В этой пошаговой инструкции о том, как добавить нужный путь в системную переменную PATH в Windows 11, Windows 10 или другой версии системы: во всех актуальных версиях ОС действия будут одинаковыми, а сделать это можно как в графическом интерфейсе, так и в командной строке или PowerShell. Отдельная инструкция про переменные среды в целом: Переменные среды Windows 11 и Windows 10.
Добавление пути в PATH в Свойствах системы
Для возможности запуска команд простым обращением к исполняемому файлу без указания пути, чтобы это не вызывало ошибок вида «Не является внутренней или внешней командой, исполняемой программой или пакетным файлом», необходимо добавить путь к этому файлу в переменную среды PATH.
Шаги будут следующими:
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре (в Windows 11 и Windows 10 можно нажать правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке Пуск и выбрать пункт «Выполнить»), введите sysdm.cpl в окно «Выполнить» и нажмите Enter.
- Перейдите на вкладку «Дополнительно» и нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды».
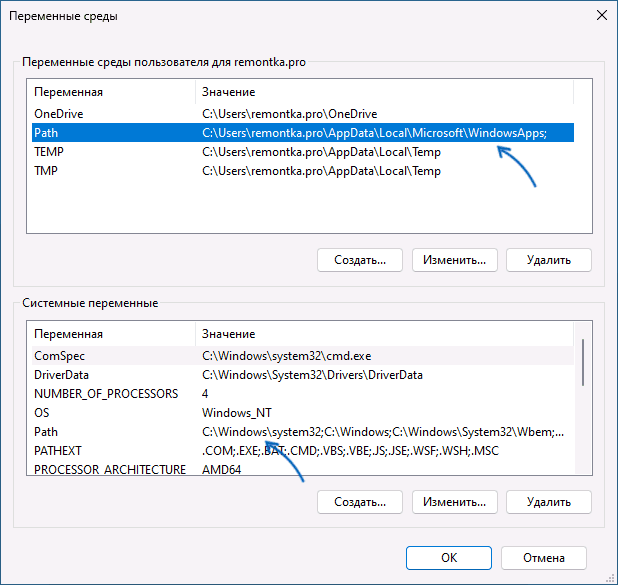
- Вы увидите список переменных среды пользователя (вверху) и системных переменных (внизу). PATH присутствует в обоих расположениях.
- Если вы хотите добавить свой путь в PATH только для текущего пользователя, выберите «Path» в верхней части и нажмите «Изменить» (или дважды нажмите по переменной PATH в списке). Если для всех пользователей — то же самое в нижней части.
- Для добавления нового пути нажмите «Создать», а затем впишите новый путь, который требуется добавить в переменную PATH в новой строке. Вместо нажатия «Создать» можно дважды кликнуть по новой строке для ввода нового пути.
- После ввода всех необходимых путей нажмите «Ок» — ваша папка или папки добавлены в переменную PATH.
Внимание: после добавления пути в переменную PATH потребуется перезапустить командную строку (если она была запущена в момент изменения), чтобы использовать команды без указания полного пути.
Как добавить путь в переменную PATH в командной строке и PowerShell
Вы можете добавить переменную PATH для текущей сессии в консоли: то есть она будет работать до следующего запуска командной строки. Для этого используйте команду:
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\ваш\путь
Есть возможность добавить путь в PATH с помощью командной строки и на постоянной основе (внимание: есть отзывы, что может повредить записи в переменной PATH, а сами изменения производятся для системной переменной PATH), команда будет следующей:
setx /M path "%path%;C:\ваш\путь"
Набор команд для добавления пути в переменную PATH пользователя с помощью PowerShell:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH")
$my_path = "C:\ваш\путь"
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$my_path", "User")
Если требуется добавить путь в системную переменную PATH для всех пользователей, последнюю команду изменяем на:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$my_path", "Machine")
Updated: 12/05/2021 by
Setting the path and environment variables differs depending on the Windows operating system version on your computer. Select a link below for your version of Windows and follow the steps.
Note
Administrator privileges are required to modify the path and environment variables.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 11
- Press the Windows key+X to access the Power User Task Menu.
- In the Power User Task Menu, select the System option.
- In the System > About window, click the Advanced system settings link below the Device specifications section.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab,if not already selected.
- Click the Environment Variables button near the bottom-right of the Advanced tab.
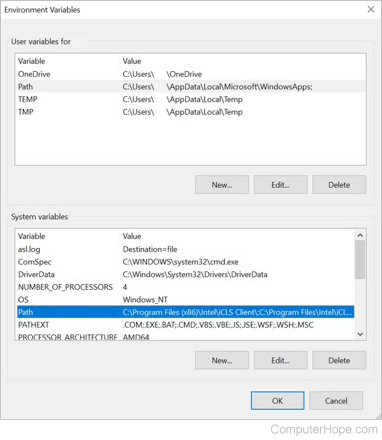
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each directory path is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
C:\Program Files;C:\Winnt;C:\Winnt\System32
- After creating or modifying the environment variables, restart the computer for those changes to take effect in Windows.
Note
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New, and enter the variable name and value.
Tip
To view and set the path through the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 10
- Press the Windows key+X to access the Power User Task Menu.
- In the Power User Task Menu, select the System option.
- In the About window, click the Advanced system settings link under Related settings on the far-right side.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variables button near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each directory path is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
C:\Program Files;C:\Winnt;C:\Winnt\System32
- After creating or modifying the environment variables, restart the computer for those changes to take effect in Windows.
Note
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New, and enter the variable name and value.
Tip
To view and set the path through the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 8
- Press the Windows key+X to access the Power User Task Menu.
- In the Power User Task Menu, select the System option.
- Click the Advanced System Settings link in the left column.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variables button near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
C:\Program Files;C:\Winnt;C:\Winnt\System32
- After creating or modifying the environment variables, restart the computer for those changes to take effect in Windows.
Note
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New, and enter the variable name and value.
Tip
To view and set the path through the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows Vista and Windows 7
- On the desktop, right-click the Computer icon and select Properties. If you don’t have a Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties.
- Click the Advanced System Settings link in the left column.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variables button near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
C:\Program Files;C:\Winnt;C:\Winnt\System32
- After creating or modifying the environment variables, restart the computer for those changes to take effect in Windows.
Note
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New, and enter the variable name and value.
Tip
To view and set the path through the Windows command line, use the path command.
Setting the path and variables in Windows 2000 and Windows XP
The path is now managed by Windows 2000 and Windows XP and not the autoexec.bat or autoexec.nt files, as was done with earlier versions of Windows. To change the system environment variables, follow the steps below.
- From the desktop, right-click My Computer and click Properties. If you don’t have a My Computer icon on your desktop, click Start, right-click the My Computer option in the Start menu, and select Properties.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab.
- In the Advanced section, click the Environment Variables button.
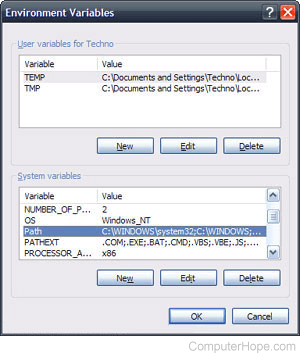
- In the Environment Variables window (as shown below), highlight the Path variable in the System Variable section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below.
C:\Program Files;C:\Winnt;C:\Winnt\System32
- After creating or modifying the environment variables, restart the computer for those changes to take effect in Windows.
Note
You can edit other environment variables by highlighting the variable in the System variables section and clicking Edit. If you need to create a new environment variable, click New, and enter the variable name and value.
Tip
To view and set the path through the Windows command line, use the path command.
What is the default Windows %PATH%?
The path is based on programs installed on the computer, so there is no «default path.» However, the Windows minimum path is often the path below.
%SystemRoot%\system32;%SystemRoot%;%SystemRoot%\System32\Wbem
Note
Realize that as you install programs, the path is updated with the paths for the newly installed programs. So, if you have erased your path after installing other programs, those programs may be affected.
Setting path in the MS-DOS and Windows command line
To view and set the path in MS-DOS and the Windows command line, use the path command.
Environment variables are variables that are defined in the operating system to configure certain parameters such as the path to search for a command or executable, folder for temporary files, application-specific options, etc,. There are two types of environment variables — user environment variables and system environment variables. User environment variables are specfic to each user that it is set for, while system environment variables are available to everyone on that computer.
In this article you will learn how to
- View Environment variables
- Add / Modify Environment variables
- Add / Modify / Remove PATH variable
- Manage environment variables from Advanced System Settings
View Environment Variables
The SET command is used to view environment variables from the command line. To view all environment variables,
- Open command prompt — click the search icon and type cmd in the search bar. Then click on the Command Prompt from the results.
-
On the Command Prompt, type set and press Enter.
C:\> set ALLUSERSPROFILE=C:\ProgramData CommonProgramFiles=C:\Program Files\Common Files CommonProgramFiles(x86)=C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files CommonProgramW6432=C:\Program Files\Common Files
-
To view any specific variable, the command is
setfollowed by that variable name.C:\> set windir windir=C:\WINDOWS
Add or Modify Environment Variable
Use the setx command to add a new environment variable permanently or to modify an existing environment variable.
If you want to add or modify a environment variable temporarily to the current command window only, then the command to use is set.
setx variableName value or set variableName=value
Example
c:\> setx TESTVAR someValue SUCCESS: Specified value was saved.
Now, open a new command prompt and run the set command to verify that the new environment variable is created.
c:\> Set testvar TESTVAR=someValue
Adding System Environment Variables
By default, the setx command adds the variables as user variable in the local environment. To add a variable to the system environment use the /m parameter. You also need run the command prompt as an administrator.
c:\> setx TESTVAR someValue /m SUCCESS: Specified value was saved.
If the command windows is not run in administrator mode then you will get the following error
ERROR: Access to the registry path is denied.
The variables in the system environment are available to all users of the computer.
Difference between SET and SETX
The SET command is used to view, create and modify environment variables temporarily for the current command window. The variable that you add using SET are not available on any future command windows.
SETX command adds the variables permanently. The variables that are added using SETX are not available on the current command window but will be available on all future windows.
You cannot use setx to remove a environment variable but you can use set to remove a variable from the current command window.
Setting PATH variable
The PATH variable defines the search path for executable files. You can set the PATH variable from the command line or GUI.
View current PATH
To view the current path you can simply run the path command or echo %PATH% command.
c:\> path PATH=C:\windows\system32;C:\windows;C:\windows\System32\Wbem;C:\windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\;C:\Program Files\Intel\Intel(R) Management Engine Components\DAL;C:\WINDOWS\system32;C:\WINDOWS;C:\WINDOWS\System32\Wbem;C:\WINDOWS\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\;C:\WINDOWS\System32\OpenSSH\;
Add path to current PATH
To add new path to the exiting path, use the SET or SETX command.
For example, to add the directory c:\NewFolder to existing path, the command is
c:\> set PATH=c:\NewFolder;%PATH%
Modify an existing path
The SET and SETX commands can be also used to modify an existing path. The syntax for this command is
set PATH=%PATH:current_path=new_path%
For example, to change c:\NewFolder in the current path to c:\AnotherFolder, the command is
set PATH=%PATH:c:\NewFolder;=c:\AnotherFolder;%
Remove path from current PATH
The syntax for removing a folder path from the current PATH is same as modifying an existing path explained above, except that you just have to omit the new path.
set PATH=%PATH:path_to_remove;=%
For example, to remove c:\AnotherFolder; from the existing path, the command is
set PATH=%PATH:c:\AnotherFolder;=%
Manage Environment variables from Advanced System Settings
You could also manage environment variables from Advanced System Settings in Windows. Type env in the search box and select Edit environment variables for your account. This will open Environment Settings dialog from where you can add, edit and delete system and user environment variables.
I am trying to add C:\xampp\php to my system PATH environment variable in Windows.
I have already added it using the Environment Variables dialog box.
But when I type into my console:
C:\>path
it doesn’t show the new C:\xampp\php directory:
PATH=D:\Program Files\Autodesk\Maya2008\bin;C:\Ruby192\bin;C:\WINDOWS\system32;C:\WINDOWS;
C:\WINDOWS\System32\Wbem;C:\PROGRA~1\DISKEE~2\DISKEE~1\;c:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL
Server\90\Tools\binn\;C:\Program Files\QuickTime\QTSystem\;D:\Program Files\TortoiseSVN\bin
;D:\Program Files\Bazaar;C:\Program Files\Android\android-sdk\tools;D:\Program Files\
Microsoft Visual Studio\Common\Tools\WinNT;D:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\Common
\MSDev98\Bin;D:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\Common\Tools;D:\Program Files\
Microsoft Visual Studio\VC98\bin
I have two questions:
- Why did this happen? Is there something I did wrong?
- Also, how do I add directories to my
PATHvariable using the console (and programmatically, with a batch file)?
asked Mar 3, 2012 at 12:58
8
Option 1
After you change PATH with the GUI, close and reopen the console window.
This works because only programs started after the change will see the new PATH.
Option 2
This option only affects your current shell session, not the whole system. Execute this command in the command window you have open:
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\your\path\here\
This command appends C:\your\path\here\ to the current PATH. If your path includes spaces, you do not need to include quote marks.
Breaking it down:
set– A command that changes cmd’s environment variables only for the current cmd session; other programs and the system are unaffected.PATH=– Signifies thatPATHis the environment variable to be temporarily changed.%PATH%;C:\your\path\here\– The%PATH%part expands to the current value ofPATH, and;C:\your\path\here\is then concatenated to it. This becomes the newPATH.
answered Mar 3, 2012 at 13:03
JimRJimR
15.6k2 gold badges20 silver badges26 bronze badges
12
WARNING: This solution may be destructive to your PATH, and the stability of your system. As a side effect, it will merge your user and system PATH, and truncate PATH to 1024 characters. The effect of this command is irreversible. Make a backup of PATH first. See the comments for more information.
Don’t blindly copy-and-paste this. Use with caution.
You can permanently add a path to PATH with the setx command:
setx /M path "%path%;C:\your\path\here\"
Remove the /M flag if you want to set the user PATH instead of the system PATH.
Notes:
- The
setxcommand is only available in Windows 7 and later. -
You should run this command from an elevated command prompt.
-
If you only want to change it for the current session, use set.
StayOnTarget
11.8k10 gold badges52 silver badges84 bronze badges
answered Feb 28, 2015 at 5:12
NafscriptNafscript
5,1752 gold badges17 silver badges15 bronze badges
15
This only modifies the registry. An existing process won’t use these values. A new process will do so if it is started after this change and doesn’t inherit the old environment from its parent.
You didn’t specify how you started the console session. The best way to ensure this is to exit the command shell and run it again. It should then inherit the updated PATH environment variable.
answered Mar 3, 2012 at 13:23
Hans PassantHans Passant
924k146 gold badges1696 silver badges2536 bronze badges
6
You don’t need any set or setx command. Simply open the terminal and type:
PATH
This shows the current value of PATH variable. Now you want to add directory to it? Simply type:
PATH %PATH%;C:\xampp\php
If for any reason you want to clear the PATH variable (no paths at all or delete all paths in it), type:
PATH ;
Update
Like Danial Wilson noted in comment below, it sets the path only in the current session. To set the path permanently, use setx but be aware, although that sets the path permanently, but not in the current session, so you have to start a new command line to see the changes. More information is here.
To check if an environmental variable exist or see its value, use the ECHO command:
echo %YOUR_ENV_VARIABLE%
answered Jul 1, 2015 at 15:11
zarzar
11.4k15 gold badges97 silver badges178 bronze badges
6
I would use PowerShell instead!
To add a directory to PATH using PowerShell, do the following:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH")
$xampp_path = "C:\xampp\php"
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path")
To set the variable for all users, machine-wide, the last line should be like:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path", "Machine")
In a PowerShell script, you might want to check for the presence of your C:\xampp\php before adding to PATH (in case it has been previously added). You can wrap it in an if conditional.
So putting it all together:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine")
$xampp_path = "C:\xampp\php"
if( $PATH -notlike "*"+$xampp_path+"*" ){
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$xampp_path", "Machine")
}
Better still, one could create a generic function. Just supply the directory you wish to add:
function AddTo-Path{
param(
[string]$Dir
)
if( !(Test-Path $Dir) ){
Write-warning "Supplied directory was not found!"
return
}
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine")
if( $PATH -notlike "*"+$Dir+"*" ){
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$Dir", "Machine")
}
}
You could make things better by doing some polishing. For example, using Test-Path to confirm that your directory actually exists.
answered Mar 17, 2015 at 20:24
Ifedi OkonkwoIfedi Okonkwo
3,4244 gold badges33 silver badges45 bronze badges
4
Safer SETX
Nod to all the comments on the @Nafscript’s initial SETX answer.
SETXby default will update your user path.SETX ... /Mwill update your system path.%PATH%contains the system path with the user path appended
Warnings
- Backup your
PATH—SETXwill truncate your junk longer than 1024 characters - Don’t call
SETX %PATH%;xxx— adds the system path into the user path - Don’t call
SETX %PATH%;xxx /M— adds the user path into the system path - Excessive batch file use can cause blindness1
The ss64 SETX page has some very good examples. Importantly it points to where the registry keys are for SETX vs SETX /M
User Variables:
HKCU\EnvironmentSystem Variables:
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment
Usage instructions
Append to User PATH
append_user_path.cmd
@ECHO OFF
REM usage: append_user_path "path"
SET Key="HKCU\Environment"
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=2*" %%A IN (`REG QUERY %Key% /v PATH`) DO Set CurrPath=%%B
ECHO %CurrPath% > user_path_bak.txt
SETX PATH "%CurrPath%";%1
Append to System PATH
append_system_path.cmd. Must be run as administrator.
(It’s basically the same except with a different Key and the SETX /M modifier.)
@ECHO OFF
REM usage: append_system_path "path"
SET Key="HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment"
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=2*" %%A IN (`REG QUERY %Key% /v PATH`) DO Set CurrPath=%%B
ECHO %CurrPath% > system_path_bak.txt
SETX PATH "%CurrPath%";%1 /M
Alternatives
Finally there’s potentially an improved version called SETENV recommended by the ss64 SETX page that splits out setting the user or system environment variables.
Example
Here’s a full example that works on Windows 7 to set the PATH environment variable system wide. The example detects if the software has already been added to the PATH before attempting to change the value. There are a number of minor technical differences from the examples given above:
@echo off
set OWNPATH=%~dp0
set PLATFORM=mswin
if defined ProgramFiles(x86) set PLATFORM=win64
if "%PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE%"=="AMD64" set PLATFORM=win64
if exist "%OWNPATH%tex\texmf-mswin\bin\context.exe" set PLATFORM=mswin
if exist "%OWNPATH%tex\texmf-win64\bin\context.exe" set PLATFORM=win64
rem Check if the PATH was updated previously
echo %PATH% | findstr "texmf-%PLATFORM%" > nul
rem Only update the PATH if not previously updated
if ERRORLEVEL 1 (
set Key="HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment"
for /F "USEBACKQ tokens=2*" %%A in (`reg query %%Key%% /v PATH`) do (
if not "%%~B" == "" (
rem Preserve the existing PATH
echo %%B > currpath.txt
rem Update the current session
set PATH=%PATH%;%OWNPATH%tex\texmf-%PLATFORM%\bin
rem Persist the PATH environment variable
setx PATH "%%B;%OWNPATH%tex\texmf-%PLATFORM%\bin" /M
)
)
)
1. Not strictly true
Dave Jarvis
30.5k41 gold badges179 silver badges317 bronze badges
answered Dec 29, 2016 at 12:04
icc97icc97
11.5k8 gold badges76 silver badges90 bronze badges
0
Handy if you are already in the directory you want to add to PATH:
set PATH=%PATH%;%CD%
It works with the standard Windows cmd, but not in PowerShell.
For PowerShell, the %CD% equivalent is [System.Environment]::CurrentDirectory.
answered Mar 18, 2016 at 16:09
nclordnclord
1,2871 gold badge16 silver badges17 bronze badges
2
Aside from all the answers, if you want a nice GUI tool to edit your Windows environment variables you can use Rapid Environment Editor.
Try it! It’s safe to use and is awesome!
answered Feb 17, 2016 at 4:10
NetoricaNetorica
18.6k17 gold badges74 silver badges108 bronze badges
1
- Command line changes will not be permanent and will be lost when the console closes.
- The path works like first comes first served.
- You may want to override other already included executables. For instance, if you already have another version on your path and you want to add different version without making a permanent change on path, you should put the directory at the beginning of the command.
To override already included executables;
set PATH=C:\xampp\php;%PATH%;
answered Sep 6, 2016 at 14:37
hevihevi
2,4722 gold badges34 silver badges51 bronze badges
Use pathed from gtools.
It does things in an intuitive way. For example:
pathed /REMOVE "c:\my\folder"
pathed /APPEND "c:\my\folder"
It shows results without the need to spawn a new cmd!
answered Mar 19, 2019 at 9:37
womdwomd
3,12727 silver badges20 bronze badges
1
Checking the above suggestions on Windows 10 LTSB, and with a glimpse on the «help» outlines (that can be viewed when typing ‘command /?’ on the cmd), brought me to the conclusion that the PATH command changes the system environment variable Path values only for the current session, but after reboot all the values reset to their default- just as they were prior to using the PATH command.
On the other hand using the SETX command with administrative privileges is way more powerful. It changes those values for good (or at least until the next time this command is used or until next time those values are manually GUI manipulated… ).
The best SETX syntax usage that worked for me:
SETX PATH "%PATH%;C:\path\to\where\the\command\resides"
where any equal sign ‘=’ should be avoided, and don’t you worry about spaces! There isn’t any need to insert any more quotation marks for a path that contains spaces inside it — the split sign ‘;’ does the job.
The PATH keyword that follows the SETX defines which set of values should be changed among the System Environment Variables possible values, and the %PATH% (the word PATH surrounded by the percent sign) inside the quotation marks, tells the OS to leave the existing PATH values as they are and add the following path (the one that follows the split sign ‘;’) to the existing values.
answered Nov 22, 2016 at 20:34
1
Regarding point 2, I’m using a simple batch file that is populating PATH or other environment variables for me. Therefore, there isn’t any pollution of environment variables by default. This batch file is accessible from everywhere so I can type:
mybatchfile
Output:
-- Here all environment variables are available
And:
php file.php
answered Oct 30, 2015 at 14:22
3
The below solution worked perfectly.
Try the below command in your Windows terminal.
setx PATH "C:\myfolder;%PATH%"
SUCCESS: Specified value was saved.
You can refer to more on here.
answered Jun 5, 2021 at 13:42
Use these commands in the Bash shell on Windows to append a new location to the PATH variable
PATH=$PATH:/path/to/mydir
Or prepend this location
PATH=/path/to/mydir:$PATH
In your case, for instance, do
PATH=$PATH:C:\xampp\php
You can echo $PATH to see the PATH variable in the shell.
answered Sep 1, 2021 at 6:48
kiriloffkiriloff
25.7k37 gold badges151 silver badges230 bronze badges
2
If you run the command cmd, it will update all system variables for that command window.
answered Oct 17, 2018 at 2:06
1
In a command prompt you tell Cmd to use Windows Explorer’s command line by prefacing it with start.
So start Yourbatchname.
Note you have to register as if its name is batchfile.exe.
Programs and documents can be added to the registry so typing their name without their path in the Start — Run dialog box or shortcut enables Windows to find them.
This is a generic reg file. Copy the lines below to a new Text Document and save it as anyname.reg. Edit it with your programs or documents.
In paths, use \\ to separate folder names in key paths as regedit uses a single \ to separate its key names. All reg files start with REGEDIT4. A semicolon turns a line into a comment. The @ symbol means to assign the value to the key rather than a named value.
The file doesn’t have to exist. This can be used to set Word.exe to open Winword.exe.
Typing start batchfile will start iexplore.exe.
REGEDIT4
;The bolded name below is the name of the document or program, <filename>.<file extension>
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\App Paths\Batchfile.exe]
; The @ means the path to the file is assigned to the default value for the key.
; The whole path in enclosed in a quotation mark ".
@="\"C:\\Program Files\\Internet Explorer\\iexplore.exe\""
; Optional Parameters. The semicolon means don't process the line. Remove it if you want to put it in the registry
; Informs the shell that the program accepts URLs.
;"useURL"="1"
; Sets the path that a program will use as its' default directory. This is commented out.
;"Path"="C:\\Program Files\\Microsoft Office\\Office\\"
You’ve already been told about path in another answer. Also see doskey /? for cmd macros (they only work when typing).
You can run startup commands for CMD. From Windows Resource Kit Technical Reference
AutoRun
HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Command Processor
Data type Range Default value
REG_SZ list of commands There is no default value for this entry.
Description
Contains commands which are executed each time you start Cmd.exe.
answered Dec 21, 2016 at 1:08
A better alternative to Control Panel is to use this freeware program from SourceForge called Pathenator.
However, it only works for a system that has .NET 4.0 or greater such as Windows 7, Windows 8, or Windows 10.
answered Aug 28, 2017 at 1:24
BimoBimo
6,0052 gold badges39 silver badges62 bronze badges
0
As trivial as it may be, I had to restart Windows when faced with this problem.
I am running Windows 7 x64. I did a manual update to the system PATH variable. This worked okay if I ran cmd.exe from the stat menu. But if I type «cmd» in the Windows Explorer address bar, it seems to load the PATH from elsewhere, which doesn’t have my manual changes.
(To avoid doubt — yes, I did close and rerun cmd a couple of times before I restarted and it didn’t help.)
answered Oct 20, 2019 at 18:03
svinecsvinec
6798 silver badges9 bronze badges
3
How to open the Environment Variables window from cmd.exe/Run… dialog
SystemPropertiesAdvancedand click «Environment Variables», no UACrundll32 sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariablesdirect, might trigger UAC
Via Can the environment variables tool in Windows be launched directly? on Server Fault.
How to open the Environment Variables window from Explorer
- right-click on «This PC»
- Click on «Properties»
- On the left panel of the window that pops up, click on «Advanced System Settings»
- Click on the «Advanced» tab
- Click on «Environment Variables» button at the bottom of the window
You can also search for Variables in the Start menu search.
Reference images how the Environment Variables window looks like:
Windows 10

via
Windows 7

via
Windows XP

via
-
I have installed PHP that time. I extracted php-7***.zip into C:\php</i>
-
Back up my current PATH environment variable: run
cmd, and execute command:path >C:\path-backup.txt -
Get my current path value into C:\path.txt file (the same way)
-
Modify path.txt (sure, my path length is more than 1024 characters, and Windows is running few years)
- I have removed duplicates paths in there, like ‘C:\Windows; or C:\Windows\System32; or C:\Windows\System32\Wbem; — I’ve got twice.
- Remove uninstalled programs paths as well. Example: C:\Program Files\NonExistSoftware;
- This way, my path string length < 1024 :)))
- at the end of the path string, add
;C:\php\ - Copy path value only into buffer with framed double quotes! Example: «C:\Windows;****;C:\php» No PATH= should be there!!!
-
Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator (e.g., Win + X).
-
Run command:
setx path "Here you should insert string from buffer (new path value)" -
Rerun your terminal (I use «Far Manager») and check:
php -v
answered Oct 24, 2018 at 20:50
SerbSerb
214 bronze badges
In my case it was just that I copied the path from the properties dialog box in Windows and it contained a blank character or something else in the text so it was not recognized. I pasted the path text in a plain text file and removed everything to the sides and my variable was recognized.
answered Jul 28 at 15:24
On Windows 10, I was able to search for set path environment variable and got these instructions:
- From the desktop, right-click the very bottom-left corner of the screen to get the Power User Task Menu.
- From the Power User Task Menu, click System.
- In the Settings window, scroll down to the Related settings section and click the System info link.
- In the System window, click the Advanced system settings link in the left navigation panel.
- In the System Properties window, click the Advanced tab, then click the Environment Variables button near the bottom of that tab.
- In the Environment Variables window (pictured below), highlight the Path variable in the System variables section and click the Edit button. Add or modify the path lines with the paths you want the computer to access. Each different directory is separated with a semicolon, as shown below:
C:\Program Files;C:\Winnt;C:\Winnt\System32
The first time I searched for it, it immediately popped up the System Properties Window. After that, I found the above instructions.
answered Nov 12, 2020 at 1:38
JaninJanin
2921 gold badge2 silver badges7 bronze badges
If you’re a coder or programmer, you probably spend a decent amount of time using the command prompt to execute programs or compile code. In order to complete those tasks, you most likely have to use a command from a library or software package installed (like Python) on your system.
By default, most of these programs will add their own custom shortcuts to the Windows environment variables. The most used environment variable in Windows is probably the PATH variable. It basically allows you to run any executables that are located inside the paths specified in the variable at the command prompt without having to give the full path to the executable.
In this article, I’ll show you how you can add more paths to the Windows PATH variable in case you want to run executables from your own custom directories. It’s worth noting that the procedure below is for Windows 10, but it’s almost exactly the same for Windows 7 also.
Add Directories to PATH Variable
To get started, right-click on the Computer or This PC icon on the desktop and select Properties. If you don’t have that icon on your desktop already, you can add any missing desktop icons easily.
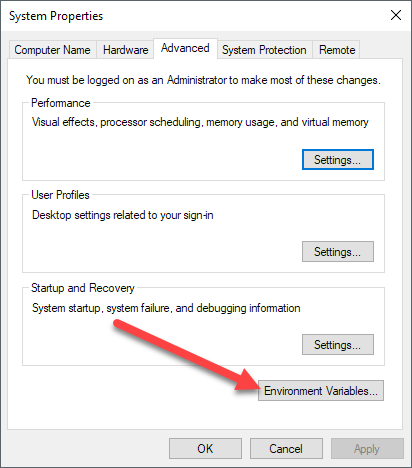
On the System dialog page, you’ll see an Advanced system settings link on the left-hand side.
This will bring up the System Properties dialog, which should already be open to the Advanced tab. Go ahead and click on the Environment Variables button at the very bottom.
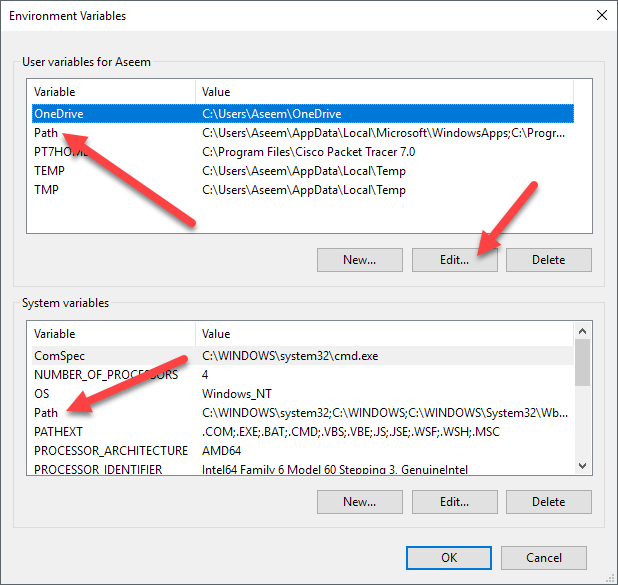
On the Environment Variables dialog, you’ll see two sets of variables: one for user variables and the other for system variables. Both lists have the PATH variable, so you have to decide which one to edit.
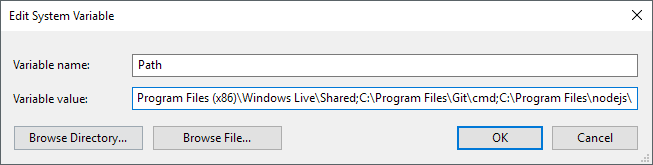
If you only need the commands for your own user account, then edit the user variable. If you need it to work across the computer system regardless of which user is logged in, then edit the system variable. Click on Path and then click on Edit.
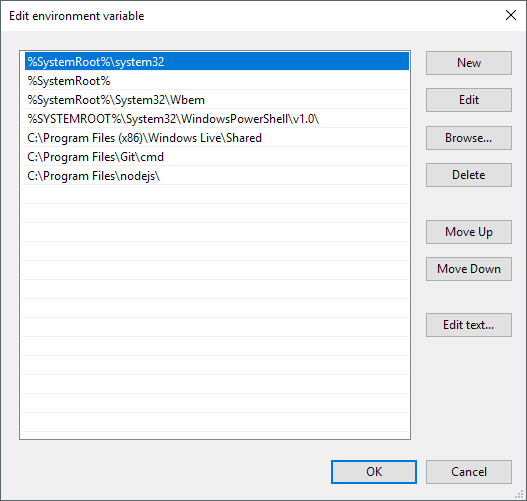
On the Edit environment variable dialog, you’ll see a list of all the paths that are currently in the PATH variable. As you can see, Node.js and Git already added their paths so that I can run Git commands and Node.js commands from anywhere while in the command prompt.
To add a new path, simply click on New and it’ll add a new line to the bottom of the list. If you know the path, simply type it in or copy and paste it. If you prefer, you can also click Browse and then navigate to the desired path.
To edit any path, simply select it and then click on the Edit button. You can also delete paths using the Delete button. Note that you can also move items up and down on the list. When you type a command at the command prompt, Windows has to search through each directory stored in the PATH variable to see if that executable exists or not. If you want your executable to be found faster, just move that path up to the top of the list.
This can also come in handy if you have multiple versions of the same command in different paths and need to have one run instead of the other. The one that shows up higher in the list will be run when you type in the command.
Lastly, if you click on Edit text, it will load a dialog where you can edit the Path variable using the old interface where all the paths are listed in one text box.
That’s all there is to it! If you want to learn more about environment variables, make sure to check out my post on how to create your own custom environment variables. Enjoy!