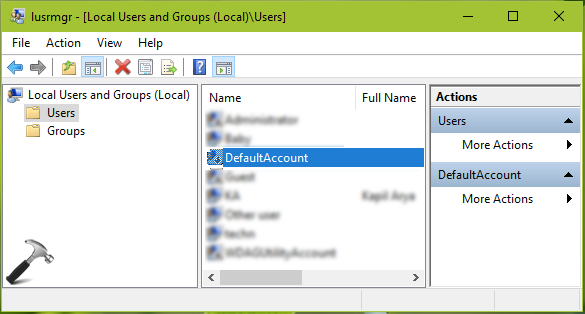
DefaultAccount — встроенная системная учетная запись, на основе которой создаются новые аккаунты (учетки), также необходима для работы приложений MUMA (функционируют еще до входа в Windows).
Сразу скажу: не стоит пробовать удалять, если только не хотите проблем. Отключить — да, это можно.
Разбираемся
- DefaultAccount это учетная запись по умолчанию, на основе которой создаются все новые учетки. Официальное описание в самой системе звучит так — Учетная запись пользователя, управляемая системой.
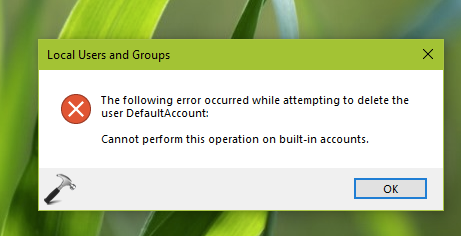
- Это встроенная учетка. Удалить нельзя (переименовать вроде можно), даже если попробовать, то Windows не разрешит вам это сделать.
- Появилась DefaultAccount в Windows 10 билд 1607. На официальном сайте Майкрософт сказано, что нужна для запуска приложений MUMA с несколькими манифестами пользователей. Если я правильно понимаю, то приложения MUMA — это те, которые могут работать до входа пользователя в систему или когда пользователь вышел из системы, но при этом работает экран блокировки. MUMA используется не только в Windows, например в XBOX оболочка — это и есть программа типа MUMA. В общем понятно одно — не просто так DefaultAccount удалить нельзя.
- Сразу можно сделать вывод — пытаться удалить эту учетку не стоит.
В интернете также нашел способ как отключить аккаунт DefaultAccount. Но стоит отметить, учитывая что она нужна для создания других учеток — имейте ввиду, что после отключения могут быть проблемы с этим делом. Итак, чтобы отключить сперва зажмите Win + R, появится окошко Выполнить, вставьте команду lusrmgr.msc и нажмите ОК:
Далее слева активируем раздел Пользователи (Users), нажимаем правой кнопкой по DefaultAccount и выбираем Свойства (Properties):
Появится окошко свойств, где нужно поставить галочку Отключать аккаунт (Account is disabled):
Отключить аккаунт DefaultAccount можно также другим способом:
- Нажмите правой кнопкой по значку Пуск или зажмите кнопки Win + X, далее выберите PowerShell от администратора. Потом вставьте команду start cmd и нажмите Enter. В итоге запустится командная строка от администратора.
- Чтобы отключить — просто выполните команду net user defaultaccount /active:no.
Удачи и добра
На главную!
23.10.2021
There are different type of local accounts comes by default in Windows 10. These accounts are designed for their specific application. For example, guest account can be used to load one-time users who doesn’t have permanent account on the system. The built-in administrator account can be enabled when you lost your admin rights. These accounts are hidden and can be enabled through lusrmgr snap-in.
Page Contents
FAQ: What Is ‘DefaultAccount’ In Windows 10?
Now there is DefaultAccount, which comes by default with Windows 10 Version 1607 or later. It is also called Default System Managed Account or DSMA. According to Microsoft, this accounts gets its usage mostly for multi-user-manifested-apps (MUMA). Such apps are designed to run for cross user experience as compared to single-user-manifested-apps (SUMA) or Desktop apps which runs when user signs in and gets automatically terminated when user signs out.
For the multi-user model and cross user experience, DSMA becomes the necessity of system. Hence due to this fact, DefaultAccount is present in Windows.
Things You Must Know About DefaultAccount
1. DefaultAccount is available in Windows 10 Version 1607, Windows Server 2016 or later.
2. DefaultAccount is member of System Managed Accounts Group.
3. By default, Defaultaccount is disabled and password is set to never expire condition. In fact, the account is neutral account and doesn’t requires password.
4. After installing Windows, when you first time boot the machine, DefaultAccount will be created.
5. You can not delete DefaultAccount using your administrator account.
6. The account type for DefaultAccount is 512 which means its local account.
7. The security identifier (SID) for DefaultAccount is S-1-5-21-{ComputerIdentifier}-503, where 503 is relative ID (RID). Note the {ComputerIdentifier} is specific for a system. The SID type for this account is 1.
8. Though you can rename the DefaultAccount but it will affect the productivity served by this account. We don’t recommend you to rename or enable this account. It should remain as it is without any modification. Note that it is only system managed account.
We hope this article have cleared your doubts about DefaultAccount!
Related: What Is defaultuser0 Account In Windows 10 And How To Remove It?
READ THESE ARTICLES NEXT
- Reset local account password in Windows 11
- Switch to local account in Windows 11
- Fix: You’ve Been Signed In With A Temporary Profile
- Solved: Lost administrator rights in Windows 11 (2023 fix)
- Configure Password Expiration in Windows 11/10
- Fix: User account disappeared in Windows 11
- How to change administrator in Windows 11/10
- Hide Specific User Account in Windows 11/10
- Fix: Family Safety not working on Windows 11/10
- Fix: Temporary Profile in Windows 11/10
Default Account (режим по умолчанию) — это учетная запись, которая создается автоматически при установке операционной системы Windows 10. Она является административной учетной записью и имеет расширенные права доступа ко всему функционалу и ресурсам компьютера.
Default Account можно использовать для различных целей, например, установки и удаления программ, изменения системных настроек, а также для работы с файлами и папками на компьютере. Однако, по умолчанию учетная запись Default Account не включена, и ее активация может потребовать некоторых дополнительных действий.
Работа с учетной записью Default Account может быть полезна в случае, если вам нужно получить доступ к определенным функциям или файлам, которые не доступны из обычной учетной записи пользователя. Однако, не злоупотребляйте этой возможностью, поскольку учетная запись Default Account имеет полный доступ ко всем функциям и ресурсам компьютера, и неконтролируемое использование может привести к потере данных или нарушению безопасности системы.
Обратите внимание, что использование учетной записи Default Account может быть опасным, поэтому перед ее активацией следует хорошо продумать необходимость и последствия данного действия. В случае, если вы не уверены в своих действиях, рекомендуется проконсультироваться с опытным специалистом или искать альтернативные способы решения задачи.
Содержание
- Default Account в Windows 10
- Роль Default Account в операционной системе Windows 10
- Настройки Default Account в Windows 10
Default Account в Windows 10
Default Account отличается от учетной записи администратора и обычной учетной записи пользователя. У данной учетной записи есть ограничения, которые предотвращают полный доступ к системным ресурсам и функциям.
Default Account обычно используется для выполнения различных служебных задач, например, для создания новых учетных записей, обновления программного обеспечения или выполнения других системных операций. Он может быть также использован для запуска служб или задач в фоновом режиме без необходимости входить в аккаунт пользователя.
Однако следует быть осторожным при работе с Default Account, так как неправильные действия или изменения в его настройках могут привести к нежелательным результатам или нарушению работы операционной системы.
Пользователи могут увидеть учетную запись Default Account в списке учетных записей в настройках Windows 10, но обычно она скрыта и недоступна для входа. В большинстве случаев для использования ее привилегий требуется специальная команда или программное обеспечение.
Overall, Default Account в Windows 10 является важным элементом операционной системы, который предоставляет специальные привилегии для выполнения системных операций. Правильное использование и осторожность при работе с Default Account помогут избежать проблем и обеспечить стабильную работу компьютера на базе Windows 10.
Роль Default Account в операционной системе Windows 10
Default Account предоставляет некоторые привилегии, которые обычные пользователи не имеют, например, доступ к системным файлам и каталогам. Она также используется для поддержки отдельных служб и приложений в Windows 10.
Default Account отличается от учетной записи администратора и других пользователей, поскольку она не предназначена для использования обычными людьми. Ее основная цель — обеспечить безопасность системы и предотвратить несанкционированный доступ к важным системным ресурсам.
Пользователи не могут войти в систему через учетную запись Default Account, так как она скрыта по умолчанию. Она может быть активирована только определенными системными программами и службами при необходимости.
В случае, если пользователь попытается изменить настройки или попытается получить доступ к системным файлам через учетную запись Default Account без соответствующих привилегий, операционная система Windows 10 автоматически блокирует доступ и предупреждает об опасности.
В целом, учетная запись Default Account является важным элементом безопасности операционной системы Windows 10 и играет важную роль в обеспечении защиты от различных угроз и атак.
Настройки Default Account в Windows 10
Default Account в Windows 10 представляет собой учетную запись, которая используется по умолчанию при создании новых пользователей или при входе в систему без указания конкретного имени пользователя. Эта учетная запись обладает особыми правами и настройками, которые могут быть изменены по вашему усмотрению.
Чтобы настроить Default Account в Windows 10, выполните следующие шаги:
| Шаг | Описание |
|---|---|
| 1 | Откройте «Панель управления» и перейдите в раздел «Учетные записи пользователей». |
| 2 | Выберите «Сменить тип учетной записи» и найдите раздел Default Account. |
| 3 | Нажмите на кнопку «Изменить тип учетной записи» и выберите нужные настройки. |
| 4 | Сохраните изменения и закройте окно «Учетные записи пользователей». |
После выполнения этих действий учетная запись Default Account будет настроена в соответствии с вашими preferencami и будет использоваться при создании новых пользователей или при входе в систему без указания имени пользователя.
Важно помнить, что изменение настроек Default Account может повлиять на работу других учетных записей в системе, поэтому будьте осторожны при внесении изменений.
In this post I want to summarize an overview from Microsoft about local accounts in windows.
Local Accounts
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/identity-protection/access-control/local-accounts
Local user accounts are stored locally on the server. These accounts can be assigned rights and permissions on a particular server, but on that server only. Local user accounts are security principals that are used to secure and manage access to the resources on a standalone or member server for services or users.
- Default local user accounts
- Administrator account
- Guest account
- HelpAssistant account (installed with a Remote Assistance session)
- DefaultAccount
- How Windows uses the DefaultAccount
- How the DefaultAccount gets created on domain controllers
- Recommendations for managing the Default Account (DSMA)
- SYSTEM
- NETWORK SERVICE
- LOCAL SERVICE
- Enforce local account restrictions for remote access
- WDAGUtilityAccount local account
Default local user accounts
The default local user accounts are built-in accounts that are created automatically when you install Windows.
After Windows is installed, the default local user accounts cannot be removed or deleted. In addition, default local user accounts do not provide access to network resources.
Default local user accounts are used to manage access to the local server’s resources based on the rights and permissions that are assigned to the account. The default local user accounts, and the local user accounts that you create, are located in the Users folder. The Users folder is located in the Local Users and Groups folder in the local Computer Management Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Computer Management is a collection of administrative tools that you can use to manage a single local or remote computer. For more information, see How to manage local accounts later in this topic.
Default local user accounts are described in the following sections.
Administrator account
The default local Administrator account is a user account for the system administrator. Every computer has an Administrator account (SID S-1-5-domain-500, display name Administrator). The Administrator account is the first account that is created during the Windows installation.
The Administrator account has full control of the files, directories, services, and other resources on the local computer. The Administrator account can create other local users, assign user rights, and assign permissions. The Administrator account can take control of local resources at any time simply by changing the user rights and permissions.
The default Administrator account cannot be deleted or locked out, but it can be renamed or disabled.
In Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016, Windows setup disables the built-in Administrator account and creates another local account that is a member of the Administrators group. Members of the Administrators groups can run apps with elevated permissions without using the Run as Administrator option. Fast User Switching is more secure than using Runas or different-user elevation.
- Get SID of a local user
wmic useraccount where name=’administrator’ get sid - Get SID for current logged in user
wmic useraccount where name=’%username%’ get sid - Get SID for current logged in domain user
whoami /user - Get SID for the local administrator of the computer
wmic useraccount where (name=’administrator’ and domain=’%computername%’) get name,sid - Get SID for the domain administrator
wmic useraccount where (name=’administrator’ and domain=’%userdomain%’) get name,sid - Find username from a SID
wmic useraccount where sid=’S-1-5-21-2593857963-3184534624-523876939-500′ get name
Account group membership
By default, the Administrator account is installed as a member of the Administrators group on the server. It is a best practice to limit the number of users in the Administrators group because members of the Administrators group on a local server have Full Control permissions on that computer.
The Administrator account cannot be deleted or removed from the Administrators group, but it can be renamed.
Security considerations
Because the Administrator account is known to exist on many versions of the Windows operating system, it is a best practice to disable the Administrator account when possible to make it more difficult for malicious users to gain access to the server or client computer.
You can rename the Administrator account. However, a renamed Administrator account continues to use the same automatically assigned security identifier (SID), which can be discovered by malicious users. For more information about how to rename or disable a user account, see Disable or activate a local user account and Rename a local user account.
As a security best practice, use your local (non-Administrator) account to sign in and then use Run as administrator to accomplish tasks that require a higher level of rights than a standard user account. Do not use the Administrator account to sign in to your computer unless it is entirely necessary. For more information, see Run a program with administrative credentials.
In comparison, on the Windows client operating system, a user with a local user account that has Administrator rights is considered the system administrator of the client computer. The first local user account that is created during installation is placed in the local Administrators group. However, when multiple users run as local administrators, the IT staff has no control over these users or their client computers.
In this case, Group Policy can be used to enable secure settings that can control the use of the local Administrators group automatically on every server or client computer. For more information about Group Policy, see Group Policy Overview.
Note Blank passwords are not allowed in the versions designated in the Applies To list at the beginning of this topic.
Important Even when the Administrator account has been disabled, it can still be used to gain access to a computer by using safe mode. In the Recovery Console or in safe mode, the Administrator account is automatically enabled. When normal operations are resumed, it is disabled.
Guest account
The Guest account is disabled by default on installation. The Guest account lets occasional or one-time users, who do not have an account on the computer, temporarily sign in to the local server or client computer with limited user rights. By default, the Guest account has a blank password. Because the Guest account can provide anonymous access, it is a security risk. For this reason, it is a best practice to leave the Guest account disabled, unless its use is entirely necessary.
Account group membership
By default, the Guest account is the only member of the default Guests group (SID S-1-5-32-546), which lets a user sign in to a server. On occasion, an administrator who is a member of the Administrators group can set up a user with a Guest account on one or more computers.
Security considerations
When enabling the Guest account, only grant limited rights and permissions. For security reasons, the Guest account should not be used over the network and made accessible to other computers.
In addition, the guest user in the Guest account should not be able to view the event logs. After the Guest account is enabled, it is a best practice to monitor the Guest account frequently to ensure that other users cannot use services and other resources, such as resources that were unintentionally left available by a previous user.
HelpAssistant account (installed with a Remote Assistance session)
The HelpAssistant account is a default local account that is enabled when a Remote Assistance session is run. This account is automatically disabled when no Remote Assistance requests are pending.
HelpAssistant is the primary account that is used to establish a Remote Assistance session. The Remote Assistance session is used to connect to another computer running the Windows operating system, and it is initiated by invitation. For solicited remote assistance, a user sends an invitation from their computer, through e-mail or as a file, to a person who can provide assistance. After the user’s invitation for a Remote Assistance session is accepted, the default HelpAssistant account is automatically created to give the person who provides assistance limited access to the computer. The HelpAssistant account is managed by the Remote Desktop Help Session Manager service.
DefaultAccount
The DefaultAccount, also known as the Default System Managed Account (DSMA), is a built-in account introduced in Windows 10 version 1607 and Windows Server 2016. The DSMA is a well-known user account type. It is a user neutral account that can be used to run processes that are either multi-user aware or user-agnostic. The DSMA is disabled by default on the desktop SKUs (full windows SKUs) and WS 2016 with the Desktop.
The DSMA has a well-known RID of 503. The security identifier (SID) of the DSMA will thus have a well-known SID in the following format: S-1-5-21-<ComputerIdentifier>-503
The DSMA is a member of the well-known group System Managed Accounts Group, which has a well-known SID of S-1-5-32-581.
The DSMA alias can be granted access to resources during offline staging even before the account itself has been created. The account and the group are created during first boot of the machine within the Security Accounts Manager (SAM).
How Windows uses the DefaultAccount
From a permission perspective, the DefaultAccount is a standard user account. The DefaultAccount is needed to run multi-user-manifested-apps (MUMA apps). MUMA apps run all the time and react to users signing in and signing out of the devices. Unlike Windows Desktop where apps run in context of the user and get terminated when the user signs off, MUMA apps run by using the DSMA.
MUMA apps are functional in shared session SKUs such as Xbox. For example, Xbox shell is a MUMA app. Today, Xbox automatically signs in as Guest account and all apps run in this context. All the apps are multi-user-aware and respond to events fired by user manager. The apps run as the Guest account.
Similarly, Phone auto logs in as a “DefApps” account which is akin to the standard user account in Windows but with a few extra privileges. Brokers, some services and apps run as this account.
In the converged user model, the multi-user-aware apps and multi-user-aware brokers will need to run in a context different from that of the users. For this purpose, the system creates DSMA.
How the DefaultAccount gets created on domain controllers
If the domain was created with domain controllers that run Windows Server 2016, the DefaultAccount will exist on all domain controllers in the domain. If the domain was created with domain controllers that run an earlier version of Windows Server, the DefaultAccount will be created after the PDC Emulator role is transferred to a domain controller that runs Windows Server 2016. The DefaultAccount will then be replicated to all other domain controllers in the domain.
Recommendations for managing the Default Account (DSMA)
Microsoft does not recommend changing the default configuration, where the account is disabled. There is no security risk with having the account in the disabled state. Changing the default configuration could hinder future scenarios that rely on this account.
Default local system accounts
SYSTEM
The SYSTEM account is used by the operating system and by services that run under Windows. There are many services and processes in the Windows operating system that need the capability to sign in internally, such as during a Windows installation. The SYSTEM account was designed for that purpose, and Windows manages the SYSTEM account’s user rights. It is an internal account that does not show up in User Manager, and it cannot be added to any groups.
On the other hand, the SYSTEM account does appear on an NTFS file system volume in File Manager in the Permissions portion of the Security menu. By default, the SYSTEM account is granted Full Control permissions to all files on an NTFS volume. Here the SYSTEM account has the same functional rights and permissions as the Administrator account.
Note To grant the account Administrators group file permissions does not implicitly give permission to the SYSTEM account. The SYSTEM account’s permissions can be removed from a file, but we do not recommend removing them.
NETWORK SERVICE
The NETWORK SERVICE account is a predefined local account used by the service control manager (SCM). A service that runs in the context of the NETWORK SERVICE account presents the computer’s credentials to remote servers.
This account is not recognized by the security subsystem, so you cannot specify its name in a call to the LookupAccountName function. It has minimum privileges on the local computer and acts as the computer on the network.
This account can be specified in a call to the CreateService and ChangeServiceConfig functions. Note that this account does not have a password, so any password information that you provide in this call is ignored. While the security subsystem localizes this account name, the SCM does not support localized names. Therefore, you will receive a localized name for this account from the LookupAccountSid function, but the name of the account must be NT AUTHORITY\NetworkService when you call CreateService or ChangeServiceConfig, regardless of the locale, or unexpected results can occur.
A service that runs in the context of the NetworkService account presents the computer’s credentials to remote servers. By default, the remote token contains SIDs for the Everyone and Authenticated Users groups. The user SID is created from the SECURITY_NETWORK_SERVICE_RID value.
The NetworkService account has its own subkey under the HKEY_USERS registry key. Therefore, the HKEY_CURRENT_USER registry key is associated with the NetworkService account.
The NetworkService account has the following privileges:
- SE_ASSIGNPRIMARYTOKEN_NAME (disabled)
- SE_AUDIT_NAME (disabled)
- SE_CHANGE_NOTIFY_NAME (enabled)
- SE_CREATE_GLOBAL_NAME (enabled)
- SE_IMPERSONATE_NAME (enabled)
- SE_INCREASE_QUOTA_NAME (disabled)
- SE_SHUTDOWN_NAME (disabled)
- SE_UNDOCK_NAME (disabled)
- Any privileges assigned to users and authenticated users
For more information, see Service Security and Access Rights.
LOCAL SERVICE
The LOCAL SERVICE account is a predefined local account used by the service control manager. It has minimum privileges on the local computer and presents anonymous credentials on the network. For more information, see LocalService Account.
Enforce local account restrictions for remote access
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/identity-protection/access-control/local-accounts#enforce-local-account-restrictions-for-remote-access
The User Account Control (UAC) is a security feature in Windows that has been in use in Windows Server 2008 and in Windows Vista, and the operating systems to which the Applies To list refers. UAC enables you to stay in control of your computer by informing you when a program makes a change that requires administrator-level permission. UAC works by adjusting the permission level of your user account. By default, UAC is set to notify you when applications try to make changes to your computer, but you can change how often UAC notifies you.
UAC makes it possible for an account with administrative rights to be treated as a standard user non-administrator account until full rights, also called elevation, is requested and approved. For example, UAC lets an administrator enter credentials during a non-administrator’s user session to perform occasional administrative tasks without having to switch users, sign out, or use the Run as command.
In addition, UAC can require administrators to specifically approve applications that make system-wide changes before those applications are granted permission to run, even in the administrator’s user session.
For example, a default feature of UAC is shown when a local account signs in from a remote computer by using Network logon (for example, by using NET.EXE USE). In this instance, it is issued a standard user token with no administrative rights, but without the ability to request or receive elevation. Consequently, local accounts that sign in by using Network logon cannot access administrative shares such as C$, or ADMIN$, or perform any remote administration.
For more information about UAC, see User Account Control.
WDAGUtilityAccount local account
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/microsoft-defender-application-guard/faq-md-app-guard#what-is-the-wdagutilityaccount-local-account
This account is part of Windows Defender Application Guard beginning with Windows 10 version 1709 (Fall Creators Update). This account remains disabled until Application Guard is enabled on your device. This item is integrated to the OS and is not considered as a threat/virus/malware.
https://www.thewindowsclub.com/what-is-wdagutilityaccount
- Разбираемся
- Проверка на скрытые учетки
- Скрытые учетки — в чем смысл?
- Вывод
Приветствую друзья! В Windows может скрываться много всякого непонятного… непонятные записи в автозагрузке, непонятные задания в планировщике.. было время я даже исследовал папку Windows/System32 — там много разных файлов исполняемых (формат exe) с необычными иконками, было интересно для чего они)) Но могут быть даже учетные записи непонятные, вы их не создавали, а они есть… одна из таких WDAGUtilityAccount, о ней сегодня и пойдет речь.
Разбираемся
WDAGUtilityAccount — скрытая учетная запись, была создана защитником Windows. Может появиться после обновления Fall Creators Update 1709. При этом читаю, что если защитник отключен, то учетка будет тоже отключена.
Удалять WDAGUtilityAccount разумеется не стоит, так как могут быть проблемы не только с защитником, но и в целом с Windows. Защитник — системный компонент, отключить его и удалить — две разные вещи. Лучше именно отключить при необходимости.
Кстати, совет! Чтобы отключить в Windows 10 все левое, шпионство и многое ненужное — я использую утилиту DoNotSpy10. Она бесплатная и представляет из себя что-то вроде твикера, при желании можно все изменения вернуть обратно.
Проверка на скрытые учетки
В интернете часто пишут про способ проверки левых учеток. Вообще удалять учетные записи — нужно осторожно и перед этим всегда стоит делать контрольную точку восстановления. В общем смотрите — зажимаете Win + R, в окошке Выполнить пишите команду:
cmd
Появится черное окно — командная строка, пишите команду:
net user
Нажимаете энтер. В итоге будут отображены ваши учетные записи. Для примера — взял из интернета картинку некого пользователя Артем:
Теперь открываем панель управления, можно сделать так — зажимаете Win + R, в окошко Выполнить пишите команду:
control panel
Или просто:
control
Откроется панель управления. Находим там Администрирование > Управление компьютером > Служебные программы> Локальные пользователи > папка Пользователи, и смотрим что в этой папке:
Вообще чтобы посмотреть локальные пользователи, то можно воспользоваться командой lusrmgr.msc (Win + R > пишем команду) — но не во всех редакциях Windows работает((
Вроде бы все понятно, верно? Теперь самое главное — все имена, которые вы видели в командной строке, но которых нет в окне Управление компьютером — скрытые учетки, их нужно удалить.
Чуть не забыл написать как удалить! Все просто — также запускаем командную строку, пишем туда уже команду:
net user ACCOUNTNAME /delete
Там где ACCOUNTNAME — имя учетной записи, а параметр /delete нужен для удаления. Если будет ошибка или какая-то трабла, то попробуйте запустить командую строку от имени администратора.
Но все равно — перед удалением сделайте точку восстановления! Вот мини-инструкция:
- Зажимаете Win + R, пишите команду:
sysdm.cplНажимаете ОК.
- Откроется окно Свойства системы, здесь идете на вкладку Защита системы, выбираете системный диск и нажимаете кнопку Создать:
У меня кнопка Создать неактивна, так как восстановление системы отключено. Но у вас скорее всего будет активна. В крайнем случае — нажимаете настроить и включаете восстановление)) Далее создаете точку — советую название указывать понятное и простое, например До удаления левой учетки))
- После созданной точки — можно пробовать удалить учетную запись, в случае проблем — восстановить ПК до момента удаления.
РЕКЛАМА
На одном сайте нашел информацию, что WDAGUtilityAccount можно скрыть командой:
WDAGUtilityAccount /active :no
Свойства WDAGUtilityAccount:
Скрытые учетки — в чем смысл?
Очень хороший вопрос. Некоторые проги могут создавать учетные записи для себя — это нормальное явление. Именно поэтому перед удалением — нужно проверить в поисковике, может учетка например.. от Майкрософт Офиса.
Но иногда учетки создают вирусы. Спросите зачем? Все просто:
- Для удаленного доступа к вашему ПК. Вирус создает учетку, данные которой передаются хакеру, а тот уже пытается подключиться к вашему ПК под созданной учеткой. И дальше использовать его в своих целях.
- Хакеру учетка может быть нужна для разных задач. Например запустить на вашем ПК хакерские проги, чтобы они работали именно на вашем ПК. В принципе это частое явление. При этом все максимально маскируется чтобы было труднее обнаружить.
- Защитить себя от всего можно установив современный антивирус, в котором есть также фаервол. Не хочу рекламировать, но мне лично нравится Касперский. Хотя Аваст тоже неплохой..
Вывод
Удалось выяснить:
- WDAGUtilityAccount — учетная запись от защитника. Но может быть нужна и для других программ или задач.
- Удалять ее, отключать — не стоит. Это сугубо системная учетная запись, Windows сама знает что с ней делать))
Надеюсь информация помогла. Удачи и добра!