To build on the previous answer. You can use wmic datafile to get info about a file, but you have to provide the full path and double-up your slashes like so
wmic datafile where Name="F:\\anyfile.txt"
This gives an unreadable mess in the console, as you’ll see:
However if you pipe this into a text file, it’s pretty legible
wmic datafile where Name="F:\\anyfile.txt" >> fileprops.txt
Fortunately, wmic can format the info as a list, and then it is actually pretty useful.
wmic datafile where Name="F:\\anyfile.txt" list /format:list
You can then provide these properties only for a simplified view, note that you must remove the list keyword.
>wmic datafile where Name="G:\\ipcamera.log" get Hidden,FileSize,Name /format:list
FileSize=20
Hidden=FALSE
Name=G:\ipcamera.log
A little piece of trivia, wmic was the foundation for what eventually became PowerShell!
Бывает, что некоторые команды Windows cmd сложно вспомнить, и сохранение их на компьютере или на бумаге в качестве шпаргалки является хорошей практикой. Этот список не является полным, но он содержит наиболее часто используемые команды. Не стесняйтесь добавить свои наиболее часто используемые команды в комментариях ниже, а так же поделиться этим списком.
Управление файлами и папками
- COPY – Копирование файлов в другое место
- DIR – Отображение файлов и папок в текущем каталоге
- DEL или ERASE – Удаление файлов
- EDIT – Запуск редактора файлов
- CD – Изменить каталог
- EXPAND – Распаковать сжатые файлы
- FC – Сравнивает файлы и показывает различия между ними
- FIND – Найти текстовую строку в файле
- MD или MAKEDIR – Создать папку
- MOVE – Переместить файлы из одной папки в другую
- PRINT – отобразить содержимое текстового файла
- RD или RMDIR – удалить папку
- REN или RENAME – переименовать файл или папку
- REPLACE – Замена файлов в одном каталоге на файлы с тем же именем в другом каталоге
- ROBOCOPY – Использует программу «Робокопи» для копирования файлов и каталогов
- TREE – Показывает структуру каталогов диска или папки
- TYPE – Отображает содержимое текстовых файлов
- OPENFILES – Управление открытыми локальными или сетевыми файлами
- XCOPY – Копирование файлов и деревьев каталогов
Приложения и процессы
- SCHTASKS – Запланированный запуск приложения приложения (планировщик задач)
- SHUTDOWN – Выключение или перезагрузка компьютера
- TASKLIST – Список выполняемых задач
- TASKKILL – Остановить или прекратить выполнение задачи (для остановки задачи используется PID, который можно узнать из TASKLIST).
- REG – Запустить редактор реестра
- RUNAS – Запуск задачи от имени другого пользователя
Управление дисками
- CHKDISK – Проверяет диск и показывает статистику
- DEFRAG – Запуск дефрагментации диска
- CHKNTFS – Отображает или изменяет выполнение проверки диска при загрузке
- COMPACT – Отображает и изменяет сжатие файлов в разделах NTFS
- CONVERT – преобразование дискового тома FAT в NTFS
- DISKPART – Отображение и настройка свойств разделов диска
- FORMAT – Форматирование диска
- FSUTIL – Отображение и настройка свойств файловой системы
- LABEL – Создание, изменение или удаление метки тома диска
- RECOVER – Восстановление данных с поврежденного или испорченного диска
- VOL – Отображение метки тома и серийного номера диска
Системная информация
- DATE – Выводит или устанавливает текущую дату
- TIME – Выводит или устанавливает системное время
- DRIVERQUERY – Отображает текущее состояние и свойства драйвера устройства
- HOSTNAME – Отображает имя компьютера
- SYSTEMINFO – Отображает информацию о конфигурации компьютера
- VER – Позволяет просмотреть версию Windows
- GPRESULT – Отображает текущие примененные групповые политики (RSoP)
- GPUPDATE – Обновление групповых политик
Сеть
- IPCONFIG – Отображает информацию о сетевых интерфейсах
- PING – Отправляет ICMP-запросы на целевой хост, проверяет его доступность
- TRACERT – Отображение пути пакетов в сети
- NSLOOKUP – Поиск IP-адреса по имени ресурса
- ROUTE – Отображает таблицы сетевых маршрутов
- ARP – Показывает таблицу с IP-адресами, преобразованными в физические адреса
- NETSH – Запускает программу управления сетевыми настройками
- GETMAC – Показывает MAC-адрес сетевого адаптера
- TFTP – Запускает TFTP-клиент в консоли
Настройка командной строки
- CLS – Очистить экран
- CMD – Отображает другую командную строку
- COLOR – Устанавливает цвет текста и фона в консоли
- PROMPT – Изменение начального текста командной строки
- TITLE – Присвоение заголовка для текущего сеанса
- HELP – Запуск справки CMD
- EXIT – Выход из командной строки
Аverage rating : 4.9
Оценок: 12
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
700
300
Командная строка (cmd) – это мощный инструмент для работы с файлами и папками на компьютере. С ее помощью можно не только выполнять различные операции с файлами, но и просматривать свойства файлов.
Свойства файла – это информация об атрибутах и параметрах файла: размер, дата создания и изменения, разрешения доступа и т. д. В Windows, чтобы узнать свойства файла, нужно нажать на него правой кнопкой мыши и выбрать «Свойства». Но в командной строке можно просмотреть свойства файла быстрее и удобнее.
Как посмотреть свойства файла?
Для того, чтобы просмотреть свойства файла в командной строке, нужно выполнить следующие шаги:
- Откройте командную строку (cmd), нажав клавишу Win+R и введя команду
cmd. - Перейдите в директорию, где находится файл, свойства которого вы хотите посмотреть. Для этого введите команду
cd <путь к директории>и нажмите Enter. Например,cd C:\Users\Username\Desktop. - Введите команду
dir <имя файла>и нажмите Enter. Например,dir example.txt. Эта команда выведет информацию о файле, включая его размер и дату создания. - Чтобы узнать более подробную информацию о файле, введите команду
dir /a <имя файла>и нажмите Enter. Например,dir /a example.txt. Эта команда выведет информацию обо всех атрибутах файла, включая разрешения доступа и дату последнего изменения.
Список команд Windows для работы с файлами
Командная строка (cmd) в Windows предоставляет множество команд для работы с файлами и папками. Некоторые из наиболее полезных команд для работы с файлами:
-
dir– выводит список файлов и папок в директории. -
cd– изменяет текущую директорию. -
md– создает новую папку. -
type– выводит содержимое файла на экран. -
del– удаляет файл. -
copy– копирует файлы. -
xcopy– рекурсивно копирует директории и их содержимое. -
ren– переименовывает файл или папку.
Вывод
Командная строка (cmd) – это мощный инструмент для работы с файлами и папками в Windows. С ее помощью можно быстро и удобно просматривать свойства файла и выполнять множество других операций. Если вы еще не знакомы с командной строкой, рекомендуется изучить базовые команды, чтобы улучшить эффективность своей работы с компьютером.
- А от какой отпечаток наложила на вас ваша профЭссия? :))
- Чтобы разглядеть в другом что-то хорошее… надо самому быть таким?
- Что рвалось у вас в самый неподходящий момент?
- Всем Добрый Вечер))) Из какого фильма данный кадр?
- Перечислите в каких сферах деятельности, люди каких профессий используют Интернет и с какой целью?
- Как отвязать телефон от ВКонтакте, если взломали страницу, заморожена фотография и требуется дополнительная фотография для подтверждения
- Назовите главных жителей деревни, придуманной для детей. Название которой походит от молочного продукта!!!
- В праздники всем приключений хватило… может повторить хотите?
This article lists down various commands that you can use to manage files and folders through Command-Line in Windows 11/10. Although a lot of users prefer using a graphical user interface to manage files for a hassle-free experience, some also use the command-line interface to perform file management tasks. In any case, it is always better to know alternative solutions to execute a task.
In this guide, I will be creating a list of useful commands that you can use for file or folder management on your Windows 10 PC. To perform a specific task on files or folders, there is a dedicated command that you need to enter in CMD. Let’s check out these commands!
Here are the commands that you should know to manage files and folders using Command Prompt in Windows 11/10:
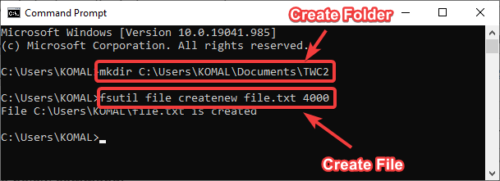
1] Create a File or Folder in CMD
To create a folder, type the folder name with the location where you want to create the folder. Here is the command:
mkdir <folder name with path>
For example;
mkdir C:\Users\KOMAL\Documents\TWC
To create a file of a specific size (in bytes), use the below command:
fsutil file createnew file.txt 4000
In place of file.txt, enter the filename with its extension and full path. And, 4000 is the file size in bytes.
Related: How to Create Multiple Folders using Command Prompt and PowerShell.
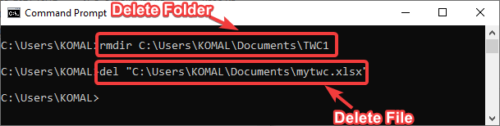
2] Delete Files or Folder in CMD
You can remove a folder using the below command:
rmdir <folder name with path>
In order to delete a file, the command is:
del "<filename with path>"
If you want to delete all files from the current folder, enter the command:
del *
To delete files with a specific extension only, say png, use the command:
del *.png
If you want to delete files with a particular string in their filename, e.g., xyz, you can use the below command:
del *xyz*
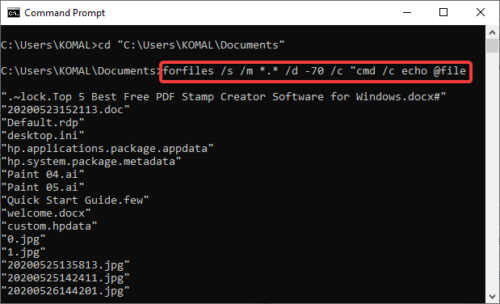
3] Find Files in a Particular Folder
To find files inside a folder based on different parameters, you first need to navigate to the folder using the command:
cd "<folder name with location>"
Now, you can find files older than n days in a specific folder using the below command:
forfiles /s /m *.* /d -n /c "cmd /c echo @file
Replace -n with the number of days. Like if you want to find files older than 2 days, type -2.
To find files larger than a specific size, use the command:
forfiles /S /M * /C "cmd /c if @fsize GEQ 3741824 echo @path"
In the above command, 3741824 is the file size to search files greater than this size.
Read: Managing Files and Folders in Windows 11 – Tips & Tricks
4] Rename all file extensions present in a folder at once
You can also batch rename file extensions in CMD. Suppose, you want to rename the file extension of all images to JPG, you can use the below command:
ren *.* *.jpg
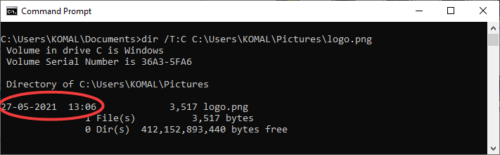
5] Get File Creation Time and Date
To check the creation time and date of a specific file, use the command:
dir /T:C filename
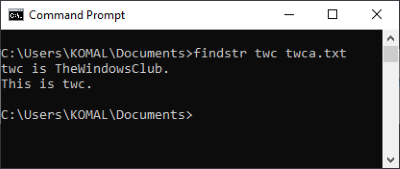
6] Check for a string inside a file
To find all lines containing a particular string in a file, you can use the command:
findstr string file-name
For example, to display all lines with “twc” in a text file, you need to enter the command:
findstr twc twc.txt
Do remember that the above command is case-sensitive.
To find sentences with any specified string, use a command like:
findstr /C:"string1 string2 string3..." filename
7] Check for all Hidden Files in a Folder
Use the below command to get a list of hidden files in a directory:
dir /A:H /B
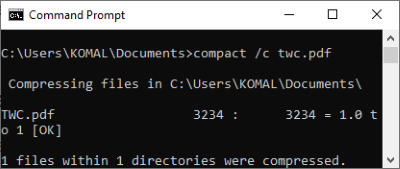
8] Compress a File in CMD
The command to compress a file in a folder is:
compact /c filename
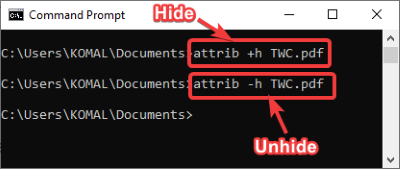
9] Hide/ Unhide a file through CMD
To hide a file, the command used is:
attrib + h filename
You can unhide the file again using the command:
attrib -h filename
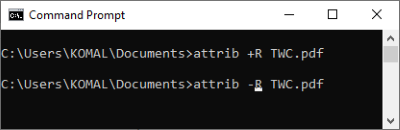
10] Set/ Unset Read-Only attribute to a file
To make a file read-only, the command is:
attrib +R filename
If you want to remove the read-only attribute from a file, the command is:
attrib -R filename
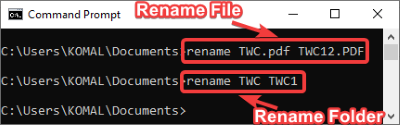
11] Command to Rename a File/Folder
rename oldfilename.pdf newfilename.pdf
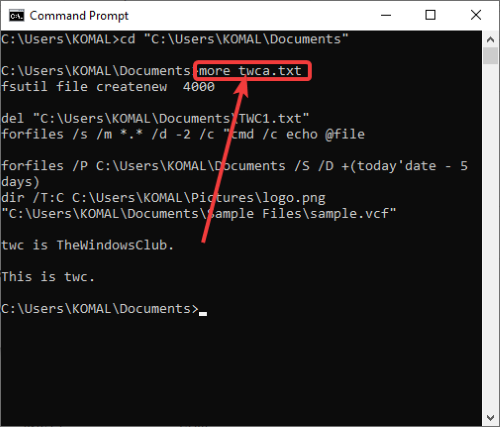
12] Read File Content in CMD
You can read text file content in CMD using the below command:
more filename
13] Open a File in Default Application
You can open a file in its default application by entering a simple command:
"filename-with-path"
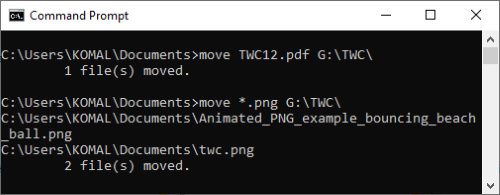
14] Move File / Folder to different Location
Suppose you want to move TWC12.pdf file to TWC folder in G drive, use below command:
move TWC12.pdf G:\TWC\
Command to move all files with a specific extension:
move *.png G:\TWC\
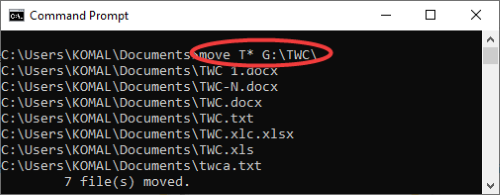
To move files starting with a particular letter, say A, command is:
move A* G:\TWC\
Similarly, you can move a folder using a command like below:
move foldername <new location>
For example:
move TWC1 G:\TWC\
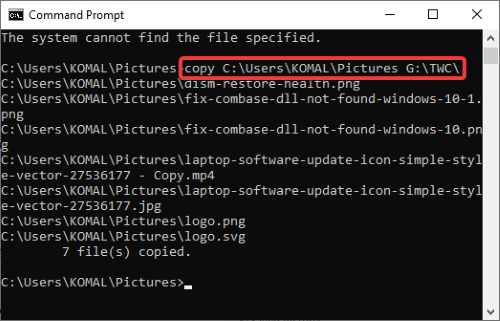
15] Command to Copy Files
You can copy files from one location to another using command:
copy Sourcefolder DestinationFolder
Hope this article helps you learn some useful commands to manage files and folders through the command line in Windows 11/10.
I want to display the content of a text file in a CMD window. In addition, I want to see the new lines that added to file, like tail -f command in Unix.
asked Jun 20, 2013 at 15:16
2
We can use the ‘type’ command to see file contents in cmd.
Example —
type abc.txt
More information can be found HERE.
answered Dec 25, 2015 at 1:22
Anmol SarafAnmol Saraf
15.1k10 gold badges51 silver badges60 bronze badges
1
I don’t think there is a built-in function for that
xxxx.txt > con
This opens the files in the default text editor in windows…
type xxxx.txt
This displays the file in the current window. Maybe this has params you can use…
There is a similar question here: CMD.EXE batch script to display last 10 lines from a txt file
So there is a «more» command to display a file from the given line, or you can use the GNU Utilities for Win32 what bryanph suggested in his link.
answered Jun 20, 2013 at 15:24
inf3rnoinf3rno
25k11 gold badges115 silver badges197 bronze badges
1
To show content of a file:
type file.txt — cmd
cat file.txt — bash/powershell
answered Apr 20, 2021 at 2:28
LaurentBajLaurentBaj
4615 silver badges10 bronze badges
You can use the ‘more’ command to see the content of the file:
more filename.txt
answered Jun 5, 2017 at 19:12
1
Using a single PowerShell command to retrieve the file ending:
powershell -nologo "& "Get-Content -Wait c:\logFile.log -Tail 10"
It applies to PowerShell 3.0 and newer.
Another option is to create a file called TAIL.CMD with this code:
powershell -nologo "& "Get-Content -Wait %1 -Tail %2"
answered Feb 17, 2016 at 12:59
EyalEyal
1611 silver badge9 bronze badges
1
To do this, you can use Microsoft’s more advanced command-line shell called «Windows PowerShell.» It should come standard on the latest versions of Windows, but you can download it from Microsoft if you don’t already have it installed.
To get the last five lines in the text file simply read the file using Get-Content, then have Select-Object pick out the last five items/lines for you:
Get-Content c:\scripts\test.txt | Select-Object -last 5
Source: Using the Get-Content Cmdlet
answered May 18, 2016 at 18:50
1
You can do that in some methods:
One is the type command: type filename
Another is the more command: more filename
With more you can also do that: type filename | more
The last option is using a for
for /f "usebackq delims=" %%A in (filename) do (echo.%%A)
This will go for each line and display it’s content. This is an equivalent of the type command, but it’s another method of reading the content.
If you are asking what to use, use the more command as it will make a pause.
answered Jun 14, 2020 at 16:01
Anic17Anic17
7115 silver badges18 bronze badges
If you want it to display the content of the file live, and update when the file is altered, just use this script:
@echo off
:start
cls
type myfile.txt
goto start
That will repeat forever until you close the cmd window.
answered Mar 11, 2017 at 3:08
1
There is no built in option available with Windows. To constantly monitor logs you can use this free application BareTailPro.
answered Jun 20, 2013 at 15:21
SudheejSudheej
1,8836 gold badges30 silver badges58 bronze badges
If you want to display for example all .config (or .ini) file name and file content into one doc for user reference (and by this I mean user not knowing shell command i.e. 95% of them), you can try this :
FORFILES /M *myFile.ini /C "cmd /c echo File name : @file >> %temp%\stdout.txt && type @path >> %temp%\stdout.txt && echo. >> %temp%\stdout.txt" | type %temp%\stdout.txt
Explanation :
- ForFiles : loop on a directory (and child, etc) each file meeting criteria
- able to return the current file name being process (@file)
- able to return the full path file being process (@path)
- Type : Output the file content
Ps : The last pipe command is pointing the %temp% file and output the aggregate content. If you wish to copy/paste in some documentation, just open the stdout.txt file in textpad.
Anic17
7115 silver badges18 bronze badges
answered Nov 19, 2019 at 18:25
0
You can use either more filename.[extension] or type filename.[extension]
StupidWolf
45.2k17 gold badges40 silver badges72 bronze badges
answered Jun 4, 2021 at 6:12
2
tail -3 d:\text_file.txt
tail -1 d:\text_file.txt
I assume this was added to Windows cmd.exe at some point.
Ian
30.3k19 gold badges70 silver badges107 bronze badges
answered Jan 29, 2016 at 14:14
2