About Lenovo
-
Our Company
-
News
-
Investor Relations
-
Sustainability
-
Product Compliance
-
Product Security
-
Lenovo Open Source
-
Legal Information
-
Jobs at Lenovo
Shop
-
Laptops & Ultrabooks
-
Tablets
-
Desktops & All-in-Ones
-
Workstations
-
Accessories & Software
-
Servers
-
Storage
-
Networking
-
Laptop Deals
-
Outlet
Support
-
Drivers & Software
-
How To’s
-
Warranty Lookup
-
Parts Lookup
-
Contact Us
-
Repair Status Check
-
Imaging & Security Resources
Resources
-
Where to Buy
-
Shopping Help
-
Track Order Status
-
Product Specifications (PSREF)
-
Forums
-
Registration
-
Product Accessibility
-
Environmental Information
-
Gaming Community
-
LenovoEDU Community
-
LenovoPRO Community
©
Lenovo.
|
|
|
|
Intel Chipset Device Software — драйверы для материнских плат на чипсетах Intel, ориентированные на обеспечение корректной поддержки функционирования шин PCI-Express, AGP, PCI, USB, IDE, а также прочих компонентов системы. В систему пользователя устанавливаются INF-файлы, определяющие конфигурацию компонентов чипсета, необходимые для правильного функционирования AGP, служб Core PCI и ISAPNP, обеспечивает поддержку жестких дисков IDE/ATA33/ATA66/ATA100/SATA, поддержку USB, идентификация IntelChipset Components в менеджере устройств.
Если средство Intel Chipset Device Software требуется для Вашей системы, его необходимо установить сразу же после установки операционной системы и пакетов обновления операционной системы, до установки прочих драйверов устройств.
В файлах, входящих в состав средства Intel Chipset Device Software, содержится информация для операционной системы о правильной настройке набора микросхем для использования тех или иных возможностей, таких как AGP, USB, базовая поддержка PCI и ISA PnP. Установка драйверов, относящихся к набору микросхем (например, драйверы графического адаптера, шины IDE и т.д.), возможна, только если операционная система полностью распознает данный набор микросхем.
После установки средства Intel Chipset Device Software все прочие драйверы устройств набора микросхем Intel® должны установиться корректно.
Поддерживаемые чипсеты
Intel Chipset Device Software 9.4.4.1006:
2nd Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
Intel(R) 6 Series Express Chipset Family;
Intel(R) Xeon Processor 5500/3500 Series Family;
Intel(R) Server/Workstation Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 800 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 900 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 3 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 4 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 3400 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 5 Series Chipset Family.
Intel Chipset Device Software 10.1.17695.8086:
8th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
7th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
6th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
5th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
4th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
3rd Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
2nd Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
Mobile 8th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
Intel(R) Xeon Phi(R) Processor x200 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) E-2100 / 8th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM);
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor P Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E7-4800/8800 v4 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E7-4800/8800 v3 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E7-4800/8800 v2 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E7-2600 v4 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E5-2600 v4 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E5-2600 v3 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E5-2600 v2 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1500 v5 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1200 v6 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1200 v5 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1200 v4 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1200 v3 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1200 v2 Product Family;
Intel(R) Celeron(R)/Pentium(R) Processor;
Intel(R) Atom(TM)/Celeron(R)/Pentium(R) Processor;
Intel(R) Atom(TM) Processor S1200 Product Family;
Intel(R) Atom(TM) Processor C3000 Product Family;
Intel(R) Atom(TM) Processor C2000 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor D-1500 Product Family;
Intel(R) C620 Series Chipset;
Intel(R) C610 Series Chipset;
Intel(R) C600 Series Chipset;
Intel(R) C240 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) C230 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) C220 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) C210 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) C200 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 300 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 200 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 100 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) X99 Chipset Family;
Intel(R) X79 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 8 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 7 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 6 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) Communications Chipset 8900 Series.
Intel(R) Atom(TM) Processor C3000 Product Family;
Intel(R) 300 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) C240 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 300 Series Chipset Family;
8th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM);
Intel(R) Celeron(R)/Pentium(R) Processor;
Intel(R) 200 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 300 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1200 v6 Product Family;
7th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
Intel(R) C620 Series Chipset;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor P Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1500 v5 Product Family;
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Processor E3-1200 v5 Product Family;
6th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
Intel(R) 100 Series Chipset;
Intel(R) C230 Series Chipset Family;
7th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
6th Generation Intel(R) Core(TM) Processor Family;
5th Gen Intel(R) Core(R) i7 Processor Product Family;
Intel(R) Atom(TM) Processor C3000 Product Family;
Intel(R) C610 Series Chipset;
Intel(R) C600 Series Chipset;
Intel(R) C240 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) C230 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) C220 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) C200 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 300 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 100 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) X99 Chipset Family;
Intel(R) X79 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 9 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 8 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 7 Series Chipset Family;
Intel(R) 6 Series Chipset Family.
Примечание
Если при установке Intel Chipset Device Software возникает ошибка, создайте ярлык файла «SetupChipset.exe». Откройте
Свойства
созданного ярлыка и в строке
Объект
допишите -overall через пробел. В итоге получится: SetupChipset.exe -overall. Запустите установку с этого ярлыка.
Лицензия: Freeware
Разработчик: Intel Corporation
Язык интерфейса: Multi / Русский
Размер: 5 Мб
Intel Chipset Device Software 10.1.19502.8391 [Windows 10/11
||
25.05.2023]
Intel Chipset Device Software Server 10.1.19485.8386 [Windows 10/11 || 08.06.2023]
Intel Chipset Device Software 10.1.17695.8086 [Windows 7/8/8.1/10
||
19.06.2018]
Intel Chipset Device Software 9.4.4.1006 [Windows XP/Vista/7/8/8.1 || 01.08.2013]
Introduction
This blog will be all about installing Intel I211, I217V, I218V and I219V drivers on Windows Server 2016 with EUFI boot. I’m running Windows Server 2016 as my main OS for lab, testing, Hyper-V with nested virtualization etc. I like it that way because I have all the options of the server OS at my disposal. Especially with the nested virtualization an NVME disk comes in handy. I also boot from NVMe so I need UEFI and use secure boot. That’s OK as it’s way better than the old BIOS and enables more scenario.
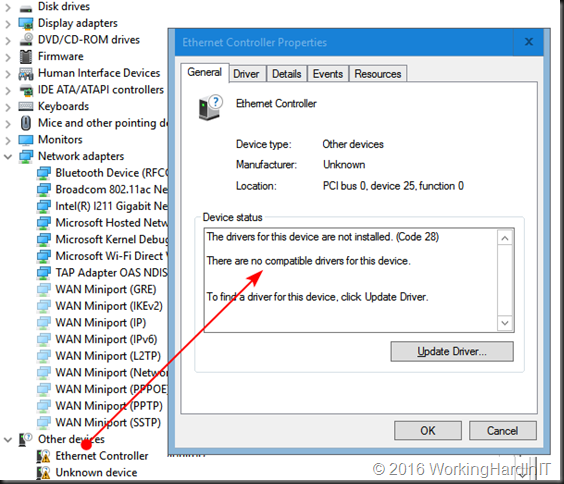
Windows Server 2016 doesn’t have any drivers for the I211, I217V, I218V and the I219V NICs.
The Intel driver for them are only for Windows 10 and won’t install on a server OS. As you can see in the screenshot above that’s a system where I have the I211 driver already installed actually. We’ll work on the I218V as an example here.
That’s nothing new and we’ve dealt with this before by editing the .inf file for the driver. What might be new to some people as EUFI & NVME become a bit more popular is how to get a driver with an edited .inf file installed on your Windows Server OS.
Don’t worry even with an OS booting from EUFI with secure boot you can still disable driver signing / integrity checking when needed. We’ll walk you through an approach for installing Intel I211, I217V, I218V and I219V drivers on Windows Server 2016 with EUFI boot.
Installing Intel I211, I217V, I218V and I219V drivers on Windows Server 2016 with EUFI boot
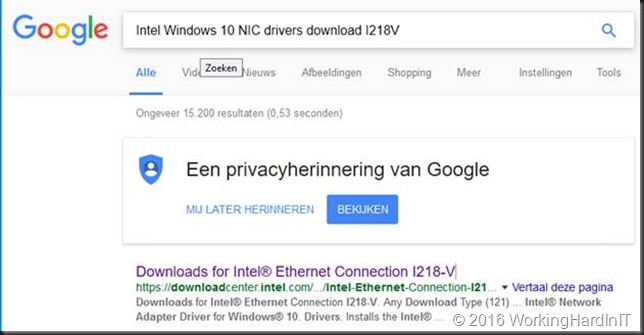
Google for the Intel drivers of your NIC. Mine is a I218V. The instructions will work for a I217V or and i219V as well. Just adapt accordingly.
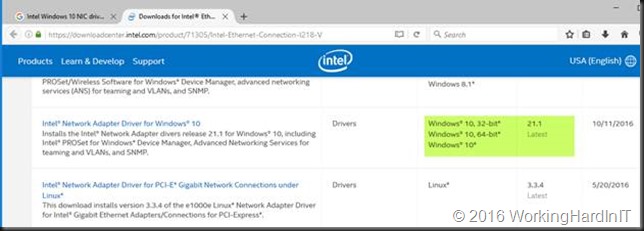
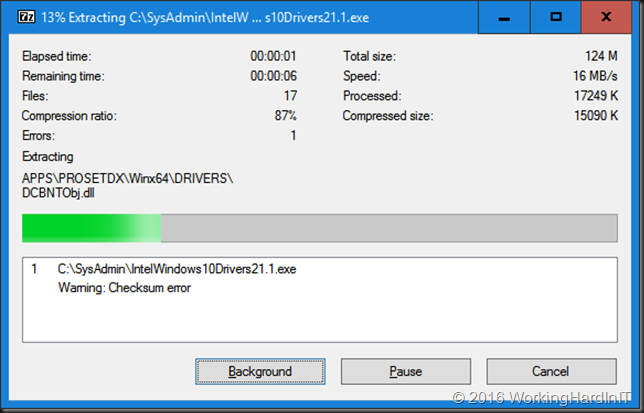
After downloading the most recent Windows 10 (x64 bit, we’ll use them with a server OS so there is no 32 bit here) Intel drivers form the Intel site we rename the exe to identify what package it is. We then extract the content to our work space. A free tool like 7zip will do the job just fine.
Prepping the .INF file
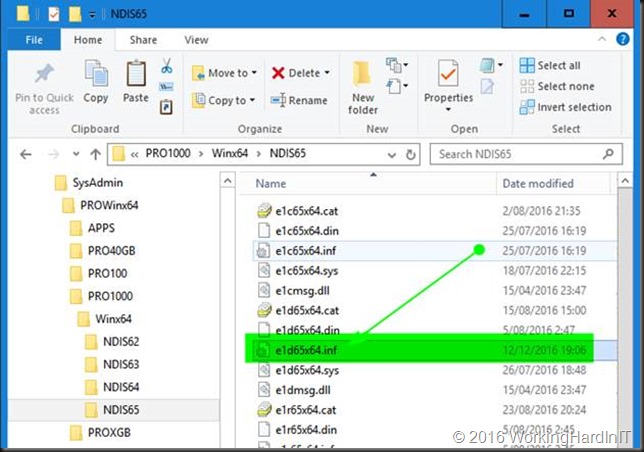
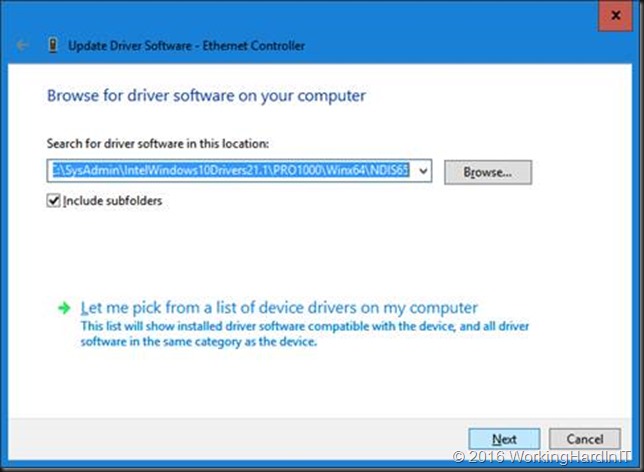
For the I211 we need to edit the .inf file and for the I217V, 218V and 219V we’ll edit the e1d65x64.inf file in note pad or your editor of choice. You’ll find it in the NDIS65 folder: C:\SysAdmin\PROWinx64\PRO1000\Winx64\NDIS65. The 65 in the folder and file names identifies our OS version (Windows 10 / Windows Server 2016).
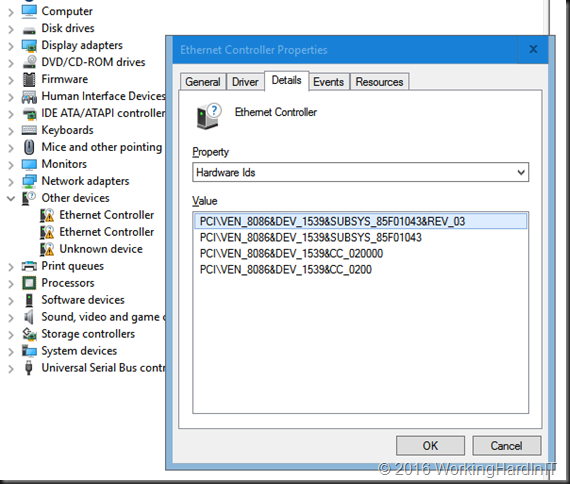
But how do we know what .inf file to edit? We grab the hardware ID’s from the properties of our NIC or NICS.
Below you see the Hardware IDs for mu I218V. The I211 has PCI\VEN_8086&DEV_1539&SUBSYS_85F01043&REV_03 and my Iv218V has PCI\VEN_8086&DEV_15A1&SUBSYS_85C41043&REV_05.
Drop the PCI\ from the beginning of the string and everything from the “&” on at the end. So for the I211 we’ll use VEN_8086&DEV_1539 and for the I218V we’ll use VEN_8086&DEV_15A1. We throw these ID strings into some PowerShell we run in our C:\SysAdmin\PROWinx64\PRO1000\Winx64\NDIS65 folder.
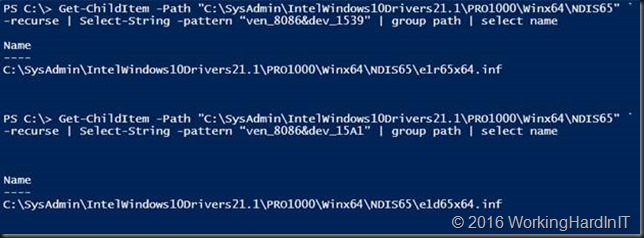
Get-ChildItem -Path “C:\SysAdmin\IntelWindows10Drivers21.1\PRO1000\Winx64\NDIS65” `
-recurse | Select-String -pattern “ven_8086&dev_1539” | group path | select name
Get-ChildItem -Path “C:\SysAdmin\IntelWindows10Drivers21.1\PRO1000\Winx64\NDIS65” `
-recurse | Select-String -pattern “ven_8086&dev_15A1” | group path | select name
So for my I218V I open op the e1d65x64.inf file in notepad++
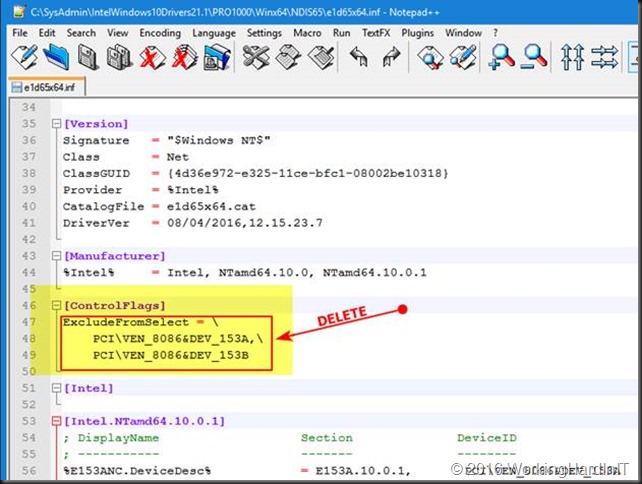
I search for [ControlFlags] section and I edit the content of that section by deleting everything in it.
So it looks likes
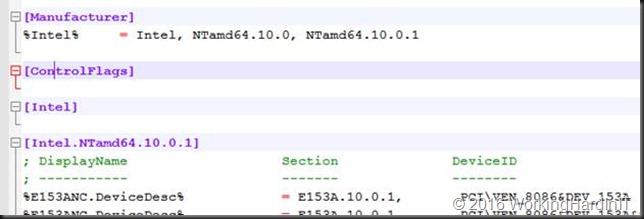
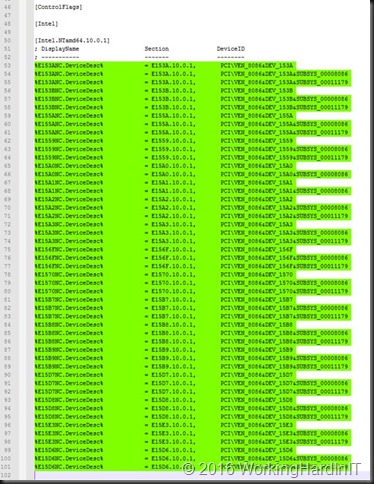
Then I search for section [Intel.NTamd64.10.0.1] and I copy everything in there (I don’t bother to only copy the entries for my particular NIC or so.
Copy everything under that heading
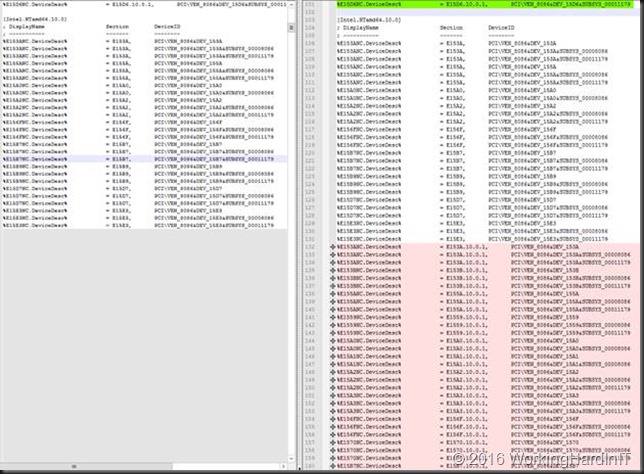
I then search for section [Intel.NTamd64.10.0] and I paste what I just copied from section [Intel.NTamd64.10.0.1] nicely underneath what’s already in there.
Save the file. Basically, you’re done here.
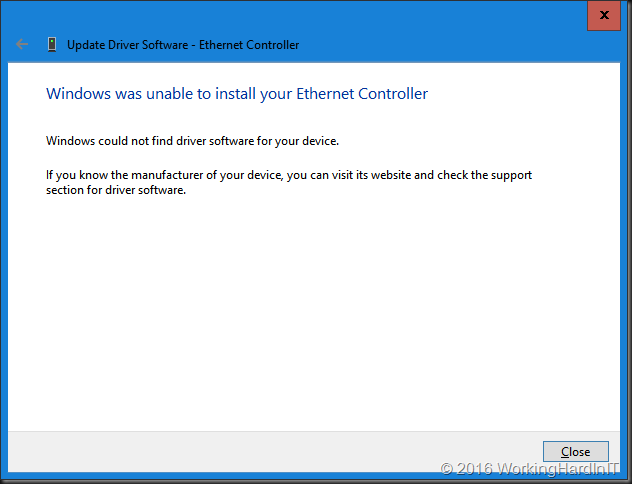
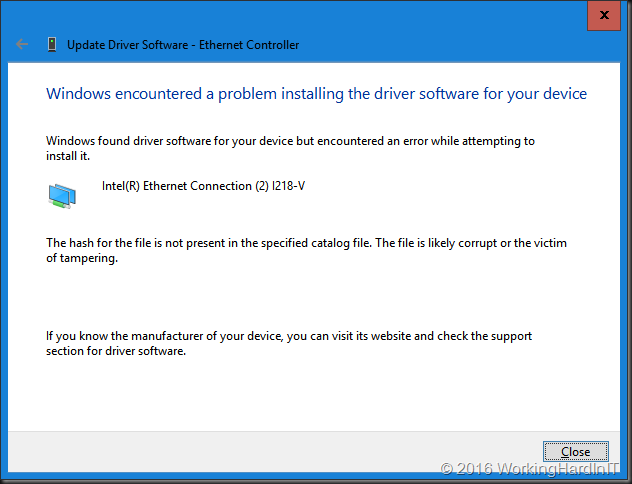
Installing the driver
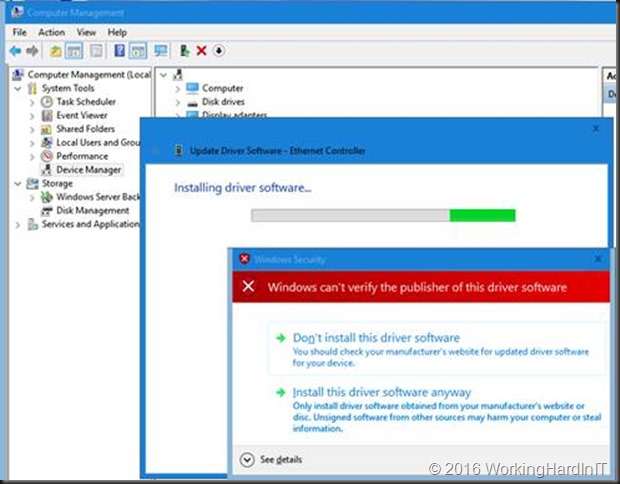
We now need to alter the standard startup setting of Windows Server 2016 temporarily because we will not be able to install a driver that’s been tampered with. If you don’t lower the security settings, you’ll get an error just like this one:
What I did is run the following in an elevated command prompt:
bcdedit /set LOADOPTIONS DISABLE_INTEGRITY_CHECKS
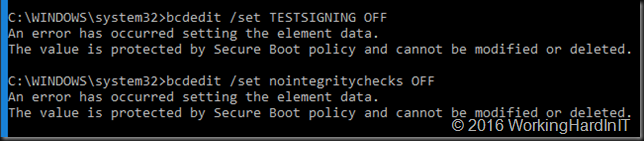
Note: as I’m using UEFI & secure boot the following won’t work as if you were using an older BIOS without secure boot.
bcdedit /set TESTSIGNING ON
bcdedit /set nointegritychecks OFF
But that’s OK. What we need to do is turn it of in another way. That last command bcdedit /set nointegritychecks OFF iIs not needed anyway. So, forget about that one. As a replacement for bcdedit /set TESTSIGNING ON you can use and advanced start option (requires reboot). You can also disable secure boot in EUFI, start again and then run bcdedit /set TESTSIGNING ON. I prefer the first as fixes itself the next boot and I don’t have to turn secure boot on again afterwards.
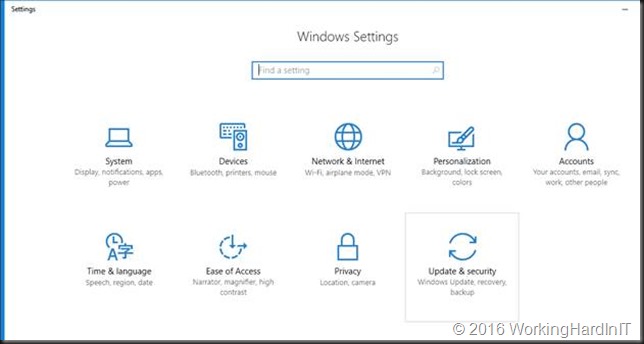
Go to setting and select Update & security.
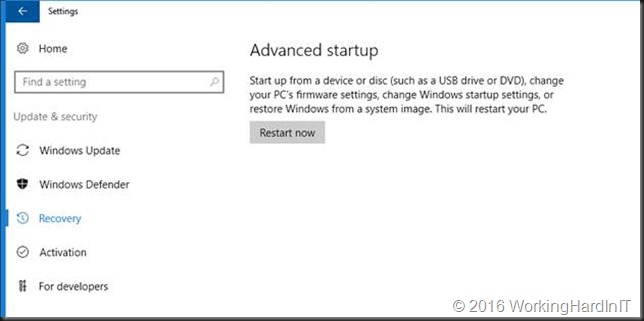
Navigate to Recovery and click Restart Now
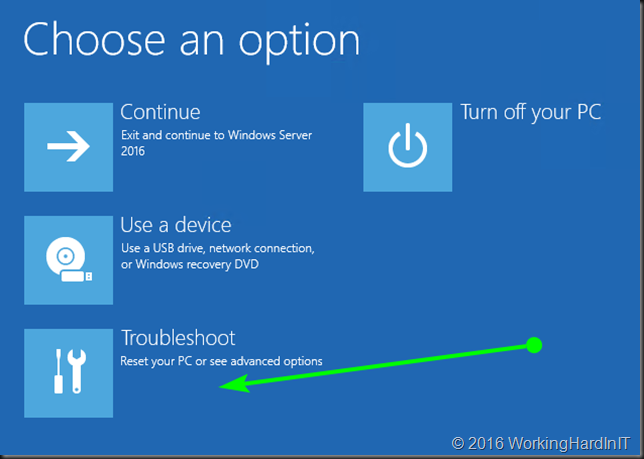
It will reboot to the following screen.Click Troubleshoot.
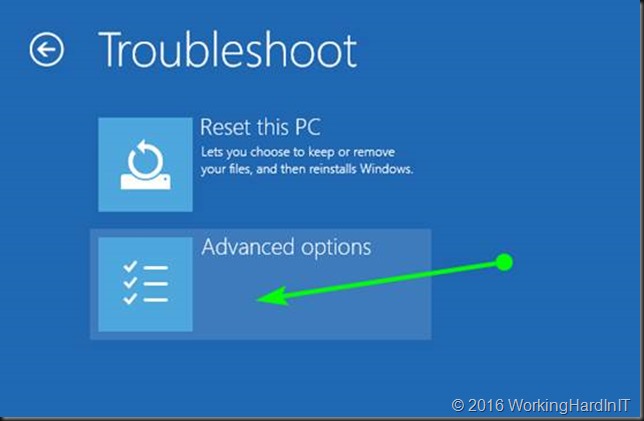
Select and click Advanced options.
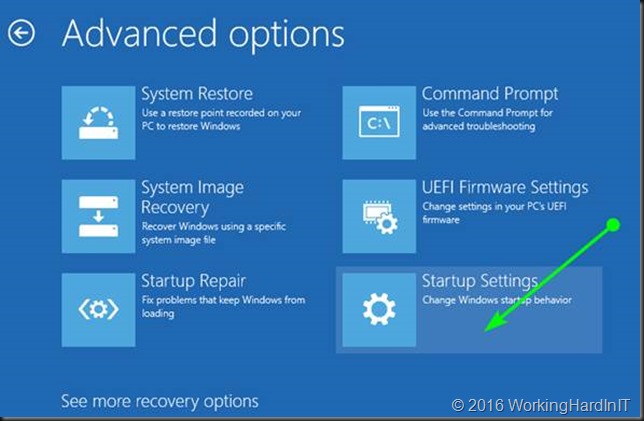
Click Startup Settings.
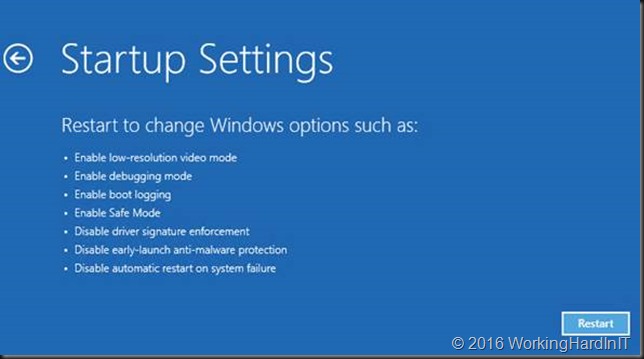
We click restart on the next screen
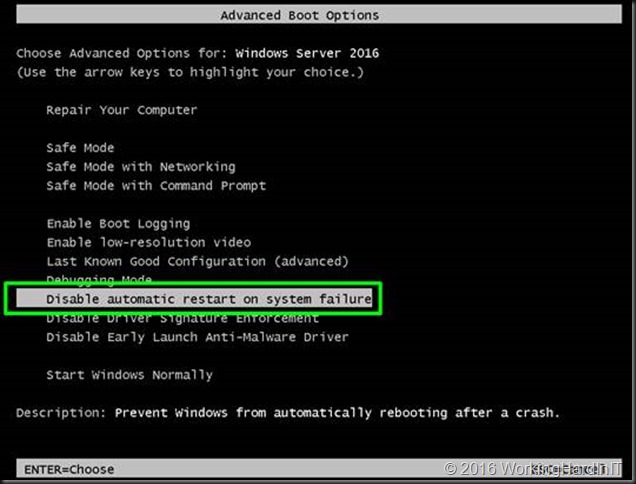
It will restart Advanced boot options. Select to disable driver signature enforcement. Hit ENTER.
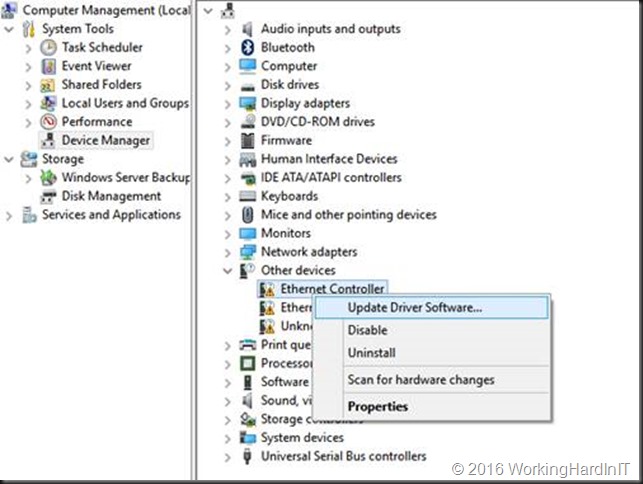
When your server has restarted, you’ll be able to install the driver you tampered with. To do so, in device manager select your NIC and click Update Driver Software.
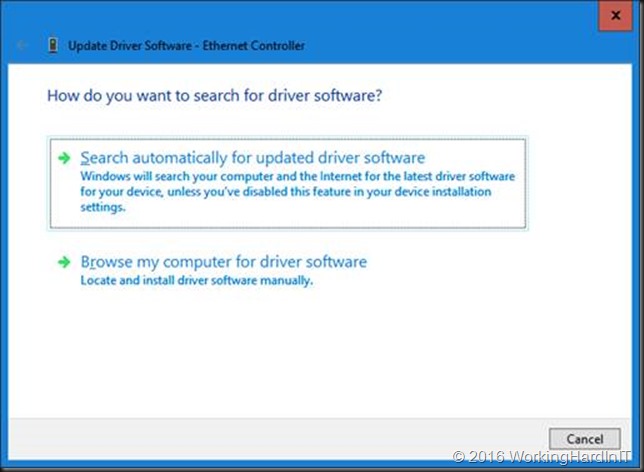
Select to Browse my computer for driver software
Point to the C:\SysAdmin\PROWinx64\PRO1000\Winx64\NDIS65 folder with your edited .inf files.
You’ll get a warning that the publisher of this driver can’t be verified. But as you’re the one doing the tampering here, you’ll be fine.
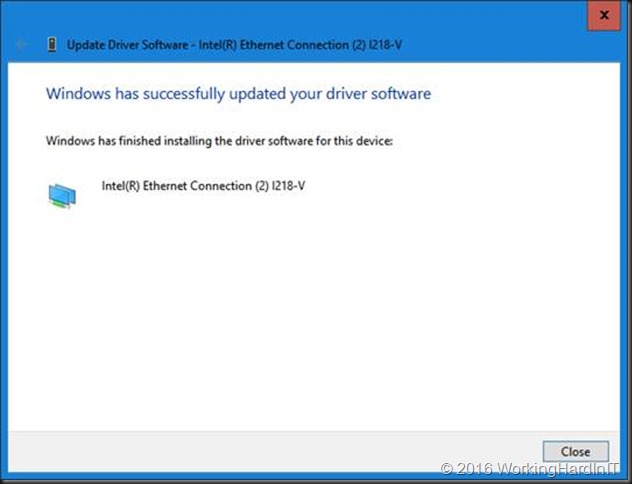
The result is successful install of the driver with a functional NIC for your system.
Cool, you’re in business!
No please reverse the setting you made to the integrity checks to make your system more secure again. From an elevated command prompt run:
bcdedit /set LOADOPTIONS ENABLE_INTEGRITY_CHECKS
Now reboot and you’re all secure again. That’s it, you’re done. I had both an I211 and an I218V NIC on my motherboard so I had to do this for both. Happy testing!
To obtain updates from this website, scripting must be enabled.
To use this site to find and download updates, you need to change your security settings to allow ActiveX controls and active scripting. To get updates but allow your security settings to continue blocking potentially harmful ActiveX controls and scripting from other sites, make this site a trusted website:
In Internet Explorer, click Tools, and then click Internet Options.
On the Security tab, click the Trusted Sites icon.
Click Sites and then add these website addresses one at a time to the list:
You can only add one address at a time and you must click Add after each one:
http://*.update.microsoft.com
https://*.update.microsoft.com
http://download.windowsupdate.com
Note:
You might have to uncheck the Require server verification (https:) for all sites in the zone option to enter all the addresses.
Intel released version 10.1.18793 of their Chipset Device Software on June 30, 2021.
This is the latest version of these drivers and should work with most newer Intel-based motherboards.
Intel Corporation
Intel’s INF updates are not drivers in the most technical sense, but are instead updates to important files that tell Windows how to use Intel integrated hardware. However, we usually still refer to them as drivers.
See What Version of This Driver Do I Have Installed? if you’re not sure which Intel Chipset driver version you have installed.
Changes in Intel Chipset Drivers v10.1
This update resolves an issue related to an incorrect version number, plus adds support for a few new devices.
If you’re not experiencing any issues with your hardware then this update probably isn’t necessary, though I’ve rarely seen Intel chipset driver updates cause any problems.
Intel Chipset Driver Download
The latest Intel chipset drivers can always be downloaded directly from Intel:
Download Intel Chipset Device Software
This updated Intel chipset driver works for both 32-bit and 64-bit editions of Windows 10, as well as Windows Server 2019, 2016, and 2012 R2.
These drivers work only with the following Intel chipsets:
- Intel B150 Chipset
- Intel B250 Chipset
- Intel B360 Chipset
- Intel Chipset Software Installation Utility
- Intel H110 Chipset
- Intel H170 Chipset
- Intel H270 Chipset
- Intel H310 Chipset
- Intel H370 Chipset
- Intel Q150 Chipset
- Intel Q170 Chipset
- Intel Q250 Chipset
- Intel Q270 Chipset
- Intel Q370 Chipset
- Intel X299 Chipset
- Intel Z170 Chipset
- Intel Z270 Chipset
- Intel Z370 Chipset
- Mobile Intel HM170 Chipset
- Mobile Intel HM175 Chipset
- Mobile Intel HM370 Chipset
- Mobile Intel QM170 Chipset
- Mobile Intel QM175 Chipset
- Mobile Intel QM370 Chipset
- Mobile Intel QMS380 Chipset
Even if your Intel chipset isn’t listed above, or you’re not sure what motherboard you have (or if it’s even an Intel motherboard or one with an Intel chipset), the software that we linked to above will help you determine what drivers you need.
Intel Chipset Drivers for Discontinued Motherboards
Intel used to keep an older version of their chipset drivers available for a long list of discontinued motherboards. Here’s an archive of that download page:
Download Intel Chipset Software v9.1.2.1008 (2010-09-29)
Support is only available up to Windows 7 for these boards.
If you’re looking for an up-to-date resource on newly released drivers, see our Windows 10 Drivers, Windows 8 Drivers, or Windows 7 Drivers pages. We keep those pages updated with information and links to new drivers available from Intel and other major hardware makers.
Having Trouble With These New Intel Chipset Drivers?
If something breaks after installing these chipset drivers, your best first step is to uninstall and then reinstall them. You can do this from the appropriate Control Panel applet.
If reinstalling the Intel chipset driver package doesn’t work, try rolling back the driver, also something you can do from Control Panel. See How to Roll Back a Driver for instructions in all versions of Windows.