I want to display the content of a text file in a CMD window. In addition, I want to see the new lines that added to file, like tail -f command in Unix.
asked Jun 20, 2013 at 15:16
2
We can use the ‘type’ command to see file contents in cmd.
Example —
type abc.txt
More information can be found HERE.
answered Dec 25, 2015 at 1:22
Anmol SarafAnmol Saraf
15.1k10 gold badges51 silver badges60 bronze badges
1
I don’t think there is a built-in function for that
xxxx.txt > con
This opens the files in the default text editor in windows…
type xxxx.txt
This displays the file in the current window. Maybe this has params you can use…
There is a similar question here: CMD.EXE batch script to display last 10 lines from a txt file
So there is a «more» command to display a file from the given line, or you can use the GNU Utilities for Win32 what bryanph suggested in his link.
answered Jun 20, 2013 at 15:24
inf3rnoinf3rno
25k11 gold badges115 silver badges197 bronze badges
1
To show content of a file:
type file.txt — cmd
cat file.txt — bash/powershell
answered Apr 20, 2021 at 2:28
LaurentBajLaurentBaj
4615 silver badges10 bronze badges
You can use the ‘more’ command to see the content of the file:
more filename.txt
answered Jun 5, 2017 at 19:12
1
Using a single PowerShell command to retrieve the file ending:
powershell -nologo "& "Get-Content -Wait c:\logFile.log -Tail 10"
It applies to PowerShell 3.0 and newer.
Another option is to create a file called TAIL.CMD with this code:
powershell -nologo "& "Get-Content -Wait %1 -Tail %2"
answered Feb 17, 2016 at 12:59
EyalEyal
1611 silver badge9 bronze badges
1
To do this, you can use Microsoft’s more advanced command-line shell called «Windows PowerShell.» It should come standard on the latest versions of Windows, but you can download it from Microsoft if you don’t already have it installed.
To get the last five lines in the text file simply read the file using Get-Content, then have Select-Object pick out the last five items/lines for you:
Get-Content c:\scripts\test.txt | Select-Object -last 5
Source: Using the Get-Content Cmdlet
answered May 18, 2016 at 18:50
1
You can do that in some methods:
One is the type command: type filename
Another is the more command: more filename
With more you can also do that: type filename | more
The last option is using a for
for /f "usebackq delims=" %%A in (filename) do (echo.%%A)
This will go for each line and display it’s content. This is an equivalent of the type command, but it’s another method of reading the content.
If you are asking what to use, use the more command as it will make a pause.
answered Jun 14, 2020 at 16:01
Anic17Anic17
7115 silver badges18 bronze badges
If you want it to display the content of the file live, and update when the file is altered, just use this script:
@echo off
:start
cls
type myfile.txt
goto start
That will repeat forever until you close the cmd window.
answered Mar 11, 2017 at 3:08
1
There is no built in option available with Windows. To constantly monitor logs you can use this free application BareTailPro.
answered Jun 20, 2013 at 15:21
SudheejSudheej
1,8836 gold badges30 silver badges58 bronze badges
If you want to display for example all .config (or .ini) file name and file content into one doc for user reference (and by this I mean user not knowing shell command i.e. 95% of them), you can try this :
FORFILES /M *myFile.ini /C "cmd /c echo File name : @file >> %temp%\stdout.txt && type @path >> %temp%\stdout.txt && echo. >> %temp%\stdout.txt" | type %temp%\stdout.txt
Explanation :
- ForFiles : loop on a directory (and child, etc) each file meeting criteria
- able to return the current file name being process (@file)
- able to return the full path file being process (@path)
- Type : Output the file content
Ps : The last pipe command is pointing the %temp% file and output the aggregate content. If you wish to copy/paste in some documentation, just open the stdout.txt file in textpad.
Anic17
7115 silver badges18 bronze badges
answered Nov 19, 2019 at 18:25
0
You can use either more filename.[extension] or type filename.[extension]
StupidWolf
45.2k17 gold badges40 silver badges72 bronze badges
answered Jun 4, 2021 at 6:12
2
tail -3 d:\text_file.txt
tail -1 d:\text_file.txt
I assume this was added to Windows cmd.exe at some point.
Ian
30.3k19 gold badges70 silver badges107 bronze badges
answered Jan 29, 2016 at 14:14
2
I want to display the content of a text file in a CMD window. In addition, I want to see the new lines that added to file, like tail -f command in Unix.
asked Jun 20, 2013 at 15:16
2
We can use the ‘type’ command to see file contents in cmd.
Example —
type abc.txt
More information can be found HERE.
answered Dec 25, 2015 at 1:22
Anmol SarafAnmol Saraf
15.1k10 gold badges51 silver badges60 bronze badges
1
I don’t think there is a built-in function for that
xxxx.txt > con
This opens the files in the default text editor in windows…
type xxxx.txt
This displays the file in the current window. Maybe this has params you can use…
There is a similar question here: CMD.EXE batch script to display last 10 lines from a txt file
So there is a «more» command to display a file from the given line, or you can use the GNU Utilities for Win32 what bryanph suggested in his link.
answered Jun 20, 2013 at 15:24
inf3rnoinf3rno
25k11 gold badges115 silver badges197 bronze badges
1
To show content of a file:
type file.txt — cmd
cat file.txt — bash/powershell
answered Apr 20, 2021 at 2:28
LaurentBajLaurentBaj
4615 silver badges10 bronze badges
You can use the ‘more’ command to see the content of the file:
more filename.txt
answered Jun 5, 2017 at 19:12
1
Using a single PowerShell command to retrieve the file ending:
powershell -nologo "& "Get-Content -Wait c:\logFile.log -Tail 10"
It applies to PowerShell 3.0 and newer.
Another option is to create a file called TAIL.CMD with this code:
powershell -nologo "& "Get-Content -Wait %1 -Tail %2"
answered Feb 17, 2016 at 12:59
EyalEyal
1611 silver badge9 bronze badges
1
To do this, you can use Microsoft’s more advanced command-line shell called «Windows PowerShell.» It should come standard on the latest versions of Windows, but you can download it from Microsoft if you don’t already have it installed.
To get the last five lines in the text file simply read the file using Get-Content, then have Select-Object pick out the last five items/lines for you:
Get-Content c:\scripts\test.txt | Select-Object -last 5
Source: Using the Get-Content Cmdlet
answered May 18, 2016 at 18:50
1
You can do that in some methods:
One is the type command: type filename
Another is the more command: more filename
With more you can also do that: type filename | more
The last option is using a for
for /f "usebackq delims=" %%A in (filename) do (echo.%%A)
This will go for each line and display it’s content. This is an equivalent of the type command, but it’s another method of reading the content.
If you are asking what to use, use the more command as it will make a pause.
answered Jun 14, 2020 at 16:01
Anic17Anic17
7115 silver badges18 bronze badges
If you want it to display the content of the file live, and update when the file is altered, just use this script:
@echo off
:start
cls
type myfile.txt
goto start
That will repeat forever until you close the cmd window.
answered Mar 11, 2017 at 3:08
1
There is no built in option available with Windows. To constantly monitor logs you can use this free application BareTailPro.
answered Jun 20, 2013 at 15:21
SudheejSudheej
1,8836 gold badges30 silver badges58 bronze badges
If you want to display for example all .config (or .ini) file name and file content into one doc for user reference (and by this I mean user not knowing shell command i.e. 95% of them), you can try this :
FORFILES /M *myFile.ini /C "cmd /c echo File name : @file >> %temp%\stdout.txt && type @path >> %temp%\stdout.txt && echo. >> %temp%\stdout.txt" | type %temp%\stdout.txt
Explanation :
- ForFiles : loop on a directory (and child, etc) each file meeting criteria
- able to return the current file name being process (@file)
- able to return the full path file being process (@path)
- Type : Output the file content
Ps : The last pipe command is pointing the %temp% file and output the aggregate content. If you wish to copy/paste in some documentation, just open the stdout.txt file in textpad.
Anic17
7115 silver badges18 bronze badges
answered Nov 19, 2019 at 18:25
0
You can use either more filename.[extension] or type filename.[extension]
StupidWolf
45.2k17 gold badges40 silver badges72 bronze badges
answered Jun 4, 2021 at 6:12
2
tail -3 d:\text_file.txt
tail -1 d:\text_file.txt
I assume this was added to Windows cmd.exe at some point.
Ian
30.3k19 gold badges70 silver badges107 bronze badges
answered Jan 29, 2016 at 14:14
2
Время чтение: 6 минут
2013-08-24
Вторая часть поста, в котором будут рассмотрены основные команды для работы с файлами. В первой части было рассказано про то, как удалить файл и каталог используя cmd.exe, если Вы не читали, то советую прочитать. В этом посте будут рассмотрены команды, которые позволят пользователю…
- Перемещать файлы.
- Переименовывать файлы.
- Выводить содержимое файлов в консоль.
- Записывать в файл (txt) результат выполнения команды.
Как всегда, все команды будут представлены Вашему вниманию в сопровождении коротких, но ясных описаниях, а так же будут прилагаться «Пошаговые» скриншоты.
Первым делом, я расскажу, как переместить файл из одной директории в другую.
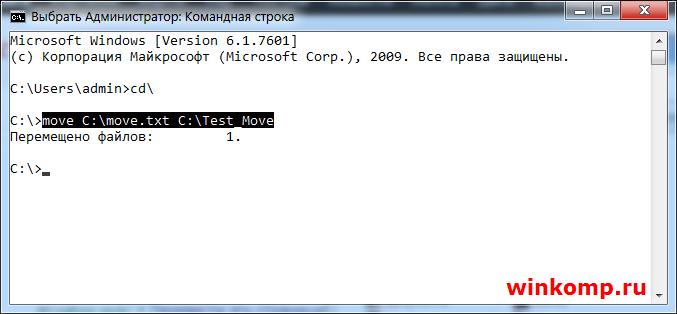
Как переместить файл через консоль?
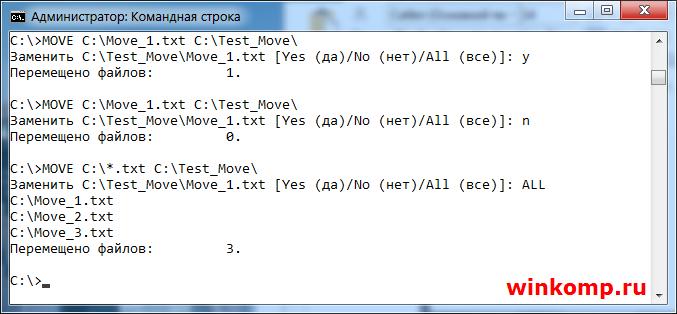
Для перемещения файлов используется команда под названием «MOVE». Что бы переместить файл из корня диска «C:\ Move.txt» в папку, в моём случаи это «С:\Test_Move» пишем в консоль:
Результат выполнения команды. Файл «Move.txt» был перемещён в папку «Test_Move»
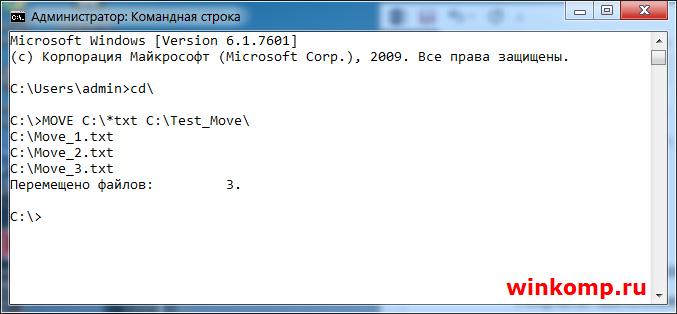
Если Вам нужно переместить все файлы с конкретным расширением, то в этом случаи стоит писать так:
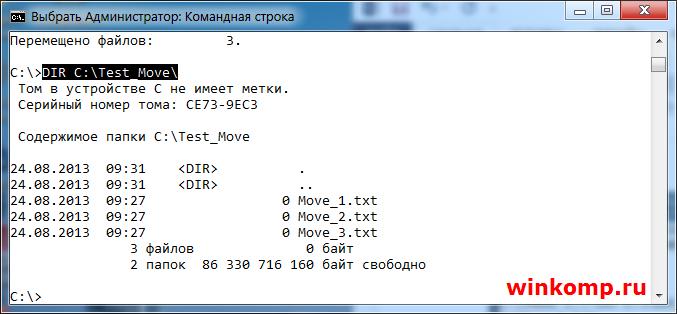
Для примера я создал 3 файла «Move_1.txt, Move_2.txt и Move_3.txt» Как видно из скриншота выше, все три файла были перемещённых. В этом можно убедится не закрывая консоль.
Для проверки используем команду «DIR»
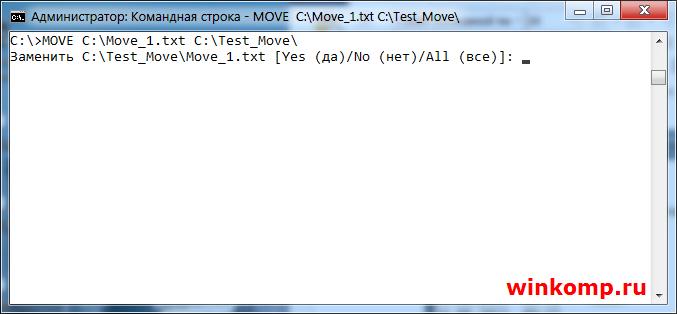
С перемещением файлов на этом все. Но, если в каталоге куда нужно переместить файл уже есть такой? То пользователь получит сообщения, в котором его спросят подтвердить, перезаписать файл или нет.
Если ввести символ «Y» то файл будет перезаписан. При этом содержимое уже имеющегося файла в каталоге «C:\Test_Move\» будут потеряны.
Если ввести символ «N» файл не будет перемещён.
Если ввести «ALL» то будут перемещены и перезаписаны все файлы с конкретным расширением. При этом, также, содержимое файлов в директории «C:\Test_Move\» будут потеряны.
Примечание: За место «ALL» можно просто ввести букву «А» результат будет додже.
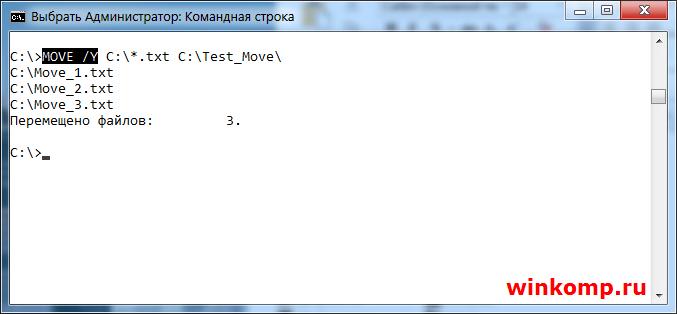
Что бы отключить предупреждения используется ключик «/Y»
Теперь все файлы будет перемещены и перезаписаны без всяких предупреждений. Будьте внимательны, можно потерять важную информацию.
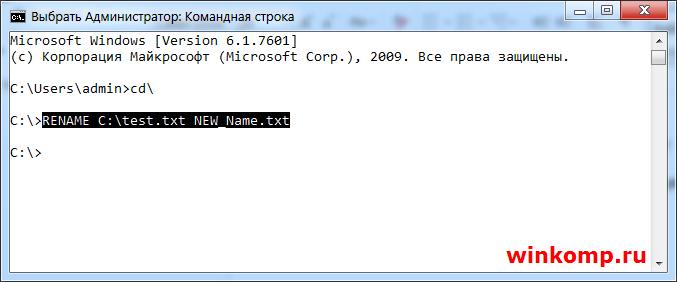
Как переименовать файл через cmd.exe?
Для того, чтобы переименовать существующий файл используется команда «RENAME» Я создал файл с именем «test.txt» в корне диска «С:\» что бы его переименовать, скажем в «NEW_Name.txt» пишем в консоли.
Файл «test.txt» будет переименован.
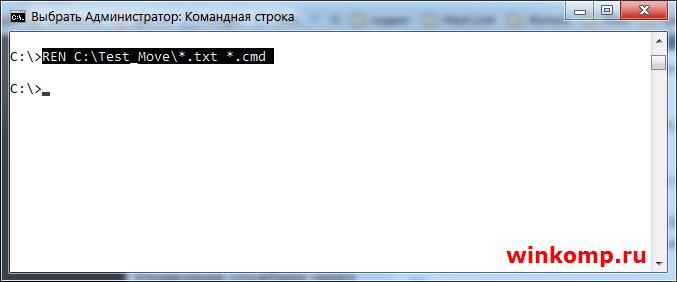
Примечание: Команду «RENAME» можно писать короче, просто «REN» от этого результат не изменится.
Можно сменить расширения у всех файлов в каталоге, например с «txt» на «cmd». Для этого делаем так:
Теперь уже в знакомой нам папке «Test_Move» все 3(три) файла приобретут расширение «cmd» за место «txt»
Как вывести содержимое файла в консоль?
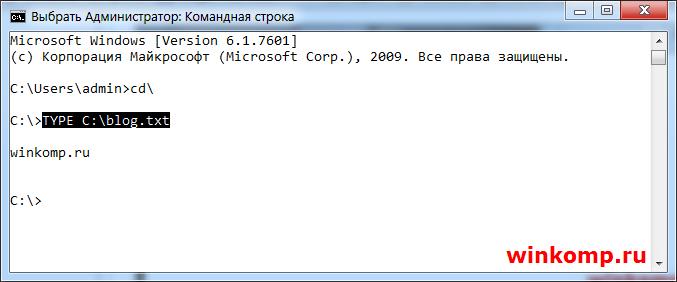
Если появилась необходимость просмотреть содержимое файла прямо в cmd. Для этого пользуемся командой «TYPE» Я создал файл и написал в нём адрес своего блога. Теперь попробуем просмотреть данный файл из консоли, не запуская его обычном, привычным образом.
В общем все просто. Но как быть с файлами большего размера, где много информации? В этак случаи содержимое файла нужно выводить с паузой, чтобы просмотреть его полностью.
Для этого пишем так:
Для примера взял текст с первого попавшегося забугорного сайта.
В конце добавляем «| more» таким образом содержимое файла будет выводится не полностью а отрывками, чтобы просмотреть следующею часть файла жмём «Enter»
Как записать в файл результат выполнения команды?
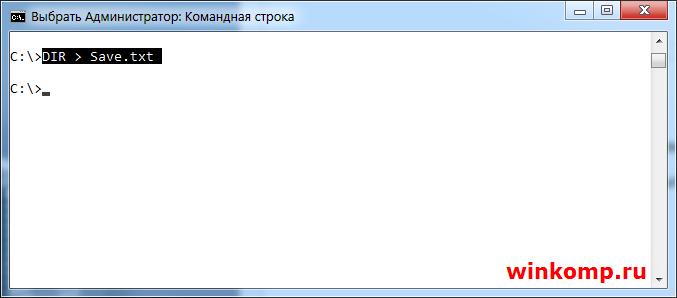
Для примера запишем в файл результат команды «DIR» В консоль пишем:
Обратите внимание на символ «>» он то и играет здесь главную роль. В итоге появится файл на диске «C:\» с именем «Save.txt» куда будет записан результат выполнения команды.
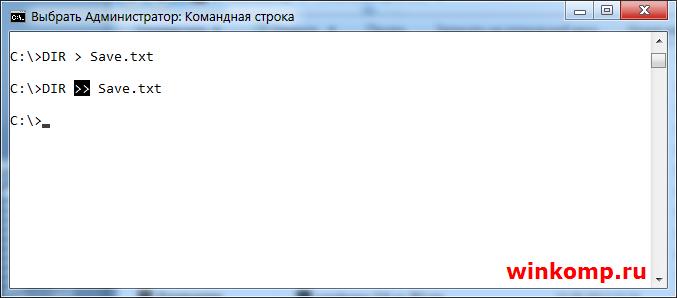
Если Вам понадобится записать результат команды «DIR» ещё раз, то файл «Save.txt» будет перезаписан и ранние содержимое файла будет удалено!
Что бы этого избежать и просто добавить новый результат не удаляя старый, стоит использовать символ «>» два раза, то есть вот так:
Теперь файл не будет перезаписан, в него просто добавится новый результат в конец файла.
На этом я пожалуй закончу пост, и отправлюсь праздновать первый день рождения сына, ему сегодня исполняется один годик!!!
Спасибо за внимание!

В этой инструкции подробно о работе с текстовыми файлами в командной строки или PowerShell (разумеется, можно и в Терминале Windows) — создание и сохранение текстовых файлов, их вывод и чтение в консоли.
Создание текстовых файлов в командной строке
Возможность создания текстовых файлов доступна как в командной строке (cmd.exe), так и в PowerShell. Начнем с первого варианта.
Во всех случаях учитывайте, что при использовании кириллицы потенциально возможны проблемы с кодировкой, а в некоторых случаях кодировка может отличаться при использовании разных команд.
Команда ECHO
Команда командной строки echo предназначена для вывода текстовых сообщений в окне консоли, например, при выполнении сценария в bat-файле, но может быть использована и для вывода текста в файл, благодаря возможности использования оператора «>» для перенаправления вывода из консоли в файл.
Пример команды:
echo Содержимое текстового файла > file.txt
В результате её выполнения в текущей рабочей папке командной строки будет создан файл с именем file.txt и содержимым «Содержимое текстового файла».
COPY CON
Команда copy с параметром con позволяет скопировать содержимое консоли в файл. Использование возможности будет состоять из следующих шагов:
- Введите команду
copy con имя_файла.txt
файл не будет создан, но после выполнения указанной команды у вас появится возможность набрать содержимое этого файла, которое по завершении процесса будет в него сохранено.
- Курсор переместится на строчку ниже, и вы сможете набирать текст так, как делаете это обычно, включая перенос строки.
- Для завершения набора и сохранения текстового файла нажмите сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Z, а затем — Enter. Это добавит отметку конца файла и сохранит его в текущей папке с указанным на 1-м шаге именем.
Создание текстового файла в PowerShell
PowerShell также имеет набор встроенных командлетов для сохранения текстовых данных в файл.
Out-File
Использование Out-File в PowerShell по своей функциональности сходно с оператором перенаправления вывода в командной строке. Вывод консоли перенаправляется в заданный файл.
Пример использования:
"Текстовая строка" | Out-File -FilePath .\file.txt
В этом примере в текущей папке PowerShell будет создан файл с именем file.txt и содержимым «Текстовая строка».
New-Item
Создание нового текстового файла в PowerShell возможно с помощью командлета New-Item. Пример команды, в которой создается текстовый файл file.txt, содержащий «Текстовая строка» в текущем расположении:
New-Item -Path . -Name "file.txt" -ItemType "file" -Value "Текстовая строка"
Set-Content и Add-Content
Ещё два командлета PowerShell для работы с текстовыми файлами:
- Set-Content — перезаписывает содержимое файла
- Add-Content — добавляет содержимое в конце выбранного файла
Их использование можно увидеть на примере следующей команды:
Add-Content -Path .\file.txt -Value "Ещё одна текстовая строка"
Вывод (чтение) текстового файла в командной строке и PowerShell
Теперь перейдем к способам просмотреть текстовые файлы в командной строке или PowerShell. Как и в предыдущем случае, учитывайте, что для файлов, содержащих кириллицу, возможны проблемы с отображением символов в правильной кодировке.
TYPE
Самый простой вариант — использование команды TYPE с указанием пути к файлу, который нужно отобразить в консоли, например:
type file.txt
MORE
Если файл объемный и содержит большое количество строк, используйте команду more, например:
more file.txt
Выполнив команду, вы увидите часть содержимого текста, которая помещается в окне консоли, далее вы можете использовать следующие клавиши:
- Enter — для отображения следующей строки файла.
- Пробел — для отображения следующих строк документа, которые поместятся в активное окно консоли.
- P — Показать следующие N строк. После нажатия этой клавиши с последующим указанием количества строк, будет выведено соответствующее количество строк текстового документа.
- S — пропустить следующие N строк, работает аналогично предыдущему варианту.
- Клавиша «=» — для отображения текущего номера строки.
- Q — для прекращения выполнения команды more.
Get-Content
Вывести содержимое текстового файла в PowerShell можно с помощью Get-Content с указанием пути к файлу, например:
Get-Content file.txt
Также вы можете выводить определенные строки файла, с помощью команд вида (вывод первых или последних 10 строк соответственно):
Get-Content file.txt | Select-Object -First 10 Get-Content file.txt | Select-Object -Last 10
Или присвоить содержимое файла переменной и вывести конкретную строку:
$file_text = Get-Content file.txt $file_text[2]
Помимо использования ручного ввода команд, вы можете использовать консольные текстовые редакторы — сторонние в версиях для Windows, такие как Vim, Nano, Kinesics Text Editor или даже старый встроенный edit.com (может отсутствовать в вашей версии системы и требовать патча NTVDMx64).
This article lists down various commands that you can use to manage files and folders through Command-Line in Windows 11/10. Although a lot of users prefer using a graphical user interface to manage files for a hassle-free experience, some also use the command-line interface to perform file management tasks. In any case, it is always better to know alternative solutions to execute a task.
In this guide, I will be creating a list of useful commands that you can use for file or folder management on your Windows 10 PC. To perform a specific task on files or folders, there is a dedicated command that you need to enter in CMD. Let’s check out these commands!
Here are the commands that you should know to manage files and folders using Command Prompt in Windows 11/10:
1] Create a File or Folder in CMD
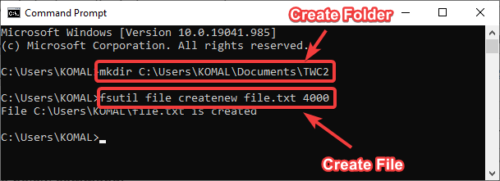
To create a folder, type the folder name with the location where you want to create the folder. Here is the command:
mkdir <folder name with path>
For example;
mkdir C:\Users\KOMAL\Documents\TWC
To create a file of a specific size (in bytes), use the below command:
fsutil file createnew file.txt 4000
In place of file.txt, enter the filename with its extension and full path. And, 4000 is the file size in bytes.
Related: How to Create Multiple Folders using Command Prompt and PowerShell.
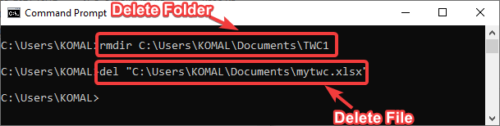
2] Delete Files or Folder in CMD
You can remove a folder using the below command:
rmdir <folder name with path>
In order to delete a file, the command is:
del "<filename with path>"
If you want to delete all files from the current folder, enter the command:
del *
To delete files with a specific extension only, say png, use the command:
del *.png
If you want to delete files with a particular string in their filename, e.g., xyz, you can use the below command:
del *xyz*
3] Find Files in a Particular Folder
To find files inside a folder based on different parameters, you first need to navigate to the folder using the command:
cd "<folder name with location>"
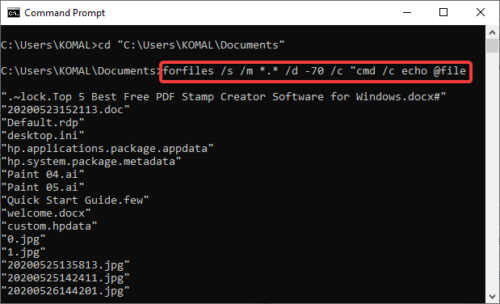
Now, you can find files older than n days in a specific folder using the below command:
forfiles /s /m *.* /d -n /c "cmd /c echo @file
Replace -n with the number of days. Like if you want to find files older than 2 days, type -2.
To find files larger than a specific size, use the command:
forfiles /S /M * /C "cmd /c if @fsize GEQ 3741824 echo @path"
In the above command, 3741824 is the file size to search files greater than this size.
Read: Managing Files and Folders in Windows 11 – Tips & Tricks
4] Rename all file extensions present in a folder at once
You can also batch rename file extensions in CMD. Suppose, you want to rename the file extension of all images to JPG, you can use the below command:
ren *.* *.jpg
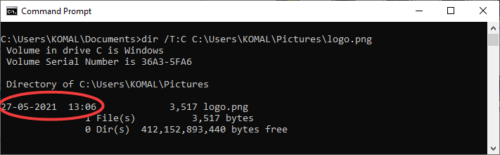
5] Get File Creation Time and Date
To check the creation time and date of a specific file, use the command:
dir /T:C filename
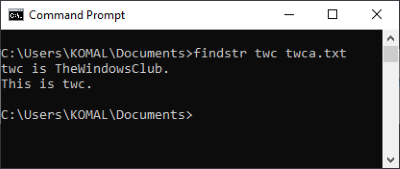
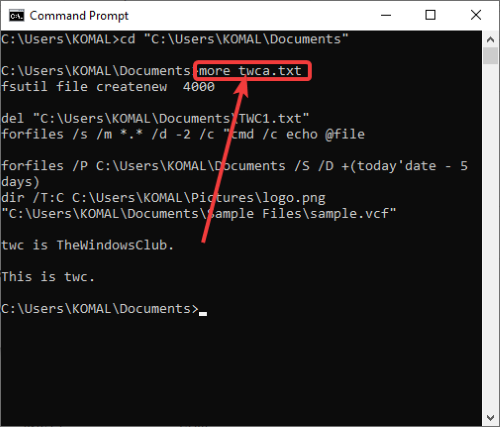
6] Check for a string inside a file
To find all lines containing a particular string in a file, you can use the command:
findstr string file-name
For example, to display all lines with “twc” in a text file, you need to enter the command:
findstr twc twc.txt
Do remember that the above command is case-sensitive.
To find sentences with any specified string, use a command like:
findstr /C:"string1 string2 string3..." filename
7] Check for all Hidden Files in a Folder
Use the below command to get a list of hidden files in a directory:
dir /A:H /B
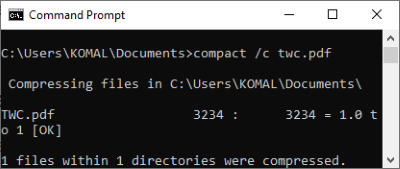
8] Compress a File in CMD
The command to compress a file in a folder is:
compact /c filename
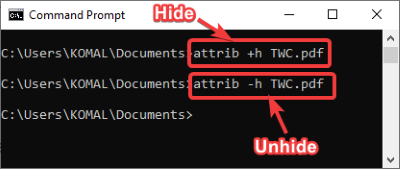
9] Hide/ Unhide a file through CMD
To hide a file, the command used is:
attrib + h filename
You can unhide the file again using the command:
attrib -h filename
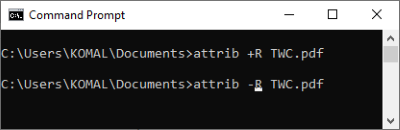
10] Set/ Unset Read-Only attribute to a file
To make a file read-only, the command is:
attrib +R filename
If you want to remove the read-only attribute from a file, the command is:
attrib -R filename
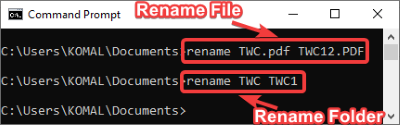
11] Command to Rename a File/Folder
rename oldfilename.pdf newfilename.pdf
12] Read File Content in CMD
You can read text file content in CMD using the below command:
more filename
13] Open a File in Default Application
You can open a file in its default application by entering a simple command:
"filename-with-path"
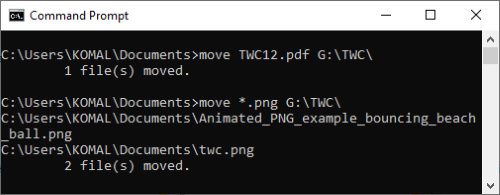
14] Move File / Folder to different Location
Suppose you want to move TWC12.pdf file to TWC folder in G drive, use below command:
move TWC12.pdf G:\TWC\
Command to move all files with a specific extension:
move *.png G:\TWC\
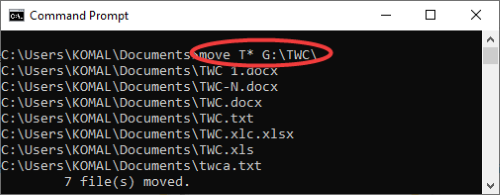
To move files starting with a particular letter, say A, command is:
move A* G:\TWC\
Similarly, you can move a folder using a command like below:
move foldername <new location>
For example:
move TWC1 G:\TWC\
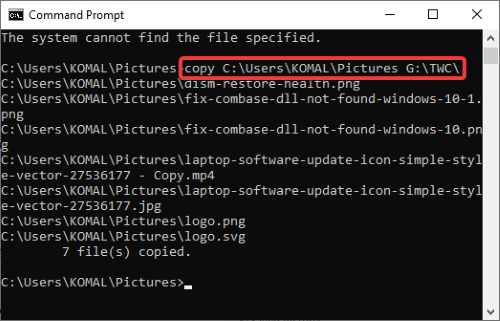
15] Command to Copy Files
You can copy files from one location to another using command:
copy Sourcefolder DestinationFolder
Hope this article helps you learn some useful commands to manage files and folders through the command line in Windows 11/10.