При запуске новых сервисов в Windows, вы можете обнаружить что нужный порт уже занят (слушается) другой программой (процессом). Разберемся, как определить какая программ прослушивает определенный TCP или UDP порт в Windows.
Например, вы не можете запустить сайт IIS на стандартном 80 порту в Windows, т.к. этот порт сейчас занят (при запуске нескольких сайтов в IIS вы можете запускать их на одном или на разных портах). Как найти службу или процесс, который занял этот порт и завершить его?
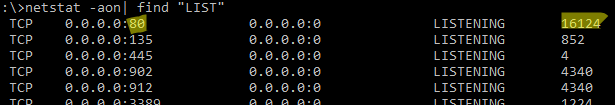
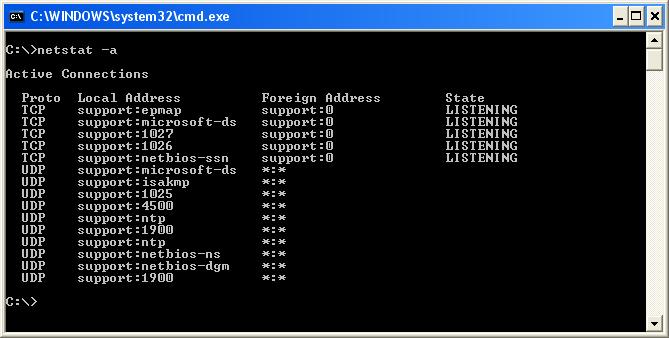
Чтобы вывести полный список TCP и UDP портов, которые прослушиваются вашим компьютером, выполните команду:
netstat -aon| find "LIST"
Или вы можете сразу указать искомый номер порта:
netstat -aon | findstr ":80" | findstr "LISTENING"
Используемые параметры команды netstat:
- a – показывать сетевые подключения и открытые порты
- o – выводить идентфикатор професса (PID) для каждого подключения
- n – показывать адреса и номера портов в числовом форматер
По выводу данной команды вы можете определить, что 80 порт TCP прослушивается (статус
LISTENING
) процессом с PID 16124.
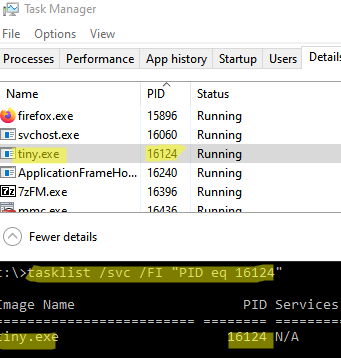
Вы можете определить исполняемый exe файл процесса с этим PID с помощью Task Manager или с помощью команды:
tasklist /FI "PID eq 16124"
Можно заменить все указанные выше команды одной:
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| findstr :80') do tasklist /FI "PID eq %a"
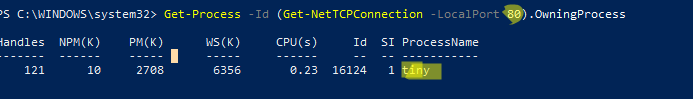
С помощью однострочной PowerShell команды можно сразу получить имя процесса, который прослушивает:
- TCP порт:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80).OwningProcess - UDP порт:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetUDPEndpoint -LocalPort 53).OwningProcess
Можно сразу завершить этот процесс, отправив результаты через pipe в командлет Stop-Process:
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 80).OwningProcess| Stop-Process
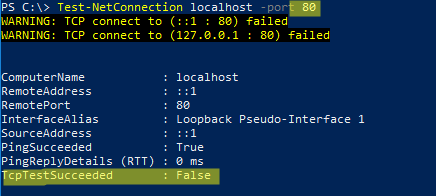
Проверьте, что порт 80 теперь свободен:
Test-NetConnection localhost -port 80
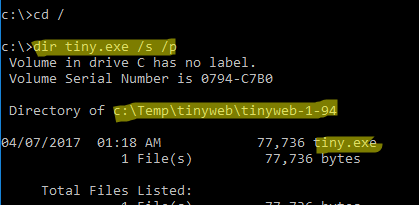
Чтобы быстрой найти путь к исполняемому файлу процесса в Windows, используйте команды:
cd /
dir tiny.exe /s /p
Или можно для поиска файла использовать встроенную команду where :
where /R C:\ tiny
В нашем случае мы нашли, что исполняемый файл
tiny.exe
(легкий HTTP сервер), который слушает 80 порт, находится в каталоге c:\Temp\tinyweb\tinyweb-1-94
How do I find out which process is listening on a TCP or UDP port on Windows?
Mateen Ulhaq
24.7k19 gold badges102 silver badges136 bronze badges
asked Sep 7, 2008 at 6:26
readonlyreadonly
344k107 gold badges204 silver badges205 bronze badges
11
PowerShell
TCP
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort YourPortNumberHere).OwningProcess
UDP
Get-Process -Id (Get-NetUDPEndpoint -LocalPort YourPortNumberHere).OwningProcess
cmd
netstat -a -b
(Add -n to stop it trying to resolve hostnames, which will make it a lot faster.)
Note Dane’s recommendation for TCPView. It looks very useful!
-a Displays all connections and listening ports.
-b Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or listening port. In some cases well-known executables host multiple independent components, and in these cases the sequence of components involved in creating the connection or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called, and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient permissions.
-n Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
-o Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.
answered Sep 7, 2008 at 6:28
15
There’s a native GUI for Windows:
-
Start menu → All Programs → Accessories → System Tools → Resource Monitor
-
or run
resmon.exe, -
or from TaskManager → Performance tab.
serge
14.1k35 gold badges124 silver badges206 bronze badges
answered May 18, 2014 at 5:02
bcorsobcorso
45.7k10 gold badges63 silver badges76 bronze badges
10
For Windows:
netstat -aon | find /i "listening"
xash
3,70210 silver badges22 bronze badges
answered Sep 7, 2008 at 6:32
akuaku
122k32 gold badges174 silver badges203 bronze badges
6
Use TCPView if you want a GUI for this. It’s the old Sysinternals application that Microsoft bought out.
answered Sep 7, 2008 at 6:38
DaneDane
9,7375 gold badges28 silver badges23 bronze badges
3
The -b switch mentioned in most answers requires you to have administrative privileges on the machine. You don’t really need elevated rights to get the process name!
Find the pid of the process running in the port number (e.g., 8080)
netstat -ano | findStr "8080"
Find the process name by pid
tasklist /fi "pid eq 2216"
Jaywalker
3,0793 gold badges29 silver badges44 bronze badges
answered Jan 24, 2018 at 3:50
Ram SharmaRam Sharma
2,4971 gold badge8 silver badges7 bronze badges
You can get more information if you run the following command:
netstat -aon | find /i "listening" |find "port"
using the ‘Find’ command allows you to filter the results. find /i "listening" will display only ports that are ‘Listening’. Note, you need the /i to ignore case, otherwise you would type find «LISTENING». | find "port" will limit the results to only those containing the specific port number. Note, on this it will also filter in results that have the port number anywhere in the response string.
answered Oct 8, 2013 at 18:56
Nathan24Nathan24
1,3721 gold badge11 silver badges20 bronze badges
4
-
Open a command prompt window (as Administrator) From «Start\Search box» Enter «cmd» then right-click on «cmd.exe» and select «Run as Administrator»
-
Enter the following text then hit Enter.
netstat -abno-a Displays all connections and listening ports.
-b Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or
listening port. In some cases well-known executables host
multiple independent components, and in these cases the
sequence of components involved in creating the connection
or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable
name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called,
and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option
can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient
permissions.-n Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form.
-o Displays the owning process ID associated with each connection.
-
Find the Port that you are listening on under «Local Address»
-
Look at the process name directly under that.
NOTE: To find the process under Task Manager
-
Note the PID (process identifier) next to the port you are looking at.
-
Open Windows Task Manager.
-
Select the Processes tab.
-
Look for the PID you noted when you did the netstat in step 1.
-
If you don’t see a PID column, click on View / Select Columns. Select PID.
-
Make sure “Show processes from all users” is selected.
-
answered Nov 8, 2012 at 1:49
CyborgCyborg
1,24412 silver badges12 bronze badges
Get PID and Image Name
Use only one command:
for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| findstr 9000') do tasklist /FI "PID eq %a"
where 9000 should be replaced by your port number.
The output will contain something like this:
Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
java.exe 5312 Services 0 130,768 K
Explanation:
-
it iterates through every line from the output of the following command:
netstat -aon | findstr 9000 -
from every line, the PID (
%a— the name is not important here) is extracted (PID is the5th element in that line) and passed to the following commandtasklist /FI "PID eq 5312"
If you want to skip the header and the return of the command prompt, you can use:
echo off & (for /f "tokens=5" %a in ('netstat -aon ^| findstr 9000') do tasklist /NH /FI "PID eq %a") & echo on
Output:
java.exe 5312 Services 0 130,768 K
answered Feb 10, 2016 at 10:17
ROMANIA_engineerROMANIA_engineer
54.6k29 gold badges203 silver badges200 bronze badges
1
First we find the process id of that particular task which we need to eliminate in order to get the port free:
Type
netstat -n -a -o
After executing this command in the Windows command line prompt (cmd), select the pid which I think the last column. Suppose this is 3312.
Now type
taskkill /F /PID 3312
You can now cross check by typing the netstat command.
NOTE: sometimes Windows doesn’t allow you to run this command directly on CMD, so first you need to go with these steps:
From the start menu -> command prompt (right click on command prompt, and run as administrator)
answered Aug 23, 2014 at 15:25
1
With PowerShell 5 on Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016, run the Get-NetTCPConnection cmdlet. I guess that it should also work on older Windows versions.
The default output of Get-NetTCPConnection does not include Process ID for some reason and it is a bit confusing. However, you could always get it by formatting the output. The property you are looking for is OwningProcess.
-
If you want to find out the ID of the process that is listening on port 443, run this command:
PS C:\> Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 443 | Format-List LocalAddress : :: LocalPort : 443 RemoteAddress : :: RemotePort : 0 State : Listen AppliedSetting : OwningProcess : 4572 CreationTime : 02.11.2016 21:55:43 OffloadState : InHost -
Format the output to a table with the properties you look for:
PS C:\> Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 443 | Format-Table -Property LocalAddress, LocalPort, State, OwningProcess LocalAddress LocalPort State OwningProcess ------------ --------- ----- ------------- :: 443 Listen 4572 0.0.0.0 443 Listen 4572 -
If you want to find out a name of the process, run this command:
PS C:\> Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 443).OwningProcess Handles NPM(K) PM(K) WS(K) CPU(s) Id SI ProcessName ------- ------ ----- ----- ------ -- -- ----------- 143 15 3448 11024 4572 0 VisualSVNServer
answered Nov 2, 2016 at 19:19
bahrepbahrep
30k12 gold badges103 silver badges151 bronze badges
To get a list of all the owning process IDs associated with each connection:
netstat -ao |find /i "listening"
If want to kill any process have the ID and use this command, so that port becomes free
Taskkill /F /IM PID of a process
answered Apr 17, 2014 at 14:38
Monis MajeedMonis Majeed
1,35814 silver badges21 bronze badges
1
It is very simple to get the port number from a PID in Windows.
The following are the steps:
-
Go to run → type cmd → press Enter.
-
Write the following command…
netstat -aon | findstr [port number](Note: Don’t include square brackets.)
-
Press Enter…
-
Then cmd will give you the detail of the service running on that port along with the PID.
-
Open Task Manager and hit the service tab and match the PID with that of the cmd, and that’s it.
answered May 30, 2016 at 6:36
Nishat LakhaniNishat Lakhani
7331 gold badge8 silver badges20 bronze badges
0
netstat -aof | findstr :8080 (Change 8080 for any port)
answered Feb 16, 2021 at 23:59
David JesusDavid Jesus
1,9812 gold badges29 silver badges34 bronze badges
To find out which specific process (PID) is using which port:
netstat -anon | findstr 1234
Where 1234 is the PID of your process. [Go to Task Manager → Services/Processes tab to find out the PID of your application.]
answered Dec 14, 2018 at 6:55
Talha ImamTalha Imam
1,0461 gold badge20 silver badges22 bronze badges
2
In case someone need an equivalent for macOS like I did, here is it:
lsof -i tcp:8080
After you get the PID of the process, you can kill it with:
kill -9 <PID>
answered Aug 12, 2020 at 11:22
wzsowzso
3,5325 gold badges28 silver badges48 bronze badges
2
Just open a command shell and type (saying your port is 123456):
netstat -a -n -o | find "123456"
You will see everything you need.
The headers are:
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID
TCP 0.0.0.0:37 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1111
This is as mentioned here.
answered Jan 25, 2017 at 0:13
1
If you’d like to use a GUI tool to do this there’s Sysinternals’ TCPView.
answered Sep 7, 2008 at 6:40
David WebbDavid Webb
191k57 gold badges313 silver badges299 bronze badges
-
Open the command prompt — start → Run →
cmd, or start menu → All Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt. -
Type
netstat -aon | findstr '[port_number]'
Replace the [port_number] with the actual port number that you want to check and hit Enter.
- If the port is being used by any application, then that application’s detail will be shown. The number, which is shown at the last column of the list, is the PID (process ID) of that application. Make note of this.
-
Type
tasklist | findstr '[PID]'
Replace the [PID] with the number from the above step and hit Enter.
- You’ll be shown the application name that is using your port number.
answered May 9, 2019 at 12:18
Anatole ABEAnatole ABE
5751 gold badge7 silver badges12 bronze badges
2
PowerShell
If you want to have a good overview, you can use this:
Get-NetTCPConnection -State Listen | Select-Object -Property *, `
@{'Name' = 'ProcessName';'Expression'={(Get-Process -Id $_.OwningProcess).Name}} `
| select ProcessName,LocalAddress,LocalPort
Then you get a table like this:
ProcessName LocalAddress LocalPort
----------- ------------ ---------
services :: 49755
jhi_service ::1 49673
svchost :: 135
services 0.0.0.0 49755
spoolsv 0.0.0.0 49672
For UDP, it is:
Get-NetUDPEndpoint | Select-Object -Property *, `
@{'Name' = 'ProcessName';'Expression'={(Get-Process -Id $_.OwningProcess).Name}} `
| select ProcessName,LocalAddress,LocalPort
answered Feb 27, 2022 at 22:16
Oliver GaidaOliver Gaida
1,7327 silver badges14 bronze badges
Netstat:
- -a displays all connection and listening ports
- -b displays executables
- -n stop resolve hostnames (numerical form)
-
-o owning process
netstat -bano | findstr "7002" netstat -ano > ano.txt
The Currports tool helps to search and filter
answered Sep 23, 2018 at 5:05
Blue CloudsBlue Clouds
7,3655 gold badges72 silver badges113 bronze badges
Type in the command: netstat -aon | findstr :DESIRED_PORT_NUMBER
For example, if I want to find port 80: netstat -aon | findstr :80
This answer was originally posted to this question.
answered Nov 22, 2016 at 15:36
TechnotronicTechnotronic
8,4744 gold badges40 silver badges53 bronze badges
netstat -ao and netstat -ab tell you the application, but if you’re not a system administrator you’ll get «The requested operation requires elevation».
It’s not ideal, but if you use Sysinternals’ Process Explorer you can go to specific processes’ properties and look at the TCP tab to see if they’re using the port you’re interested in. It is a bit of a needle and haystack thing, but maybe it’ll help someone…
answered Mar 13, 2014 at 19:57
Tony DelroyTony Delroy
103k15 gold badges177 silver badges253 bronze badges
1
Using Windows’ default shell (PowerShell) and without external applications
For those using PowerShell, try Get-NetworkStatistics:
> Get-NetworkStatistics | where Localport -eq 8000
ComputerName : DESKTOP-JL59SC6
Protocol : TCP
LocalAddress : 0.0.0.0
LocalPort : 8000
RemoteAddress : 0.0.0.0
RemotePort : 0
State : LISTENING
ProcessName : node
PID : 11552
answered Aug 25, 2016 at 13:36
mikemaccanamikemaccana
112k99 gold badges392 silver badges497 bronze badges
3
I recommend CurrPorts from NirSoft.
CurrPorts can filter the displayed results. TCPView doesn’t have this feature.
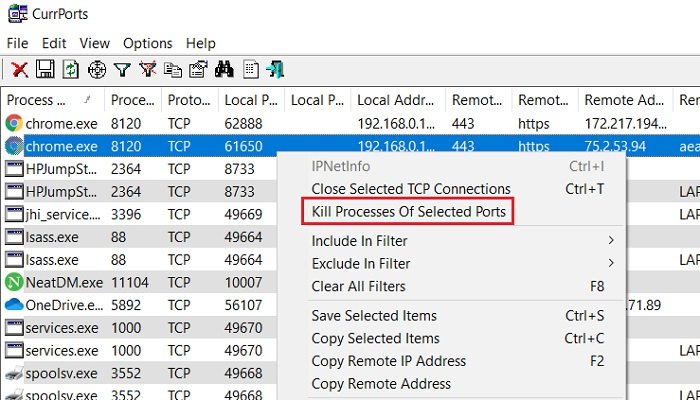
Note: You can right click a process’s socket connection and select «Close Selected TCP Connections» (You can also do this in TCPView). This often fixes connectivity issues I have with Outlook and Lync after I switch VPNs. With CurrPorts, you can also close connections from the command line with the «/close» parameter.
answered Jun 29, 2015 at 22:07
JoshJosh
2,1422 gold badges23 silver badges20 bronze badges
0
A single-line solution that helps me is this one. Just substitute 3000 with your port:
$P = Get-Process -Id (Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 3000).OwningProcess; Stop-Process $P.Id
Edit: Changed kill to Stop-Process for more PowerShell-like language
answered Feb 3, 2019 at 14:46
Angel VenchevAngel Venchev
7071 gold badge7 silver badges18 bronze badges
2
Use:
netstat -a -o
This shows the PID of the process running on a particular port.
Keep in mind the process ID and go to Task Manager and services or details tab and end the process which has the same PID.
Thus you can kill a process running on a particular port in Windows.
answered Aug 13, 2013 at 2:32
nishanisha
7112 gold badges14 silver badges28 bronze badges
To find pid who using port 8000
netstat -aon | findstr '8000'
To Kill that Process in windows
taskkill /pid pid /f
where pid is the process id which you get form first command
answered Jul 14, 2020 at 6:13
jizjiz
3083 silver badges7 bronze badges
2
Follow these tools: From cmd: C:\> netstat -anob with Administrator privileges.
Process Explorer
Process Dump
Port Monitor
All from sysinternals.com.
If you just want to know process running and threads under each process, I recommend learning about wmic. It is a wonderful command-line tool, which gives you much more than you can know.
Example:
c:\> wmic process list brief /every:5
The above command will show an all process list in brief every 5 seconds. To know more, you can just go with /? command of windows , for example,
c:\> wmic /?
c:\> wmic process /?
c:\> wmic prcess list /?
And so on and so forth. 
1
You can also check the reserved ports with the command below. Hyper-V reserve some ports, for instance.
netsh int ipv4 show excludedportrange protocol=tcp
answered Nov 24, 2020 at 14:50
A Port basically serves as an interface between your computer and the internet or other computers in the network. Every communication over the web is exchanged using these ports, so they are an essential part of the entire internet communication model.
Every IP address has a total of 65,535 ports, and it’s either a UDP port or a TCP port. An open port in a computer refers to a port that is configured to accept the connections, and a port that rejects connections is obviously a closed port.
While open ports are necessary for internet communication, they can be dangerous if the service listening on the port has bad security rules and is misconfigured. Such open ports are vulnerable to attacks.
In this post today, we will learn how to check which ports are being used in your machine, how to test if a Firewall is blocking a Port, and also learn how to check which process or service is using the open port.
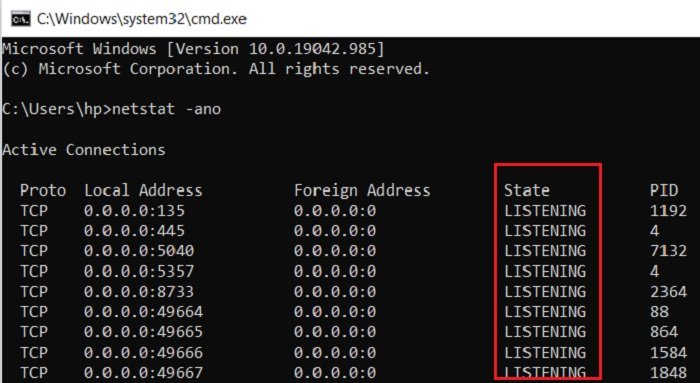
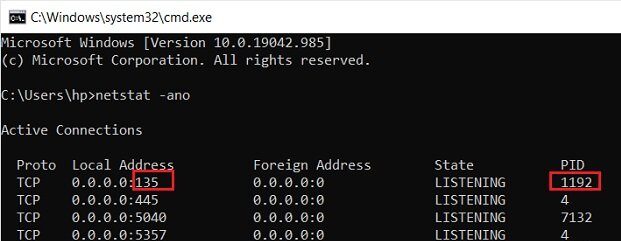
Open Command Prompt, type the following, and hit Enter to view the Ports used along with the Process Identifiers (PIDs):
netstat -ano
This will display the ports on your PC. It will display the details in 5 columns-
- Protocols,
- Local Address,
- Foreign Address,
- State, and
- PID (Process Identifier).
The port numbers here are displayed under the Local Adress column, for example, if the Local Adress is 0.0.0.0:5040, 5040 here is the port number.
Under the State tab, you can check whether a port is open or not.
- LISTENING means that it just waits and it is ready to send an answer whenever a client program requests it. The connection becomes open when a client connects to that port and a conversation begins.
- ESTABLISHED means that the connection has been established.
- TIME_WAIT means it’s waiting for a reply or connection. this often happens when a port is activated and the connection has not yet. been established
- CLOSE_WAIT means that the other side of the connection has closed the connection.
This is how you check what all ports are open in your Windows 10.
You can also view the Ports used along with the Process Names by running this command:
netstat -ab
Read: How to use Port Query Tool (PortQry.exe).
Check which process or service is using the open port
Now when we know what all ports are open in our system, we can also check which service is using which open port. To check that, go to the PID (Process ID) tab.
Let’s take the example of our first open port in the list, port 135, and its PID is 1192.
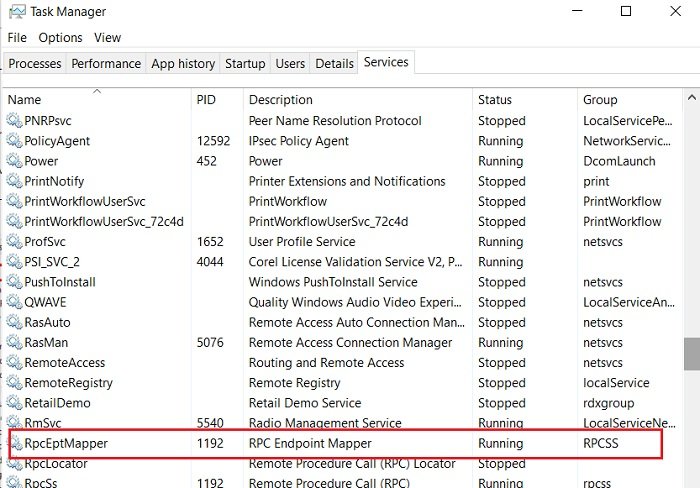
Now open the Task Manager by hitting Ctrl+Alt+Delete. Go to the Services tab and check for PID 1192.
Under the Description tab, you will see which app/program uses that port. End that particular task if you want to close that connection.
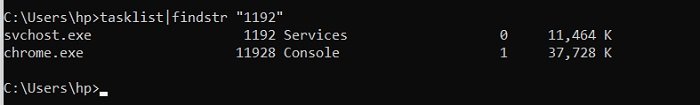
Alternatively, you can also find this using this command:
takslist|findstr "1192"
This will display the program using the selected port.
If you are looking for an easy way, you can also use some third-party software to check what all ports are open in your Windows 10. There is quite a few such freeware available on the web which tell what all websites your computer is connecting to and what all ports are open in your PC. One of such freeware is CurrPorts.
Read: How to Block or Open a Port in Windows Firewall.
How to test if Firewall is blocking a Port
CurrPorts is a simple and portable freeware to check open ports that comes in a zip file and takes no time to download on your PC. Since it is portable software, you do not need to install it. Simply download it, extract all the files and run it. Make sure you download the correct version as per your machine’s configuration.
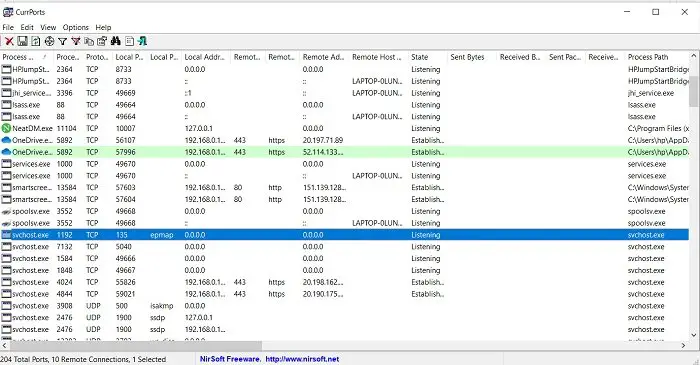
CurrPorts is a network monitoring software that displays the entire list of all open ports of your PC. Apart from the port number and its State, the freeware also shows detailed information about the processes using the open ports, the complete path of the process, file description, product name, file version, date and time it was created, and much more.
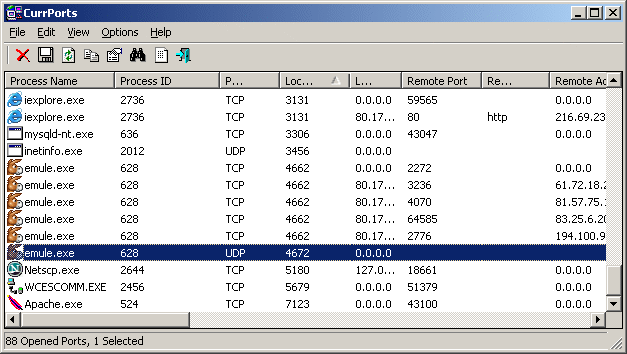
Once you download CurrPorts and run it, the main overview has it all. It displays the entire thing in one single window. You can check all the currently opened TCP and UDP ports and the program using that particular port in a single window. Check the screenshot below. You can select one or more processes at a time, check their ports and kill them if they seem to be unwanted. It also allows you to save the port information to an HTML/XML/Text file.
Furthermore, CurrPorts also lets you kill the process from the same window. Simply select the processes you want to kill, right-click and select ‘Kill processes of selected ports’ from the dropdown menu.
Another benefit of using CurrPorts is that it marks the suspicious TCP/UDP ports owned by the unidentified applications. So you can directly kill them and save your PC from a possible attack.
Certainly, using this freeware is an easier option as compared to the Command Prompt option mentioned above. You can download the software from the official website Nirsoft.net. Please note that there is a separate download link for x64 versions of Windows. This utility works fine with almost every version of Windows. It is a standalone executable utility so it doesn’t require any installation.
Read: Closed Port vs Stealth Port.
Некоторые приложения, которые работают через интернет, отказывают в доступе, если для них заблокирован порт. В данном случае речь идет, конечно, не о разъемах устройства, а совершенно о другом термине. Каждый владелец компьютера должен знать, как посмотреть открытые порты в операционной системе Windows 10, чтобы в дальнейшем их принудительно открыть и дать зеленый свет на работу отдельных программ.
Что такое порт
Сначала нужно пояснить, что собой представляет сетевой порт. Это канал, через который компьютер может принимать и отправлять информацию. Он является своего рода дополнением к сетевому адресу, а его номер необходим для понимания того, на какой адрес нужно доставлять данные.
На заметку. Большое количество открытых портов не только предлагает широкие возможности обмена информацией, но и вызывает риск заражения компьютера вирусами.
Сетевые координаты отличаются по своему предназначению. Одни выполняют функцию прямой отправки файлов, вторые тестируют связь, а третьи осуществляют поиск ресурсов. Поэтому современный компьютер поддерживает огромное количество портов, для каждого из которых присвоен определенный номер. Также отличается протокол, используемый для конкретной «тропинки».
Как проверить, открыт ли порт
Просмотр списка открытых портов необходим сразу в нескольких ситуациях. Например, когда есть подозрение на то, что один из них заблокирован, в связи с чем приложение с доступом к интернету не может осуществлять работу. Также проверка требуется в обратной ситуации, если хочется убедиться в закрытии того или иного порта во избежание заражения устройства.
Вне зависимости от того, какую цель преследует пользователь, он может ознакомиться со списком активных «тропинок» несколькими способами. Представленные ниже варианты отличаются уровнем удобства и количеством шагов, необходимых для проверки. Поэтому изучите инструкцию для каждого из них в отдельности, чтобы выбрать оптимальный метод.
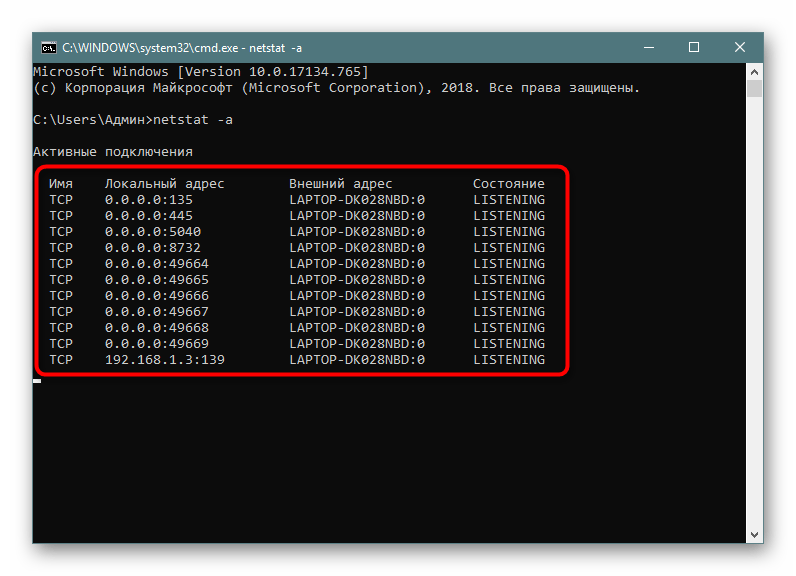
Утилита Netstat
Проверить открытые порты можно встроенными средствами компьютера без скачивания дополнительного программного обеспечения и посещения специализированных сайтов. Список координат предлагается получить через Командную строку. Если вы никогда не пользовались этим интерфейсом, то выполните следующие шаги:
- Кликните ПКМ по иконке «Пуск».
- Выберите запуск Командной строки с административными правами.
- Введите значение «netstat -a».
- Нажмите на клавишу «Enter».
После этого внутри КС появится список всех активных портов, и вы сможете проверить наличие в нем необходимой «тропинки». Отсутствие искомых координат будет говорить о том, что они заблокированы.
NirSoft CurrPorts
Внешний вид Командной строки многим людям кажется неудобным и даже пугающим за счет своего чрезмерного минимализма. Если вам тоже не понравился первый вариант, то скачайте и установите на компьютер утилиту NirSoft CurrPorts, а затем действуйте по алгоритму:
- Запустите приложение.
- Щелкните ЛКМ по вкладке «Локальный порт» для сортировки.
- Проверьте, использует ли хотя бы одно из приложений искомый порт.
Недостаток данного метода заключается в том, что он позволяет осуществить просмотр только в рамках запущенных программ. Закрытые приложения не поделятся координатами, а потому придется обращаться к альтернативным вариантам.
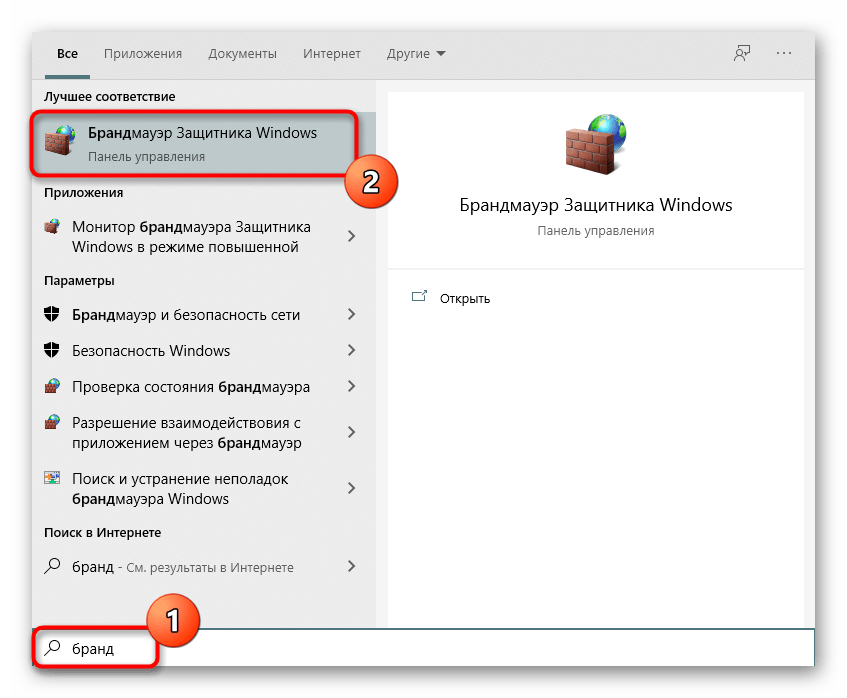
Через брандмауэр Windows
Вариант без использования сторонних программ, но тоже имеющий определенные ограничения. В частности, брандмауэр показывает локальный порт для каждого входящего подключения по отдельности. Процесс проверки будет рутинным и ресурсозатратным. Поэтому к данному методу стоит обращаться только в том случае, если нужен просмотр портов для определенного соединения:
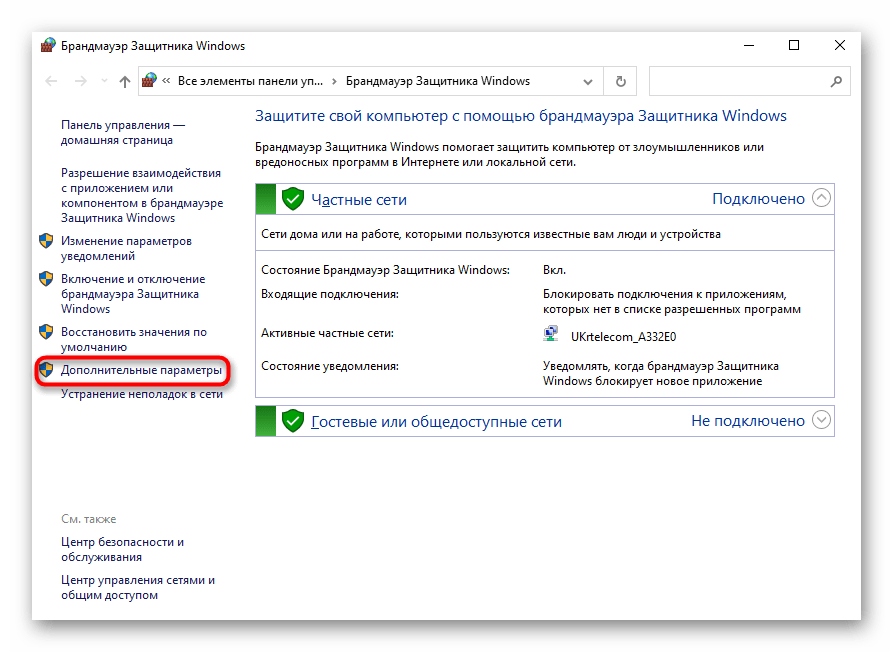
- Через поисковую строку найдите и запустите «Брандмауэр Защитника Windows».
- Перейдите во вкладку «Дополнительные параметры».
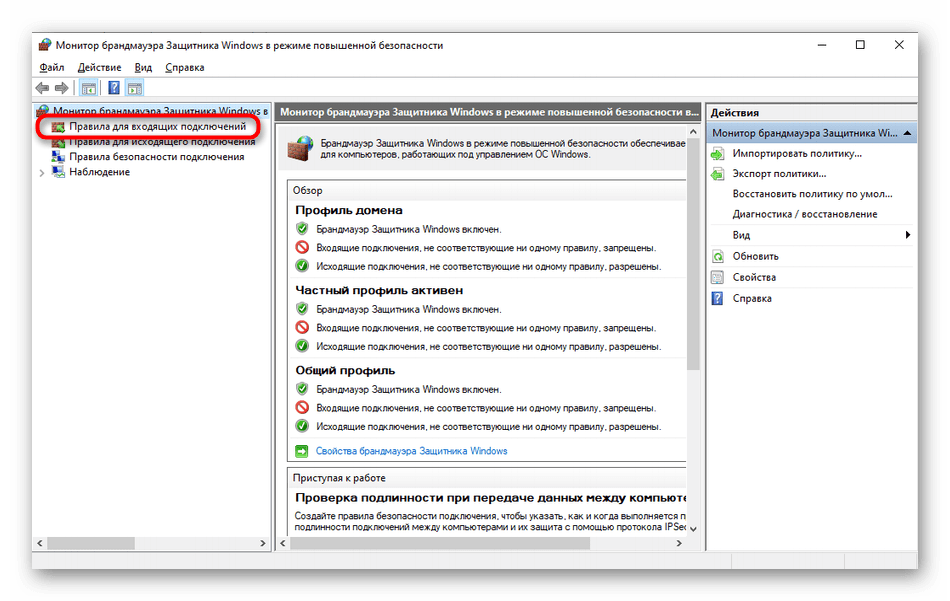
- Кликните ЛКМ по обозначению «Правила для входящих подключений».
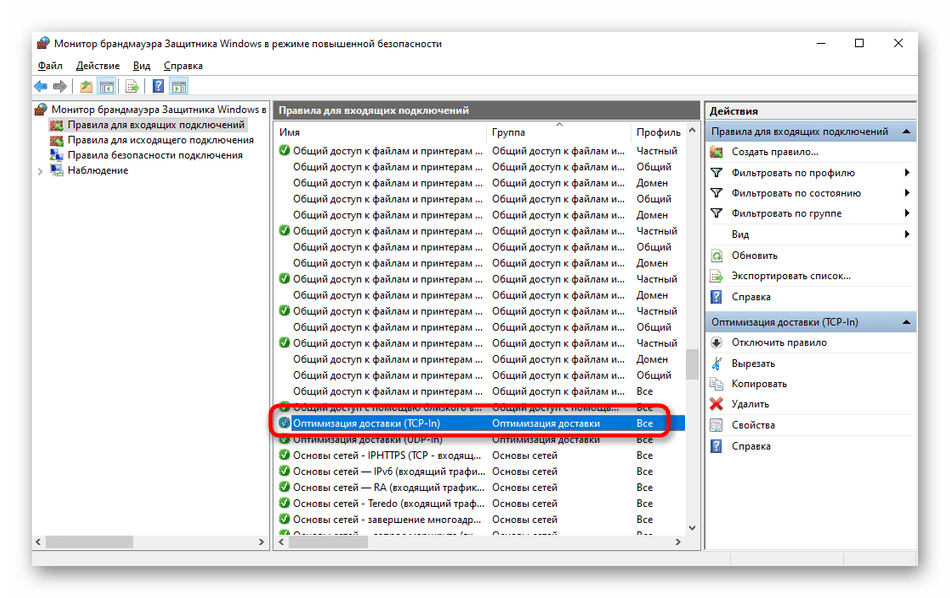
- Двойным щелчком ЛКМ откройте интересующее соединение.
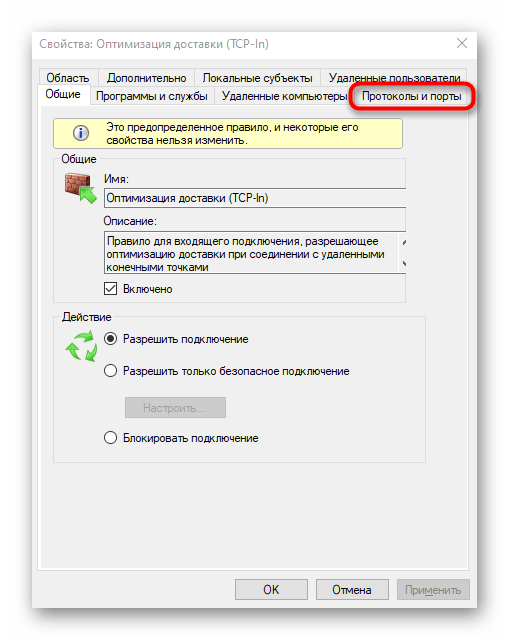
- Откройте вкладку «Протоколы и порты».
Далее остается ознакомиться с представленной информацией и сделать собственные выводы.
С помощью онлайн-сервисов
Намного более удобным и информативным вариантом является обращение к специальным онлайн-ресурсам, в числе которых можно выделить:
- Portscan;
- Hide my name;
- Тест IP.
Пользователю достаточно посетить один из предложенных сервисов через браузер и запустить сканирование портов. Через несколько секунд на экране появится подробная информация об открытых и закрытых «тропинках».
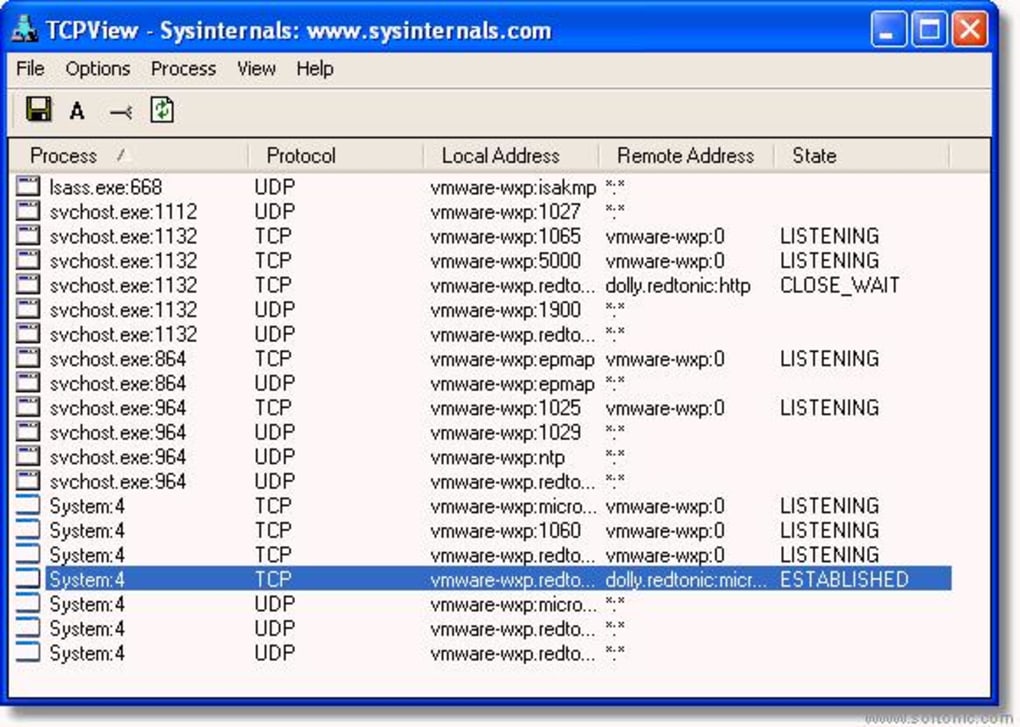
TCPView
Утилита, которая принадлежит компании Microsoft. Ее можно найти в магазине приложений Microsoft Store, где TCPView доступна для бесплатного скачивания. После установки приложения необходимо его запустить и дождаться окончания сканирования. Процесс займет не более пары минут. Далее в окне программы вы увидите список открытых портов и процессов, которые к ним обращаются.
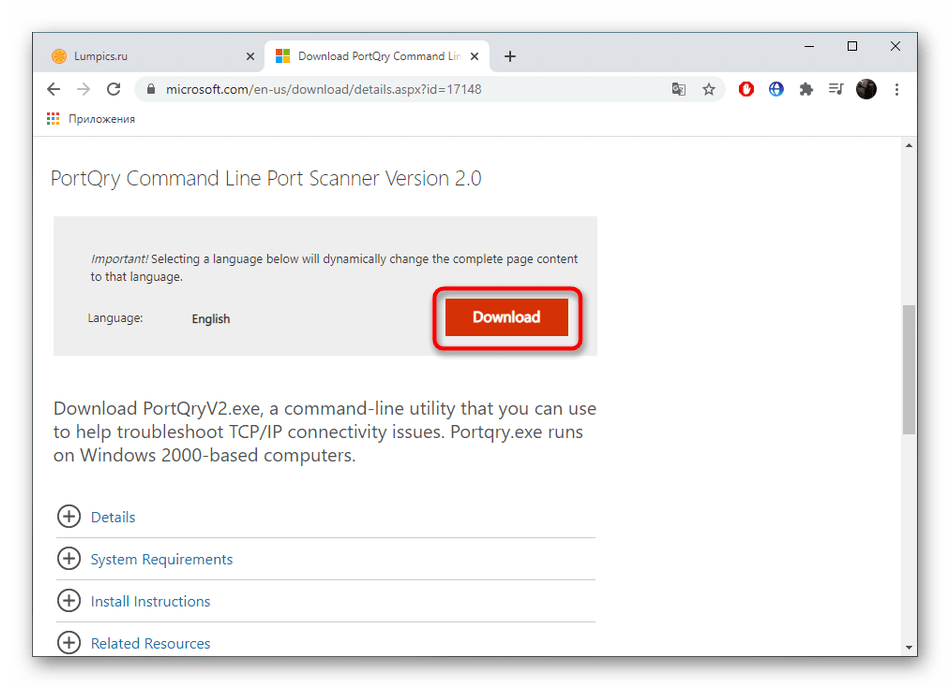
PortQry
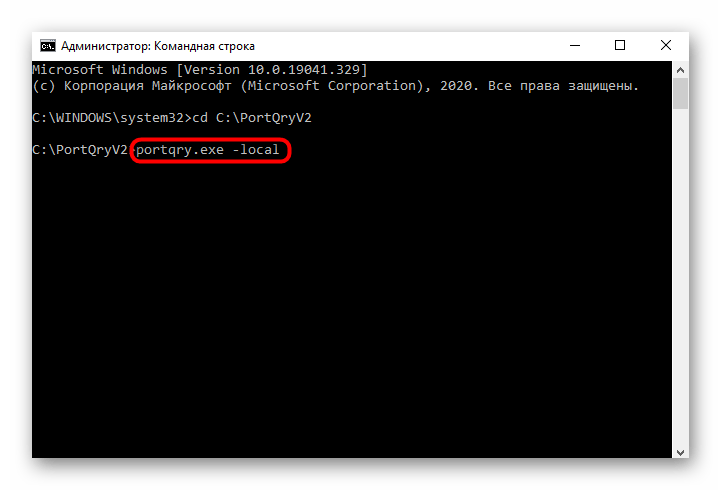
Еще одна утилита, доступная для бесплатного скачивания через Microsoft Store. Отличительной особенностью PortQry является то, что приложение не имеет графического интерфейса. Следовательно, проверка осуществляется встроенными средствами ПК:
- Скачайте и установите PortQry.
- Запустите Командную строку.
- Укажите адрес директории, куда была сохранена программа.
- Нажмите на клавишу «Enter».
- Введите команду «portqry.exe –local» и еще раз нажмите на «Enter».
Осуществление сканирования этим способом занимает больше времени, чем при помощи основного варианта, рассмотренного в самом начале материала (Командная строка). Поэтому обращайтесь к PortQry только в том случае, если запрос «netstat -a» не обрабатывается в КС.
Веб-интерфейс маршрутизатора
Заключительный вариант, заслуживающий внимания. Алгоритм будет отличаться в зависимости от производителя вашего роутера. Мы же рассмотрим процесс выполнения операции на примере маршрутизаторов TP-Link:
- Откройте браузер.
- В адресной строке введите 192.168.1.1 или 192.168.0.1.
- В открывшемся окне пройдите авторизацию, указав логин и пароль оборудования (обычно используется «admin» для обоих пунктов).
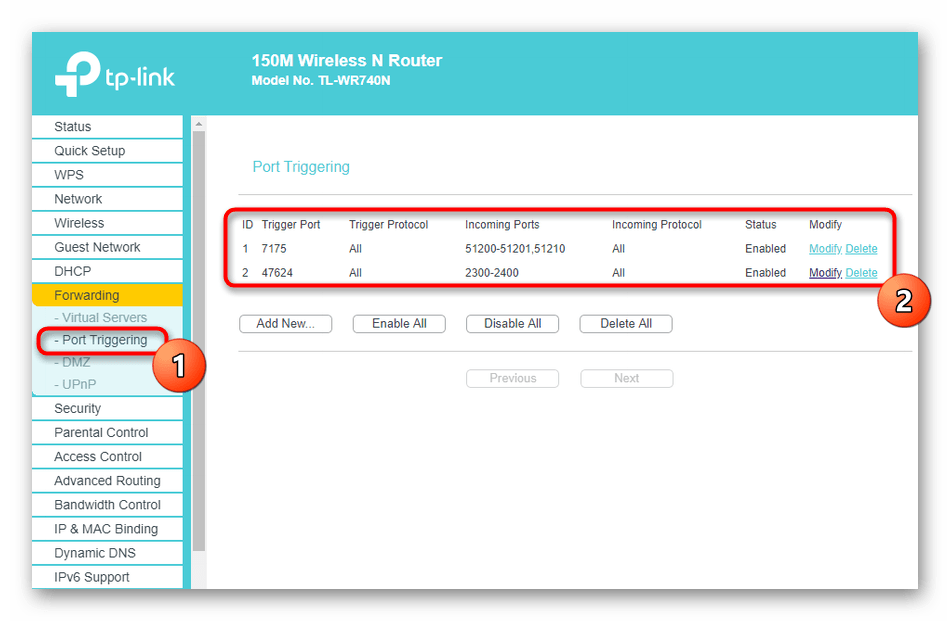
- Перейдите в раздел «Forwarding», а затем во вкладку «Port Triggering».
- Ознакомьтесь с информацией об открытых портах.
При использовании маршрутизаторов других марок совпадать будут только шаги 1-3. Дальнейшие действия зависят от оформления меню, где вам следует отталкиваться от пунктов со словом «Port» в названии.
Статья обновлена: 10 сентября 2021
ID: 101
Чтобы посмотреть список открытых портов:
- Откройте командную строку. Инструкция в статье.
- Выполните команду:
netstat -a
- Нажмите Enter на клавиатуре.
Вы получите список открытых портов в Windows.
Спасибо за ваш отзыв, вы помогаете нам становиться лучше!
Спасибо за ваш отзыв, вы помогаете нам становиться лучше!