The move is an internal command found in the Windows Command Interpreter (cmd) that is used to move files and folders/directories. The command is robust than a regular move operation, as it allows for pattern matching via the inclusion of Wildcards in the source path.
The command is a very generic one and is available (in one form or the other) in almost every single operating system out there (under different aliases). In this article, we will learn about the move command and would learn various uses/applications of it.
Description of the Command :
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]dirname1 dirname2
- [drive:][path]filename1 –
Specifies the location and name of the file or files you want to move. - destination –
Specifies the new location of the file. The destination can consist of a drive letter and colon, a directory name, or a combination. If you are moving only one file, you can also include a filename if you want to rename the file when you move it. - [drive:][path]dirname1 –
Specifies the directory you want to rename. - dirname2 –
Specifies the new name of the directory. - /Y –
Suppresses prompting to confirm you want to overwrite an existing destination file. - /Y –
Causes prompting to confirm you want to overwrite an existing destination file.
The switch /Y may be present in the COPYCMD environment variable. This may be overridden with /-Y on the command line. The default is to prompt on overwrites unless the MOVE command is being executed from within a batch script. The above output can be obtained by executing the command move /? in cmd.
The above text is a little cryptic at first, but the command is really basic and follows the minimal blueprint.
Syntax :
MOVE [options] (Source) (Target)
Key :
- [option] –
An optional flag denoted by /Y or /-Y, that is used to suppress the confirmation prompt on overwritten files. The default is to prompt on overwrites unless the MOVE command is being executed from within a batch script. - (Source) –
A path of the file/files that would be used to move them. This path can contain wildcards ( * ? ) in the path. If more then files are made to move, then wildcards are used. - (Target) –
A path for the new location of the file.
Using the Command :
Throughout this section, we would take the following directory as example for demonstrating the usage of move command.
Moving a File from One Folder to Another :
move source_path destination_path
- source_path –
It is the path of the file which we are willing to move, and the destination_path is the location to which we want the file to be moved.
Example :
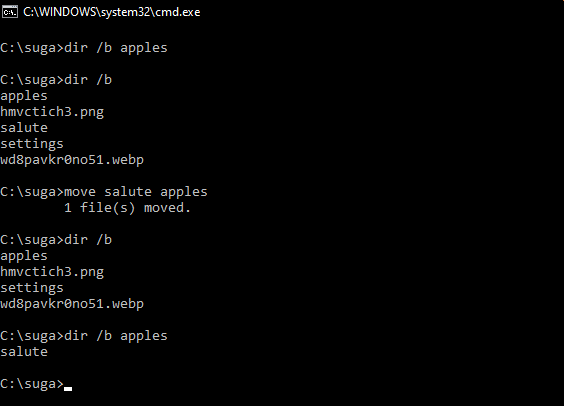
- The Dir /b command is used to list all the files and folders inside a directory.
- In the above example, we have moved an extension-less file named salute from C:\suga to C:\suga\apples directory.
Moving Multiple Files from One Path to Another :
move source_path destination_path
- source_path –
It is a path containing wildcards that will allow more than one file to be taken as a source. The destination_path is now a path to a directory where the moved files would reside (should not contain wildcards).
Example :
- In the above example we have moved all the files inside C:\suga folder which matches the pattern *.* to C:\suga\Apples directory.
- It should be noted that wildcard in source_path should match with the file(s) otherwise it would result in source_path being null, and a subsequent error.
Moving Directory from One Path to Another :
move source_dir_path Destination_dir_path
- source_dir_path –
It is the path to the directory to which we are moving, and destination_dir_path is the new location where it would be moved to.
Example :
- In the above example, we have moved the C:\suga\apples directory to C:\Users\Public directory.
- Multiple Directories can be moved using the method described in Moving multiple files from one path to another (with little modification to make is eligible for directories).
Moving a File to Another Folder with a Same Name File already existing :
There are two ways to tackle this situation –
- Abort the move process.
- Continue the move process, by overwriting the existing file with the newer one.
By default, the move command upon encountering any name collisions would prompt the user, asking whether he wants to rewrite the existing file with the new one, or stop the move process (via a Y/N prompt). To abort the move process, the user can simply enter N in the prompt input, stating that the file should not be overwritten. The prompt seeking for user input (for overwrite of files) appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All):
When the users enter N in the prompt the output appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All): N
0 file(s) moved.
When the user enters Y in the prompt the output appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All): Y
1 file(s) moved.
To continue the move process by overwriting existing files (on all name collisions), a /Y switch needs to be added to the command as follows –
move /Y source_path destination_path
Last Updated :
20 Oct, 2020
Like Article
Save Article
You can use move for this. The documentation from help move states:
Moves files and renames files and directories.
To move one or more files:
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]filename1[,...] destination
To rename a directory:
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]dirname1 dirname2
[drive:][path]filename1 Specifies the location and name of the file
or files you want to move.
destination Specifies the new location of the file. Destination
can consist of a drive letter and colon, a
directory name, or a combination. If you are moving
only one file, you can also include a filename if
you want to rename the file when you move it.
[drive:][path]dirname1 Specifies the directory you want to rename.
dirname2 Specifies the new name of the directory.
/Y Suppresses prompting to confirm you want to
overwrite an existing destination file.
/-Y Causes prompting to confirm you want to overwrite
an existing destination file.
The switch /Y may be present in the COPYCMD environment variable.
This may be overridden with /-Y on the command line. Default is
to prompt on overwrites unless MOVE command is being executed from
within a batch script.
See the following transcript for an example where it initially shows the qq1 and qq2 directories as having three and no files respectively. Then, we do the move and we find that the three files have been moved from qq1 to qq2 as expected.
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>dir qq1
Volume in drive C is Primary
Volume Serial Number is 04F7-0E7B
Directory of C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1
20/01/2011 11:36 AM <DIR> .
20/01/2011 11:36 AM <DIR> ..
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx1
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx2
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx3
3 File(s) 39 bytes
2 Dir(s) 20,092,547,072 bytes free
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>dir qq2
Volume in drive C is Primary
Volume Serial Number is 04F7-0E7B
Directory of C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq2
20/01/2011 11:36 AM <DIR> .
20/01/2011 11:36 AM <DIR> ..
0 File(s) 0 bytes
2 Dir(s) 20,092,547,072 bytes free
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>move qq1\* qq2
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1\xx1
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1\xx2
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1\xx3
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>dir qq1
Volume in drive C is Primary
Volume Serial Number is 04F7-0E7B
Directory of C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1
20/01/2011 11:37 AM <DIR> .
20/01/2011 11:37 AM <DIR> ..
0 File(s) 0 bytes
2 Dir(s) 20,092,547,072 bytes free
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>dir qq2
Volume in drive C is Primary
Volume Serial Number is 04F7-0E7B
Directory of C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq2
20/01/2011 11:37 AM <DIR> .
20/01/2011 11:37 AM <DIR> ..
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx1
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx2
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx3
3 File(s) 39 bytes
2 Dir(s) 20,092,547,072 bytes free
In the Windows Command Prompt, we use the move command to move files from one directory to another (cut and paste).
The syntax of the move command is as follows:
move <Source> <Target>We can also use the move command to move folders from one location to another.
Command Options
| /Y | Do not ask for confirmation if a duplicate file is found at the destination. The destination file will be overwritten. |
| /-Y | Ask before overwriting destination files. |
Examples
Move sales.doc in the current directory to C:\backup directory:
move sales.doc C:\backupMove C:\data\sales.doc to C:\backup directory. The file will be overwritten if it already exists in the destination folder:
move /y C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupMove C:\data\finance to C:\backup folder:
move C:\data\finance C:\backupMove all files in a directory
You can use wildcards with the move command. For example, the following command moves all files in the C:\data to C:\backup.
move /y C:\data\* C:\backupThe following command moves all files with a .doc extension to the backup folder:
move /y C:\data\*.doc C:\backupIn the following example, all files whose names start with screenshot are moved to the C:\backup directory.
move /y C:\data\screenshot* C:\backupMove two or more files
To move two or more files without using wildcards, you have to use a for loop, as shown in the following example:
for %i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do move /y %i C:\backupIf you want to run the for command in a batch file, you would use two % (%%) with the variable.
for %%i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do move /y %%i C:\backupThe move command deletes the source file after it is copied to the destination. If you want to keep the original file, use the copy or xcopy.
Время чтение: 6 минут
2013-08-24
Вторая часть поста, в котором будут рассмотрены основные команды для работы с файлами. В первой части было рассказано про то, как удалить файл и каталог используя cmd.exe, если Вы не читали, то советую прочитать. В этом посте будут рассмотрены команды, которые позволят пользователю…
- Перемещать файлы.
- Переименовывать файлы.
- Выводить содержимое файлов в консоль.
- Записывать в файл (txt) результат выполнения команды.
Как всегда, все команды будут представлены Вашему вниманию в сопровождении коротких, но ясных описаниях, а так же будут прилагаться «Пошаговые» скриншоты.
Первым делом, я расскажу, как переместить файл из одной директории в другую.
Как переместить файл через консоль?
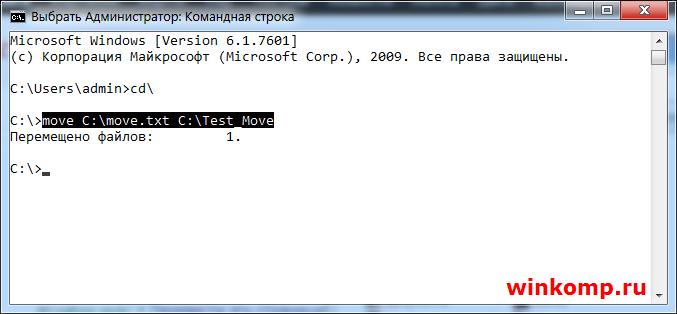
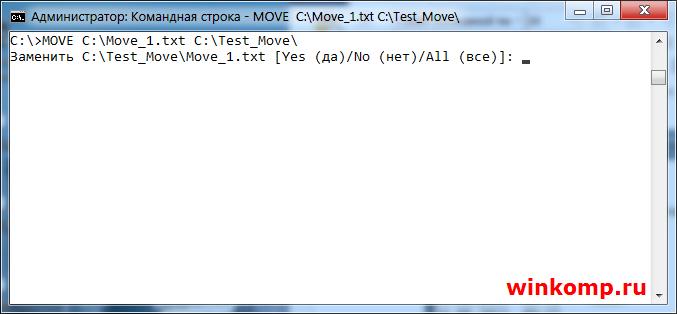
Для перемещения файлов используется команда под названием «MOVE». Что бы переместить файл из корня диска «C:\ Move.txt» в папку, в моём случаи это «С:\Test_Move» пишем в консоль:
Результат выполнения команды. Файл «Move.txt» был перемещён в папку «Test_Move»
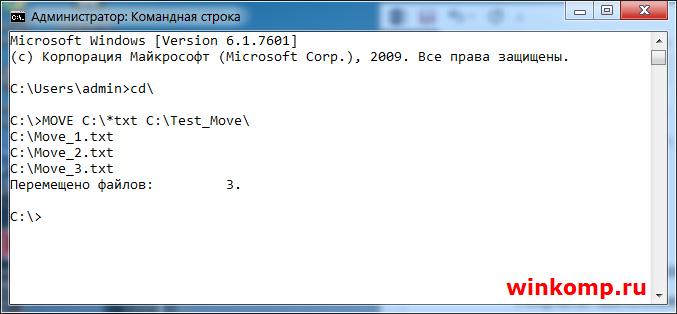
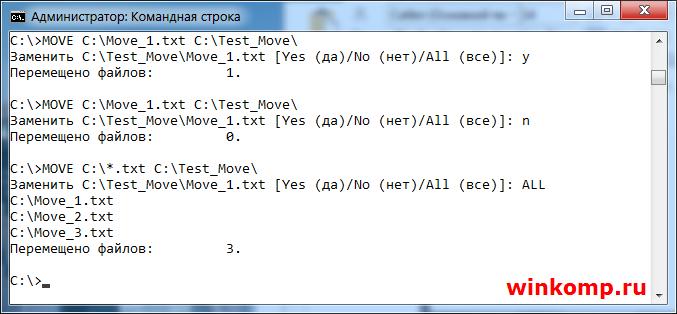
Если Вам нужно переместить все файлы с конкретным расширением, то в этом случаи стоит писать так:
Для примера я создал 3 файла «Move_1.txt, Move_2.txt и Move_3.txt» Как видно из скриншота выше, все три файла были перемещённых. В этом можно убедится не закрывая консоль.
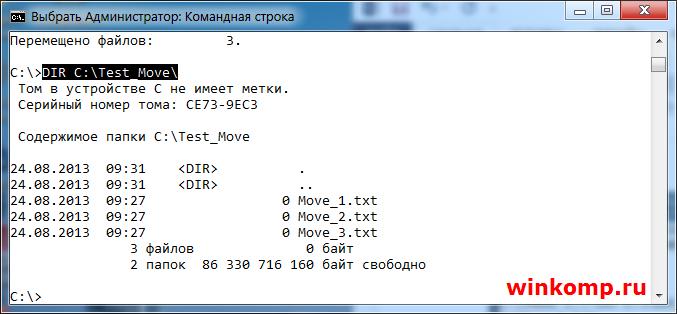
Для проверки используем команду «DIR»
С перемещением файлов на этом все. Но, если в каталоге куда нужно переместить файл уже есть такой? То пользователь получит сообщения, в котором его спросят подтвердить, перезаписать файл или нет.
Если ввести символ «Y» то файл будет перезаписан. При этом содержимое уже имеющегося файла в каталоге «C:\Test_Move\» будут потеряны.
Если ввести символ «N» файл не будет перемещён.
Если ввести «ALL» то будут перемещены и перезаписаны все файлы с конкретным расширением. При этом, также, содержимое файлов в директории «C:\Test_Move\» будут потеряны.
Примечание: За место «ALL» можно просто ввести букву «А» результат будет додже.
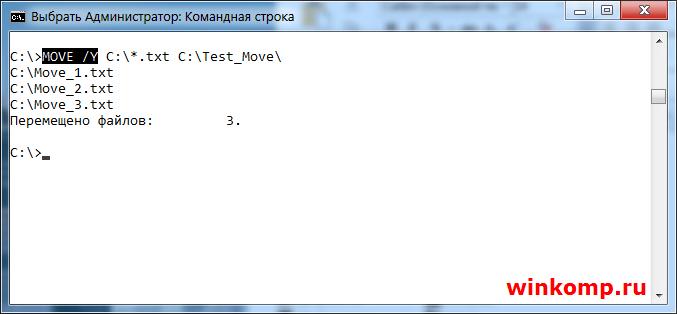
Что бы отключить предупреждения используется ключик «/Y»
Теперь все файлы будет перемещены и перезаписаны без всяких предупреждений. Будьте внимательны, можно потерять важную информацию.
Как переименовать файл через cmd.exe?
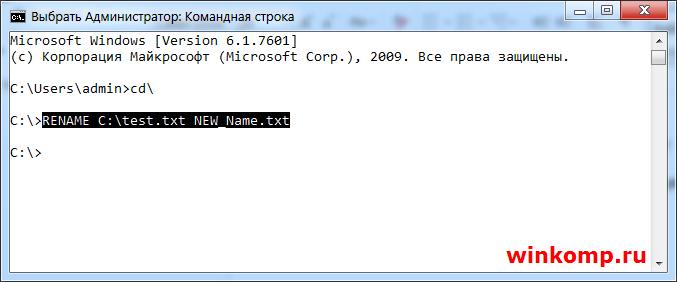
Для того, чтобы переименовать существующий файл используется команда «RENAME» Я создал файл с именем «test.txt» в корне диска «С:\» что бы его переименовать, скажем в «NEW_Name.txt» пишем в консоли.
Файл «test.txt» будет переименован.
Примечание: Команду «RENAME» можно писать короче, просто «REN» от этого результат не изменится.
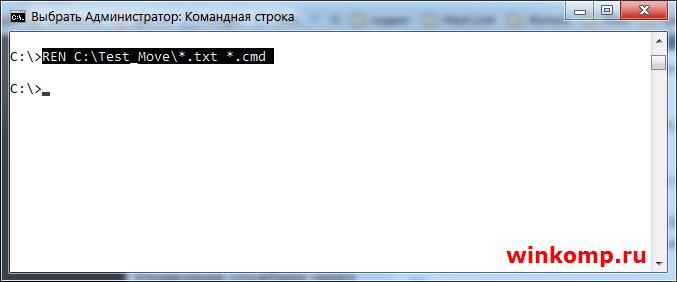
Можно сменить расширения у всех файлов в каталоге, например с «txt» на «cmd». Для этого делаем так:
Теперь уже в знакомой нам папке «Test_Move» все 3(три) файла приобретут расширение «cmd» за место «txt»
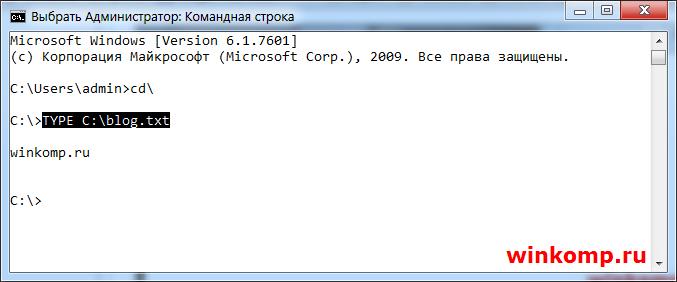
Как вывести содержимое файла в консоль?
Если появилась необходимость просмотреть содержимое файла прямо в cmd. Для этого пользуемся командой «TYPE» Я создал файл и написал в нём адрес своего блога. Теперь попробуем просмотреть данный файл из консоли, не запуская его обычном, привычным образом.
В общем все просто. Но как быть с файлами большего размера, где много информации? В этак случаи содержимое файла нужно выводить с паузой, чтобы просмотреть его полностью.
Для этого пишем так:
Для примера взял текст с первого попавшегося забугорного сайта.
В конце добавляем «| more» таким образом содержимое файла будет выводится не полностью а отрывками, чтобы просмотреть следующею часть файла жмём «Enter»
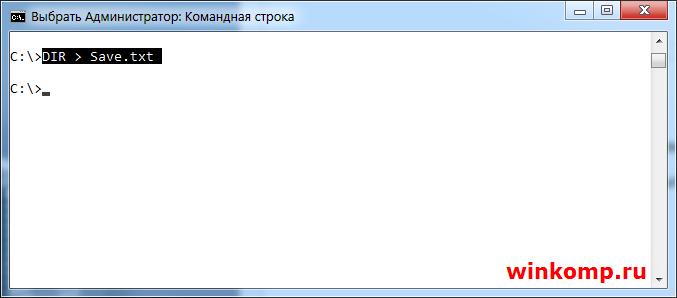
Как записать в файл результат выполнения команды?
Для примера запишем в файл результат команды «DIR» В консоль пишем:
Обратите внимание на символ «>» он то и играет здесь главную роль. В итоге появится файл на диске «C:\» с именем «Save.txt» куда будет записан результат выполнения команды.
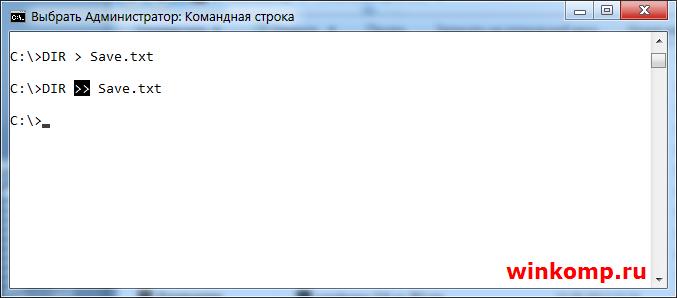
Если Вам понадобится записать результат команды «DIR» ещё раз, то файл «Save.txt» будет перезаписан и ранние содержимое файла будет удалено!
Что бы этого избежать и просто добавить новый результат не удаляя старый, стоит использовать символ «>» два раза, то есть вот так:
Теперь файл не будет перезаписан, в него просто добавится новый результат в конец файла.
На этом я пожалуй закончу пост, и отправлюсь праздновать первый день рождения сына, ему сегодня исполняется один годик!!!
Спасибо за внимание!
Команда MOVE используется для перемещения или переименования файлов и каталогов.
1. Описание команды MOVE.
1.1. Формат командной строки:
Перемещение одного или более файлов:
C:\ MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [диск:][путь]имя_файла1[,...] назначение
Переименование папки:
C:\ MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [диск:][путь]имя_папки новое_имя_папки
1.2. Параметры командной строки:
- [диск:][путь]имя_файла1 — Определяет местоположение файла или файлов, которые необходимо переместить.
- Назначение — Определяет новое местоположение файла. Назначение может состоять из буквы диска (с последующим двоеточием), имени папки или их комбинации. При перемещении только одного файла, можно указать и его новое имя, если хотите выполнить его одновременное переименование при перемещении.
- [диск:][путь]имя_папки — Определяет папку, которую необходимо переименовать.
- новое_имя_папки — Определяет новое имя папки.
- /Y — Перезаписывать существующие файлы назначения без предупреждения.
- /-Y — Предупреждать при перезаписи существующего файла назначения.
Ключ /Y может присутствовать в значении переменной среды окружения COPYCMD. Оно может перекрываться ключом /-Y в командной строке. По умолчанию используется предупреждение о перезаписи, если только команда MOVE не выполняется как часть пакетного файла.
2. Примеры использования.
2.1. Отобразить подсказку по использованию команды:
C:\ move /?
2.2. Переименовать папку с именем folder1 в folder2 в текущем каталоге:
C:\ move folder1 folder2
2.3. Переименование с указанием абсолютных путей:
C:\ move E:\test\folder1 E:\test\folder2
2.4. Переместить файл file1.txt с диска C: на диск D:
C:\ move C:\file1.txt D:\
2.5. Перенести файл file1.txt из каталога test диска C: в каталог folder2 диска D: под именем file2.txt:
C:\ move c:\test\file1.txt D:\folder2\file2.txt -
2.6. Переместить все файлы из каталога Folder1 диска C: в каталог Folder2 диска D:
C:\ move C:\Folder1\*.* D:\Folder2\
Реализация в ОС Windows данной команды не позволяет перемещать папки на другие логические диски.
2.7. Переместить каталог folder1 из корня диска C: в подкаталог \folder2\folder3:
C:\ move C:\folder1 C:\folder2\folder3\folder1
При перемещении папки в несуществующий каталог он не будет создан автоматически и команда завершится ошибкой. Команда move не работает с файлами, имеющими атрибуты «скрытый » и «системный».