I get this error when I try to run the command. Any ideas how to fix this?
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : Feature name Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux is unknown.
At line:1 char:1
- Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows- …
-
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature], COMException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Dism.Commands.EnableWindowsOptionalFeatureCommand
Document Details
⚠ Do not edit this section. It is required for docs.microsoft.com ➟ GitHub issue linking.
- ID: f2668f02-b96f-7f16-6fc5-950a1e5f86b9
- Version Independent ID: 75f3a2fb-99bd-0161-28ba-5c86e917f4d5
- Content: Install the Linux Subsystem on Windows 10
- Content Source: WSL/install-win10.md
- Service: windows-subsystem-for-linux
- Product: windows-subsystem-for-linux
- GitHub Login: @scooley
- Microsoft Alias: scooley
Are you running Windows 10 x64 Creators Update Home, Pro, or Enterprise (non-LTSB SKU) or later?
…
—
Michael Bloem, PhD | Consulting Analyst | Advanced Analytics | Steelcase.com | 650.762.5636
From: Rich Turner [mailto:notifications@github.com]
Sent: Tuesday, July 17, 2018 1:26 PM
To: MicrosoftDocs/WSL <WSL@noreply.github.com>
Cc: Bloem, Michael <MBLOEM@steelcase.com>; Author <author@noreply.github.com>
Subject: Re: [MicrosoftDocs/WSL] Feature name Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux is unknown (#226)
Are you running Windows 10 x64 Creators Update Home, Pro, or Enterprise (non-LTSB SKU) or later?
—
You are receiving this because you authored the thread.
Reply to this email directly, view it on GitHub<#226 (comment)>, or mute the thread<https://github.com/notifications/unsubscribe-auth/ANJTTlMiikAq9a1ovYBs1eXXt54b4b6Jks5uHh4tgaJpZM4VMHZd>.
@mbloem-Steelcase — don’t think images attached to emails survive conversion into GitHub comments — could you either apply your image to the message above, or type the version number? Thanks.
Hi I’ve added the content you requested above — any thoughts on how I should proceed?
1511? That’s Threshold 2 — which was released in Nov 2015 … and is no longer supported!!
Is there a reason you’re not running a current and supported version of Win10?
You can’t enable WSL on 1511 because it’s not in 1511 — WSL was first introduced in April 2016, as a beta feature in Insiders builds released in the lead-up to Win10 1609 (Anniversary Update). WSL has received HUGE updates with each subsequent release, dramatically improving its ability to run ever more Linux tools and binaries.
- Windows 10 Creators Update: What’s new in Bash/WSL & Windows Console
- What’s new in WSL in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update
- And many of the other posts on our blog: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/commandline
The current latest, supported version of WSL is available in Win10 1803 (Spring 2018 Update), and the next major Win10 release later this year will include yet more improvements and fixes.
If you’re going to run WSL, we STRONGLY encourage you to run the latest version of Windows that you can in order to get the best experience.
Thanks!
Asking my IT department about upgrading Windows now…
Hi, I have exactly the same command written as @mbloem-Steelcase but I’m running on windows 10 (familial) x64 and with the 1803 version. Can someone help me?
Thanks!
@Crozon29 — are you running Windows 10 LTSB?
Please reply with the (suitably redacted) output of running systeminfo from a PowerShell/Cmd prompt.
Hi @bitcrazed I don’t really know, when I run «gwmi win32_operatingsystem | select OperatingSystemSKU» it says 101 so I don’t think so.
I actually managed to run : Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux tonight after several attempts but I don’t have the possibility to restart my computer as said in the development to follow.
I have in output:
Path:
Online: True
RestartNeeded: False
Thank you for your help and sorry as you can see I am a beginner in this kind of stuff!
@Crozon29 gwmi win32_operatingsystem|select Version would be more useful 
My guess (based on the number of times I’ve gotten it wrong myself) is that when this failed in the past, you may have omitted the -Online argument.
You must be sure to reboot your computer after enabling WSL though: WSL needs to start-up very early in the Windows bootup sequence, before any 3rd party code is loaded, to ensure a solid «chain of trust». Once enabled, you should be able to download and install your chosen distro(s) from the Windows Store.
@bitcrazed Thank you for the command.
Unfortunately I used the command » Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux » without omitting the -Online but it doesn’t work.
It’s to put in the Bash command (found on the search bar and runned as an admin)?
Hi all,
I got following message, any recommendation what to do next:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : The requested operation requires elevation.
At line:1 char:1
- Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows- …
-
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature], COMException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Dism.Commands.EnableWindowsOptionalFeatureCommand
I got the same error
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : Feature name Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux is unknown.
At line:1 char:1
+ Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows- ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature], COMException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Dism.Commands.EnableWindowsOptionalFeatureCommand
I’m running on Windows Server 2016 Datacenter 64-bit (10.0, Build 14393) (14393.rs1_release.170602-2252)
Closing this issue: For anyone else who see’s this error, note that you need to be running:
- Windows 10 x64 build 14316 or later (note — LTSB builds do not currently support WSL)
- Windows Server build 16237 or later
For the best WSL experience, we encourage you to run the most recent build of Windows that you can since WSL has improved CONSIDERABLY since its early releases.
Closing this issue: For anyone else who see’s this error, note that you need to be running:
- Windows 10 x64 build 14316 or later (note — LTSB builds do not currently support WSL)
- Windows Server build 16237 or later
For the best WSL experience, we encourage you to run the most recent build of Windows that you can since WSL has improved CONSIDERABLY since its early releases.
hello. i have a same problem.
I use 17763 insider prew build. And could not turn on case sensitive feature
Same issue on Windows 10 Pro 10.0.17134. WSL is missing in «turn windows features on and off» as well as getting the error as in the OP message.
@juso — Are you running Windows 10 LTSB?
@bitcrazed — no, it’s not LTSB to my understand
PS C:\> gwmi win32_operatingsystem | select OperatingSystemSKU
OperatingSystemSKU
------------------
48
and value at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProductName is Windows 10 Pro
Same issues here:
<gwmi win32_operatingsystem | select OperatingSystemSKU
OperatingSystemSKU
<Betriebsystemname Microsoft Windows 10 Pro
Version 10.0.17134 Build 17134
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : Der Featurename «Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux» ist
unbekannt.
Having similar issue in
Windows 10 Pro, Version 1903. OS build: 18362.295
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : Feature name Mircrosoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux is unknown.
At line:1 char:1
+ Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -online -FeatureName Mircrosoft-Windows ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature], COMException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Dism.Commands.EnableWindowsOptionalFeatureCommand
@eNipu could you try using the GUI approach to install WSL? Open the start menu and search for Turn Windows Features On or Off and then check the Windows Subsystem for Linux option.
If that doesn’t work please open an issue on our WSL Github repo: https://github.com/microsoft/wsl/issues and we will help you out there.
@eNipu could you try using the GUI approach to install WSL? Open the start menu and search for
Turn Windows Features On or Offand then check theWindows Subsystem for Linuxoption.If that doesn’t work please open an issue on our WSL Github repo: https://github.com/microsoft/wsl/issues and we will help you out there.
Fixed the problem for GUI. Thanks !
Windows Subsystem for Linux is not listed in the turn windows On or Off dialogue box
@eNipu — just spotted that you’re trying to install Mircrosoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux … which is mis-spelled.
Please run the following from an elevated PowerShell Console/Terminal:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureNameMicrosoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Hey I have the problem, too, this is what happens when I run systeminfo
Host Name: ALIENMACHINE
OS Name: Microsoft Windows 10 Pro
OS Version: 10.0.19041 N/A Build 19041
OS Manufacturer: Microsoft Corporation
OS Configuration: Standalone Workstation
OS Build Type: Multiprocessor Free
Registered Owner: N/A
Registered Organization: N/A
Product ID: 00331-10000-00001-AA033
Original Install Date: 3/27/2020, 6:29:23 AM
System Boot Time: 4/15/2020, 1:07:57 AM
System Manufacturer: Hewlett-Packard
System Model: HP ProBook 6450b
System Type: X86-based PC
Processor(s): 1 Processor(s) Installed.
[01]: x64 Family 6 Model 37 Stepping 5 GenuineIntel ~2400 Mhz
BIOS Version: Hewlett-Packard 68CDE Ver. F.03, 10/4/2010
Windows Directory: C:\WINDOWS
System Directory: C:\WINDOWS\system32
Boot Device: \Device\HarddiskVolume1
System Locale: en-us;English (United States)
Input Locale: en-gb;English (United Kingdom)
Time Zone: (UTC+02:00) Cairo
Total Physical Memory: 2,991 MB
Available Physical Memory: 257 MB
Virtual Memory: Max Size: 12,207 MB
Virtual Memory: Available: 6,009 MB
Virtual Memory: In Use: 6,198 MB
Page File Location(s): C:\pagefile.sys
Domain: WORKGROUP
Logon Server: \\ALIENMACHINE
Hotfix(s): 4 Hotfix(s) Installed.
[01]: KB4534170
[02]: KB4537759
[03]: KB4545706
[04]: KB4541738
Network Card(s): 2 NIC(s) Installed.
[01]: Intel(R) 82577LC Gigabit Network Connection
Connection Name: Ethernet
Status: Media disconnected
[02]: Broadcom 4313 802.11b/g/n
Connection Name: Wi-Fi
DHCP Enabled: Yes
DHCP Server: 192.168.8.1
IP address(es)
[01]: 192.168.8.113
[02]: fe80::d193:1076:4f7a:d19b
[03]: fd90:2bd2:2993:7200:75cc:2e41:d01a:2e0c
[04]: fd90:2bd2:2993:7200:d193:1076:4f7a:d19b
Hyper-V Requirements: VM Monitor Mode Extensions: Yes
Virtualization Enabled In Firmware: No
Second Level Address Translation: Yes
Data Execution Prevention Available: Yes
Having this same issue, I am running LTSC in Bootcamp:
PS C:\Windows\system32> Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : Feature name Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux is unknown.
Version ------- 10.0.17763
@sambragg According to the LTSC page, you’re not running LTSC:
| LTSC release | Equivalent SAC release | Availability date |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSC | Windows 10, Version 1507 | 7/29/2015 |
| Windows 10 Enterprise 2016 LTSC | Windows 10, Version 1607 | 8/2/2016 |
| Windows 10 Enterprise 2019 LTSC | Windows 10, Version 1809 | 11/13/2018 |
17763 was the fall 2018 Win10 release.
If you copy this: Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux, and paste it into an ELEVATED Terminal, you should see something like the following:
If not, please follow @craigloewen-msft’s instructions above.
@gibsonjc1 — Windows Server 2016 was released before WSL was first released (fall 2017).
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
__Deployment Image Servicing and Management tool
Version: 10.0.19041.329
Image Version: 10.0.19041.329
Error: 0x800f080c
Feature name Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux is unknown.
A Windows feature name was not recognized.
Use the /Get-Features option to find the name of the feature in the image and try the command again.
The DISM log file can be found at C:\WINDOWS\Logs\DISM\dism.log__
My windows version is:
Version 2004 (OS Build 19041.329)
I think we’d need more info to solve the problem then. Could you please open an issue on the official WSL repo here describing your problem?
Thanks!
@eNipu could you try using the GUI approach to install WSL? Open the start menu and search for
Turn Windows Features On or Offand then check theWindows Subsystem for Linuxoption.If that doesn’t work please open an issue on our WSL Github repo: https://github.com/microsoft/wsl/issues and we will help you out there.
i don’t have Windows Subsystem for Linux option there
Hello, I’m running into the same issue and am trying the GUI method with the following selections:
Role-based or feature-based installation > Microsoft Windows Server 2016 OS (for the Server Pool)
I don’t see Windows Subsytem for Linux there either.
I tried everything PowerShell, enabling developer mode everything and
nothing seems to work.
You are using the incorrect command.
You should be using Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux instead. You must run this command in an elevated PowerShell command prompt. You should restart when prompted.
Once you have installed the feature, run through the rest of the instructions, to actually install Ubuntu on Windows the above procedure only installs WSL.
You can verify the name of the feature by using this command.
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-*
I am trying to enable linux subsystem on a Windows Server 2016 on AWS EC2 by following these instructions https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-on-server
Here is the error message:
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : Feature name Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux is unknown.
At line:1 char:1
+ Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows- ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature], COMException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Dism.Commands.EnableWindowsOptionalFeatureCommand
My windows server is created based on an AWS ami.
How can I find out if my window server supports the linux subsystem? Is there anything I can do to enable the feature?
Update:
> systeminfo | Select-String "^OS Name","^OS Version"
OS Name: Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Datacenter
OS Version: 10.0.14393 N/A Build 14393
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) — подсистема ОС Windows 10, позволяющая разработчикам, тестировщикам запускать нативные приложения Linux, писать скрипты, выполнять команды непосредственно из Windows. В обновлённой Windows 10 (2004) появилась 2я версия WSL, в которой используется полноценное ядро Linux с возможностью запуска приложений и контейнеров Docker, реализована высокая скорость загрузки, небольшой объем потребляемых ресурсов, управление в фоновом режиме, обновление ядра. Таким образом вы сможете запускать ELF64 программы, которые могут получать доступ к файловой системе Windows без использования сторонних порто (таких как Cygwin).
Образ ядра Linux (версия ядра 4.19) в Windows 10 представляет собой легкую виртуальную машину, для запуска которой не нужно ставить полноценную роль Hyper-V. Системные вызовы Linux транслируются на лету в вызовы Windows без использования эмулятора (в отличии от WSL1).
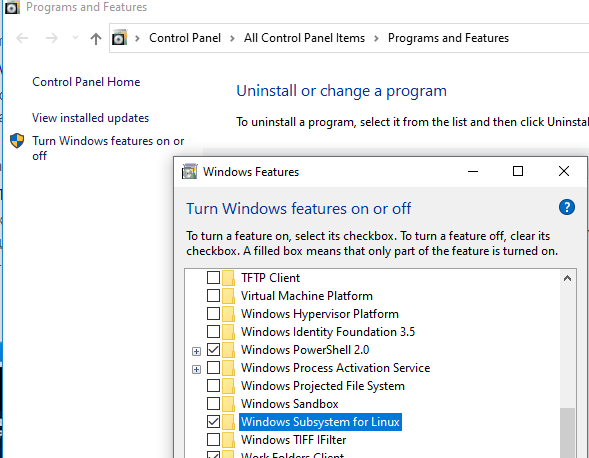
Изначально компонент WSL отключен. Чтобы его включить, вам необходимо зайти в Пуск -> Панель управления -> Программы и компоненты -> Включение и отключение компонентов Windows (Control PanelAll Control Panel ItemsPrograms and FeaturesTurn Windows features on or off), активировать галочку Подсистема Windows для Linux (Windows Subsystem for Linux), нажать кнопку ОК, и перезагрузить компьютер.
Вы можете включить компоненты WSL в Windows 10 с помощью dism:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux /all /norestart
или PowerShell
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName VirtualMachinePlatform
В Windows Server 2004 Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) для установки компонента WSL используется командлет Install-WindowsFeature:
Install-WindowsFeature -Name Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
После этого также необходимо перезагрузить компьютер.
В настройка BIOS/UEFI компьютера должна быть включена поддержка аппаратной виртуализации: Intel VT (Intel Virtualization Technology) или AMD-V.
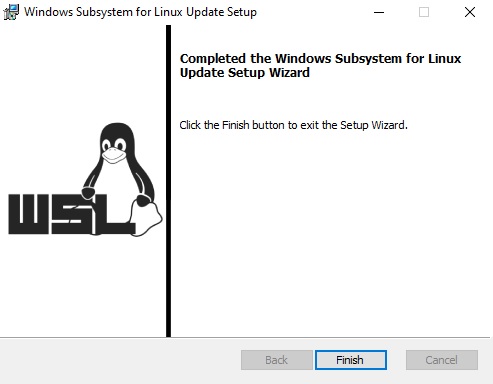
Теперь вам нужно выполнить обновление WSL до версии 2. Для этого требуется зайти на сайт https://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/windows/wsl/wsl2-kernel, скачать файл wsl_update_x64.msi, установить его. По завершении увидите картинку
Чтобы сделать WSL2 архитектурой по умолчанию для новых дистрибутивов, в PowerShell выполните команду:
wsl --set-default-version 2
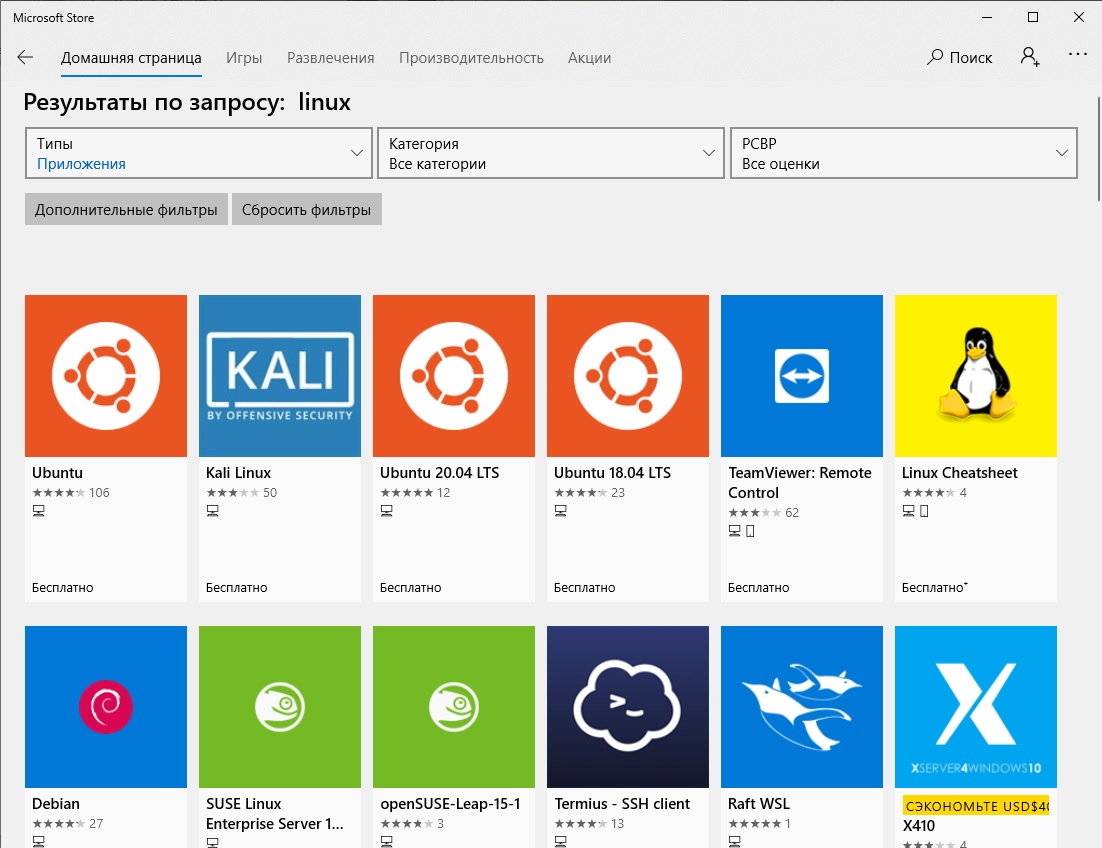
Далее вам необходимо открыть Microsoft Store, в поиске ввести слово “Linux”. В появившемся списке выберите нужный дистрибутив. Доступные Ubuntu, Debian, Kali Linux, Linux Cheatsheet, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server15, openSUSE Leap 15-1, Pengwin Enterprise, Fedora Remix for WSL или другие. В нашем примере мы будем использовать Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, нажмите кнопку Получить.
Если у вас отключен Windows Store или вы хотите установить дистрибутив WSL в Core редакции Windows Server, вы можете скачать дистрибутив Ubuntu с помощью PowerShell командлета Invoke-WebRequest:
Invoke-WebRequest https://aka.ms/wslubuntu2004 -OutFile ubuntu-2004.zip –UseBasicParsing
Распакуйте архив:
Expand-Archive -Path .ubuntu-2004.zip
Запустите установку образа Linux с помощью файла Ubuntu.exe.
Также вы можете скачать образ в виде appx файла и установить его с помощью командлета Add-AppxPackage.
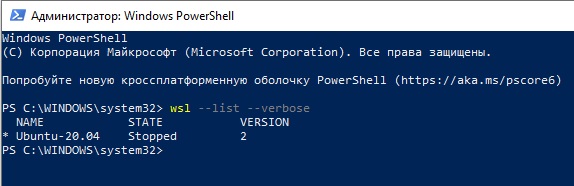
После установки можно проверить используемую версию WSL с помощью команды
wsl --list –-verbose
Если у вашей среды Linux указана версия 1, нужно изменить ее на WSL2 командой:
wsl --set-version Ubuntu-20.04 2
Файл жёсткого диска с образом виртуальной машины ОС Linux Ubuntu 20.04 будет располагаться в профиле пользователя: C:Users234AppDataLocalPackagesCanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu20.04onWindows_79rhkp1fndgscLocalState.
После установки дистрибутива в стартовом меню появляется ярлык на него. Для запуска Ubuntu зайдите в меню Пуск, нажмите на соответствующем ярлыке и получите в отдельном окне полноценную командную оболочку Bash. Запускать WSL можно и с помощью команды wsl. При первом запуске образа в командной строке Bash вам будет предложено создать пользователя и пароль (которые не должны совпадать с учётной записью Windows). Чтобы выполнять команды с правами root, необходимо использовать дополнительный ключ (префикс) sudo. В WSL есть общие команды для Bash и CMD, и тут нужно не забывать, что система Linux чувствительна к регистру.
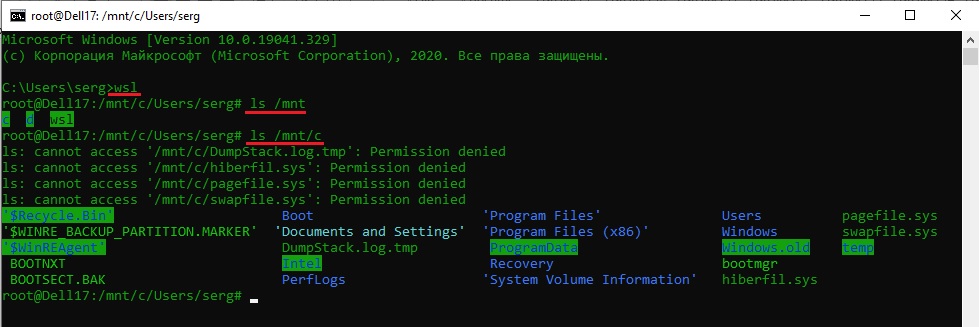
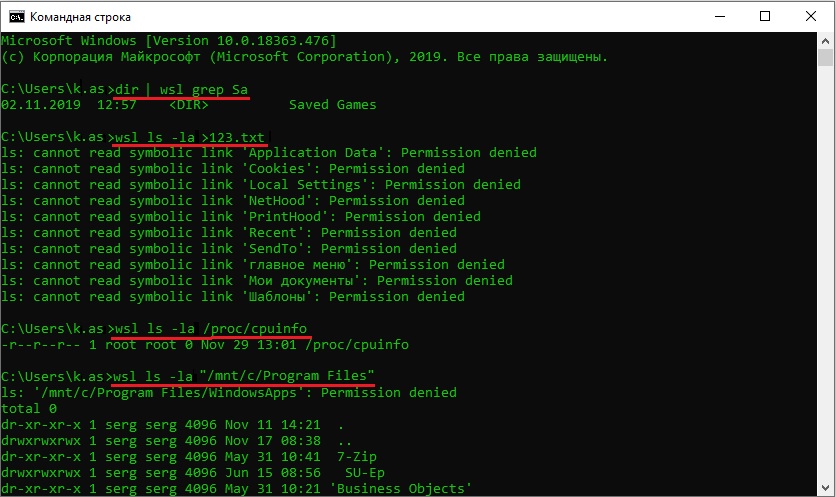
Вы можете выполнить Linux-команды из CMD. Для этого необходимо вначале указать “WSL”. Например, для просмотра списка файлов и папок в каталоге Windows, выполните:
wsl
ls /mnt
ls/mnt/c
dir | wsl grep Sa
wsl ls ‑la > 123.txt
wsl ls ‑la /proc/cpuinfo
wsl ls ‑la “/mnt/c/Program Files”
Также вы можете открыть проводник командой explorer.exe, калькулятор – calc.exe, блокнот – notepad.exe, paint – mspaint.exe, календарь – cal, погоду – curl wttr.in
Ещё один пример взаимосвязи 2х систем – вы можете открыть в Windows файл из WSL-дистрибутива по сетевому пути. Для этого в CMD наберите путь к файлу:
notepad \wsl$Ubuntu-20.04home1122.txt
Из окна консоли вы можете обновить список пакетов в Ubuntu с помощью команд:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
После обновления Ubuntu папка …/LocalState будет занимать 1.5 Гб.
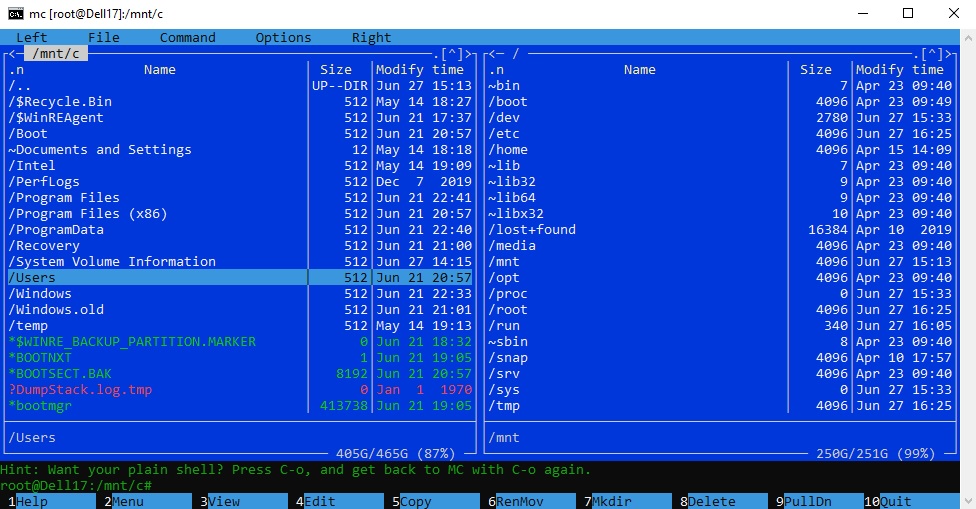
Из командной строки Linux можно не только просмотреть Windows-файлы и каталоги, но и получить к ним доступ. Чтобы удобнее копировать файлы, просматривать директории и их содержимое, установите файловый менеджер Midnight Commander с помощью команды
sudo apt-get install mc
Вы можете запустить Midnight Commander как в командной оболочке Bash, так и внутри CMD. На скриншоте ниже показано, что в двух панелях MC показывается список файлов с обеих ОС.
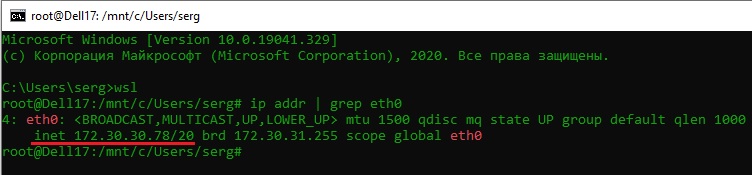
Можно отобрахить сетевые настройки (IP адрес) IP-адрес Linux-системы:
ip addr | grep eth0
В WSL не предусмотрена работа приложений с графическим интерфейсом. Тем не менее вы можете попробовать их установить и использовать. Чтобы запускать графические приложения в Linux, нужно скачать и установить в Windows программу VcXsrv Windows X Server (https://sourceforge.net/projects/vcxsrv/).
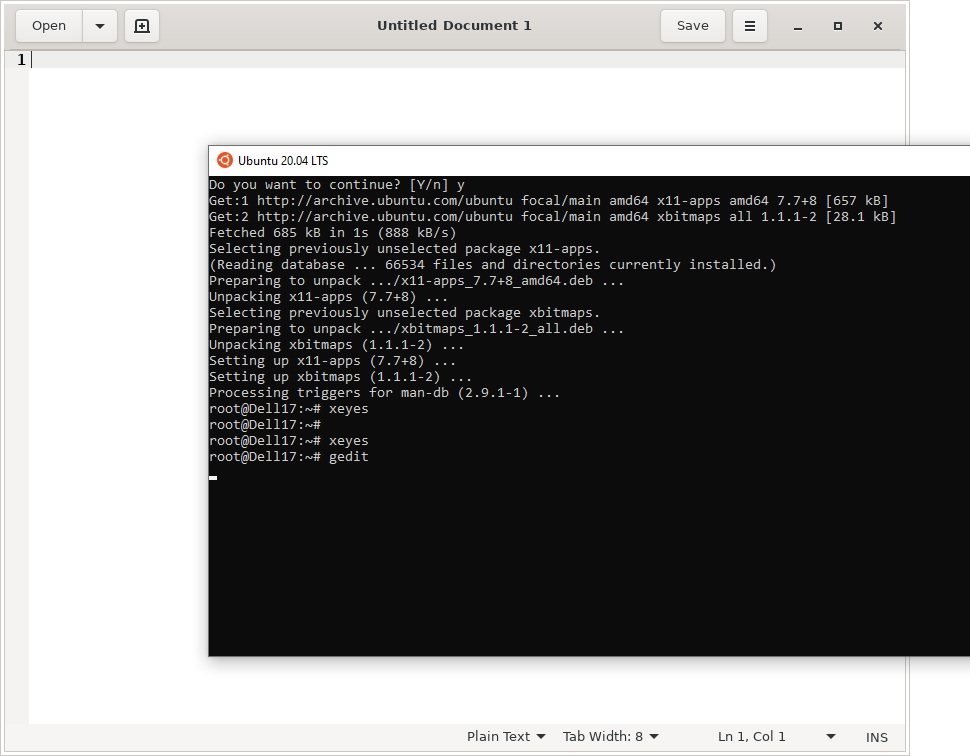
С помощью пакетного менеджера apt-get установим несколько графических программ: например, браузер, текстовый редактор или что-то ещё:
sudo apt-get install gedit
sudo apt-get install firefox
sudo apt-get install x11-app
Затем создайте файл в директории root:
cd /~
vim .bash_login
впишите строку
export DISPLAY=$(cat /etc/resolv.conf | grep nameserver | awk '{print $2}'):0
сохраните запись
Esc -> :wr -> :q
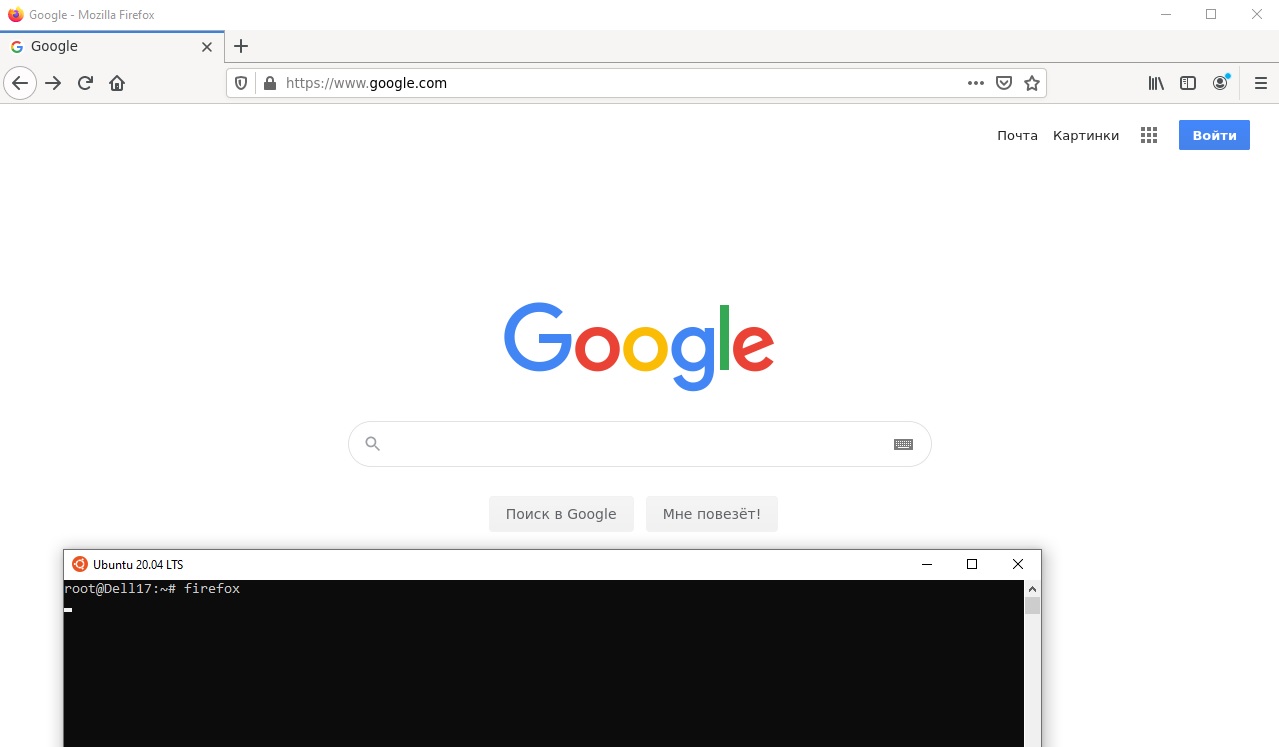
Теперь можете запустить графические программы Linux через WSL командами:
firefox
или
gedit
Вы можете установить в Windows 10 несколько дистрибутивов Linux и запускать одновременно в разных окнах WSL. Вывести весь перечень установленных дистрибутивов можете с помощью команды:
wsl --list –all
чтобы завершить работу всех запущенных дистрибутивов и ядра WSL 2, выполните команду:
wsl --shutdown
| title | description | ms.date | ms.topic |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Troubleshooting Windows Subsystem for Linux |
Provides detailed information about common errors and issues people run into while running Linux on the Windows Subsystem for Linux. |
09/27/2021 |
article |
Troubleshooting Windows Subsystem for Linux
We have covered some common troubleshooting scenarios associated with WSL below, but please consider searching the issues filed in the WSL product repo on GitHub as well.
File an issue, bug report, feature request
The WSL product repo issues enables you to:
- Search existing issues to see if there are any associated with a problem that you are having. Note that in the search bar, you can remove «is:open» to include issues that have already been resolved in your search. Please consider commenting or giving a thumbs up to any open issues that you would like to express your interest in moving forward as a priority.
- File a new issue. If you have found a problem with WSL and there does not appear to be an existing issue, you can select the green New issue button and then choose WSL — Bug Report. You will need to include a title for the issue, your Windows build number (run
cmd.exe /c verto see your current build #), whether you’re running WSL 1 or 2, your current Linux Kernel version # (runwsl.exe --statusorcat /proc/version), the version # of your distribution (runlsb_release -r), any other software versions involved, the repro steps, expected behavior, actual behavior, and diagnostic logs if available and appropriate. For more info, see contributing to WSL. - File a feature request by selecting the green New issue button and then select Feature request. You will need to address a few questions describing your request.
You can also:
- File a documentation issue using the WSL docs repo. To contribute to the WSL docs, see the Microsoft Docs contributor guide.
- File a Windows Terminal issue using the the Windows Terminal product repo if your problem is related more to the Windows Terminal, Windows Console, or the command-line UI.
Installation issues
-
Installation failed with error 0x80070003
-
WslRegisterDistribution failed with error 0x8007019e
- The Windows Subsystem for Linux optional component is not enabled:
- Open Control Panel -> Programs and Features -> Turn Windows Feature on or off -> Check Windows Subsystem for Linux or using the PowerShell cmdlet mentioned at the beginning of this article.
-
Installation failed with error 0x80070003 or error 0x80370102
- Please make sure that virtualization is enabled inside of your computer’s BIOS. The instructions on how to do this will vary from computer to computer, and will most likely be under CPU related options.
- WSL2 requires that your CPU supports the Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) feature, which was introduced in Intel Nehalem processors (Intel Core 1st Generation) and AMD Opteron. Older CPUs (such as the Intel Core 2 Duo) will not be able to run WSL2, even if the Virtual Machine Platform is successfully installed.
-
Error when trying to upgrade:
Invalid command line option: wsl --set-version Ubuntu 2- Ensure that you have the Windows Subsystem for Linux enabled, and that you’re using Windows Build version 18362 or later. To enable WSL run this command in a PowerShell prompt with admin privileges:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux.
- Ensure that you have the Windows Subsystem for Linux enabled, and that you’re using Windows Build version 18362 or later. To enable WSL run this command in a PowerShell prompt with admin privileges:
-
The requested operation could not be completed due to a virtual disk system limitation. Virtual hard disk files must be uncompressed and unencrypted and must not be sparse.
- Deselect “Compress contents” (as well as “Encrypt contents” if that’s checked) by opening the profile folder for your Linux distribution. It should be located in a folder on your Windows file system, something like:
%USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalPackagesCanonicalGroupLimited... - In this Linux distro profile, there should be a LocalState folder. Right-click this folder to display a menu of options. Select Properties > Advanced and then ensure that the “Compress contents to save disk space” and “Encrypt contents to secure data” checkboxes are unselected (not checked). If you are asked whether to apply this to just to the current folder or to all subfolders and files, select “just this folder” because you are only clearing the compress flag. After this, the
wsl --set-versioncommand should work.
- Deselect “Compress contents” (as well as “Encrypt contents” if that’s checked) by opening the profile folder for your Linux distribution. It should be located in a folder on your Windows file system, something like:
[!NOTE]
In my case, the LocalState folder for my Ubuntu 18.04 distribution was located at C:Users<my-user-name>AppDataLocalPackagesCanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu18.04onWindows_79rhkp1fndgscCheck WSL Docs GitHub thread #4103 where this issue is being tracked for updated information.
-
The term ‘wsl’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program.
- Ensure that the Windows Subsystem for Linux Optional Component is installed. Additionally, if you are using an ARM64 device and running this command from PowerShell, you will receive this error. Instead run
wsl.exefrom PowerShell Core, or Command Prompt.
- Ensure that the Windows Subsystem for Linux Optional Component is installed. Additionally, if you are using an ARM64 device and running this command from PowerShell, you will receive this error. Instead run
-
Error: Windows Subsystem for Linux has no installed distributions.
- If you receive this error after you have already installed WSL distributions:
- Run the distribution at least once before invoking it from the command line.
- Check whether you may be running separate user accounts. Running your primary user account with elevated permissions (in admin mode) should not result in this error, but you should ensure that you aren’t accidentally running the built-in Administrator account that comes with Windows. This is a separate user account and will not show any installed WSL distributions by design. For more info, see Enable and Disable the Built-in Administrator Account.
- The WSL executable is only installed to the native system directory. When you’re running a 32-bit process on 64-bit Windows (or on ARM64, any non-native combination), the hosted non-native process actually sees a different System32 folder. (The one a 32-bit process sees on x64 Windows is stored on disk at WindowsSysWOW64.) You can access the “native” system32 from a hosted process by looking in the virtual folder:
Windowssysnative. It won’t actually be present on disk, mind you, but the filesystem path resolver will find it.
-
Error: This update only applies to machines with the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
- To install the Linux kernel update MSI package, WSL is required and should be enabled first. If it fails, it you will see the message:
This update only applies to machines with the Windows Subsystem for Linux. - There are three possible reason you see this message:
-
You are still in old version of Windows which doesn’t support WSL 2. See step #2 for version requirements and links to update.
-
WSL is not enabled. You will need to return to step #1 and ensure that the optional WSL feature is enabled on your machine.
-
After you enabled WSL, a reboot is required for it to take effect, reboot your machine and try again.
- To install the Linux kernel update MSI package, WSL is required and should be enabled first. If it fails, it you will see the message:
-
Error: WSL 2 requires an update to its kernel component. For information please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel .
- If the Linux kernel package is missing in the %SystemRoot%system32lxsstools folder, you will encounter this error. Resolve it by installing the Linux kernel update MSI package in step #4 of these installation instructions. You may need to uninstall the MSI from ‘Add or Remove Programs’, and install it again.
Common issues
I’m on Windows 10 version 1903 and I still do not see options for WSL 2
This is likely because your machine has not yet taken the backport for WSL 2. The simplest way to resolve this is by going to Windows Settings and clicking ‘Check for Updates’ to install the latest updates on your system. See the full instructions on taking the backport.
If you hit ‘Check for Updates’ and still do not receive the update you can install KB KB4566116 manually.
Error: 0x1bc when wsl --set-default-version 2
This may happen when ‘Display Language’ or ‘System Locale’ setting is not English.
wsl --set-default-version 2 Error: 0x1bc For information on key differences with WSL 2 please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2
The actual error for 0x1bc is:
WSL 2 requires an update to its kernel component. For information please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel
For more information, please refer to issue 5749
Cannot access WSL files from Windows
A 9p protocol file server provides the service on the Linux side to allow Windows to access the Linux file system. If you cannot access WSL using \wsl$ on Windows, it could be because 9P did not start correctly.
To check this, you can check the start up logs using: dmesg |grep 9p, and this will show you any errors. A successful output looks like the following:
[ 0.363323] 9p: Installing v9fs 9p2000 file system support [ 0.363336] FS-Cache: Netfs '9p' registered for caching [ 0.398989] 9pnet: Installing 9P2000 support
Please see this Github thread for further discussion on this issue.
Can’t start WSL 2 distribution and only see ‘WSL 2’ in output
If your display language is not English, then it is possible you are seeing a truncated version of an error text.
To resolve this issue, please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel and install the kernel manually by following the directions on that doc page.
command not found when executing windows .exe in linux
Users can run Windows executables like notepad.exe directly from Linux. Sometimes, you may hit «command not found» like below:
$ notepad.exe
-bash: notepad.exe: command not found
If there are no win32 paths in your $PATH, interop isn’t going to find the .exe.
You can verify it by running echo $PATH in Linux. It’s expected that you will see a win32 path (for example, /mnt/c/Windows) in the output.
If you can’t see any Windows paths then most likely your PATH is being overwritten by your Linux shell.
Here is a an example that /etc/profile on Debian contributed to the problem:
if [ "`id -u`" -eq 0 ]; then PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin" else PATH="/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games" fi
The correct way on Debian is to remove above lines.
You may also append $PATH during the assignment like below, but this lead to some other problems with WSL and VSCode..
if [ "`id -u`" -eq 0 ]; then PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:$PATH" else PATH="/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games:$PATH" fi
For more information, see issue 5296 and issue 5779.
«Error: 0x80370102 The virtual machine could not be started because a required feature is not installed.»
Please enable the Virtual Machine Platform Windows feature and ensure virtualization is enabled in the BIOS.
-
Check the Hyper-V system requirements
-
If your machine is a VM, please enable nested virtualization manually. Launch powershell with admin, and run:
Set-VMProcessor -VMName <VMName> -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions $true
-
Please follow guidelines from your PC’s manufacturer on how to enable virtualization. In general, this can involve using the system BIOS to ensure that these features are enabled on your CPU. Instructions for this process can vary from machine to machine, please see this article from Bleeping Computer for an example.
-
Restart your machine after enabling the
Virtual Machine Platformoptional component. -
Make sure that the hypervisor launch is enabled in your boot configuration. You can validate this by running (elevated powershell):
bcdedit /enum | findstr -i hypervisorlaunchtype
If you see
hypervisorlaunchtype Off, then the hypervisor is disabled. To enable it run in an elevated powershell:bcdedit /set {current} hypervisorlaunchtype Auto -
Additionally, if you have 3rd party hypervisors installed (Such as VMware or VirtualBox) then please ensure you have these on the latest versions which can support HyperV (VMware 15.5.5+ and VirtualBox 6+) or are turned off.
Learn more about how to Configure Nested Virtualization when running Hyper-V in a Virtual Machine.
WSL has no network connection on my work machine or in an Enterpise environment
Business or Enterprise environments may have Windows Defender Firewall settings configured to block unauthorized network traffic. If local rule merging is set to «No» then WSL networking will not work by default, and your administrator will need to add a firewall rule to allow it.
You can confirm local rule merging’s setting by following these steps:
- Open «Windows Defender Firewall with advanced security» (this is different than «Windows Defender Firewall» in the Control Panel)
- Right-click on the «Windows Defender Firewall with advanced security on Local Computer» tab
- Select «Properties»
- Select the «Public Profile» tab on the new Window that opens
- Select «Customize» under the «Settings» section
- Check in the «Customize Settings for the Public Profile» window that opens to see if «Rule Merging» is set to «No». This will block access to WSL.
You can find instructions on how to change this Firewall setting in Enterprise environment: Set up WSL for your company.
WSL has no network connectivity once connected to a VPN
If after connecting to a VPN on Windows, bash loses network connectivity, try this workaround from within bash. This workaround will allow you to manually override the DNS resolution through /etc/resolv.conf.
- Take a note of the DNS server of the VPN from doing
ipconfig.exe /all - Make a copy of the existing resolv.conf
sudo cp /etc/resolv.conf /etc/resolv.conf.new - Unlink the current resolv.conf
sudo unlink /etc/resolv.conf sudo mv /etc/resolv.conf.new /etc/resolv.conf- Edit
/etc/wsl.confand add this content to the file. (More info on this set up can be found in Advanced settings configuration)
[network]
generateResolvConf=false
- Open
/etc/resolv.confand
a. Delete the first line from the file which has a comment describing automatic generation
b. Add the DNS entry from (1) above as the very first entry in the list of DNS servers.
c. Close the file.
Once you have disconnected the VPN, you will have to revert the changes to /etc/resolv.conf. To do this, do:
cd /etcsudo mv resolv.conf resolv.conf.newsudo ln -s ../run/resolvconf/resolv.conf resolv.conf
Starting WSL or installing a distribution returns an error code
Follow these instructions to collect detailed logs and file an issue on our GitHub.
Updating WSL
There are two components of Windows Subsystem for Linux that can require updating.
-
To update the Windows Subsystem for Linux itself, use the command
wsl --updatein PowerShell or CMD. -
To update the specific Linux distribution user binaries, use the command:
apt-get update | apt-get upgradein the Linux distribution that you are seeking to update.
Apt-get upgrade errors
Some packages use features that we haven’t implemented yet. udev, for example, isn’t supported yet and causes several apt-get upgrade errors.
To fix issues related to udev, follow the following steps:
-
Write the following to
/usr/sbin/policy-rc.dand save your changes. -
Add execute permissions to
/usr/sbin/policy-rc.d:chmod +x /usr/sbin/policy-rc.d
-
Run the following commands:
dpkg-divert --local --rename --add /sbin/initctl ln -s /bin/true /sbin/initctl
«Error: 0x80040306» on installation
This has to do with the fact that we do not support legacy console.
To turn off legacy console:
- Open cmd.exe
- Right click title bar -> Properties -> Uncheck Use legacy console
- Click OK
«Error: 0x80040154» after Windows update
The Windows Subsystem for Linux feature may be disabled during a Windows update. If this happens the Windows feature must be re-enabled. Instructions for enabling the Windows Subsystem for Linux can be found in the Manual Installation Guide.
Changing the display language
WSL install will try to automatically change the Ubuntu locale to match the locale of your Windows install. If you do not want this behavior you can run this command to change the Ubuntu locale after install completes. You will have to relaunch bash.exe for this change to take effect.
The below example changes to locale to en-US:
sudo update-locale LANG=en_US.UTF8
Installation issues after Windows system restore
- Delete the
%windir%System32TasksMicrosoftWindowsWindows Subsystem for Linuxfolder.
Note: Do not do this if your optional feature is fully installed and working. - Enable the WSL optional feature (if not already)
- Reboot
- lxrun /uninstall /full
- Install bash
No internet access in WSL
Some users have reported issues with specific firewall applications blocking internet access in WSL. The firewalls reported are:
- Kaspersky
- AVG
- Avast
- Symantec Endpoint Protection
In some cases turning off the firewall allows for access. In some cases simply having the firewall installed looks to block access.
If you are using Microsoft Defender Firewall, unchecking «Blocks all incoming connections, including those in the list of allowed apps.» allows for access.
Permission Denied error when using ping
For Windows Anniversary Update, version 1607,
administrator privileges in Windows are required to run ping in WSL. To run ping, run Bash on Ubuntu on Windows as an administrator, or run bash.exe from a CMD/PowerShell prompt with administrator privileges.
For later versions of Windows, Build 14926+, administrator privileges are no longer required.
Bash is hung
If while working with bash, you find that bash is hung (or deadlocked) and not responding to inputs, help us diagnose the issue by collecting and reporting a memory dump. Note that these steps will crash your system. Do not do this if you are not comfortable with that or save your work prior to doing this.
To collect a memory dump
-
Change the memory dump type to «complete memory dump». While changing the dump type, take a note of your current type.
-
Use the steps to configure crash using keyboard control.
-
Repro the hang or deadlock.
-
Crash the system using the key sequence from (2).
-
The system will crash and collect the memory dump.
-
Once the system reboots, report the memory.dmp to secure@microsoft.com. The default location of the dump file is %SystemRoot%memory.dmp or C:Windowsmemory.dmp if C: is the system drive. In the email, note that the dump is for the WSL or Bash on Windows team.
-
Restore the memory dump type to the original setting.
Check your build number
To find your PC’s architecture and Windows build number, open
Settings > System > About
Look for the OS Build and System Type fields.
To find your Windows Server build number, run the following in PowerShell:
systeminfo | Select-String "^OS Name","^OS Version"
Confirm WSL is enabled
You can confirm that the Windows Subsystem for Linux is enabled by running the following in an elevated PowerShell window:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
OpenSSH-Server connection issues
Trying to connect your SSH server is failed with the following error: «Connection closed by 127.0.0.1 port 22».
-
Make sure your OpenSSH Server is running:
and you’ve followed this tutorial:
https://ubuntu.com/server/docs/service-openssh -
Stop the sshd service and start sshd in debug mode:
sudo service ssh stop sudo /usr/sbin/sshd -d
-
Check the startup logs and make sure HostKeys are available and you don’t see log messages such as:
debug1: sshd version OpenSSH_7.2, OpenSSL 1.0.2g 1 Mar 2016 debug1: key_load_private: incorrect passphrase supplied to decrypt private key debug1: key_load_public: No such file or directory Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key debug1: key_load_private: No such file or directory debug1: key_load_public: No such file or directory Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key debug1: key_load_private: No such file or directory debug1: key_load_public: No such file or directory Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key debug1: key_load_private: No such file or directory debug1: key_load_public: No such file or directory Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key
If you do see such messages and the keys are missing under /etc/ssh/, you will have to regenerate the keys or just purge&install openssh-server:
sudo apt-get purge openssh-server sudo apt-get install openssh-server
«The referenced assembly could not be found.» when enabling the WSL optional feature
This error is related to being in a bad install state. Please complete the following steps to try and fix this issue:
-
If you are running the enable WSL feature command from PowerShell, try using the GUI instead by opening the start menu, searching for ‘Turn Windows features on or off’ and then in the list select ‘Windows Subsystem for Linux’ which will install the optional component.
-
Update your version of Windows by going to Settings, Updates, and clicking ‘Check for Updates’
-
If both of those fail and you need to access WSL please consider upgrading in place by reinstalling Windows using installation media and selecting ‘Keep Everything’ to ensure your apps and files are preserved. You can find instructions on how to do so at the Reinstall Windows 10 page.
Correct (SSH related) permission errors
If you’re seeing this error:
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ @ WARNING: UNPROTECTED PRIVATE KEY FILE! @ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ Permissions 0777 for '/home/artur/.ssh/private-key.pem' are too open.
To fix this, append the following to the the /etc/wsl.conf file:
[automount]
enabled = true
options = metadata,uid=1000,gid=1000,umask=0022
Please note that adding this command will include metadata and modify the file permissions on the Windows files seen from WSL. Please see the File System Permissions for more information.
Running Windows commands fails inside a distribution
Some distributions available in Microsoft Store are yet not fully compatible to run Windows commands out of the box. If you get an error -bash: powershell.exe: command not found running powershell.exe /c start . or any other Windows command, you can resolve it following these steps:
- In your WSL distribution run
echo $PATH.
If it does not include:/mnt/c/Windows/system32something is redefining the standard PATH variable. - Check profile settings with
cat /etc/profile.
If it contains assignment of the PATH variable, edit the file to comment out PATH assignment block with a # character. - Check if wsl.conf is present
cat /etc/wsl.confand make sure it does not containappendWindowsPath=false, otherwise comment it out. - Restart distribution by typing
wsl -tfollowed by distribution name or runwsl --shutdowneither in cmd or PowerShell.
Unable to boot after installing WSL 2
We are aware of an issue affecting users where they are unable to boot after installing WSL 2. While we fully diagnose those issue, users have reported that changing the buffer size or installing the right drivers can help address this. Please view this Github issue to see the latest updates on this issue.
WSL 2 errors when ICS is disabled
Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) is a required component of WSL 2. The ICS service is used by the Host Network Service (HNS) to create the underlying virtual network which WSL 2 relies on for NAT, DNS, DHCP, and host connection sharing.
Disabling the ICS service (SharedAccess) or disabling ICS through group policy will prevent the WSL HNS network from being created. This will result in failures when creating a new WSL version 2 image, and the following error when trying to convert a version 1 image to version 2.
There are no more endpoints available from the endpoint mapper.
Systems that require WSL 2 should leave the ICS service (SharedAccess) in it’s default start state, Manual (Trigger Start), and any policy that disables ICS should be overwritten or removed. While disabling the ICS service will break WSL 2, and we do not recommend disabling ICS, portions of ICS can be disabled using these instructions
Using older versions of Windows and WSL
There are several differences to note if you’re running an older version of Windows and WSL, like the Windows 10 Creators Update (Oct 2017, Build 16299) or Anniversary Update (Aug 2016, Build 14393). We recommend that you update to the latest Windows version, but if that’s not possible, we have outlined some of the differences below.
Interoperability command differences:
bash.exehas been replaced withwsl.exe. Linux commands can be run from the Windows Command Prompt or from PowerShell, but for early Windows versions, you may need to use thebashcommand. For example:C:temp> bash -c "ls -la". The WSL commands passed intobash -care forwarded to the WSL process without modification. File paths must be specified in the WSL format and care must be taken to escape relevant characters. For example:C:temp> bash -c "ls -la /proc/cpuinfo"orC:temp> bash -c "ls -la "/mnt/c/Program Files"".- To see what commands are available for a particular distribution, run
[distro.exe] /?. For example, with Ubuntu:C:> ubuntu.exe /?. - Windows path is included in the WSL
$PATH. - When calling a Windows tool from a WSL distribution in an earlier version of Windows 10, you will need to specify the directory path. For example, to call the Windows Notepad app from your WSL command line, enter:
/mnt/c/Windows/System32/notepad.exe - To change the default user to
rootuse this command in PowerShell:C:> lxrun /setdefaultuser rootand then run Bash.exe to log in:C:> bash.exe. Reset your password using the distributions password command:$ passwd usernameand then close the Linux command line:$ exit. From Windows command prompt or Powershell, reset your default user back to your normal Linux user account:C:> lxrun.exe /setdefaultuser username.
Uninstall legacy version of WSL
If you originally installed WSL on a version of Windows 10 prior to Creators update (Oct 2017, Build 16299), we recommend that you migrate any necessary files, data, etc. from the older Linux distribution you installed, to a newer distribution installed via the Microsoft Store. To remove the legacy distribution from your machine, run the following from a Command Line or PowerShell instance: wsl --unregister Legacy. You also have the option to manually remove the older legacy distribution by deleting the %localappdata%lxss folder (and all it’s sub-contents) using Windows File Explorer or with PowerShell: rm -Recurse $env:localappdata/lxss/.
| title | description | ms.date | ms.topic |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Troubleshooting Windows Subsystem for Linux |
Provides detailed information about common errors and issues people run into while running Linux on the Windows Subsystem for Linux. |
09/27/2021 |
article |
Troubleshooting Windows Subsystem for Linux
We have covered some common troubleshooting scenarios associated with WSL below, but please consider searching the issues filed in the WSL product repo on GitHub as well.
File an issue, bug report, feature request
The WSL product repo issues enables you to:
- Search existing issues to see if there are any associated with a problem that you are having. Note that in the search bar, you can remove «is:open» to include issues that have already been resolved in your search. Please consider commenting or giving a thumbs up to any open issues that you would like to express your interest in moving forward as a priority.
- File a new issue. If you have found a problem with WSL and there does not appear to be an existing issue, you can select the green New issue button and then choose WSL — Bug Report. You will need to include a title for the issue, your Windows build number (run
cmd.exe /c verto see your current build #), whether you’re running WSL 1 or 2, your current Linux Kernel version # (runwsl.exe --statusorcat /proc/version), the version # of your distribution (runlsb_release -r), any other software versions involved, the repro steps, expected behavior, actual behavior, and diagnostic logs if available and appropriate. For more info, see contributing to WSL. - File a feature request by selecting the green New issue button and then select Feature request. You will need to address a few questions describing your request.
You can also:
- File a documentation issue using the WSL docs repo. To contribute to the WSL docs, see the Microsoft Docs contributor guide.
- File a Windows Terminal issue using the the Windows Terminal product repo if your problem is related more to the Windows Terminal, Windows Console, or the command-line UI.
Installation issues
-
Installation failed with error 0x80070003
-
WslRegisterDistribution failed with error 0x8007019e
- The Windows Subsystem for Linux optional component is not enabled:
- Open Control Panel -> Programs and Features -> Turn Windows Feature on or off -> Check Windows Subsystem for Linux or using the PowerShell cmdlet mentioned at the beginning of this article.
-
Installation failed with error 0x80070003 or error 0x80370102
- Please make sure that virtualization is enabled inside of your computer’s BIOS. The instructions on how to do this will vary from computer to computer, and will most likely be under CPU related options.
- WSL2 requires that your CPU supports the Second Level Address Translation (SLAT) feature, which was introduced in Intel Nehalem processors (Intel Core 1st Generation) and AMD Opteron. Older CPUs (such as the Intel Core 2 Duo) will not be able to run WSL2, even if the Virtual Machine Platform is successfully installed.
-
Error when trying to upgrade:
Invalid command line option: wsl --set-version Ubuntu 2- Ensure that you have the Windows Subsystem for Linux enabled, and that you’re using Windows Build version 18362 or later. To enable WSL run this command in a PowerShell prompt with admin privileges:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux.
- Ensure that you have the Windows Subsystem for Linux enabled, and that you’re using Windows Build version 18362 or later. To enable WSL run this command in a PowerShell prompt with admin privileges:
-
The requested operation could not be completed due to a virtual disk system limitation. Virtual hard disk files must be uncompressed and unencrypted and must not be sparse.
- Deselect “Compress contents” (as well as “Encrypt contents” if that’s checked) by opening the profile folder for your Linux distribution. It should be located in a folder on your Windows file system, something like:
%USERPROFILE%AppDataLocalPackagesCanonicalGroupLimited... - In this Linux distro profile, there should be a LocalState folder. Right-click this folder to display a menu of options. Select Properties > Advanced and then ensure that the “Compress contents to save disk space” and “Encrypt contents to secure data” checkboxes are unselected (not checked). If you are asked whether to apply this to just to the current folder or to all subfolders and files, select “just this folder” because you are only clearing the compress flag. After this, the
wsl --set-versioncommand should work.
- Deselect “Compress contents” (as well as “Encrypt contents” if that’s checked) by opening the profile folder for your Linux distribution. It should be located in a folder on your Windows file system, something like:
[!NOTE]
In my case, the LocalState folder for my Ubuntu 18.04 distribution was located at C:Users<my-user-name>AppDataLocalPackagesCanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu18.04onWindows_79rhkp1fndgscCheck WSL Docs GitHub thread #4103 where this issue is being tracked for updated information.
-
The term ‘wsl’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program.
- Ensure that the Windows Subsystem for Linux Optional Component is installed. Additionally, if you are using an ARM64 device and running this command from PowerShell, you will receive this error. Instead run
wsl.exefrom PowerShell Core, or Command Prompt.
- Ensure that the Windows Subsystem for Linux Optional Component is installed. Additionally, if you are using an ARM64 device and running this command from PowerShell, you will receive this error. Instead run
-
Error: Windows Subsystem for Linux has no installed distributions.
- If you receive this error after you have already installed WSL distributions:
- Run the distribution at least once before invoking it from the command line.
- Check whether you may be running separate user accounts. Running your primary user account with elevated permissions (in admin mode) should not result in this error, but you should ensure that you aren’t accidentally running the built-in Administrator account that comes with Windows. This is a separate user account and will not show any installed WSL distributions by design. For more info, see Enable and Disable the Built-in Administrator Account.
- The WSL executable is only installed to the native system directory. When you’re running a 32-bit process on 64-bit Windows (or on ARM64, any non-native combination), the hosted non-native process actually sees a different System32 folder. (The one a 32-bit process sees on x64 Windows is stored on disk at WindowsSysWOW64.) You can access the “native” system32 from a hosted process by looking in the virtual folder:
Windowssysnative. It won’t actually be present on disk, mind you, but the filesystem path resolver will find it.
-
Error: This update only applies to machines with the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
- To install the Linux kernel update MSI package, WSL is required and should be enabled first. If it fails, it you will see the message:
This update only applies to machines with the Windows Subsystem for Linux. - There are three possible reason you see this message:
-
You are still in old version of Windows which doesn’t support WSL 2. See step #2 for version requirements and links to update.
-
WSL is not enabled. You will need to return to step #1 and ensure that the optional WSL feature is enabled on your machine.
-
After you enabled WSL, a reboot is required for it to take effect, reboot your machine and try again.
- To install the Linux kernel update MSI package, WSL is required and should be enabled first. If it fails, it you will see the message:
-
Error: WSL 2 requires an update to its kernel component. For information please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel .
- If the Linux kernel package is missing in the %SystemRoot%system32lxsstools folder, you will encounter this error. Resolve it by installing the Linux kernel update MSI package in step #4 of these installation instructions. You may need to uninstall the MSI from ‘Add or Remove Programs’, and install it again.
Common issues
I’m on Windows 10 version 1903 and I still do not see options for WSL 2
This is likely because your machine has not yet taken the backport for WSL 2. The simplest way to resolve this is by going to Windows Settings and clicking ‘Check for Updates’ to install the latest updates on your system. See the full instructions on taking the backport.
If you hit ‘Check for Updates’ and still do not receive the update you can install KB KB4566116 manually.
Error: 0x1bc when wsl --set-default-version 2
This may happen when ‘Display Language’ or ‘System Locale’ setting is not English.
wsl --set-default-version 2 Error: 0x1bc For information on key differences with WSL 2 please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2
The actual error for 0x1bc is:
WSL 2 requires an update to its kernel component. For information please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel
For more information, please refer to issue 5749
Cannot access WSL files from Windows
A 9p protocol file server provides the service on the Linux side to allow Windows to access the Linux file system. If you cannot access WSL using \wsl$ on Windows, it could be because 9P did not start correctly.
To check this, you can check the start up logs using: dmesg |grep 9p, and this will show you any errors. A successful output looks like the following:
[ 0.363323] 9p: Installing v9fs 9p2000 file system support [ 0.363336] FS-Cache: Netfs '9p' registered for caching [ 0.398989] 9pnet: Installing 9P2000 support
Please see this Github thread for further discussion on this issue.
Can’t start WSL 2 distribution and only see ‘WSL 2’ in output
If your display language is not English, then it is possible you are seeing a truncated version of an error text.
To resolve this issue, please visit https://aka.ms/wsl2kernel and install the kernel manually by following the directions on that doc page.
command not found when executing windows .exe in linux
Users can run Windows executables like notepad.exe directly from Linux. Sometimes, you may hit «command not found» like below:
$ notepad.exe
-bash: notepad.exe: command not found
If there are no win32 paths in your $PATH, interop isn’t going to find the .exe.
You can verify it by running echo $PATH in Linux. It’s expected that you will see a win32 path (for example, /mnt/c/Windows) in the output.
If you can’t see any Windows paths then most likely your PATH is being overwritten by your Linux shell.
Here is a an example that /etc/profile on Debian contributed to the problem:
if [ "`id -u`" -eq 0 ]; then PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin" else PATH="/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games" fi
The correct way on Debian is to remove above lines.
You may also append $PATH during the assignment like below, but this lead to some other problems with WSL and VSCode..
if [ "`id -u`" -eq 0 ]; then PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:$PATH" else PATH="/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/local/games:/usr/games:$PATH" fi
For more information, see issue 5296 and issue 5779.
«Error: 0x80370102 The virtual machine could not be started because a required feature is not installed.»
Please enable the Virtual Machine Platform Windows feature and ensure virtualization is enabled in the BIOS.
-
Check the Hyper-V system requirements
-
If your machine is a VM, please enable nested virtualization manually. Launch powershell with admin, and run:
Set-VMProcessor -VMName <VMName> -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions $true
-
Please follow guidelines from your PC’s manufacturer on how to enable virtualization. In general, this can involve using the system BIOS to ensure that these features are enabled on your CPU. Instructions for this process can vary from machine to machine, please see this article from Bleeping Computer for an example.
-
Restart your machine after enabling the
Virtual Machine Platformoptional component. -
Make sure that the hypervisor launch is enabled in your boot configuration. You can validate this by running (elevated powershell):
bcdedit /enum | findstr -i hypervisorlaunchtype
If you see
hypervisorlaunchtype Off, then the hypervisor is disabled. To enable it run in an elevated powershell:bcdedit /set {current} hypervisorlaunchtype Auto -
Additionally, if you have 3rd party hypervisors installed (Such as VMware or VirtualBox) then please ensure you have these on the latest versions which can support HyperV (VMware 15.5.5+ and VirtualBox 6+) or are turned off.
Learn more about how to Configure Nested Virtualization when running Hyper-V in a Virtual Machine.
WSL has no network connection on my work machine or in an Enterpise environment
Business or Enterprise environments may have Windows Defender Firewall settings configured to block unauthorized network traffic. If local rule merging is set to «No» then WSL networking will not work by default, and your administrator will need to add a firewall rule to allow it.
You can confirm local rule merging’s setting by following these steps:
- Open «Windows Defender Firewall with advanced security» (this is different than «Windows Defender Firewall» in the Control Panel)
- Right-click on the «Windows Defender Firewall with advanced security on Local Computer» tab
- Select «Properties»
- Select the «Public Profile» tab on the new Window that opens
- Select «Customize» under the «Settings» section
- Check in the «Customize Settings for the Public Profile» window that opens to see if «Rule Merging» is set to «No». This will block access to WSL.
You can find instructions on how to change this Firewall setting in Enterprise environment: Set up WSL for your company.
WSL has no network connectivity once connected to a VPN
If after connecting to a VPN on Windows, bash loses network connectivity, try this workaround from within bash. This workaround will allow you to manually override the DNS resolution through /etc/resolv.conf.
- Take a note of the DNS server of the VPN from doing
ipconfig.exe /all - Make a copy of the existing resolv.conf
sudo cp /etc/resolv.conf /etc/resolv.conf.new - Unlink the current resolv.conf
sudo unlink /etc/resolv.conf sudo mv /etc/resolv.conf.new /etc/resolv.conf- Edit
/etc/wsl.confand add this content to the file. (More info on this set up can be found in Advanced settings configuration)
[network]
generateResolvConf=false
- Open
/etc/resolv.confand
a. Delete the first line from the file which has a comment describing automatic generation
b. Add the DNS entry from (1) above as the very first entry in the list of DNS servers.
c. Close the file.
Once you have disconnected the VPN, you will have to revert the changes to /etc/resolv.conf. To do this, do:
cd /etcsudo mv resolv.conf resolv.conf.newsudo ln -s ../run/resolvconf/resolv.conf resolv.conf
Starting WSL or installing a distribution returns an error code
Follow these instructions to collect detailed logs and file an issue on our GitHub.
Updating WSL
There are two components of Windows Subsystem for Linux that can require updating.
-
To update the Windows Subsystem for Linux itself, use the command
wsl --updatein PowerShell or CMD. -
To update the specific Linux distribution user binaries, use the command:
apt-get update | apt-get upgradein the Linux distribution that you are seeking to update.
Apt-get upgrade errors
Some packages use features that we haven’t implemented yet. udev, for example, isn’t supported yet and causes several apt-get upgrade errors.
To fix issues related to udev, follow the following steps:
-
Write the following to
/usr/sbin/policy-rc.dand save your changes. -
Add execute permissions to
/usr/sbin/policy-rc.d:chmod +x /usr/sbin/policy-rc.d
-
Run the following commands:
dpkg-divert --local --rename --add /sbin/initctl ln -s /bin/true /sbin/initctl
«Error: 0x80040306» on installation
This has to do with the fact that we do not support legacy console.
To turn off legacy console:
- Open cmd.exe
- Right click title bar -> Properties -> Uncheck Use legacy console
- Click OK
«Error: 0x80040154» after Windows update
The Windows Subsystem for Linux feature may be disabled during a Windows update. If this happens the Windows feature must be re-enabled. Instructions for enabling the Windows Subsystem for Linux can be found in the Manual Installation Guide.
Changing the display language
WSL install will try to automatically change the Ubuntu locale to match the locale of your Windows install. If you do not want this behavior you can run this command to change the Ubuntu locale after install completes. You will have to relaunch bash.exe for this change to take effect.
The below example changes to locale to en-US:
sudo update-locale LANG=en_US.UTF8
Installation issues after Windows system restore
- Delete the
%windir%System32TasksMicrosoftWindowsWindows Subsystem for Linuxfolder.
Note: Do not do this if your optional feature is fully installed and working. - Enable the WSL optional feature (if not already)
- Reboot
- lxrun /uninstall /full
- Install bash
No internet access in WSL
Some users have reported issues with specific firewall applications blocking internet access in WSL. The firewalls reported are:
- Kaspersky
- AVG
- Avast
- Symantec Endpoint Protection
In some cases turning off the firewall allows for access. In some cases simply having the firewall installed looks to block access.
If you are using Microsoft Defender Firewall, unchecking «Blocks all incoming connections, including those in the list of allowed apps.» allows for access.
Permission Denied error when using ping
For Windows Anniversary Update, version 1607,
administrator privileges in Windows are required to run ping in WSL. To run ping, run Bash on Ubuntu on Windows as an administrator, or run bash.exe from a CMD/PowerShell prompt with administrator privileges.
For later versions of Windows, Build 14926+, administrator privileges are no longer required.
Bash is hung
If while working with bash, you find that bash is hung (or deadlocked) and not responding to inputs, help us diagnose the issue by collecting and reporting a memory dump. Note that these steps will crash your system. Do not do this if you are not comfortable with that or save your work prior to doing this.
To collect a memory dump
-
Change the memory dump type to «complete memory dump». While changing the dump type, take a note of your current type.
-
Use the steps to configure crash using keyboard control.
-
Repro the hang or deadlock.
-
Crash the system using the key sequence from (2).
-
The system will crash and collect the memory dump.
-
Once the system reboots, report the memory.dmp to secure@microsoft.com. The default location of the dump file is %SystemRoot%memory.dmp or C:Windowsmemory.dmp if C: is the system drive. In the email, note that the dump is for the WSL or Bash on Windows team.
-
Restore the memory dump type to the original setting.
Check your build number
To find your PC’s architecture and Windows build number, open
Settings > System > About
Look for the OS Build and System Type fields.
To find your Windows Server build number, run the following in PowerShell:
systeminfo | Select-String "^OS Name","^OS Version"
Confirm WSL is enabled
You can confirm that the Windows Subsystem for Linux is enabled by running the following in an elevated PowerShell window:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
OpenSSH-Server connection issues
Trying to connect your SSH server is failed with the following error: «Connection closed by 127.0.0.1 port 22».
-
Make sure your OpenSSH Server is running:
and you’ve followed this tutorial:
https://ubuntu.com/server/docs/service-openssh -
Stop the sshd service and start sshd in debug mode:
sudo service ssh stop sudo /usr/sbin/sshd -d
-
Check the startup logs and make sure HostKeys are available and you don’t see log messages such as:
debug1: sshd version OpenSSH_7.2, OpenSSL 1.0.2g 1 Mar 2016 debug1: key_load_private: incorrect passphrase supplied to decrypt private key debug1: key_load_public: No such file or directory Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key debug1: key_load_private: No such file or directory debug1: key_load_public: No such file or directory Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key debug1: key_load_private: No such file or directory debug1: key_load_public: No such file or directory Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key debug1: key_load_private: No such file or directory debug1: key_load_public: No such file or directory Could not load host key: /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key
If you do see such messages and the keys are missing under /etc/ssh/, you will have to regenerate the keys or just purge&install openssh-server:
sudo apt-get purge openssh-server sudo apt-get install openssh-server
«The referenced assembly could not be found.» when enabling the WSL optional feature
This error is related to being in a bad install state. Please complete the following steps to try and fix this issue:
-
If you are running the enable WSL feature command from PowerShell, try using the GUI instead by opening the start menu, searching for ‘Turn Windows features on or off’ and then in the list select ‘Windows Subsystem for Linux’ which will install the optional component.
-
Update your version of Windows by going to Settings, Updates, and clicking ‘Check for Updates’
-
If both of those fail and you need to access WSL please consider upgrading in place by reinstalling Windows using installation media and selecting ‘Keep Everything’ to ensure your apps and files are preserved. You can find instructions on how to do so at the Reinstall Windows 10 page.
Correct (SSH related) permission errors
If you’re seeing this error:
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ @ WARNING: UNPROTECTED PRIVATE KEY FILE! @ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ Permissions 0777 for '/home/artur/.ssh/private-key.pem' are too open.
To fix this, append the following to the the /etc/wsl.conf file:
[automount]
enabled = true
options = metadata,uid=1000,gid=1000,umask=0022
Please note that adding this command will include metadata and modify the file permissions on the Windows files seen from WSL. Please see the File System Permissions for more information.
Running Windows commands fails inside a distribution
Some distributions available in Microsoft Store are yet not fully compatible to run Windows commands out of the box. If you get an error -bash: powershell.exe: command not found running powershell.exe /c start . or any other Windows command, you can resolve it following these steps:
- In your WSL distribution run
echo $PATH.
If it does not include:/mnt/c/Windows/system32something is redefining the standard PATH variable. - Check profile settings with
cat /etc/profile.
If it contains assignment of the PATH variable, edit the file to comment out PATH assignment block with a # character. - Check if wsl.conf is present
cat /etc/wsl.confand make sure it does not containappendWindowsPath=false, otherwise comment it out. - Restart distribution by typing
wsl -tfollowed by distribution name or runwsl --shutdowneither in cmd or PowerShell.
Unable to boot after installing WSL 2
We are aware of an issue affecting users where they are unable to boot after installing WSL 2. While we fully diagnose those issue, users have reported that changing the buffer size or installing the right drivers can help address this. Please view this Github issue to see the latest updates on this issue.
WSL 2 errors when ICS is disabled
Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) is a required component of WSL 2. The ICS service is used by the Host Network Service (HNS) to create the underlying virtual network which WSL 2 relies on for NAT, DNS, DHCP, and host connection sharing.
Disabling the ICS service (SharedAccess) or disabling ICS through group policy will prevent the WSL HNS network from being created. This will result in failures when creating a new WSL version 2 image, and the following error when trying to convert a version 1 image to version 2.
There are no more endpoints available from the endpoint mapper.
Systems that require WSL 2 should leave the ICS service (SharedAccess) in it’s default start state, Manual (Trigger Start), and any policy that disables ICS should be overwritten or removed. While disabling the ICS service will break WSL 2, and we do not recommend disabling ICS, portions of ICS can be disabled using these instructions
Using older versions of Windows and WSL
There are several differences to note if you’re running an older version of Windows and WSL, like the Windows 10 Creators Update (Oct 2017, Build 16299) or Anniversary Update (Aug 2016, Build 14393). We recommend that you update to the latest Windows version, but if that’s not possible, we have outlined some of the differences below.
Interoperability command differences:
bash.exehas been replaced withwsl.exe. Linux commands can be run from the Windows Command Prompt or from PowerShell, but for early Windows versions, you may need to use thebashcommand. For example:C:temp> bash -c "ls -la". The WSL commands passed intobash -care forwarded to the WSL process without modification. File paths must be specified in the WSL format and care must be taken to escape relevant characters. For example:C:temp> bash -c "ls -la /proc/cpuinfo"orC:temp> bash -c "ls -la "/mnt/c/Program Files"".- To see what commands are available for a particular distribution, run
[distro.exe] /?. For example, with Ubuntu:C:> ubuntu.exe /?. - Windows path is included in the WSL
$PATH. - When calling a Windows tool from a WSL distribution in an earlier version of Windows 10, you will need to specify the directory path. For example, to call the Windows Notepad app from your WSL command line, enter:
/mnt/c/Windows/System32/notepad.exe - To change the default user to
rootuse this command in PowerShell:C:> lxrun /setdefaultuser rootand then run Bash.exe to log in:C:> bash.exe. Reset your password using the distributions password command:$ passwd usernameand then close the Linux command line:$ exit. From Windows command prompt or Powershell, reset your default user back to your normal Linux user account:C:> lxrun.exe /setdefaultuser username.
Uninstall legacy version of WSL
If you originally installed WSL on a version of Windows 10 prior to Creators update (Oct 2017, Build 16299), we recommend that you migrate any necessary files, data, etc. from the older Linux distribution you installed, to a newer distribution installed via the Microsoft Store. To remove the legacy distribution from your machine, run the following from a Command Line or PowerShell instance: wsl --unregister Legacy. You also have the option to manually remove the older legacy distribution by deleting the %localappdata%lxss folder (and all it’s sub-contents) using Windows File Explorer or with PowerShell: rm -Recurse $env:localappdata/lxss/.
WSL, подсистема Windows для Linux, не работает у пользователей сразу после обновления до Windows 11. По словам пользователей, происходит сбой при попытке запустить ее.
Мы изучили проблему и обнаружили, что эта проблема может быть вызвана рядом причин:
- WSL отключен — функция WSL должна быть включена в диалоговом окне функций Windows, чтобы вы могли ее использовать. Бывают случаи, когда обновление автоматически отключает эту функцию, что приводит к возникновению проблемы.
- Виртуальная машина отключена — как и WSL, функция виртуальной машины также должна быть включена в системе, чтобы вы могли переключиться на другую ОС в Windows. Если эта функция отключена, вы можете включить ее вручную, чтобы решить проблему.
- Поврежденная установка приложения Linux — установочный файл приложения Linux (Ubuntu) может быть поврежден или содержит ошибки, что не позволяет использовать WSL. В этом случае вы можете восстановить приложение или переустановить его, чтобы решить проблему.
- Вредоносное ПО — ваша система Windows может иметь дело с ошибкой повреждения или вредоносным ПО, из-за чего некоторые функции и приложения не работают. Если этот сценарий применим, вы можете запустить сканирование на наличие вредоносных программ, чтобы определить проблему и решить ее.
- Неисправное обновление. Если вы столкнулись с ошибкой после установки обновления системы, есть вероятность, что виновником является ошибочное обновление. К счастью, Windows предлагает способ удаления обновлений, поэтому вы можете удалить обновление из своей системы и посмотреть, имеет ли это какое-то значение.
Теперь, когда мы знаем о потенциальных причинах проблемы, давайте рассмотрим методы устранения неполадок, которые сработали для других затронутых пользователей. Надеюсь, они также помогут вам решить проблему навсегда. Однако, прежде чем приступить к методам, убедитесь, что вы вошли в систему как администратор.
Давайте начнем с наиболее эффективного решения в случаях ошибок, подобных этой.
В большинстве случаев пользователи не могли использовать WSL, потому что эта функция автоматически отключалась при обновлении до Windows 11. Решение в этом случае простое, так как все, что вам нужно сделать, это снова включить эту функцию вручную.
Вот как вы можете это сделать:
- Запустите поиск Windows через панель задач и введите «Включить или отключить функции Windows».
- Нажмите Открыть из списка доступных вариантов.
- В следующем диалоговом окне найдите подсистему Windows для Linux и установите флажок, связанный с ней.
Включить подсистему Windows для Linux - Нажмите OK, чтобы сохранить изменения.
Кроме того, вы также можете использовать Windows Powershell для внесения этих изменений. Если шаги, упомянутые выше, не сработали для вас, выполните следующие действия:
- Введите Windows Powershell в области поиска на панели задач и нажмите «Запуск от имени администратора».
- В следующем окне введите команду, указанную ниже, и нажмите Enter, чтобы выполнить ее.
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-LinuxВключить подсистему Windows для Linux - После выполнения команды перезагрузите компьютер. После перезагрузки функция должна быть включена.
Если функция была отключена, ее включение должно решить проблему. Однако, если эта функция уже была включена, перейдите к следующему способу устранения неполадок ниже.
Чтобы любая из подсистем работала в Windows, виртуальная машина в вашей системе должна работать правильно. Виртуальные машины используются для одновременного запуска нескольких операционных систем на одном оборудовании. Если бы у нас не было виртуализации, нам потребовались бы два отдельных физических устройства для запуска Windows и Linux.
Если функция WSL уже включена в системе, вам нужно проверить, включена ли виртуальная машина. Шаги для этого очень похожи на те, которые мы перечислили выше:
- Введите Включение или отключение компонентов Windows в области поиска на панели задач и нажмите Открыть.
- Теперь найдите платформу виртуальной машины в следующем диалоговом окне и установите флажок, связанный с ней, чтобы включить ее.
Включить платформу виртуальной машины - Пока вы это делаете, мы также рекомендуем включить Hyper-V в том же окне. Hyper-V помогает создать в системе виртуальную среду.
После этого закройте диалоговое окно функций Windows и проверьте, можете ли вы теперь без проблем использовать WSL.
3. Используйте Microsoft Store для запуска WSL
Возможно, вы также не сможете использовать WSL из-за временного сбоя в установленном приложении. В этом случае вы можете попробовать запустить приложение из Магазина Microsoft, а не открывать его напрямую.
Это может показаться слишком простым для работы, но, поскольку это сработало для нескольких других пользователей, мы рекомендуем вам попробовать.
Вот что вам нужно сделать:
- Запустите Microsoft Store и перейдите в раздел «Моя библиотека» в левом нижнем углу.
Нажмите на значок библиотеки - В списке доступных приложений найдите приложение дистрибутива Linux и запустите его.
Если вы по-прежнему не можете запустить приложение, перейдите к следующему способу ниже.
4. Восстановите или переустановите приложение дистрибутива Linux.
Ваше приложение дистрибутива Linux может иметь дело с поврежденной ошибкой или просто может быть устаревшим, что мешает вам использовать его должным образом.
Чтобы проверить, не в этом ли проблема, вы можете сначала попробовать восстановить приложение и посмотреть, имеет ли это какое-то значение. Если ошибка не устранена, вы можете удалить приложение и переустановить его с нуля. Это устранит любые проблемы с повреждением в приложении, которые могут быть причиной проблемы.
Чтобы продолжить, выполните следующие действия:
- Нажмите Win + I, чтобы открыть приложение «Настройки».
- Выберите Приложения на левой панели.
- Нажмите «Приложения и функции» в правой части окна.
Нажмите «Приложения и функции» на правой панели. - В следующем окне прокрутите вниз, чтобы найти приложение дистрибутива Linux.
- Нажмите на три точки, связанные с ним, и выберите «Дополнительные параметры».
Нажмите Дополнительные параметры - Затем перейдите в раздел «Сброс» и нажмите там кнопку «Восстановить».
Нажмите на кнопку Восстановить - Следуйте инструкциям на экране, чтобы продолжить, и дождитесь завершения действия.
После завершения процесса проверьте, можете ли вы сейчас использовать WSL. Если нет, выполните следующие действия, чтобы удалить приложение:
- Повторите шаги 1-4 еще раз.
- Нажмите на три точки, связанные с приложением, и выберите «Удалить» в контекстном меню.
- Следуйте инструкциям на экране, чтобы продолжить.
После удаления приложения переустановите последнюю версию и проверьте, устраняет ли это проблему.
5. Удалить обновления
Если вы начали сталкиваться с проблемой сразу после установки ожидающего обновления системы, есть большая вероятность, что обновление было ошибочным. Пользователи Windows нередко сталкиваются с проблемами из-за поврежденных обновлений.
Лучший способ решить эту проблему — удалить обновление через панель управления.
Вот как вы можете это сделать:
- Введите «Панель управления» в поиске Windows и нажмите «Открыть».
- Выберите Просмотр установленных обновлений.
Просмотр установленных обновлений - В следующем окне вы должны увидеть список всех установленных обновлений в Windows. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши проблемный и выберите «Удалить».
Нажмите кнопку «Удалить».
6. Запустите сканирование на наличие вредоносных программ
Наконец, последний метод в нашем списке — сканирование на наличие вредоносных программ.
Ваша система может иметь дело с вирусом или вредоносным ПО, которое вызывает сбои в работе определенных компонентов и функций. В такой ситуации сканирование вредоносных программ Защитником Windows является наиболее эффективным решением.
Вот как вы можете запустить полное сканирование системы на наличие вредоносных программ с помощью Защитника:
- Введите «Безопасность Windows» в поиске Windows и нажмите «Открыть».
- Выберите Защита от вирусов и угроз на левой панели.
Доступ к настройкам защиты от вирусов и угроз - Переместитесь в правую часть окна и щелкните гиперссылку Параметры сканирования.
Нажмите на параметры сканирования - Нажмите «Полное сканирование» > «Сканировать сейчас».
Выполнить сканирование
Теперь дождитесь завершения сканирования и после его завершения попробуйте снова использовать WSL.
Вы можете столкнуться с ошибкой сбоя выполнения сервера в WSL в одном или нескольких экземплярах вашей системы Windows 11 или Windows 10; в том числе когда вы пытаетесь запустить дистрибутив Linux, когда вы пытаетесь запустить команду bash в этой среде или когда вы пытаетесь обновить/установить WSL или обновить WSL 1 до WSL 2. В этом посте представлены наиболее подходящие исправления этой ошибки в все случаи. Имейте в виду, что устранение ошибки может зависеть от сценария вашей среды.
Если В WSL произошла ошибка сбоя выполнения сервера. среды на вашем компьютере с Windows 11/10, вы можете попробовать наши рекомендуемые ниже решения в произвольном порядке и посмотреть, поможет ли это решить проблему.
- Начальный контрольный список
- Отключить и снова включить WSL
- Отключить платформу виртуальной машины
- Сбросить Windows 11/10
Давайте взглянем на описание процесса, связанного с каждым из перечисленных решений.
1]Начальный контрольный список
Прежде чем попробовать приведенные ниже решения, вы можете сделать следующее и после каждой задачи посмотреть, сможете ли вы выполнить без проблем начальную задачу, которая выдавала ошибку в выделении:
- Перезапустите службу LxssManager. LxssManager — это служба диспетчера сеансов пользовательского режима, которая запускает новый экземпляр WSL с собственными двоичными файлами ELF. Если эта служба остановлена или отключена, эти двоичные файлы больше не будут работать. Чтобы перезапустить службу LxssManager, следуйте инструкциям в сообщении WslRegisterDistribution не удалось с ошибкой: 0x800700b7 или 0x80080005.
- Перезагрузите ПК. Если перезапуск службы LxssManager застрял на этапе «Остановка» или действие завершено, но проблема не устранена, вы можете просто перезагрузить систему вообще.
- Обновите Виндовс. Если Windows не обновлена в вашей системе, вероятно, некоторые функции или возможности не будут работать должным образом. Итак, проверьте наличие обновлений и установите все доступные биты на свое устройство с Windows 11/10 и посмотрите, не появится ли ошибка снова. С другой стороны, если ошибка возникла после недавнего обновления Windows, вы можете выполнить восстановление системы или удалить обновление, но если вы предпочитаете выполнять любую задачу в крайнем случае, вы можете перейти к решениям, приведенным ниже.
2]Отключить и снова включить WSL
Если вы столкнулись с Ошибка выполнения сервера в WSL на вашем компьютере с Windows 11/10, вы можете устранить ошибку WSL, отключив и повторно включив подсистему Windows для Linux на вашем устройстве.
Чтобы отключить и снова включить WSL, достаточно просто включить или выключить эту функцию в апплете дополнительных функций Windows на панели управления или запустить командлет PowerShell.
Чтобы включить подсистему Windows для Linux с помощью Включение или отключение функций Windows диалоговое окно, вам нужно найти Включение или отключение компонентов Windows в поле поиска Windows.
В заполненном списке отметьте опцию для Подсистема Windows для Linux. Выберите ОК. Он найдет и установит некоторые необходимые системные файлы и попросит вас перезагрузить компьютер. После перезагрузки компьютера ваш дистрибутив Linux будет работать без проблем.
Либо откройте Windows PowerShell с правами администратора. Выполните следующую команду, чтобы включить функцию подсистемы Windows для Linux:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Он начнет поиск и установку некоторых необходимых системных файлов.
При появлении запроса вам нужно ввести Y, чтобы перезагрузка твой компьютер.
Он установит все необходимые системные файлы, и теперь ваш дистрибутив Linux обычно работает.
Обязательно перезагрузите ПК после отключения, и еще раз перезагрузите после включения.
Однако это решение может быть не идеальным, если ошибка возникает несколько раз, как сообщают некоторые затронутые пользователи ПК. В этом случае вы можете попробовать любое другое решение в этом посте.
3]Отключить платформу виртуальной машины
Это решение требует, чтобы вы отключили платформу виртуальной машины, а не только отключили Hyper-V на вашем компьютере с Windows 11/10. Для выполнения этой задачи выполните следующие действия:
- Нажмите клавишу Windows + X, чтобы открыть меню опытного пользователя.
- Нажмите A на клавиатуре, чтобы запустить PowerShell в режиме администратора/с повышенными правами.
- В консоли PowerShell скопируйте и вставьте приведенную ниже команду и нажмите Enter:
$ dism.exe/online/disable-feature/featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform/norestart $ dism.exe/online/disable-feature/featurename:Microsoft-Hyper-V/norestart
- Выйдите из PowerShell после выполнения команды.
- Перезапустить компьютер.
4]Сбросить Windows 11/10
Если до сих пор ничего не сработало, возможно, вы имеете дело с серьезным повреждением системы, которое, например, нельзя устранить обычными методами; Сканирование SFC/DISM. В этом случае, чтобы увидеть, будет ли проблема устранена, вы можете сбросить Windows 11/10 с возможностью сохранить свои личные файлы. После сброса вы можете заново настроить WSL на своем устройстве.
В маловероятном случае, если рассматриваемая проблема сохраняется после процедуры сброса, вы можете задать вопрос на GitHub.com по вопросам, связанным с WSL.
Надеюсь, этот пост поможет вам!
Сообщение по теме: Ошибка выполнения Windows Backup Server (0x80080005)
Почему я продолжаю получать сообщения о сбое выполнения сервера?
Ошибка Windows Media Player Ошибка выполнения сервера может быть вызвана повреждением системных файлов Windows. Эта ошибка также может возникнуть, если по какой-либо причине сетевая служба проигрывателя Windows Media остановлена или возникла проблема с вашей учетной записью пользователя.
Почему мой WSL не работает?
Если WSL не работает на вашем ПК с Windows 11/10, это может быть связано с рядом причин, включая устаревшую ОС или поврежденные системные файлы. Как правило, вы можете обновить свою версию Windows. Если проблема не устранена и вам нужен доступ к WSL, попробуйте выполнить обновление на месте, переустановив Windows с помощью установочного носителя и выбрав Сохранить все чтобы обеспечить сохранность ваших приложений и файлов.
Связанный: Ошибка выполнения сервера Explorer.exe
WSL быстрее, чем виртуальная машина?
Кроме того, гораздо быстрее запустить терминал WSL, чем запустить полноценную виртуальную машину. WSL также гораздо полнее интегрируется в Windows, чем обычная виртуальная машина в VirtualBox. Хотя есть способы интегрировать рабочий стол Windows и виртуальную машину Linux в VirtualBox, для правильной работы может потребоваться некоторое время. WSL 2 работает как виртуальная машина Hyper-V.
I am attempting to install the Windows Subsystem for Linux on my Windows 7 machine, following the instructions shown in this documentation.
The first step there says to run the command
> Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
However, my machine does not recognize the Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature command.
PS C:> Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : The term 'Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature' is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet,
function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the
path is correct and try again.
At line:1 char:1
+ Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows- ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : ObjectNotFound: (Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature:String) [], CommandNotFoundException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : CommandNotFoundException
- Why does my machine not recognize the
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature - How can I proceed to install the Windows Subsystem for Linux?
Я пытаюсь включить подсистему Linux на Windows Server 2016 на AWS EC2, выполнив следующие действия. эти инструкции https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install-on-server
Вот сообщение об ошибке:
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature : Feature name Microsoft-Windows-Subsystem-Linux is unknown.
At line:1 char:1
+ Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Windows- ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature], COMException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : Microsoft.Dism.Commands.EnableWindowsOptionalFeatureCommand
Мой сервер Windows создан на основе AMI AWS .
Как я могу узнать, поддерживает ли мой оконный сервер подсистему linux? Могу ли я что-нибудь сделать, чтобы включить эту функцию?
Обновление:
> systeminfo | Select-String "^OS Name","^OS Version"
OS Name: Microsoft Windows Server 2016 Datacenter
OS Version: 10.0.14393 N/A Build 14393
задан
6 February 2018 в 02:33
Ссылка