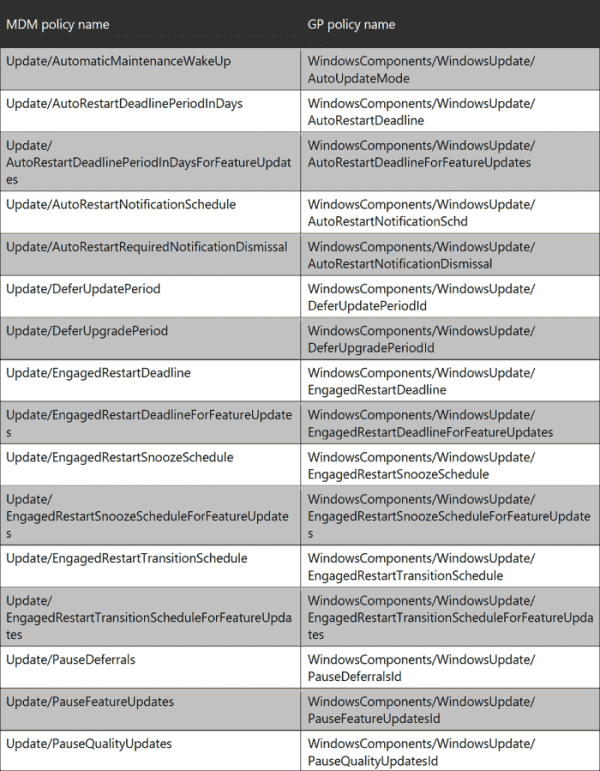
I am still pretty early in my journey of learning how to manage Windows 10 Pro updates, but I am a little encouraged to find that there are several setting in Group Policy that are not available in the UI. If it works as expected (and documented), at least with build 1709, you have these capabilities:
- Extend maximum Active Hours from 12 to 18
- Schedule updates e.g. during the night; can even restrict to certain days of the week and/or weeks of the month
- Prevent restarts if a user is logged on
The two key article on this are Build deployment rings for Windows 10 updates and Walkthrough: use Group Policy to configure Windows Update for Business (currently only updated to version 1607).
Manage device restarts after updates has valuable info on group policy settings and the corresponding registry keys for gaining control over restarts.
Even if the machine is not domain-joined, if it’s Pro, you can set these values directly in the registry. Configure Automatic Updates using Registry Editor is a reference of all registry settings.
Group Policy Setup
To see these features in Group Policy Management, you’ll have to install the latest Administrative Templates (.admx) for group policy. The 1709 templates are here.
Loosely following the “Build deployment rings” article above, I decided to create three policies:
- Windows 10 Update – Common Settings (uses WMI to target Windows 10 computers)
- Windows 10 Update – Broad Ring (uses WMI to target Windows 10 computers)
- Windows 10 Update – Fast IT Ring (applies only to my own management computer)
Note If you set your Windows 10 WMI filter to
select * from Win32_OperatingSystem Where Version like '10.%'
it will also include (and apply these policies to) Windows Server 2016. This filter forces it to apply to Windows 10 clients only:
select * from Win32_OperatingSystem Where Version like '10.%' and ProductType='1'
I’ll post my current settings in each policy below.
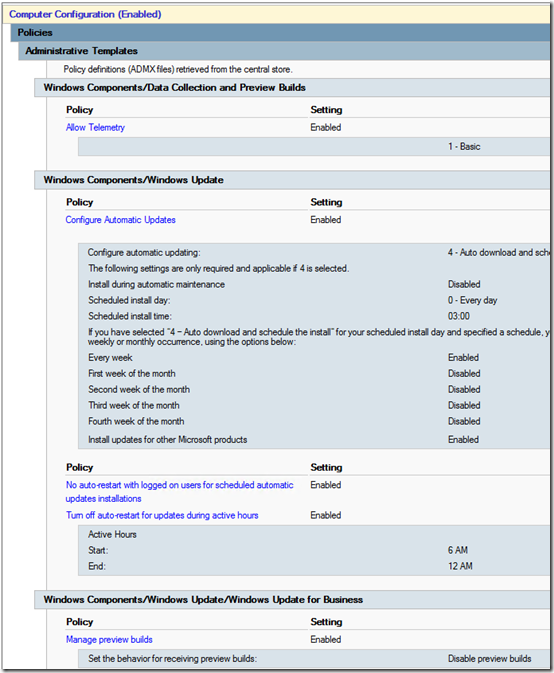
Windows 10 Update – Common Settings
Note that Allow Telemetry must be at least 1 for any of this to work, and Automatic updating must be 4 for scheduled updates to work. I’m doing 3am updates every day, don’t restart if someone is logged on, use an 18-hour Active Hours window of 6am to midnight, and block preview builds.
Update April 9, 2018 4/9/2018 If you use WSUS, under Windows Components > Windows Update, enable “Do not allow update deferral policies to cause scans against Windows Update” per Susan Bradley’s recommendation here. See more info in this TechNet article. The setting has no effect if you’re not using WSUS.
Update May 26, 2020 It turns out that “Turn off auto-restart for updates during active hours” has no effect when “No auto-restart with logged on users” is enabled (see the instructions in the GPO itself). I have now disabled “Turn off auto-restart for updates during active hours.” This allows machines to automatically reboot after installation of updates, as long as no one is logged in. Paired with a script that automatically logs off users each evening, this works pretty well to get Windows 10 machines patched without further intervention.
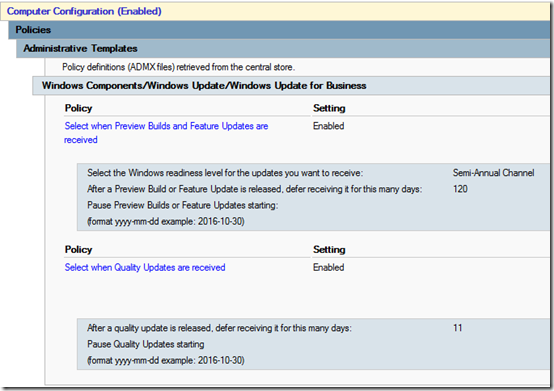
Windows 10 Update – Broad Ring
Yes, 11 days, thinking that if an update comes out on Tuesday, I want it installed on Saturday.
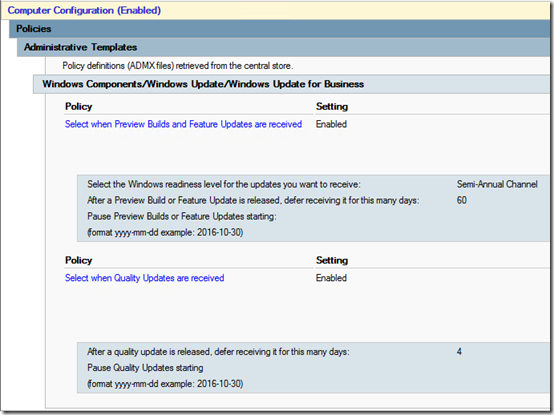
Windows 10 Update – Fast IT Ring
Not dropping to Semi-Annual (Targeted) as recommend by Microsoft; just getting the Semi-Annual Channel after 60 days instead of 120 and quality updates after 4 days.
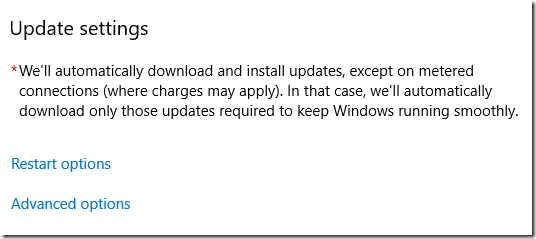
Client View
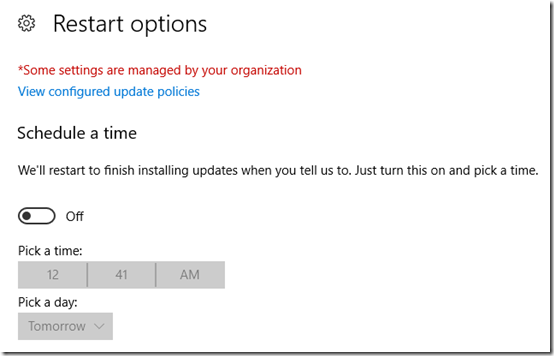
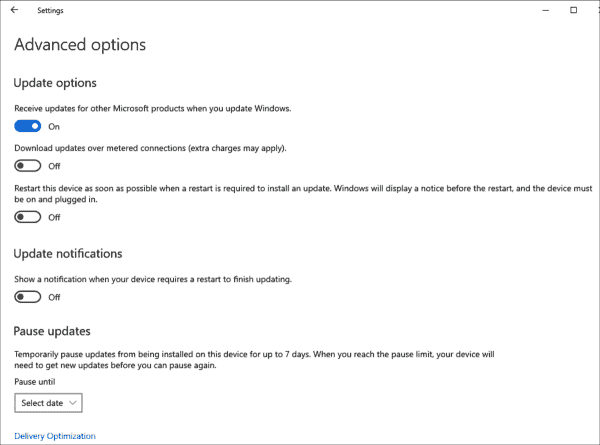
After setting up and applying the policies, it takes awhile (20-30 minutes?) until the Settings app reflects the change. The Active hours option disappears:
Restart options shows the time, but gives the option to change the schedule:
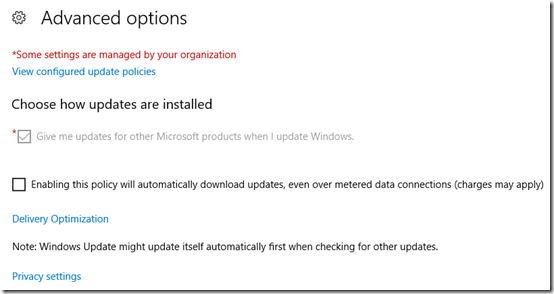
Advanced options was originally showing the 120- and 11-day values, grayed out. Maybe they will return once updates have installed.
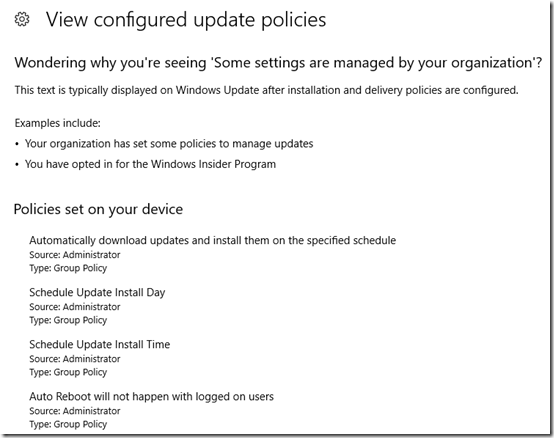
View configured update policies shows what settings are coming from Group Policy, but not what the values are:
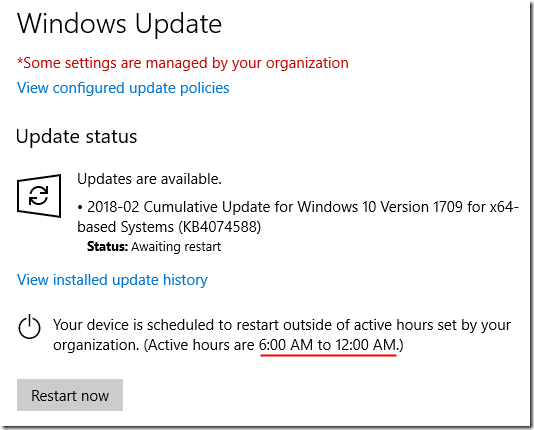
I left my computer logged on last night. It apparently installed updates overnight, but the restart was blocked by policy. I see this now:
Registry values
Most of the settings wind up in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate and the AU subkey. Here’s what those keys look like in a domain-joined Windows 10 1709 machine (paste to a .reg file if you want to import). This list does not include “Do not allow update deferral policies to cause scans against Windows Update” as it was created for a non-WSUS environment.
Update May 26, 2020 This now shows a Windows 10 1909 machine with the SetActiveHours option disabled. See details above.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate] "DeferFeatureUpdates"=dword:00000001 "BranchReadinessLevel"=dword:00000020 "DeferFeatureUpdatesPeriodInDays"=dword:00000078 "PauseFeatureUpdatesStartTime"="" "DeferQualityUpdates"=dword:00000001 "DeferQualityUpdatesPeriodInDays"=dword:0000000b "PauseQualityUpdatesStartTime"="" "ManagePreviewBuilds"=dword:00000001 "ManagePreviewBuildsPolicyValue"=dword:00000000 "DisableDualScan"=dword:00000001 "SetActiveHours"=dword:00000000 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU] "NoAutoRebootWithLoggedOnUsers"=dword:00000001 "NoAutoUpdate"=dword:00000000 "AUOptions"=dword:00000004 "ScheduledInstallDay"=dword:00000000 "ScheduledInstallTime"=dword:00000003 "ScheduledInstallEveryWeek"=dword:00000001 "AllowMUUpdateService"=dword:00000001
In this post I’ll walk through how I manage and test the delivery of Windows Updates to all my clients and servers. I’ll also go through how I manage essential servers like Domain Controllers, Hyper-V hosts and I’ll touch on getting started with Cluster-Aware Updating. We’re going to group our machines into Clients and Servers, and then group each of those groups into Ring 1 and Ring 2. If you want, you can create more rings for more control, but generally I find two rings are sufficient.
Ring 1 Testing
Updates are initially approved here and installed on specially selected machines that you have chosen. For clients I’d suggest a cross section of users, preferably who are communicative and easy to work with. I find it helps if they have volunteered to begin your victims beta testers. For servers, you’ll want a selection of non-critical servers running a variety of services.
Ring 2 General Availability
When updates have passed testing, they can be approved for general availability and installed on all clients and servers.
Special Note
I know that a lot of people have the viewpoint that they “shouldn’t have to be testing Microsoft’s updates for them” and I can understand this frustration, but the reality is that currently the updates coming out have issues that aren’t being picked up by internal testing. So to look at it from a slightly different perspective; you’re not testing for Microsoft, you’re doing your due diligence, testing for your systems to maximise up time and also reduce the stress and extra work that you and/or your team have to cope with.
Getting Started
To put this all in place we need to create some Group Policy Objects, Active Directory groups and make some changes to WSUS. To Install and configure Active Directory Domain Controllers, click here. To install and configure WSUS, click here.
Create the following Group Policy Objects:
- WSUS_General
- WSUS_Clients_Ring1
- WSUS_Servers_Ring1
Create the following Active Directory groups:
- WSUS_Clients_Ring1
- WSUS_Clients_Ring2
- WSUS_Servers_Ring1
- WSUS_Servers_Ring2
Create the follow computer groups in WSUS:
- Clients — Ring 1
- Clients — Ring 2
- Servers — Ring 1
- Servers — Ring 2
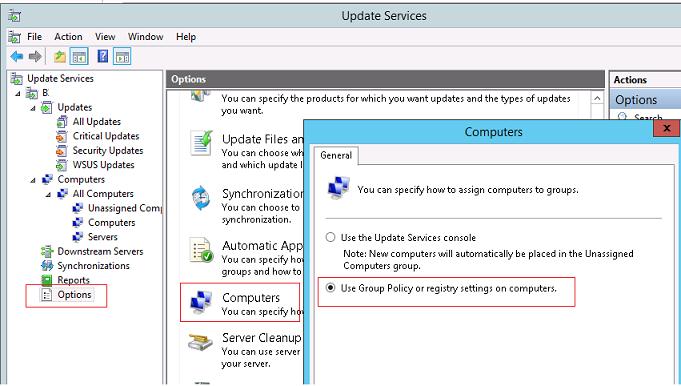
You’ll also need to change some options in WSUS: Under the Options node, go to Computers and select Use Group Policy or registry settings on computers.
Group Policy Object Settings
The WSUS_General GPO is where we will configure core settings that we want to apply to all computers regardless of which ring they will be in. Configure the following settings:
Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Delivery Optimization
Download Mode > Enabled — Lan (1)
Explanation: Enable the above setting to allow your clients and servers to download updates from each other. They will still only download and install updates that have been approved for their group, but it will lighten the load on your WSUS server.
Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Windows Update
Specify intranet Microsoft update service location > Enabled
Set the intranet update service for detecting updates > http://wsus.contoso.com:8530
Set the intranet statistics server > http://wsus.contoso.com:8530
Set the alternate download server > http://wsus.contoso.com:8530
Download files with no Url in the metadata if alternate download server is set > Disabled
Client Group Policy Object Settings
We’re now going to configure the WSUS_Clients_Ring1 GPO. We’re going to use this GPO as a template for the other client ring GPOs too. The reason we’re not putting all these common settings in the general GPO above, is because these settings control the installation of updates and if we need to tweak them in future, we can test the settings first using the ring system.
Configure the settings in the WSUS_Clients_Ring1 GPO as below:
Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Windows Update
Automatic Updates detection frequency > Enabled
Check for updates at the following interval (hours) > 4
Configure Automatic Updates > Enabled
Configure automatic updating > 4 — Auto download and schedule the install
Install during automatic maintenance > Disabled
Scheduled install day > 0 — Every day
Scheduled install time > 17:00
Every week > Enabled
Install updates for other Microsoft products > Disabled
Configure auto-restart reminder notifications for updates > Enabled
Specify the period for auto-restart reminder notifications > 60
Enable client-side targeting > Enabled
Target group name for this computer > Clients — Ring 1
No auto-restart with logged on users for scheduled automatic updates installations > Disabled
Specify deadline before auto-restart for update installation > Enabled
Specify the number of days before a pending restart will automatically be executed outside of active hours:
Quality Updates (days) > 7
Feature Updates (days) > 7
Turn off auto-restart for updates during active hours > Enabled
Active Hours Start > 8 AM
Active Hours End > 5 PM
Explanation: With the settings above, this should provide a good balance of getting updates installed without interrupting users. The active hours ensure that automatic reboots will not happen during these hours. Now we’re going to ensure that this GPO only applies to the clients we want it to by using Active Directory groups and Security Filtering on the GPO.
Using Group Policy Management, go to Group Policy Objects > WSUS_Clients_Ring1 and click on the GPO.
Select the Scope tab in the larger right hand pane, and under the Security Filtering section, remove the Authenticated Users group and add the WSUS_Clients_Ring1 group we created earlier.
You might be wondering why we didn’t create the WSUS_Clients_Ring2 GPO above. We’re going to copy the WSUS_Clients_Ring1 and use it as a template.
To copy the Group Policy, right-click on the WSUS_Clients_Ring1 and select Copy, then right-click on the Group Policy Objects node in the left hand side of the Group Policy Management console and select Paste.
Specify the permissions for the new GPO and then click on OK.
You will now have a GPO called Copy of WSUS_Clients_Ring1. Rename the GPO to WSUS_Clients_Ring2 and then edit it and change the setting below:
Target group name for this computer > Clients — Ring 2
Server Group Policy Object Settings
We’re now going to setup the WSUS_Servers_Ring1. Like the client GPO this as a template for the other server ring GPOs too. The reason we’re not putting all these common settings in the general GPO, is because these settings control the installation of updates and if we need to tweak them in future, we can test the settings first.
Configure the settings in the WSUS_Servers_Ring1 GPO as below.
Allow Automatic Updates immediate installation > Enabled
Automatic Updates detection frequency > Enabled
Check for updates at the following interval (hours) > 4
Configure Automatic Updates > Enabled
Configure automatic updating > 4 — Auto download and schedule the install
Install during automatic maintenance > Disabled
Scheduled install day > 0 — Every day
Scheduled install time > 06:00
Every week > Enabled
Install updates for other Microsoft products > Disabled
Enable client-side targeting > Enabled
Target group name for this computer > Servers — Ring 1
No auto-restart with logged on users for scheduled automatic updates installations > Disabled
Turn off auto-restart for updates during active hours > Enabled
Active Hours Start > 6AM
Active Hours End > 11PM
Explanation: With the settings above, the servers should reboot only when an update requires it and only outside of the active hours configured. It’s important to note that the Active Hours can only have a maximum range of 18 hours.
Now just like the clients GPO we’re going to set up this GPO so it only applies to the servers we want it to by using Active Directory groups and Security Filtering on the GPO.
Using Group Policy Management, go to Group Policy Objects > WSUS_Servers_Ring1 and click on the GPO. Select the Scope tab in the larger right hand pane, and under the Security Filtering section, remove the Authenticated Users group and add the WSUS_Servers_Ring1 group we created earlier.
We’re now going to copy the WSUS_Servers_Ring1 and use it as a template for the ring 2 GPO. To copy the Group Policy, right-click on the WSUS_Servers_Ring1 and select Copy, then right-click on the Group Policy Objects node in the left hand side of the Group Policy Management console and select Paste.
Specify the permissions for the new GPO and then click on OK. You will now have a GPO called Copy of WSUS_Servers_Ring1. Rename the GPO to WSUS_Servers_Ring2 and then edit it and change the setting below:
Target group name for this computer > Servers — Ring 2
Putting It All Together
In Active Directory, find the computer accounts you want to use for testing updates and add them to the group WSUS_Clients_Ring1. Add all the other computer accounts to the WSUS_Clients_Ring2 group.
Next add the servers that you are going top test updates on to the WSUS_Servers_Ring1 group, and the other servers to the WSUS_Servers_Ring2 group.
Do not add Domain Controllers, Hyper-V hosts or servers that are in clusters, we’ll cover how to manage updates for these later on.
Link the WSUS_General GPO to the most top level Organisational Unit(s) you can that contains the computer accounts you want to receive the settings.
Now link the WSUS_Clients_Ring1 GPO to the OU(s). Only the computer accounts that are in the WSUS_Clients_Ring1 group will receive the settings.
Repeat these steps for the WSUS_Clients_Ring2 GPO and the WSUS_Servers_Ring_1 & 2 GPOs.
Over time (a reboot may be required for the settings to fully take effect) the clients and servers should begin to appear in the WSUS console under the Computers node in the configured groups.
Domain Controllers
I separate domain controllers from the other servers because they need to have a staggered reboot from each other. If they reboot at the same time the whole domain goes down, and this is a bad thing not desirable. To do this I create GPOs for each DC, with different install times and I put the DCs in ring 2, so they only install updates which have been tested.
Here are the settings for the WSUS_DC01_Ring2 GPO:
Allow Automatic Updates immediate installation > Enabled
Automatic Updates detection frequency > Enabled
Check for updates at the following interval (hours) > 4
Configure Automatic Updates > Enabled
Configure automatic updating > 4 — Auto download and schedule the install
Install during automatic maintenance > Disabled
Scheduled install day > 0 — Every day
Scheduled install time > 01:00
Every week > Enabled
Install updates for other Microsoft products > Disabled
Enable client-side targeting > Enabled
Target group name for this computer > Servers — Ring 2
No auto-restart with logged on users for scheduled automatic updates installations > Disabled
Turn off auto-restart for updates during active hours > Enabled
Active Hours Start > 6 AM
Active Hours End > 11 PM
The GPO settings for WSUS_DC02_Ring2 are the same, except I set a different install time:
Scheduled install time > 02:00
This gives DC01 an hour to install, restart and stabilize before DC02 installs its updates and restarts. We now need to link the GPOs to the DCs. One way we can accomplish this is by linking the GPOs to the Domain Controllers OU and set security filtering on the GPOs for each DC.
So WSUS_DC01_Ring2 would have Authenticated Users removed from security filtering and the DC01$ computer account would be in its place.
However, I’ve had trouble getting this to work recently. So, I’ve taken to creating an OU for each DC, and then linking the GPO to the OU and leaving Authenticated Users in the security filtering. See below:
[
This may not be the best way to do it, but for a small number of DCs, I think it’s good enough. For larger numbers of DCs (more than four I’d say), I’d recommend creating groups, and grouping up the DCs, as with running more than four DCs rebooting a couple at the same time shouldn’t be an issue.
Hyper-V Hosts
Like with Domain Controllers, I separate the Hyper-V hosts if they are not in a cluster. For the Hyper-V hosts I copy the WSUS_Servers_Ring2 GPO and set the install time setting to something that doesn’t conflict with the DCs or the other servers.
Since Windows Server 2012 R2 there’s been a setting for updates to Install during automatic maintenance. This sounds like a good idea as it installs updates and restarts at a random point within a period of time that you can set. Unfortunately, I’ve never been able to get it to work reliably on Windows Server 2016 and 2019, so I don’t use it.
Here are the settings for my WSUS_VS01_Ring2 GPO:
Allow Automatic Updates immediate installation > Enabled
Automatic Updates detection frequency > Enabled
Check for updates at the following interval (hours) > 4
Configure Automatic Updates > Enabled
Configure automatic updating > 4 — Auto download and schedule the install
Install during automatic maintenance > Disabled
Scheduled install day > 0 — Every day
Scheduled install time > 03:00
Every week > Enabled
Install updates for other Microsoft products > Disabled
Enable client-side targeting > Enabled
Target group name for this computer > Servers — Ring 2
No auto-restart with logged on users for scheduled automatic updates installations > Disabled
Turn off auto-restart for updates during active hours > Enabled
Active Hours Start > 6 AM
Active Hours End > 11 PM
I don’t configure security filtering on this GPO, leaving Authenticated Users in place.
Cluster-Aware Updating (CAU)
Cluster-Aware Updating is entirely different and doesn’t use Group Policy at all, except to disable Windows managing updates itself. To use Cluster-Aware Updating, open the application named Cluster-Aware Updating in the Windows Administration Tools and connect to the failover cluster you wish to manage.
Once connected you can configure how you want updates to be installed and when just like with Group Policy, except CAU manages the installs and reboots for each node in a cluster, making sure the cluster stays up. One change you have to make when setting up Cluster-Aware Updating is disabling Windows from managing updates using GPO. To achieve this, it’s best if you have an Organisation Unit setup for each cluster, and all the AD objects for that cluster inside the OU. We’ll create a GPO named WSUS_Disabled_CAU and disable Automatic Updates entirely.
Computer Configuration/Policies/Administrative Templates/Windows Components/Windows Update
Configure Automatic Updates > Disable
Link this GPO to the OU containing the cluster objects and now the cluster should install updates as configured in the Cluster-Aware Updating tool.
If you have any questions or comments please leave them below.
-Mike
В одной из предыдущих статей мы подробно описали процедуру установки сервера WSUS на базе Windows Server 2012 R2 / 2016. После того, как вы настроили сервер, нужно настроить Windows-клиентов (сервера и рабочие станции) на использование сервера WSUS для получения обновлений, чтобы клиенты получали обновления с внутреннего сервера обновлений, а не с серверов Microsoft Update через Интернет. В этой статье мы рассмотрим процедуру настройки клиентов на использование сервера WSUS с помощью групповых политик домена Active Directory.
Содержание:
- Групповая политика WSUS для серверов Windows
- Политика установки обновлений WSUS для рабочих станций
- Назначаем политики WSUS на OU Active Directory
Групповые политики AD позволяют администратору автоматически назначить компьютеры в различные группы WSUS, избавляя его от необходимости ручного перемещения компьютеров между группами в консоли WSUS и поддержки этих групп в актуальном состоянии. Назначение клиентов к различным целевым группам WSUS основывается на метке в реестре на клиенте (метки задаются групповой политикой или прямым редактированием реестра). Такой тип соотнесения клиентов к группам WSUS называется client side targeting (Таргетинг на стороне клиента).
Предполагается, что в нашей сети будут использоваться две различные политики обновления — отдельная политика установки обновлений для серверов (Servers) и для рабочих станций (Workstations). Эти две группы нужно создать в консоли WSUS в секции All Computers.
Совет. Политика использования сервера обновлений WSUS клиентами во многом зависит от организационной структуры OU в Active Directory и правил установки обновлении в организации. В этой статье мы рассмотрим всего лишь частный вариант, позволяющий понять базовые принципы использования политик AD для установки обновлений Windows.
В первую очередь необходимо указать правило группировки компьютеров в консоли WSUS (targeting). По умолчанию в консоли WSUS компьютеры распределяются администратором по группам вручную (server side targeting). Нас это не устраивает, поэтому укажем, что компьютеры распределяются в группы на основе client side targeting (по определенному ключу в реестре клиента). Для этого в консоли WSUS перейдите в раздел Options и откройте параметр Computers. Поменяйте значение на Use Group Policy or registry setting on computers (Использовать на компьютерах групповую политику или параметры реестра).
Теперь можно создать GPO для настройки клиентов WSUS. Откройте доменную консоль управления групповыми политиками (Group Policy Management) и создайте две новые групповые политики: ServerWSUSPolicy и WorkstationWSUSPolicy.
Групповая политика WSUS для серверов Windows
Начнем с описания серверной политики ServerWSUSPolicy.
Настройки групповых политик, отвечающих за работу службы обновлений Windows, находятся в разделе GPO: Computer Configuration -> Policies-> Administrative templates-> Windows Component-> Windows Update (Конфигурация компьютера -> Административные шаблоны -> Компоненты Windows -> Центр обновления Windows).
В нашей организации мы предполагаем использовать данную политику для установки обновлений WSUS на сервера Windows. Предполагается, что все попадающие под эту политику компьютеры будут отнесены к группе Servers в консоли WSUS. Кроме того, мы хотим запретить автоматическую установку обновлений на серверах при их получении. Клиент WSUS должен просто скачать доступные обновления на диск, отобразить оповещение о наличии новых обновлений в системном трее и ожидать запуска установки администратором (ручной или удаленной с помощью модуля PSWindowsUpdate) для начала установки. Это значит, что продуктивные сервера не будут автоматически устанавливать обновления и перезагружаться без подтверждения администратора (обычно эти работы выполняются системным администратором в рамках ежемесячных плановых регламентных работ). Для реализации такой схемы зададим следующие политики:
- Configure Automatic Updates (Настройка автоматического обновления): Enable. 3 – Auto download and notify for install (Автоматически загружать обновления и уведомлять об их готовности к установке) – клиент автоматически скачивает новые обновлений и оповещает об их появлении;
- Specify Intranet Microsoft update service location (Указать размещение службы обновлений Майкрософт в интрасети): Enable. Set the intranet update service for detecting updates (Укажите службу обновлений в интрасети для поиска обновлений): http://srv-wsus.winitpro.ru:8530, Set the intranet statistics server (Укажите сервер статистики в интрасети): http://srv-wsus.winitpro.ru:8530 – здесь нужно указать адрес вашего сервера WSUS и сервера статистики (обычно они совпадают);
- No auto-restart with logged on users for scheduled automatic updates installations (Не выполнять автоматическую перезагрузку при автоматической установке обновлений, если в системе работают пользователя): Enable – запретить автоматическую перезагрузку при наличии сессии пользователя;
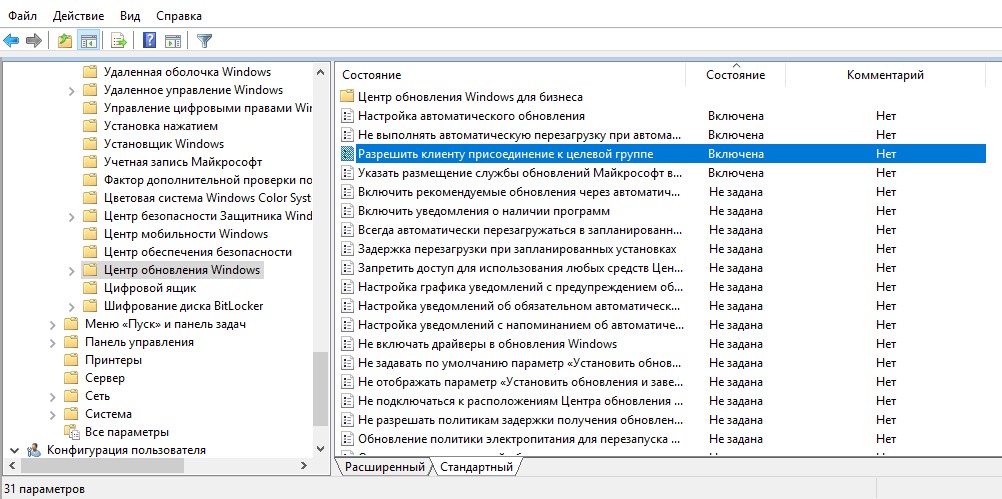
- Enable client-side targeting (Разрешить клиенту присоединение к целевой группе): Enable. Target group name for this computer (Имя целевой группу для данного компьютера): Servers – в консоли WSUS отнести клиенты к группе Servers.
Примечание. При настройке политики обновления советуем внимательно познакомиться со всеми настройками, доступными в каждой из опций раздела GPO Windows Update и задать подходящие для вашей инфраструктуры и организации параметры.
Политика установки обновлений WSUS для рабочих станций
Мы предполагаем, что обновления на клиентские рабочие станции, в отличии от серверной политики, будут устанавливаться автоматически ночью сразу после получения обновлений. Компьютеры после установки обновлений должны перезагружаться автоматически (предупреждая пользователя за 5 минут).
В данной GPO (WorkstationWSUSPolicy) мы указываем:
- Allow Automatic Updates immediate installation (Разрешить немедленную установку автоматических обновлений): Disabled — запрет на немедленную установку обновлений при их получении;
- Allow non-administrators to receive update notifications (Разрешить пользователям, не являющимся администраторами, получать уведомления об обновлениях): Enabled — отображать не-администраторам предупреждение о появлении новых обновлений и разрешить их ручную установку;
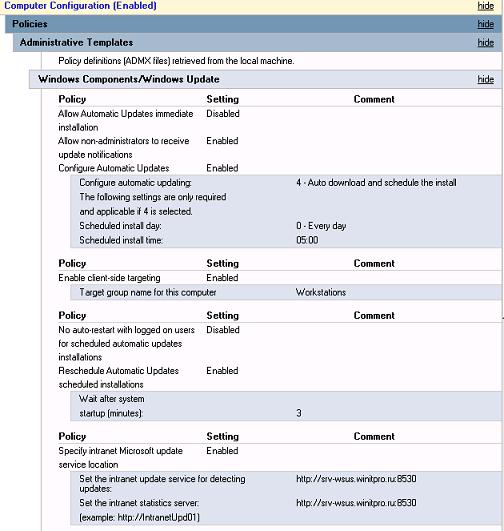
- Configure Automatic Updates: Enabled. Configure automatic updating: 4 — Auto download and schedule the install. Scheduled install day: 0 — Every day. Scheduled install time: 05:00 – при получении новых обновлений клиент скачивает в локлаьный кэш и планирует их автоматическую установку на 5:00 утра;
- Target group name for this computer: Workstations – в консоли WSUS отнести клиента к группе Workstations;
- No auto-restart with logged on users for scheduled automatic updates installations: Disabled — система автоматически перезагрузится через 5 минут после окончания установки обновлений;
- Specify Intranet Microsoft update service location: Enable. Set the intranet update service for detecting updates: http://srv-wsus.winitpro.ru:8530, Set the intranet statistics server: http://srv-wsus.winitpro.ru:8530 –адрес корпоративного WSUS сервера.
В Windows 10 1607 и выше, несмотря на то, что вы указали им получать обновления с внутреннего WSUS, все еще могут пытаться обращаться к серверам Windows Update в интернете. Эта «фича» называется Dual Scan. Для отключения получения обновлений из интернета нужно дополнительно включать политику Do not allow update deferral policies to cause scans against Windows Update (ссылка).
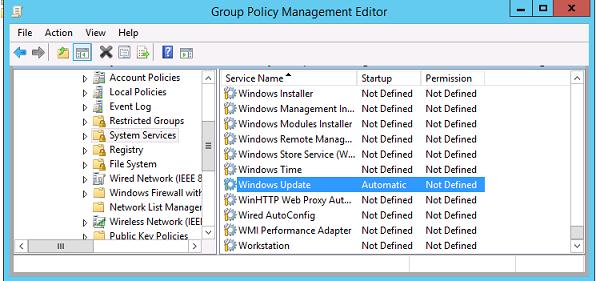
Совет. Чтобы улучшить «уровень пропатченности» компьютеров в организации, в обоих политиках можно настроить принудительный запуск службы обновлений (wuauserv) на клиентах. Для этого в разделе Computer Configuration -> Policies-> Windows Setings -> Security Settings -> System Services найдите службу Windows Update и задайте для нее автоматический запуск (Automatic).
Назначаем политики WSUS на OU Active Directory
Следующий шаг – назначить созданные политики на соответствующие контейнеры (OU) Active Directory. В нашем примере структура OU в домене AD максимально простая: имеются два контейнера – Servers (в нем содержаться все сервера организации, помимо контроллеров домена) и WKS (Workstations –компьютеры пользователей).
Совет. Мы рассматриваем лишь один довольно простой вариант привязки политик WSUS к клиентам. В реальных организациях возможно привязать одну политику WSUS на все компьютеры домена (GPO с настройками WSUS вешается на корень домена), разнести различные виды клиентов по разным OU (как в нашем примере – мы создали разные политики WSUS для серверов и рабочих станций), в больших распределенных доменах можно привязывать различные WSUS сервера к сайтам AD, или же назначать GPO на основании фильтров WMI, или скомбинировать перечисленные способы.
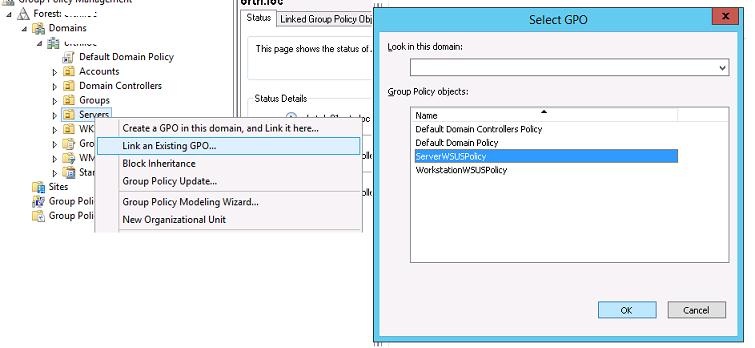
Чтобы назначить политику на OU, щелкните в консоли управления групповыми политиками по нужному OU, выберите пункт меню Link as Existing GPO и выберите соответствующую политику.
Совет. Не забудьте про отдельную OU с контроллерами домена (Domain Controllers), в большинстве случаев на этот контейнер следует привязать «серверную» политику WSUS.
Точно таким же способом нужно назначить политику WorkstationWSUSPolicy на контейнер AD WKS, в котором находятся рабочие станции Windows.
Осталось обновить групповые политики на клиентах для привязки клиента к серверу WSUS:
gpupdate /force
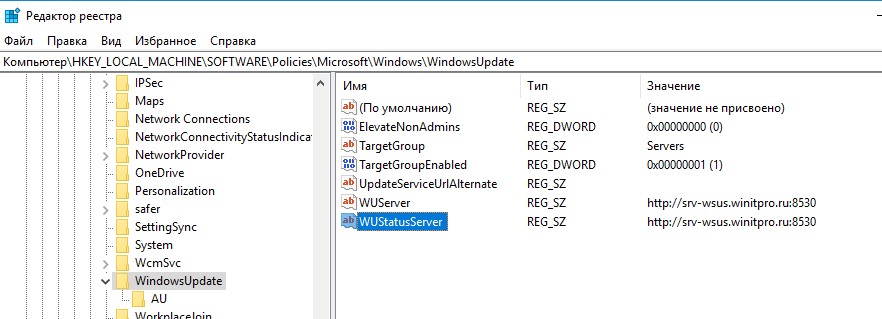
Все настройки системы обновлений Windows, которые мы задали групповыми политиками должны появится в реестре клиента в ветке HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate.
Данный reg файл можно использовать для переноса настроек WSUS на другие компьютеры, на которых не удается настроить параметры обновлений с помощью GPO (компьютеры в рабочей группе, изолированных сегментах, DMZ и т.д.)
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate]
"WUServer"="http://srv-wsus.winitpro.ru:8530"
"WUStatusServer"="http://srv-wsus.winitpro.ru:8530"
"UpdateServiceUrlAlternate"=""
"TargetGroupEnabled"=dword:00000001
"TargetGroup"="Servers"
"ElevateNonAdmins"=dword:00000000
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\AU]
"NoAutoUpdate"=dword:00000000 –
"AUOptions"=dword:00000003
"ScheduledInstallDay"=dword:00000000
"ScheduledInstallTime"=dword:00000003
"ScheduledInstallEveryWeek"=dword:00000001
"UseWUServer"=dword:00000001
"NoAutoRebootWithLoggedOnUsers"=dword:00000001
Также удобно контролировать применённые настройки WSUS на клиентах с помощью rsop.msc.
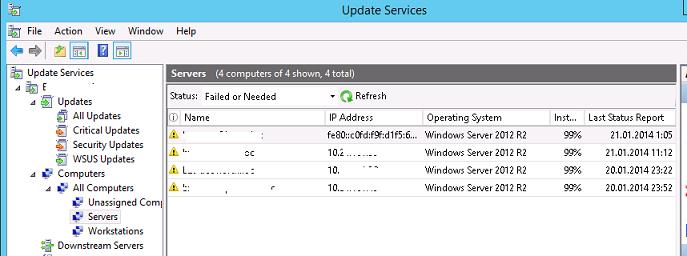
И через некоторое время (зависит от количества обновлений и пропускной способности канала до сервера WSUS) нужно проверить в трее наличие всплывающего оповещений о наличии новых обновлений. В консоли WSUS в соответствующих группах должны появиться клиенты (в табличном виде отображается имя клиента, IP, ОС, процент их «пропатченности» и дата последнего обновлений статуса). Т.к. мы политиками привязали компьютеры и серверы к различным группам WSUS, они будут получать только обновления, одобренные к установке на соответствующие группы WSUS.
Примечание. Если на клиенте обновления не появляются, рекомендуется внимательно изучить на проблемном клиенте лог службы обновлений Windows (C:\Windows\WindowsUpdate.log). Обратите внимание, что в Windows 10 (Windows Server 2016) используется другой формат журнала обновлений WindowsUpdate.log. Клиент скачивает обновления в локальную папку C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution\Download. Чтобы запустить поиск новых обновлений на WSUS сервере, нужно выполнить команду:
wuauclt /detectnow
Также иногда приходится принудительно перерегистрировать клиента на сервере WSUS:
wuauclt /detectnow /resetAuthorization
В особо сложных случаях можно попробовать починить службу wuauserv так. При возникновении ошибки 0x80244010 при получении обновлений на клиентах, попробуйте изменить частоту проверки обновлений на сервере WSUS с помощью политики Automatic Update detection frequency.
В следующей статье мы опишем особенности одобрения обновлений на сервере WSUS. Также рекомендуем ознакомиться со статьей о переносе одобренных обновлений между группами на WSUS сервере.
With Windows 10 1903, Microsoft introduced a new Group Policy setting to speed up the distribution of updates. It overrides a number of older options. In addition, they will soon deprecate several Windows Update settings, giving admins less control.
Contents
- Countdown starting with the release of an update
- Interaction with active hours
- Converting from notifications to reminders
- New setting deactivates four old ones
- Various update settings outdated
- Outlook
- Author
- Recent Posts
Wolfgang Sommergut has over 20 years of experience in IT journalism. He has also worked as a system administrator and as a tech consultant. Today he runs the German publication WindowsPro.de.
Microsoft has repeatedly introduced new concepts to determine when to download and install updates and when to restart the computer. These concepts are reflected in a long list of settings, some of which are mutually exclusive or no longer have any effect in Windows 10.
The aim of all methods is to get security-critical updates to computers as quickly as possible and to set the reboots in such a way that they will not interrupt users’ work or even cause them to lose data.
Countdown starting with the release of an update
The primary goal of the new setting Specify deadlines for automatic updates and restarts is to ensure update distribution as quickly as possible. Therefore, the configured deadlines relate to the patch release dates.
A new setting for Windows Update allows you to force the installation of patches within a certain period
All previous options for controlling reboots only began counting from the point at which the update was installed and a restart was pending.
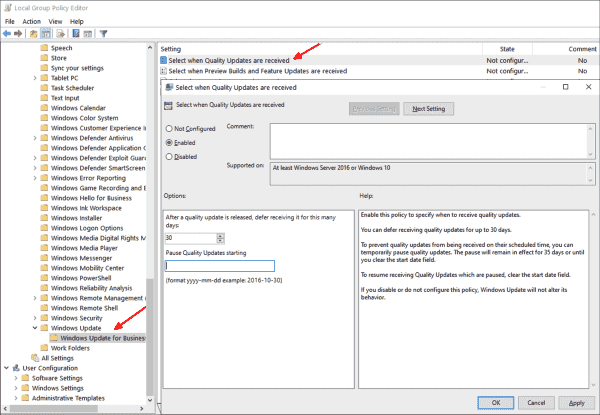
This applies, for example, to Specify the deadline before a pending restart will automatically be executed outside of active hours. Microsoft only introduced this setting with Windows 10, and it is the predecessor of the new option.
Both options let you set your own deadlines for quality and feature updates, up to a maximum of 30 days (the default is 7 days). After the deadlines expire, users can no longer postpone restarting their computers, and updates will take effect immediately afterward.
However, the new setting offers two additional options. First, you can set an additional «grace period» so that users do not have to restart their computers immediately after a long absence, for example, after returning to work from a holiday.
Interaction with active hours
Furthermore, the option Do not restart automatically until end of grace means that computers will only be updated after a manual reboot within the set period. If you do not check this box, Windows will try to find a convenient time for a reboot outside of the «active hours.»
After the grace period expires, Windows Update will force users to reboot even during working hours.
This option has the same effect as the setting Turn off auto-restart for updates during active hours. However, this requires a static definition of the active hours.
To prevent restarts during active hours, specify the start and end times
Since version 1903, Windows 10 determines the active hours automatically based on user activity. If you want to use this feature, you should therefore avoid defining fixed start and end times.
Converting from notifications to reminders
During the defined period, the update client changes the way it interacts with the user. In the first few days, it uses toast notifications to alert the user to a pending update.
After that, it automatically switches to the Engaged restart reminder, where the user can initiate a reboot immediately, schedule it for a specific time, or simply postpone it.
After a few days, Windows 10 switches to the insistent reminder
You can explicitly configure the switch from the toast notification to the more urgent version using the setting Specify Engaged restart transition and notification schedule for updates. Here you set the time for the notification change yourself.
Up till now, you could configure the changeover of upcoming update notifications exactly, but the new option disallows this
However, if you use the new setting to plan the restart, it will override the configuration for this transition. The new option is therefore much more robust than the previous one, which always deactivated itself in case of conflicts.
New setting deactivates four old ones
The goal is largely to determine the behavior of the update installation and the reboot with a single setting. This is also demonstrated by the fact that it eliminates another important option. Until now, it was possible for users to prevent reboots as long as they were logged in. However, this no longer applies with the new setting.
In summary, the new setting overrides four previous ones if they are enabled. These are:
- Specify the deadline before a pending restart will automatically be executed outside of active hours
- Specify Engaged restart transition and notification schedule for updates
- Always automatically restart at the scheduled time
- No auto-restart with logged-on users for scheduled automatic update installations
Various update settings outdated
A recent Microsoft white paper contains a table with Group Policy Object (GPO) and mobile device management (MDM) settings for Windows Update that the vendor recommends you should disable. They are either obsolete or will be phased out in the near future.
GPO and MDM settings for Windows Update that Microsoft recommends you no longer use
Interestingly, this also includes the configuration of automatic updates. As is well known, this setting is required for clients who get their updates from WSUS. Thus, group policies in this respect only catch up with the settings app where automatic update configuration has already disappeared with previous versions of Windows 10.
The GUI no longer provides configuration of automatic updates
The Microsoft document does not detail the impact of this decision, but in another section, it says that in case of delayed updates, you should check whether Dual Scan was intentionally deactivated, and hence, clients switched back to WSUS.
Outlook
This means Microsoft apparently considers Dual Scan to be the preferred configuration. Thus, the big picture for the new update management becomes visible. Users should generally obtain OS updates via Windows Update and restrict WSUS to other products such as Office. WSUS support for the Unified Update Platform has not been available to date and may never come, which further confirms this.
Client configuration will boil down to a single setting described above, which sets deadlines for installing the updates. It completely defines the system behavior during this phase. It’s possible to adjust the power options via GPO to increase the maintenance window for patch management as a complementary action.
The goal of these changes is to speed up update distribution by disallowing admins from explicitly approving patches as in WSUS. And users can only delay rebooting their computers up to a maximum of 30 days after an update’s release.
The same timeframe is available to admins in Windows Update for Business (WUfB) to postpone quality updates. However, the recommendation in Microsoft’s white paper is two to three days. Overall, there’s no additional deferral gained by this because with the new setting, the clock is ticking from the time Microsoft releases an update.
Subscribe to 4sysops newsletter!
WUfB also only grants a 30 day delay from the release of a quality update
The new setting’s importance is also clear because Microsoft has updated the servicing stack of older Windows 10 versions (1709 and later) to support it there also. But to configure it, you need the .admx templates for 1903 or 1909.
When a Configuration Manager client is installed and configured to use the software updates agent, it will automatically configured with a local Group Policy setting that specifies the Configuration Manager software update point. The Group Policy setting used is the intranet Microsoft update service location, specified as a Windows Update computer administrative template.
The following snippet shows the local group policy setting for the client that is enabled with software update agent.
GPO:
In case you have a local Group Policy setting that is configured with Microsoft update service location which will always be overwritten by an Active Directory Group Policy setting, and this can result in the Configuration Manager client failing to obtain software updates using Configuration Manager.
Jason has written 2 blogs on GPO and software update management, please read the following.
https://home.memftw.com/software-update-management-and-group-policy-for-configmgr-what-else/
https://home.memftw.com/software-updates-management-and-group-policy-for-configmgr-cont/
It is always recommended to create GPO to disable automatic updates and let the software update patching happens through ConfigMgr. This will help you to do the windows update patching in a controlled way.
So until now, you have a good understanding of the software update management and group policy.
One of my customer recently reached out to me and asking for help to block users doing manual windows update process on their devices.
The reason they want to block all available windows update options is that recently Microsoft released an update (KB4577586 ) to remove Adobe flash from windows.
Removing of the adobe flash will impact their applications (legacy) that use adobe flash.
When I have asked customer to send a screenshot of the windows update setting, it has the following.
As you can see above, 1st option, It already has the automatic updates disabled through GPO so there wont be any automatic windows update process but if you look at the 2nd, user still have option to click on ‘Check online for updates from Microsoft update’ and do windows update.
Configuring the GPO ‘Disable automatic updates’ will only help to disable the automatic update schedule that happens every day night around 3AM or so but it will still leave an option for user to click on ‘Check online for updates from Microsoft update’. This process will initiate the windows update, search, download, install and reboot the device.
In the above screenshot, I have a GPO to turn off automatic updates but user can still trigger the windows update using Check online for updates from Microsoft update.
How do we disable/hide ‘Check online for updates from Microsoft update’?
Create a GPO and configure the following setting.
Computer Configuration/Administrative Templates/System/Internet Communication Management/Internet Communication settings
Turn off access to all Windows Update features = Enabled
Link the GPO to test OU, test the windows store and update functions before deploying the policy to all production machines.
End-results:
The policy will now hide ‘Check online for updates from Microsoft update’ setting.
There is new registry key that gets created with this setting.
Registry Path:
Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\WindowsUpdate\DisableWindowsUpdateAccess
Hope it helps!