Как посмотреть ошибки системы в Windows Server 2019
При работе с различным программным обеспечением на Windows VDS может возникнуть задача посмотреть лог ошибок Windows. Также это может быть полезно для режим отладки, периодического контроля Windows, проверки что все работает должным образом.
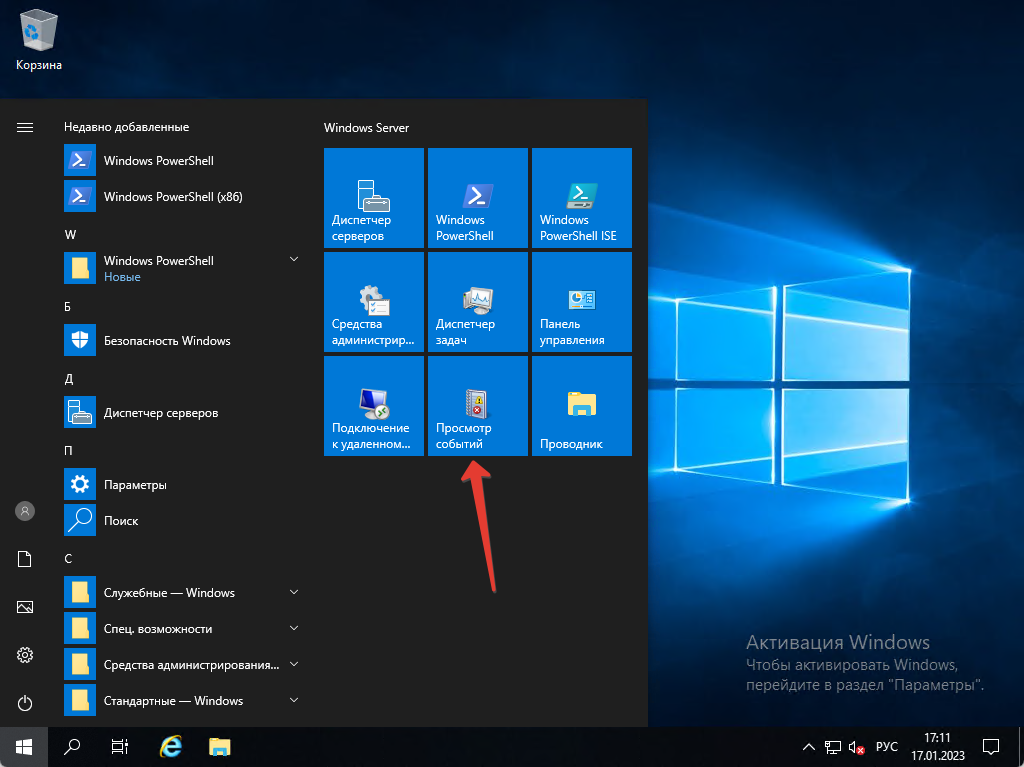
Итак. Сначала мы должны войти на наш сервер, затем нажать на «Пуск», а затем нажать на «Просмотр событий».
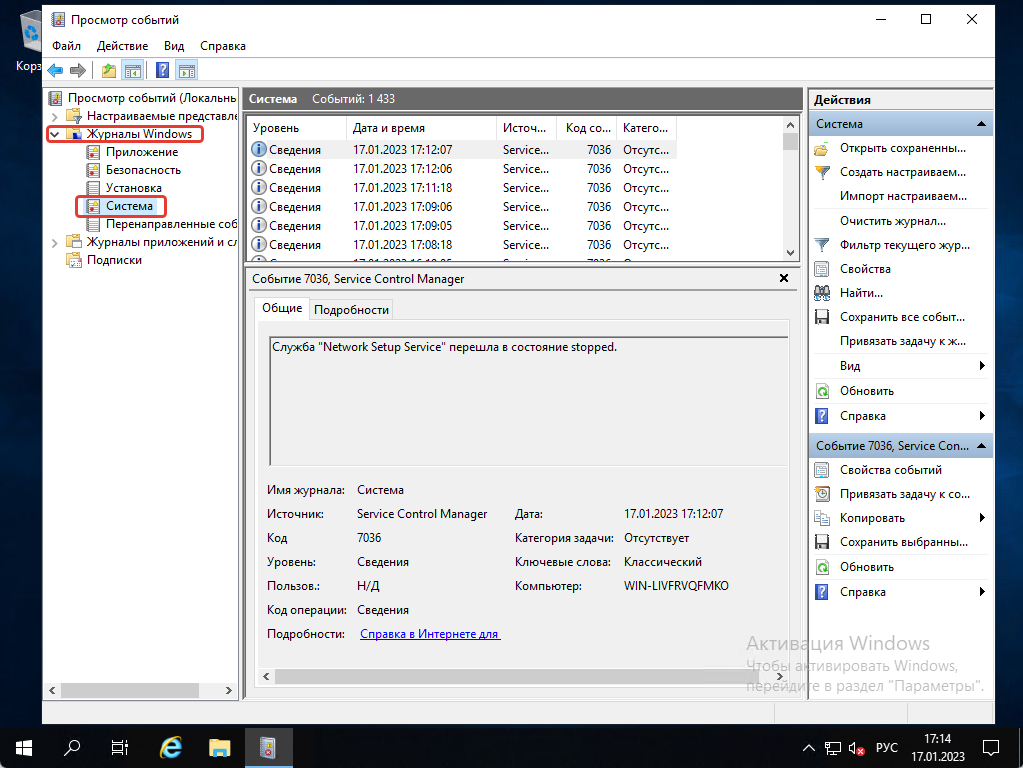
После этого как открылось новое окно мы можем посмотреть логи системы — нажимаем на «Журналы Windows» и выбираем «Система». Тут мы можем посмотреть все логи, которые связаны с самой системой.
Как сохранить логи системы
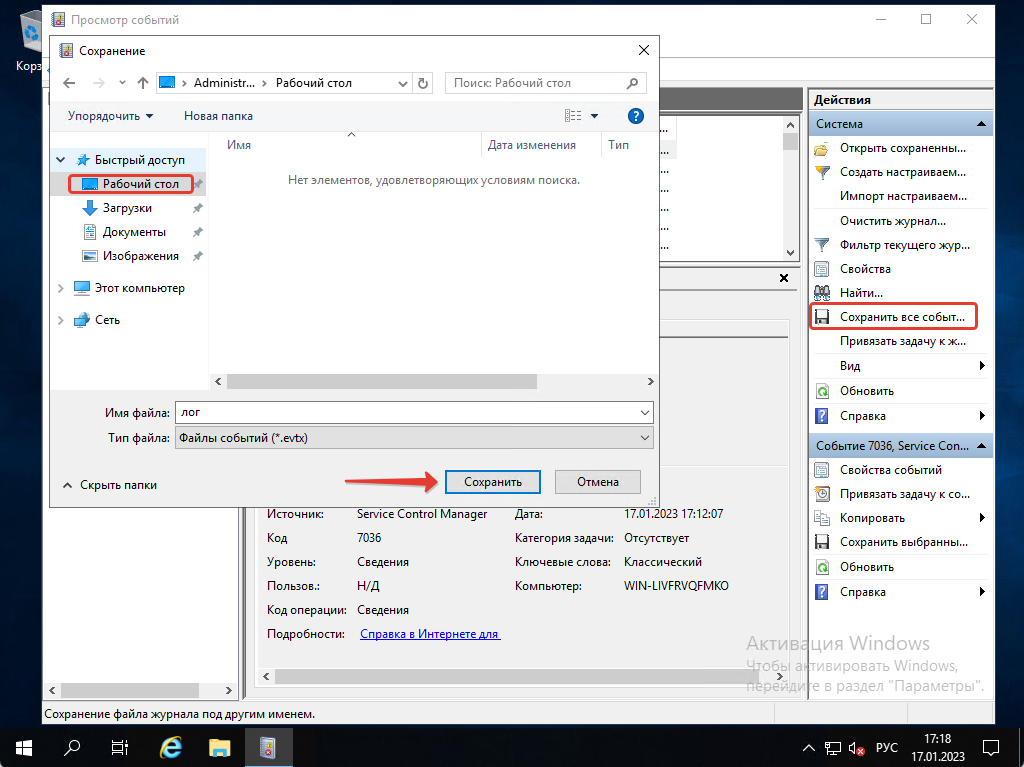
Если вы хотите посмотреть логи на другом ПК, вы можете их сохранить. Нажимаем на «Сохранить все события как», выбираем где мы хотим сохранить лог и нажимаем на «Сохранить».
Сохранить лог вы можете также в текстовом формате, если вам будет удобнее смотреть логи именно так.
How to check Windows server logs (Windows Event Log Types. Microsoft Windows Server is an operating system that provides network administrators with a collection of enterprise level management features. Accordingly, some of these features include data storage, applications, security, network, and hardware management.
Similarly, Microsoft’s collection of desktop operating systems allow you to view event logs through a set of Administrative Tools. So, Windows Server offers similar features but in a more enterprise capacity. After all, event logging and tracing are important parts of running servers. Thus, this guide will explore how you can find Windows server logs and how to interpret the information from them.
Shall we start with How to check Windows server logs (Windows Event Log Types).
Understanding The Windows Event Log

If your servers are positioned in a fairly medium or large company, they may be collecting thousands of events hourly. Especially if you have not configured your Windows Server Event Logs. Basically, the event log is separated into channels. The four most important are:
- System: Features events related to system software and/or hardware. For instance, driver failures or installations.
- Application: Contains events logged by (mostly) Windows applications.
- Security: Contains events pertaining to the security of the Windows system. This may include failed login attempts.
- Setup: Features system related event logs for setups and updates. For instance, Windows updates.
Besides, Microsoft also has channels for its features such as BitLocker, AppLocker, and Windows Firewall. Additionally, the event log may also contain channels for third party software. As a result, Windows Server allows you to collect all your events from separate servers and combine them in a central location. Alternatively, you could feed event logs to a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution that isn’t Microsoft based.
While there is a lot of information collected by the events log by default, it is the auditing feature in Windows that determines what information gets collected and logged.
How to Check Windows Server Logs
There are two main graphical ways you can access the Windows Server event log:
- Event Viewer Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
- Windows Admin Center (WAC)
The WAC isn’t as fully-featured as the Event Viewer. Nonetheless, you can access the Event Viewer from the server or client machine(s) using Windows Administrative Tools. Alternatively, you can use the Windows Server Manager to run the Event Viewer.
Launching The Windows Server Manager
Again, there are quite a few ways you can check server event logs from Windows Server. One of the best ways is using Windows Server Manager which acts as a central hub for our server. By default, Windows Server Manager is a Windows Server start up application. This means that it’s one of the first applications to run when you launch Windows Server. However, you can also run the Server Manager from the start menu or search bar:
- Open the Start Menu (WinKey).
- Search through the applications list for Server Manager or type it into the search field.
- Double click on the Server Manager item.

How to Launch The Event Viewer
Once again, the best way to check Windows Event Logs is through the Event Viewer. You can launch it from the Server Manager using the following steps:
- Click on the top Tools menu button.
- Search the list for Event Viewer.
- Double click on it to open it .

Using The Roles and Server Groups Section To Check Events
You may have noticed that the Events Viewer isn’t the only place you can view events from the Server Manager. As seen, the Server Manager also allows you to view roles and server specific events on the dashboard. You can view File and Storage, Local Server, and All Servers events by using the various widgets in the dashboard.

Clicking on one of the Events options in these widgets will launch a screen similar to this one:

This is called the Events Detail View. It gives you a list of filtration options including:
- Event Security Levels: Filter events according to their severity.
- Event Sources: Origin of an event (applications, services, etc).
- Servers: The machine the event occurred on.
- Time Period: The hours and/or minutes the event occurred in between.
- Event IDs: Each event has a unique ID. You can filter events using these IDs.
Again, we’ll stick to using the Event Viewer because it’s the most fully featured option.
Navigating Through the Event Viewer

One of the most unfortunate facts about Windows Server’s event management system is its lack of built in alerts or notifications. However, you can apply a script or run a program that is triggered when a particular event enters one of your custom views.
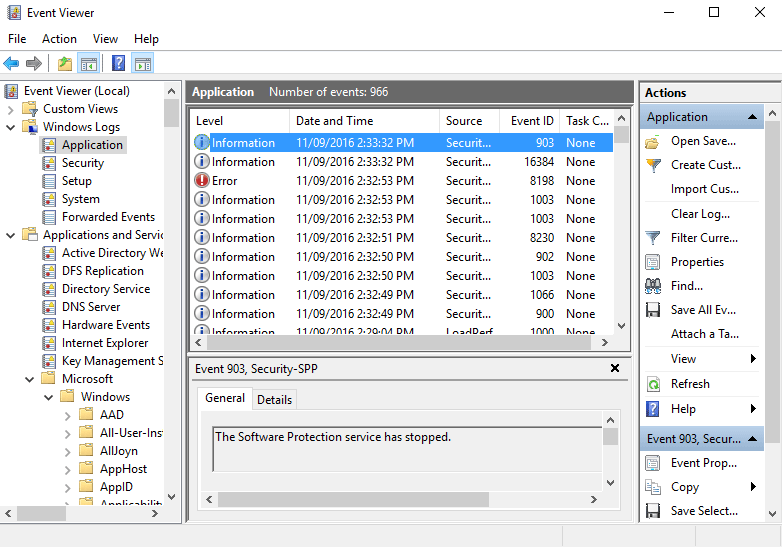
Nevertheless, you should be able to see the four channels we previously mentioned under the Windows Logs folder. You can use the above image as a reference. Ultimately, this is where you will check your Windows Servers Log.
You will notice that the above image features an additional channel called Forwarded Events. This channel is used by servers that have been set up as event collectors. It allows you to see events from other servers.
If you scan through the Event Viewer tree, you should notice a top folder labeled Applications and Services Log. It contains event channels related to installed server software and hardware.
Event Log Levels
When checking Windows Server Logs through the Event Viewer, you’re bound to run into a plethora of event types. They include:
- Information: Logs information event. For instance, when a task is completed successfully or when the system informs the user of something.
- Warning: Used to log system and software warnings. They don’t demand immediate action. However, they may warn you of a future problem, like disk space running out.
- Error: Indicates a system, software, or hardware issue that requires immediate action. For instance, a driver failing to load upon start up.
- Success Audit (Security log): This signifies the success of an audited security event. For instance, a user successfully logging onto the server or client.
- Failure Audit (Security log): This signifies the success of an audited security event. For instance, a user failing to log onto a server or client.
It is time to explain How to Check Windows Server Logs (Windows Event Log Types).
Event Log Types
In this section of the guide, you’ll explore the event types (Event Sources) you should be monitoring. Ultimately, keeping track of important logs requires you to use event sources to identify vulnerabilities in your system. Certainly, you’ll be able to find the event source by using the Source tab for each event.

Alternatively, you can create a custom view by:
- Right clicking on any one of the folders or objects on the right tree panel eg. Windows Logs.
- Next, select Create Custom View… from the context menu.
If you execute the above steps correctly, you should be presented with this screen.

You can then use either the filer screen or XML screen to create an event source-based view.
1. Application Whitelisting
As shown, you should have a list of approved services and applications. Anything that doesn’t appear on your whitelist should be flagged as suspicious. Consequently, there are two systems built into the latest versions of Windows for application control:
- AppLocker
- Microsoft Defender Device Guard
You can either use these systems individually or in tandem. Regardless, DeviceGuard is considered the most difficult to configure but also the most secure. As such, admins may elect to use it over AppLocker. AppLocker is easy to bypass by compromising the Windows NT Kernel. Comparatively, the Device Guard is much more robust and much more secure against exploits against the Windows NT Kernel.
However, if it’s your first time working with application control software, it is recommended that you use AppLocker with the Event Viewer.
What Should You Do When You Encounter This Event?
Your event source is dependent on the application control solution you’ve chosen to use for black and whitelisting. For instance, any event related to the AppLocker will use AppLocker as a source. Likewise, if you use Microsoft Defender, Device Guard events will use DeviceGuard as a source. It’s important that you investigate any suspicious events related to these sources. Correspondingly, bad actors may be trying to whitelist apps that you’ve previously blacklisted because of the vulnerabilities they impose on your system. You should:
- Check your app control configurations.
- Consult with a network security specialist to track down the person that may have changed your rules.
- Change all necessary Passovers.
2. Randomly Cleared Events and Audit Logs
If you notice that some of your events have been randomly cleared, then your network/system has most likely been compromised by bad actors. Especially, these bad actors may be trying to hide malicious activity by purging events. At this time it’s important to remember that event logs are not typically cleared during normal operations. As such, if you notice the following event logs, you should be worried:

What Should You Do When You Encounter This Event?
Nevertheless, collecting logs centrally on a server that only you (or your network’s admin) can access is the best way to protect yourself against cleared event logs. This will allow you to view deleted or cleared event logs without restoring your server from a backup. You can then confirm if a bad actor compromised your system.
3.Account Usage
A variety of users will log in to your server(s). You can use these event types and IDs to detect unauthorized account usage and remote desktop logins. Some users can use Windows Remote Desktop to configure systems that they should not be allowed to. Equally, users should not be logging into your server using Remote Desktop when there are other tools such as Power Share, Windows Admin Console (WAC), etc.
You (or your network administrator) should especially be paying attention to privileged Active Directory groups such as the domain and enterprise admin groups. Furthermore, you must make sure that your system isn’t adding or removing users from these groups without permission.
Account lockouts are important events that should be monitored. They can often signify brute force attempts by malicious actors. These bad actors may be trying to guess a user’s password. Nevertheless, the following are the events that fall under this category:

What Should You Do When You Encounter This Event?
When you encounter this event, it’s important to connect all related users and/or groups. First step is to investigate why a specific user was locked out. Was it indeed a bad actor or have they forgotten their password? Once you’ve fully ascertained the reasons for the user’s failed login attempts, you can act accordingly.
4. Group Policy Errors
Evidently, you use Group Policy Objects (GPOs) to configure and enforce your organization’s security policy. Thus, if the group policies you’ve set aren’t enforced, then your system may be compromised. In most cases, it may be the result of a bad actor attempting to prevent your system from enforcing certain policies so they can enact their own.
However, it can also be something benign or innocent. For instance, the group policy client may be failing for some reason. Regardless, it’s always important to monitor your group policies as they may indicate something nefarious occurring on your network..

What Should You Do When You Encounter This Event?
Your group policies can be viewed in the GroupPolicy channel (Microsoft > Windows > GroupPolicy). It allows you to see if your system is applying Group Policy Objects (GPOs) successfully. Once you encounter any errors in this view, you should first determine why the error is concerning. It may not be the result of a breach or attempted exploit. One of your machines may be struggling with low system resources. Make sure to check if your GroupPolicies are operational.
5. Software and Service Installation
By the same token, you may be regularly installing and updating software and services on your server. However, installations occur daily. Of course, this depends on the server’s usage and age. Freshly commissioned servers may require daily installations, backups, and updates. Nonetheless, if you see suspicious software and service-related events, then it may be a sign of malicious activity carried out by a bad actor.
What Should You Do When You Encounter This Event?
Look out for keywords in events such as “Installed”, “New”, “Removed”, “Update”, and ”Updated”. You can find the above keywords by using a search or a custom view of your creation. You must investigate every suspicious occurrence you find and review logs to ensure that every software/service installation and removal has been approved.
6. Windows Updates
As with the desktop version of the operating system, Windows Server also requires regular updates. These updates are imperative because they often contain important system patches. If these Windows updates fail, it may leave your system vulnerable.
Consequently, you must check the WindowUpdateClient and Servicing event sources from the System channel. Alternatively, you can create a custom view filtered according to these event sources. Nevertheless, you must validate that there are no errors or information events that indicate Windows Update failures.
What Should You Do When You Encounter This Event?
The first thing you must do is investigate why your Windows Updates are being interrupted. It may not be a result of a malicious. Your server(s) may be low on system resources or your system may be experiencing a network error. As you investigate the source of the issue, you must ensure that your Windows Server operating system is up to date. You can manually download and install Windows Server Cumulative Updates.
7. Windows Firewall
The Windows Firewall is enabled by default. It protects servers and clients against malicious activities from your internal trusted network. Henceforth, it’s just as important as any firewall you have segregated in your network. Thus, you must check that your firewall is it’s working, and if the status and/or rules have been updated or changed, etc.
Event sources to look out for include: Firewall, Firewall-Client, Firewall-CPL, Firewall-Driver, and Firewall-Service. Again, you can create a custom view with these event sources.
What Should You Do When You Encounter This Event?
Again, you must determine the source of the issue. Is someone trying to reconfigure your firewall? You should consider using third party firewalls for your internal system. There are other steps you can take to improve your overall cybersecurity.
8. Application Crashes
Application crashes are fairly common. However, they may indicate a malicious attack where a bad actor is forcing processes and services to shut down. Therefore, you or your system administrator must check the event logs for instances of Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), Windows Error Reporting (WER), Application Crashes, and Hang events.

What Should You Do When You Encounter This Event?
Again, you should determine the source of the crash, freeze, etc. Are the affected applications important to the security of your network? Which machines are they specifically related to? This will help you decide if you must investigate further or change the posture of your network’s security.
Thank you for reading How to Check Windows Server Logs (Windows Event Log Types Explained). We shall conclude.
How to Check Windows Server Logs (Windows Event Log Types) Conclusion
Posted by
on September 27, 2016
This post will show you where the .evtx log files can be found in Windows Server 2016, as well as how they can be viewed with Event Viewer.
Viewing Log Files
The easiest way to view the log files in Windows Server 2016 is through the Event Viewer, here we can see logs for different areas of the system.
Event viewer can be opened through the MMC, or through the Start menu by selecting All apps, Windows Administrative Tools, followed by Event Viewer.
Through Event Viewer we have the ability to search the logs for a particular string, export the logs to a file, and even schedule a task to take place each time a specific event occurs.
Log File Location
While this allows us to read the logs, you may be after the full path to where the actual .evtx files are stored. These log files can be found in the C:\Windows\System32\winevt\logs folder, as shown below.
These files can be double clicked and they will automatically open with Event Viewer, and these are the files that are read when browsing through Event Viewer
Note that specific applications may have their own custom log locations, in which case you will need to check the vendors documentation regarding log file location.
Summary
We have seen that important application, security and system events that have been logged are stored in the C:\Windows\System32\winevt\logs directory as .evtx files, which can be viewed through Event Viewer.
So, you installed Windows Server Core without the Desktop Experience. Everything has been going fine with Server 2016 without the GUI until suddenly you start encountering an error. Now, how do read the Event Log for more troubleshooting information? Event Viewer, where are you?
If you have a Windows desktop computer nearby and remote management enabled on the server, you can connect remotely through Computer Management and read the event logs like you are used to doing. Alternatively, when it comes to Server Core, it’s up to PowerShell.
After logging into the server, you arrive at the command prompt. Enter ‘PowerShell.exe’ to change the command prompt to PowerShell.
To see the event logs available, enter this command:
get-eventlog -list
This will show you the event logs available such as Application, HardwareEvents, Internet Explorer, Security, System, and others depending on the roles and software you have installed. This command will also show you the event log policies for maximum size, retention, overwrite action, and the number of entries.
To open a particular event log, use the command:
get-eventlog [log name]
Replace [log name] with the name of the log you are interested in viewing. For example:
get-eventlog Application
This lists the entries in the table format in the default order (most recent events at the top).
Since there can be a lot of logs, you can use -after to limit the search to the last few hours entries.
get-eventlog Application -after (get-date).addhours(-1)
You can also filter the list to just show a particular type of entry such as errors or warnings.
get-eventlog System -after (get-date).addhours(-1) | where Entrytype -eq Error
This would get entries from the System log that occurred within the last hour and were logged as errors.
Now that you have browsed the logs, you might have found a particular instance that you wanted to see the full details. Use this command with the number from the index column in the logs:
get-eventlog System | where index -eq 93 | format-list *
This allows you to see all of the details of the entries without them being truncated.
Since this is PowerShell, you can use all of the tricks you are familiar with to optimize your use of the event log such as sorting, filtering, or exporting to a file. It’s a pretty simple process and should be faster than the MMC snap-in for Event Viewer.
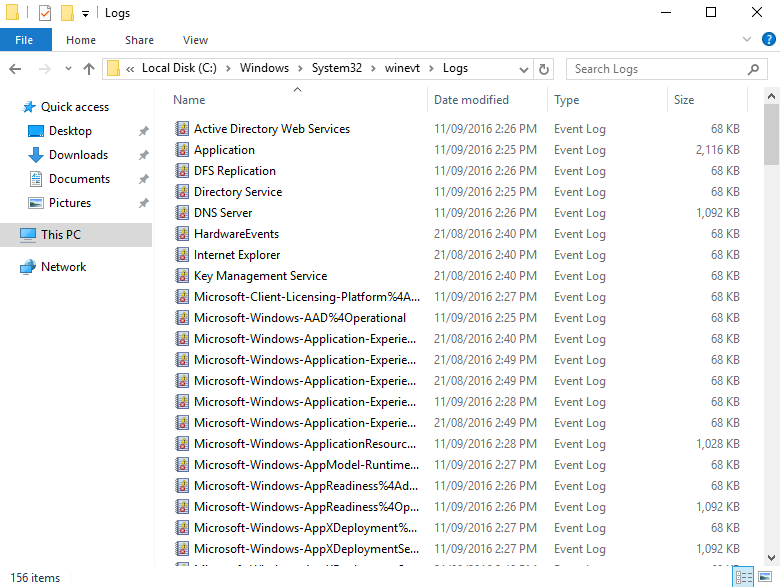
Для того что бы открыть Журнал Windows сервера нужно последовательно выполнить:
Пуск-Панель управления-Администрирование-Просмотр событий-Журналы WindowsЖурнал Windows сервера состоит из 5 разделов. В каждый раздел идет запись событий в зависимости от категории.
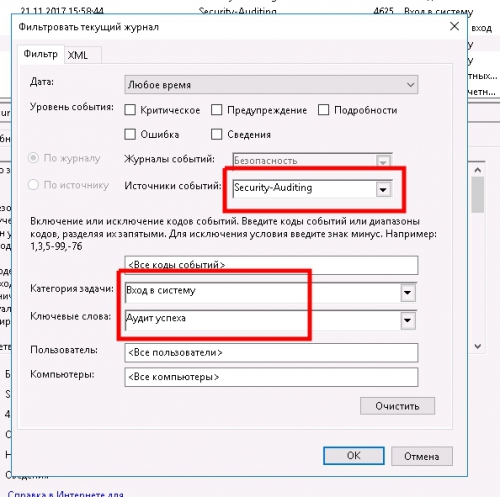
Например если нам нужно посмотреть удачные авторизации в системе по RDP и ip адрес с которого была авторизация, нужно выбрать раздел: Безопасность, далее включить фильтр и установить параметры фильтрации как указано на скрине:
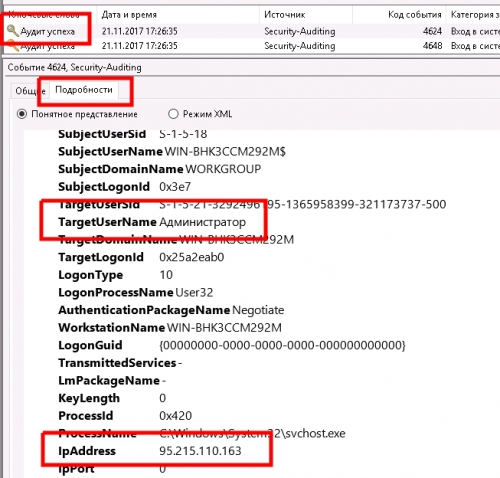
После установки фильтра вы сможете посмотреть ip авторизации и логин пользователя Windows как показано на скрине: