. Помните, что файлы с исходным кодом на языке C++ имеют расширение .cpp, а не .c.
Реклама
Что вам понадобится
- Компьютер под управлением Linux или Windows
- Базовые знания GNU/Linux и знание того, как устанавливать приложения
- Программный код
- Текстовый редактор (например, Emacs)
Об этой статье
Эту страницу просматривали 80 155 раз.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
Прежде чем
двигаться дальше, нам нужно настроить рабочее место для написания программ на
Си. А, именно, установить (если его еще нет) компилятор и интегрированную среду
разработки для написания, компиляции и отладки программ. Начнем с выбора и
установки компилятора. На сегодняшний день одним из самых популярных является
компилятор gcc. Это сокращение
от:
GNU Compiler Collection
Если вы
работаете под ОС Linux, то, этот компилятор должен быть уже
установлен в системе. Если же вы работаете под ОС Windows, то компилятор
нужно устанавливать самим. Давайте это сделаем.
Так как я
работаю под ОС Windows, то буду показывать порядок установки
всех средств именно на этой ОС. Итак, первым делом нужно перейти на официальный
сайт компилятора gcc, предназначенных для ОС Windows:
https://gcc.gnu.org
Далее, переходим
в раздел Download/Binaries (бинарники) и
видим несколько вариантов способов установки gcc на систему. Наиболее
удобный, на мой взгляд, является использование, так называемого, порта MinGW с установкой
только необходимых (минимального набора) компонент компилятора gcc.
Здесь есть два
варианта MinGW: старый
32-битный и новый – 64-битный. Я рекомендую воспользоваться старым вариантом,
т.к. он хорошо себя зарекомендовал и, что называется, проверен временем. С
новым могут возникать проблемы, да и для языка Си стандарта C99 он явно
избыточен.
Нажимаем на
ссылку MinGW и нас
перенаправляют на страницу:
https://osdn.net/projects/mingw/
и здесь нам
нужно скачать установщик mingw-get-setup.exe.
Запускаем эту
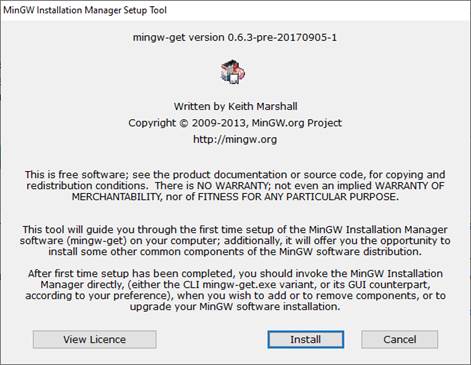
программу. Появится следующее диалоговое окно:
Нажимаем здесь
кнопку «Install». В следующем
окне соглашаемся со всеми настройками по умолчанию, в том числе и с маршрутом
распаковки «C:\MinGW» (если вас он
не устраивает, то можете изменить на свой) и нажимаем на кнопку «Continue». Начнется
скачивание и установка. После установки этот инсталлятор автоматически
запустится:
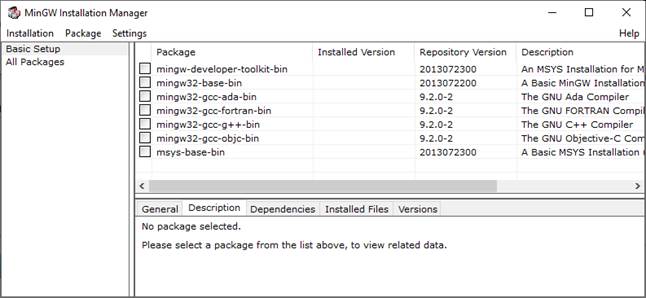
В диалоговом
окне нам нужно выбрать все необходимые компоненты для установки компилятора gcc для языка Си. Они
следующие:
- mingw32-gcc-bin (после отметки
также дополнительно отмечаются другие компоненты, с которыми mingw32-gcc-bin работает
совместно); - mingw32-gcc-g++-bin (для установки
линкера для компилятора Си); - mingw32-make-bin;
- mingw32-gdb-bin (дебаггер, для
отладки кода).
После этого в
меню «Installation» выбираем пункт
«Apply Changes» и в окне
нажимаем кнопку «Apply»:
Начнется
установка выбранных компонент для компилятора gcc в указанный
каталог.
Далее, нужно
прописать в системе путь к каталогу компилятора gcc. Для этого
нажимаем правую кнопку мыши на кнопке «Пуск» и выбираем «система». В
появившемся диалоговом окне щелкаем на «Дополнительные параметры системы», и
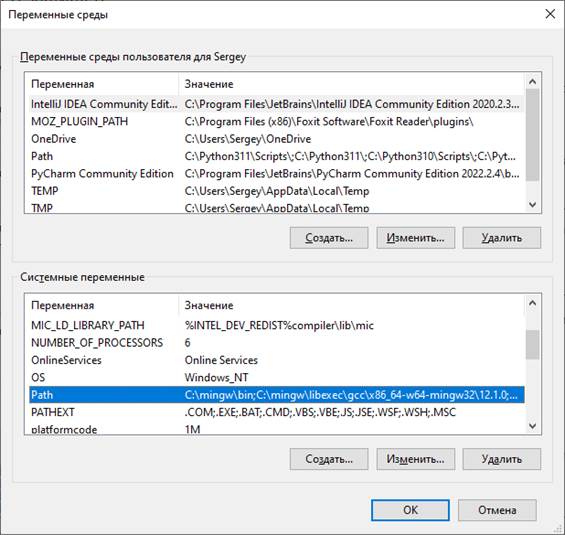
затем «Переменные среды…». Появится еще одно диалоговое окно, в котором нас
будет интересовать системная переменная Path:
Два раза щелкаем
по строчке с переменной Path, появится следующее окно, в котором
следует добавить путь «C:\mingw\bin» в переменную Path.
Все, компилятор gcc установлен в ОС Windows и готов к
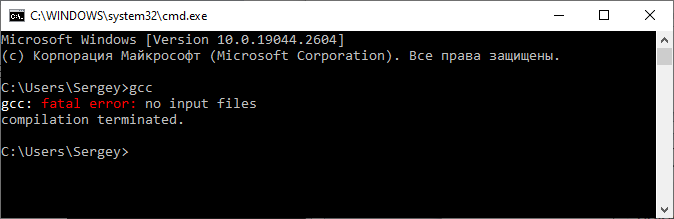
работе. Чтобы в этом убедиться, откроем командное окно (комбинация Win+R, набираем cmd и кнопка «OK»), набираем в
нем gcc и должны
увидеть следующие строчки:
Если у вас все
отображается именно так, то компилятор был успешно установлен.
Установка и настройка Visual Studio Code
Следующим шагом
нам нужно установить интегрированную среду для написания, компиляции и отладки
наших программ написанных на языке Си. Для этого, на мой взгляд, удобно
воспользоваться программой Visual Studio Code, доступной на
странице официального сайта:
https://code.visualstudio.com
Именно в ней я
буду писать и показывать все тексты программ данного курса. При желании, вы,
конечно, можете использовать любую другую среду, главное, чтобы в ней было
удобно компилировать и отлаживать программы на Си.
Первым делом,
конечно же, нужно скачать дистрибутив программы Visual Studio Code и установить
себе на компьютер. Ничего сложно в этом нет. Далее, открываем эту программу.
Для начала работы нам нужно определиться, где будут располагаться файлы
текущего проекта. Делается это очень просто. На диске в любом желаемом месте
создается папка, которая, затем, выбирается в программе VS Code. В моем случае
– это путь:
D:\Visual
Studio\Code\course
У вас может быть
любой другой. Сейчас каталог пустой. Поэтому для начала работы в него нужно
поместить файл, в котором будем писать текст программы. Например, его можно
назвать так:
lessons.c
Обратите
внимание, файл с текстом программы на языке Си должен иметь расширение «c». Теперь здесь
можно написать простую программу. Пусть это будет классический «Hello, world!»:
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { printf("Hello, world\n"); return 0; }
Не беспокойтесь
пока о том, что содержимое этой программы вам, возможно, непонятно. Ее мы
подробно еще будем разбирать. Пока, на этом этапе, нам нужно просто настроить
среду разработки для компиляции и запуска программ на Си.
По идее, мы уже
сейчас можем достаточно просто скомпилировать эту программу. Для этого нажимаем
Ctrl + ~, появится
окно powershell и в нем вручную
можно вызвать компилятор gcc следующим образом:
gcc lessons.c
Если мы все
сделали правильно, то в текущем каталоге появится исполняемый файл a.exe, который
выводит в консоль сообщение «Hello, world!»:
.\a
Конечно,
постоянно выполнять компиляцию через терминал очень неудобно, поэтому нам нужно
настроить редактор VS Code под компиляцию
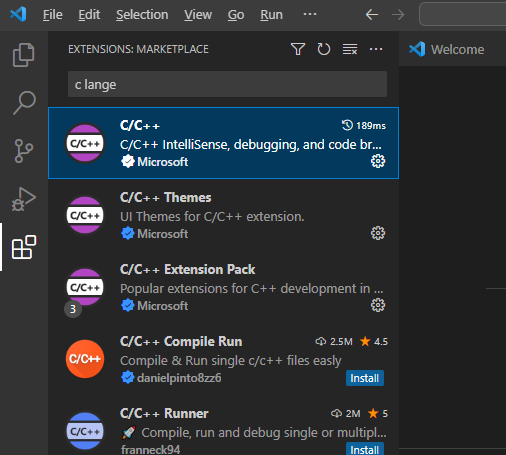
Си-программ. Для этого необходимо установить некоторые полезные расширения (extensions). Щелкаем слева
на кнопку с квадратиками и в поиске набираем «c lange»:
Выбираем первый
компонент C/C++ компании Microsoft, которая
позволяет выполнять разработку программ на языке Си.
После этого,
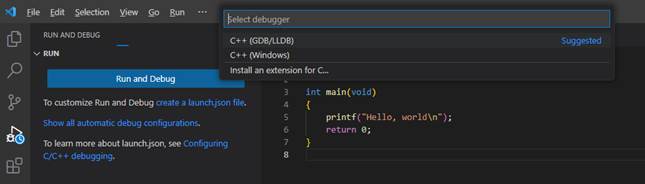
слева щелкаем на кнопку с треугольником (Run and Debug) и нажимаем на
кнопку «Run and Debug». Сверху в
выпадающем списке следует выбрать «C++ (GDB/LLDB)» (это ранее
установленный компилятор gcc), затем, скомпилировать и выполнить
программу в режиме Debug (отладки):
Например, можно
поставить в любом месте программы точку останова, снова запустить, и программа
остановится на выбранной строке. Это, как раз и есть процесс отладки кода.
Далее установим
еще одно расширение, которое будет отвечать за простой процесс запуска кода без
режима отладки. Чтобы можно было быстро и просто запустить программу и
посмотреть, что получается. Для этого переходим на вкладку «extensions» и набираем:
code runner
Это расширение
позволяет с помощью комбинации клавиш Ctrl+Alt+N компилировать и запускать
код. Результат отображается во вкладке «OUTPUT».
Настройка компилятора на стандарт C99
Последнее, что
нам осталось – это настроить компилятор на стандарт C99. Формально,
это делается с помощью специального флага -std следующим
образом:
gcc
-std=c99 -o outputfile sourcefile.c
Такой флаг нам
нужно добавить в настройках компилятора. Первым делом откроем файл tasks.json в
текущем каталоге и пропишем для ключа «args» первым
элементом этот ключ:
«args»: [
«-std=c99»,
…
]
Этот флаг будет
срабатывать при перекомпиляции проекта – комбинация клавиш Ctrl+Shift+B.
Точно такой же
ключ нужно добавить для компилятора, используемого расширением «Code Runner». Для этого переходим в меню File->Preferences->Settings и в строке набираем «code
runner run in terminal». Ставим
галочку.
Затем, в этом же
окне настроек набираем в строке «Run Code Configuration». Находим в настройках
раздел «Code-runner: Executor Map» и нажимаем на редактирование. Для ключа «c» после «gcc» прописываем «-std=c99» и ключ «code-runner.runInTerminal» устанавливаем в
false. Все, теперь
компилятор будет ориентироваться на стандарт c99 при
компиляции наших программ.
Видео по теме
-
1
Go to https://cygwin.com/install.html. Cygwin is a free Windows tool that allows you to use the GCC C compiler from a Unix command line.
-
2
Click the setup-x86.exe file for your Windows version. If you’re using the 64-bit version of Windows, download setup-x86_64.exe. If you have the 32-bit version, download setup-x86.exe.
Advertisement
-
3
Run the installer. Double-click the downloaded file to open the setup wizard. Downloaded files usually save to the Downloads folder.
- If prompted to give permission for the installer to run, click Yes.
-
4
Click Next on the first screen.
-
5
Select Install from Internet and click Next.
-
6
Choose where to install the app and click Next.
-
7
Select local package directory and click Next. This is where packages you download will be saved.
-
8
Choose your internet settings and click Next. The installer will connect to the internet and then display a list of download sites.
-
9
Select a download site and click Next. These sites all host the same files. This downloads the installation files to your computer.
- If there’s a problem with one site, try another on the list.
-
10
Select packages to install. Follow these steps to ensure the C compiler is installed:
- Click the + next to «Devel» to expand the options.
- Scroll down and click the down-arrow next to gcc core.
- Click the most recent (highest) version number.
-
11
Click Next. It’s at the bottom-right corner. A confirmation message will appear.
-
12
Click Next to start the installation. Cygwin will now download all selected tools and install them on your computer. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
-
13
Open Cygwin. It’ll be in the Start menu (called either Cygwin64 or Cygwin32, depending on your version).
-
14
Use the cd command to navigate to the location of your C code. You’re looking for the file you coded with «.c» at the end. For example, if your code is located in your Documents folder, you would type cd c:\Users\(yourusername)\Documents and press ↵ Enter.[1]
- A quick way to find the full path to your file: Press ⊞ Win+E to open the File Explorer, go to the folder that contains your file, click the file once to select it, then click Copy Path at the top of the screen. Now you can right-click the Cygwin command line and select Paste.
-
15
Type gcc yourcode.c –o yourcode.exe and press ↵ Enter. Replace «yourcode.c» with the name of the file, and «yourcode.exe» with the name of your program.[2]
Your code is now compiled.
Advertisement
-
1
Open Developer Command Prompt for VS. This app is separate than the main Visual Studio app. To find it, click the Start menu, expand the Visual Studio 2017 folder, then click Developer Command Prompt for VS 2017 (or your version number).[3]
-
2
Use the cd command to navigate to the location of your C code. You’re looking for the file you coded with «.c» at the end. For example, if your code is located in your Documents folder, you would type cd c:\Users\(yourusername)\Documents and press ↵ Enter
- Your code must be in a file that ends with the «.c» extension to use this method.
-
3
Type cl yourcode.c and press ↵ Enter. Replace «yourcode.c» with the name of your file. This creates a file called yourcode.exe from your code file.
Advertisement
-
1
Install Xcode on your Mac.[4]
-
Mavericks (10.9) and later: Open the App Store
and search for xcode. Click GET to install, and follow any on-screen instructions.
- Lion and Mountain Lion (10.7 and 10.8): Follow the instructions for Mavericks and later. Once installed, open the app (it’s in the Applications folder), click the File menu and then Preferences. Click the Downloads tab, then click Install next to «Command Line Tools.»
-
Mavericks (10.9) and later: Open the App Store
-
2
Open Xcode. Now that it’s installed, you’ll find it in the Applications folder.
-
3
Click the File and select Open.
-
4
Select your code file and click Open. The contents of your code will appear.[5]
-
5
Click the Product menu. It’s at the top of the screen.
-
6
Click Archive. This compiles and links your C code. When it’s ready to be exported, a window containing options will appear.
-
7
Select Export as an Xcode Archive and click Next. Xcode will create a new folder (inside the folder where your code is saved) and place the executable file inside.
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
References
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 25,966 times.
Is this article up to date?
Using GCC with MinGW
In this tutorial, you configure Visual Studio Code to use the GCC C++ compiler (g++) and GDB debugger from mingw-w64 to create programs that run on Windows. After configuring VS Code, you will compile, run, and debug a simple Hello World program.
This tutorial does not teach you about GCC, GDB, minGW-w64, or the C++ language. For those subjects, there are many good resources available on the Web.
If you have any problems, feel free to file an issue for this tutorial in the VS Code documentation repository.
Prerequisites
To successfully complete this tutorial, you must do the following steps:
-
Install Visual Studio Code.
-
Install the C/C++ extension for VS Code. You can install the C/C++ extension by searching for ‘C++’ in the Extensions view (⇧⌘X (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+X)).
Get the latest version of MinGW-w64 via MSYS2, which provides up-to-date native builds of GCC, MinGW-w64, and other helpful C++ tools and libraries. This will provide you with the necessary tools to compile your code, debug it, and configure it to work with IntelliSense.
-
You can download the latest installer from the MSYS2 page or use this direct link to the installer.
-
Run the installer and follow the steps of the installation wizard. Note that MSYS2 requires 64 bit Windows 8.1 or newer.
-
In the wizard, choose your desired Installation Folder. Record this directory for later. In most cases, the recommended directory is acceptable. The same applies when you get to setting the start menu shortcuts step. When complete, ensure the Run MSYS2 now box is checked and select Finish. This will open a MSYS2 terminal window for you.
-
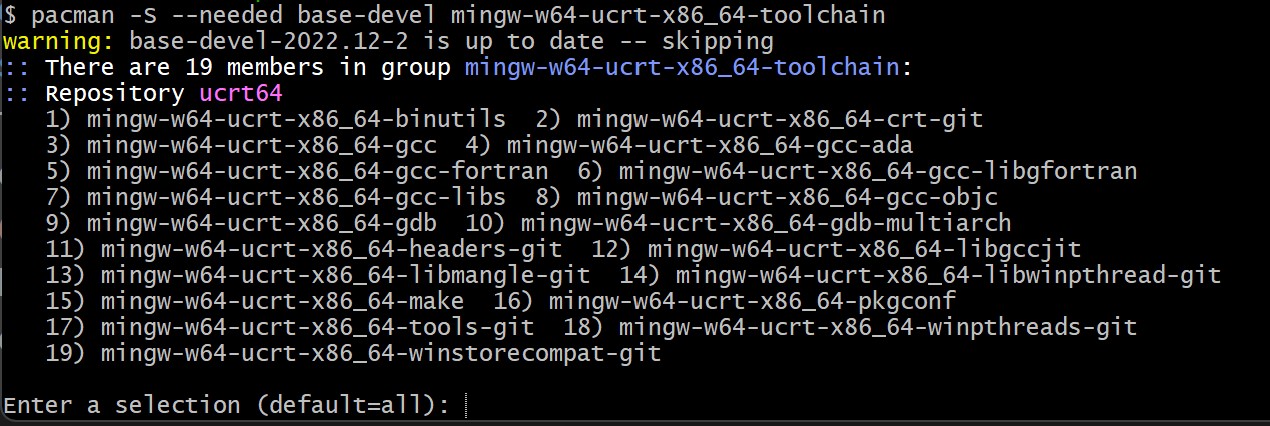
In this terminal, install the MinGW-w64 toolchain by running the following command:
pacman -S --needed base-devel mingw-w64-ucrt-x86_64-toolchain -
Accept the default number of packages in the
toolchaingroup by pressing Enter. -
Enter
Ywhen prompted whether to proceed with the installation. -
Add the path to your MinGW-w64
binfolder to the WindowsPATHenvironment variable by using the following steps:- In the Windows search bar, type Settings to open your Windows Settings.
- Search for Edit environment variables for your account.
- In your User variables, select the
Pathvariable and then select Edit. - Select New and add the MinGW-w64 destination folder you recorded during the installation process to the list. If you used the default settings above, then this will be the path:
C:\msys64\ucrt64\bin. - Select OK to save the updated PATH. You will need to reopen any console windows for the new PATH location to be available.
Check your MinGW installation
To check that your MinGW-w64 tools are correctly installed and available, open a new Command Prompt and type:
gcc --version
g++ --version
gdb --version
You should see output that states which versions of GCC, g++ and GDB you have installed. If this is not the case:
- Make sure your PATH variable entry matches the MinGW-w64 binary location where the toochain was installed. If the compilers do not exist at that PATH entry, make sure you followed the previous instructions.
- If
gcchas the correct output but notgdb, then you need to install the packages you are missing from the MinGW-w64 toolset.- If on compilation you are getting the «The value of miDebuggerPath is invalid.» message, one cause can be you are missing the
mingw-w64-gdbpackage.
- If on compilation you are getting the «The value of miDebuggerPath is invalid.» message, one cause can be you are missing the
Create a Hello World app
First, lets get a project set up.
- Launch a Windows command prompt (Enter Windows command prompt in the Windows search bar), then
- Run the following commands. These will create an empty folder called
projectswhere you can place all your VS Code projects. There, the next commands will create and navigate to a sub-folder calledhelloworld. From there, you will openhelloworlddirectly in VS Code.
mkdir projects
cd projects
mkdir helloworld
cd helloworld
code .
The «code .» command opens VS Code in the current working folder, which becomes your «workspace». Accept the Workspace Trust dialog by selecting Yes, I trust the authors since this is a folder you created.
As you go through the tutorial, you will see three files created in a .vscode folder in the workspace:
tasks.json(build instructions)launch.json(debugger settings)c_cpp_properties.json(compiler path and IntelliSense settings)
Add a source code file
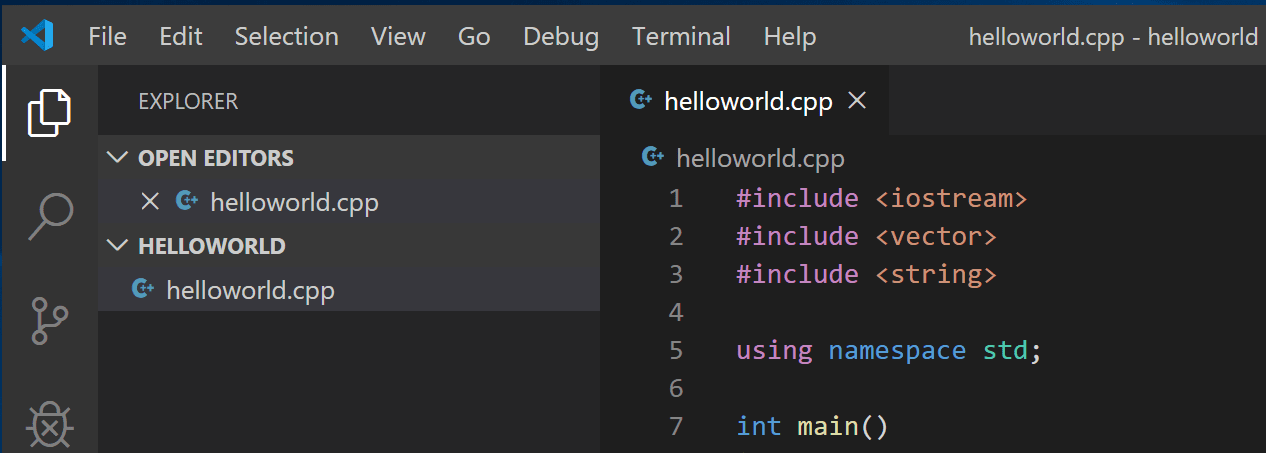
In the File Explorer title bar, select the New File button and name the file helloworld.cpp.
Add hello world source code
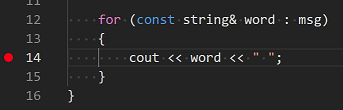
Now paste in this source code:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
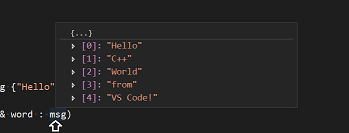
vector<string> msg {"Hello", "C++", "World", "from", "VS Code", "and the C++ extension!"};
for (const string& word : msg)
{
cout << word << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
Now press ⌘S (Windows, Linux Ctrl+S) to save the file. Notice how the file you just added appears in the File Explorer view (⇧⌘E (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+E)) in the side bar of VS Code:
You can also enable Auto Save to automatically save your file changes, by selecting File > Auto Save. You can find out more about the other views in the VS Code User Interface documentation.
Note: When you save or open a C++ file, you may see a notification from the C/C++ extension about the availability of an Insiders version, which lets you test new features and fixes. You can ignore this notification by selecting the
X(Clear Notification).
Explore IntelliSense
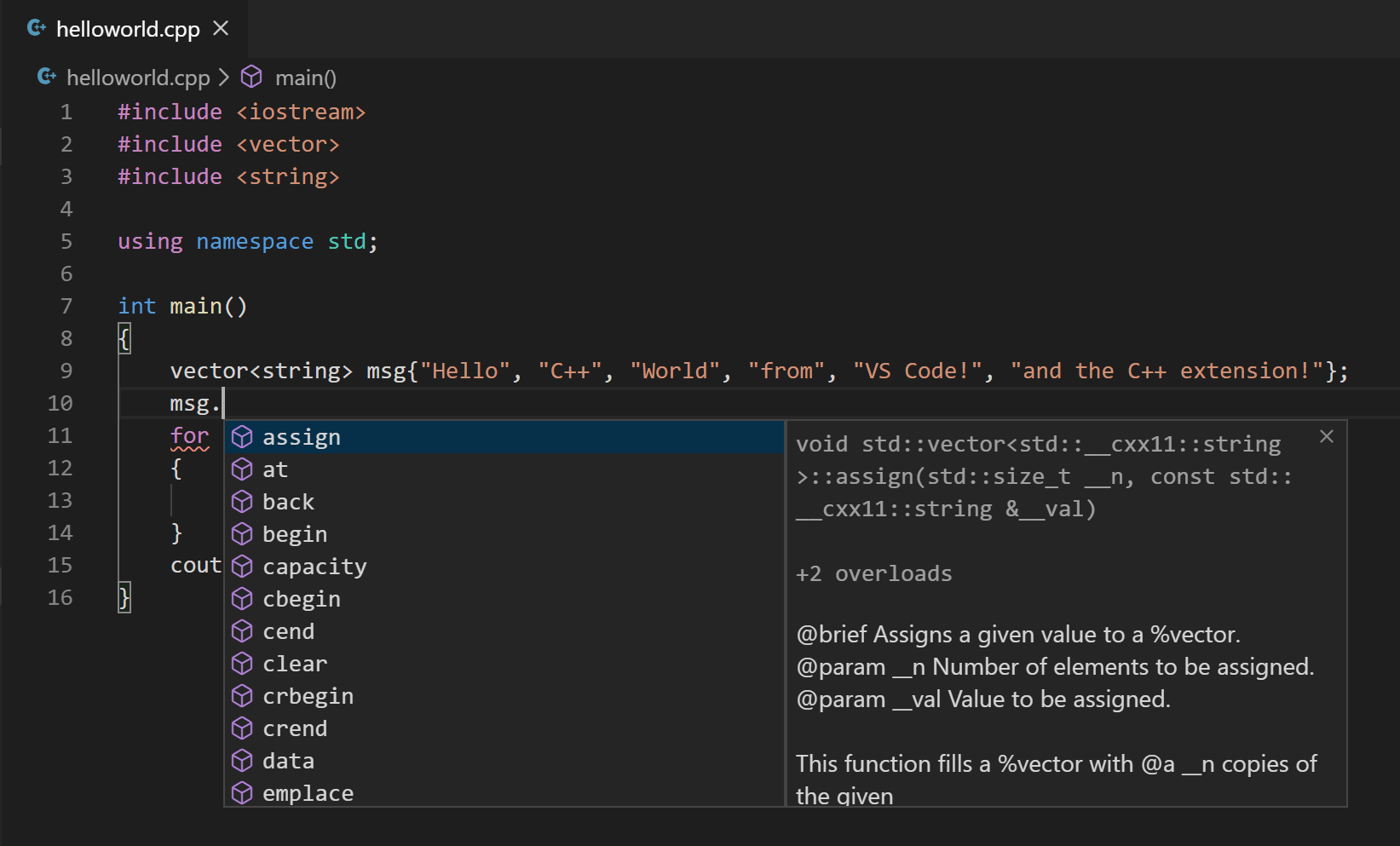
IntelliSense is a tool to help you code faster and more efficently by adding code editing features such as code completion, parameter info, quick info, and member lists.
To see IntelliSense in action,
hover over vector or string to see their type information. If you type msg. in line 10, you can see a completion list of recommended member functions to call, all generated by IntelliSense:
You can press the Tab key to insert a selected member. If you then add open parenthesis, IntelliSense will show information on which arguments are required.
If IntelliSense is not already configured, open the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)) and enter Select IntelliSense Configuration. From the dropdown of compilers, select Use gcc.exe to configure.
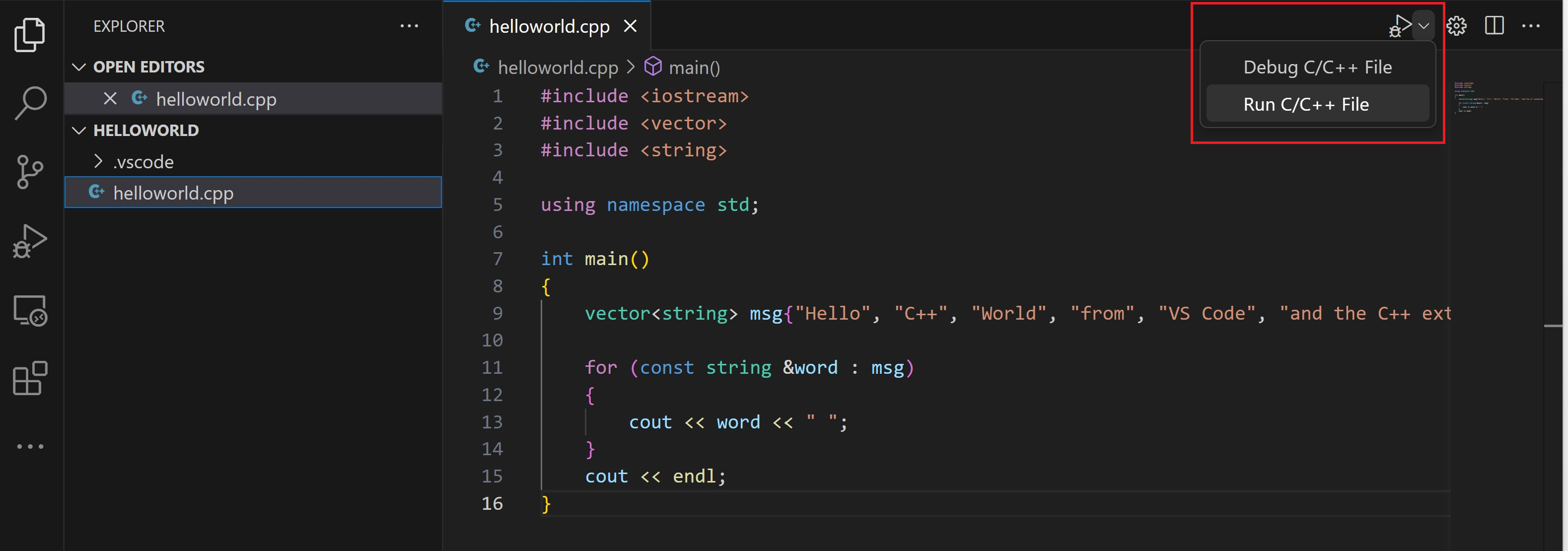
Run helloworld.cpp
Remember, the C++ extension uses the C++ compiler you have installed on your machine to build your program. Make sure you have completed the «Installing the MinGW-w64 toolchain» step before attempting to run and debug helloworld.cpp in VS Code.
-
Open
helloworld.cppso that it is the active file. -
Press the play button in the top right corner of the editor.
-
Choose C/C++: g++.exe build and debug active file from the list of detected compilers on your system.
You’ll only be asked to choose a compiler the first time you run helloworld.cpp. This compiler will be set as the «default» compiler in tasks.json file.
-
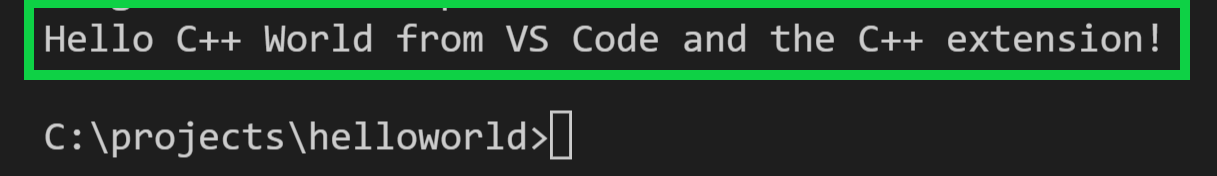
After the build succeeds, your program’s output will appear in the integrated Terminal.
Congratulations! You’ve just run your first C++ program in VS Code!
Understanding tasks.json
The first time you run your program, the C++ extension creates a tasks.json file, which you’ll find in your project’s .vscode folder. tasks.json stores your build configurations.
Your new tasks.json file should look similar to the JSON below:
{
"tasks": [
{
"type": "cppbuild",
"label": "C/C++: g++.exe build active file",
"command": "C:\\msys64\\ucrt64\\bin\\g++.exe",
"args": [
"-fdiagnostics-color=always",
"-g",
"${file}",
"-o",
"${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe"
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${fileDirname}"
},
"problemMatcher": ["$gcc"],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"detail": "Task generated by Debugger."
}
],
"version": "2.0.0"
}
Note: You can learn more about
tasks.jsonvariables in the variables reference.
The command setting specifies the program to run; in this case that is g++.
The args array specifies the command-line arguments that will be passed to g++. These arguments are listed in this file in the specific order expected by the compiler.
This task tells g++ to take the active file (${file}), compile it, and create an executable file in the current directory (${fileDirname}) with the same name as the active file but with the .exe extension (${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe). For us, this results in helloworld.exe.
The label value is what you will see in the tasks list; you can name this whatever you like.
The detail value is what you will as the description of the task in the tasks list. It’s highly recommended to rename this value to differentiate it from similar tasks.
From now on, the play button will read from tasks.json to figure out how to build and run your program. You can define multiple build tasks in tasks.json, and whichever task is marked as the default will be used by the play button. In case you need to change the default compiler, you can run Tasks: Configure Default Build Task in the Command Palette. Alternatively you can modify the tasks.json file and remove the default by replacing this segment:
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
with this:
"group": "build",
Modifying tasks.json
You can modify your tasks.json to build multiple C++ files by using an argument like "${workspaceFolder}/*.cpp" instead of ${file}.This will build all .cpp files in your current folder. You can also modify the output filename by replacing "${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe" with a hard-coded filename (for example "${workspaceFolder}\\myProgram.exe").
Debug helloworld.cpp
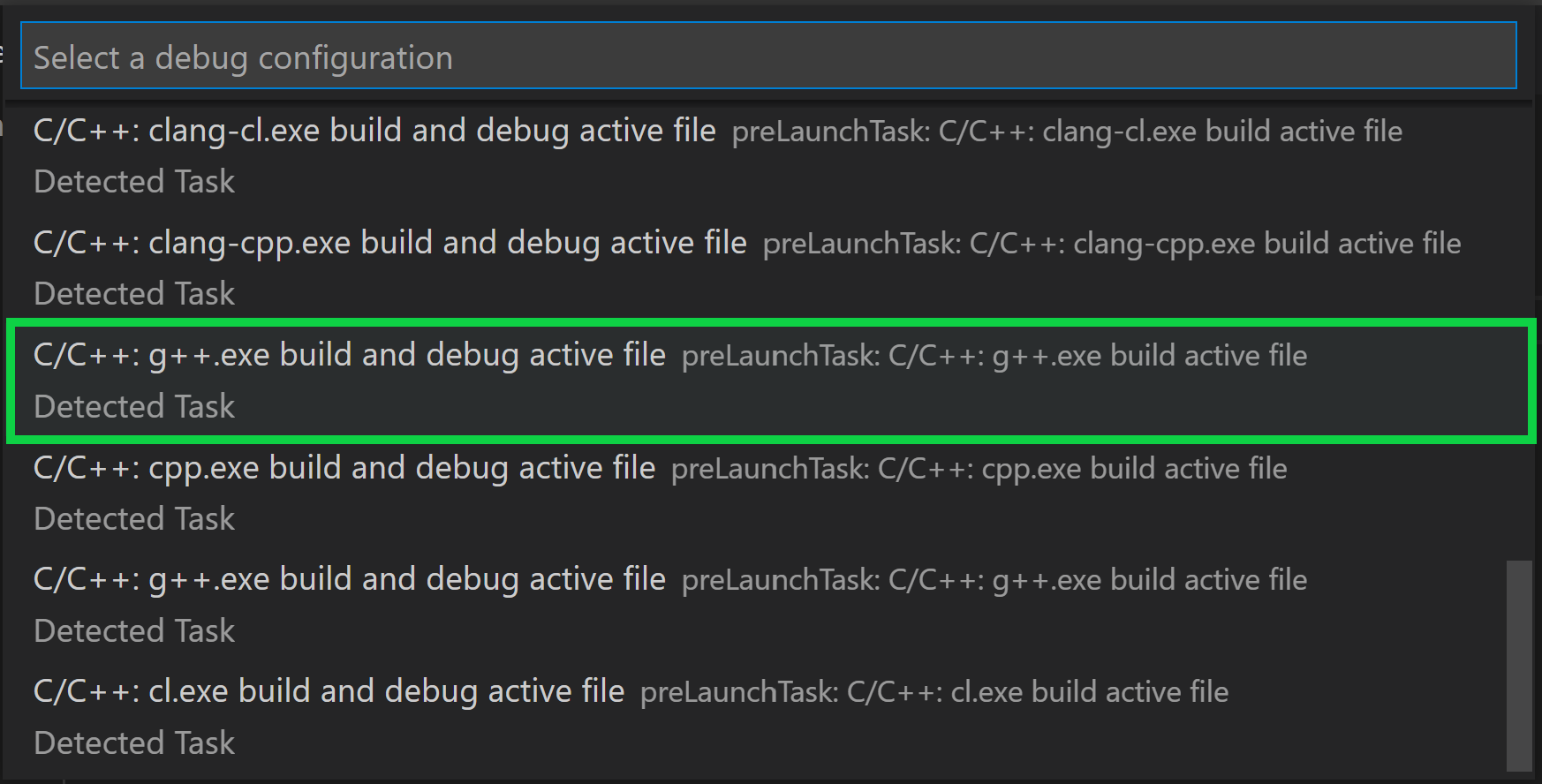
To debug your code,
-
Go back to
helloworld.cppso that it is the active file. -
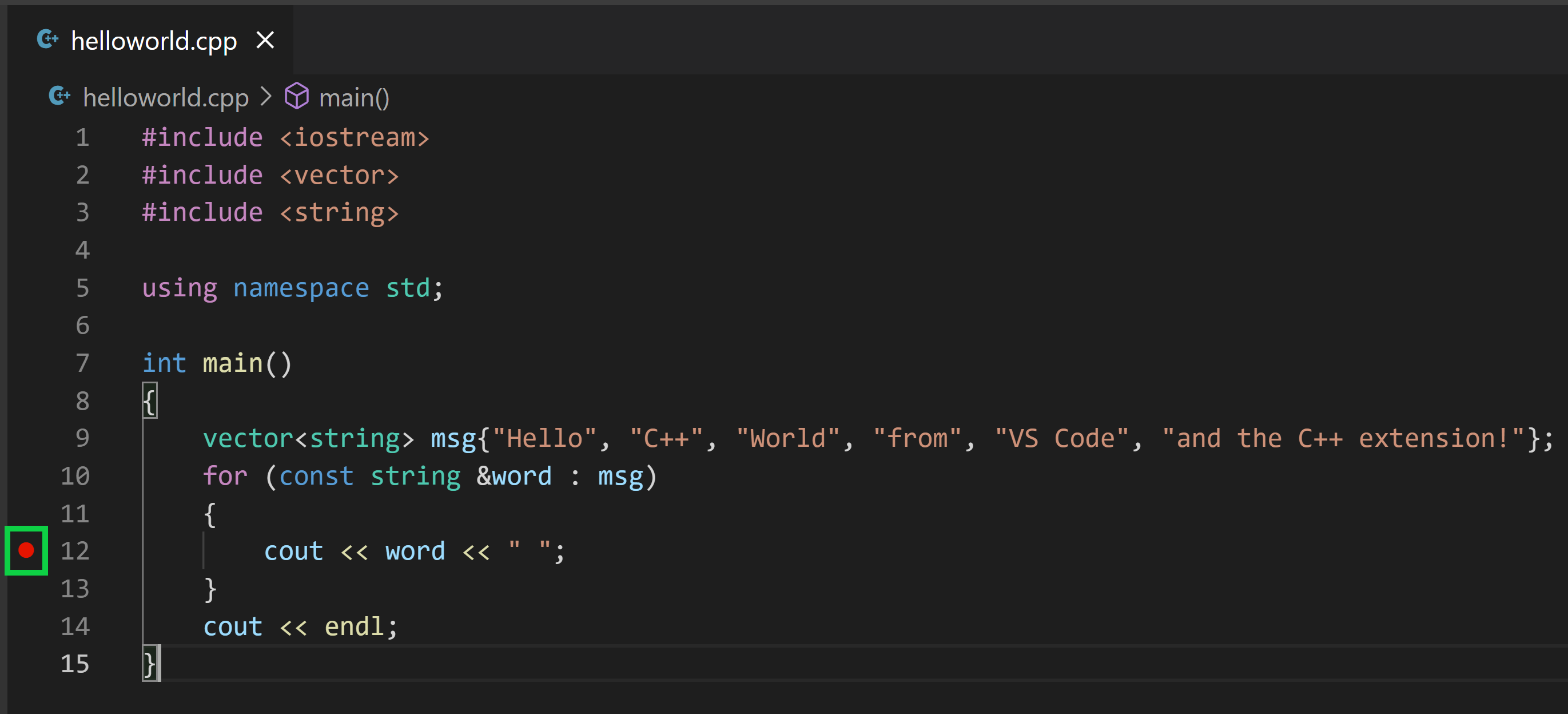
Set a breakpoint by clicking on the editor margin or using F9 on the current line.
-
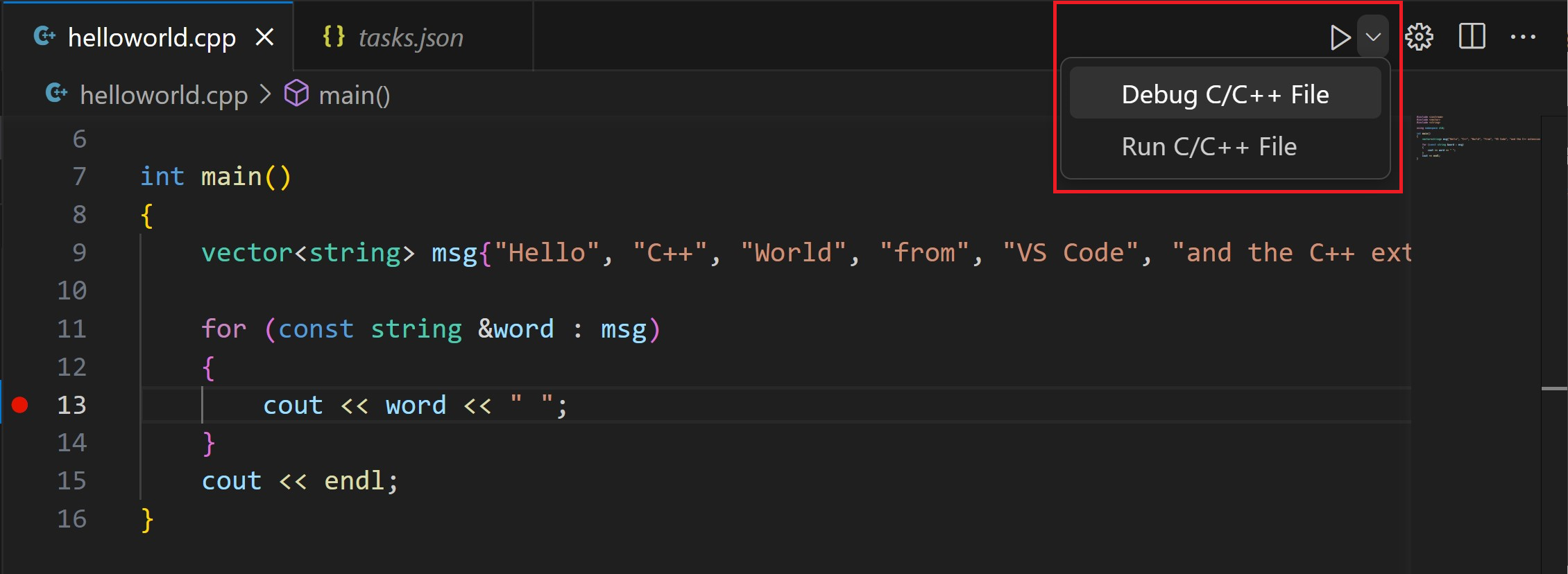
From the drop-down next to the play button, select Debug C/C++ File.
-
Choose C/C++: g++ build and debug active file from the list of detected compilers on your system (you’ll only be asked to choose a compiler the first time you run or debug
helloworld.cpp).
The play button has two modes: Run C/C++ File and Debug C/C++ File. It will default to the last-used mode. If you see the debug icon in the play button, you can just select the play button to debug, instead of using the drop-down.
Explore the debugger
Before you start stepping through the code, let’s take a moment to notice several changes in the user interface:
-
The Integrated Terminal appears at the bottom of the source code editor. In the Debug Output tab, you see output that indicates the debugger is up and running.
-
The editor highlights the line where you set a breakpoint before starting the debugger:
-
The Run and Debug view on the left shows debugging information. You’ll see an example later in the tutorial.
-
At the top of the code editor, a debugging control panel appears. You can move this around the screen by grabbing the dots on the left side.
Step through the code
Now you’re ready to start stepping through the code.
-
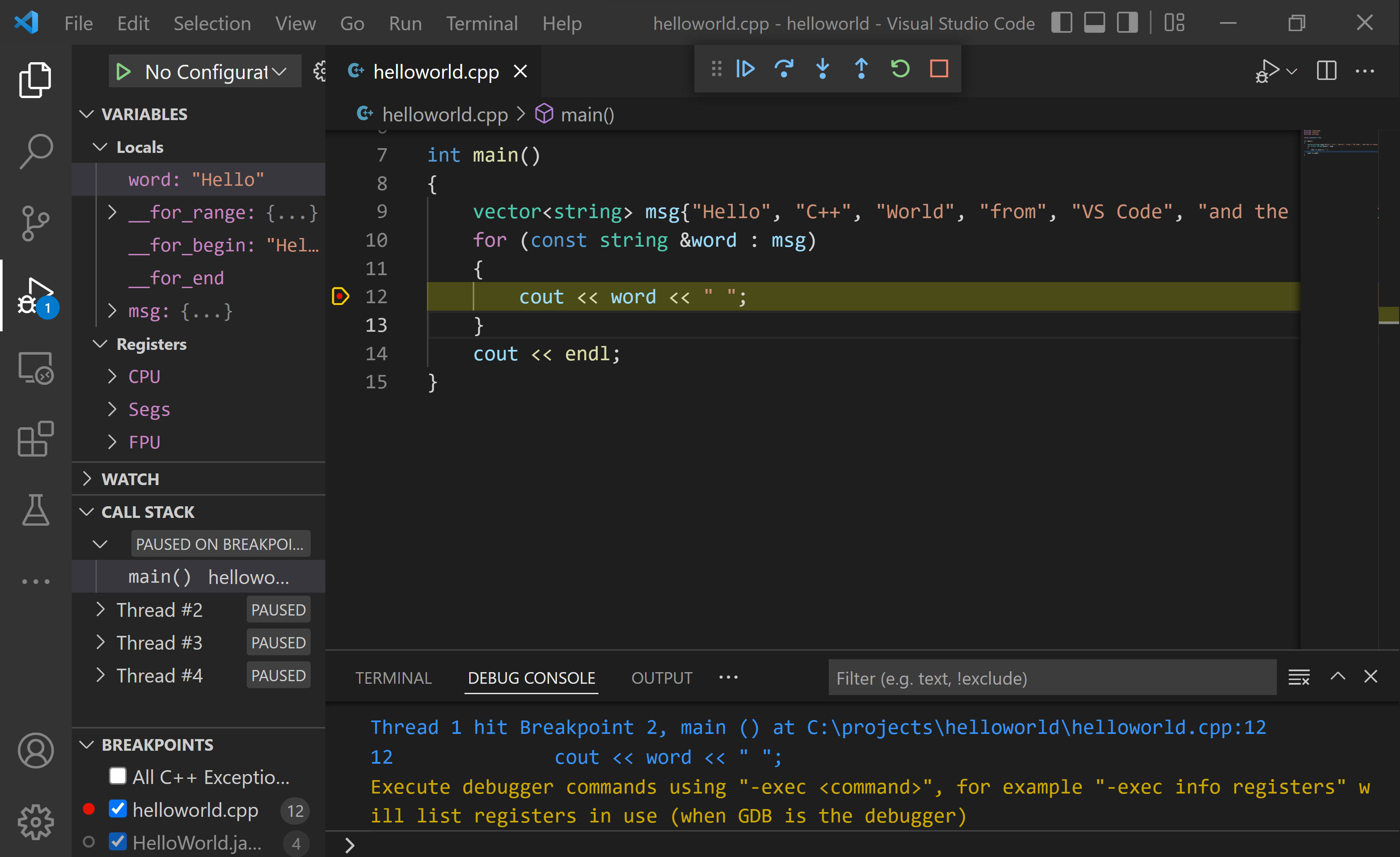
Click or press the Step over icon in the debugging control panel.
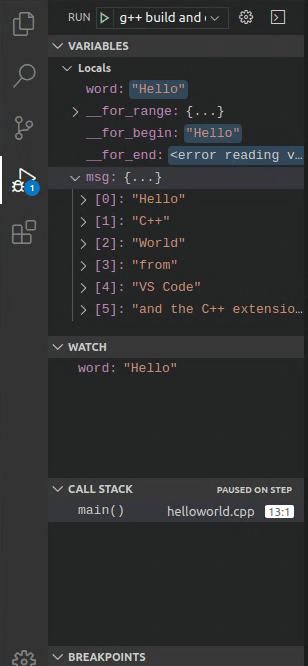
This will advance program execution to the first line of the for loop, and skip over all the internal function calls within the
vectorandstringclasses that are invoked when themsgvariable is created and initialized. Notice the change in the Variables window on the left.In this case, the errors are expected because, although the variable names for the loop are now visible to the debugger, the statement has not executed yet, so there is nothing to read at this point. The contents of
msgare visible, however, because that statement has completed. -
Press Step over again to advance to the next statement in this program (skipping over all the internal code that is executed to initialize the loop). Now, the Variables window shows information about the loop variables.
-
Press Step over again to execute the
coutstatement. (Note that as of the March 2019 release, the C++ extension does not print any output to the Debug Console until the loop exits.) -
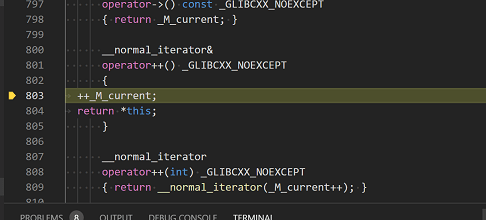
If you like, you can keep pressing Step over until all the words in the vector have been printed to the console. But if you are curious, try pressing the Step Into button to step through source code in the C++ standard library!
To return to your own code, one way is to keep pressing Step over. Another way is to set a breakpoint in your code by switching to the
helloworld.cpptab in the code editor, putting the insertion point somewhere on thecoutstatement inside the loop, and pressing F9. A red dot appears in the gutter on the left to indicate that a breakpoint has been set on this line.Then press F5 to start execution from the current line in the standard library header. Execution will break on
cout. If you like, you can press F9 again to toggle off the breakpoint.When the loop has completed, you can see the output in the Integrated Terminal, along with some other diagnostic information that is output by GDB.
Set a watch
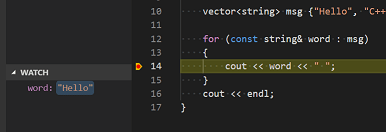
Sometimes you might want to keep track of the value of a variable as your program executes. You can do this by setting a watch on the variable.
-
Place the insertion point inside the loop. In the Watch window, click the plus sign and in the text box, type
word, which is the name of the loop variable. Now view the Watch window as you step through the loop. -
Add another watch by adding this statement before the loop:
int i = 0;. Then, inside the loop, add this statement:++i;. Now add a watch forias you did in the previous step. -
To quickly view the value of any variable while execution is paused on a breakpoint, you can hover over it with the mouse pointer.
Customize debugging with launch.json
When you debug with the play button or F5, the C++ extension creates a dynamic debug configuration on the fly.
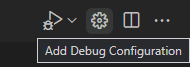
There are cases where you’d want to customize your debug configuration, such as specifying arguments to pass to the program at runtime. You can define custom debug configurations in a launch.json file.
To create launch.json, choose Add Debug Configuration from the play button drop-down menu.
You’ll then see a dropdown for various predefined debugging configurations. Choose C/C++: g++.exe build and debug active file.
VS Code creates a launch.json file in the .vscode folder`, which looks something like this:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "C/C++: g++.exe build and debug active file",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${fileDirname}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": false,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "C:\\msys64\\ucrt64\\bin\\gdb.exe",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
},
{
"description": "Set Disassembly Flavor to Intel",
"text": "-gdb-set disassembly-flavor intel",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
],
"preLaunchTask": "C/C++: g++.exe build active file"
}
],
"version": "2.0.0"
}
In the JSON above, program specifies the program you want to debug. Here it is set to the active file folder (${fileDirname}) and active filename with the .exe extension (${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe), which if helloworld.cpp is the active file will be helloworld.exe. The args property is an array of arguments to pass to the program at runtime.
By default, the C++ extension won’t add any breakpoints to your source code and the stopAtEntry value is set to false.
Change the stopAtEntry value to true to cause the debugger to stop on the main method when you start debugging.
From now on, the play button and F5 will read from your
launch.jsonfile when launching your program for debugging.
Adding additional C/C++ settings
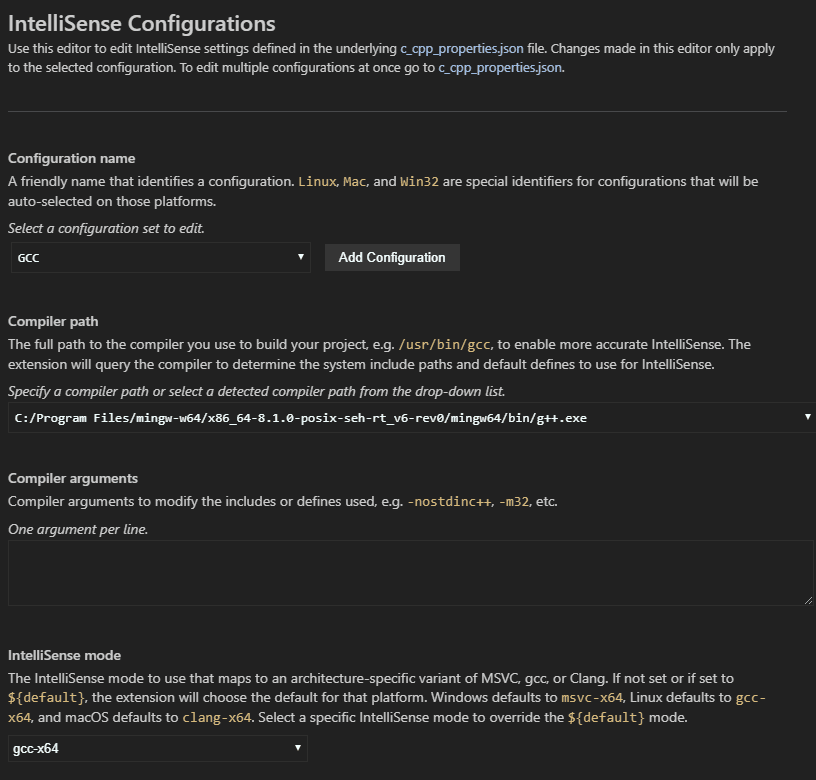
If you want more control over the C/C++ extension, you can create a c_cpp_properties.json file, which will allow you to change settings such as the path to the compiler, include paths, C++ standard (default is C++17), and more.
You can view the C/C++ configuration UI by running the command C/C++: Edit Configurations (UI) from the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+P)).
This opens the C/C++ Configurations page. When you make changes here, VS Code writes them to a file called c_cpp_properties.json in the .vscode folder.
Here, we’ve changed the Configuration name to GCC, set the Compiler path dropdown to the g++ compiler, and the IntelliSense mode to match the compiler (gcc-x64).
Visual Studio Code places these settings in .vscode\c_cpp_properties.json. If you open that file directly, it should look something like this:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "GCC",
"includePath": ["${workspaceFolder}/**"],
"defines": ["_DEBUG", "UNICODE", "_UNICODE"],
"windowsSdkVersion": "10.0.22000.0",
"compilerPath": "C:/msys64/mingw64/bin/g++.exe",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "windows-gcc-x64"
}
],
"version": 4
}
You only need to add to the Include path array setting if your program includes header files that are not in your workspace or in the standard library path.
Compiler path
The extension uses the compilerPath setting to infer the path to the C++ standard library header files. When the extension knows where to find those files, it can provide features like smart completions and Go to Definition navigation.
The C/C++ extension attempts to populate compilerPath with the default compiler location based on what it finds on your system. The extension looks in several common compiler locations.
The compilerPath search order is:
- First check for the Microsoft Visual C++ compiler
- Then look for g++ on Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)
- Then g++ for MinGW-w64.
If you have Visual Studio or WSL installed, you may need to change compilerPath to match the preferred compiler for your project. For example, if you installed MinGW-w64 version 8.1.0 using the i686 architecture, Win32 threading, and sjlj exception handling install options, the path would look like this: C:\Program Files (x86)\mingw-w64\i686-8.1.0-win32-sjlj-rt_v6-rev0\mingw64\bin\g++.exe.
Troubleshooting
MSYS2 is installed, but g++ and gdb are still not found
You must follow the steps on the MSYS2 website to use the MSYS CLI to install the full MinGW-w64 toolchain(pacman -S --needed base-devel mingw-w64-ucrt-x86_64-toolchain), as well as all required prerequisites. The toolchain includes g++ and gdb.
As a Windows user, running the pacman command gives me an error
UCRT on Windows machines is only included in Windows 10 or later. If you are using another version of Windows, run the following command that does not use UCRT:
pacman -S --needed base-devel mingw-w64-x86_64-toolchain
When adding the the MinGW-w64 destination folder to your list of environment variables, the default path will then be: C:\msys64\mingw64\bin.
MinGW 32-bit
If you need a 32-bit version of the MinGW toolset, consult the Downloading section on the MSYS2 wiki. It includes links to both 32-bit and 64-bit installation options.
Next steps
- Explore the VS Code User Guide.
- Review the Overview of the C++ extension.
- Create a new workspace, copy your
.vscodeJSON files to it, adjust the necessary settings for the new workspace path, program name, etc. and start coding!
7/14/2023