The third-party Git Credential Manager (GCM) can be used as alternative method of connecting to Bitbucket Cloud from the Git CLI. If you do not want to configure SSH access for your Bitbucket Cloud account, you can use the GCM, which is installed by default with Git for Windows, or you can download and install it from Git Credential Manager on GitHub. Note that the GCM works over HTTPS, not SSH. Ensure your Git remotes are using HTTPS, such as:
git clone https://{username}@bitbucket.org/{workspace}/{repository}.git
The Secure Shell protocol (SSH) is used to create secure connections between your device and Bitbucket Cloud. The connection is authenticated using public SSH keys, which are derived from a private SSH key (also known as a private/public key pair). The secure (encrypted) connection is used to securely transmit your source code between your local device and Bitbucket Cloud. To set up your device for connecting Bitbucket Cloud using SSH, you need to:
-
Install OpenSSH on your device.
-
Start the SSH service.
-
Create an SSH key pair.
-
Add your key to the SSH agent.
-
Provide Bitbucket Cloud with your public key.
-
Check that your SSH authentication works.
Install OpenSSH on Microsoft Windows
There are 3 methods for installing OpenSSH on Microsoft Windows:
-
Download and run the Git for Windows installer.
-
Use winget to run the Git for Windows installer.
-
Install the Windows version of OpenSSH.
Download and install Git for Windows
-
Download and run the installer from https://gitforwindows.org/. The options at each step should be suitable. When you reach the step about choosing the SSH executable, ensure the bundled OpenSSH is selected.
-
Once the installation is complete, open Git Bash from the Start menu.
In the terminal, check that OpenSSH has been successfully installed by running the following command:
1
ssh -V
The output should show the installed version of OpenSSH.
Install Git for Windows with winget
To install OpenSSH as part of Git for Windows with the Windows package manager winget:
-
Check that winget is installed. Open PowerShell and run:
1
winget -v -
To install Git for Windows using winget install, run:
1
winget install --id Git.Git -e --source winget -
Once the installation is complete, open Git Bash from the Start menu.
In the terminal, check that OpenSSH has been successfully installed by running the following command:
1
ssh -V
The output should show the installed version of OpenSSH.
Install the Windows version of OpenSSH
This procedure assumes Git is already installed and accessible in PowerShell. If Git is installed and not accessible in PowerShell, you may need to add Git to the PATH environmental variable.
To install the Windows version of OpenSSH, follow the instructions in the Microsoft Docs Get Started with OpenSSH for Windows guide. Once OpenSSH is installed, you need to configure Git to use OpenSSH.
In PowerShell, check that OpenSSH has been successfully installed by running the following command:
1
ssh -V
The output should show the installed version of OpenSSH.
To find where ssh was installed, run Get-Command. For example:
1
2
3
4
5
> Get-Command ssh
CommandType Name Version Source
----------- ---- ------- ------
Application ssh.exe 8.1.0.1 C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\ssh.exe
To configure Git to use the Windows version of OpenSSH, update the SSH command with git config, such as:
1
git config --global core.sshCommand C:/Windows/System32/OpenSSH/ssh.exe
Start the SSH agent
To allow git to use your SSH key, an SSH agent needs to be running on your device. The method for starting the SSH agent depends on how OpenSSH was installed.
Git for Windows users (including Winget-based Git installations)
From a git bash terminal, check if the SSH agent is running using the ps command. If the ssh-agent is already running, it should appear in the output, such as:
1
2
$ ps -a | grep ssh-agent
tkelly 3291 0.0 0.0 6028 464 ? Ss 07:29 0:00 ssh-agent
To start the agent:
1
eval $(ssh-agent)
You may need to add this command to your ~/.bashrc to ensure the agent starts when you open a Git Bash terminal.
Windows OpenSSH users
From a PowerShell, check if the SSH Agent is running using the Get-Service command. For example:
1
2
3
4
5
> Get-Service ssh-agent
Status Name DisplayName
------ ---- -----------
Stopped ssh-agent OpenSSH Authentication Agent
To start the agent:
1
> Start-Service ssh-agent
To configure the SSH agent to start each time the device is started, use the Set-Service command, such as:
1
> Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Create an SSH key pair
To create an SSH key pair:
-
Open a terminal and navigate to your home or user directory using cd, for example:
1
cd ~ -
Generate a SSH key pair using ssh-keygen, such as:
1
ssh-keygen -t ed25519 -b 4096 -C "{username@emaildomain.com}" -f {ssh-key-name}Where:
-
{username@emaildomain.com} is the email address associated with the Bitbucket Cloud account, such as your work email account.
-
{ssh-key-name} is the output filename for the keys. We recommend using a identifiable name such as bitbucket_work.
-
-
When prompted to Enter passphrase, you can either provide a password or leave the password empty. If you input a password, you will be prompted for this password each time SSH is used, such as using Git command that contact Bitbucket Cloud (such as git push, git pull, and git fetch). Providing a password will prevent other users with access to the device from using your keys.
Once complete, ssh-keygen will output two files:
-
{ssh-key-name} — the private key.
-
{ssh-key-name}.pub — the public key.
These files will be stored in your user folder, such as C:\Users\<username>\<ssh-key-name>.
Add your key to the SSH agent
To add the SSH key to your SSH agent (ssh-agent):
-
Run the following command, replacing the {ssh-key-name} with the name of the private key:
1
ssh-add ~/{ssh-key-name} -
To ensure the correct SSH key is used when connecting to Bitbucket, update or create your SSH configuration file (~/.ssh/config) with the following settings:
1
2
3
Host bitbucket.org
AddKeysToAgent yes
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/{ssh-key-name}Where {ssh-key-name} is the location of the private key file once it has been added to the ssh-agent.
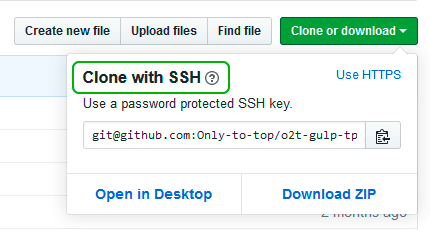
Provide Bitbucket Cloud with your public key
To add an SSH key to your user account:
-
Select the Settings cog on the top navigation bar.
-
From the Settings dropdown menu, select Personal Bitbucket settings.
-
Under Security, select SSH keys.
-
Select Add key.
-
In the Add SSH key dialog, provide a Label to help you identify which key you are adding. For example, Work Laptop <Manufacturer> <Model>. A meaning full label will help you identify old or unwanted keys in the future.
-
Open the public SSH key file (public keys have the .pub file extension) in a text editor. The public key should be in the .ssh/ directory of your user (or home) directory. The contents will be similar to:
1
ssh-ed25529 LLoWYaPswHzVqQ7L7B07LzIJbntgmHqrE40t17nGXL71QX9IoFGKYoF5pJKUMvR+DZotTm user@example.com -
Copy the contents of the public key file and paste the key into the Key field of the Add SSH key dialog.
-
Select Add key.
-
If the key is added successfully, the dialog will close and the key will be listed on the SSH keys page.
-
If you receive the error That SSH key is invalid, check that you copied the entire contents of the public key (.pub file).
-
Check that your SSH authentication works
To test that the SSH key was added successfully, open a terminal on your device and run the following command:
1
ssh -T git@bitbucket.org
If SSH can successfully connect with Bitbucket using your SSH keys, the command will produce output similar to:
1
2
3
authenticated via ssh key.
You can use git to connect to Bitbucket. Shell access is disabled
bdbch
Posted on
• Updated on
Welcome to my first official guide on Dev.to. Today I want to explain how you can setup SSH and Git on your Windows 10 computer.
Note: This is not about 100% securing your keys but about how to generate keys for use with GitHub.
Thanks to garethdd for his constructive feedback.
What is SSH?
SSH stands for Secure Shell and is an awesome way to authenticate yourself on remote servers (for example the Github server) without typing in a password everytime.
SSH works via two keys, the Private Key and the Public Key. While the private key should always stay private and safe, the public key can be shared around the internet without any problems.
The private key allows you to get access to servers that have your public key registered, so your access can only be stolen if the attacker somehow gets your Secret Key so keep it safe!
SSH should be preinstalled on new Windows 10 machines.
What is Git?
Git is a free version management tool that helps you to versionize your code and potentially save it on a remote server (for example Github, Gitlab or Bitbucket).
You can install Git from here:
https://git-scm.com/download/win
You can also install Git via chocolatey:
choco install git -Y
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Create a SSH Key
The first step is to generate a new SSH key. Use cmd or Powershell and run the following command:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
You can but don’t need to give it a passphrase since you should never share your secret key around but using one will secure your keys. Keep in mind that everybody can have as many private keys as they want.
This generates a new private SSH key with rsa encryption and 4096 bits. It also generates a public key from the secret key which you can share around.
There will be a new folder and files in your Windows user folder.
In general you can create as many keys as you want. The id_rsa key is the default key generated by ssh and will be automatically be used by your ssh-agent if you don’t tell it to use another key.
What is an ssh-agent?
An ssh-agent is the agent process used to actually authenticate yourself with ssh. There are a few out there (PuTTY with Pageant for example) but for this example we’ll use the ssh-agent provided by the native and default Windows 10 ssh-agent.
If you want to you can use PuTTY and Pageant to make your keys even more secure. Read this post on Digital Ocean for more information.
If you want to change the key used by your ssh-agent, you must first start the service. The service will be disabled on Windows 10 by default. Search for Services and open the Services settings and look for the «OpenSSH Authentication Agent» and Activate it:
Now you will be able to access the ssh-agent from your console via ssh-agent.
For this example we’re going to try to load another key called example into our agent and use it instead of the id_rsa key. To do this you can run the following command:
ssh-add example
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Now you will have both keys available for this session.
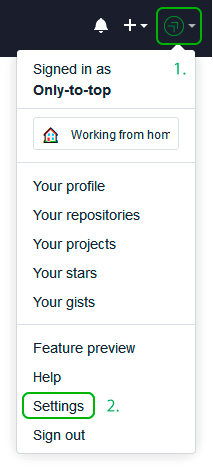
Register your SSH Key on Github
The next step is to register your generated SSH key on Github. For that, run the following command:
type C:\Users\your_user_name\.ssh\id_rsa.pub
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
and copy the output string into your clipboard. Now go to your Github keys settings and add a new SSH key with your public key and save it.
Congratulations! You now are able to get and push code to Github without any password!
Note: There should also be a C:\Users\your_user_name\.ssh\id_rsa file. This is your private key, don’t share this around!
Setup Github in your Shell
Now it’s time to setup Git on your machine. After installing it from the link above, open a new cmd or Powershell window. Now we need to set your public Git name and Git email address. This will always be public when pushing code.
Luckily Github gives you a privatized email address for use. Go to https://github.com/settings/emails and you will find a @users.noreply.github.com email address for your account. Copy this email address.
Next register your name and email in Git:
git config --global user.name "Your Name"
git config --global user.email your_email@users.noreply.github.com
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Congratulations! Now all your Commits will be registered as being commited from your Github user.
Signing your GitHub commits (Optional Step)
To sign your commits you first must install the GPG command line tools. After you installed the GPG toolkit, you can run the following command to generate a new gpg key:
gpg --full-generate-key
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
This will ask you what kind of key you want. Go for RSA and RSA.
Now you need to enter a bit length. The recommendation is 4096 bits.
After that you can specify a expiration length or if the key should never expire. Pick as you want. Expiring keys are more secure in general because you have to renew them every now and then.
Now enter your personal informations to verifying your identity with your gpg key.
When you’re done you will be asked for a passphrase. Give it a secure passphrase and you will be done with your gpg-key generation.
After that you will be able to find your key in your users .gnupg folder as specified in the success message.
If you want to list your gpg keys, simply run
// short version
gpg --list-secret-keys
// long version
gpg --list-secret-keys --keyid-format LONG
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Your GPG key you can share with Github is the key coming after sec rsa4096/ so for example in
/Users/hubot/.gnupg/secring.gpg
------------------------------------
sec 4096R/3AA5C34371567BD2 2016-03-10 [expires: 2017-03-10]
uid Hubot
ssb 4096R/42B317FD4BA89E7A 2016-03-10
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
the gpg key would be 3AA5C34371567BD2
To get your public key block, simply run
gpg --armor --export YOUR_GPG_KEY
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
which will output your public GPG Key Block. Copy it and paste it to your GitHub Account here.
From now on your commits will be signed when commited.
Use Git
Now you’re ready to actually use Git. From now you can clone repositories via git clone or push new code to Github. Here is a quick reference:
# Clone a repository to the current directory
git clone [REPOSITORY_CLONE_URL]
# Create a new commit with a message
git commit -m "Your commit message"
# Add files to the commit
git add .
git add ./filename.ext
# Push your commits to Github
git push origin master
git push origin [YOUR_BRANCH_NAME]
# Reset your repo to the last version
git reset --hard
# Create a new branch
git checkout -b [YOUR_BRANCH_NAME]
# Switch branches
git checkout [YOUR_BRANCH_NAME]
git checkout master
# Reset a single file
git checkout ./filename.ext
Enter fullscreen mode
Exit fullscreen mode
Conclusion
Thanks for reading this post. I hope it helped you with the setup. If you need help or have questions let me know!
Prepararation
- Create a folder at the root of your user home folder
(Example:C:/Users/uname/) called.ssh. - Create the following files if they do not already
exist (paths begin from the root of your user home
folder):.ssh/config.bash_profile.bashrc
Create a New SSH Key
Follow the steps in the section named «Generating a new SSH
Key» found in the following documentation from GitHub:
Generating a new SSH key and adding it to the ssh-agent
Configure SSH for Git Hosting Server
Add the following text to .ssh/config (.ssh should be found
in the root of your user home folder):
Host github.com
Hostname github.com
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Enable SSH Agent Startup Whenever Git Bash is Started
First, ensure that following lines are added to .bash_profile,
which should be found in your root user home folder:
test -f ~/.profile && . ~/.profile test -f ~/.bashrc && . ~/.bashrc
Now, add the following text to .bashrc, which should be found
in your root user home folder:
# Start SSH Agent #---------------------------- SSH_ENV="$HOME/.ssh/environment" function run_ssh_env { . "${SSH_ENV}" > /dev/null } function start_ssh_agent { echo "Initializing new SSH agent..." ssh-agent | sed 's/^echo/#echo/' > "${SSH_ENV}" echo "succeeded" chmod 600 "${SSH_ENV}" run_ssh_env; ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa; } if [ -f "${SSH_ENV}" ]; then run_ssh_env; ps -ef | grep ${SSH_AGENT_PID} | grep ssh-agent$ > /dev/null || { start_ssh_agent; } else start_ssh_agent; fi
Инструменты
Git SSH Windows — пошаговое руководство
Дата размещения статьи 08/12/2019 👁31067
Git SSH Windows — пошаговое руководство
Настроим пошагово Git SSH для Windows 10. Это позволит вам выполнять команды git без ввода пароля от своей учетной записи GitHub.
Порядок действий:
- Генерация ключа SSH.
- Добавление SSH-ключа в ssh-agent.
- Добавление ключа SSH в учетную запись GitHub.
Генерация ключа SSH
Откройте bash/терминал. Добавьте следующий текст, подставив свой адрес электронной почты GitHub.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "ваша@почта.com"Будет создан ключ ssh, используя e-mail в качестве метки.
Когда вам будет предложено «Введите файл, в котором вы хотите сохранить ключ», нажмите Enter. Это установит в местоположение по умолчанию.
Enter a file in which to save the key (/c/Users/you/.ssh/id_rsa):[Press enter]
Далее введите безопасную фразу-пароль дважды или просто нажмите Enter.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Type a passphrase]
Enter same passphrase again: [Type passphrase again]
Добавление SSH-ключа в ssh-agent
Чтобы запустить ssh-агент введите следующую команду.
На экране отобразится похожая строка.
Agent pid 31724
Добавим свой закрытый ключ SSH в ssh-agent. Если вы создали свой ключ с другим именем (или добавляете существующий ключ с другим именем), замените в команде id_rsa на имя вашего файла закрытого (приватного) ключа.
Ключ будет успешно добавлен в ssh-агент.
Добавление ключа SSH в учетную запись GitHub
Мы сгенерировали у себя на компьютере закрытый ключ SSH и добавили его в ssh-агент. Теперь нам необходимо добавить SSH ключ в учетную запись GitHub.
Сейчас нам необходимо скопировать SSH ключ в буфер обмена.
Способов есть несколько, но я же вам предлагаю следующее решения для Windows 10: введите команду ниже.
Прямо в терминале вы увидите содержимое необходимого файла с ключем. Скопируйте его в буфер.
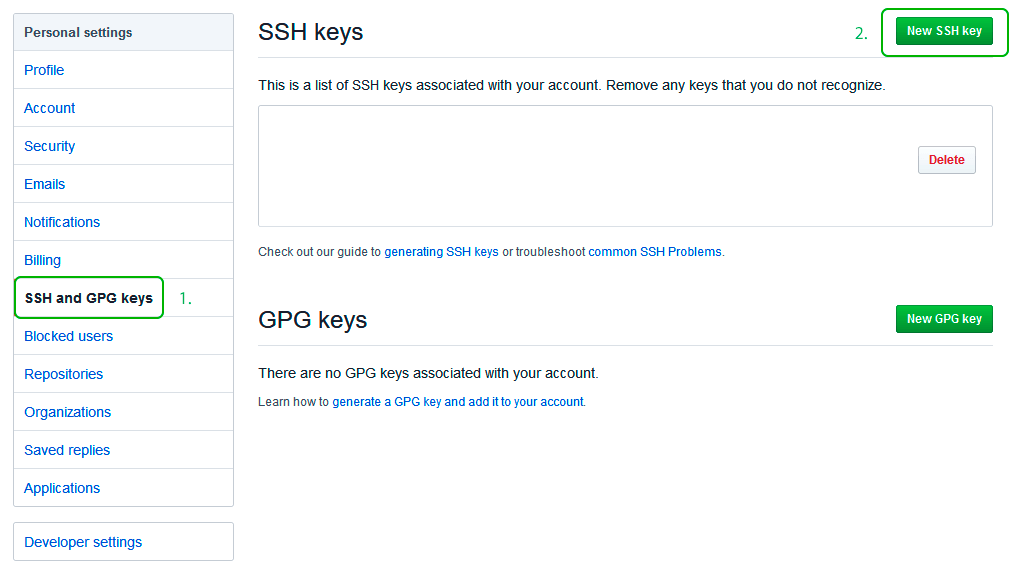
Теперь зайдите на вашу страницу GitHub » Settings.
Перейдите во вкладку SSH and GPG keys и нажмите на кнопку New SSH key для добавления SSH ключа в вашу учетную запись GitHub.
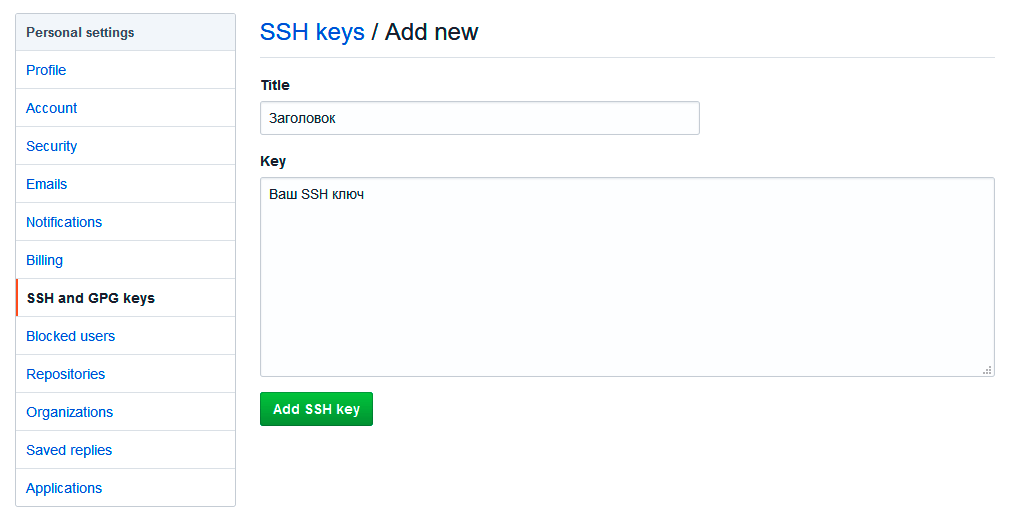
В поле Title добавьте заголовок для данного ключа. Например, если вы захотите настроить SSH доступ на нескольких устройствах, то вы будите понимать какой ключ принадлежит какому устройству.
В поле Key добавьте свой ssh-ключ, который вы скопировали в буфер обмена на предыдущем шаге.
Нажмите Add SSH key.
Для подтверждения вам потребуется ввести свой пароль от учетной записи GitHub.
На этом настройка SSH для вашего устройства завершена, теперь вы можете работать с git без ввода пароля от своей учетной записи.
Если вам понравилась данная статья, можете прочитать как настроить моментальную загрузку сайта на хостинг и синхронизацию файлов.
JavaScript: Window Location Checkbox Checked — Проверка Состояния Чекбокса ✔️
Надеюсь, вам понравилась данная информация. Если вам интересна тема web-разработки,
то можете следить за выходом новых статей в Telegram.
- Настройка Gulp Babel
- Микроразметка сайта
- Как перенести сайт WordPress на хостинг
- Настройте показ всего текста во время загрузки веб-шрифтов
- Сниппеты в VS Code
- Не удается проверить так как не задан исполняемый PHP-файл
Время на прочтение
2 мин
Количество просмотров 107K
Много статей (в том числе и на Хабре) посвящено подключению к Git по SSH-ключам. Почти во всех из них используется один из двух способов: либо с помощью puttygen.exe, либо командами ssh-keygen или ssh-add.
Вчера на одном из компьютеров у меня не получилось сделать это для msysgit ни одним из описанных в интернете способов, и я потратил несколько часов на попытки настроить SSH-доступ, так ни чего и не добившись.
Как я решил эту проблему — под катом.
BitBucket всё время ругался на то, что ему требуется подключение с помощью ключа:
Permission denied (publickey).
fatal: Could not read from remote repository.
Please make sure you have the correct access rights and the repository exists.
Мои попытки сгенерировать ключи, указать пути в переменных среды, привязать ключи к гиту были бесполезны. Либо гит ругался крякозябрами (в случае ssh-agent cmd.exe), либо просто игнорировал всё предложенное.
Решение оказалось куда удобнее и проще. Достаточно запустить в локальном репозитории GIT GUI Here, и в меню перейти в
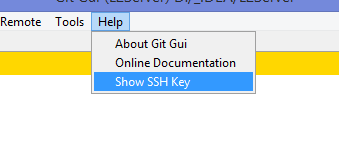
Help -> Show SSH Key:
Скрины
Если вы столкнулись с такой проблемой, то скорее всего у вас там ни чего не будет:
Окно генерации SSH Key
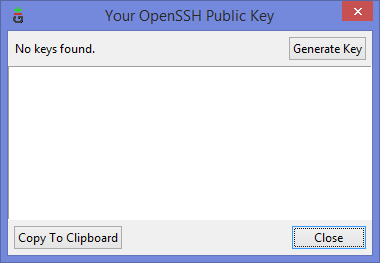
Ну а дальше читать будут, скорее всего, только самые педантичные… Жмём Generate key, видим окно запроса пароля (два раза) для приватного ключа:
Запрос пароля
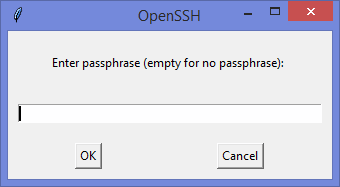
И видим сгенерировавшийся публичный ключ:
Публичный ключ

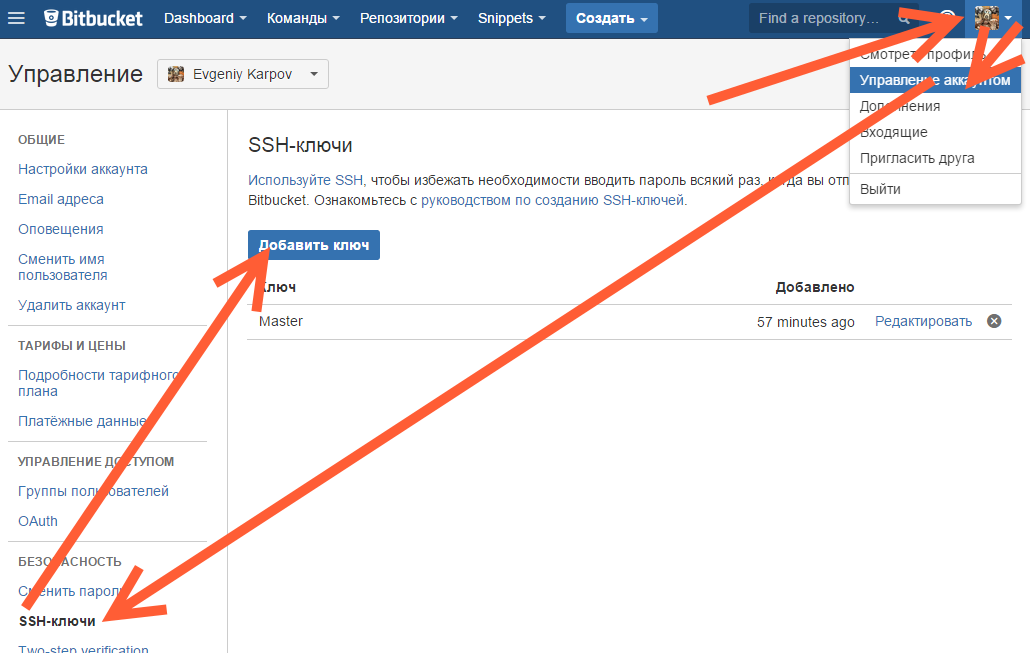
Копируем его, и добавляем вэб-морду ГИТа (в моём случае это BitBucket; ключи там можно добавить в двух местах — в настройках аккаунта и в настройках проекта, нам первый вариант, ибо второй — для деплоя проекта) [Аккаунт] — Управление аккаунтом — SSH-ключи — Добавить ключ:
Добавление ключа в BitBucket
Ну, а дальше — просто делаем что нужно — или пуш, или клон (предполагается, что git remote add вы уже сделали сами). Git спросит, можно ли добавить хост к доверенным, и запросит passphrase (пароль приватного ключа). Всё, можно работать.
Удачных разработок!
PS: Большое спасибо за наводку на решение моему коллеге Ивану!