This tutorial explains how to move files or directories to another location on a Windows system.
Move files to another directory
move filename destinationFolder
Example: to move file ‘data.docx’ to the folder ‘d:\backup\folder’
move data.docx d:\backup\folder\
You can also rename the file while moving it to the new location
move data.docx d:\backup\folder\newData.docx
We can’t move multiple files with single command. i.e the below command would not work.
move file1 file2 D:\folder1\folder2
This would give the error The syntax of the command is incorrect.
However we can use wildcards to move files in bulk. For example, if you want to move all text files from current folder to a new location you can use the below command.
move *.txt destinationDirectory
To move all files starting with letter ‘A’, you can use below command.
move A* destinationDirectory
Move directories
Syntax:
move directory newDirectoryPath
Example: To move the directory ‘data’ to ‘D:\data\folder1\’
move data D:\data\folder1
1. Can we move multiple directories using wild cards like the way we do it with files?
No, wild cards does not work for directories. You get the below error
C:\>move tmp* Documents\folder1\ The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect.
2. How to specify the directories/files which have white spaces in the names?
You need to enclose the name of the file/directory in double quotes.
Example: move "file with spaces" "D:\directory with spaces"
Errors
If you do not have write privileges on source file/directory or on the destination folder, you would get error as below.
C:\Users\user1>move mydata.pdf c:\users\user2
Access is denied.
0 file(s) moved.
You can use move for this. The documentation from help move states:
Moves files and renames files and directories.
To move one or more files:
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]filename1[,...] destination
To rename a directory:
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]dirname1 dirname2
[drive:][path]filename1 Specifies the location and name of the file
or files you want to move.
destination Specifies the new location of the file. Destination
can consist of a drive letter and colon, a
directory name, or a combination. If you are moving
only one file, you can also include a filename if
you want to rename the file when you move it.
[drive:][path]dirname1 Specifies the directory you want to rename.
dirname2 Specifies the new name of the directory.
/Y Suppresses prompting to confirm you want to
overwrite an existing destination file.
/-Y Causes prompting to confirm you want to overwrite
an existing destination file.
The switch /Y may be present in the COPYCMD environment variable.
This may be overridden with /-Y on the command line. Default is
to prompt on overwrites unless MOVE command is being executed from
within a batch script.
See the following transcript for an example where it initially shows the qq1 and qq2 directories as having three and no files respectively. Then, we do the move and we find that the three files have been moved from qq1 to qq2 as expected.
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>dir qq1
Volume in drive C is Primary
Volume Serial Number is 04F7-0E7B
Directory of C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1
20/01/2011 11:36 AM <DIR> .
20/01/2011 11:36 AM <DIR> ..
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx1
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx2
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx3
3 File(s) 39 bytes
2 Dir(s) 20,092,547,072 bytes free
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>dir qq2
Volume in drive C is Primary
Volume Serial Number is 04F7-0E7B
Directory of C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq2
20/01/2011 11:36 AM <DIR> .
20/01/2011 11:36 AM <DIR> ..
0 File(s) 0 bytes
2 Dir(s) 20,092,547,072 bytes free
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>move qq1\* qq2
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1\xx1
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1\xx2
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1\xx3
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>dir qq1
Volume in drive C is Primary
Volume Serial Number is 04F7-0E7B
Directory of C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq1
20/01/2011 11:37 AM <DIR> .
20/01/2011 11:37 AM <DIR> ..
0 File(s) 0 bytes
2 Dir(s) 20,092,547,072 bytes free
C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents>dir qq2
Volume in drive C is Primary
Volume Serial Number is 04F7-0E7B
Directory of C:\Documents and Settings\Pax\My Documents\qq2
20/01/2011 11:37 AM <DIR> .
20/01/2011 11:37 AM <DIR> ..
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx1
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx2
20/01/2011 11:36 AM 13 xx3
3 File(s) 39 bytes
2 Dir(s) 20,092,547,072 bytes free
In the Windows Command Prompt, we use the move command to move files from one directory to another (cut and paste).
The syntax of the move command is as follows:
move <Source> <Target>We can also use the move command to move folders from one location to another.
Command Options
| /Y | Do not ask for confirmation if a duplicate file is found at the destination. The destination file will be overwritten. |
| /-Y | Ask before overwriting destination files. |
Examples
Move sales.doc in the current directory to C:\backup directory:
move sales.doc C:\backupMove C:\data\sales.doc to C:\backup directory. The file will be overwritten if it already exists in the destination folder:
move /y C:\data\sales.doc C:\backupMove C:\data\finance to C:\backup folder:
move C:\data\finance C:\backupMove all files in a directory
You can use wildcards with the move command. For example, the following command moves all files in the C:\data to C:\backup.
move /y C:\data\* C:\backupThe following command moves all files with a .doc extension to the backup folder:
move /y C:\data\*.doc C:\backupIn the following example, all files whose names start with screenshot are moved to the C:\backup directory.
move /y C:\data\screenshot* C:\backupMove two or more files
To move two or more files without using wildcards, you have to use a for loop, as shown in the following example:
for %i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do move /y %i C:\backupIf you want to run the for command in a batch file, you would use two % (%%) with the variable.
for %%i in (sales.doc, products.doc) do move /y %%i C:\backupThe move command deletes the source file after it is copied to the destination. If you want to keep the original file, use the copy or xcopy.
Updated: 12/31/2020 by
There are several methods available to move, or transfer, computer files and folders (directories) from one source or level to another. Click one of the links below to view steps relating to the operating system you need help with, or scroll down to review them all.
Note
When moving files or folders, you’re going to have only one copy of the files moved. If you want more than one copy of the files, copy the files and not move them. See: How to copy files.
How to move files in Windows
In Windows, you can move files using several method. You can drag-and-drop, cut and paste, or use the «Move to Folder» command. Below are the steps on how you can move files in Windows. Choose the option that works best for you.
Cut and paste
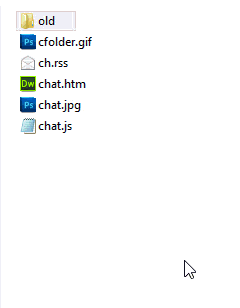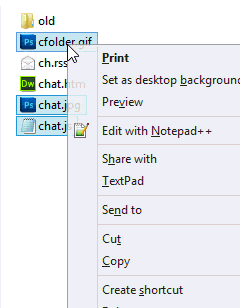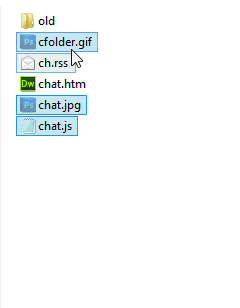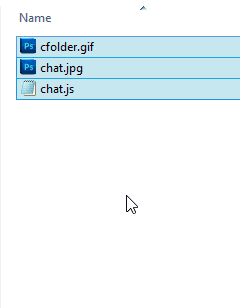
To cut and paste a file, select the file you want to move, right-click the highlighted file, and then select Cut. Browse to the folder you want to move the file to, right-click in the folder, and select Paste.
Alternatively, click Edit from the file menu, select Cut to cut the files, browse to where you want to move the files, then select Edit and Paste in the file menu.
Finally, you can also use keyboard shortcuts to cut and paste files. Select the files you want to cut, then press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+X to cut the files. «Cutting» the files is like cutting text in a document: it moves the files to a temporary «clipboard» until you «paste» them somewhere. Navigate to the destination folder and press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+V to paste the files. The files are now in your destination folder.
- How to select or highlight multiple files and folders.
Drag-and-drop
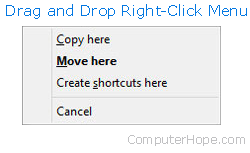
Highlight the files you want to move, press and hold your right mouse button, and drag-and-drop the files to where you want to move them. When you release the mouse button, a menu appears, similar to the example shown in the picture. Select the Move here option to move the files.
Note
For drag-and-drop to work, you’ll need to be able to see the window of where you are moving the files.
Use «Move to Folder»
To use the «Move to Folder» command, select the file by clicking the file name. Click the Edit menu near the top-left of the window and select the Move to Folder option. In the new window browse to the folder you want to move the file, then click the Move button to move the file to that folder.
If you are using Windows 8, once the files are selected the Move to option is shown under the Home tab.
How to move files in the Windows command line (MS-DOS)
In the Windows command line and MS-DOS, you can move files using the move command. For example, if you want to move a file named «stats.doc» to the «c:\statistics» folder, you would type the following command, then press the Enter key.
move stats.doc c:\statistics
If you’d like to move multiple files, you can separate the file names with a comma, as in the following command.
move stats.doc, morestats.doc c:\statistics
In the next example, we are moving the file «example.doc» to the D:\ drive.
move example.doc d:\
You can also move multiple files with wildcards. In the example below, the move command moves all files that have the «.doc» file extension to the «c:\statistics» directory.
move *.doc c:\statistics
Using the move command, you can also move a directory (folder). In the example below, the move command moves the «example» directory in the current directory to the «new» directory also in the current directory.
move example new
Tip
To move a directory or file into a different directory, you need to specify the full path.
- See our move command reference for full information, available options, and other examples on this command.
How to move files in macOS
There are several ways to move files in macOS.
Drag-and-drop
In the macOS Finder, you can drag-and-drop one or more file icons, moving them from one folder to another. To drag-and-drop a file, highlight the files you want to move. Click any of them, and before you release the mouse button, move the mouse cursor until it is over the destination folder. Release the mouse button to move the files to this location.
Keyboard shortcut
You can also move files using keyboard shortcuts by following the steps below.
- Highlight the files you want to move.
- Press the keyboard shortcut Command+C.
- Move to the location you want to move the files and press Option+Command+V to move the files.
Terminal
To move files in the Terminal command line, use the mv command.
How to move files in Linux
In Linux, using the command shell, you can move files or directories with the mv command. For example, if you wanted to move a file named «myfile.txt» to the folder named «backup,» you would type the following command.
mv myfile.txt backup
For more information, see our mv command reference.
The move is an internal command found in the Windows Command Interpreter (cmd) that is used to move files and folders/directories. The command is robust than a regular move operation, as it allows for pattern matching via the inclusion of Wildcards in the source path.
The command is a very generic one and is available (in one form or the other) in almost every single operating system out there (under different aliases). In this article, we will learn about the move command and would learn various uses/applications of it.
Description of the Command :
MOVE [/Y | /-Y] [drive:][path]dirname1 dirname2
- [drive:][path]filename1 –
Specifies the location and name of the file or files you want to move. - destination –
Specifies the new location of the file. The destination can consist of a drive letter and colon, a directory name, or a combination. If you are moving only one file, you can also include a filename if you want to rename the file when you move it. - [drive:][path]dirname1 –
Specifies the directory you want to rename. - dirname2 –
Specifies the new name of the directory. - /Y –
Suppresses prompting to confirm you want to overwrite an existing destination file. - /Y –
Causes prompting to confirm you want to overwrite an existing destination file.
The switch /Y may be present in the COPYCMD environment variable. This may be overridden with /-Y on the command line. The default is to prompt on overwrites unless the MOVE command is being executed from within a batch script. The above output can be obtained by executing the command move /? in cmd.
The above text is a little cryptic at first, but the command is really basic and follows the minimal blueprint.
Syntax :
MOVE [options] (Source) (Target)
Key :
- [option] –
An optional flag denoted by /Y or /-Y, that is used to suppress the confirmation prompt on overwritten files. The default is to prompt on overwrites unless the MOVE command is being executed from within a batch script. - (Source) –
A path of the file/files that would be used to move them. This path can contain wildcards ( * ? ) in the path. If more then files are made to move, then wildcards are used. - (Target) –
A path for the new location of the file.
Using the Command :
Throughout this section, we would take the following directory as example for demonstrating the usage of move command.
Moving a File from One Folder to Another :
move source_path destination_path
- source_path –
It is the path of the file which we are willing to move, and the destination_path is the location to which we want the file to be moved.
Example :
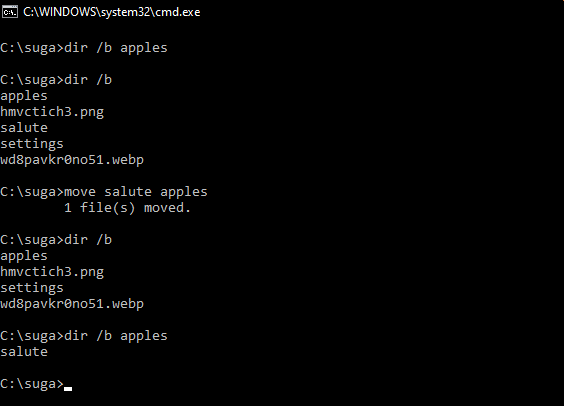
- The Dir /b command is used to list all the files and folders inside a directory.
- In the above example, we have moved an extension-less file named salute from C:\suga to C:\suga\apples directory.
Moving Multiple Files from One Path to Another :
move source_path destination_path
- source_path –
It is a path containing wildcards that will allow more than one file to be taken as a source. The destination_path is now a path to a directory where the moved files would reside (should not contain wildcards).
Example :
- In the above example we have moved all the files inside C:\suga folder which matches the pattern *.* to C:\suga\Apples directory.
- It should be noted that wildcard in source_path should match with the file(s) otherwise it would result in source_path being null, and a subsequent error.
Moving Directory from One Path to Another :
move source_dir_path Destination_dir_path
- source_dir_path –
It is the path to the directory to which we are moving, and destination_dir_path is the new location where it would be moved to.
Example :
- In the above example, we have moved the C:\suga\apples directory to C:\Users\Public directory.
- Multiple Directories can be moved using the method described in Moving multiple files from one path to another (with little modification to make is eligible for directories).
Moving a File to Another Folder with a Same Name File already existing :
There are two ways to tackle this situation –
- Abort the move process.
- Continue the move process, by overwriting the existing file with the newer one.
By default, the move command upon encountering any name collisions would prompt the user, asking whether he wants to rewrite the existing file with the new one, or stop the move process (via a Y/N prompt). To abort the move process, the user can simply enter N in the prompt input, stating that the file should not be overwritten. The prompt seeking for user input (for overwrite of files) appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All):
When the users enter N in the prompt the output appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All): N
0 file(s) moved.
When the user enters Y in the prompt the output appears as follows –
Overwrite {full_file_path}? (Yes/No/All): Y
1 file(s) moved.
To continue the move process by overwriting existing files (on all name collisions), a /Y switch needs to be added to the command as follows –
move /Y source_path destination_path
Last Updated :
20 Oct, 2020
Like Article
Save Article