The #1 containerization software for developers and teams
Your command center for innovative container development
What’s Docker Desktop?
The fastest way to containerize applications
Docker Desktop is secure, out-of-the-box containerization software offering developers and teams a robust, hybrid toolkit to build, share, and run applications anywhere.
Why developers love Docker
Quick to set up
Start developing on your local machine and immediately connect with remote resources. Docker Desktop’s single installer sets up everything you need to start building, sharing, and running containers in seconds.
Simple to maintain
Our monthly releases include new features to help developers, team leads, and businesses rapidly deliver secure and innovative applications. Docker Desktop is also regularly maintained with bug fixes and security updates.
Secure from the start
We’re setting the standard for enterprise-ready container development solutions. Docker Desktop is secure from the first download, consistently monitoring and managing patches and security fixes as needed.
Easy to scale
Whether you’re a small startup or an organization with 1,000+ developers, Docker Desktop is designed to grow with you. Scale confidently with features such as Hardened Docker Desktop.
Enterprise ready
Develop with Docker containers at scale
Whether you’re orchestrating mid-sized to large development teams or require advanced security and management tools, Docker is your unwavering partner in providing a complete suite of developer tools and services. Trusted by an astounding 70% of Fortune 100 companies, we’re helping our customers streamline how they build, share, and run applications.
Get started with Docker Business
Your perfect pricing
A subscription level for everyone
Choose the subscription level that supports your development velocity and start building with Docker Desktop today.
Pro
Includes pro tools for individual developers who want to accelerate their productivity.
Buy now
Team
For smaller teams requiring collaboration and productivity tools.
Buy now
Business
Ideal for businesses looking for centralized management and advanced security capabilities.
Buy now
Docker Desktop Extensions
Extend the power of Docker Desktop
Extensions expand Docker Desktop’s capabilities and establish new functionalities, integrating your most critical tools seamlessly. At Docker we’re invested in ensuring individual developers and teams can build their ideal development environment.
Docker Extensions
Our community
Find your pod with Docker
Our worldwide community means you can find a peer community near you.
Join our pod
Connect with developers
Collaborate with our over 200+ user groups either virtually or in person.
Join Docker events
Learn about new products, features, and other topics at Docker-sponsored events.
Meet Docker Captains
In every friend group, there are always go-to experts you look to for advice — those are our Docker Captains.
Developer resources
Find support
Get the help you need to build, share, and run your Docker applications with confidence.
Get support
Get started
Learn more about Docker and customize your experience with additional tools.
Download and install
Visit our Docs for instructions on quickly installing Docker Desktop for Windows, Linux, or Mac.
Get the latest news
Read the blog to stay current on new releases, products, features, and much more.
Эта статья даст вам полное представление о Docker Desktop для пользователей Windows и MAC. Мы изучим установку Docker Desktop на компьютерах с Windows и Mac. После установки мы также попытаемся выполнить некоторые операции Docker.
Docker Desktop — это собственное настольное приложение, разработанное Docker для пользователей Windows и MAC. Это самый простой способ запуска, сборки, отладки и тестирования приложений Dockerized.
Docker Desktop предлагает важные и наиболее полезные функции, такие как быстрые циклы редактирования, уведомления об изменениях файлов, встроенная поддержка корпоративной сети и гибкость для работы с собственным выбором прокси и VPN.
Docker Desktop состоит из инструментов для разработчика, приложения Docker, Kubernetes и синхронизации версий. Он позволяет вам создавать сертифицированные образы и шаблоны языков и инструментов.
Скорость, безопасность и выбор — все, что вам нужно для разработки и доставки контейнерных приложений, доступных на вашем рабочем столе, будет представлено вам.
Прежде чем перейти к процессу установки, давайте разберемся с его версиями.
Версии Docker
Docker в основном поставляется в двух версиях, в Community и ENterprise.
Community версия поставляется с бесплатным набором продуктов Docker. ENterprise корпоративная версия представляет собой сертифицированную контейнерную платформу, которая предоставляет коммерческим пользователям дополнительные функции, такие как безопасность образов, управление образами, оркестровка и управление средой выполнения контейнеров, но по разумной цене.
Мы начнем наше обучение с Community Edition. Контейнеры Docker, работающие в конкретной операционной системе, совместно используют ядро ОС. Это означает, что мы не можем использовать ядро Windows (хост) для запуска контейнеров Linux или наоборот. Чтобы проделать это, у нас есть Docker Desktop для Windows и MAC.
Выпуски Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop выпускается в двух вариантах.
- Stable: как видно из названия, стабильный выпуск тщательно протестирован и может быть использован при разработке более надежных приложений. Его версии полностью синхронизированы с версиями Docker Engine.
- Edge: эти версии состоят из всех новых и экспериментальных функций Docker Engine. Есть больше шансов ошибок, сбоев и проблем, которые могут возникнуть. Тем не менее, пользователи получат возможность ознакомиться с предстоящими функциями.
Docker на Windows
Есть два варианта Docker на Windows.
1. Использование Docker Toolbox
Docker Toolbox предоставляет набор легких инструментов.
- Oracle virtual box
- Docker Engine
- Docker Machine
- Docker compose
- Kitematic GUI
Вышеуказанные инструменты устраняют необходимость развертывания отдельной виртуальной машины для запуска Docker. Просто установите исполняемый файл панели инструментов Docker непосредственно в Windows и начните разработку приложений. Требуется 64-битная ОС и Windows 7 или выше с включенным режимом виртуализации.
Но опять же, панель инструментов Docker — это оригинальная поддержка, предоставляемая в Windows для запуска Docker и его устаревшего решения для всех ОС Windows, которые не соответствуют требуемой конфигурации.
2. Использование Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop — это новейшая технология, используемая для Docker в Windows. Он заменяет виртуальную машину Oracle собственной технологией виртуализации, доступной в Windows, то есть Microsoft Hyper-V.
Он по-прежнему будет запускать Docker на Linux-машине, созданной под ним. Но на этот раз вместо виртуальной машины Oracle мы использовали нативный Microsoft Hyper-V.
Установка Docker на Windows
Вы можете скачать репозиторий Docker Desktop из Docker Hub.
истемные требования:
- Windows 10 или Windows Server 2016 Professional или Enterprise Edition
- Поддержка Hyper-V.
Чтобы запустить Hyper-V, оборудование должно соответствовать следующим требованиям:
- 64-битный процессор
- > = 4 ГБ ОЗУ
- Поддержка виртуализации оборудования на уровне BIOS
Следовательно, программная и аппаратная зависимость заключается в запуске Docker Desktop на Windows.
Установка Docker на macOS
Вы можете скачать репозиторий Docker Desktop из Docker Hub.
Системные требования:
- MAC Hardware 2010 или новее с аппаратной поддержкой управления памятью и неограниченным режимом. Выполните команду kern.hv_support, чтобы проверить, поддерживает ли оборудование MAC инфраструктуру гипервизора.
- MAC OS версии 10.13 или новее.
- > = 4 ГБ ОЗУ
- Virtual-Box до версии 4.3.30
Работа с образами
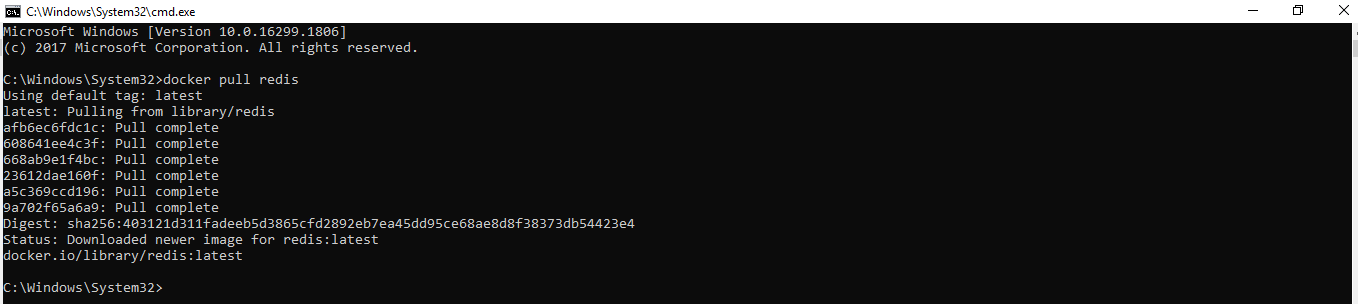
После установки проверьте версию установленного Docker Engine.
docker --versionDocker работает с доставкой и запуском контейнерных приложений. Вам либо нужно создать свое собственное контейнерное приложение, либо Docker поддерживает контейнерные образы в Docker Hub, и его можно легко загрузить с помощью простой команды docker run.
Здесь мы будем тянуть образ Redis.
docker pull redisС помощью простой команды run образы можно скачивать и загружать на GitHub или Docker Hub, и любой пользователь во всем мире может получить к нему доступ и начать работать с ним.
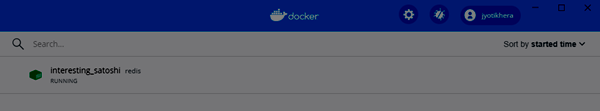
Docker Container запускает образ Docker. Следующим шагом является запуск контейнера.
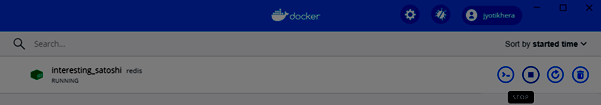
docker run -p 6379 RedisБудет создан зашифрованный идентификатор контейнера. Вы можете быстро проверить состояние работающего экземпляра в Docker, нажав на Dashboard option.
Обязательно остановите контейнер, прежде чем удалять его из Docker Engine.
Возможности Docker Desktop
Существует множество преимуществ:
- Поддерживает широкий спектр инструментов разработки.
- Обеспечьте быстрый и оптимизированный способ создания и публикации контейнерного образа на любой облачной платформе.
- Простота установки и настройки полной среды Docker
- Повышение производительности благодаря встроенной виртуализации Hyper-V для Windows и HyperKit для MAC.
- Возможность работать в Linux через WSL 2 на компьютерах с Windows.
- Легкий доступ к работающим контейнерам в локальной сети.
- Возможность поделиться любым приложением на облачной платформе, на разных языках и в разных средах.
- Для обеспечения безопасности и актуальности выполняются автоматические обновления.
- Включены последние версии Kubernetes.
- Возможность переключения между Linux и Windows сервером на Windows.
Docker Desktop — это нативное приложение, разработанное на Windows и MAC OS для запуска, сборки и доставки контейнерных приложений или сервисов.
Однако
Docker Desktop предназначен не для производственной среды, а для рабочего стола и среды разработки.
Также рекомендуем прочитать:
- Docker для начинающих — технология контейнеров
- В чем разница между Docker и Kubernetes?
- Введение в Docker Hub и все, что вы должны знать о нем
- Как установить Docker на Ubuntu, Windows, Debian и CentOS?
- Kubernetes — Введение для начинающих
- Docker посмотреть запущенные контейнеры, запустить или остановить контейнеры
Docker Desktop for Windows is a version of the Docker platform that is designed to work on Windows operating systems. It allows developers to create, deploy, and run containerised applications on their Windows development machine. To run Windows containers, you need Windows 10 or Windows 11 Professional or Enterprise edition. Windows Home or Education editions will only allow you to run Linux containers.
Docker Desktop uses Hyper-V
Internally, Docker Desktop for Windows uses the Hyper-V technology built into Windows to create a lightweight virtual machine (VM) that runs the Docker Engine. This VM runs a minimal Linux distribution, such as Moby Linux, which is specifically designed to support the Docker Engine.
When you run a container on Docker Desktop for Windows, the Docker Engine in the VM creates a new container process and isolates it from the host operating system using the Linux kernel’s built-in containerization features. The container process runs inside the VM, but it can access the host’s filesystem, network, and other resources through a set of virtualized interfaces provided by the Docker Engine.
Components of Docker Desktop for Windows
In Docker Desktop for Windows, the various components you mentioned are part of the overall architecture that provides an easy-to-use environment for building, shipping, and running Docker containers. Here’s a brief description of each component:
1. Bootstrapper
The bootstrapper is the component responsible for setting up and starting the Docker engine in Windows. It performs tasks such as installing the Docker engine and configuring the necessary environment variables.
2. Life Cycle Controller
The life cycle controller is responsible for managing the lifecycle of containers, such as starting and stopping containers, and managing the resources allocated to containers.
The Windows native symlinks are visible within the containers as symlinks, whereas symlinks created inside a container are represented as mfsymlinks. These are regular Windows files with a special metadata. Therefore the symlinks created inside a container appear as symlinks inside the container, but not on the host.
3.Docker Proxy
The Docker proxy is a component that provides a secure, encrypted connection between the Docker client and the Docker engine. It acts as a bridge between the client and the engine, and helps to ensure that sensitive information, such as authentication credentials, are transmitted securely.
4. DockerD (Windows)
DockerD (Windows) is the Docker daemon that runs in the background on Windows. It communicates with the Docker client and provides the necessary resources to run containers.
5. CLI Plugins
CLI plugins are components that extend the functionality of the Docker client by adding new commands and options. They can be installed to add support for new technologies or to provide additional functionality beyond what is provided by the base Docker client.
These components work together to provide an easy-to-use environment for building, shipping, and running Docker containers on Windows. They allow users to manage containers, interact with Docker Hub, and access the Docker engine, all from a single, user-friendly interface.
6. Docker Integrated Package
In Docker Desktop for Windows, the Docker Integrated package is a feature that allows you to run the Docker daemon and client directly inside the Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL 2) virtual machine (VM) that Docker Desktop creates. This allows you to run Linux containers natively on the Windows host, without the need for a separate virtual machine (VM) to run the Docker Engine.
When you enable the Docker Integrated package in WSL 2, the Docker daemon and client are installed inside the WSL 2 VM, and the Docker Engine runs natively on the Linux kernel that WSL 2 uses. This means that you can use the Docker command line and API directly inside the WSL 2 VM, just as you would on a Linux machine.
The Docker Integrated package also allows you to access the host’s filesystem, network, and other resources from inside the WSL 2 VM. This is done by mapping the host’s resources to the WSL 2 file system and network interfaces, which makes them available to the Docker daemon and client running inside the WSL 2 VM.
The Docker Integrated package also includes an integration with the Windows Docker client, which allows you to use the Docker command line and API from the Windows host, while the actual container runs on the WSL 2 VM.
With the Docker Integrated package, you can use the same Docker commands and configuration files that you use on Linux, and you can run the same Linux containers that you would run on a Linux machine. This makes it easy to switch between Windows and Linux development environments without having to learn new tools or workflows.
Please note that the Docker Integrated package is an experimental feature and it’s still in development.
7. Docker Proxy
The Docker Proxy is a feature of Docker Desktop for Windows that allows you to run Linux containers on the Windows host, by routing the container’s network traffic through a proxy that runs inside the Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL 2) virtual machine (VM).
When you run a Linux container on Docker Desktop for Windows, the Docker Engine creates a new container process and isolates it from the host operating system using the Linux kernel’s built-in containerization features. However, the container process runs inside the WSL 2 VM, which is isolated from the host network and cannot access the host’s network resources directly.
The Docker Proxy feature allows the container to access the host’s network resources by routing the container’s network traffic through a proxy that runs inside the WSL 2 VM. The proxy listens for incoming traffic on the host’s loopback interface and forwards it to the container running inside the WSL 2 VM. This allows the container to access the host’s network resources, such as the host’s IP address and ports, as if it were running directly on the host.
The Docker Proxy feature also allows you to access the container’s network resources from the host, by routing the host’s network traffic to the container through the proxy. This allows you to access the container’s services, such as web servers or databases, using the host’s IP address and ports.
The Docker Proxy feature is enabled by default when you run Linux containers on Docker Desktop for Windows, and it’s transparent to the user.
Additionally, Docker Desktop for Windows allows you to run both Linux and Windows container at the same time by leveraging Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) 2. With this setup, you can run Linux containers on the WSL 2 virtualized Linux kernel, while still having access to the host’s resources.
Docker Desktop for Windows also includes a built-in Kubernetes engine, which allows you to deploy, scale and manage containerized applications using Kubernetes.
8. Containerd
In Docker Desktop for Windows, containerd is a core component that runs on the Windows host and provides the container runtime for the Docker Engine. It works in conjunction with the Windows Subsystem for Linux 2 (WSL 2) to enable running Linux containers on Windows.
When you run a Linux container, the Docker Engine sends a request to containerd to start the container. containerd then uses WSL 2 to launch a lightweight virtual machine (VM) that runs the container process inside. This VM runs a minimal Linux distribution, such as Alpine Linux, that is specifically designed to support the container runtime.
The container process runs inside the WSL 2 VM, but it can access the host’s filesystem, network, and other resources through a set of virtualized interfaces provided by containerd. These interfaces are implemented using the 9P protocol and are mapped to the host’s resources using the WSL 2 file system and network interfaces.
containerd also provides the container runtime, which is responsible for starting and stopping container processes, and managing their lifecycle. This runtime is based on the OCI (Open Container Initiative) runtime specification, which is an open standard for container runtimes.
In summary, Docker Desktop for Windows uses containerd to run Linux containers on Windows by leveraging the WSL 2 technology. containerd provides the container runtime and handles the communication between the host and the WSL 2 VM, while WSL 2 provides the virtualization and isolation of the container process from the host.
Please follow and like us:
Docker Desktop is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) tool that covers a virtual machine installation. Docker components are unrestricted for Windows, Mac, and Linux, and most Docker containers operate on Linux; Desktop is only open for Windows and Mac. This virtual machine is not required on Linux, as the Docker Engine can execute directly here. Docker Desktop is utilized on Windows and Mac to handle various Docker components and functions, including containers, images, volumes, local Kubernetes, etc. If you’re a container creator, using the latest runtime engine version is always advisable. Jack Wallen shows you how to install that most up-to-date Docker version.
However, the most recent Desktop Docker release is 4.12.0(released June 6, 2021). It may not contain bold new features, but it will undoubtedly include bug fixes and various patches—upgraded kernel to 5.10.124. In specific circumstances, it benefits from installing the latest Docker version. The below article will talk about the overview, features, installation, etc. of the Docker Desktop latest version. Anyone interested in learning Docker will benefit from the Docker online course. This DCA course also is well-suited for freshers, Software developers, Software engineers, Technical leads, System administrators etc.
Docker Desktop Overview
One of the most reasonable ways to start with Docker is installing Docker Desktop on Mac or Windows. Everyone would wonder, «What is Docker Desktop, and how’s it distinguishable from the Docker Engine (open-source)?»
Docker Desktop version is a GUI on top of Docker Engine and is an easy-to-install application. It includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose version, Docker Content Trust, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper. Docker Desktop still utilizes Docker Engine at its core. These tools seamlessly integrate, and interoperability makes Docker Desktop user-friendly—regardless of the experience with Docker.
Following are the features we get after installing and using Docker Desktop.
- Easy to use and install the environment to build, ship, and run your containers.
- An effortless way to design and manage using volumes.
- Management within Locally or remotely of Docker images.
- Collaborating in a better way by sharing repeatable and reproducible development from your local machine to the container.
- Straightforward, one-click Kubernetes setup for your local machine.
- A dashboard for a quick summary of containers running, images, and volumes.
- Support for developing and employing multi-architecture images.
Docker Desktop adds features atop open-source tooling, allowing it to maintain, monitor easily, and update Docker tooling. Docker Desktop collaborates easily using Docker Dev Environments, authorizing teams to transmit the work with one click via Git or Docker Hub.
It has an easy-to-use UI with everyday actions:
- Starting a container
- Pausing and resuming a container
- Stopping a container
- Establishing a single-node local Kubernetes cluster
- Designing or deleting volumes
GUI and CLI are also always available to you based on your preferences.
Docker Desktop 4.12.0 — What has Changed?
Docker Desktop version is a GUI on top of Docker Engine and is an easy-to-install application. Below details the information about the new features, improvements, known issues, and bug fixes in Docker Desktop releases.
- Added the ability to utilize the Container for pulling and accumulating images.
- Search capacities were added to Docker Extension’s Marketplace.
- The ability to zoom in and out capability of the Docker Desktop to Actual Size was added.
- Compose stop button was added.
- Separate compose containers are deletable from the Container.
- It has executed an integrated terminal for containers.
- Added a tooltip to portray the link address for all external links.
- Bug fixes and minor changes.
For all platforms
- Compose V2 is enabled on new installations of Docker Desktop.
- Upgraded kernel version to 5.10.124.
- Improved general performance issues rendered by computing disk size.
- Fixed a bug that made Docker clients hang on docker exec in some languages.
- Fixed a bug that induced extensions to be portrayed as disabled in the left menu when they were not.
- Fixed docker login to private registries.
- Fixed a bug where Docker Desktop fails to start the Kubernetes cluster if the current cluster metadata is not accumulated in the .kube/config file.
For Mac
- The minimum version required to install or update Docker Desktop on macOS is now 10.15.
- After applying an update Docker Desktop didn’t restart. This was a bug and fixed.
- Fixed a bug that caused the connection to Docker to be lost when the computer sleeps if a user is using virtualization.
- Disabled both Virtualization Framework and VirtioFS for users running macOS < 12.5
For Windows
-
Fixed a bug where versions displayed during an update could be incorrect. Security
For all platforms
-
Fix RCE via extension description/changelog which a malicious extension could abuse.
For Windows
-
Fixed the argument injection to the Docker Desktop installer, which may escalate local privilege.
Docker Desktop 4.9.0
Docker Desktop 4.9.1 is packed with Docker Engine 20.10.16 and Compose 2.6.0. A new release is available for download, and users can update if the existing 4.9.0 version is in the system.
Below are the few notable changes and new features introduced with the 4.9.1 release:
- The new release has added additional guides on the homepage for Elasticsearch, MariaDB, Memcached, MySQL, RabbitMQ, and Ubuntu.
- Added a footer to the Docker Dashboard having general information regarding the Docker Desktop status update and Docker Engine statistics.
- Added below components and Re-designed the containers table:
- Added a button to copy a container ID to the clipboard.
- Added to each container is a pause button.
- Column resizing for each containers table
- Sorting and resizing for the containers table
- Bulk deletion allowed for the containers table
- The docker/disk-usage extension updated to v0.2.4 allows to view disk space used by Docker and recycle disk space in one click.
- Re-designed the Containers tables.
- Resizing columns and bulk delete containers is possible.
- Sorting is also now continued.
- New actions, i.e., to copy the Container ID or pause a container, are feasible.
How to Download and Install Docker Desktop 4.12.0 (Win, macOS, Linux)
Docker Installation on Windows
-
Navigate to the website https://docs.docker.com/docker-for-windows/install/ and download the docker file.
Note: A 64-bit processor and 4GB system RAM are the hardware prerequisites to run Docker on Windows 10 successfully.
- Double-click on the Docker Desktop Installer.exe to execute the installer.
- Note: Installer (Docker Desktop Installer.exe) is not downloaded; get it from Docker Hub and run it whenever required.
- Enable Hyper-V Windows Feature on the Configuration page after docker is installed.
- Follow the installation process to permit the installer and pause till the process is done.
- After the installation is completed, click Close and restart.
Docker Installation on Linux
Below will explain instructions on installing and updating Docker Desktop for Linux.
System requirements
- To have Docker Desktop installed Linux host successfully should meet the following requirements:
- CPU support for virtualization and 64-bit kernel.
- KVM virtualization support. Check if KVM kernel modules are enabled and access is provided to the KVM device.
- QEMU must be version 5.2 or newer
- At least 4 GB of RAM.
Click on the link to the docker and Kubernetes online training, which will navigate to the KnowledgeHut site, which provides expert training for all individuals who seek to shape their career in the Containerization area.
Installation steps
Download the accurate package for Linux and install it with the related package manager. Supported Platforms are Debian, Fedora, Ubuntu, Arch.
Open the Applications menu in Gnome/KDE Desktop and explorer Docker Desktop.
- Choose Docker Desktop to begin Docker.
- The Docker menu () demonstrates the Docker Subscription Service Agreement window.
- Set the checkbox to accept the updated terms and click Accept to continue. Docker Desktop begins after you accept the terms.
Docker installation on Mac
Below is information about Docker Desktop for Mac system requirements, download URLs, and instructions to install and update Docker Desktop for Mac. Download Docker Desktop for Mac
- Open the installer by double clicking on Docker.dmg. Docker icon to be extracted to the Applications folder.
- Double-click Docker.app found in the Applications folder to start Docker. The application folder is within the grid” view mode.
- The Docker Subscription Service Agreement window is revealed within The Docker menu (). Docker Desktop begins after you accept the terms.
Downloading Docker.dmg, execute the following commands in a terminal to install Docker Desktop
$ sudo hdiutil attach Docker.dmg $ sudo /Volumes/Docker/Docker.app/Contents/MacOS/install $ sudo hdiutil detach /Volumes/Docker
macOS generally conducts security reviews for the first time an application is used; the install command can take several minutes to execute.
If you want to learn more about docker desktop in Windows, Linux, and macOS along with the best courses for DevOps, check out our courses.
Rolling Back to a Previous Version of Docker Desktop
Navigate to docker to find a list of all releases with links to download for Windows, macOS, and various Linux distros.
Download the release to roll back the installer. It will prompt you to replace the current version of Docker Desktop with the new one; click yes or no to abort the installation.
Images and volumes that you had previously should still be available after the replacement.
Unfortunately, this doesn’t always work for all versions or operating systems. For example, it would be necessary to uninstall the existing version and install the new one on Windows. It is a bit more inconvenient than replacing the current version since it is required to rebuild the whole image, but in the end, it does let you roll back to an older version!
Checking Docker Desktop and Docker Engine Versions (Win, macOS, Linux)
The Docker engine version can be determined using the command line or GUI (graphical user interface).
Using Command Line
Run the following command on the terminal
docker version
Results can be obtained as follows (besides the Docker engine version, there is some helpful information):
Using GUI
This method is available if Docker Desktop is installed.
In the Docker dashboard, click on the gear icon to go to the Settings area:
The version number can be viewed by selecting Docker Engine from the left-hand sidebar
For Mac Users
Click on Docker Desktop and select About Docker Desktop from the drop-down menu:
The version of your Docker Desktop app will show up within a dialog window.
For Windows Users
Right-click on the Docker icon from the system tray
Select About Docker Desktop from the menu:
Notes on Earlier Docker Desktop Versions
Following are the notes for the earlier docker desktop versions
Docker Desktop 4.10.0
- Environment variables can be added before operating an image in Docker Desktop.
- Features added to work with a container’s logs, such as regular expression search and the ability to clear container logs while the container is still running.
- Implemented feedback on the containers table.
- Added two new extensions, Ddosify and Lacework, to the Extensions Marketplace
Docker Desktop 4.9.0
- Added additional directions on the homepage for Elasticsearch, MariaDB, Memcached, MySQL, RabbitMQ, and Ubuntu.
- Added a footer to the Docker Dashboard with general information about the Docker Desktop update status and Docker Engine statistics
- Re-designed the containers table by adding a button to copy a container ID to the clipboard, a pause button for each container, Column resizing for the containers table, Persistence of sorting and resizing for the containers table, Bulk deletion for the containers table
Docker Desktop 4.8.0
- Docker Desktop for Linux was released.
- Docker Extensions and Extensions SDK (beta versions) was released.
- Docker Homepage, where you can run popular images and discover how to use them, was created.
- Compose V2 is now GA
Docker Desktop 4.7.0
- IT Administrators can easily install Docker Desktop remotely utilizing the command line.
- Added Docker Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) CLI plugin.
- For all platforms: Registry Access Management policy bug would never get refreshed after a failure. Login feedback has improved.
- For Mac: An issue that caused Docker Desktop to portray a blank white screen has been fixed.
- For Windows: Fixed volume title. A bug in the WSL 2 integration that caused Docker commands to stop working after restarting Docker Desktop or switching to Windows containers has been fixed.
Docker Desktop 4.6.0
- For all platforms: Fixed issue that could help attackers to alter files in container images on the host from inside a container
- For Windows: Fixed an issue that allowed an attacker to overwrite any administrator writable file on the system during the installation or the update of Docker Desktop.
New
- For all platforms: The Docker Dashboard Volume Management feature now offers the ability to clean up volumes using multi-select checkboxes efficiently.
- For Mac: Docker Desktop allows macOS users to enable a new experimental file-sharing technology called VirtioFS.
Docker Desktop 4.5.0
Security:
- For Mac: It fixed an issue where Docker Desktop is used to access any user file on the host from a container, bypassing the permitted list of shared folders.
- For Windows: It Fixed an issue where Docker Desktop permits assailants to push or move arbitrary files.
- New: Introduces the latest version of the Docker menu, creating a consistent user experience across all operating systems. The ‘docker version’ displays the version of the Docker Desktop installed on the machine.
Docker Desktop 4.4.0
For Windows: Fixed login issues in from WSL 2
Docker Desktop 4.3.0
- For all platforms: Added a self-diagnose notification if the host lacks Internet connectivity.
- For Mac: Docker Desktop on Apple silicon no longer requires Rosetta 2, except for three optional command line tools.
- For Windows: It fixed an issue causing Docker Desktop to fail during startup if the home directory path contains a character used in regular expressions.
Docker Desktop 4.2.0
- Pause/Resume: It is now possible to pause the Docker Desktop session when not actively used, saving CPU resources on your machine.
- Software Updates: Integrated option to turn off the automatic check for updates is available for users on all Docker subscriptions, including Docker Personal and Docker Pro.
- Window management: The Docker Dashboard window size and position endure when you close and reopen Docker Desktop. Fixed Docker Desktop as it sometimes hung when clicking Exit in the fatal error dialog.
- Mac: Fixed issue that caused Docker Desktop to stop reacting upon clicking Exit on the fatal error dialog.
Docker Desktop 4.1.0
Docket had a few enhancement integrated as follows:
- Software Updates: The Software Updates section informs you about new updates and permits you to download, update or view information on what’s included in the more recent version.
- Compose V2 Select to use Docker Compose V2 in the General settings.
- Volume Management: Volume management is open for users on any subscription, including Docker Personal.
For Windows
Rectified bug associated with anti-malware software triggering; self-diagnose avoids calling the net.exe utility.
Docker Desktop 4.0.0
- Docker announced updates and extensions to the product subscriptions to increase productivity and collaboration and added security for our developers and businesses.
- Docker Desktop stays free for small businesses, personal use, education, and non-commercial open-source projects.
- It demands a paid subscription (Pro, Team, or Business), for as little as $5 a month, for professional use in larger enterprises.
- Docker was released for Mac and windows.
Summary
Docker Desktop is an easy-to-install application on Mac or Windows that helps you build and share containerized applications and microservices. It delivers a simple interface that handles containers, applications, and images directly from the machine without including the CLI to perform core actions. Docker Desktop operates with the choice of development tools and languages and delivers a vast library of certified images and templates in Docker Hub.
Docker Desktop for Windows
Getting Docker Desktop for Windows
Docker Desktop for Windows is free to download.
Documentation
If you don’t understand something about Docker Desktop for Windows, the extensive
documentation is a great place
to look for answers.
Support
Support for Docker Desktop is available to Docker customers on a Pro or Team plan
by completing the Desktop support form.
Bugs with the Docker Desktop for Windows software can be filed as issues in this
(docker/for-win) repository, which we respond to
on a best-effort basis. Support requests in this repository (i.e., trouble installing
or using the software) will be ignored, but community support is available from the
Docker community Slack.
This Repository
This repository contains an issue tracker for Docker Desktop for Windows — an
integrated Docker experience on Microsoft Windows. If you find a problem
with the software, first browse the existing
issues or search from the bar
at the top (s to focus) and then, if you don’t find your issue, open
a new issue.
Component Projects
Docker Desktop for Windows uses many open source components. A full list of
components and licenses is available inside of Docker Desktop from About Docker Desktop -> Acknowledgements in the 🐳 menu.
Some notable components include:
- DataKit, a tool to orchestrate
applications using a 9P dataflow - VPNKit, a set of tools and
services for helping HyperKit VMs interoperate with host VPN
configurations