Is there a way to restart a Windows service from the command prompt?
asked Jun 24, 2011 at 17:54
You can use net stop [service name] to stop it and net start [service name] to start it up again basically restarting the service.
To combine them just do this — net stop [service name] && net start [service name].
There is also a command built specifically for messing with services: sc
DESCRIPTION:
SC is a command line program used for communicating with the
Service Control Manager and services.
USAGE:
sc [command] [service name] ...
The option has the form "\\ServerName"
Further help on commands can be obtained by typing: "sc [command]"
Commands:
query-----------Queries the status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
queryex---------Queries the extended status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
start-----------Starts a service.
pause-----------Sends a PAUSE control request to a service.
interrogate-----Sends an INTERROGATE control request to a service.
continue--------Sends a CONTINUE control request to a service.
stop------------Sends a STOP request to a service.
config----------Changes the configuration of a service (persistent).
description-----Changes the description of a service.
failure---------Changes the actions taken by a service upon failure.
failureflag-----Changes the failure actions flag of a service.
sidtype---------Changes the service SID type of a service.
privs-----------Changes the required privileges of a service.
managedaccount--Changes the service to mark the service account
password as managed by LSA.
qc--------------Queries the configuration information for a service.
qdescription----Queries the description for a service.
qfailure--------Queries the actions taken by a service upon failure.
qfailureflag----Queries the failure actions flag of a service.
qsidtype--------Queries the service SID type of a service.
qprivs----------Queries the required privileges of a service.
qtriggerinfo----Queries the trigger parameters of a service.
qpreferrednode--Queries the preferred NUMA node of a service.
qrunlevel-------Queries the run level of a service.
qmanagedaccount-Queries whether a services uses an account with a
password managed by LSA.
qprotection-----Queries the process protection level of a service.
delete----------Deletes a service (from the registry).
create----------Creates a service. (adds it to the registry).
control---------Sends a control to a service.
sdshow----------Displays a service's security descriptor.
sdset-----------Sets a service's security descriptor.
showsid---------Displays the service SID string corresponding to an arbitrary name.
triggerinfo-----Configures the trigger parameters of a service.
preferrednode---Sets the preferred NUMA node of a service.
runlevel--------Sets the run level of a service.
GetDisplayName--Gets the DisplayName for a service.
GetKeyName------Gets the ServiceKeyName for a service.
EnumDepend------Enumerates Service Dependencies.
The following commands don't require a service name:
sc
boot------------(ok | bad) Indicates whether the last boot should
be saved as the last-known-good boot configuration
Lock------------Locks the Service Database
QueryLock-------Queries the LockStatus for the SCManager Database
EXAMPLE:
sc start MyService
QUERY and QUERYEX OPTIONS:
If the query command is followed by a service name, the status
for that service is returned. Further options do not apply in
this case. If the query command is followed by nothing or one of
the options listed below, the services are enumerated.
type= Type of services to enumerate (driver, service, all)
(default = service)
state= State of services to enumerate (inactive, all)
(default = active)
bufsize= The size (in bytes) of the enumeration buffer
(default = 4096)
ri= The resume index number at which to begin the enumeration
(default = 0)
group= Service group to enumerate
(default = all groups)
SYNTAX EXAMPLES
sc query - Enumerates status for active services & drivers
sc query eventlog - Displays status for the eventlog service
sc queryex eventlog - Displays extended status for the eventlog service
sc query type= driver - Enumerates only active drivers
sc query type= service - Enumerates only Win32 services
sc query state= all - Enumerates all services & drivers
sc query bufsize= 50 - Enumerates with a 50 byte buffer
sc query ri= 14 - Enumerates with resume index = 14
sc queryex group= "" - Enumerates active services not in a group
sc query type= interact - Enumerates all interactive services
sc query type= driver group= NDIS - Enumerates all NDIS drivers
answered Jun 24, 2011 at 17:58
paradd0xparadd0x
9,1497 gold badges37 silver badges44 bronze badges
9
Please, note that if there are other services that depends on this service — usual net stop & net start will not restart them. net stop /y will stop all dependencies
Most common example — SQL Server & SQL Agent.
I do recommend PowerShell cmdlet to solve this:
powershell -command "Restart-Service MSSQLSERVER -Force"
After MSSQLSERVER starts — cmdlet starts all previously stopped dependancies.
PS: Make sure you are running command as admin
answered Mar 15, 2017 at 13:57
2
To restart a Windows service from the command prompt or scheduled tasks, use this:
cmd /c "net stop "Service Name" & sc start "Service Name""
answered Feb 12, 2013 at 7:27
KikiKiki
1311 silver badge2 bronze badges
1
You could also use PowerShell:
stop-Service
Gaff
18.6k15 gold badges57 silver badges68 bronze badges
answered Jun 24, 2011 at 18:12
devlifedevlife
2411 gold badge2 silver badges7 bronze badges
1
To solve the annoying Wacom Intuous Driver not running Error I get on every reboot.
Windows key + R, paste, Bam!
sc stop WTabletServicePro && sc start WTabletServicePro
Simon E.
3,8615 gold badges29 silver badges31 bronze badges
answered Oct 20, 2014 at 3:45
GeorgeGeorge
611 silver badge1 bronze badge
1
The PsService utility from PsTools provides a restart command for services, with additional parameters to run it on another machine.
psservice [-accepteula] [\\Computer [-u Username [-p Password]]] restart <service-name>
The -accepteula flag saves you the EULA window just in case it’s the first time you use this utility with the current user.
answered May 22, 2018 at 16:00
cdlvcdlvcdlvcdlv
1,4711 gold badge19 silver badges27 bronze badges
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
При сбое в работе любой службы Windows нужно либо перезапустить службу, либо перезагрузить систему. Перезагрузка компьютера неудобна, поскольку занимает время и закрывает все окна. Если не получается остановить службу через Панель управления, можно перезапустить службу Windows из командной строки.
Открыть настройки служб Windows можно 4 способами:
- Нажать Win+R, в окне Выполнить ввести services.msc и нажать Enter. Откроется Диспетчер служб.
- Нажать Пуск, в поиске ввести Службы, открыть настройки.
- Открыть Панель управления -> Система и безопасность -> Администрирование -> Службы.
- Нажать ПКМ на кнопке Пуск или клавиши Win+X. Перейти в «Управление компьютером -> Службы и приложения -> Службы.
К счастью, от версии к версии Windows этот раздел настроек практически не изменялся. В Windows 7, Vista, 8 и 10 «Службы» будут выглядеть почти одинаково.
Перезапуск через Панель управления
Возможностей стандартных настроек в Панели управления достаточно, чтобы останавливать и запускать системные сервисы. Есть возможность полностью отключить ненужные службы — это немного повысит производительность устройства.
Остановка и повторный запуск служб Windows:
- Открыть любым способом окно Службы, найти нужную.
- Нажать по нужной службе правой кнопкой мыши и выбрать Перезапустить.
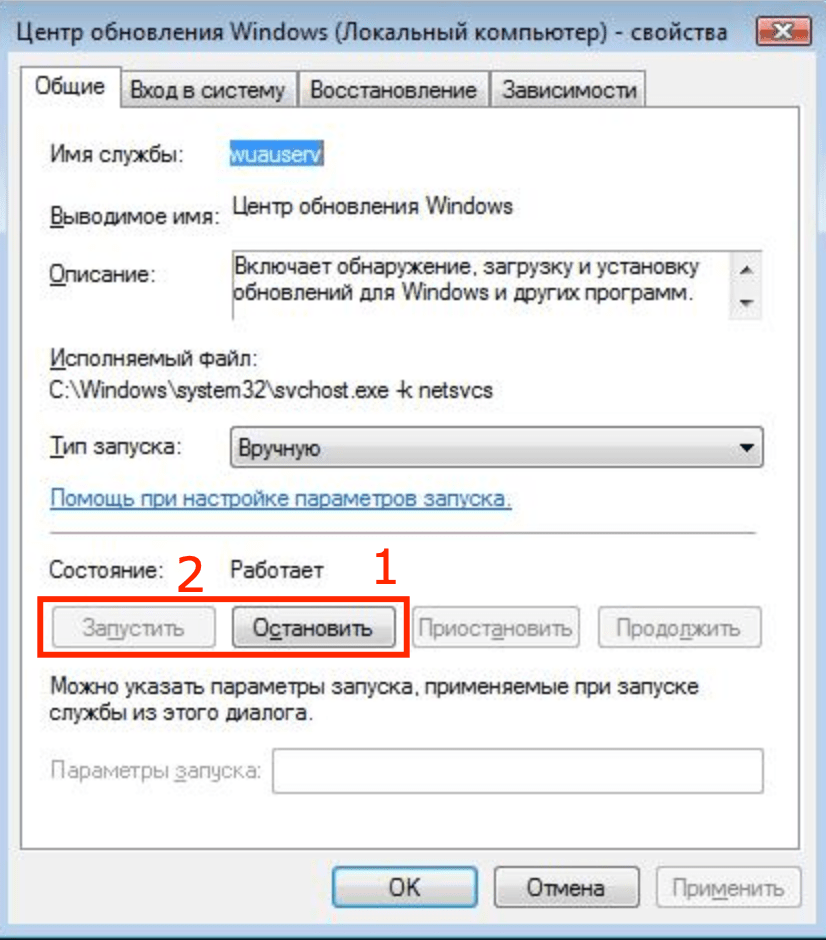
- Если кнопка Перезапустить неактивна — нажать Свойства.
- Нажать Остановить, дождаться остановки службы.
- Нажать на кнопку Запустить.
Если служба зависла или не остановилась — открыть диспетчер задач (Ctrl+Alt+Del) и завершить все процессы, связанные с проблемной службой.
Перезапуск через Командную строку
Если Панель управления не справляется со своими обязанностями, отключить или перезапустить службу можно через Командную строку (cmd.exe). Командная строка должна быть запущена от имени администратора.
Для управления службами существует 4 команды, дублирующие функционал Панели управления:
- net stopservice — Остановить выбранную службу.
- net startservice — Запустить.
- net pauseservice — Приостановить обслуживание.
- net continueservice — Возобновить обслуживание.
Для работы со службой нужно знать её название. Например, запуск службы Windows Audio будет выполнен по команде net start audiosrv. Здесь audiosrv — системное название службы.
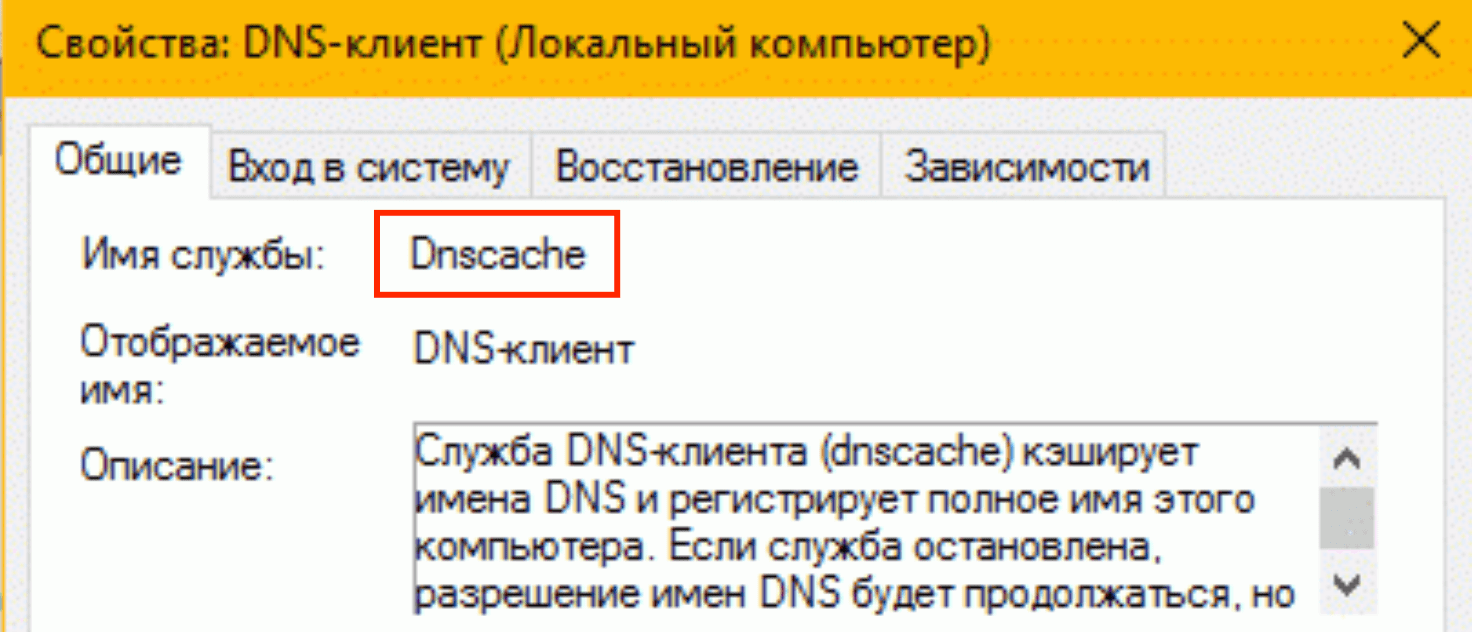
Чтобы его узнать, нужно зайти в свойства. Нужная строка будет в самом верху — «Имя службы». Вывести списком имена всех активных служб можно прямо в Командной строке, введя sc query type= service.
Через консоль можно не только перезапустить службу, но и изменить её тип запуска командой sc config *СЛУЖБА* start=*ТИП_ЗАПУСКА*.
Доступные типы запуска:
- auto — Автоматически.
- demand — Вручную (по требованию).
- delayed-auto — Отложенный запуск.
Например, команда sc config audiosrv start=auto переведет службу Windows Audio в тип запуска Автоматически.
Для полноты нужно упомянуть еще один способ перезапуска — через Диспетчер задач. Для этого нужно нажать комбинацию клавиш Ctrl+Alt+Del (или Ctrl-Shift-Esc), выбрать Диспетчер задач и перейти на вкладку Службы. По нажатию правой кнопки мыши на любой службе появляется контекстное меню, откуда доступна и остановка, и запуск, и перезагрузка.
How can I script a bat or cmd to stop and start a service reliably with error checking (or let me know that it wasn’t successful for whatever reason)?
mmcdole
91.6k60 gold badges186 silver badges222 bronze badges
asked Sep 25, 2008 at 15:09
0
Use the SC (service control) command, it gives you a lot more options than just start & stop.
DESCRIPTION:
SC is a command line program used for communicating with the
NT Service Controller and services.
USAGE:
sc <server> [command] [service name] ...
The option <server> has the form "\\ServerName"
Further help on commands can be obtained by typing: "sc [command]"
Commands:
query-----------Queries the status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
queryex---------Queries the extended status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
start-----------Starts a service.
pause-----------Sends a PAUSE control request to a service.
interrogate-----Sends an INTERROGATE control request to a service.
continue--------Sends a CONTINUE control request to a service.
stop------------Sends a STOP request to a service.
config----------Changes the configuration of a service (persistant).
description-----Changes the description of a service.
failure---------Changes the actions taken by a service upon failure.
qc--------------Queries the configuration information for a service.
qdescription----Queries the description for a service.
qfailure--------Queries the actions taken by a service upon failure.
delete----------Deletes a service (from the registry).
create----------Creates a service. (adds it to the registry).
control---------Sends a control to a service.
sdshow----------Displays a service's security descriptor.
sdset-----------Sets a service's security descriptor.
GetDisplayName--Gets the DisplayName for a service.
GetKeyName------Gets the ServiceKeyName for a service.
EnumDepend------Enumerates Service Dependencies.
The following commands don't require a service name:
sc <server> <command> <option>
boot------------(ok | bad) Indicates whether the last boot should
be saved as the last-known-good boot configuration
Lock------------Locks the Service Database
QueryLock-------Queries the LockStatus for the SCManager Database
EXAMPLE:
sc start MyService
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:15
FerruccioFerruccio
99k38 gold badges226 silver badges299 bronze badges
4
net start [serviceName]
and
net stop [serviceName]
tell you whether they have succeeded or failed pretty clearly. For example
U:\>net stop alerter
The Alerter service is not started.
More help is available by typing NET HELPMSG 3521.
If running from a batch file, you have access to the ERRORLEVEL of the return code. 0 indicates success. Anything higher indicates failure.
As a bat file, error.bat:
@echo off
net stop alerter
if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto error
exit
:error
echo There was a problem
pause
The output looks like this:
U:\>error.bat
The Alerter service is not started.
More help is available by typing NET HELPMSG 3521.
There was a problem
Press any key to continue . . .
Return Codes
- 0 = Success
- 1 = Not Supported
- 2 = Access Denied
- 3 = Dependent Services Running
- 4 = Invalid Service Control
- 5 = Service Cannot Accept Control
- 6 = Service Not Active
- 7 = Service Request Timeout
- 8 = Unknown Failure
- 9 = Path Not Found
- 10 = Service Already Running
- 11 = Service Database Locked
- 12 = Service Dependency Deleted
- 13 = Service Dependency Failure
- 14 = Service Disabled
- 15 = Service Logon Failure
- 16 = Service Marked For Deletion
- 17 = Service No Thread
- 18 = Status Circular Dependency
- 19 = Status Duplicate Name
- 20 = Status Invalid Name
- 21 = Status Invalid Parameter
- 22 = Status Invalid Service Account
- 23 = Status Service Exists
- 24 = Service Already Paused
Edit 20.04.2015
Return Codes:
The NET command does not return the documented Win32_Service class return codes (Service Not Active,Service Request Timeout, etc) and for many errors will simply return Errorlevel 2.
Look here: http://ss64.com/nt/net_service.html
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:13
Bill MichellBill Michell
8,2703 gold badges29 silver badges33 bronze badges
3
You can use the NET START command and then check the ERRORLEVEL environment variable, e.g.
net start [your service]
if %errorlevel% == 2 echo Could not start service.
if %errorlevel% == 0 echo Service started successfully.
echo Errorlevel: %errorlevel%
Disclaimer: I’ve written this from the top of my head, but I think it’ll work.
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:15
Jonas EngströmJonas Engström
5,0153 gold badges38 silver badges36 bronze badges
0
Instead of checking codes, this works too
net start "Apache tomcat" || goto ExitError
:End
exit 0
:ExitError
echo An error has occurred while starting the tomcat services
exit 1
Mr_Green
40.8k45 gold badges160 silver badges271 bronze badges
answered Dec 7, 2013 at 16:45
vanvalvanval
9971 gold badge9 silver badges19 bronze badges
I have created my personal batch file for this, mine is a little different but feel free to modify as you see fit.
I created this a little while ago because I was bored and wanted to make a simple way for people to be able to input ending, starting, stopping, or setting to auto. This BAT file simply requests that you input the service name and it will do the rest for you. I didn’t realize that he was looking for something that stated any error, I must have misread that part. Though typically this can be done by inputting >> output.txt on the end of the line.
The %var% is just a way for the user to be able to input their own service into this, instead of having to go modify the bat file every time that you want to start/stop a different service.
If I am wrong, anyone can feel free to correct me on this.
@echo off
set /p c= Would you like to start a service [Y/N]?
if /I "%c%" EQU "Y" goto :1
if /I "%c%" EQU "N" goto :2
:1
set /p var= Service name:
:2
set /p c= Would you like to stop a service [Y/N]?
if /I "%c%" EQU "Y" goto :3
if /I "%c%" EQU "N" goto :4
:3
set /p var1= Service name:
:4
set /p c= Would you like to disable a service [Y/N]?
if /I "%c%" EQU "Y" goto :5
if /I "%c%" EQU "N" goto :6
:5
set /p var2= Service name:
:6
set /p c= Would you like to set a service to auto [Y/N]?
if /I "%c%" EQU "Y" goto :7
if /I "%c%" EQU "N" goto :10
:7
set /p var3= Service name:
:10
sc start %var%
sc stop %var1%
sc config %var2% start=disabled
sc config %var3% start=auto
answered Jun 13, 2015 at 1:31
2
Using the return codes from net start and net stop seems like the best method to me. Try a look at this: Net Start return codes.
bluish
26.4k28 gold badges122 silver badges181 bronze badges
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:12
ZombieSheepZombieSheep
29.6k12 gold badges67 silver badges114 bronze badges
1
Syntax always gets me…. so…
Here is explicitly how to add a line to a batch file that will kill a remote service (on another machine) if you are an admin on both machines, run the .bat as an administrator, and the machines are on the same domain. The machine name follows the UNC format \myserver
sc \\ip.ip.ip.ip stop p4_1
In this case… p4_1 was both the Service Name and the Display Name, when you view the Properties for the service in Service Manager. You must use the Service Name.
For your Service Ops junkies… be sure to append your reason code and comment! i.e. ‘4’ which equals ‘Planned’ and comment ‘Stopping server for maintenance’
sc \\ip.ip.ip.ip stop p4_1 4 Stopping server for maintenance
answered Jan 28, 2014 at 20:52
ATSiemATSiem
1,19412 silver badges19 bronze badges
2
We’d like to think that «net stop » will stop the service. Sadly, reality isn’t that black and white. If the service takes a long time to stop, the command will return before the service has stopped. You won’t know, though, unless you check errorlevel.
The solution seems to be to loop round looking for the state of the service until it is stopped, with a pause each time round the loop.
But then again…
I’m seeing the first service take a long time to stop, then the «net stop» for a subsequent service just appears to do nothing. Look at the service in the services manager, and its state is still «Started» — no change to «Stopping». Yet I can stop this second service manually using the SCM, and it stops in 3 or 4 seconds.
answered Feb 10, 2014 at 17:04
DaveHDaveH
511 silver badge1 bronze badge
or you can start remote service with this cmd : sc \\<computer> start <service>
answered Jan 27, 2012 at 8:56
onionpsyonionpsy
1,50211 silver badges15 bronze badges
I just used Jonas’ example above and created full list of 0 to 24 errorlevels. Other post is correct that net start and net stop only use errorlevel 0 for success and 2 for failure.
But this is what worked for me:
net stop postgresql-9.1
if %errorlevel% == 2 echo Access Denied - Could not stop service
if %errorlevel% == 0 echo Service stopped successfully
echo Errorlevel: %errorlevel%
Change stop to start and works in reverse.
answered Feb 12, 2016 at 16:33
Manual service restart is ok — services.msc has «Restart» button, but in command line both sc and net commands lacks a «restart» switch and if restart is scheduled in cmd/bat file, service is stopped and started immediately, sometimes it gets an error because service is not stopped yet, it needs some time to shut things down.
This may generate an error:
sc stop
sc start
It is a good idea to insert timeout, I use ping (it pings every 1 second):
sc stop
ping localhost -n 60
sc start
answered May 24, 2016 at 8:55
KulerisKuleris
1011 silver badge3 bronze badges
Here is the Windows 10 command to start System Restore using batch :
sc config swprv start= Auto
You may also like those commands :
-
Change registry value to auto start System restore
REG ADD «HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRestore» /v DisableSR /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
-
Create a system restore point
Wmic.exe /Namespace:\root\default Path SystemRestore Call CreateRestorePoint «djibe saved your PC», 100, 12
-
Change System Restore disk usage
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /for=C: /on=C: /maxsize=10%
Enjoy
answered Nov 26, 2018 at 19:53
djibedjibe
2,7732 gold badges17 silver badges26 bronze badges
- SC
- NET STOP/START
- PsService
- WMIC
- Powershell is also easy for use option
SC and NET are already given as an anwests. PsService add some neat features but requires a download from Microsoft.
But my favorite way is with WMIC as the WQL syntax gives a powerful way to manage more than one service with one line (WMI objects can be also used through powershell/vbscript/jscript/c#).
The easiest way to use it:
wmic service MyService call StartService
wmic service MyService call StopService
And example with WQL
wmic service where "name like '%%32Time%%' and ErrorControl='Normal'" call StartService
This will start all services that have a name containing 32Time and have normal error control.
Here are the methods you can use.
With :
wmic service get /FORMAT:VALUE
you can see the available information about the services.
answered Nov 5, 2020 at 16:15
npocmakanpocmaka
55.6k18 gold badges148 silver badges188 bronze badges
SC can do everything with services… start, stop, check, configure, and more…
bluish
26.4k28 gold badges122 silver badges181 bronze badges
answered Sep 25, 2008 at 15:26
AxemanAxeman
3491 silver badge7 bronze badges
Sometimes you can find the stop does not work..
My SQlServer sometimes does this. Using the following commandline kills it. If you really really need your script to kill stuff that doesn’t stop. I would have it do this as a last resort
taskkill /pid [pid number] /f
answered May 9, 2018 at 9:52
andrew pateandrew pate
3,85336 silver badges28 bronze badges
I am writing a windows service in C#, the stop/uninstall/build/install/start loop got too tiring. Wrote a mini script, called it reploy.bat and dropped in my Visual Studio output directory (one that has the built service executable) to automate the loop.
Just set these 3 vars
servicename : this shows up on the Windows Service control panel (services.msc)
slndir : folder (not the full path) containing your solution (.sln) file
binpath : full path (not the folder path) to the service executable from the build
NOTE: This needs to be run from the Visual Studio Developer Command Line for the msbuild command to work.
SET servicename="My Amazing Service"
SET slndir="C:dir\that\contains\sln\file"
SET binpath="C:path\to\service.exe"
SET currdir=%cd%
call net stop %servicename%
call sc delete %servicename%
cd %slndir%
call msbuild
cd %bindir%
call sc create %servicename% binpath=%binpath%
call net start %servicename%
cd %currdir%
Maybe this helps someone 
answered Oct 5, 2018 at 18:53
sh87sh87
1,06310 silver badges12 bronze badges
1
I didn’t find any of the answers above to offer a satisfactory solution so I wrote the following batch script…
:loop
net stop tomcat8
sc query tomcat8 | find "STOPPED"
if errorlevel 1 (
timeout 1
goto loop
)
:loop2
net start tomcat8
sc query tomcat8 | find "RUNNING"
if errorlevel 1 (
timeout 1
goto loop2
)
It keeps running net stop until the service status is STOPPED, only after the status is stopped does it run net start. If a service takes a long time to stop, net stop can terminate unsuccessfully. If for some reason the service does not start successfully, it will keep attempting to start the service until the state is RUNNING.
answered Nov 25, 2021 at 2:59
MickMick
6,5774 gold badges52 silver badges68 bronze badges
With this can start a service or program that need a service
@echo
taskkill /im service.exe /f
taskkill /im service.exe /f
set "reply=y"
set /p "reply=Restart service? [y|n]: "
if /i not "%reply%" == "y" goto :eof
cd "C:\Users\user\Desktop"
start service.lnk
sc start service
eof
exit
answered Mar 10, 2022 at 17:46
on August 15, 2010
We normally use Services.msc to start or stop or disable or enable any service. We can do the same from windows command line also using net and sc utilities. Below are commands for controlling the operation of a service.
Command to stop a service:
net stop servicename
To start a service:
net start servicename
You need to have administrator privileges to run net start/stop commands. If you are just a normal user on the computer, you would get an error like below.
C:\>net start webclient System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied. C:\>
To disable a service:
sc config servicename start= disabled
To enable a service:
sc config servicename start= demand
To make a service start automatically with system boot:
sc config servicename start= auto
Note: Space is mandatory after ‘=’ in the above sc commands.
This SC command works on a Windows 7 machine and also on the down-level editions of Windows i.e Windows XP/2003 and Windows Vista. Again, if you do not have administrator previliges you would get the below error.
C:\>sc config webclient start= auto [SC] OpenService FAILED 5: Access is denied.
Note that the service name is not the display name of a service. Each service is given a unique identification name which can be used with net or sc commands. For example, Remote procedure call (RPC) is the display name of the service. But the service name we need to use in the above commands is RpcSs.
So to start Remote procedure call service the command is:
net start RpcSsTo stop Remote procedure call service
net stop RpcSs
These service names are listed below for each service. The first column shows the display name of a service and the second column shows the service name that should be used in net start or net stop or sc config commands.
| Display Name of the service | ServiceName which should be used with ‘net’ and ‘sc config’ commands. |
| Alerter | Alerter |
| Application Layer Gateway Service | ALG |
| Application Management | AppMgmt |
| ASP.NET State Service | aspnet_state |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service | BITS |
| Computer Browser | Browser |
| Bluetooth Support Service | BthServ |
| Bluetooth Service | btwdins |
| SMS Agent Host | CcmExec |
| Indexing Service | CiSvc |
| ClipBook | ClipSrv |
| .NET Runtime Optimization Service v2.0.50727_X86 | clr_optimization_v2.0.50727_32 |
| COM+ System Application | COMSysApp |
| Cryptographic Services | CryptSvc |
| Cisco Systems, Inc. VPN Service | CVPND |
| DCOM Server Process Launcher | DcomLaunch |
| DHCP Client | Dhcp |
| Logical Disk Manager Administrative Service | dmadmin |
| Logical Disk Manager | dmserver |
| DNS Client | Dnscache |
| Lenovo Doze Mode Service | DozeSvc |
| Error Reporting Service | ERSvc |
| Event Log | Eventlog |
| COM+ Event System | EventSystem |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Event Log | EvtEng |
| Fast User Switching Compatibility | FastUserSwitchingCompatibility |
| Windows Presentation Foundation Font Cache 3.0.0.0 | FontCache3.0.0.0 |
| Group Policy Monitor | GPMON_SRV |
| Help and Support | helpsvc |
| HID Input Service | HidServ |
| HTTP SSL | HTTPFilter |
| ThinkPad PM Service | IBMPMSVC |
| Windows CardSpace | idsvc |
| IMAPI CD-Burning COM Service | ImapiService |
| iPassConnectEngine | iPassConnectEngine |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateApp | iPassPeriodicUpdateApp |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateService | iPassPeriodicUpdateService |
| IviRegMgr | IviRegMgr |
| Server | lanmanserver |
| Workstation | lanmanworkstation |
| Lenovo Camera Mute | LENOVO.CAMMUTE |
| Lenovo Microphone Mute | Lenovo.micmute |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts |
| Intel(R) Management and Security Application Local Management Service | LMS |
| McAfee Framework Service | McAfeeFramework |
| McAfee McShield | McShield |
| McAfee Task Manager | McTaskManager |
| Machine Debug Manager | MDM |
| Messenger | Messenger |
| NetMeeting Remote Desktop Sharing | mnmsrvc |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator | MSDTC |
| Windows Installer | MSIServer |
| Net Driver HPZ12 | Net Driver HPZ12 |
| Network DDE | NetDDE |
| Network DDE DSDM | NetDDEdsdm |
| Net Logon | Netlogon |
| Network Connections | Netman |
| Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service | NetTcpPortSharing |
| Network Location Awareness (NLA) | Nla |
| NT LM Security Support Provider | NtLmSsp |
| Removable Storage | NtmsSvc |
| Microsoft Office Diagnostics Service | odserv |
| Office Source Engine | ose |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay |
| Pml Driver HPZ12 | Pml Driver HPZ12 |
| IPSEC Services | PolicyAgent |
| Power Manager DBC Service | Power Manager DBC Service |
| Protected Storage | ProtectedStorage |
| Remote Access Auto Connection Manager | RasAuto |
| Remote Access Connection Manager | RasMan |
| Remote Desktop Help Session Manager | RDSessMgr |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Registry Service | RegSrvc |
| Routing and Remote Access | RemoteAccess |
| Remote Registry | RemoteRegistry |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator | RpcLocator |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs |
| QoS RSVP | RSVP |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi Service | S24EventMonitor |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs |
| Smart Card | SCardSvr |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule |
| Secondary Logon | seclogon |
| System Event Notification | SENS |
| Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess |
| Shell Hardware Detection | ShellHWDetection |
| Print Spooler | Spooler |
| System Restore Service | srservice |
| SSDP Discovery Service | SSDPSRV |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | stisvc |
| System Update | SUService |
| MS Software Shadow Copy Provider | SwPrv |
| Performance Logs and Alerts | SysmonLog |
| Telephony | TapiSrv |
| Terminal Services | TermService |
| Themes | Themes |
| ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service | ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service |
| Telnet | TlntSvr |
| On Screen Display | TPHKSVC |
| Distributed Link Tracking Client | TrkWks |
| TVT Scheduler | TVT Scheduler |
| Windows User Mode Driver Framework | UMWdf |
| Intel(R) Management & Security Application User Notification Service | UNS |
| Universal Plug and Play Device Host | upnphost |
| Uninterruptible Power Supply | UPS |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS |
| Windows Time | W32Time |
| WebClient | WebClient |
| Windows Management Instrumentation | winmgmt |
| Portable Media Serial Number Service | WmdmPmSN |
| Windows Management Instrumentation Driver Extensions | Wmi |
| WMI Performance Adapter | WmiApSrv |
| Security Center | wscsvc |
| Automatic Updates | wuauserv |
| SMS Remote Control Agent | Wuser32 |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSVC |
| Network Provisioning Service | xmlprov |
In this post, we will be discussing the topic of how to Enable or Disable Services and how to Start, Stop, Refresh and Restart Services in Windows 11 or Windows 10 using PowerShell, Command Prompt, Task Manager and Net Command.
Windows Services are applications that typically start when the computer is booted and run quietly in the background until it is shut down. Essentially, a service is any Windows application that is implemented with the services API and handles low-level tasks that require little or no user interaction.
The Windows OS when installed and running on your device, actually does a great job of automatically managing services, but sometimes you may need to manually enable or disable a service on demand. Keep in mind that if you disable a service, any dependent services are also affected; and enabling a service does not automatically restart its dependent services.
All Windows Services can be accessed after opening the Windows Services Manager and you can Start, Stop, Disable Windows Services using it.
But you can also use PowerShell and Command Prompt to manage Services.
You must be signed in as an administrator to enable and disable services. It is not recommended to disable services unless you know what functions will be affected, and how the system performance will be impacted generally. If you disable a service and you’re unable to access your computer, you can boot into Safe Mode to enable the service.
Before making changes to the services, we recommend you create a system restore point as a necessary precautionary measure in case the procedure causes system malfunction, you can be able to perform System Restore using the restore point to undo the changes.
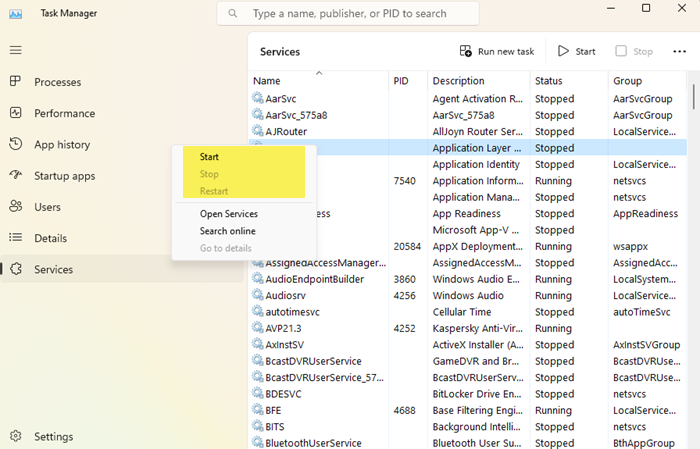
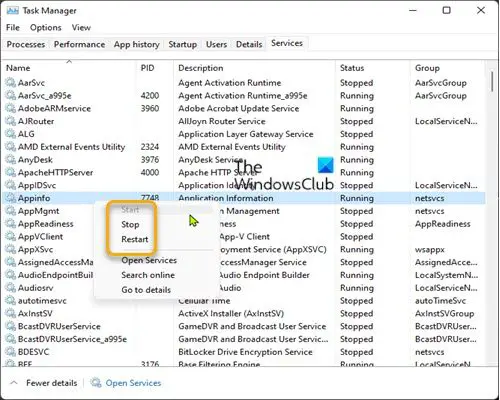
Use Task Manager to Stop, Restart or Start Windows Services
You can also Stop, Restart or Start Services using the Task Manager.
Open the Services tab, right-click on the Service and you will see the available options.
Enable or Disable Windows Services using PowerShell
To enable or disable Services using PowerShell in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Press Windows key + X to open Power User Menu.
- Tap A on the keyboard to launch PowerShell (Windows Terminal) in admin/elevated mode.
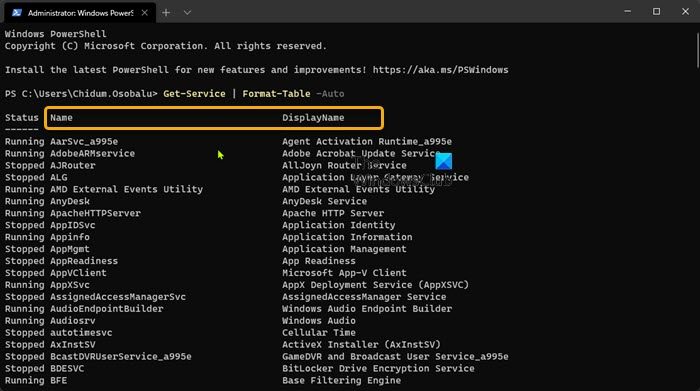
- In the PowerShell console, type or copy and paste in the command below and hit Enter to check the current state of all Services:
Get-Service | Format-Table -Auto
To Enable a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
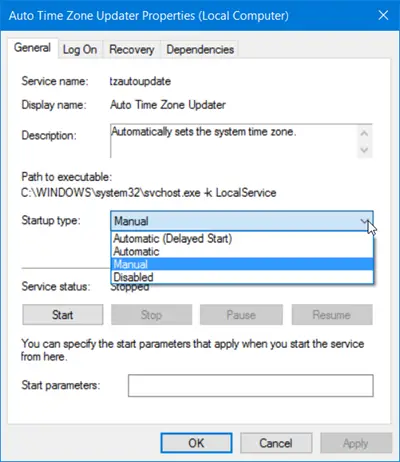
Note: Substitute the ServiceName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name you want to enable or disable.
(Automatic (Delayed Start))
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType AutomaticDelayedStart
OR
(Automatic)
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Automatic
OR
(Manual)
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Manual
To Enable and Start a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
(Automatic (Delayed Start))
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType AutomaticDelayedStart -Status Running
OR
(Automatic)
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Automatic -Status Running
OR
(Manual)
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Manual -Status Running
To Stop and Disable a Service, type the command below into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Set-Service -Name "ServiceName" -StartupType Disabled -Status Stopped
- Exit PowerShell when done.
Enable or Disable Windows Services using Command Prompt
To enable or disable Services using Command Prompt in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Press Windows key + X to open Power User Menu.
- Tap A on the keyboard to open Windows Terminal in admin/elevated mode.
- Select Command Prompt.
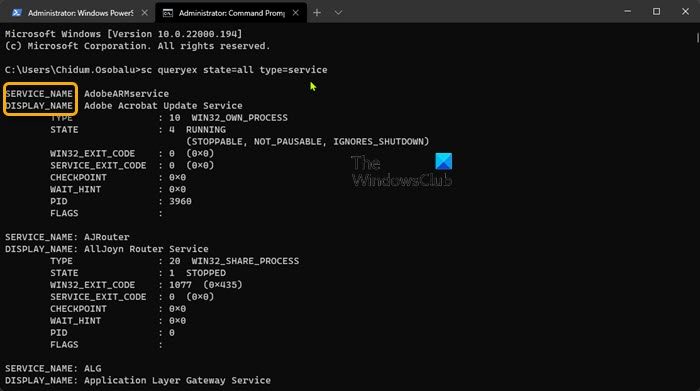
- In the CMD prompt console, type or copy and paste in the command below and hit Enter to check the current state of all Services:
sc queryex state=all type=service
To Enable a Service, type the command below you want into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name you want to enable or disable.
(Automatic (Delayed Start))
sc config "ServiceName" start=delayed-auto
OR
(Automatic)
sc config "ServiceName" start=auto
OR
(Manual)
sc config "ServiceName" start=demand
To Enable and Start a Service, type the command below you want into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
(Automatic (Delayed Start))
sc config "ServiceName" start=delayed-auto && sc start "ServiceName"
OR
(Automatic)
sc config "ServiceName" start=auto && sc start "ServiceName"
OR
(Manual)
sc config "ServiceName" start=demand && sc start "ServiceName"
To Stop and Disable a Service, type the command below into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
sc stop "ServiceName" && sc config "ServiceName" start=disabled
- Exit Command Prompt when done.
That’s it!
You must be signed in as an administrator to start, stop, or restart service. Also, you will not be able to start a disabled service until you enable the service.
Start, Stop, or Restart Windows Services using PowerShell
To Start, Stop, or Restart Services in PowerShell in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open PowerShell (Windows Terminal) in admin/elevated mode.
To Start a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName and DisplayName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name and display name respectively for the Service you want to Start, Stop, or Restart.
Start-Service -Name "ServiceName"
OR
Start-Service -DisplayName "DisplayName"
To Stop a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Stop-Service -Name "ServiceName"
OR
Stop-Service -DisplayName "DisplayName"
To Restart a Service, type the command below you want into the PowerShell console and hit Enter:
Restart-Service -Force -Name "ServiceName"
OR
Restart-Service -Force -DisplayName "DisplayName"
- Exit PowerShell when done.
To Start, Stop, or Restart Services in Task Manager in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open Task Manager.
- Click/tap on the Services tab.
- Now, right-click or press and hold on a Service.
- Click/tap on Start, Stop, or Restart.
Note: Start will only be available if the service status is currently stopped. Stop and Restart will only be available if the service status is currently running.
- Exit Task Manager when done.
Start, Stop, or Restart Windows Services using Net Command
To Start, Stop, or Restart Services using Net Command in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open Windows Terminal in admin/elevated mode.
- Select Command Prompt or PowerShell.
To Start a Service, type the command below you want into the console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName and DisplayName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name and display name respectively for the Service you want to Start, Stop, or Restart.
net start ServiceName
OR
net start "DisplayName"
To Stop a Service, type the command below you want into the console and hit Enter:
net stop ServiceName
OR
net stop "DisplayName"
- Exit Windows Terminal when done.
Start, Stop, or Restart Services using Command Prompt
To Start, Stop, or Restart Services using Command Prompt in Windows 11/10, do the following:
- Open Windows Terminal in admin/elevated mode.
- Select Command Prompt.
To Start a Service, type the command below into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
Note: Substitute the ServiceName placeholder in each of the commands with the actual service name for the Service you want to Start, Stop, or Restart.
sc start ServiceName
To Stop a Service, type the command below into the CMD prompt console and hit Enter:
sc start ServiceName
- Exit Command Prompt when done.
How to Refresh a Windows Service?
When you refresh any Windows Service, the contents are re-read into the memory and the changes are reflected the next time the service is accessed. Here’s how you can Refresh a Service:
- Open Services Manager
- Locate the Service you want to refresh
- Right-click on it and select Refresh.
That’s it! Hope you find this post informative and helpful enough.
Read: Services Start, Stop or Startup type grayed out in Windows
What Microsoft startup services can I disable?
There are a couple of Windows 11/10 Services that are safe to disable, including:
- AVCTP service – Disable it if you do not use Bluetooth Audio Device or Wireless Headphones.
- BitLocker Drive Encryption Service – disable it if you do not use BitLocker storage encryption.
- Bluetooth Support Service – Disable it if you do not use any Bluetooth device
- Computer Browser – This will then disable Network discovery of systems on the local network
- Connected User Experiences and Telemetry – Disables Feedback, Telemetry and Data Collection
- Diagnostic Policy Service
- Etc.
Read: Services Start, Stop or Startup type grayed out in Windows
What happens if I disable all Microsoft services?
For example, the wireless services control your Wi-Fi card and if you disable that service, you may be unable to wirelessly connect your Windows 11/10 to a network. Intel has quite a few services which never really hog system resources. Lastly, any graphics card services should remain enabled.
HOT TIP: Windows 11 Repair and Recovery Tool is available FREE for now; go get it while you can as you never know when you may need it!