Рассмотрим установку Docker Desktop for Windows — это Community-версия Docker для систем Microsoft Windows.
Системные требования
- Windows 10 64-bit: Pro, Enterprise, Education (Build 16299 или выше).
Для успешного запуска Client Hyper-V в Windows 10 требуются следующие предварительные требования к оборудованию:
- 64 bit процессор c поддержкой Second Level Address Translation (SLAT).
- 4GB системной памяти.
- Поддержка аппаратной виртуализации на уровне BIOS должна быть включена в настройках BIOS.
Подготовка
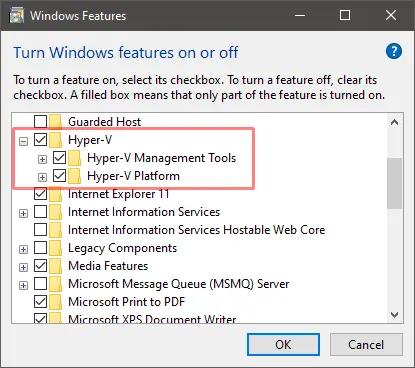
Включаем функции Hyper-V Containers Window. Для этого переходим в панель управления — установка и удаление программ — включение или отключение компонентов Windows. Активируем пункт Hyper-V, который включает Hyper-V Managment Tools, Hyper-V Platform.
Также это можно выполнить через powershell или dism (все команды необходимо выполнять с правами администратора).
Powershell:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Microsoft-Hyper-V -All
DISM:
DISM /Online /Enable-Feature /All /FeatureName:Microsoft-Hyper-V
Установка
Скачиваем установщик Docker (Docker Desktop Installer) с Docker Hub.
Установка Docker Desktop включает Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes и Credential Helper. Контейнеры и образы, созданные с помощью Docker Desktop, используются всеми учетными записями пользователей на компьютерах, на которых он установлен. Это связано с тем, что все учетные записи Windows используют одну и ту же виртуальную машину для создания и запуска контейнеров. При использовании Docker Desktop WSL 2 невозможно обмениваться контейнерами и образами между учетными записями пользователей.
Запускаем установщик Docker Desktop Installer.exe и ожидаем пока он скачает все необходимые компоненты.
После установки система потребует перезагрузки. Перезагружаемся и входим в систему.
После входа может возникнут запрос на установку дополнительного компонента WSL2. Переходим по ссылке и скачиваем необходимый пакет с официального сайта Microsoft.
После скачивания выполняем установку WSL2, после которой снова потребуется перезагрузка.
Настройка и запуск приложения
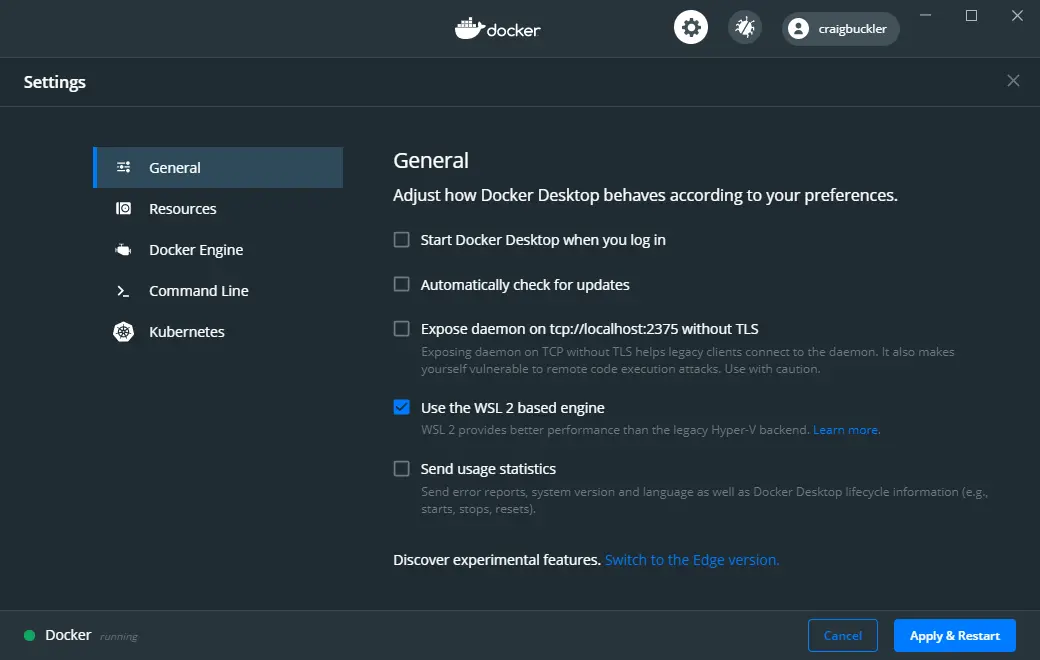
Входим в систему и ждем запуска всех служб Docker. Когда все службы будут запущены, мы увидим в трее классический значок Docker — это значит что служба установлена и запущена. Далее можно запустить приложение Docker desktop. Далее можно изменить настройки Docker при необходимости:

Рисунок 1 — Изменение параметров Docker desktop
Далее управление Docker выполняется через Powershell. Проверяем версию и выполняем тестовый запуск контейнера:

Рисунок 2 — Проверка версии Docker
После выполнения всех этих действий, Docker готов к использованию.
Нужна помощь? Настройки docker/docker swarm/docker compose мы осуществляем в рамках услуги DevOps-аутсорсинг.
В этой заметке я расскажу как поставить Докер на Windows 10, но сначала я опишу установку Windows Subsystem for Linux. Работу с самим Докером я описывать не буду, сделаю это позже.
Установка WSL2 на Windows 10
Установка элементарная, главное проверьте чтобы ваш компьютер и Windows 10 отвечали минимальным требованиям.
UPD.
Для Windows 11 и Windows 10 (сборка 19041 и выше) для установки WSL достаточно одной команды (PowerShell с правами администратора):
wsl --installЭта команда включит все необходимые компоненты и установит дистрибутив Linux (по умолчанию Ubuntu), вам нужно будет только перезагрузить компьютер.
Подробный процесс установки описан на сайте Microsoft https://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/windows/wsl/install-win10 там же указаны минимальные требования.
Если коротко, то установка WSL2 на Windows 10 сводится к следующим шагам:
1) Запускаем PowerShell с правами администратора и включаем компонент «Подсистема Windows для Linux», для этого вводим команду:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
2) Далее необходимо включить необязательный компонент «Платформа виртуальных машин», для этого в PowerShell с правами администратора выполняем команду:
dism.exe /online /enable-feature /featurename:VirtualMachinePlatform /all /norestart
Перезапускаем компьютер.
3) Скачиваем и устанавливаем пакет обновления ядра Linux https://wslstorestorage.blob.core.windows.net/wslblob/wsl_update_x64.msi
4) Выбираем WSL 2 в качестве версии по умолчанию, если этого не сделать новые дистрибутивы Linux будут установлены в WSL 1. Вновь запускаем PowerShell с правами администратора и добавляем команду:
wsl --set-default-version 2
Готово.
Далее нужно выбрать в магазине Microsoft Store нужный нам дистрибутив Linux и установить его, как обычное приложение из магазина. Я установил Ubuntu 18.04 (https://www.microsoft.com/store/apps/9N9TNGVNDL3Q)
После я запускаю установленную Убунту и задаю логин и пароль.
Все, Убунту можно закрыть.
Установка Docker на Windows 10
Теперь установим Docker Desktop WSL 2 backend, идем по ссылке https://hub.docker.com/editions/community/docker-ce-desktop-windows/ Скачиваем и устанавливаем Docker Desktop for Windows (stable).
Запускаем скачанный файл и производим обычную установку приложения Windows.
При установке убедитесь что установлена галочка на Enable WSL 2 Windows Features.
После установки следуйте инструкциям и перелогиньтесь в Windows, Докер запуститься при следующем входе в Windows, иногда в первый раз может понадобится довольно длительное время.
Когда он запустится, рекомендую в окне приветствия нажать Start и пройти небольшое обучение.
После обучающего урока у вас будет запущен ваш первый Docker контейнер.
И теперь по адресу http://localhost/tutorial/ вы можете увидеть инструкцию по дальнейшей работе.
Теперь вы можете заниматься разработкой в Windows 10 использую Docker.
Кстати, я не хочу чтобы Докер запускался каждый раз при включении компьютера, поэтому в настройках я убрал галочку Start Docker Desktop when you log in.
dockerwsl
Skip to content
Install Docker Desktop on Windows 10
In this tutorials, we are going to show how to install Docker Desktop on Windows 10 operating system.
Technology versions :
- Windows 10 64 Bit Operating System
- Docker Engine 18.09.1
Download Docker Desktop for Windows :
Step 1: Get Docker Desktop from the official docker hub.

Click on Get Docker button, will download the Docker for Windows Installer.
Install Docker Desktop on Windows 10:
Step 2: After successfully downloaded, double click on the Docker For Windows Installer file then you can see the below window saying downloading packages.

Step 3: Soon after you can see the below window, asking for Add the desktop shortcut. You can leave it as is and click on Ok.

Step 4: Now you can see the installation process.
Step 5: If everything is done well, you can see the below success window saying Installation succeeded. Click on Close.

Step 6: Then go to windows command prompt and check for the installation confirmation. Check the installed docker version.

Step 7: Now let’s start docker by double-clicking on the desktop icon, it will take a while to start docker daemon. After a successful start, you can see the below window asking for docker hub credentials. If you have your docker hud credentials you can directly login from here.

That’s it, now the docker desktop is successfully installed on Windows 10 operating system.
Docker Desktop Settings:
After all the above steps done successfully, you can see a small docker icon on your windows taskbar like below.
Right click on the docker icon there you can see the settings option, click on Settings you can see the below window having all the docker related setting tabs.
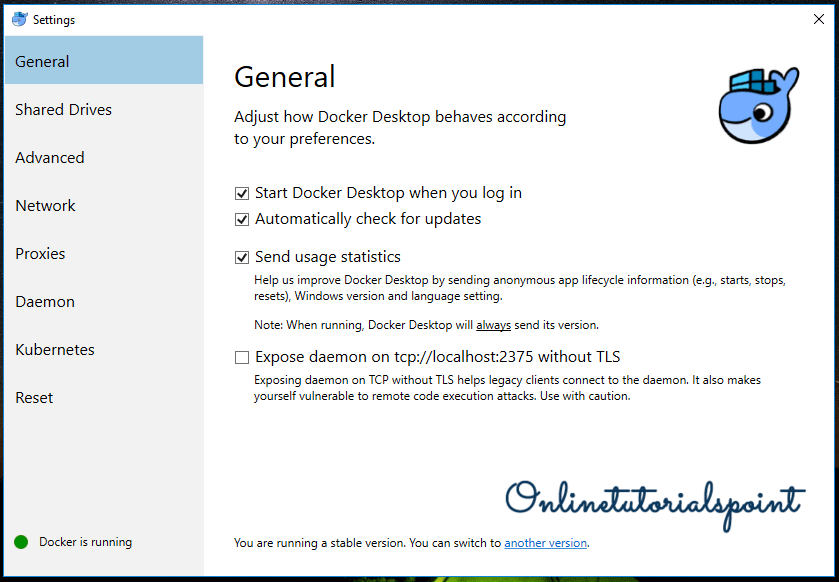
General Settings:
Here you can setup docker startup, updates and statistics settings.
Shared Drives:
If you want to make available your containers to a specific drive, you can do the drive settings here.

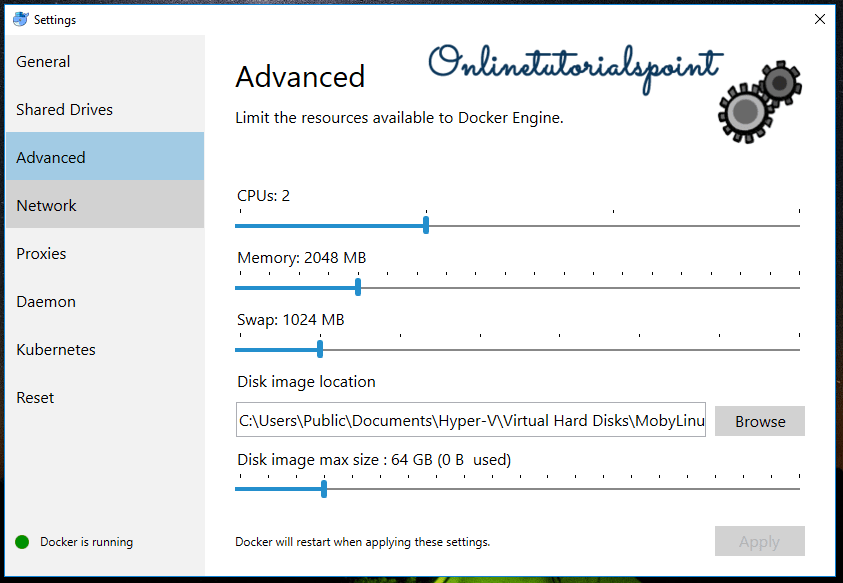
Advanced Settings:
Advanced settings are all about defining a number of cores, memory allocations. By default number of core defined based on your system settings and memory allocation would be 2 GB. You can freely alter this setting at any time.
Network Settings:
Configuring the way Docker containers interact with the network.

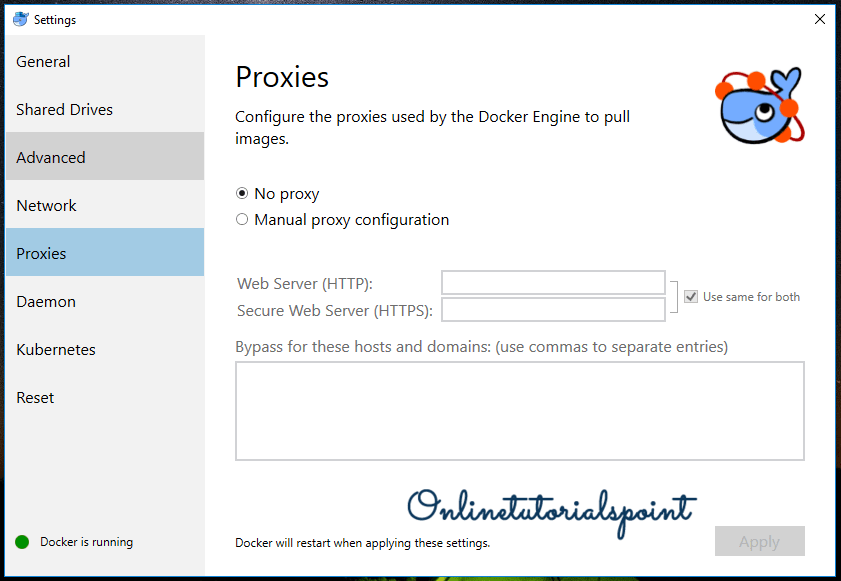
Proxy Settings:
It is used to configure the proxies used by the docker engine to pull the images.
Deamon Settings:
If you wanted to set the docker daemon settings, this is the right place to modify. Click on the configuration file hyperlink and do your modifications.

Kubernetes Settings:
There you can enable the kubernetes for docker. By enabling the kubernetes, by default it will start a single-node cluster for docker desktop.

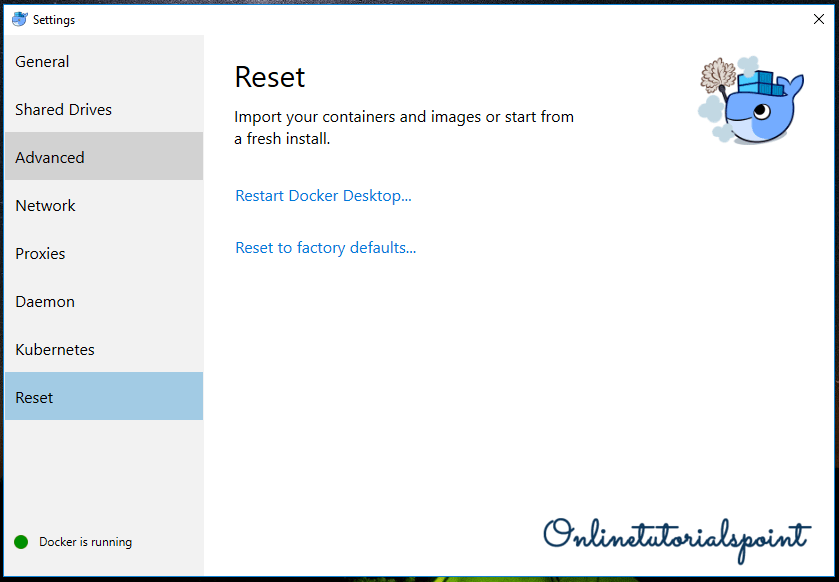
Reset Settings:
If you want to reset all your settings, you can do here.
References:
- Docker Installation
Happy Learning 🙂
Share a word.
Related Posts
Page load link
For many developers, Docker is the platform for creating and deploying applications in self-sufficient containers. It is an OS-level virtualization platform that helps users build and manage applications without worrying about dependencies and underlying OS.
In this guide, we will see how to install Docker desktop on Windows 10 or Windows 11. We’ll also mention the benefits of Docker on Windows and how you can uninstall it from the Windows environment.
Let’s start with the benefits of Docker on Windows.
Table Of Content
- What are the Benefits of Working with Docker on Windows?
- Install Docker on Windows 10 & 11
- Prerequisites
- Install Docker Desktop on Windows 11
- Start Docker Desktop Tool
- How To Install Docker on Windows 10?
- How to Install Docker From the Command Prompt
- Uninstall the Docker Desktop Tool
- Conclusion
What are the Benefits of Working with Docker on Windows?
Docker on Windows brings a range of benefits to the development process and application deployment, including:
- The simple user interface allows you to view and monitor all Docker containers from one location.
- Docker takes care of allocating the required resources and memory space for the containers.
- Supports HTTP proxy settings
- Docker allows developers to create containerized applications that can run in a Windows environment. This makes it easy to build and test applications on Windows and then deploy them to other platforms without compatibility issues.
- Docker images can be easily moved between development, testing, and production environments, which makes it easier to maintain consistency and reduce the risk of errors or bugs caused by differences between environments
Like all environments, you need the following elements to run Docker containers in a Windows environment:
- Docker Engine: This runs on the host machine to build and run containers.
- Docker Client: This receives the commands from the users, translates them into REST API, and delivers them to the Docker Daemon.
- Docker Daemon: This manages Docker containers
- Docker Compose: This runs multiple container applications.
Now that you know what you need, we’ll explain the installation process of Docker on the Windows operating system.
Before we discuss the installation process, we should go into the details of prerequisites and related information so that you have a solid foundation on installing Docker on Windows 10 & 11, especially if using it with a dedicated server.
Prerequisites
- Windows 10 64-bit or Windows 11 64-bit (version 2004 or higher for Pro edition; version 1909 or higher for Enterprise and Education editions)
- The target machine should have a 64-bit processor with support for Second Level Address Translation (SLAT).
Minimum 4 GB RAM. - BIOS settings and hardware virtualization support must be enabled.
- Support for Windows Hyper-V enabled.
- Support for Older Windows versions
Install Docker Desktop on Windows 11
Let’s start with the process of installing Docker Desktop on Windows 11. The process involves several steps that are detailed below.
- Visit the Docker Desktop For Windows download page and download the Docker Desktop installation file.
Note: The target machine should have a 64-bit processor and 4GB system RAM to run Docker successfully on Windows 10.
- Run the installer and remember to enable the Hyper-V Windows feature on the Configuration page.
- Complete the installation process and restart the computer once the process finishes.
Start Docker Desktop Tool
After completing the installation, you’ll need to start the Docker tool manually. For this, locate or search for “Docker Desktop” in the desktop search bar.
Before you can get started with Docker, you’ll need to go through the onboarding tutorial. This will help you learn how to build a Docker image and run a container.
Once you’ve completed the tutorial, you’ll be up and running with Docker Desktop on Windows. To verify if everything is working correctly, go to the Docker CLI and run the “docker version” command. This will tell you the Docker version installed on your system.
At this point, Docker has been installed on your Windows 11 machine and is ready for running containers and Docker images.
How To Install Docker on Windows 10?
The process of installing Docker on Windows 10 is similar to installing Docker on Windows 11. Let’s see the major steps of the process.
Start by downloading the installer from the official Docker for Windows page.
Once the download finishes, locate the downloaded file and run it.
On the setup page, you must choose the options, such as the Hyper-V and WSL 2 features. Then, click “OK” and follow the instructions of the wizard. Close the wizard when it finishes.
When using Docker, it’s important to know that the administrator account and Docker user accounts are often the same. If you don’t have a Docker user group, you will need to create one and add your user account to it.
Initially, run the admin panel as computer management.
You can add new users to the Docker group by going to the Local Users and Groups and, from there, find Docker user groups.
After you’ve completed all these steps, restart your computer to update and start Docker Desktop on Windows 10.
Once the system comes back online, start Docker Desktop.
It will prompt you to review and accept the Subscription Services Agreement for Docker Desktop. Once you accept and agree to the terms and conditions, the Docker Desktop window will appear, and you’re ready to work!
Remember to go through the Quick Start guide included with Docker Desktop for a better experience.
Resolving the WSL Kernel Version Error
Some Windows 10 systems can show the following error about Docker Desktop requiring a newer version of the WSL kernel.
To resolve this error, launch the Command Prompt and run the following command:
wsl --update
How to Install Docker From the Command Prompt
If you wish, you can install Docker Desktop from the Command Prompt. This is a simple process where you enter a simple command to initiate the installation process. But first, you need to download the Docker Desktop installer from the official site.
Here are the commands you’ll need to run:
If you’re in a terminal window, run the following command:
"Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install
If you’re in the PowerShell, run the following command:
Start-Process '.\win\build\Docker Desktop Installer.exe' -Wait install
Finally, if you’re at the Command Prompt, run the following command:
start /w "" "Docker Desktop Installer.exe" install
When the process finishes, don’t forget to add your user account to the Docker user group, especially if your admin account and user account are not the same. To do that, run this command:
net localgroup docker-users <users>/add
How do I Know if Docker is Installed on my Windows 10/ Windows 11 Machine?
After the installation finishes, it is always a good idea to verify if everything is working as intended. For this, you can try the following ideas:
- If you’re using a Windows terminal, you can use the following command line to launch Docker:
docker-run
- From Powershell, you can verify the Docker version and installation by entering the following command:
docker --version
- You can also check the latest version of the Docker desktop from the Docker option.
- Alternatively, you can check for a web server by running the Docker desktop.
Uninstall the Docker Desktop Tool
There are times when you might want to remove Docker from the Windows machine. Like the installation process, the uninstallation process is straightforward.
1. Go to the Windows Start menu.
2. Choose Settings > Apps > Apps & features.
3. Docker Desktop should be present in the Apps & features list.
4. Click Uninstall.
Conclusion
Docker on Windows is a quick and easy way to run applications in containers on Windows operating systems. Developers can build, package, and deploy applications more efficiently and consistently across different environments using containers. This improved productivity and reduced complexity help organizations save time and money.
Docker on Windows is the perfect way to utilize the features of both Windows and Linux-based containers. However, it is important to note that Docker on Windows does have some limitations and requirements, such as minimum hardware specifications and the use of Windows 10 Professional or Enterprise editions with the Hyper-V feature enabled.
1,600 words, 8-minute read
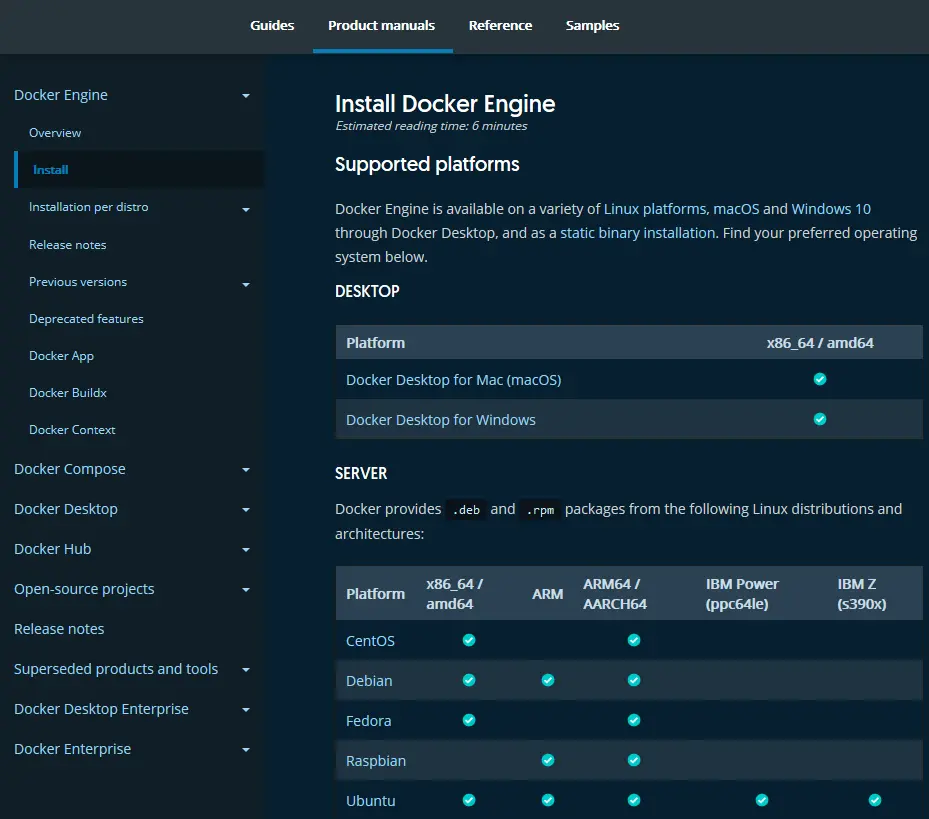
Docker can be installed on Linux, mac OS, or Windows.
Requirements and installation instructions can be found on the Docker Docs help pages.
Install Docker on Linux #
Docker Desktop for Linux can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The installer includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Alternatively, the Docker command-line tool is available in official Linux repositories although these are often older editions. The latest edition is supported on recent 64-bit editions of popular Linux distros:
- Ubuntu (and derivatives such as Mint)
- CentOS
- Debian
- Fedora
Static binaries are available for other distros, although Googling “install Docker on [your OS]” may provide easier instructions, e.g. “install Docker on a Raspberry Pi”.
Follow the Docker documentation for your distro. For example, Docker for Ubuntu is installed with the following commands:
sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-pluginTo run Docker commands as a non-root user (without sudo), create and add yourself to a docker group:
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USERThen reboot to apply all changes.
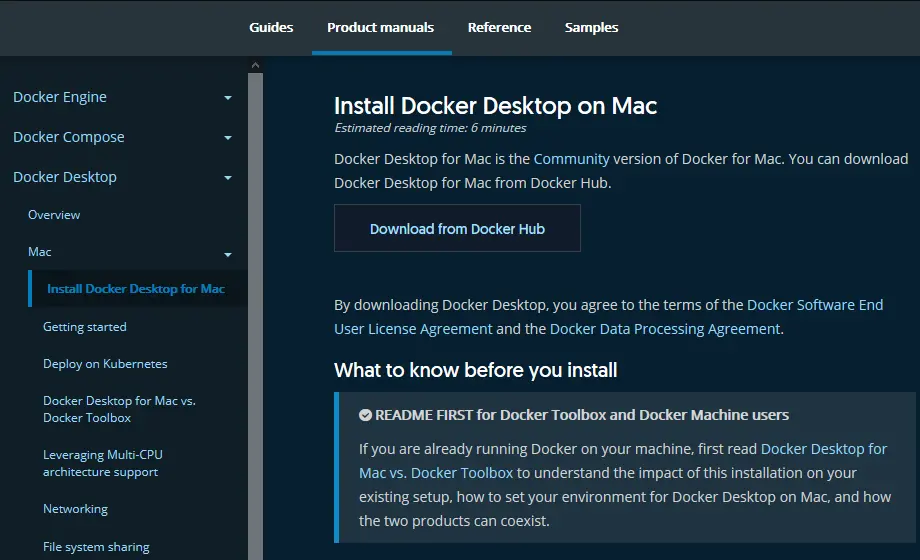
Install Docker on macOS #
Docker Desktop for macOS Sierra 10.13 and above can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The package includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Two editions are available: stable and edge with experimental features. The stable version is best for most developers.
Double-click Docker.dmg to open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder. Double-click Docker.app in that folder to launch Docker.
After completion, the whale icon in the status bar indicates Docker is running and commands can be entered in the terminal.
Install Docker on Windows #
Docker Desktop for Windows requires either WSL2 or Hyper-V.
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) 2 #
WSL allows you to run full Linux environments directly on Windows 10 or Windows 11.
IMPORTANT!
You can not install the Linux edition of Docker within a WSL-powered Linux distro. You must install Docker Desktop for Windows which allows Docker commands to be run in all Windows and Linux terminals.
WSL2 is the recommended default option for Docker on Windows. It is faster than Hyper-V and available in all editions of Windows 11 and Windows 10 from the May 2020 update (version 2004, OS build 19041).
To install WSL2:
-
Enable hardware virtualization support in your BIOS.
This will be active on most devices, but check by rebooting and accessing your PC’s BIOS panels – typically by hitting DEL, F2, or F10 as your system starts. Look for Virtualization Technology, VTx or similar options. Ensure they are enabled, save, and reboot.
WARNING! Be careful when changing BIOS settings – one wrong move could trash your PC.
-
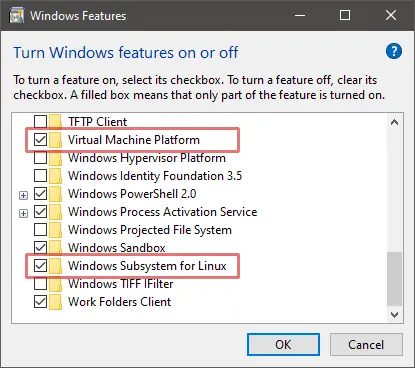
Enable the Virtual Machine Platform and Windows Subsystem for Linux options in the Turn Windows features on or off panel:
This can be accessed by hitting the Start button and typing the panel name or from Programs and Features in the classic Control Panel.
-
Reboot, then enter the following command in a Windows Powershell or
cmdprompt to set WSL2 as the default:wsl --set-default-version 2 -
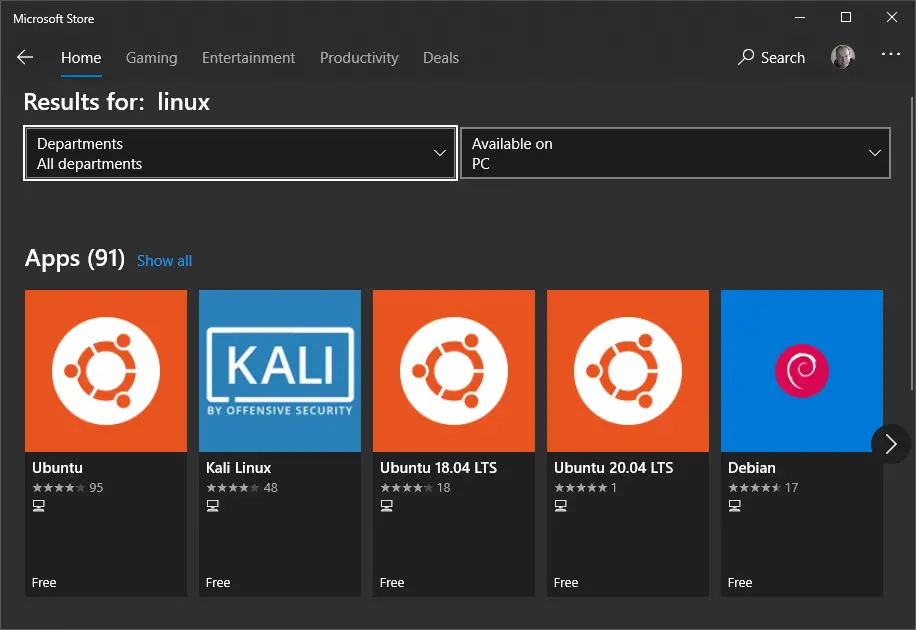
Download and install your preferred distro by searching for “Linux” in the Microsoft Store app. Ubuntu is a good choice.
-
To complete the installation, launch your distro by clicking its Store’s Launch button or choosing its icon from the Start menu.
You may be prompted to install a kernel update – follow the instructions and launch the distro again.
-
Enter a Linux username and password. These are separate from your Windows credentials although choosing the same ones can be practical.
-
Ensure your distro is up-to-date. For example, on an Ubuntu bash prompt enter:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
You can now install Docker Desktop (see below). For the best performance and stability, store development files in your Linux file system and run Docker from your Linux terminal.
More information about installing and using WSL2:
- Windows Subsystem for Linux 2: The Complete Guide, and
- optionally, Windows Terminal: The Complete Guide.
Hyper-V #
The Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor is provided free with Windows 10 and 11 Professional and Enterprise. (Windows Home users must use WSL2.)
To install Hyper-V:
-
Enable hardware virtualization support in your BIOS.
This will be active on most devices, but check by rebooting and accessing your PC’s BIOS panels – typically by hitting DEL, F2, or F10 as your system starts. Look for Virtualization Technology, VTx or similar options. Ensure they are enabled, save, and reboot.
WARNING! Be careful when changing BIOS settings – one wrong move could trash your PC.
-
Enable the Hyper-V option in the Turn Windows features on or off panel then reboot.
This can be accessed by hitting the Start button and typing the panel name or from Programs and Features in the classic Control Panel.
You can now install Docker Desktop.
Install Docker Desktop for Windows #
Docker Desktop for Windows 10 and 11 can be downloaded from Docker Hub. The installer includes the Docker server, CLI, Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, and Kubernetes.
Two editions are available: stable and edge with experimental features. The stable version is best for most developers.
Double-click Docker Desktop Installer.exe to start the installation process. After completion and launch, the whale icon in the notification area of the task bar indicates Docker is running and ready to accept commands in the Windows Powershell/cmd terminal (and Linux if using WSL2).
Docker Engine Settings #
Docker uses WSL2 as the default engine when available. You will be prompted to confirm this choice during installation and after WSL2 is installed.
Alternatively, WSL2 can be enabled by checking Use the WSL 2 based engine in the General tab of Settings accessed from the Docker task bar icon. Unchecking the option reverts to Hyper-V.
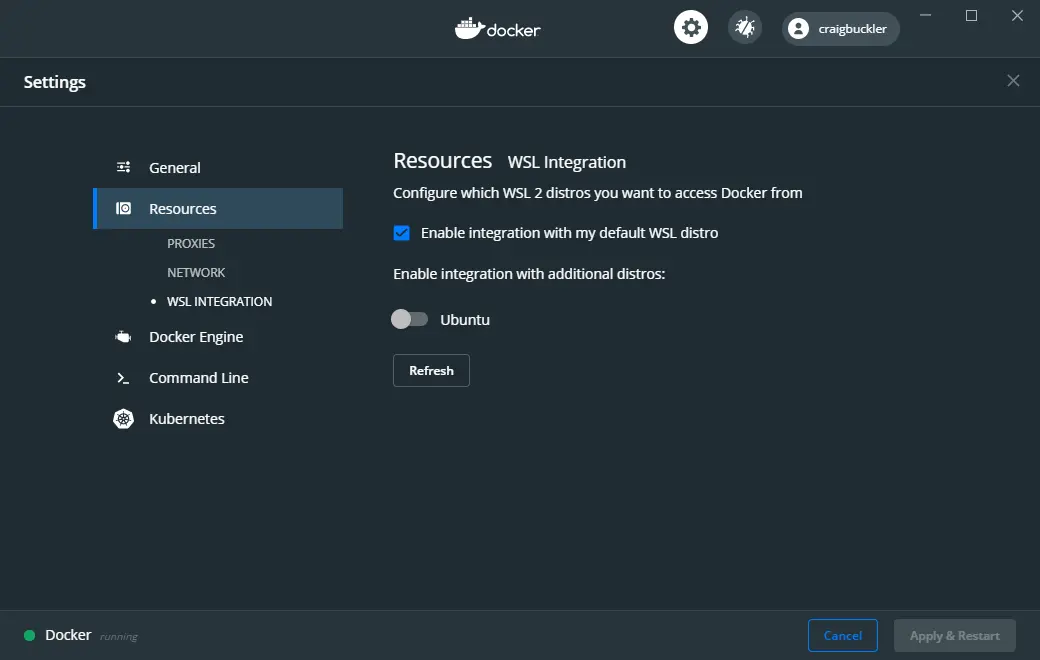
When using WSL2, at least one Linux distro must be enabled – the default is chosen. You can also permit Docker commands in other distros by accessing the WSL integration panel in the Resources section of the Docker Settings:
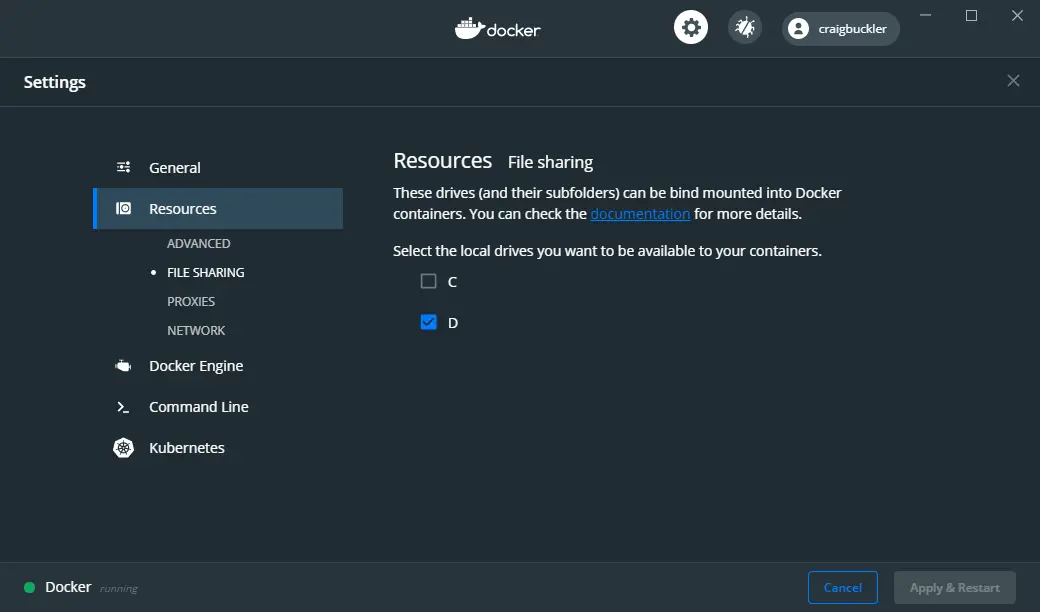
When using Hyper-V, Docker must be granted access to the Windows file system. Select the drives it is permitted to use by accessing the File Sharing panel in the Resources section of the Docker Settings:
(This option was named Shared Drives in previous editions of Docker Desktop.)
Test your Docker installation #
Check Docker has successfully installed by entering the following command in your terminal:
docker versionA response similar to the following is displayed:
Client: Docker Engine - Community
Version: 19.03.12
API version: 1.40
Go version: go1.13.10
Git commit: abcdef0
Built: Mon Jun 22 15:45:36 2020
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 19.03.12
API version: 1.40 (minimum version 1.12)
...etc...Ensure Docker Compose is working by entering:
docker-compose versionTo receive something like:
docker-compose version 1.27.2, build 8d51620a
docker-py version: 4.3.1
CPython version: 3.7.7
OpenSSL version: OpenSSL 1.1.1c 10 Sep 2019Optionally, try entering:
docker run hello-worldto verify Docker can pull an image from Docker Hub and start containers as expected…
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
1b930d010525: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:f9dfddf63636d84ef479d645ab5885156ae030f611a56f3a7ac
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows your installation appears to be working correctly.Key points #
What you’ve learned in this chapter:
- How to install and configure Docker on your Linux, macOS, or Windows system.
- How to install Docker Compose.
- How to test the Docker installation.
The following chapters demonstrate how to use Docker during development…
…but to continue reading, you need to buy the book.
Do you want an easy-to-follow course which demonstrates how to use Docker and create practical web development environments on your Windows, macOS, or Linux PC?
Buy the «Docker for Web Developers» book & video course…
-
full course
$99 $50 £43 / €49
buy all
-
ebooks only
$30 $15 £13 / €15
buy books
-
videos only
$80 $40 £34 / €40
buy videos
plus your country’s sales tax where applicable