-
Home
-
Partition Magic
- What Is “Host Process for Windows Tasks” & Can I Disable It
By Irene |
Last Updated
If you open Task Manager, you may notice a process named “Host Process for Windows Tasks” running in the background. What is Host Process for Windows Tasks? Can I disable it? This post from MiniTool will show you the answers.
When you open Task Manager on your PC, you may find many Host Process for Windows Tasks processes running in the background. What is Host Process for Windows Tasks? Is it a virus? Can I disable it? To learn more information, please keep reading.
What Is Host Process for Windows Tasks
Host Process for Windows Tasks is a core process of Microsoft Windows. In a Windows OS, there are a lot of core processes in Windows that are used to host one to multiple Windows services. And Host Process for Windows Tasks is one of them.
To understand what Host Process for Windows Tasks is, first you should understand that in Task Manager, there are two types of processes: processes that are loaded from Executable files and processes that are loaded from DLL files.
In Windows, a service loaded from an executable (exe) can institute itself as a complete, independent process on the system and it will be listed by its own name in Task Manager. While for a service loaded from a Dynamic Linked Library (DLL) file, it cannot set itself as a full process. And in this case, Host Process for Windows Tasks will act as a host for this kind of services.
In Task Manager, you will see a separate Host Process for Windows Tasks entry running for each DLL-based service or a group of DLL-based services loaded into Windows. If you see many of the same entries, this means that more programs relying on the Host Process for Windows Tasks are currently running on your computer.
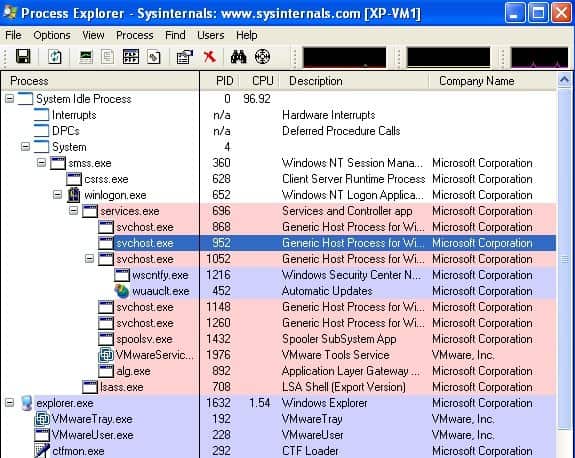
You are not able to view what services are attached to each Host Process for Windows Tasks entry in Task Manager. But other tools like Process Explorer, a utility developed by Sysinternals and acquired by Microsoft, allows you to view the full list of Processes.
If you encounter Host Process for Windows Tasks high disk or high CPU issue, you can download one to check the processes involved.
Can I Disable Host Process for Windows Tasks
You shouldn’t remove, disable or stop Host Process for Windows Tasks on your computer. Host Process for Windows Tasks plays an important role in loading DLL-based services onto your system. Disabling Host Process for Windows Tasks may cause a system crash.
So don’t end Host Process for Windows Tasks process in Task Manager, if you find Host Process for Windows Tasks consuming a lot of resources, you can use the Process Explorer to check the full list of processes, find out the responsible program and remove it directly.
Is Host Process for Windows Tasks a Virus
As mentioned before, Host Process for Windows Tasks is a core Windows process. Normally it can’t be a virus. But, it is also possible that a virus may disguise itself as the Host Process for Windows Tasks on your PC.
How to check if the Host Process for Windows Tasks on your PC is the real one?
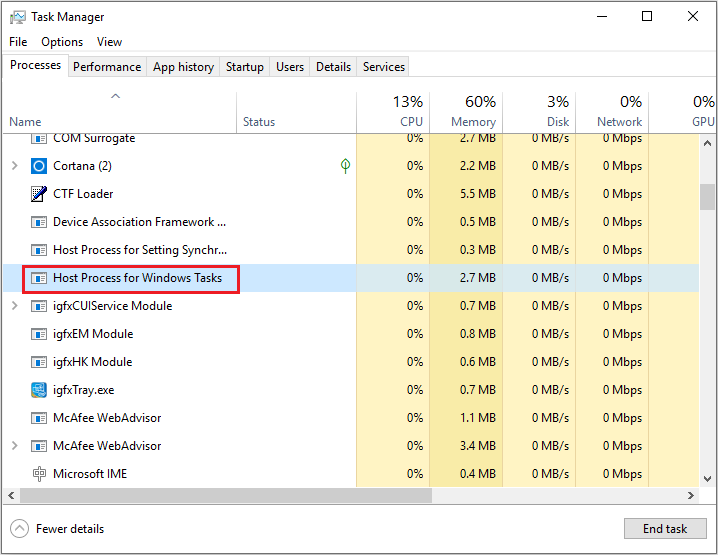
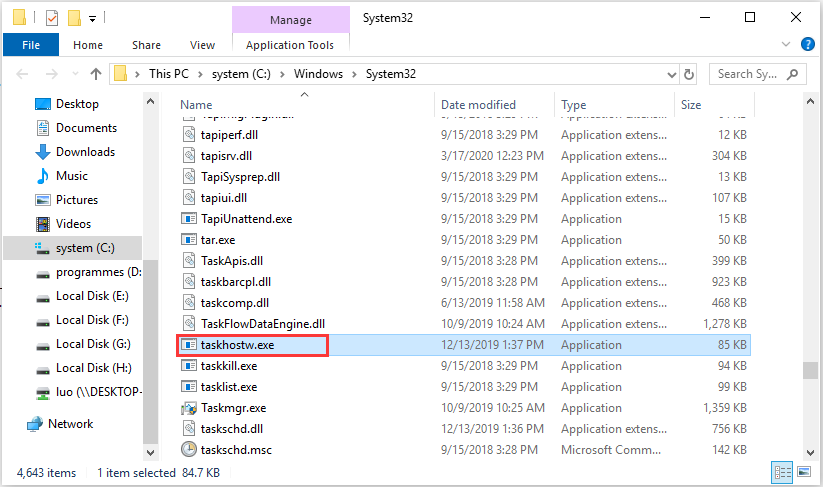
Well, you can check its file location: open Task Manager, right-click Host Process for Windows Tasks from the list and choose the Open File Location option. If the file is located in the System32 folder and it is named as taskhostw.exe, or taskhost.exe in Windows 7, it is the genuine one.
If the file is located in any other location, it could a virus. At this time, you can perform a virus check as soon as possible.
Conclusion
After reading this post, now you should know what Host Process for Windows Tasks is. Do you have different opinions about Host Process for Windows Tasks? We are glad to have you share it with us.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Irene joined MiniTool in 2018 and has since become a professional in the areas of disk management and Windows tricks. Irene’s expertise allows her to assist clients with managing their hard drives, optimizing their Windows operating system, and troubleshooting any technical issues that arise.
For years, we’ve listened to the complaints saying that the Host Process for Windows Tasks is taking up all your system resources. Obviously, when you think your system is lagging, you’ll open Windows Task Manager. In the window, you can see the list of ongoing tasks, services, and other details – in multiple tabs. If you have done that, you would have noticed something named Host Process for Windows Tasks.
The reason is simple: there are multiple entries with the same name, consuming a lot of resources at once. Some people believe that multiple numbers of Host Process for Windows Tasks is a virus. On the other hand, some expect it to be an error. But, it’s not both. In fact, before you try to stop the program or end task, you should better know about the Host Process for Windows Tasks.
Note: This is an ongoing article explaining the computer processes. You can also check other articles about CRDOWNLOAD, Windows 10 Fast User Switching, Jusched.exe, Windows Startup Repair, Windows Shell Experience Host.
In this article, we’ll talk about the Host Process for Windows Tasks in the common terms. So, the next time you see a bunch of these tasks, you’d know the right thing to do.
What is Host Process for Windows Tasks – An Introduction
Being an Operating System, Microsoft Windows has a bunch of core processes. These are required for the proper functioning of the OS as well as the installed apps. However, at times, the Host Process for Windows Tasks will have to act as a host for other services. To understand this, you should know the two types of processes. It can also be seen as svchost.exe.
First, there are processes that are loaded from Executable files. Depending on the program, you can find one file named programname.exe. These processes are seen separately in the Windows Task Manager. They do have a full stand on their own.
Secondly, there are processes loaded from DLL files. These processes cannot exist in the Task Manager list on their own. So, there comes the role of the Host Process for Windows Tasks.
In the second type of Windows processes, the Host Process for Windows Tasks will act as a host. That is, one or several DLL-based processes can be attached to this Host Process for Windows Tasks. There are certain limits as to how many processes can be attached to one entry of the Host Process for Windows Tasks. So, depending on the actual number of processes on your computer, you may see one or many entries in Task Manager.
In the simplest terms, the Host Process for Windows Tasks isn’t a dedicated task. On the other hand, it functions as a label for many other DLL-based processes on your computer. If you see a lot more entries of the same, it means a lot more programs are currently running on your PC. These are the basics to know, but we’re sure that you have some doubts.
Understanding the Real Consumers behind Host Process for Windows Tasks
We already told you that the Host Process for Windows Tasks, as such, cannot consume your system resources. Despite that fact, you might have seen an incredible resource consumption by the same task. The reason is quite simple: more programs are relying on the Host Process for Windows Tasks. That is, if you want to make the PC any faster, you need to find the real consumers behind the entry.
It’s a fact that Windows Task Manager became so better from Windows 8 and 10. Still, there isn’t any built-in way to know the programs that are consuming resources under the Host Process for Windows Tasks label. Do not worry, we have a solace – Process Explorer from Microsoft. It was actually developed by Sysinternals but was acquired by Microsoft afterward.
Process Explorer is a detailed but portable solution for knowing about Windows processes. Just download and open the app and you can see the full list of Processes. From the side-pan, you can choose taskhostw.exe and see what all programs are associated with it. In the lower window-pane, you can see the list of processes involved. From the name and location, you can assume the program responsible for high resource needs.
As said, Process Explorer is completely free to use and works portably. You can download it from here. It will help you when you think a lot of resources are being spent for the Host Process for Windows Tasks. In that case, you can find the responsible program and remove it if you don’t really need its support. In most cases, you will find some driver-related stuff in there, but there have been exceptions.
So, the download takes like just 1 minute and you can get the whole inspection done in a few minutes. And, the results are worth what you do – we mean, it’s the better to speed at the end, you know!
The Startup Scenario
During system startup, it’s natural for Host Process for Windows Tasks to consume a lot of system resources. In normal cases, your system will be back to the normal resource-consumption rates in a few minutes. Here, too, we have a simple reason.
It’s in the startup period that the Host Process for Windows Tasks will be loading the associated DLL processes into it. So, it’s preparing itself as a host. The highest level of resources will be in terms of CPU. However, if it does not go back to the normal stage after startup, you may need the help of Process Explorer.
The point here is simple: you don’t have to get tensed if the Host Process for Windows Tasks seems to consume a lot of CPU resources during System Startup. We hope that’s clear enough.
It’s Can’t Be (Mostly) a Virus – And You Don’t Have to Remove It
Many people have been asking whether Host Process for Windows Tasks is a virus! The answer is no, in most cases. Host Process for Windows Tasks is not actually used for virus infection purposes. And, you can confirm the legitimacy by doing something simple. Right click on Host Process for Windows Tasks and select option to ‘Open Location’. If you are lead to the System32 folder, it’s not a virus. Hurray!
More importantly, you must not try to Remove, Disable or Stop Host Process for Windows Tasks in your PC. It may end up in a system crash, and there will be no saving of resources either. So, the idea is to find what is consuming the actual resources and then act. Quick decisions don’t work when it comes to Host Process for Windows Tasks.
Summing Up – Host Process for Windows Tasks, Myth Debunk
This is how you can deal with most issues regarding the Host Process for Windows Tasks. As you see, it’s quite safer than you expect. All you need is a little patience and the help of some tools like Process Explorer. If you ask us, we really recommend using Process Explorer to understand what is consuming your system resources. It is because of another reason. At certain times, some spyware can be running in the background. So, if you think something is happening, an in-depth look at Windows Processes will help you.
Disclosure: Content published on TechLila is reader-supported. We may receive a commission for purchases made through our affiliate links at no extra cost to you. Read our Disclaimer page to know more about our funding, editorial policies, and ways to support us.
We often hear that the Host Process for Windows Tasks is consuming all resources of the computer. Usually, you open up the Windows Task Manager every time your system lags to check if something is wrong or not. While doing so, you must have noticed a couple of entries named “Host Process for Windows Tasks.”
Now, some people might panic upon seeing multiple entries for the same process, thinking it to be a virus or an error. If you don’t know what this “Host Process for Windows Tasks” or “Service Host” means, then this article will help you out.
Also, we’ll give you tips on what to do if the Host Process has crashed or is consuming an unusually high amount of resources.

What is Meant by the Windows Host Process And Why Are There So Many in Task Manager?
Windows has several core processes running in the background to host one or multiple of its services and the host process is one such core process. To understand what the Host Process is and why there could be a lot of entries of the same in the Task Manager, you need to know a few things about Windows OS:
First, we have the processes that are loaded from Executable files. These can also be seen in the Task Manager and are complete on their own.
Next, we have the processes written in DLL files that cannot exist on their own in the Task Manager list. However, these are easy to maintain and update and that is why Microsoft uses them so much.
The DLL files need a host process for their execution and one to multiple such DLL processes can be attached to a single entry of the Host Process.
So, to sum up, the Host Process for Windows (that you see as taskhost in Windows) is actually a label for other DLL processes. And if you see a lot of entries of the Host Process, it means that several programs are running on your computer currently.
Each Host Process for Windows on your list of tasks is a label for every DLL-based file or a group of DLL-based services loaded into your OS.
However, the Task Manager does not provide any way to check exactly what these services attached to every Host Process are. Tools like Process Explorer can help you see the exact services attached to a particular Host Process entry.
Why Does It Use So Many Resources at Windows Startup?
The CPU and memory, used by every entry of the Host Process for Windows, depends on the type of service it is attached to. As usual, every service utilizes all the resources it needs for its job and then goes back to a baseline level of activity.
But, if it comes to your attention that any single entry of Host Process uses a lot of resources than what is normal, then you need to track down what service is attached to the same (via Process Explorer or other such software). And then, troubleshoot this service.
Another thing to keep in mind is that after startup, all the entries of Host Process consume more CPU than they normally should. This isn’t anything you should be worried about because these can settle down real quick.
What happens is that after starting, the Host Process for Windows Tasks makes a list of all the DLL files that are needed to load. Then, it loads all those files and so, a considerable amount of CPU is consumed during that time.
Could This Process Be a Virus?
Host process is one of the core processes of Microsoft Windows OS. Usually, it is not a virus, but there is a possibility that a virus may be disguised as your Windows Tasks host process. Don’t worry, you can check if it is a virus or not. Here’s how:
Step 1. Open your computer’s Task Manager
Step 2. A list showing all the current tasks will be shown in the Task Manager window. Right-click on the “Host Process” option for Windows Tasks from the list.
Step 3. If you find the location of the file to be the System32 folder with a name like “taskhostw.exe” or “taskhost.exe”, then it is a genuine host process. Else, if you find it located in some other folder, then it might be a virus.
In this case, you should perform a security scan ASAP. Else, you can right-click on the entry in the task manager list, then click on “Go to Services.” Then right-click on the service and choose. “Stop”.

Can I Disable the Host Process for Windows Tasks?
It is not recommended to disable, stop, or remove the Host Process for Windows. These are essential to load the DLL-based files onto the system and so, disabling the host process might cause your system to crash.
Hence, you can’t end Host Processes but if you notice that the host process is taking a lot of resources, then you can individually check out the process responsible and remove it.
How to fix the “Host Process for Windows Tasks has stopped working” error
If a host process for Windows Tasks has stopped working message pops up, then you should try out the following troubleshooting methods:
- Repair broken BITS files
Step 1. Press the Windows and R keys together to open the Run utility.
Step 2. Type in the following:
Programdata\Microsoft\network\downloaderStep 3. Hit enter and click on “Continue” if prompted.
Step 4. The File Explorer will open up with the “Downloader” folder. Delete all the files that begin with qmgr
Step 5. Now, update your Windows OS from Settings->Update & Security->Windows Update.
2. Via the System File Checker
Step 1. Open the command prompt from the search icon next to the Start menu.
Step 2. Type in the command: sfc/scannow and then press Enter.

Step 3. The SFC scan will scan your System and repair all the corrupt files. This might take a long time.
Step 4. Once done, restart your device.
3. Run the DISM command
Step 1. Open the command prompt and type in the given commands:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /StartComponentCleanup
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth
Step 2. Press Enter after each command and then, once the commands finish execution, restart your computer.
4. Windows Memory Diagnostic tool
Step 1. Open the run utility by pressing the Windows and R keys together. Type in mdsched.exe
Step 2. Click on “Restart now and check for problems” to start a memory scan. Then, click on “Check for problems next time I start my computer”

Step 3. After a restart, the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool will check for issues.

Step 4. Once the memory scan is done, you will be able to view all the issues found.
5. By Cleaning Your Registry and Computer With CCleaner

Step 1. Download and install CCleaner from its official website.
Step 2. Now, you can click on “Run Cleaner” to start cleaning your system and then choose “Registry”
Step 3. Click on “Scan for Issues” and then, after a while on “Fix selected issues”
Step 4. Finally, restart your system.
How to fix the Host Process for Windows Tasks rundll32 high CPU, RAM, or Disk usage
- Running a script in the PowerShell
Step 1. Right-click on your Desktop (in the empty area) and click on “New” followed by “Text document.”
Step 2. Open the new text file and paste the given script:
Get-ScheduledJob | ? Name -eq “Kill SettingSyncHost” | Unregister-ScheduledJob
Register-ScheduledJob -Name “Kill SettingSyncHost” -RunNow -RunEvery “00:05:00” -Credential (Get-Credential) -ScheduledJobOption (New-ScheduledJobOption -StartIfOnBattery -ContinueIfGoingOnBattery) -ScriptBlock {
Get-Process | ?{ $_.Name -eq “SettingSyncHost” -and $_.StartTime -lt ([System.DateTime]::Now).AddMinutes(-5) } | Stop-Process -Force
}Step 3. Click on “File” from the header menu and then on “Save As” to save the text file.
Step 4. Make sure that you change the file type to “All files” while saving.
Step 5. Also, remove the “.txt” extension and rename the file to “CPU Fix.ps1” without any quotes.
Step 6. Right-click on the file and click on “Run with PowerShell”
Step 7. Remember to repeat the previous step every time your computer restarts to make sure that the process does not hog your resources.
2. Perform An Antivirus Scan of Your Computer

It is also possible that a virus has taken over your computer’s registers and is disguising itself as a Host Process consuming a lot of resources. In this case, immediately perform a full system scan with whichever antivirus software is installed on your computer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Host Process for Windows Services a virus?
No, the host process is not a virus. It is responsible for running DLL-based services but a virus might disguise itself as the host process. In such a case, inspect the individual process via Process Explorer.
Can I disable Windows Host Process Rundll32?
No, disabling Windows Host Process is not possible. It is responsible for loading important DLL files into the system and ending it might result in a system crash.
How do I fix Windows Host Process?
There are several ways to fix various errors related to the Windows host process. Please find the same in the above article.
Recommended Articles
Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
Whenever we face some performance issues with our computer, the first thing we do is open up the Task Manager, and then look for the applications or components which are using the most resources. If you are familiar with Task Manager, then you must have also noticed that at times, the ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’ or ‘Service Host’ process consuming resources. What these processes and what can you do if your Host process has stopped working or consumes high CPU, Disk or Memory usage.
Windows is essentially working just because of its Services. A large number of services running the background facilitate your daily tasks and operations. Some of these services are compiled into EXE files, and they are complete in themselves. These services show up in the Task Manager. But some services are written in DLL files, and they cannot be executed directly. Microsoft shifted to DLL files as they were easy to maintain and update from a programming point of view. DLL services require a host process, an EXE that can execute them and this is what ‘taskhost’ in Windows is.
Taskhost in Windows 11/10 is a core file located in the System32 folder and has been renamed as ‘taskhostw.exe’, from ‘taskhost.exe’ in Windows 7. If you find a file with this name in any other location, it could well be a virus and you might want to get it checked with your security software.
Each ‘Host Process for Windows Task’ is an instance of ‘taskhost’ running some service in the background. Although Windows Task Manager does not exactly let you view what services it is running, other tools can.
Host Process for Windows Services has stopped working or consuming High resources
If you see a ‘stopped working’ message box, you can try the following troubleshooting suggestions:
- Open Task Scheduler. In the left pane, click on Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows> RAC. Next, click the View Menu and select Show Hidden Tasks. In the middle pane, right-click on RAC Task and click Disable. See if this helps. If not, reverse the change made.
- Open Event Viewer and select the latest Application event log in the left pane which has a red mark. Double-click an event to view the details of the event. See if you find any useful information here. If it displays Host process for Windows has stopped working message, it could help.
- Perform Clean Boot and troubleshoot the issue manually.
There might be times when you find that this process is using high resources. You can now understand that this is caused due to the underlying service and not the process itself. Also, you might notice high consumption of resources at Windows startup. That is just because the taskhost is loading all the DLL files and schedule to run them. Once it is completed, the usage will settle down to a lower value and will remain pretty low for the rest of the time.
I mentioned earlier that the Task Manager does not let you view the underlying services. But you can use Process Explorer from Microsoft to view the services beneath the taskhost. It is a portable utility, and you can run it directly after downloading. You can use this tool to view all the details associated with the taskhost.
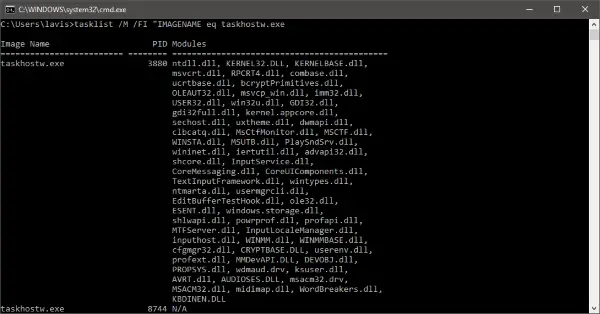
Find ‘taskhostw.exe’ in the left pane, and you can read all the details in the lower pane. Another way to view the list of DLL files loaded by taskhost is by typing in the following command in a cmd window:
tasklist /M /FI "IMAGENAME eq taskhostw.exe
This command will list all the DLL files that were loaded by this process on Windows Startup. If you go through the list, you will find out some essential files that provide core functionality to Windows.
So, in a nutshell, Taskhost is a core Windows process that provides functionality to load and execute dynamic link libraries. Since it hosts various DLL files, sometimes it can consume resources at a more than normal rate. If you are facing any such issues where the process has stopped responding or is using a lot of resources. Use the Process Explorer, Performance Monitor and Resource Monitor, and try to troubleshoot the problem manually.
Want to know about these processes, files or file types?
Windows.edb files | csrss.exe | Svchost.exe | StorDiag.exe | MOM.exe | ApplicationFrameHost.exe | ShellExperienceHost.exe | winlogon.exe | atieclxx.exe | Conhost.exe | mDNSResponder.exe.
Lavish loves to follow up on the latest happenings in technology. He loves to try out new Windows-based software and gadgets and is currently learning JAVA. He loves to develop new software for Windows. Creating a System Restore Point first before installing a new software is always recommended, he feels.
‘host process for windows tasks’ is an official microsoft system process. Processes that are loaded from executable files can be seen separately in windows task manager. Can ‘host process for windows tasks’ be disabled? no, you can’t disable it as its a system process it starts automatically. It loads all dll. …
If you have seen Task Manager Window, you might have seen a process named ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’. Also, you might have seen its multiple instances running at the same time. You might be wondering, what is this process, why is it used and can I kill it. We will resolve all your queries as you go through the post.
What is ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’?
Basically, it’s an official Microsoft System Process. There are many system processes in windows which are very important for proper functioning of the OS. To understand it, we have to understand the two types of processes that we will look below:
- Processes that are loaded from Executable files. For example, you start any application, you click on yourprogram.exe and then the process is started and your Program opens. These processes can be seen separately in Windows Task Manager. They run fully on their own i.e they are stand-alone processes.
- Processes that are loaded from DLL files. These processes need other processes to run it. The process which helps these processes that are loaded from DLL is called ‘Host Process For Windows Tasks’.
These Host Process for Windows Tasks will act as hosts for other processes. As there can be multiple instances of a DLL-based process therefore there can be multiple Host Process for Windows Tasks for each of them or there can be multiple DLL-based processes attached to a single Host Process for Windows Tasks.
Why does ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’ uses so many Resources at Windows Startup?
Basically, the CPU and Memory usage depends on each instance of Host Process for Windows Tasks on which process it is attached to. Normally, a process or service will consume resources as long as it needs to do its job and then the resources will be freed. If your system hangs or slows down, then it is due to a service which is attached to Host Process for Windows Tasks as it is consuming many resources, so you will need to track down which service is consuming most resources and troubleshoot it yourself by killing it.
At Windows Startup, you may observe many instances of Host Process for Windows Tasks and it may look that they are consuming many resources but this is normal behavior and will quickly settle down.
Why your system slows down at startup for some time?
As Host Process for Windows Tasks scans all services entries in Registry and then generates the list of all DLL-based services that need to be loaded. It then loads all those services and due to this only you notice some amount of CPU being consumed during that time.
Can ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’ be Disabled?
No, you can’t disable it as its a system process it starts automatically. And you should not try to as you know its importance, it loads all DLL-based services onto your system, and if you disable it then your system could break on any number of things. That is why you won’t be able to disable it temporarily also.
Could ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’ Process be a Virus?
No, as it’s an Official Windows Component. But it may be possible that a virus has replaced the real Host Process for Windows Tasks with its own executable process. But this is very unlikely as there is a virus known to cause this till now. However, if you want to be sure that it’s the real Host Process for Windows Tasks, then follow the steps as follows:
- Goto Task Manager
- Right Click ‘Host Proces for Windows Tasks’
- Then select ‘Open File Location’ option
The file should be stored in the WindowsSystem32 folder, by this, you can be 100 percent sure that it’s a genuine process. Otherwise, its time to clean viruses on your computer. You can use any of your best Antivirus Softwares for this.
Conclusion – What exactly is ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’?
Well by now, you must have understood that ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’ is a very important process and definitely not a virus. However, if you want to look into more depth about which process is running under it you have to use Process Explorer. Using TaskManager these processes are not visible.
I hope you would have understood the importance and use of ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’.
Thanks for reading the articles,
Hope you enjoyed reading it,
Do visit ursuperb.com for more Superb Tech Articles.
Hello friends. I am John from USA and very passionate about technology. I love reading Motivational Books, playing Piano and doing Blogging.