I am developing a website and need to refresh data. Therefore MySQL must be stopped.
How can I stop the service?
When I look at control panel services it is started without stop or restart option.
Ahmad Alfy
13.1k6 gold badges65 silver badges100 bronze badges
asked Jun 4, 2012 at 16:53
2
On Windows
If you are using Windows Open the Command Prompt and type
To Stop MySQL Service:
net stop MySQL80
To Start MySQL Service:
net start MySQL80
On Linux
# /etc/init.d/mysqld start
# /etc/init.d/mysqld stop
# /etc/init.d/mysqld restart
Fedora / Red Hat also support this:
# service mysqld start
# service mysqld stop
# service mysqld restart
Also Systemd based distrubutions (like Ubuntu or Arch Linux) support this:
# systemctl start mysql
# systemctl stop mysql
# systemctl restart mysql
I know this answer is late but i hope it helps for some one.
answered Jan 11, 2013 at 17:24
vinothpvinothp
9,94919 gold badges61 silver badges103 bronze badges
5
You can set its startup type to manual in services.msc. This way it will not start automatically unless required. Simply get the name of the service from services.msc as shown here:
You can create batch files to start and stop the service fairly easily as well. Now use this name in batch files.
Your start.bat:
net start "mysql"
And in your stop.bat:
net stop "mysql"
answered Jun 4, 2012 at 17:12
Nishu TayalNishu Tayal
20.1k8 gold badges49 silver badges101 bronze badges
0
The Top Voted Answer is out of date. I just installed MySQL 5.7 and the service name is now MySQL57 so the new command is
net stop MySQL57
answered Dec 29, 2015 at 19:39
3
Start Powershell as administrator and run:
net start [MySQL-service-name]
Find the service name:
run ‘services.msc’, look for MySQL and click on properties
answered Nov 14, 2017 at 8:54
Bar HoringBar Horing
5,3873 gold badges30 silver badges27 bronze badges
If MySQL 57.
net start MySQL57
OR
net stop MySQL57
answered Oct 2, 2017 at 4:32
1
For Windows there’s a couple of tricks to take care of…
(Assuming you’ve installed MySQL from Oracle’s site but maybe have chosen not to run the service at startup)…
-
To use «mysqld stop» from the command line for WinVista/Win7 you must right click on Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Command Prompt -> Run As Administrator
-
Now that you have local OS admin access you can use «mysqld stop» (which will simply return)
IF YOU SEE THE FOLLOWING YOU ARE TRYING IT WITH A USER/COMMAND PROMPT THAT DOES NOT HAVE THE CORRECT PRIVILEGES:
121228 11:54:50 [Warning] Can't create test file c:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.5\data\hpdv7.lower-test
121228 11:54:50 [Warning] Can't create test file c:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.5\data\hpdv7.lower-test
121228 11:54:50 [Note] Plugin 'FEDERATED' is disabled.
121228 11:54:50 InnoDB: The InnoDB memory heap is disabled
121228 11:54:50 InnoDB: Mutexes and rw_locks use Windows interlocked functions
121228 11:54:50 InnoDB: Compressed tables use zlib 1.2.3
121228 11:54:50 InnoDB: Initializing buffer pool, size = 128.0M
121228 11:54:50 InnoDB: Completed initialization of buffer pool
121228 11:54:50 InnoDB: Operating system error number 5 in a file operation.
InnoDB: The error means mysqld does not have the access rights to
InnoDB: the directory. It may also be you have created a subdirectory
InnoDB: of the same name as a data file.
InnoDB: File name .\ibdata1
InnoDB: File operation call: 'create'.
InnoDB: Cannot continue operation.
If mysqld does not appear as a known system command, try adding it to your class path
- Right click on My Computer
- Advanced System Settings
- Environment Variables
- System variables
- look for and left click select the variable named path
-
click on «Edit» and copy out the string to notepad and append at the end the full path to your MySQL bin directory , e.g.
%SystemRoot%\system32;%SystemRoot%;%SystemRoot%\System32\Wbem;c:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.5\bin
answered Dec 28, 2012 at 20:05
foupfeifferfoupfeiffer
6877 silver badges4 bronze badges
net stop MySQL*
or
mysqld stop
or
mysql stop
in the window’s command line prompt.
<*> if you’re using windows XP, you need the name of your service, which can be obtained doing this: (credits @Atli)
right click the «My Computer» shortcut in the Start menu, select
«Manage», click «Services» in the «Services and applications» group.
And then search the list of services until you find the MySQL service.Then you can start [or stop] the service by using that name. It is can sometimes
be called «mysql5» or «mysql51», or something like that. Depends on
who installed it.
answered Jun 4, 2012 at 16:55
SebasSebas
21.2k9 gold badges56 silver badges109 bronze badges
3
I’m on XP. I’ve installed MySQL-5.6.10 manually from .zip, no Windows auto-installer provided by MySQL site. The /bin directory of my MySQL is in my PATH. So I start the server with mysqld --console command, like this:
C:\Documents and Settings\User>mysqld --console
2013-04-12 14:39:19 0 [Warning] TIMESTAMP with implicit DEFAULT value is deprecated. Please use --explicit_defaults_for_times
tamp server option (see documentation for more details).
From now on it is running. And that cmd window is occupied. I open and use another one.
I’ve tried to use the answers from above but none of them can stop the server. Only errors are throw. So I stop the server with mysqladmin -u root shutdown on the other cmd window or with Ctrl + C on the cmd window it is running in. The latter works not so good as the former, sometimes I have to click Ctrl + C twice or more.
The log of the shutdown process is like this:
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Giving 0 client threads a chance to die gracefully
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Event Scheduler: Purging the queue. 0 events
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down slave threads
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Forcefully disconnecting 0 remaining clients
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Binlog end
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'partition'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_DATAFILES'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_TABLESPACES'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN_COLS'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_FOREIGN'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_FIELDS'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_COLUMNS'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_INDEXES'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_TABLESTATS'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_SYS_TABLES'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_FT_INDEX_TABLE'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_FT_INDEX_CACHE'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_FT_CONFIG'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_FT_BEING_DELETED'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_FT_DELETED'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_FT_INSERTED'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_FT_DEFAULT_STOPWORD'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_METRICS'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_BUFFER_POOL_STATS'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE_LRU'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_BUFFER_PAGE'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX_RESET'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_CMP_PER_INDEX'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_CMPMEM_RESET'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_CMPMEM'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_CMP_RESET'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_CMP'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_LOCK_WAITS'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_LOCKS'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'INNODB_TRX'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'InnoDB'
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] InnoDB: FTS optimize thread exiting.
2013-04-12 17:55:29 3968 [Note] InnoDB: Starting shutdown...
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] InnoDB: Shutdown completed; log sequence number 1719777
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'BLACKHOLE'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'ARCHIVE'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'MRG_MYISAM'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'MyISAM'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'MEMORY'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'CSV'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'sha256_password'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'mysql_old_password'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'mysql_native_password'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] Shutting down plugin 'binlog'
2013-04-12 17:55:30 3968 [Note] mysqld: Shutdown complete
And I still don’t know if it is 100% right way to shutdown the server, but it works 
answered Apr 12, 2013 at 15:05
GreenGreen
28.9k61 gold badges159 silver badges247 bronze badges
to stop the service:
sc stop mysql56
and to start it:
sc start mysql56
you might need to change the mysql56 to whatever your version is.
answered Jul 21, 2015 at 8:15
YarYar
7,06011 gold badges50 silver badges70 bronze badges
On windows 10
If you wanna close it open command prompt with work with admin. Write NET STOP MySQL80. Its done. If you wanna open again so you must write NET START MySQL80
If you do not want it to be turned on automatically when not in use, it automatically runs when the computer is turned on and consumes some ram.
Open services.msc find Mysql80 , look at properties and turn start type manuel or otomaticly again as you wish.
answered Jan 17, 2020 at 14:01
huzeyfetashuzeyfetas
862 silver badges6 bronze badges
This is a newer and easier answer.
- Run cmd as admin
- Type «net start mysql» then the version number, in my case «net start mysql80» for MySQL 8.0.
- If it says it’s already running great, otherwise now mysql is running.
- Exit cmd, WIN+R and type services.msc, scroll down until you find my sql with the right version.
- Right-Click for properties, under startup type select ‘Manual’, then under service status select ‘Stop’
- Now you stopped mysql service and it will not run automatically again.
- To turn it back on, in cmd admin ‘net start mysql’ and the version number, in my case ‘net start mysql80’
answered Feb 25, 2021 at 1:49
EduardEduard
1111 silver badge10 bronze badges
If you are running windows try this:
- click start button on a keyboard
- type task manager
- right click and click run as administrator
when the task manager opens - click on services then look for MySQL then
- right click on it then click stop
then close task manager and you are done.
to start it when you wand to use it, follow the same steps and click start this time
hering
1,9564 gold badges28 silver badges43 bronze badges
answered Feb 28, 2017 at 15:02
Easy way to shutdown mySQL server for Windows7 :
My Computer > Manage > Services and Application > Services > select «MySQL 56»(the name depends upon the version of MySQL installed.)
three options are present at left top corner.
Stop the Service
pause the Service
Restart the Service
choose Stop the service > to stop the server
Again to start you can come to the same location or we can chose tools options on mySQL GUI
Server > Startup/Shutdown > Choose to Startup or Shutdown
PS: some times it is not possible to stop the server from the GUI even though the options are provided. so is the reason the above alternative method is provided.
share the ans. to improve.
thanks
answered Feb 8, 2015 at 15:32
To successfully stop MySQL Service on Windows
- Check on services the name of the service for MySQL
- Run as administrator :
net stop [MySQL Service name]
answered Apr 3, 2020 at 13:01
I got the same problem and here my solution:
- go to service.msc and find mysql service. set it as start manually.
- go to task manager — processes tab and find mysqld. stop it
- go to task manager — services tab find mysql service and stop it
answered Sep 2, 2019 at 5:38
As people already explained,
-
In windows, open Command Prompt as Administrator
-
if you’re using MySQL 8.0
net start mysql80 — to start MySQL
net stop mysql80 — to stop MySQL
(if you’re using MySQL 5.7 then net stop mysql57, similar for other versions)
(Additional method) — via bat file
just in case, if you forget the command often and want to do it via few clicks instead of opening command prompt and typing command every time,
-
open notepad type,
cmd /k net stop mysql80
-
save as stop_mysql.bat
-
right click on file ‘stop_mysql.bat’, run as Administrator to run the MySQL stop command. This will run above stop command to stop MySQL
-
You can also create another bat file for starting MySQL with the other command
Thanks.
answered May 10, 2022 at 8:56
just type exit
and u are out of mysql in cmd in windows
answered Jan 14, 2017 at 12:37
MySQL server is an open-source relational database management system which is a major support for web based applications. Databases and related tables are the main component of many websites and applications as the data is stored and exchanged over the web.
In this article, we will understand how to start and stop the MySQL servers on windows and Linux.
On Windows :
Starting the Server:
There are three ways, which are :
1. With Services.msc :
- Step 1: Open services tab.
- Step 2: Search for MySQL service.
- Step 3: Click on the start or restart button to start the MySQL daemon/
2. With Command Prompt:
- Step 1: Open command prompt
- Step 2: Type mysqld
3. With Mysql workbench:
- Step 1: Open MySQL workbench which comes with MySQL complete package.
- Step 2: Navigate to the administration’s tab.
- Step 3: Navigate to the startup/shutdown tab.
- Step 4: You will find an option to start the server only when the server is not on.
Stopping the Server:
1. Using Services as specified above
2. With mysqladmin :
mysqladmin -u <username> shutdown
3. Using MySQL workbench startup/shutdown tab.
On Linux :
Starting the Server:
1. With Command Line:
- Step1 : Open the linux CLI and move to the directory where mysqld is stored.
- Step 2: Type mysqld start.
mysqld start
2. Using service command( In specific Linux distribution)
Step 1:Ttype sudo service mysqld start.
mysqld start
Stopping the Server:
1. Using the command line type mysqld stop or sudo service mysqld stop
2. With mysqladmin :
mysqladmin -u <username> shutdown
3. Using the MySQL workbench startup/shutdown tab.
Last Updated :
06 Oct, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to stop MySQL Server on Windows and Linux.
On Windows, you can stop MySQL Server using the program mysqladmin.
The program mysqladmin locates in the folder <path_to_installation_dir>\bin, where path_to_installation_dir is the path to the installation directory e.g., C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\
Typically, you should add the pathname of the MySQL bin directory to Windows path environment variable to access any MySQL programs in the bin directory faster.
To stop MySQL, you follow these steps:
First, launch the Command Prompt by pressing Windows+R to open the Run box and type cmd and press Enter.
Second, navigate to the bin folder of the MySQL if it is not in the Window path environment.
Third, use the following command to stop MySQL Server:
mysqladmin -u root -p shutdown
Enter password: ********It prompts for a password of the root account. You need to enter the password and press the Enter keyboard.
The program will stop the MySQL Server.
Stop MySQL Server on Linux
To stop MySQL Server on Linux, you use the following command:
/etc/init.d/mysqld stop Some Linux distributions provide server command:
service mysqld stop Or
service mysql stop In this tutorial, you have learned how to stop MySQL Server on Windows and Linux.
Was this tutorial helpful?
There are several ways to start, stop and restart the MySQL server depending upon the operating system you are using. In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to start-stop and restart MySQL servers in windows, mac, and Linux operating systems.
There are 3 ways by which you can perform these tasks on the MySQL server on Windows:
- Using services.msc
- Using Command Prompt
- Using MySQL Workbench
We’ll learn all three methods one by one:
Using services.msc
Step 1: On the keyboard press Windows, Type run on the search area, and click on open:
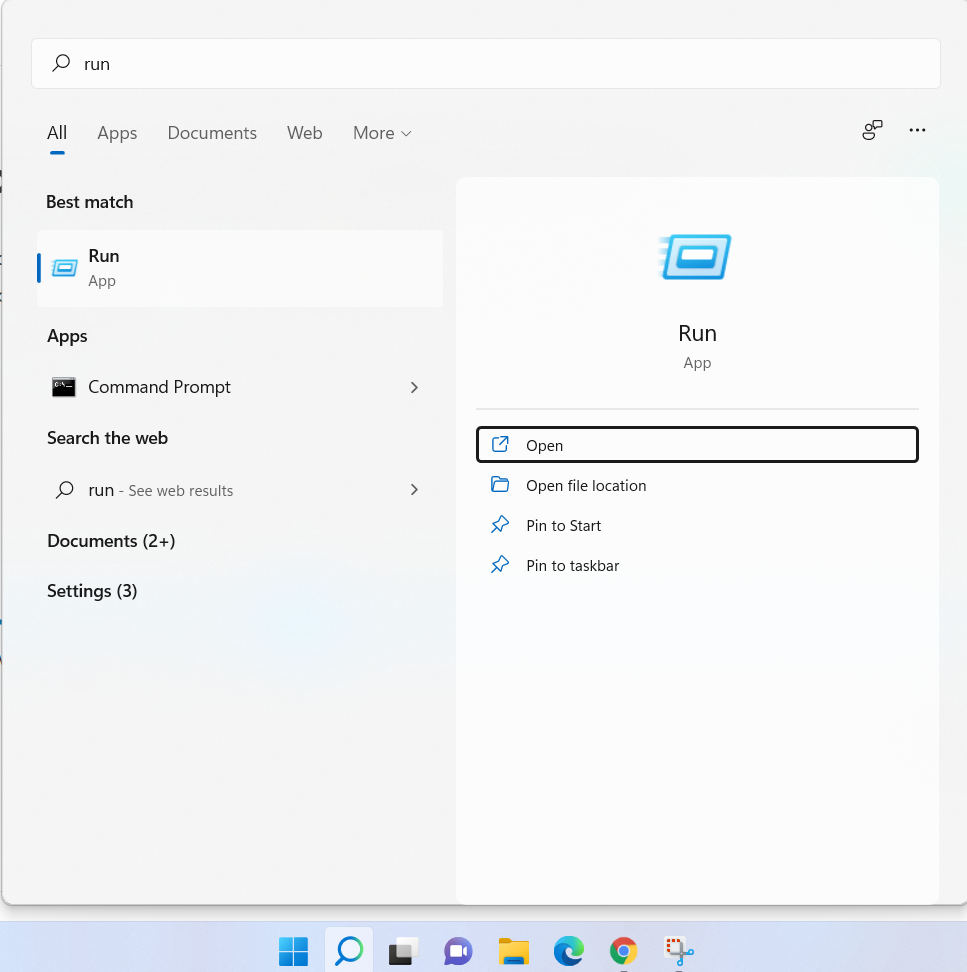
Step 2: Type Services.msc on run and click on OK:
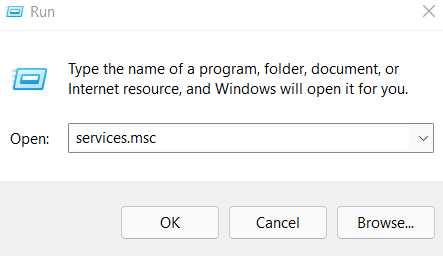
Step 3: Search for MySQL under the name column, Please keep in mind that the numeric extension after MySQL, as in the below example is MySQL80 may vary depending on the version of MySQL installed on your desktop. You can click on the MySQL80 section and a section on the left-hand side will be available to you with all the operations you can perform on that service.
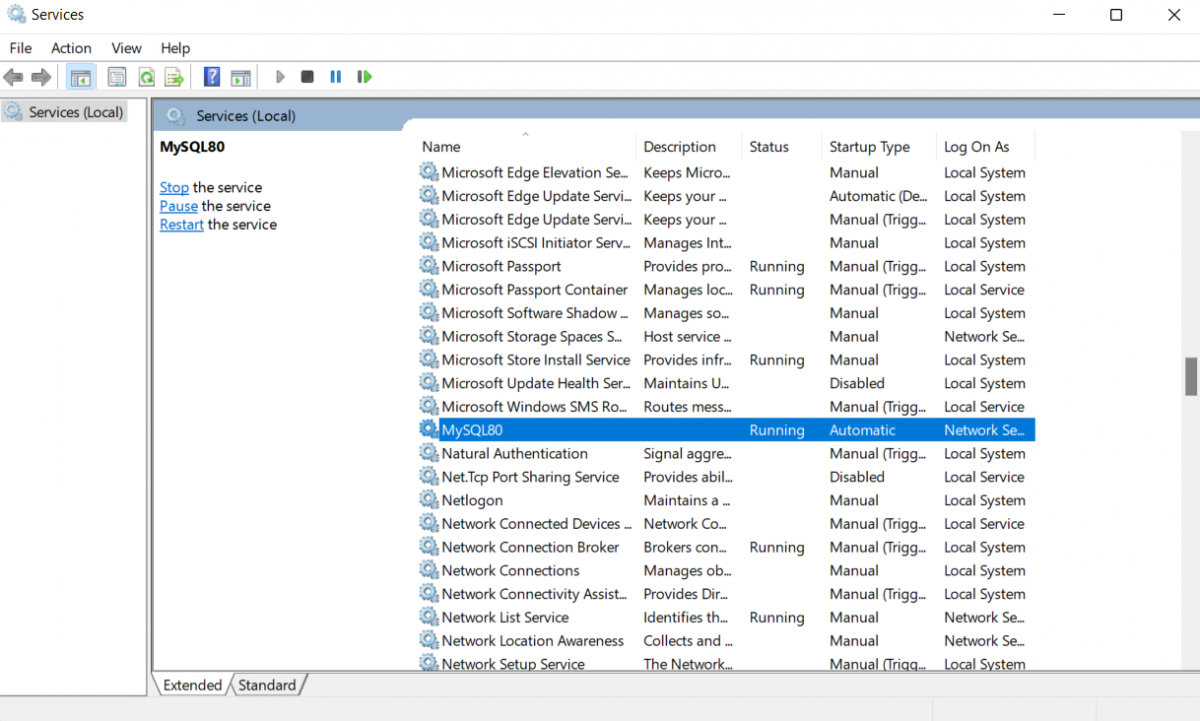
Step 4: Currently MySQL server is running, you can either choose to start, stop and restart the service from the left-hand side panel by selecting any of the options, or you can right-click on MySQL80 service and restart or stop the MySQL server from there.
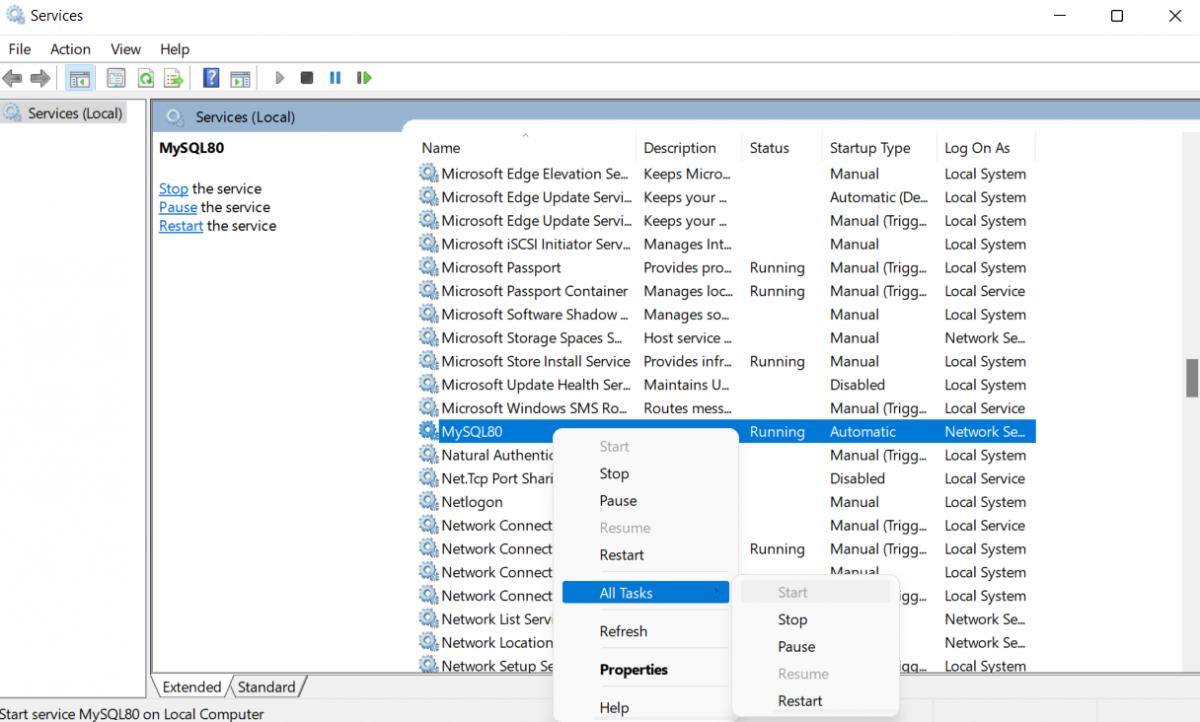
That’s how you can start, stop or restart the MySQL server in windows using services.
Using Windows Command Line
Step 1: Open Command Prompt, you can open it by pressing the Windows key on your keyboard and typing cmd on the search area.
Step 2: Start, stop or restart the MySQL server.
To stop the MySQL server you can type the following command:
net stop MySQL80Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To start the MySQL server you can type the following command:
net start MySQL80Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Using MySQL Workbench
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type MySQL Workbench on the search bar, and open MySQL Workbench.
Step 2: Select the Administrator tab, in the Instances section select the Startup/Shutdown section.
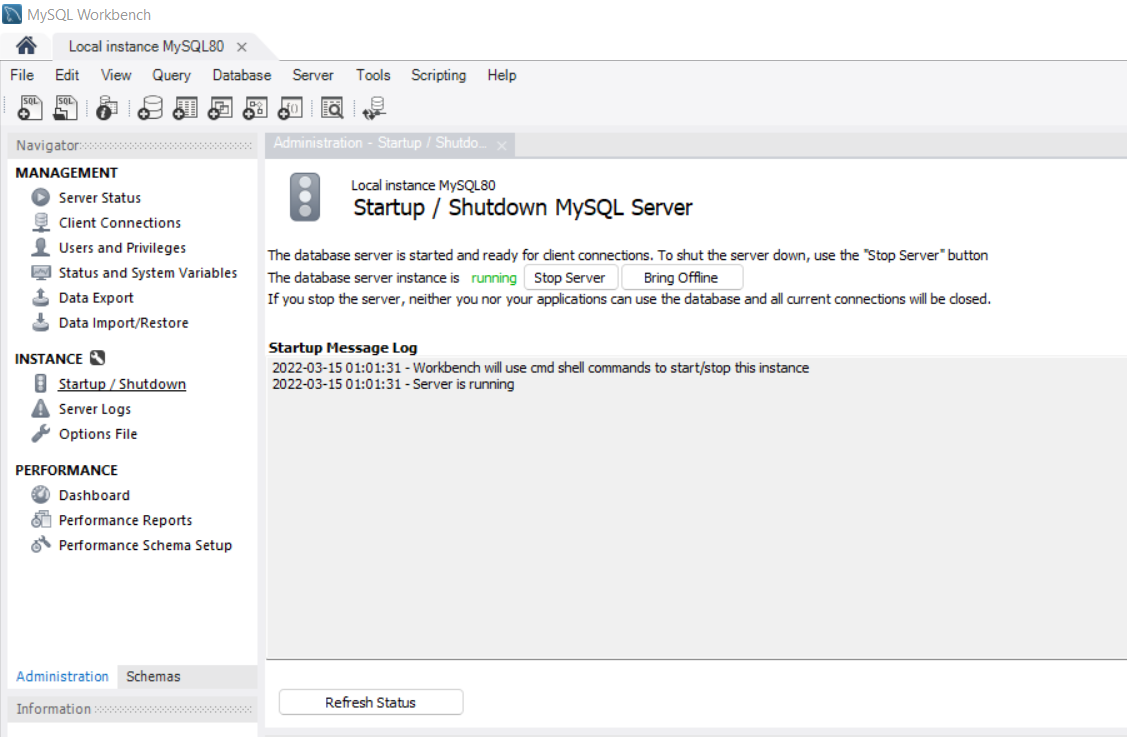
Step 3: You can start or stop the server in this window.
These are the three ways, you can use to start or stop of MySQL server.
Start, Stop and restart MySQL Server on Linux
For performing these activities on Linux, you must be a superuser as only the superuser has these privileges.
Step 1: Open your Linux terminal and we need to check if MySQL is running on your operating system or not. To do so, we’ll need to type the following command:
service mysqld statusCode language: Bash (bash)If MySQL is properly configured on your OS then the command will return Active status as Active(running) which means that MySQL is running on your operating system.
Step 2: Start, stop or restart MySQL
There will be two commands, service and sudo, both should work properly, but it depends if you have the privilege to use the service or sudo command on Linux. Make sure that you are a root user or a super user to perform the activity on MySQL.
To stop the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld stop
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stopCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will stop the MySQL server. Now if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will show inactive(dead) on the active status.
To Start the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld start
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql startCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will start the MySQL server. Now, if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will again be active(running) on the active status.
To restart the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld restart
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restartCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will restart the MySQL server. Now, if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will again be active(running) on the active status because we restarted the server.
Start, Stop or Restart MySQL Server on macOS
Open terminal on your Mac, we’ll be using the Sudo command to start, stop or restart the MySQL server.
For MySQL versions which are newer than 5.7:
To start MySQL server on Mac:
sudo launchctl load -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plistCode language: Bash (bash)To Stop MySQL server on Mac:
sudo launchctl unload -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plistCode language: Bash (bash)For versions older than MySQL 5.7:
To Start MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server startCode language: Bash (bash)To Stop MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stopCode language: Bash (bash)To Restart MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restartCode language: Bash (bash)Conclusion
Mysql is a powerful database management system. In order to use it effectively, you need to be familiar with the different ways to start, stop and restart it. By following the instructions in this article, you should be able to do just that. Thank you for reading!
Starting the MySQL Server on Linux
The server can be started from a command line:
# service mysql start
Starting the server follows this progression:
The server can be started on Linux using several methods:
- mysql.server: Used as a wrapper around mysqld_safefor systems such as Linux and Oracle Solaris that are using System V run-level directories
- mysqld_safe: Sets up the error log and then launches mysqld and monitors it. If mysqldterminates abnormally, mysqld_safe restarts it. If the server does not start properly, look in the error log.
- mysqld: Invokes the server manually to debug the MySQL server. The error messages go to the terminal by default rather than to the error log.
- mysqld_multi: Perl script that is intended to simplify the management of multiple servers on a single host. It can start or stop servers, or it can report whether servers are running.
Install the correct script to have the server run automatically at startup: — On BSD-style Linux systems, it is most common to invoke mysqld_safe from one of the system startup scripts, such as the rc.local script in the /etc directory. — Linux and UNIX System V variants with run-level directories under /etc/init.d use the mysql.server script. Pre-built Linux binary packages install mysql.server under the name mysql for the appropriate run levels. Invoke it manually with an argument of start or stop, either directly or by using the service command.
Stopping the MySQL Server on Linux
Methods for stopping the server:
| Script | Method Description |
|---|---|
| mysqladmin | Connects to the server as a client to shut down the server (local or remote) |
| mysql.server | Stops and/or shuts down the local server |
| mysqld_multi | Invokes mysqladmin to stop and/or shut down servers that it manages |
Stop the server from command line:
# service mysql stop
Check whether the server is running or not:
# service mysql status
To stop the server manually, use one of the following techniques:
- mysqladmin:Has a shutdown command. It connects to the server as a client and can shut down local or remote servers.
- mysql.server:Stops and/or shuts down the local server when invoked with an argument of stop
- mysqld_multi:Stops and/or shuts down any of the servers that it manages. It does so by invoking mysqladmin
mysqld_safe has no server shutdown capability. You can use mysqladmin shutdown instead. Note that if you forcibly terminate mysqld by using the ‘kill -9’ command to send it a signal, then mysqld_safedetects that mysqld terminated abnormally and restarts it. You can work around this by killing mysqld_safefirst and then killing mysqld, but it is better to use mysqladmin shutdown, which initiates a normal (clean) server shutdown.
Running MySQL on Windows
Methods for Running MySQL on Windows:
Server
— Start manually — Stop manually
Service
— Install manually — Start/stop manually or automatically — Use GUI
Run a Windows MySQL server manually from the command line of a console window by using the mysqld command (with extra options, if needed). You stop the server by using the mysqladmin shutdown command.
To run the MySQL server so that Windows itself starts and stops the server when Windows starts and stops, install the server as a Windows service. To do this, invoke the server from the command line using the mysqld –install command (with extra options if needed).
You can also start and stop the service manually from the command line by using the net start MySQL and net stop MySQL commands.
To start and stop the service by using the Windows Services GUI, select the MySQL service in the Administrative Tools and then click the Start or Stop link. You can configure manual or automatic startup in the Services GUI. To remove the service after it has been stopped, use mysqld with the –remove option.


