What is the best way to find the user’s home directory in Java?
The difficulty is that the solution should be cross-platform; it should work on Windows 2000, XP, Vista, OS X, Linux, and other Unix variants. I am looking for a snippet of code that can accomplish this for all platforms, and a way to detect the platform.
Per Java bug 4787931, system property user.home does not work correctly on Windows XP, so using this system property is not an acceptable solution as it is not cross-platform.
M. Justin
14.9k7 gold badges95 silver badges132 bronze badges
asked Feb 25, 2009 at 10:46
Bruno RanschaertBruno Ranschaert
7,4385 gold badges37 silver badges46 bronze badges
4
The bug you reference (bug 4787391) has been fixed in Java 8. Even if you are using an older version of Java, the System.getProperty("user.home") approach is probably still the best. The user.home approach seems to work in a very large number of cases. A 100% bulletproof solution on Windows is hard, because Windows has a shifting concept of what the home directory means.
If user.home isn’t good enough for you I would suggest choosing a definition of home directory for windows and using it, getting the appropriate environment variable with System.getenv(String).
answered Feb 25, 2009 at 15:05
1
Actually with Java 8 the right way is to use:
System.getProperty("user.home");
The bug JDK-6519127 has been fixed and the «Incompatibilities between JDK 8 and JDK 7» section of the release notes states:
Area: Core Libs / java.lang
Synopsis
The steps used to determine the user’s home directory on Windows have changed to follow the Microsoft recommended approach. This change
might be observable on older editions of Windows or where registry
settings or environment variables are set to other directories. Nature
of Incompatibilitybehavioral RFE 6519127
Despite the question being old I leave this for future reference.
answered Nov 13, 2014 at 14:52
Paulo FidalgoPaulo Fidalgo
21.8k7 gold badges99 silver badges115 bronze badges
System.getProperty("user.home");
See the JavaDoc.
Captain Man
7,0576 gold badges48 silver badges75 bronze badges
answered Feb 25, 2009 at 10:53
Joachim SauerJoachim Sauer
303k57 gold badges556 silver badges614 bronze badges
2
The concept of a HOME directory seems to be a bit vague when it comes to Windows. If the environment variables (HOMEDRIVE/HOMEPATH/USERPROFILE) aren’t enough, you may have to resort to using native functions via JNI or JNA. SHGetFolderPath allows you to retrieve special folders, like My Documents (CSIDL_PERSONAL) or Local Settings\Application Data (CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA).
Sample JNA code:
public class PrintAppDataDir {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (com.sun.jna.Platform.isWindows()) {
HWND hwndOwner = null;
int nFolder = Shell32.CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA;
HANDLE hToken = null;
int dwFlags = Shell32.SHGFP_TYPE_CURRENT;
char[] pszPath = new char[Shell32.MAX_PATH];
int hResult = Shell32.INSTANCE.SHGetFolderPath(hwndOwner, nFolder,
hToken, dwFlags, pszPath);
if (Shell32.S_OK == hResult) {
String path = new String(pszPath);
int len = path.indexOf('\0');
path = path.substring(0, len);
System.out.println(path);
} else {
System.err.println("Error: " + hResult);
}
}
}
private static Map<String, Object> OPTIONS = new HashMap<String, Object>();
static {
OPTIONS.put(Library.OPTION_TYPE_MAPPER, W32APITypeMapper.UNICODE);
OPTIONS.put(Library.OPTION_FUNCTION_MAPPER,
W32APIFunctionMapper.UNICODE);
}
static class HANDLE extends PointerType implements NativeMapped {
}
static class HWND extends HANDLE {
}
static interface Shell32 extends Library {
public static final int MAX_PATH = 260;
public static final int CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA = 0x001c;
public static final int SHGFP_TYPE_CURRENT = 0;
public static final int SHGFP_TYPE_DEFAULT = 1;
public static final int S_OK = 0;
static Shell32 INSTANCE = (Shell32) Native.loadLibrary("shell32",
Shell32.class, OPTIONS);
/**
* see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb762181(VS.85).aspx
*
* HRESULT SHGetFolderPath( HWND hwndOwner, int nFolder, HANDLE hToken,
* DWORD dwFlags, LPTSTR pszPath);
*/
public int SHGetFolderPath(HWND hwndOwner, int nFolder, HANDLE hToken,
int dwFlags, char[] pszPath);
}
}
answered Feb 25, 2009 at 17:10
McDowellMcDowell
108k31 gold badges204 silver badges267 bronze badges
3
Others have answered the question before me but a useful program to print out all available properties is:
for (Map.Entry<?,?> e : System.getProperties().entrySet()) {
System.out.println(String.format("%s = %s", e.getKey(), e.getValue()));
}
answered Feb 25, 2009 at 11:03
oxbow_lakesoxbow_lakes
133k56 gold badges318 silver badges449 bronze badges
2
Alternative would be to use Apache CommonsIO FileUtils.getUserDirectory() instead of System.getProperty("user.home"). It will get you the same result and there is no chance to introduce a typo when specifying system property.
There is a big chance you already have Apache CommonsIO library in your project. Don’t introduce it if you plan to use it only for getting user home directory.
answered Oct 11, 2018 at 10:36
mladzomladzo
1,9151 gold badge18 silver badges10 bronze badges
1
As I was searching for Scala version, all I could find was McDowell’s JNA code above. I include my Scala port here, as there currently isn’t anywhere more appropriate.
import com.sun.jna.platform.win32._
object jna {
def getHome: java.io.File = {
if (!com.sun.jna.Platform.isWindows()) {
new java.io.File(System.getProperty("user.home"))
}
else {
val pszPath: Array[Char] = new Array[Char](WinDef.MAX_PATH)
new java.io.File(Shell32.INSTANCE.SHGetSpecialFolderPath(null, pszPath, ShlObj.CSIDL_MYDOCUMENTS, false) match {
case true => new String(pszPath.takeWhile(c => c != '\0'))
case _ => System.getProperty("user.home")
})
}
}
}
As with the Java version, you will need to add Java Native Access, including both jar files, to your referenced libraries.
It’s nice to see that JNA now makes this much easier than when the original code was posted.
answered Jun 22, 2014 at 13:30
PeterPeter
711 silver badge2 bronze badges
I would use the algorithm detailed in the bug report using System.getenv(String), and fallback to using the user.dir property if none of the environment variables indicated a valid existing directory. This should work cross-platform.
I think, under Windows, what you are really after is the user’s notional «documents» directory.
answered Feb 26, 2009 at 8:34
Lawrence DolLawrence Dol
63.2k25 gold badges140 silver badges189 bronze badges
If you want something that works well on windows there is a package called WinFoldersJava which wraps the native call to get the ‘special’ directories on Windows. We use it frequently and it works well.
answered Sep 5, 2017 at 10:24
Neil BennNeil Benn
9041 gold badge12 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
What is the best way to find the user’s home directory in Java?
The difficulty is that the solution should be cross-platform; it should work on Windows 2000, XP, Vista, OS X, Linux, and other Unix variants. I am looking for a snippet of code that can accomplish this for all platforms, and a way to detect the platform.
Per Java bug 4787931, system property user.home does not work correctly on Windows XP, so using this system property is not an acceptable solution as it is not cross-platform.
M. Justin
14.9k7 gold badges95 silver badges132 bronze badges
asked Feb 25, 2009 at 10:46
Bruno RanschaertBruno Ranschaert
7,4385 gold badges37 silver badges46 bronze badges
4
The bug you reference (bug 4787391) has been fixed in Java 8. Even if you are using an older version of Java, the System.getProperty("user.home") approach is probably still the best. The user.home approach seems to work in a very large number of cases. A 100% bulletproof solution on Windows is hard, because Windows has a shifting concept of what the home directory means.
If user.home isn’t good enough for you I would suggest choosing a definition of home directory for windows and using it, getting the appropriate environment variable with System.getenv(String).
answered Feb 25, 2009 at 15:05
1
Actually with Java 8 the right way is to use:
System.getProperty("user.home");
The bug JDK-6519127 has been fixed and the «Incompatibilities between JDK 8 and JDK 7» section of the release notes states:
Area: Core Libs / java.lang
Synopsis
The steps used to determine the user’s home directory on Windows have changed to follow the Microsoft recommended approach. This change
might be observable on older editions of Windows or where registry
settings or environment variables are set to other directories. Nature
of Incompatibilitybehavioral RFE 6519127
Despite the question being old I leave this for future reference.
answered Nov 13, 2014 at 14:52
Paulo FidalgoPaulo Fidalgo
21.8k7 gold badges99 silver badges115 bronze badges
System.getProperty("user.home");
See the JavaDoc.
Captain Man
7,0576 gold badges48 silver badges75 bronze badges
answered Feb 25, 2009 at 10:53
Joachim SauerJoachim Sauer
303k57 gold badges556 silver badges614 bronze badges
2
The concept of a HOME directory seems to be a bit vague when it comes to Windows. If the environment variables (HOMEDRIVE/HOMEPATH/USERPROFILE) aren’t enough, you may have to resort to using native functions via JNI or JNA. SHGetFolderPath allows you to retrieve special folders, like My Documents (CSIDL_PERSONAL) or Local Settings\Application Data (CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA).
Sample JNA code:
public class PrintAppDataDir {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (com.sun.jna.Platform.isWindows()) {
HWND hwndOwner = null;
int nFolder = Shell32.CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA;
HANDLE hToken = null;
int dwFlags = Shell32.SHGFP_TYPE_CURRENT;
char[] pszPath = new char[Shell32.MAX_PATH];
int hResult = Shell32.INSTANCE.SHGetFolderPath(hwndOwner, nFolder,
hToken, dwFlags, pszPath);
if (Shell32.S_OK == hResult) {
String path = new String(pszPath);
int len = path.indexOf('\0');
path = path.substring(0, len);
System.out.println(path);
} else {
System.err.println("Error: " + hResult);
}
}
}
private static Map<String, Object> OPTIONS = new HashMap<String, Object>();
static {
OPTIONS.put(Library.OPTION_TYPE_MAPPER, W32APITypeMapper.UNICODE);
OPTIONS.put(Library.OPTION_FUNCTION_MAPPER,
W32APIFunctionMapper.UNICODE);
}
static class HANDLE extends PointerType implements NativeMapped {
}
static class HWND extends HANDLE {
}
static interface Shell32 extends Library {
public static final int MAX_PATH = 260;
public static final int CSIDL_LOCAL_APPDATA = 0x001c;
public static final int SHGFP_TYPE_CURRENT = 0;
public static final int SHGFP_TYPE_DEFAULT = 1;
public static final int S_OK = 0;
static Shell32 INSTANCE = (Shell32) Native.loadLibrary("shell32",
Shell32.class, OPTIONS);
/**
* see http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb762181(VS.85).aspx
*
* HRESULT SHGetFolderPath( HWND hwndOwner, int nFolder, HANDLE hToken,
* DWORD dwFlags, LPTSTR pszPath);
*/
public int SHGetFolderPath(HWND hwndOwner, int nFolder, HANDLE hToken,
int dwFlags, char[] pszPath);
}
}
answered Feb 25, 2009 at 17:10
McDowellMcDowell
108k31 gold badges204 silver badges267 bronze badges
3
Others have answered the question before me but a useful program to print out all available properties is:
for (Map.Entry<?,?> e : System.getProperties().entrySet()) {
System.out.println(String.format("%s = %s", e.getKey(), e.getValue()));
}
answered Feb 25, 2009 at 11:03
oxbow_lakesoxbow_lakes
133k56 gold badges318 silver badges449 bronze badges
2
Alternative would be to use Apache CommonsIO FileUtils.getUserDirectory() instead of System.getProperty("user.home"). It will get you the same result and there is no chance to introduce a typo when specifying system property.
There is a big chance you already have Apache CommonsIO library in your project. Don’t introduce it if you plan to use it only for getting user home directory.
answered Oct 11, 2018 at 10:36
mladzomladzo
1,9151 gold badge18 silver badges10 bronze badges
1
As I was searching for Scala version, all I could find was McDowell’s JNA code above. I include my Scala port here, as there currently isn’t anywhere more appropriate.
import com.sun.jna.platform.win32._
object jna {
def getHome: java.io.File = {
if (!com.sun.jna.Platform.isWindows()) {
new java.io.File(System.getProperty("user.home"))
}
else {
val pszPath: Array[Char] = new Array[Char](WinDef.MAX_PATH)
new java.io.File(Shell32.INSTANCE.SHGetSpecialFolderPath(null, pszPath, ShlObj.CSIDL_MYDOCUMENTS, false) match {
case true => new String(pszPath.takeWhile(c => c != '\0'))
case _ => System.getProperty("user.home")
})
}
}
}
As with the Java version, you will need to add Java Native Access, including both jar files, to your referenced libraries.
It’s nice to see that JNA now makes this much easier than when the original code was posted.
answered Jun 22, 2014 at 13:30
PeterPeter
711 silver badge2 bronze badges
I would use the algorithm detailed in the bug report using System.getenv(String), and fallback to using the user.dir property if none of the environment variables indicated a valid existing directory. This should work cross-platform.
I think, under Windows, what you are really after is the user’s notional «documents» directory.
answered Feb 26, 2009 at 8:34
Lawrence DolLawrence Dol
63.2k25 gold badges140 silver badges189 bronze badges
If you want something that works well on windows there is a package called WinFoldersJava which wraps the native call to get the ‘special’ directories on Windows. We use it frequently and it works well.
answered Sep 5, 2017 at 10:24
Neil BennNeil Benn
9041 gold badge12 silver badges31 bronze badges
1
- Get the User’s Home Directory Using the
System.getProperty()Method in Java - Get the User’s Home Directory Using the Apache CommonsIO Library in Java
- Get the User’s Home Directory Using the
System.getenv()Method in Java - Summary
This tutorial introduces how to get the user home directory in Java and lists some example codes to guide you on the topic.
For a multi-user operating system, there exists a file system directory for every user; this directory is known as the user’s home directory. There are different ways to find the user home directory in Java. Let’s look at each one of them.
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the System.getProperty() Method in Java
The System class in Java has a Properties object used to store different properties and configurations of the current working environment. It also holds the user’s home directory.
We can access these properties by using the getProperty() method of this class. We need to pass the name of the system property that we want to view. In our case, it would be user.home.
The following code demonstrates how it works.
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String userHomeDir = System.getProperty("user.home");
System.out.printf("The User Home Directory is %s", userHomeDir);
}
}
Output:
The User Home Directory is C:\Users\Lenovo
If you’re curious and want to view all the system properties, you can use the getProperties() method. The code for the getProperties() method is shown below.
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Properties props = System.getProperties();
for(Map.Entry<Object, Object> prop : props.entrySet())
System.out.println("Property: +" + prop.getKey() + "\tValue: " + prop.getValue());
}
}
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the Apache CommonsIO Library in Java
Apache Commons is a very powerful library, and the FileUtils class of the CommonsIO library can be used to fetch the home directory.
We can simply use the getUserDirectory() method of this class to view the user’s home directory. It returns a File object that represents the home directory. We can also get a String path of the home directory by using the getUserDirectoryPath() method.
The code and output for these methods are shown below.
import java.io.File;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
File homeDir = FileUtils.getUserDirectory();
String homeDirPath = FileUtils.getUserDirectoryPath();
System.out.printf("The User Home Directory is %s\n", homeDir);
System.out.printf("The path of User Home Directory is %s", homeDirPath);
}
}
Output:
The User Home Directory is C:\Users\Lenovo
The path of User Home Directory is C:\Users\Lenovo
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the System.getenv() Method in Java
The getenv() method of the System class is used to get the value of system environment variables. We need to pass the name of the environment variable that we want to access.
To get the user’s home directory, we need to use the string USERPROFILE. The following program demonstrates the working of the getenv() method.
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String userHomeDir = System.getenv("USERPROFILE");
System.out.printf("The User Home Directory is %s", userHomeDir);
}
}
Output:
The User Home Directory is C:\Users\Lenovo
You can also use this method to view all the environment variables. Run the following program if you are curious to know more about your system’s environment variables.
import java.util.Map;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Map<String, String> envVars = System.getenv();
for(Map.Entry<String, String> var : envVars.entrySet())
System.out.println(var.getKey() + " ---> " + var.getValue());
}
}
Summary
In this guide, we learn how to get the user’s home directory in Java. For some Windows platforms running older Java versions (before Java 8), the System.getProperty() method may not give the desired result due to the presence of a bug with ID 4787931.
Another similar bug (Bug ID 6519127) also exists. Because of this, the getProperty() method gives undesirable results. However, both of these bugs have already been resolved.
In most cases, the getProperty() method will work just fine, but we can use the alternative System.getenv() method to get the user home directory.
Во многих статьях в интернете, документации к инструментам для разработки на Java и в книгах зачастую упоминается JAVA_HOME. Что же такое JAVA_HOME?
JAVA_HOME это переменная окружения, указывающая на директорию с установленным JDK (Java Development Kit, комплект разработчика Java). JAVA_HOME это соглашение, используемое во многих программах из экосистемы Java.
Какие программы используют JAVA_HOME
- Intellij IDEA, Eclipse, NetBeans
- Apache Maven, Apache Ant, Gradle
- Apache Tomcat
- Jenkins
Некоторые игры, написанные на Java (например, Minecraft), тоже могут требовать установленной переменной JAVA_HOME.
Ошибки, связанные с JAVA_HOME
Если переменная окружения JAVA_HOME не определена, некоторые программы могут выдавать следующие ошибки:
- Переменная среды java_home не определена
- Cannot determine a valid Java Home
- JAVA_HOME is set to an invalid directory
- JAVA_HOME is not defined correctly
- JAVA_HOME environment variable is not set
- JAVA_HOME command not found
- JAVA_HOME not found in your environment
- JAVA_HOME does not point to the JDK
При появлении таких ошибок просто установите переменную JAVA_HOME
Как установить переменную окружения JAVA_HOME в Windows
Сперва вам нужно установить JDK или JRE.
- Установите JDK, если вы занимаетесь разработкой программ на Java
- Установите JRE, если вам нужно только запустить прикладную программу на Java
После установки JDK либо JRE запишите путь установки, он понадобится.
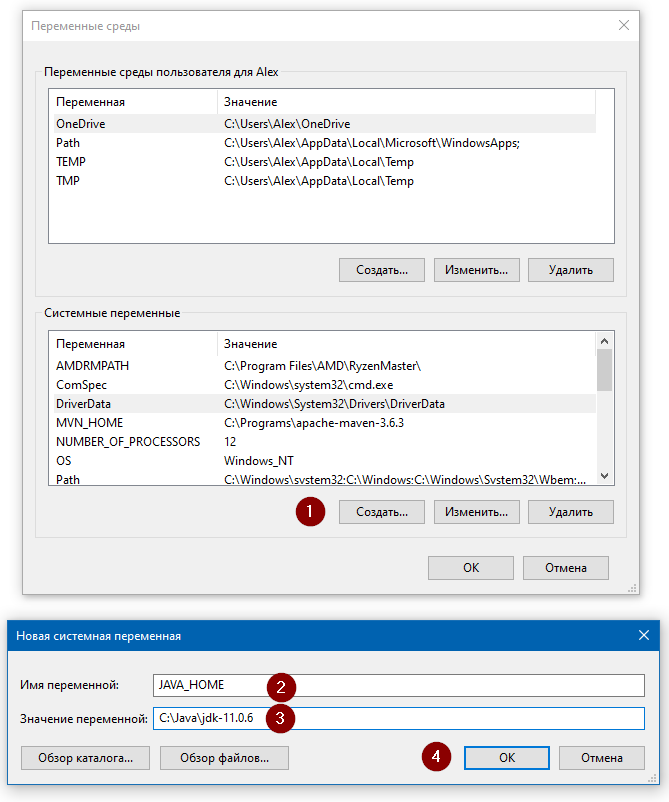
Теперь щёлкните правой кнопкой на «Мой компьютер» → «Свойства» → «Дополнительные параметры системы» → «Переменные среды…». В разделе «Системные переменные» нажмите кнопку «Создать…» и укажите следующие данные:
| Имя переменной | JAVA_HOME |
| Значение переменной | Путь к директории JDK / JRE, например: C:\Java\jdk-11.0.6 |
Сохраните изменения, кликнув «OK». Теперь выберите в списке переменную окружения Path и нажмите «Изменить…». В конце списка добавьте строчку со значением «%JAVA_HOME%\bin«

Для проверки откройте консоль (Win+R, cmd) и укажите последовательно укажите две команды:
echo %JAVA_HOME%
java --version
Если вы правильно установили JDK/JRE и правильно установили переменные окружения, вы увидите вывод наподобие этого:
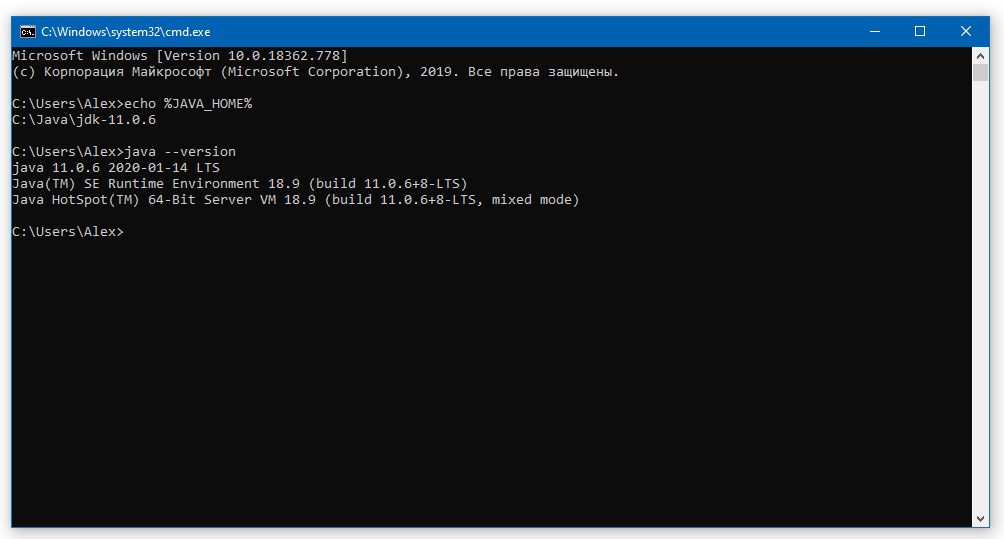
Это будет служить результатом того, что переменная JAVA_HOME установлена правильно и Java работает из командной строки.
Резюме
В данной статье мы рассказали вам, что являет собой переменная окружения JAVA_HOME, где она используется и как её корректно указать.
Looking for a way to get the user’s home directory in Java? You’re in luck! If you are new to the Java programming language and want to know how how to get a user home directory in Java then, this article is just for you. 🙂
There are several different ways to get the user’s home directory in Java, depending on your specific needs and the environment in which your Java code is running.
Before illustrating the methods of getting the user’s home directory in Java, we should have basic concepts of the user’s home directory and how we can check the current directory in the Windows command prompt. So without wasting time, let’s start the topic.
Table of Contents
- What is User Home Directory?
- How to Check the User’s Home Directory in Windows?
- 6 Ways to Get the User Home Directory in Java
- Method 1: Using File Object
- Method 2: Using Path.gets()
- Method 3: Using System.getProperty()
- Method 4: Using System.getenv()
- Method 5: Using FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory()
- Method 6: Using the Paths Class
What is User Home Directory?
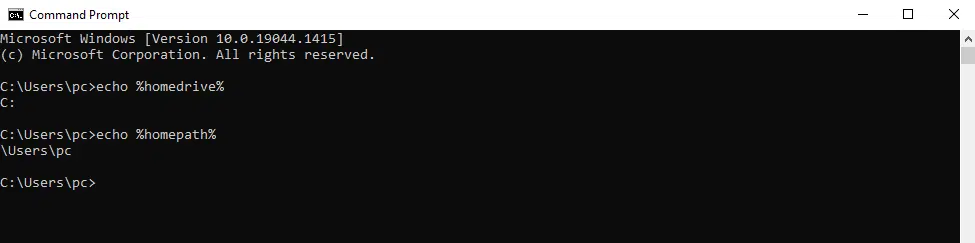
A user home directory is a directory or folder commonly given to a user on an operating system. The home directory allows users to store all their personal information, data files, and user information. In the case of the Windows operating system, the user home Directory is also known as the current working directory. Most commonly Java root directory is boot drive:\Users\PC Name, for example:
C:\Users\pc
How to Check the User’s Home Directory in Windows?
Follow these steps to check the User home directory in Windows:
- Open a command prompt window (Windows button + R, type cmd and press Enter).
- Enter the command echo %homedrive% to check the drive name
- Enter the command echo %homepath% to check the drive name
This command will return the path of the user’s home directory; in my case, this command returns:
We have the following four different ways to get the user home directory in Java:
- Using File object.
- Using Paths.get().
- Using System.getProperty().
- Using System.getenv().
- Using FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory().
- Using the Paths class.
Now explore these ways in detail one by one.
Method 1: Using File Object
File and directory names have different formats on different operating systems, so a simple string is not sufficient to name them. Here we need a File class to handle the situation. The File class contains useful methods for working with the path, renaming, creating, and deleting files. The File object represents the actual file or directory on the disk drive.
Hierarchy of File Class
java.lang.Object java.io.File
We can create an object of File Class by importing the java.io.File package first. After importing the package, we can create a File object by passing a string representing a file’s name. The general syntax of creating a File object is as follows.
File a = new File(String filepath);
To get the user home directory, we have to pass an empty string to the File object, resulting in an empty abstract pathname that always returns the current user directory. Now understand this concept with the help of an example:
Code
import java.io.File;
public class Main {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Create File obj with empty string
File fileObj = new File("");
// In case of an empty absolute path curDir got the Home Directory path
String curDir = fileObj.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("User home directory is:");
System.out.println(curDir);
}
}
Output
User home directory is: C:\Users\pc\IdeaProjects\userhomedirectory
Method 2: Using Path.gets()
Gets() is a method of the Path interface that contains static methods that return a Path by converting a path string or URI. If we pass an empty string to this method, it will return the path of the user’s home directory.
To use this method, we have to import java.nio.file.Path and java.nio.file.Paths. We use the toAbsolutePath() method to get a complete path starting from the root and show all subdirectories with file separator (/). Let’s see how it works with the help of an example:
Code
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Pass an empty string so have the user's current directory
Path mypath = Paths.get("");
// Use toabsolutepath method to get a complete path
Path currentdir = mypath.toAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("User Current Directory is: " + currentdir);
}
}
Output
User Current Directory is: C:\Users\pc\IdeaProjects\userhomedirectory
Method 3: Using System.getProperty()
This method is my favorite; it is easy and to the point. getProperty is the method of System Class if we pass the user.dir key to this method, we will get the user’s home directory. The System class provides access to system-level functions and variables, and the getProperty() method allows you to get the value of a specific system property. Here’s an example of how to use the System class and the getProperty() method to get the user’s home directory:
Code
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// calling getproperty method with user.dir key will return the current directory
String currentdir = System.getProperty("user.dir");;
System.out.println("User Current Directory is: " + currentdir);
}
}
Output
User Current Directory is: C:\Users\pc\IdeaProjects\userhomedirectory
This code uses the System.getProperty() method to get the value of the user.dir system property, which represents the user’s home directory. The currentdir variable is then used to store the value of the user.dir property.
Method 4: Using System.getenv()
One way to get the user’s home directory in a more reliable way is to use the System.getenv() method to get the value of the HOME environment variable. The HOME environment variable is usually set to the user’s home directory, and it is available on most operating systems.
We can get the user’s home directory with the help of System.getenv(). In this method, we must pass the string USERPROFILE, which will return the user’s home directory. Now understand this method with the help of an example:
Code
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// calling the getenv method with the string USERPROFILE will return the home directory
String homedir = System.getenv("USERPROFILE");
System.out.println("User Home Directory is: " + homedir);
}
}
Output
User Home Directory is: C:\Users\pc
This code uses the System.getenv() method to get the value of the USERPROFILE environment variable, and stores it in the homeDir variable.
By using the System.getProperty() method, the FileSystemView.getHomeDirectory() method, or the System.getenv() method, you can get the user’s home directory in Java. Which method you choose will depend on your specific needs and the environment in which your Java code is running. Regardless of which method you choose, you should now have a better understanding of how to get the user’s home directory in Java.
Method 5: Using FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory()
Another way to get the user’s home directory in Java is to use the FileSystemView class and the getHomeDirectory() method. The FileSystemView class provides information about the file system and its components, and the getHomeDirectory() method allows you to get the user’s home directory as a File object. Here’s an example of how to use the FileSystemView class and the getHomeDirectory() method to get the user’s home directory:
File homeDir = FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory();
This code uses the FileSystemView.getFileSystemView() method to get an instance of the ‘FileSystemView’ class, and then calls the getHomeDirectory() method on that instance to get the user’s home directory as a File object.
It’s worth noting that the getProperty() method of the System class and the getHomeDirectory() method of the FileSystemView class may not work in all environments. For example, they may not work correctly in certain types of containers, such as Docker containers, or in certain types of environments, such as Google App Engine. In these cases, you may need to use a different approach to get the user’s home directory.
Method 6: Using the Paths Class
It’s also worth noting that you can use the Paths class and the get() method to get the user’s home directory in Java. The Paths class provides utility methods for working with Path objects, and the get() method allows you to get a Path object by providing a string representation of a file or directory. Here’s an example of how to use the Paths class and the get() method to get the user’s home directory:
Path homeDir = Paths.get(System.getProperty("user.home"));
This code uses the System.getProperty() method to get the value of the user.home system property, which represents the user’s home directory, and then passes that value to the Paths.get() method to get a Path object for the user’s home directory. The homeDir variable is then used to store the Path object.
By using the Paths class and the get() method, you can get the user’s home directory as a Path object, which can be useful if you need to perform operations on the directory, such as reading or writing files.
Conclusion
To summarize the article on how to check a user home directory in Java, In this article, we have discussed four different methods to get the user home directory in Java, including File object, Path.gets(), System.getproperty(), System.getenv,FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory(), and the Paths class.
Among all these different methods the System.getProperty (user.dir) works best; no doubt other methods are also useful and used in scenarios, but getProperty() is a simple and easy way to get the job done.
In conclusion, there are several different ways to get the user’s home directory in Java, depending on your specific needs and the environment in which your Java code is running.
Let’s have a quick review of the topics discussed in this article.
- What is User Home Directory?
- How to check the user’s home directory?
- Ways to get user home directory
- How to get the user’s current directory using a File object?
- How to get the user’s current directory using Path.gets()?
- How to get the user’s current directory using System.getProperty()?
- How to get the user’s current directory using System.getenv()?
- How to get the user’s current directory using FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory()?
- How to get the user’s current directory using Paths Class?
If you’ve found this article helpful, don’t forget to share it with your coding mates, also comment below 👇 which solution has worked in your case.
Happy coding!🥳