Работая в классической командной строке или PowerShell, вы в любой момент можете нажать F7 и просмотреть историю всех выполненных команд. И не только просмотреть, но и выбрать любую из них. Это очень удобная и полезная функция, которая позволяет экономить время при повторном наборе команд, но пользоваться ее преимуществами получится только в текущем сеансе.
Как только сессия закрывается, вся история команд тут же удаляется. Если вас это не устраивает, и вы хотите сохранять историю так, чтобы она была доступна и после закрытия консоли, придется обратиться к ее расширенным возможностям. Поддерживаются таковые и классической командной строкой, и более совершенным ее аналогом PowerShell.
Командная строка
Для получения списка выполненных команд помимо клавиши F7 можно использовать специальную команду doskey с ключом history. История выводится непосредственно в консоль и также доступна только в текущей сессии, поэтому для ее сохранения используем обычное перенаправление в файл, например, вот так, дешево и сердито:
doskey /history > C:/20.05.20.log
Формат файла истории не обязательно должен быть LOG, уместны также форматы TХT, HTML, CSV и даже RTF.
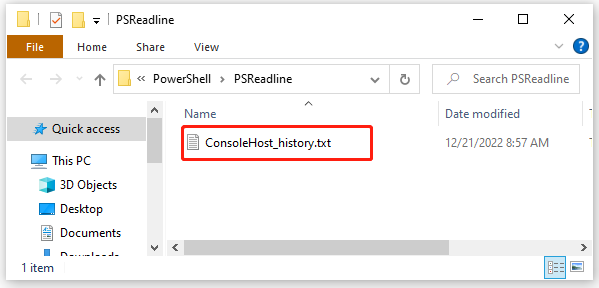
В случае с консолью PowerShell всё куда интереснее. Начиная с пятой версии консоль сохраняет все введенные и выполненные командлеты в текстовый лог ConsoleHost_history.tхt, расположенный по пути %userprofile%/AppData/Roaming/Microsoft/Windows/PowerShell/PSReadline.
Даже если вы завершите сессию в консоли и выключите компьютер, команды останутся сохраненными и будут доступны для вызова в PowerShell нажатием клавиши «Стрелка вверх». Каждое нажатие выводит предыдущую команду, но можно отобразить и весь список выполненных команд сразу. Делается это так:
cat (Get-PSReadlineOption).HistorySavePath
Отвечающий за историю модуль поддерживает и другие функции. Если вы введете команду Get-PSReadlineOption, то получите в консоли приличный список доступных параметров. Ознакомиться с их назначением можно в официальной документации к PowerShell, но смысл некоторых из них понятен и так. К примеру, нетрудно догадаться, что ключ MaximumHistoryCount устанавливает максимальное число элементов, сохраняемых в список истории.
Команда Remove-Item (Get-PSReadlineOption).HistorySavePath очищает историю введенных команд, Set-PSReadlineOption -HistorySaveStyle SaveNothing запрещает ведение истории, Set-PSReadlineOption -HistorySaveStyle SaveIncrementally вновь разрешает сохранение данных.
В целом, начинающему администратору вполне должно хватить данного функционала для облегчения работы в консоли. Если же вдруг при выполнении любой из приведенных выше команд появится ошибка «имя командлета не распознано», это с большой долей вероятности укажет на отсутствие требуемого модуля. Установить его в Windows 10 с PowerShell v5 можно командой Install-Module PSReadLine с последующим разрешением на подключение поставщика NuGet.

Эксперт по ремонту и настройке ПК с более чем 5-летним опытом работы. Имеет профильное образование по специальности оператор ЭВМ.
Задать вопрос
-
Home
-
Partition Magic
- How to View CMD History in Command Prompt/PowerShell [Full Guide]
By Ariel | Follow |
Last Updated
Sometimes you may need to view the CMD history on Windows 10/11. How to list the history of Command Prompt? If you are trying to figure it out, this post of
MiniTool
is what you need. It provides detailed steps to get Windows CMD history in Command Prompt and PowerShell.
Command Prompt (CMD) is a widely popular and practical Windows command-line tool that can be used to deal with various works, such as CMD rename file, CMD ping test, CMD list files, CMD copy files, CMD list drives, CMD check WiFi password, and more.
However, a great many users and even professionals are unclear about these commands. For example, some users want to check the Command Prompt history in Windows 10/11 but don’t know how to do that. So, here we provide a full guide to list the CMD history in Command Prompt and PowerShell.
Can I View CMD History after Close
Unfortunately, you can only view the CMD history for current version. This is because the CMD history is not stored anywhere on Windows.
How to View CMD History in Command Prompt
How to check Command Prompt history Windows 10/11 in Command Prompt? There are 2 methods to view CMD history for currwent version. You can use the keyboard or the Doskey.
# 1. Check Windows CMD History Using the Keyboard
The first and simplest method is to use your keyboard with the Command Prompt. To do this work, follow the steps below:
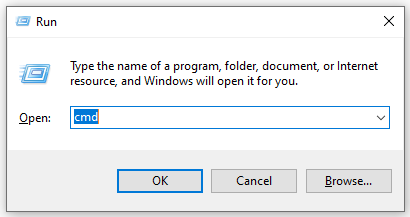
Step 1. Press Win + R keys to open the Run dialog box, and then type cmd in it and hit Enter.
Step 2. In the Command Prompt window, press and hold the F7 key to view the history of Command Prompt. Then it will open the list of commands you currently typed in.
Step 3. With the command history Windows opened, you can run the command again using the up or down arrow keys. Also, you can press the Esc key to exit the Command Prompt window without running any command.
Tips:
You can press Alt + F7 key to wipe the Windows Command Prompt history from the current session.
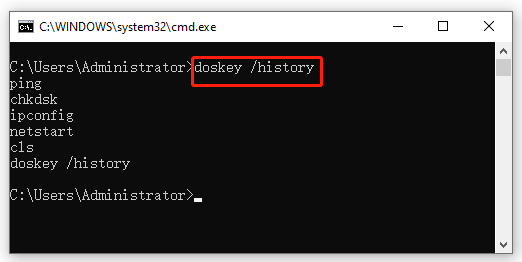
# 2. Check Windows CMD History Using the Doskey
The Doskey is another simple tool that can list the previously entered commands, edit command lines, and create macros. Here’s how to view Windows Command Prompt history using the Doskey.exe.
Step 1. Open the Command Prompt window again as we explained above.
Step 2. Type the following command and hit Enter. Then the command lines you recently executed will appear in the Command Prompt window.
doskey /history
Step 3. If you want to select and run the command, you can use the Up or Down arrow key and hit Enter. In addition, you can press the Page Down key to reenter the last command from the current session history or Page Up key to reenter the first command.
Note:
Windows will automatically clear the history of CMD logs and restart it for the new session once you restart your computer.
Step 4. If there are some useful commands that you may want to save for future use, you can run the following command to export the CMD history to a txt file. You can find the txt file in your WIndows Users folder.
doskey /HISTORY > history.txt
How to View CMD History in PowerShell
PowerShell can help you find the command history on Windows 10/11 as well. It’s very simple to view the PowerShell command history. Right click the Start menu from the bottom left screen and select Windows PowerShell. In the pop-up window, type the history command and hit Enter.
In addition, you can press Win + R keys to open the Run box, and then copy and paste the following command in it and hit Enter. It will direct you to a txt file that stores the command history of all sessions in PowerShell.
%userprofile%AppDataRoamingMicrosoftWindowsPowerShellPSReadline
Further reading: If you enter some issues like file system corruption and low disk space on Windows 10/11, don’t worry. MiniTool Partition Wizard can help you fix them easily by checking file system errors, extending/resizing partitions, analyzing disk space, upgrading to a larger hard disk, etc.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Ariel has been working as a highly professional computer-relevant technology editor at MiniTool for many years. She has a strong passion for researching all knowledge related to the computer’s disk, partition, and Windows OS. Up till now, she has finished thousands of articles covering a broad range of topics and helped lots of users fix various problems. She focuses on the fields of disk management, OS backup, and PDF editing and provides her readers with insightful and informative content.
The Command Prompt is nothing but a black and white command-line utility that comes out of the box on Windows 11/10. But for those who know its true potential, it is a great replacement for many of the users’ third-party software. For example, it can help you in organizing your hard drive partitions, create a bootable USB drive for you, refresh all the BIOS files, and much more. Many administrators and power users tend to make use of multiple commands on this command line to get their work done. Today, we will be talking about methods that will help the user view their Command Prompt history and to save that Command Prompt history on Windows 11/10.
We will cover the following topics:
- View using DOSKEY.
- View using the F7 key.
- Save the Command Prompt History.
- Clear command prompt history.
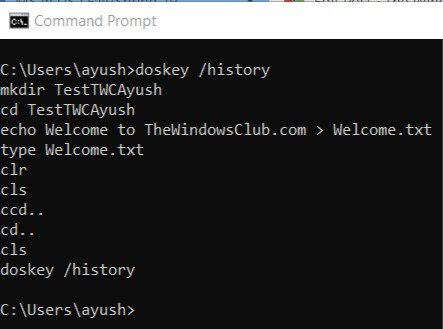
1] View command history using DOSKEY
This method is a pretty straightforward one. After you have entered a series of commands in the Command Prompt window, all you need to do is enter the following command inside the same Command Prompt window-
doskey /history
After that, you will be able to check all the commands that you just entered during that session in the Command Prompt in the same sequence as you entered it.
You can check a screen snippet of the same above.
Read: How to clear CMD screen?
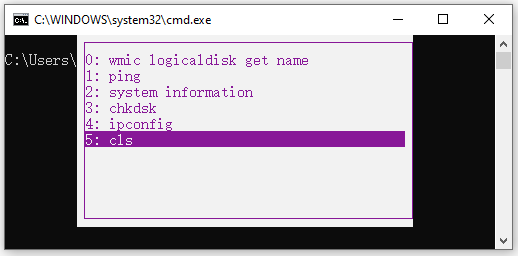
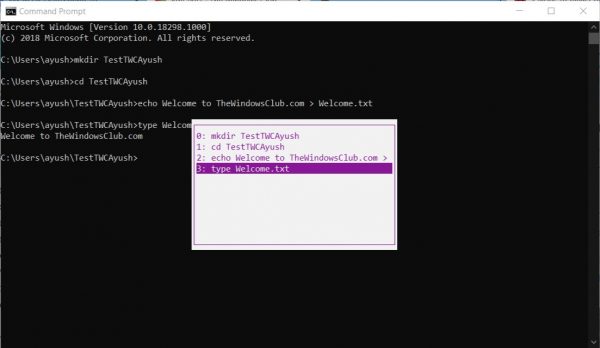
2] View CMD history using the F7 key
This is better than the DOSKEY method mentioned above. I am not claiming that because this is better, but if you just want to get back to any previously executed command, it is really reliable.
To view the command history, you need to hit the F7 key. F7 works for Command Prompt and PowerShell as well.
This will lead to a small pop-up to appear with the list of all the previously executed commands in the session.
You can use the up and down arrow key to navigate through the list and hit the Enter key to select any of them.
2] Save the Command Prompt History
Sometimes, you might need to keep a record of the commands they used in a session using the Command Prompt in a TXT, HTML, CSV or a RTF file.
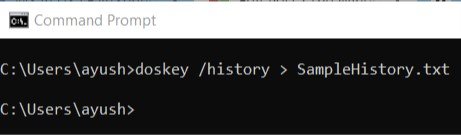
For that, you can use an extension of the DOSKEY command.
You just need to enter the following command and then hit the Enter key,
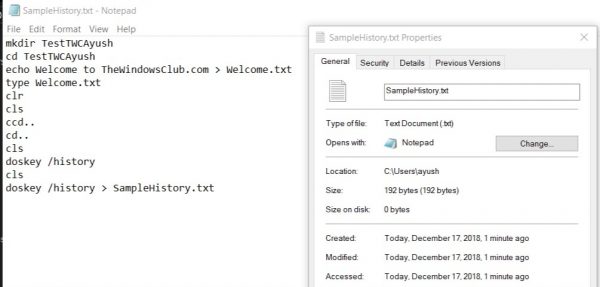
doskey /HISTORY > SampleHistory.txt
Then, your backed-up history file will be saved in a location where you executed the command in the Command Prompt window.
4] Clear command prompt history using Alt+F7
The simplest way is to restart the Command Prompt. The command history is cleared automatically every time you close it and start the command prompt again.
To clear the command history, you can also use Alt+F7 keyboard shortcut. Alt+F7 works for Command Prompt and PowerShell as well.
You can also delete the command history by using the Registry Editor. Navigate to the following key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\RunMRU
Next, select RunMRU and erase all the values having a name, a letter of the alphabet in the right pane. After this, right-click on MRUList > Edit, and delete the contents of Value data.
More Command Prompt tips & tricks here.
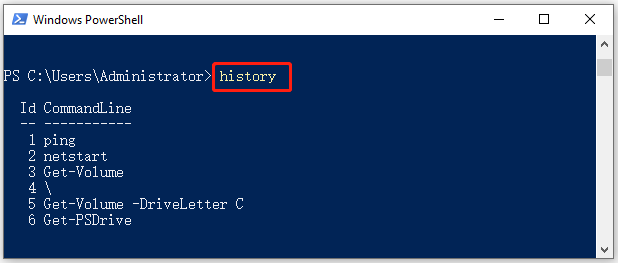
How to view command history in Windows PowerShell?
Like Command Prompt, Windows PowerShell also keeps a history of commands executed by you. Open PowerShell in Windows 11/10 and execute the following command:
Get-History
If you want, you can get more information for each command (command ID, execution status, command line, start execution time, and end execution time). For this, use the command given below:
Get-History | Format-List -Property *
How to export command history in PowerShell?
You can export or save the command history of PowerShell as a CSV file to your desktop or any location on your Windows 11/10 system. For this, you need to use the Export-CSV cmdlet, the path for the output file and file format. The command would be:
Get-History | Export-CSV C:\Users\Username\Desktop\CommandHistory.CSV
Replace Username with the actual username, the Desktop with the location or folder where you want to save the output, and CommandHistory with the file name of your choice.
If you’re a frequent user of the Windows 10 Command Prompt, the «command history» feature allows you to view and quickly reuse recent command instead of having to retype them, making your daily tasks more efficient.
In this Windows 10 guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to access your command history and export your recently typed command to a file while in Command Prompt.
- How to view Command Prompt history with F7
- How to view Command Prompt history with doskey
- How to export Command Prompt history to file
How to view Command Prompt history with F7
To use the F7 key to view your Command Prompt history, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, and click the top result to open the console.
- Press the F7 key.
Using the F7 key will open the graphical interface with a list of commands you typed in the current session, even if you mistyped them.
While in the command history, you can use the up or down arrow keys to select the command that you want to reuse. If you want to exit without running any command, press the Esc key.
How to view Command Prompt history with doskey
On Command Prompt, the doskey is a command line tool that recalls previously typed commands, edits command lines, and you can even use it to create macros.
In this case, you can use the command to view a list of the command history from the current session. Here’s how:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, and click the top result to open the console.
- Type the following command to view the command history and press Enter:
doskey /history
The only caveat with this tool is that you can view your current history, but you can’t select the command like using the F7 key. However, you can use the arrows and pages keys on the keyboard to cycle and run previously typed commands.
- Down arrow — Re-enters the next command that you typed. If you hit the arrow key repeatedly, it’ll scroll down through the command history currently in memory.
- Up arrow — Re-enters up the previous command that you typed. If you hit the arrow key repeatedly, it’ll scroll up through the command history currently in memory.
- Page Down — Re-enters the last command from the current session history.
- Page Up — Re-enters up the first command from the current session history.
- Esc — Deletes the current content of the console line.
How to export Command Prompt history to file
Unlike the Linux console, command history is only available for the current session. If you close Command Prompt, it will also clear the history, but you can the doskey command to save the history of the commands you typed to a file.
To export your command history, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and click the Run as administrator option.
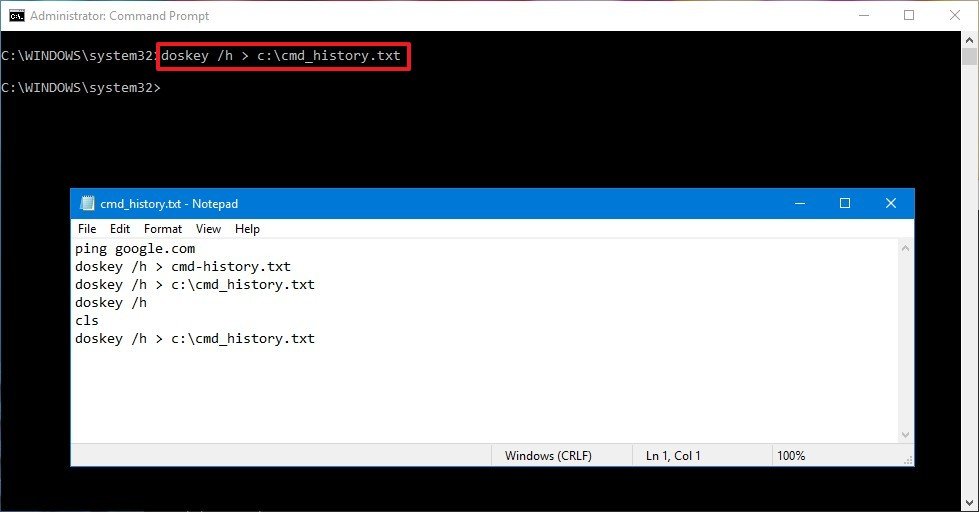
- Type the following command to save the command history and press Enter:
doskey /h > c:\cmd_history.txtIn the command, change the c:\cmd_history.txt for the path and name of the file you want to use to export the current history.
Once you’ve completed the steps, the Command Prompt history will be saved on the location you specified.
We’re focusing this guide on Windows 10, but command history for Command Prompt has been around for years, which means that you can also use this feature on Windows 8.1, Windows 7, and previous versions.
More Windows 10 resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10, visit the following resources:
- Windows 10 on Windows Central – All you need to know
- Windows 10 help, tips, and tricks
- Windows 10 forums on Windows Central
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
Mauro Huculak is technical writer for WindowsCentral.com. His primary focus is to write comprehensive how-tos to help users get the most out of Windows 10 and its many related technologies. He has an IT background with professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, and CompTIA, and he’s a recognized member of the Microsoft MVP community.
Command Prompt (cmd) is a widely used command-line tool for Windows. One of the shortcomings of CMD is that it only shows the history of commands you recently executed in the current session.
If you close the current window, all history is gone. There are multiple ways to quickly access the history of commands, clear the command history, and save your command history for future reference.
We will discuss these scenarios in this article. Please note that the commands mentioned in this article work on all versions of Windows, including Windows 7, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11.
Table of contents
- View Command History in Command Prompt using Doskey
- View Command History in Command Prompt using Keyboard Shortcut
- Search for Commands in the Command History
- Execute Commands from CMD History
- How to save Command Prompt History
- How to Clear CMD History
- View Command History in Command Prompt using Clink
- View Command History in PowerShell and Terminal
- Conclusion
View Command History in Command Prompt using Doskey
To view your command history in Command Prompt, simply type the following command in your CMD window.
doskey /historyAll the previously executed commands you typed in the current session will be listed on the cmd screen.
View Command History in Command Prompt using Keyboard Shortcut
You will only see the history for the current session in the Command Prompt window. Upon closing the Command Prompt window, all previous commands will be lost after restarting the program.
Once you have opened the Command Prompt window and started executing commands, Windows will save the history for your active session.
To see the list of recently executed commands in CMD, press the F7 key. This will open a pop-up inside CMD showing the list of recently executed commands. You can select any command and press enter and that specific command will be executed again.
Select the command and press the Enter button. And here you are. Your command has been executed.
Search for Commands in the Command History
You can also search for a specific command from your CMD history. To search for a specific command from the history, just press the F8 key, type whatever you remember, and then press the F8 key to cycle through the possibilities from the history.
For example, if the command I’m searching for starts with “ip“, I will type ip and then press the F8 key. Pressing the F8 key again will bring another possible result from history if any. Keep pressing the F8 key again and again until the history list ends.
Execute Commands from CMD History
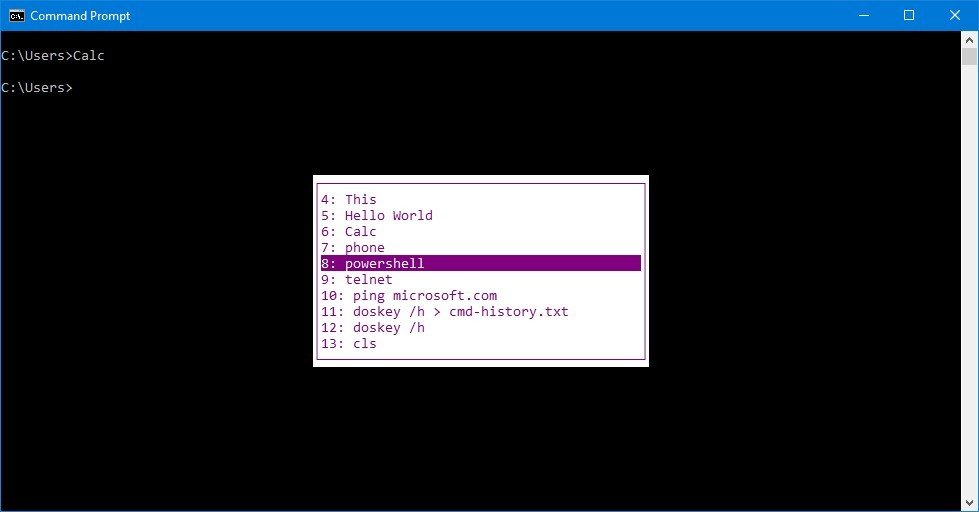
When we pressed the F7 key, you should have noticed that each command starts with a number. If you want to use the command again and again, you can call it by its number by using the F9 key.
For example, if the command number 3 is the one I have to run, again and again, I will press the F9 key, type 3, and then press Enter. This will execute command no. 3 from the command history.
doskey /historyUse the Up and Down arrow keys to select the command. Or you can also Copy and Paste the commands from the history that has appeared on your screen, within the CMD window.
How to save Command Prompt History
You can only view the history of commands as long as your CMD window stays open. When you close it, all commands will be gone with no mark of history. What if you need the same commands for the next use of CMD window, but you do not know which commands you executed before?
You can save your commands list as a TXT, HTML, CSV or RTF file before closing the window so that you can have a backup of your entered commands.
Type the following command to save the command history in Command Prompt:
doskey /HISTORY > history.txt
Your file will be saved in the Users folder. Now go to the user folder and see if that has the file saved there or not.
Please check the history of all commands and save them in a notepad file to use any of your commands anytime you need.
You can also automatically save the commands you typed in the file when you exit Command Prompt.
To do so, run the following macro:
doskey exit=(echo/ ^& echo **** %date% %time% ****) $g$g %USERPROFILE%\commands.log ^& doskey /history $g$g %USERPROFILE%\commands.log ^& ECHO Command history saved, exiting ^& exit $*This remaps the EXIT command to copy the command line history into your user profile folder (C:\Users\yourname\commands.log in the above example). I’ve taken this solution from serverfault. There are many other solutions for persistent history given on the page. You can check it out here.
How to Clear CMD History
Since the command history in CMD and PowerShell is not persistent, history can be cleared by closing the current CMD window. If you do not want to close the CMD window, you can also use the Alt + F7 key. This will clear the CMD history from your current session.
View Command History in Command Prompt using Clink
Clink is software that merges with the existing Command Prompt on your Windows PC. It adds extra command line features like rich command completion, cmdlet history browsing and execution, and line-editing capabilities.
These features are added by combining the existing cmd.exe file with GNU Readline libraries.
Note: Currently, Clink only works on Windows 10 and below.
Here is a complete list of the command line features which you will get in Command Prompt after installing Clink:
- The same line editing as Bash (from GNU’s Readline library).
- History persistence between sessions.
- Context-sensitive completion;
- Executables (and aliases).
- Directory commands.
- Environment variables
- Third-party tools; Git, Mercurial, SVN, Go, and P4.
- New keyboard shortcuts;
- Paste from the clipboard (Ctrl-V).
- Incremental history search (Ctrl-R/Ctrl-S).
- Powerful completion (TAB).
- Undo (Ctrl-Z).
- Automatic “cd ..” (Ctrl-Alt-U).
- Environment variable expansion (Ctrl-Alt-E).
- (press Alt-H for many more…)
- Scriptable completion with Lua.
- Coloured and scriptable prompt.
- Auto-answering of the “Terminate batch job?” prompt.
Let us now show you how to use Clink to view command history in Command Prompt:
-
Download and install Clink with default settings.
-
Run the Command Prompt.
-
Press CTRL + R shortcut keys to enter reverse search mode.
Enter reverse incremental search mode with Clink -
Enter the keywords for the command to search.
Search command by keyword The command will then appear after the colon.
-
When the correct command appears, press Enter to run it.
Run command from Command Prompt history using Clink
Clink stores command history between sessions. This means that even if you close the window, you can search for the previously-run cmdlets in a new Command Prompt instance using the CTRL + R shortcut keys.
If you want to get rid of these extra features, all you must do is delete Clink from your PC from the Programs and Features Control Panel applet.
View Command History in PowerShell and Terminal
PowerShell can also be used in place of the Command Prompt. PowerShell can run all the commands for CMD plus many more. If you want to view the history of your commands in PowerShell, you have to type the history command. This will show a list of all recently typed commands inside the current PowerShell session.
I hope you have a clear understanding of how to view your history in CMD and how to save that history. If you have any questions, comment below to ask.
Conclusion
Although Microsoft has introduced a new command line tool in Windows, Command Prompt is still popular among users. Windows 11 comes with Terminal, a console program that integrates Command Prompt and PowerShell into the same program.
The new terminal has many features of the Linux command line, including the persistent command history. That’s a step in a positive direction. While it will take time to upgrade to the new programs, DOS should not be left alone until everyone is upgraded.