Introduction
The Windows operating system features over 280 commands for CMD (Command Prompt). Some commands are specific to Windows servers, while others are available for desktop versions. In both cases, CMD commands communicate directly with the OS and allow to perform various IT automation tasks.
This guide showcases important Windows CMD commands and provides hands-on examples.

Prerequisites
- Access to the command prompt (CMD).
- Administrator privileges (for some commands).
Commands are built-in programs that run through the Command Prompt program. The main use for commands is to automate various tasks, such as user provisioning and other routine actions.
Below is an overview of some common Windows CMD (Command Prompt) commands. Every command has a brief explanation and an example use case.
Note: All commands were tested on a Windows 10 machine in Command Prompt.
1. arp Command
The arp (address resolution protocol) command shows and modifies entries in the ARP cache. The cache contains one or multiple tables that map IP addresses to resolved physical addresses.
The syntax for the command is:
arp <options> <address>Without any parameters, the arp command shows the help window.
To show the ARP cache table, run the following command:
arp -a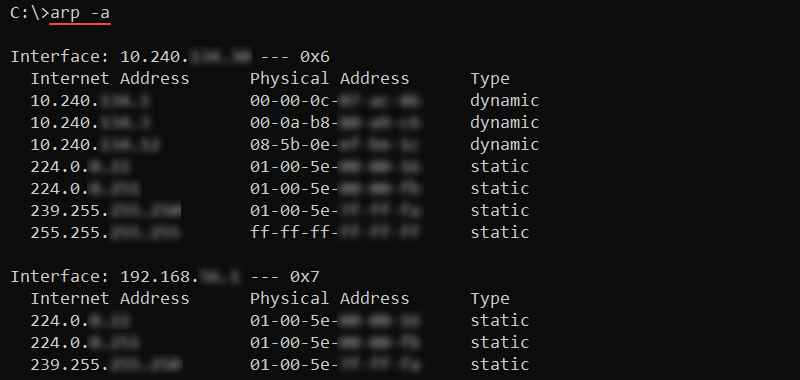
The output lists all the current ARP entries grouped by the interface.
2. assoc Command
The assoc (association) command lists and modifies file extension associations on the system. The syntax for the command is:
assoc .<extension>=<filetype>Without any parameters, the command prints the current file extension associations.
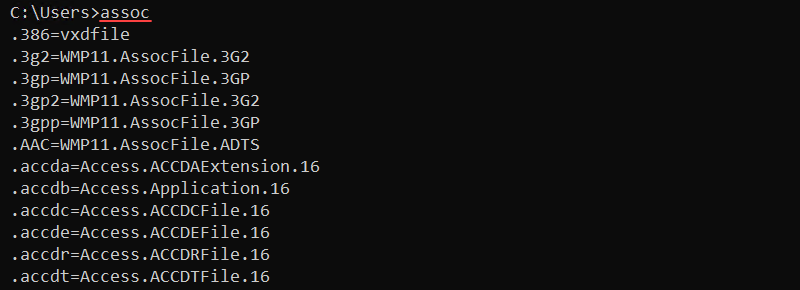
Use the assoc command to view, change, or remove file associations. For example, to view the .log file associations, run:
assoc .log
Change the file association with:
assoc .log=txtfileAlternatively, remove all file associations for files with the .log extension by running:
assoc .log= The command requires adding a space after the equals sign to remove the association.
3. attrib Command
The attrib (attribute) command shows or changes file attributes. The possible attributes are:
- R — Read-only.
- H — Hidden.
- S — System file.
The syntax for the attrib command is:
attrib <+ or -> <attribute>The plus sign (+) sets an attribute, while the minus sign (-) removes an attribute from a file. Without any options, the command shows the file attributes in the current directory.
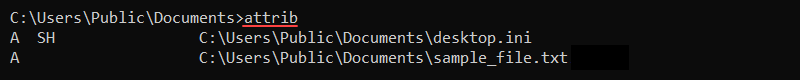
To set a file to have the read-only (R) and hidden (H) attributes, use the following command:
attrib +R +H sample_file.txt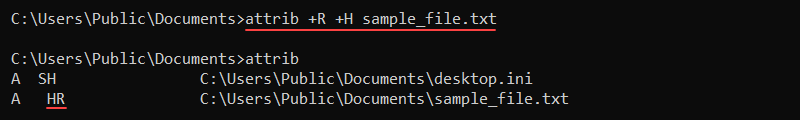
To make a file visible, remove the hidden (H) attribute:
attrib -H sample_file.txt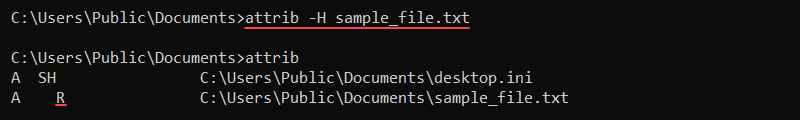
The minus removes the attribute from the file and returns the file to the default visible state.
4. bcdboot Command
The bcdboot (boot configuration data boot) command sets up a system partition by copying BCD files into an empty partition.
The syntax for the command is:
bcdboot <path>For example, to copy the BCD files into C:\Windows, use:
bcdboot C:\Windows
The output prints a confirmation message about file creation.
5. cd Command
The cd (change directory) command shows or changes the current location. The syntax for the command is:
cd <directory>The directory parameter is optional, and without it, the command prints the current working directory.
For example, to change the location to a directory named Public, add the directory name after the command:
cd Public
The prompt reflects the change and shows the new location.
To change the location to a different disk, add the /d option before the path. For example, to change to disk S:\ use:
cd /d S:
Without the option, the command prints the path without changing to the provided location.
To change to the parent directory, use the following shortcut:
cd ..
The current directory changes to one directory above the current location.
6. chkdsk Command
The chkdsk command scans the local file system and metadata for errors. The syntax for checking a disk is:
chkdsk <volume> <options>Without additional parameters, the chkdsk command shows the current disk state without fixing any errors.
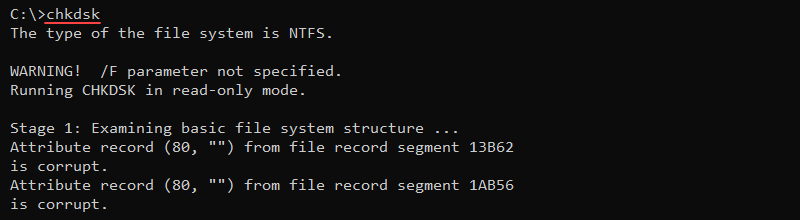
Additional parameters enable fixing errors on a disk, such as the /f option:
chkdsk <volume> /f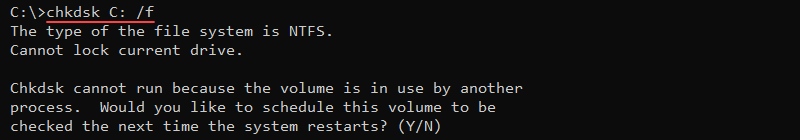
The command attempts to fix errors on the disk. If the disk is in use, run the check on the next system restart. Stopping the command does not affect the system, but ensure to run the scan later to fix any potential data corruption.
7. choice Command
The choice command prompts a user to choose an answer from a list of options. Without any parameters, the command prompts the user to choose between Y and N options.
Additional options control the number of choices and the prompt text. For example, to add a third choice, use the /c parameter and list the three option names:
choice /c ync
Insert additional text to explain the available options with the /m parameter. For example:
choice /c ync /m "Yes, No, Continue"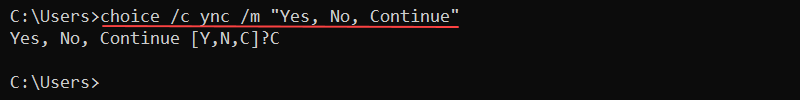
In all cases, the command returns the choice index and exits.
8. cipher Command
The cipher command shows and modifies the encryption for files or directories. The command syntax is:
cipher <option> <file or directory>Without any options, the cipher command shows the encryption state for all files and directories in the current location. The U represents «unencrypted,» whereas E is «encrypted.»
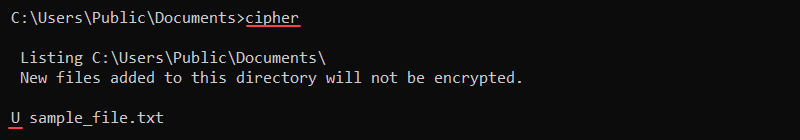
To encrypt a file in the current directory, use the /e parameter:
cipher /e <file name>The file’s indicator changes from U to E, which marks the file as encrypted.
Note: The encrypting and unencrypting files and directories feature is available for Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions.
9. clip Command
The clip command copies a command output or file contents to the clipboard. The syntax for copying a command’s output in CMD is:
<command> | clipFor example, to copy the current directory path, pipe the cd command to clip:
cd | clipPaste the contents anywhere in the window using CTRL+V (or right-click in CMD).
To copy the contents of a file, use redirection:
clip < <filename>For example, to copy the contents of a sample.txt file to the clipboard, run:
clip < sample.txtThe file’s contents are saved to the clipboard and can you can paste them anywhere.
10. cls Command
The cls command clears the text in a command prompt window and returns a blank surface. Use the command to clear the screen contents.
Note that the previous contents and output do not return to the screen.
11. cmd Command
The cmd command starts a new instance of the command interpreter. Use the following syntax to run the command:
cmd <options> <command>Without additional parameters, the cmd command shows the current cmd.exe program version.
Use cmd to run commands without affecting the current session. For example, to test a command and return to the current command interpreter session, use the /c parameter:
cmd /c cd ..The new interpreter changes the directory. However, the /c tag ensures the interpreter returns to the original session, and the directory stays unchanged.
To run a command and stay in the new session, use the /k parameter:
cmd /k cd ..
The /k parameter switches to the new session and runs the cd command to switch to the parent directory.
12. color Command
The color command changes the default console background and text colors. The command syntax is:
color <background><font>The color attributes are hexadecimal numbers from 0 to f. The help window displays all the possible color options:
help color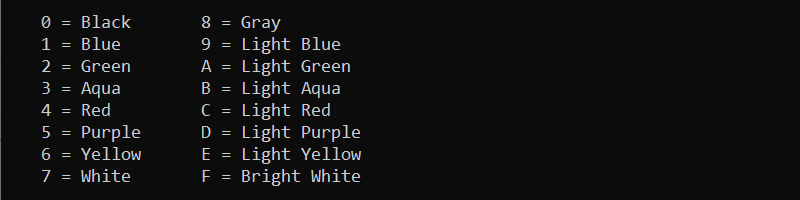
For example, to change the background to blue (1) and the font to light aqua (b), run:
color 1b
To return to the default console colors, run the color command without options.
13. comp Command
The comp command compares the contents of two files. The comparator program inspects file bytes and outputs characters where the two files differ.
The syntax for the command is:
comp <file 1> <file 2> <options>Without any options, the comp command starts an interactive prompt to enter file names and additional options.
To demonstrate how the command works, compare two text files with the following contents:
- sample_file_1.txt contains «test»
- sample_file_2.txt contains «text»
Run the comp command and provide the two file names:
comp sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt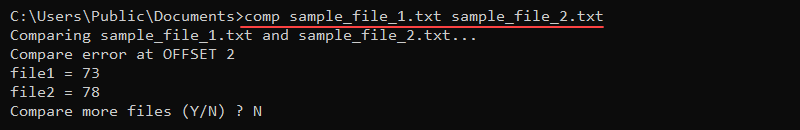
The output prints the comparison error as characters in hexadecimal format and asks to compare more files (enter N to exit).
To print the comp results in human-readable format, use the /a parameter:
comp /a sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt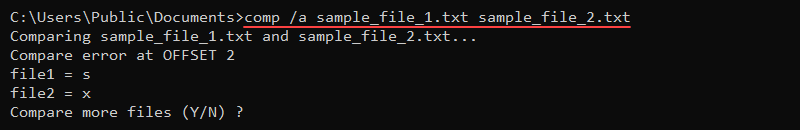
The comparison fails at character «s» in the first file and character «x» in the second file.
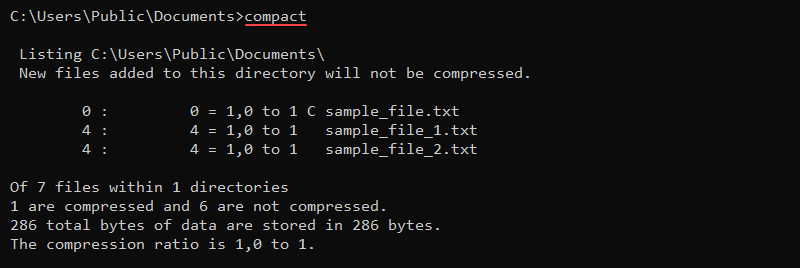
14. compact Command
The compact command is a built-in feature for compressing files and folders. The syntax for the command is:
compact <options> <file>Without any options or parameters, the compact command prints the compression state in the current directory.
For example, to compress a file, use the /c parameter and provide the file name:
compact /c sample_file.txt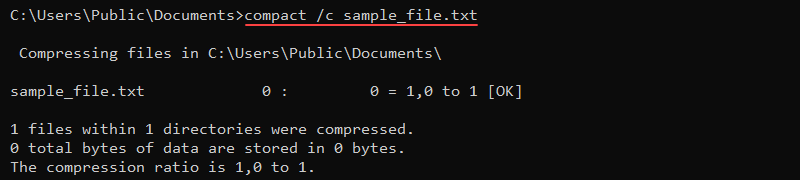
To uncompress a file, use the /u parameter:
compact /u sample_file_1.txt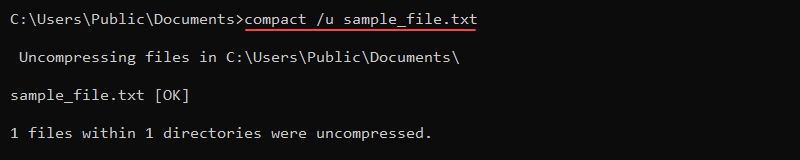
Use the compact command to save disk space and compress large files and directories.
15. copy Command
The copy command copies one or multiple files from one location to another. The command syntax is:
copy <options> <source> <destination>For example, to copy a file’s contents into a new file in the same location, use:
copy sample_file.txt sample_file_copy.txtThe command creates the new file and copies all the contents from the source file.
16. date Command
The date command shows and modifies the current date on the system. Without any parameters, the command prints the current date and requests to enter a new date:
date
Enter the date as mm-dd-yyyy to change the current date on the system or exit with CTRL+C.
Use the /t parameter to avoid modifying the system state and only print the current date:
date /t
The command shows the day of the week and the current date.
17. defrag Command
The defrag (defragmentation) command finds and aggregates fragmented files on the system. The command reduces unnecessary empty data blocks and improves system performance.
The syntax for the defrag command is:
defrag <volumes> <options>For example, to defragment the C:\ drive, run:
defrag C:\ /u /v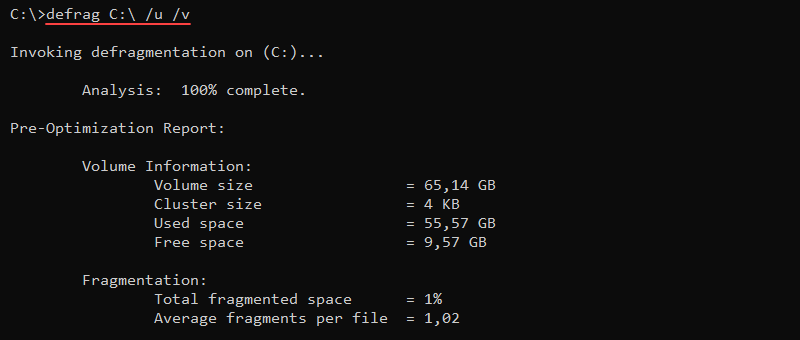
The /u parameter prints the progress, while /v shows a verbose output. These parameters are optional.
18. del and erase Commands
The del and erase commands delete one or more files. The syntax for the commands is:
del <options> <file(s)>erase <options> <files(s)>Both commands permanently delete the specified file or files from a disk and are irretrievable.
For example, to delete a file with the name sample.txt, run:
del sample.txtOr alternatively:
erase sample.txtTo avoid accidental deletion, use the /p parameter:
del /p sample.txt
The output shows a prompt with the file name and requires confirmation before deleting the file.
19. dir Command
The dir (directory) command lists directory contents, including files and subdirectories. The syntax for the command is:
dir <drive><path><filename> <options>The dir command without options shows information for the current directory.
To show the C:\ drive contents, run:
dir C:\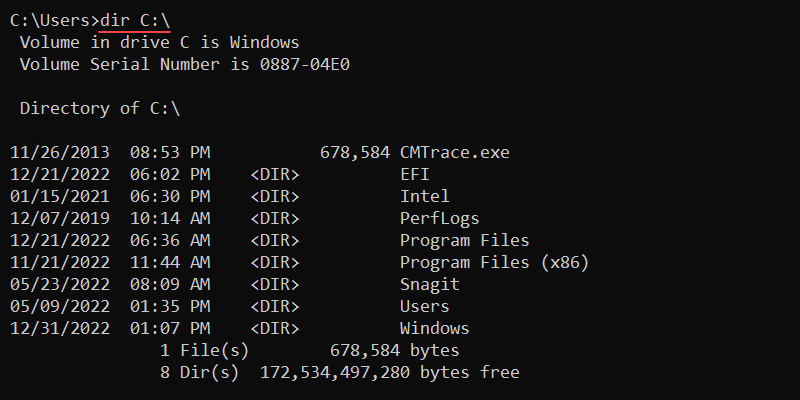
The output shows the following information:
- Volume drive.
- Volume serial number.
- Directory contents with modification time.
- File and directory count.
20. doskey Command
The doskey command starts the Doskey.exe program for the previously entered commands. The command helps recall command history and create macros.
For example, to see the command history from the current command prompt session, run:
doskey /history
The output shows all the commands from the CMD session from oldest to newest.
21. driverquery Command
The driverquery command is a command for admins to display the installed device drivers and their information. The command works for both local and remote access machines.
The syntax for the command is:
driverquery <options>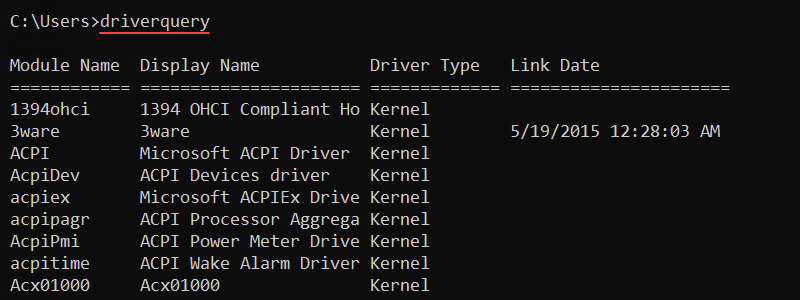
Without any options, the driverquery command shows device drivers on the local machine. Additional options control the output format or allow querying remote machine drivers.
22. echo Command
The echo command prints a message to the console and controls the settings for the command. The syntax for the command is:
echo <message>Without any parameters, the command shows the current settings.
To use the command and show a «Hello, world!» message to the screen, run:
echo "Hello, world!"
The echo command often appears in scripts to print useful information while the script runs.
23. exit Command
The exit command ends the current batch script or the command interpreter session. To exit a batch script, add the /b parameter:
exit /bWithout the /b option, the exit command closes the command interpreter.
24. fc Command
The fc (file compare) command compares two or more files. The output prints the contents to the console if there is a difference between the files.
The syntax for fc is the following:
fc <options> <file 1> <file 2> For example, to compare two sample files, sample_file_1.txt and sample_file_2.txt, run:
fc sample_file_1.txt sample_file_2.txt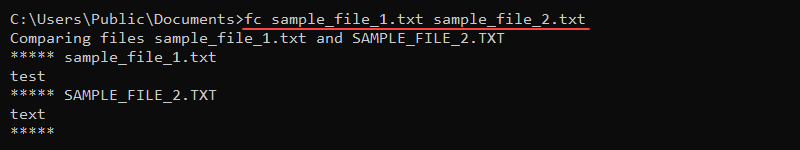
The command prints the file contents, indicating there is a difference between the two files.
25. find Command
The find command searches for a string in a file and prints the line of text when there is a result. The command syntax is:
find <string> <file>For example, to search for the string «text» in a file, use:
find "text" <file>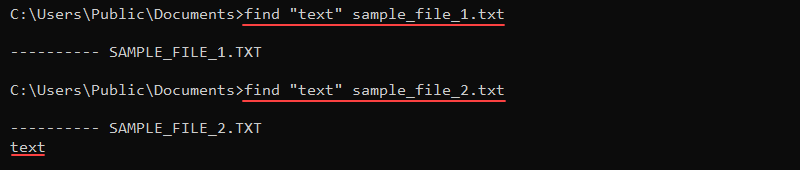
The command looks for an exact match and returns the file name along with the line of text that contains the string. If a file does not contain the text, the command returns the file name without the text.
26. findstr Command
The findstr (find string) command performs a similar task to the find command. The command returns the whole line where the text is located without the file name. This feature makes it more convenient for use in scripts.
The command syntax is:
findstr <string> <file>For example, to find a string «text» in a file, run:
findstr "text" <file>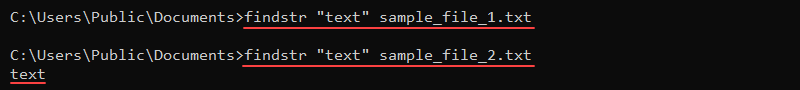
If the command does not return a result, the string is not in the file.
27. ftype Command
The ftype (file type) command shows and changes a file type and extension association. The command syntax is:
ftype <file type>=<open command>The file type parameter is the file to show or modify (such as txtfile), while the open command option is a string that calls a program to read the file type. The open command string substitutes the file name into the open command to run a file in the provided program.
Without any options, ftype prints all file types and extension associations.
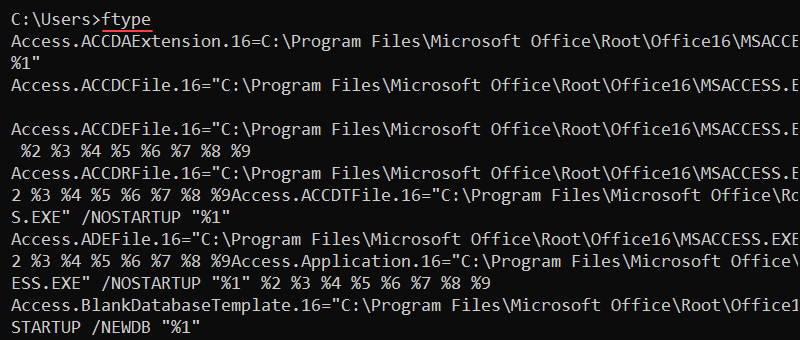
To show the current file type and extension association for text files, enter:
ftype txtfile
To remove file type association, append an (=) sign:
ftype txtfile=The command omits the program for opening files and removes the program association.
28. getmac Command
The getmac command fetches the MAC addresses for all network cards on the computer or in the network. The command also shows the protocols associated with each address.
The syntax is:
getmac <options>Additional options provide detailed information about a remote computer or control the output display. For example, to show the MAC addresses in the CSV format, use:
getmac /fo csv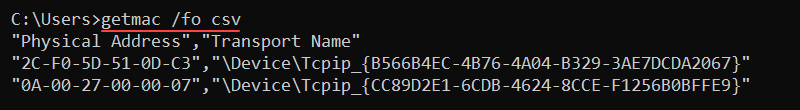
Use the command to parse the MAC address to a network monitoring tool or to check the protocols on network adapters.
29. help Command
The help command shows detailed information for a specific command. Without any parameters, the help command lists all available system commands.
The syntax for the command is:
help <command>For example, to view the help menu for the cd command, run:
help cd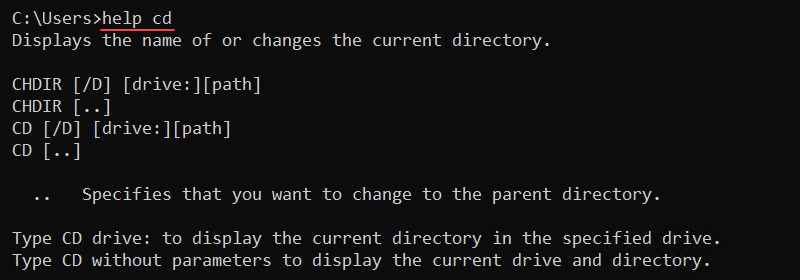
Use any key to go through the pages if the help page is larger than the command line. Alternatively, press CTRL+C to exit.
Note: For non-system commands, use the following format to see the help window:
<command> /?
30. hostname Command
The hostname command is a simple command to display a machine’s host name. Run the command to see the name of the computer:
hostname
The command does not have options, and providing any additional parameters throws an error. The hostname command is available for systems with TCP/IP installed on a network adapter.
31. ipconfig Command
The ipconfig (IP configuration) command is a networking CMD tool that shows all current TCP/IP network configuration information. The command also refreshes DHCP and DNS settings.
The syntax for the command is:
ipconfig <options>Omitting options shows the basic TCP/IP configuration for all adapters:
ipconfig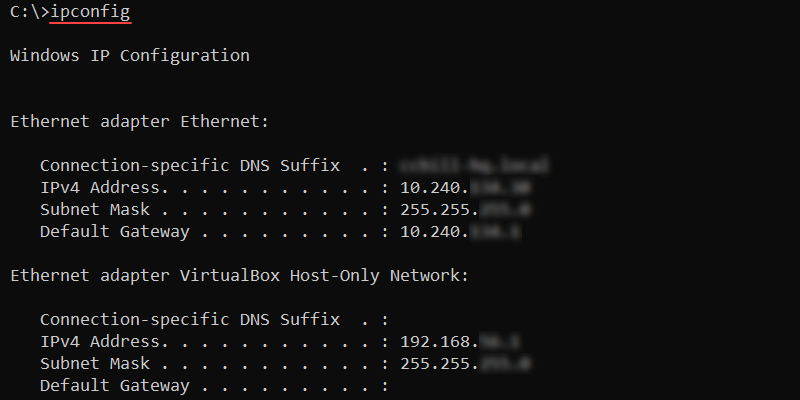
To show the full TCP/IP configuration for all adapters, run:
ipconfig /allRenew the DHCP IP address for the local area connection with:
ipconfig /renew Local Area ConnectionTo flush the DNS cache, use:
ipconfig /flushdnsUse the command when troubleshooting DNS issues.
32. label Command
The label command shows, changes, or removes the volume label (name) of a disk. The command requires administrator privileges to perform any changes.
Without any options, the label command shows the label for the C:\ drive and starts a prompt to change the name:
label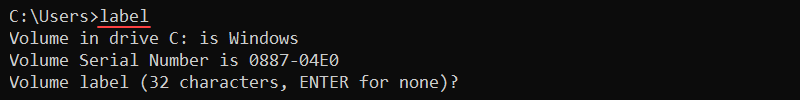
Press Enter to remove the label, or enter a new name to change the current label name. Confirm the change with Y or press N to keep the existing name.
33. makecab Command
The makecab command creates a cabinet (.cab) file. Cabinet files are an archive format specific to Windows systems with support for lossless data compression and archive integrity.
Use the following syntax to create .cab files with the makecab command:
makecab <options> <source> <destination>For example, to create a sample_cab.cab file in the current directory and add a sample_file.txt file to the archive, use:
makecab sample_file.txt sample_cab.cab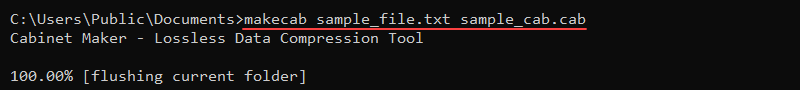
The output prints the compression progress and exits when done.
34. md and mkdir Commands
The md and mkdir (make directory) commands create a new directory or subdirectory. The command syntax is:
md <path>mkdir <path>For example, to make a new subdirectory called Subdir in the current location, run:
mkdir SubdirThe command extensions enable md and mkdir to create a directory tree:
md Subdir\Subsubdir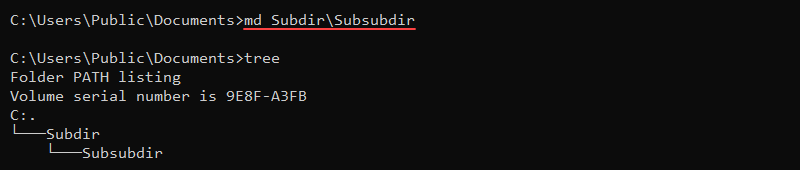
The command immediately creates all intermediate subdirectories.
35. mklink Command
The mklink (make link) command creates a hard or symbolic link to a file or directory. The command requires administrator privileges to run and uses the following syntax:
mklink <options> <link> <target>Without any additional options, the mlink command creates a symbolic link to a file. For example:
mklink my_link sample_file.txt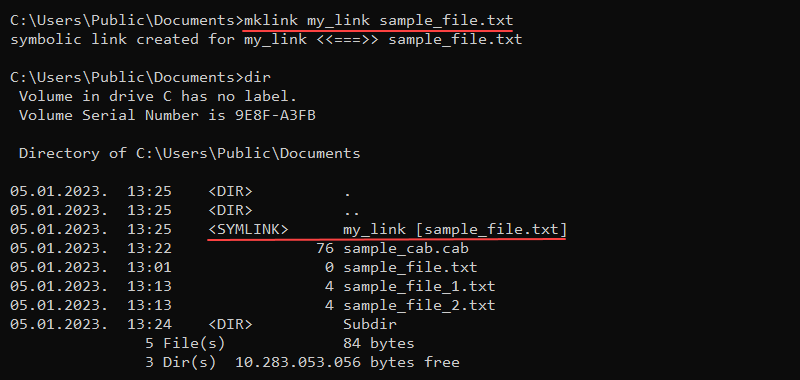
To create a hard link instead of a symbolic link, use the /h parameter:
mklink /h my_link sample_file.txtCreate a directory link with the /d parameter:
mklink /d \Docs \Users\milicad\DocumentsThe dir command shows the links in the directory listing. To enter the directory, use the cd command and treat the link as a regular directory (cd Docs).
36. more Command
The more command is a Windows CMD utility for displaying long documents or outputs one screen at a time. To use more with a command, use the pipe character:
<command> | more <options>Alternatively, use the command to display long files page by page:
more <path>For example, run the help cd command and pipe the more command to truncate the output:
help cd | more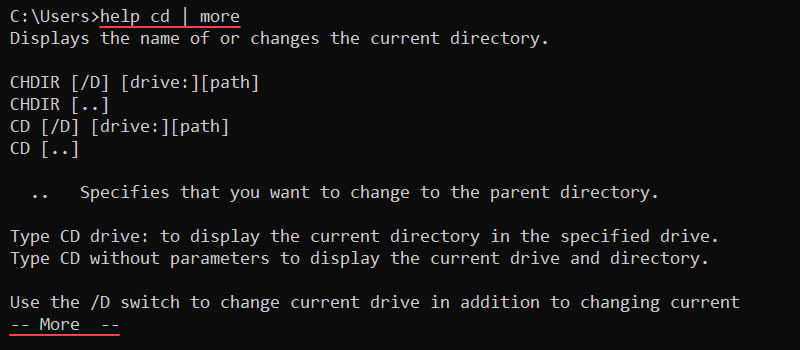
Press Enter to go to the following line and Space to go to the next page. To exit, press q.
37. mountvol Command
The mountvol command creates, removes, or shows a volume mount point. Mounting a volume makes data on a storage device available for local users through the file system.
The command syntax is:
mountvol <path> <volume name>The command does not require a drive letter to link a volume. Without any parameters, the mountvol command shows the help menu, mount points, and possible volume names.
For example, to list the volume name and current mount point for the C:\ drive, run:
mountvol C:\ /l
The output shows the GUID for the volume, which is a unique unchanging identifier.
38. move Command
The move command is a CMD shell command for moving files from one location to another. The syntax for the command is:
move <options> <source> <destination>The source and destination are either a folder or a file. The move command renames a file if the source and destination locations are the same but have different file names.
For example, the following command renames a file named sample_file.txt to file.txt:
move sample_file.txt file.txt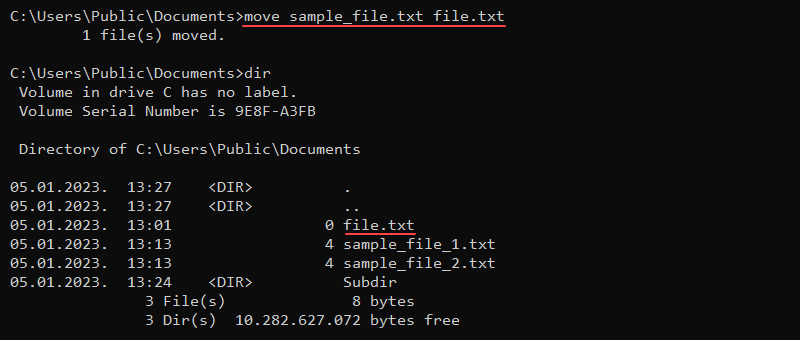
Provide the full path to move a file to another location:
move C:\Users\Public\Downloads\my_file.txt C:\Users\Public\Desktop\my_file.txt If overwriting an existing file, the command prompts to confirm, unless the command runs as part of a batch script.
39. msiexec Command
The msiexec program runs the Windows Installer program for installing, managing, and removing .msi software packages. The command syntax is:
msiexec <options> <path to package>The program features various install, display, update, and repair options. Without any options, the msiexec command opens a window to show the command information.
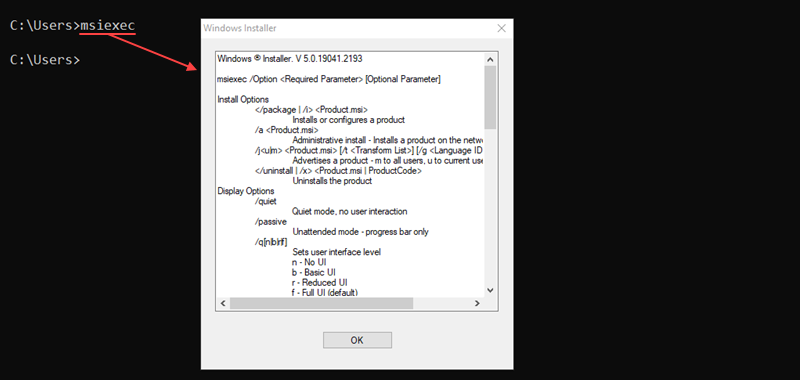
For example, to perform a normal installation of a .msi package, run:
msiexec /i "C:\example.msi"The /i option indicates a normal installation of the .msi package located at the provided path.
40. msinfo32 Command
The msinfo32 command opens the System Information window, which has details about the system.
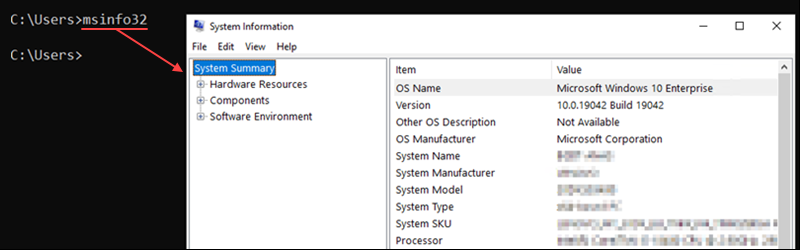
The command syntax is:
msinfo32 <options>Additional options filter the information or export the data into specific file formats. For example, to export all system information into an.nfo file, use:
msinfo /nfo sysinfo.nfoThe command automatically appends the .nfo extension if omitted.
41. mstsc Command
The mstsc command starts the Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) program to connect to a remote machine. Use the command for remote connection or to alter an existing .rdp file.
The command syntax is:
mstsc <options> <file>For example, to start an RDC session in full-screen mode, use this command:
mstsc /f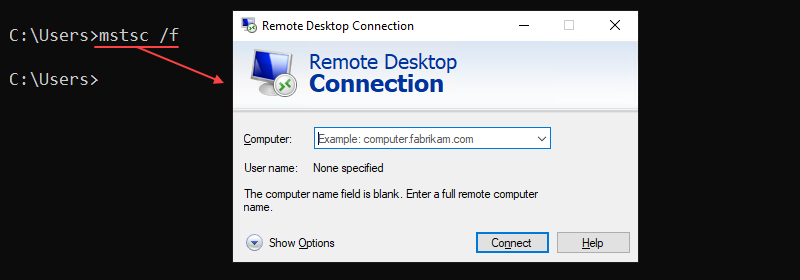
To edit an existing connection, use the /edit parameter and provide the file name:
mstsc /edit example.rdpUser-created .rdp files are in the Documents folder by default.
42. net Commands
net commands are a set of commands for managing various network aspects, such as users and network services.
The command syntax is:
net <subcommand> <options>Without additional parameters, the net command shows all available subcommands with a short description.
Use the net start command to list all running Windows services:
net start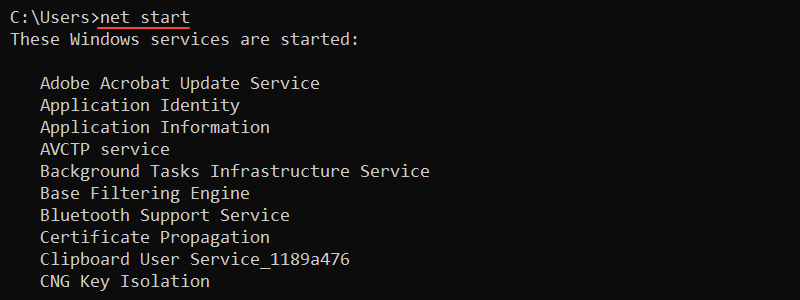
To stop a service, use the following command:
net stop <service>View the login and password requirements for a user with the following:
net accounts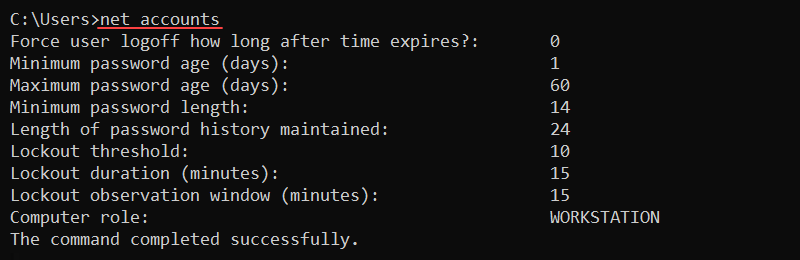
Display additional help for a subcommand using the following syntax:
net help <command>The output shows a detailed help window for any provided command.
43. netstat Command
The netstat (network statistics) command is a crucial command for network administrators. The command lets you view various network statistics.
The basic syntax for the command is:
netstat <options>The command displays active TCP connections when used without options. The output shows the protocol, local and foreign addresses, and the TCP connection state.
Add the -a option to display all active TCP connections and listening TCP and UDP ports:
netstat -a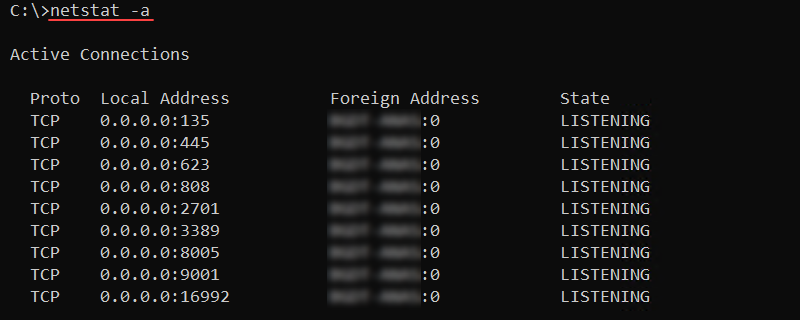
Use the command to scan for open ports or to check the port protocol type.
44. nslookup Command
The nslookup command is a DNS infrastructure diagnostics tool for web servers. The command features a non-interactive mode for looking up a single piece of information and an interactive mode for looking up additional data.
The syntax for nslookup is:
nslookup <host> <command> <options>Without any options, nslookup enters interactive mode. To find DNS records for a specific domain name, use:
nslookup <domain>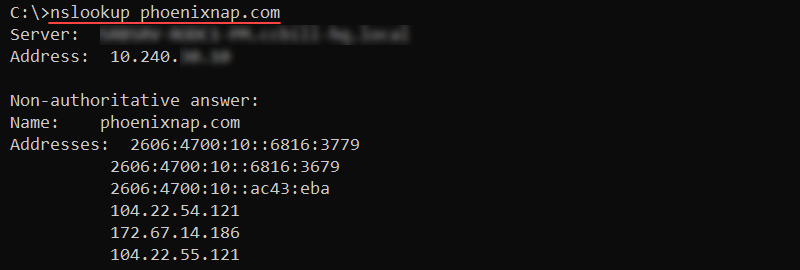
The output prints the A records for the provided domain.
45. path Command
The path command helps add directories to the PATH environment variable. The variable contains a set of directories that point to executable files.
The command syntax looks like the following:
path <location>Without any parameters, path shows the current state of the PATH variable.
To add multiple locations to PATH, separate each location with a semicolon (;) as in the following example:
path <location 1>; <location 2>Both locations append to the variable.
46. ping Command
The ping command is another essential network troubleshooting tool. The command checks the connectivity with another machine by sending ICMP request messages.
The syntax for the command is:
ping <options> <host>For example, to check connectivity to the phoenixNAP website, use:
ping phoenixnap.com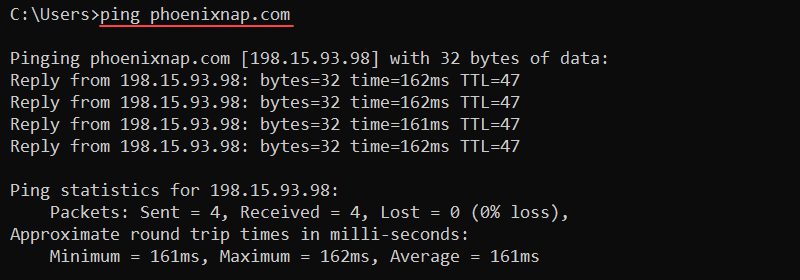
The output prints corresponding reply messages and round-trip times. Use the command to check for connectivity and name resolution issues.
47. powercfg Command
The powercfg (power configure) command runs the powercfg.exe program for controlling the system’s power plans. The monitoring tool also helps troubleshoot battery life and energy efficiency problems on a device.
The command syntax is:
powercfg <options> <arguments>To list the current power plan setup on a device, use:
powercfg /list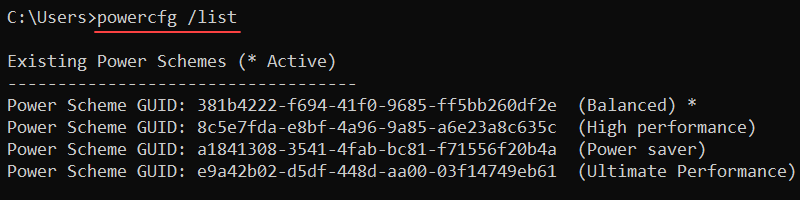
The output lists all power schemes on the system. The active power scheme has an asterisk (*).
48. prompt Command
The prompt command allows changing the CMD prompt display to the specified string. By default, the prompt shows the current location and the greater-than sign (>).
The command syntax is:
prompt <string and variables>The prompt command offers various variables to add special characters or additional features to the prompt. For example, to change the prompt to an arrow, use:
prompt --$g
The $g variable represents the greater-than sign (>) and the prompt stays during the command-line session.
49. rd and rmdir Commands
The rd and rmdir commands remove an empty directory from the system. The syntax for the commands is:
rd <path>rmdir <path>Attempting to delete a directory with files results in an error message. Add the /s parameter to delete a directory with subdirectories and files to avoid the error message:
rd /s <path>The command deletes the complete subdirectory tree and all files.
50. ren and rename Commands
The ren and rename commands rename files or directories. The syntax for the two commands is:
ren <path><old name> <new name>rename <path><old name> <new name>The commands do not allow moving the files to a different location. Wildcard characters work for multiple files. For example, to change all .txt files to .c files, use:
ren *.txt *.c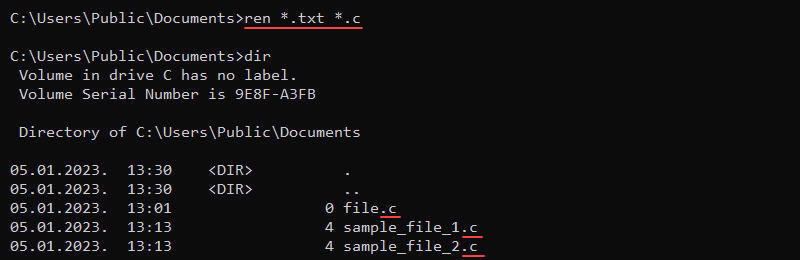
The asterisk (*) character helps discover all file names in the current directory with the .txt extension and renames the files to have the .c extension.
51. robocopy Command
The robocopy command is a robust command for copying files and directories. The syntax for the command is:
robocopy <source> <destination> <file> <options>The main benefit when using robocopy is the /mt parameter for higher-performance multithreading. Additionally, the /z parameter lets you restart a transfer in case of interruptions.
An example transfer looks like the following:
robocopy C:\Users\user\Downloads C:\Users\user\Documents database.db /mt /z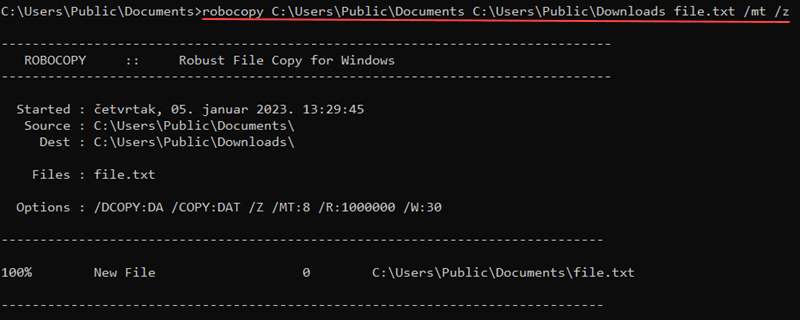
Use the command for large file transfers that are sensitive to interruptions.
52. route Command
The route command shows and alters entries in the local routing table. The command syntax is:
route <options> <command> <value>The different available commands are:
add— Adds a route entry to the table.change— Modifies an entry in the table.delete— Removes a route from the table.print— Displays a route or routes.
For example, to print all routes from the table, use:
route print 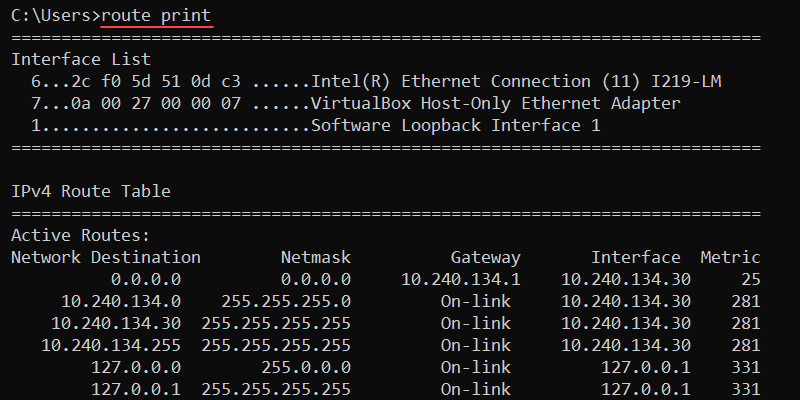
The output prints the interface list, and IPv4 and IPv6 routing tables.
53. schtasks Commands
The schtasks command helps schedule commands or programs to run on the system. The tasks run at specified times or periodically. The syntax for the commands is:
schtasks /<subcommand>The following subcommands are available:
change— Modifies existing properties of a task.create— Creates a new task.delete— Removes a task.end— Stops a program started by a task.query— Prints scheduled tasks on the machine.run— Starts a scheduled task.
For example, to show currently scheduled tasks on the system, use:
schtasks /query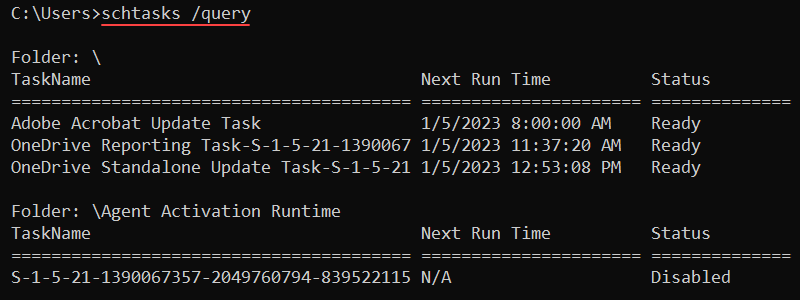
The output displays task names, next run times, and task statuses.
54. set Command
The set command shows, sets, and removes environment variables in the CMD. The syntax for the command is:
set <variable>=<value>Without additional parameters, the set command shows all environment variables.
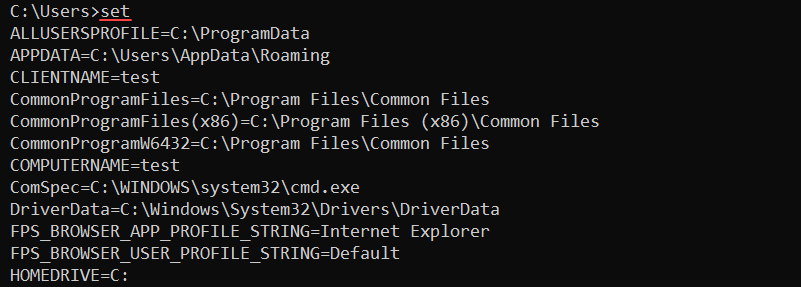
The variables are available to use with any command. For example, to create a new CMD variable called message, use:
set message="Hello, world!"Reference the variable using the following syntax:
echo %message%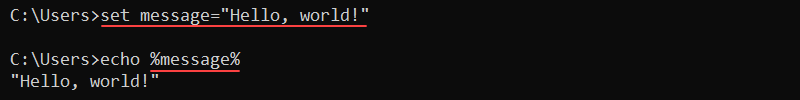
Encasing the variable in the percent signs (%) reads the value and outputs it to the screen.
Note: The variables do not persist and are only valid for the current command-prompt session.
55. sfc Command
The sfc (system file checker) is an administrator command for checking protected file version integrity. The command also replaces incorrect overwritten protected files with the correct file version.
The syntax for the command is:
sfc <options> <files or directories>For example, to scan the system and repair all files, use the following command:
sfc /scannow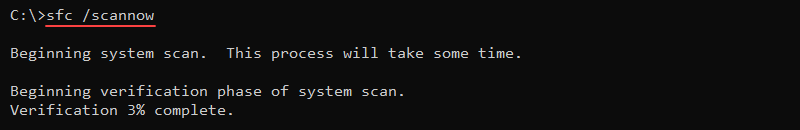
The command scans all protected system files and repairs problematic files when possible.
56. shutdown Command
The shutdown command restarts or shuts down a local or remote computer. The command syntax is:
shutdown <options>Without any arguments, the shutdown command opens the help menu.
For example, to shut down and restart the computer, use the /r option:
shutdown /r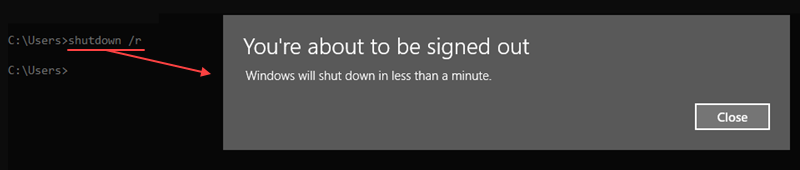
To shut down without restarting, use the /s argument:
shutdown /sIn both cases, the shutdown is not immediate. To cancel the action, use the /a option:
shutdown /aThe option ensures that a previously executed shutdown command aborts.
57. sort Command
The sort command allows sorting provided data from a file or user input. Additional options control the sorting mechanism and from which point to start sorting.
To use the command interactively, do the following:
1. Run sort without any options.
2. Enter a new word in each line.
3. Press CTRL+Z and Enter at the end of the list to sort the input values alphabetically.

Alternatively, use the sort command on files:
sort sample_file.txt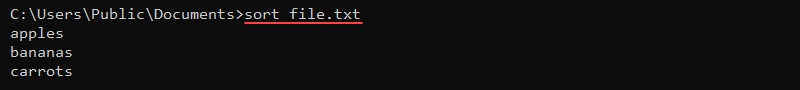
The command sorts the file contents and prints the result to the console.
58. start Command
The start command opens a new command-prompt window according to the specified options. The command syntax is:
start <title> <options>For example, to load start a new command-prompt session with the title «Hello, world!» and set the path to C:\. enter the following command:
start "Hello, world!" /d C:\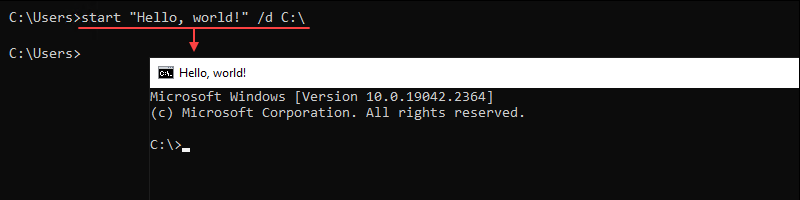
A new CMD window opens with the starting path on the C:\ drive and a custom title.
59. systeminfo Command
The systeminfo command displays detailed system information about the OS and computer, including hardware properties. The command works on both local and remote machines.
Use the command without options to show the local system information:
systeminfo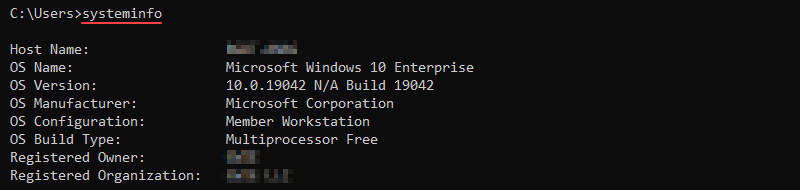
Additional options allow checking system information for remote computers or controlling the output format. For example, show the output in CSV format with:
systeminfo /fo csvDifferent formats enable parsing the information through scripts effectively.
60. takeown Command
The takeown (take ownership) command allows an administrator account to take ownership of a file. The command provides access to a file for an administrator and makes the administrator the owner.
Add the /f option and specify the file name:
takeown /f <file>
The administrator now has full permissions over the file.
61. taskkill Command
The taskkill command ends a running process or task on the Windows system through the command line. Use the command to forcefully end processes and tasks which did not end correctly.
The syntax for the command is:
taskkill <options> <task or process>A common way to end a task is to find the process ID (PID) with the tasklist command and end the process with:
taskkill /pid <Process ID>
The command finds the process by ID and kills it.
62. tasklist Command
The tasklist command shows all running processes on a local or remote computer and their memory usage. The command helps locate and reference specific processes.
The syntax for tasklist is:
tasklist <options>Without additional options, the command shows all currently running processes.
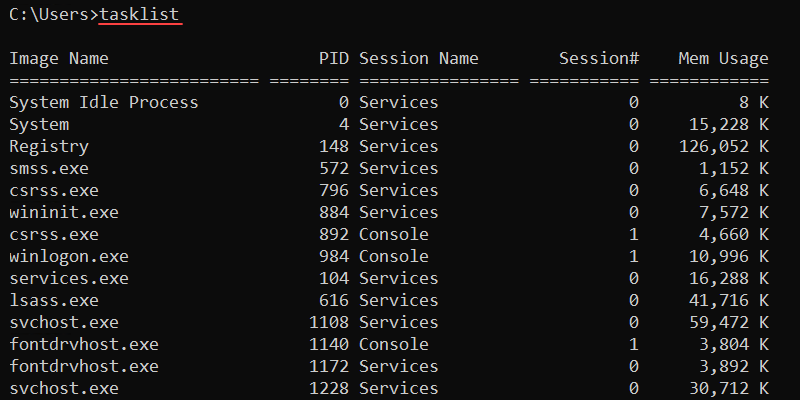
The image name and PID are unique identifiers for a process. The final column shows the memory usage for a process. This is a good indicator for identifying processes that slow down the system.
63. telnet Command
The telnet command is a Windows tool for bidirectional CLI communication. The tool uses the Telnet protocol to send messages and enable an interactive communication channel.
The syntax for the command is:
telnet <command> <options>See our detailed guide for using Telnet on Windows.
64. time Command
The time command manages and displays the current system time. Without any options, the command prints the current time and prompts to enter a new time:
time
Enter a new time to change the system time or exit the prompt using CTRL+C. Use the /t option to avoid making modifications:
time /t
The command prints the current time and returns to the command line.
65. timeout Command
The timeout command pauses the command line for a specified number of seconds. The syntax for the command is:
timeout /t <seconds>For example, to pause the interpreter for ten seconds, run:
timeout /t 10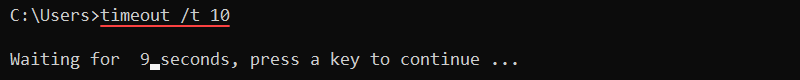
The output counts down and returns to the command line. Press any key to interrupt the timeout earlier. Use the command in scripts to wait for execution between two commands.
66. title Command
The title command is a simple utility for changing the command prompt’s title. The syntax is:
title <string>For example, to set the title to "Hello, world!", use:
title "Hello, world!"
The CMD window title changes to the provided string. Use the command when running multiple batch scripts to differentiate between different command prompts.
67. tracert Command
The tracert (traceroute) command is a networking tool for determining the path from a local computer to a destination. The command sends ICMP messages with increasing TTL values to map routers along the path.
The syntax for tracert is:
tracert <options> <destination>For example, to trace the path to phoenixnap.com, use:
tracert phoenixnap.comAlternatively, use the IP address of the destination.
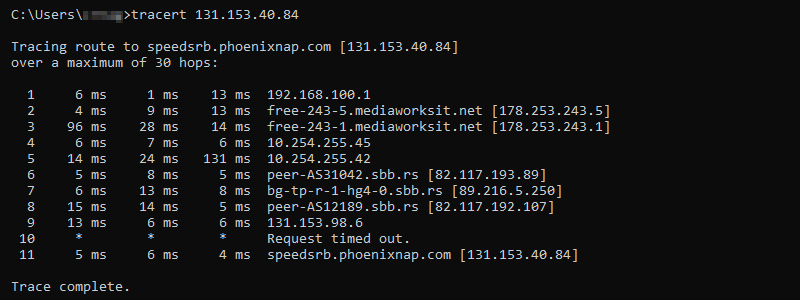
The output shows the hops between the source and destination, providing an IP address and name resolution where applicable. Use the command to discover connectivity issues to a host.
68. tree Command
The tree command displays the contents inside a drive or directory in a tree-like structure. The syntax is:
tree <options> <path>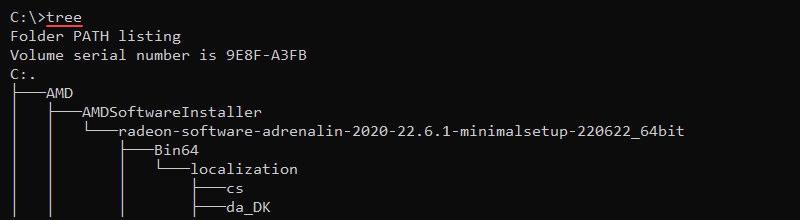
Without any options, the tree command displays the directory structure of the C:\ drive.
69. type Command
The type command is a built-in command for showing file contents. The command allows viewing a file directly in CMD without modifying the text.
The syntax for the type command is:
type <file path>For example, to show the contents of the file called sample_file.txt, run:
type sample_file.txt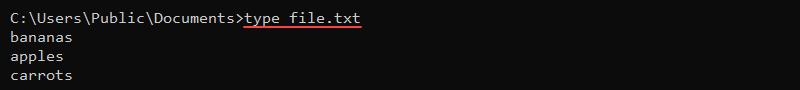
The output prints the file’s contents to the command line. Use this command to preview files directly in the command prompt.
70. tzutil Command
The tzutil (time zone utility) command helps modify and display the currently set time zone on the system. Without any options, the command shows the help window.
Display the current time zone with:
tzutil /g
The output shows the time zone ID. List all available time zone IDs with:
tzutil /l | moreThe more command helps truncate long outputs. Use the /s parameter and provide the time zone ID to change the system time zone.
71. ver Command
The ver command is a simple utility to show the operating system version. Use the command to find the exact version of the operating system:
ver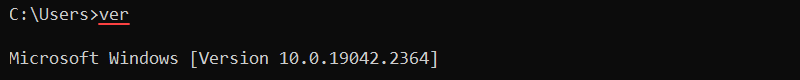
The version prints to the output and returns to the command line.
72. vol Command
The vol command prints the disk volume and label. The syntax for the command is:
vol <drive>:
Without a specified drive, the vol command shows information for the currently selected drive.
73. where Command
The where command searches for the location of a file using a search pattern and prints the location to the command line. The syntax for the command is:
where <options> <location to search> <file name>Omitting the location searches for the file in the current directory without going through subdirectories. To perform a recursive search, add the /r parameter. For example:
where /r C:\ sample_file.txt
The command searches the C:\ drive and all subdirectories. If the file is found, the command returns the location path.
74. whoami Command
The whoami command shows the current user’s domain and username. The syntax for the command is:
whoami <options>Without options, the command shows the domain and user name.

Add the /all parameter to show detailed information for the current user:
whoami /all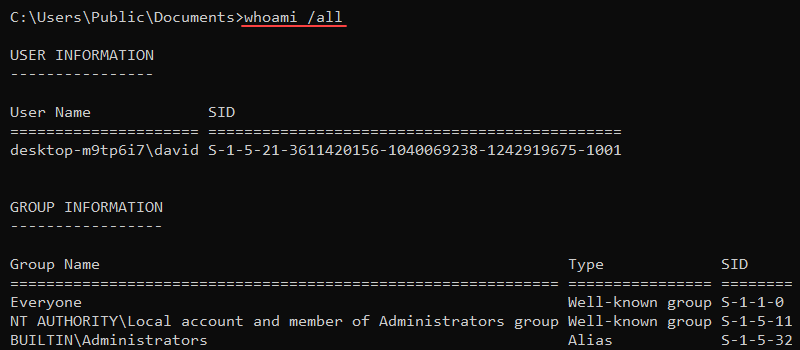
The user’s name, security ID, groups, and privileges print to the console.
75. xcopy Command
The xcopy command copies files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another. The syntax for the command is:
xcopy <source> <destination> <options>For example, use the following command to copy contents from one location to another, including subdirectories (even if empty):
xcopy <source> <destination> /s /e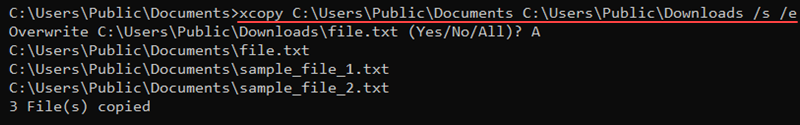
The /s parameter enables subdirectory copy, while /e includes empty directories. If any files with the same name exist in the destination, the command prompts before overwriting.
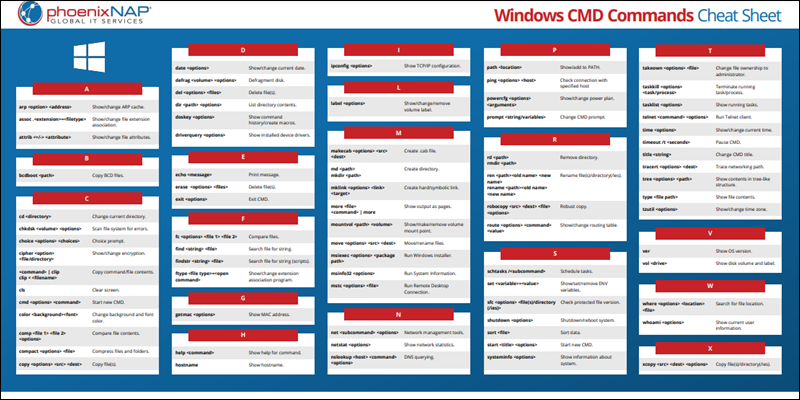
Windows CMD Commands Cheat Sheet
All the listed commands are available in a single-page cheat sheet in PDF format. Save the cheat sheet for future use and reference by clicking the Download Windows CMD Commands Cheat Sheet button below.
Conclusion
After reading and trying out the commands from this guide, you’ve familiarized yourself with the Windows Command Prompt (CMD) tool. Windows allows performing a variety of tasks through the command prompt using just commands.
Continue practicing and researching commands further to master the Command Prompt in Windows.
Бывает, что некоторые команды Windows cmd сложно вспомнить, и сохранение их на компьютере или на бумаге в качестве шпаргалки является хорошей практикой. Этот список не является полным, но он содержит наиболее часто используемые команды. Не стесняйтесь добавить свои наиболее часто используемые команды в комментариях ниже, а так же поделиться этим списком.
Управление файлами и папками
- COPY – Копирование файлов в другое место
- DIR – Отображение файлов и папок в текущем каталоге
- DEL или ERASE – Удаление файлов
- EDIT – Запуск редактора файлов
- CD – Изменить каталог
- EXPAND – Распаковать сжатые файлы
- FC – Сравнивает файлы и показывает различия между ними
- FIND – Найти текстовую строку в файле
- MD или MAKEDIR – Создать папку
- MOVE – Переместить файлы из одной папки в другую
- PRINT – отобразить содержимое текстового файла
- RD или RMDIR – удалить папку
- REN или RENAME – переименовать файл или папку
- REPLACE – Замена файлов в одном каталоге на файлы с тем же именем в другом каталоге
- ROBOCOPY – Использует программу «Робокопи» для копирования файлов и каталогов
- TREE – Показывает структуру каталогов диска или папки
- TYPE – Отображает содержимое текстовых файлов
- OPENFILES – Управление открытыми локальными или сетевыми файлами
- XCOPY – Копирование файлов и деревьев каталогов
Приложения и процессы
- SCHTASKS – Запланированный запуск приложения приложения (планировщик задач)
- SHUTDOWN – Выключение или перезагрузка компьютера
- TASKLIST – Список выполняемых задач
- TASKKILL – Остановить или прекратить выполнение задачи (для остановки задачи используется PID, который можно узнать из TASKLIST).
- REG – Запустить редактор реестра
- RUNAS – Запуск задачи от имени другого пользователя
Управление дисками
- CHKDISK – Проверяет диск и показывает статистику
- DEFRAG – Запуск дефрагментации диска
- CHKNTFS – Отображает или изменяет выполнение проверки диска при загрузке
- COMPACT – Отображает и изменяет сжатие файлов в разделах NTFS
- CONVERT – преобразование дискового тома FAT в NTFS
- DISKPART – Отображение и настройка свойств разделов диска
- FORMAT – Форматирование диска
- FSUTIL – Отображение и настройка свойств файловой системы
- LABEL – Создание, изменение или удаление метки тома диска
- RECOVER – Восстановление данных с поврежденного или испорченного диска
- VOL – Отображение метки тома и серийного номера диска
Системная информация
- DATE – Выводит или устанавливает текущую дату
- TIME – Выводит или устанавливает системное время
- DRIVERQUERY – Отображает текущее состояние и свойства драйвера устройства
- HOSTNAME – Отображает имя компьютера
- SYSTEMINFO – Отображает информацию о конфигурации компьютера
- VER – Позволяет просмотреть версию Windows
- GPRESULT – Отображает текущие примененные групповые политики (RSoP)
- GPUPDATE – Обновление групповых политик
Сеть
- IPCONFIG – Отображает информацию о сетевых интерфейсах
- PING – Отправляет ICMP-запросы на целевой хост, проверяет его доступность
- TRACERT – Отображение пути пакетов в сети
- NSLOOKUP – Поиск IP-адреса по имени ресурса
- ROUTE – Отображает таблицы сетевых маршрутов
- ARP – Показывает таблицу с IP-адресами, преобразованными в физические адреса
- NETSH – Запускает программу управления сетевыми настройками
- GETMAC – Показывает MAC-адрес сетевого адаптера
- TFTP – Запускает TFTP-клиент в консоли
Настройка командной строки
- CLS – Очистить экран
- CMD – Отображает другую командную строку
- COLOR – Устанавливает цвет текста и фона в консоли
- PROMPT – Изменение начального текста командной строки
- TITLE – Присвоение заголовка для текущего сеанса
- HELP – Запуск справки CMD
- EXIT – Выход из командной строки
Аverage rating : 4.9
Оценок: 12
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
191028
Санкт-Петербург
Литейный пр., д. 26, Лит. А
+7 (812) 403-06-99
700
300
ООО «ИТГЛОБАЛКОМ ЛАБС»
700
300
The Command Prompt, also known as CMD or Command Line Interface (CLI), is a powerful tool in the Windows operating system.
While modern graphical user interfaces have become the norm, the command prompt remains an essential tool for advanced users and system administrators.
You can efficiently perform various tasks, automate processes, troubleshoot issues, and unleash the full potential of your Windows machine, thanks to a deep understanding of CMD commands.
This article will introduce some of the most useful CMD commands. These commands cover network administration, device management, and file and data manipulation.
Table Of Content
- The cd Command
- The chkdsk Command
- The choice Command
- The cipher Command
- The color Command
- The comp Command
- The compact Command
- The copy Command
- The date Command
- The defrag Command
- The del and erase Commands
- The driverquery Command
- The fc Command
- The find Command
- The ftype Command
- The getmac Command
- The label Command
- The makecab Command
- The msinfo32 Command
- The nslookuo Command
- The path Command
- The powercfg Command
- The prompt Command
- The route Command
- The schtasks Command
- The tasklist Command
- The tree Command
- Conclusion
- FAQ’s
01. The cd Command
The current directory location can be seen or modified with the cd (change directory) command.
> cd <directory>
When used with a directory parameter, the command outputs the current working directory.
If you wish to switch to another directory, simply add the name of the directory as the parameter. For instance, to change the location to a directory named Users, you can use the following command:
cd User
As you can see, the prompt changes to reflect the successful execution of the cd command.
Switch to a Different Disk
The /d flag before the path allows you to move to a destination located on a different disk. For instance, to switch to disk G, use the following version of the cd command:
cd /d G:
You can also use the cd command to go back to the previous directory:
cd ..
02. The chkdsk Command
The main use of the chkdsk command is to scan the local file system and metadata for any potential errors.
chkdsk <volume> <options>
Note that If you use the chkdsk command without any parameters of flags, it will display the present state of the disk but doesn’t rectify any errors.
You can use additional settings, like the /f option, to fix disk errors.
chkdsk <volume> /f
As you saw, the command makes an effort to correct disk defects. If the disk is in use by another user, the command won’t run because it could potentially disrupt the process of saving data for that user.
If you chose “Y”, the command would run after the next system restart. On the other hand, the system remains unaffected if you enter “N”
03. The choice Command
This is an interesting command where you ask a user to choose from a list of predetermined choices.
Note that, if you don’t provide a list of choices, the system will simply generate two options – Y and N.
You can use the /c flag to use the command to show a list of choices. For instance, the following version displays three choices, “Y”, “N”, and “C”.
choice /c ync
You can add additional information with the /m flag. For instance, in the following example, you can see that we combined the /c and /m flags to offer more information about the choices displayed on the screen:
choice /c ync /m "Yes, No, Continue"
04. The cipher Command
The” command displays and changes a file or directory’s encryption.
> cipher <option> <file or directory>
When used without any parameters, the command displays the encryption status for all files and directories in the current location. As you can guess, U stands for “unencrypted,” whereas ‘E’ stands for “encrypted.”
Next, you can use the /e option can be used to encrypt a file in the current directory:
cipher /e <File Name>
As you can see, the command encrypted the file. This can be further verified by running the command without any parameter.
The E indicates that the file has been encrypted.
05. The color Command
The color command modifies the text and background colors in the terminal.
color <background><text>
The color choices are based on hexadecimal values between 0 and f. You can run the help command to get the full list of color choices.
help color
For instance, use the following command to make the background purple (5) and the typeface light green (a).
color 5a
Run the “color” command without any parameters to go back to the console’s default colors.
06. The comp Command
The comp (short for compare) command is used to compare the contents of two files. When two files vary, the command indicates that the contents are different.
comp <file 1> <file 2> <options>
The comp command also provides an interactive prompt to enter file names and extra options when used without any arguments.
The following screenshot shows the output when the comp command iss used to compare two files – f1.txt and f2.txt.
07. The compact Command
The compact command launches a built-in utility for compressing (and decompressing) files and directories.
compact <options> <file>
When used without any additional parameters, the command reports the current directory’s compression status.
If you wish to compress a file, use the /c flag and the file name:
compact /c User_testfile1.txt
In contrast, you can use the /u argument to uncompress a file.
The compact command is a really simple way of compressing big files and directories to conserve disk space.
08. The copy Command
The copy command is used to copy one or more files from one location to another. The syntax of the command is:
copy <options> <source> <destination>
For example, try the following to duplicate the content of one file into another at the same location:
copy User_testfile1.txt User_testfile1_copy.txt
The command transfers all the contents from the source file into the new one.
09. The date Command
The date command displays and changes the system’s current date.
When used without any parameters, the command prints the current date and asks if you wish to set a new date:
date
To change the system’s current date, enter the date in the format mm-dd-yyyy, or press CTRL+C to quit.
To print simply the current date without changing the system state, use the /t parameter:
> date /t
10. The defrag Command
Did you know that files are stored as fragments on the disk?
The defrag command consolidates file fragments and “defrags” the disk. As a result, you’ll see a marked improvement in the system’s performance.
defrag <volumes> <options>
You can use the following version of the command to defrag the disk and optimize the disk storage structure.
defrag C:\ /d /g
11. The del and erase Commands
The del and erase commands have similar operations, in that they remove files permanently from the disk. We recommend you should study the technical differences between deleting and erasing data from disk.
del <options> <file(s)>
erase <options> <files(s)>
12. The driverquery Command
Administrators often need to view the details of the installed device drivers and related information.
For this, you can use the driverquery command. This command works for both local and remote systems.
driverquery <options>
As you can see, when you use driverquery command without any parameters, it displays device driver information for the local computer. You can use additional parameters to format the output or run the command on a remote machine.
13. The fc Command
If you need to compare two or more files, you can use the fc (file compare) command. If there is a discrepancy between the files, the output prints the contents to the console.
fc <options> <file 1> <file 2>
<
14. The find Command
You may use the “find” command to look for a specified string in a file and get the relevant line of text. When a match is discovered, the result is output.
find <string> <file>
The command searches for an exact match before returning the file name and the text line containing the string. If the command can’t find the text in the file, it simply returns the filename.
15. The ftype Command
This command displays and modifies the file type and extension association..
ftype <file type>=<open command>
As you can see, the command displays the programs associated with each file so that you know which file extension is set to open with which software.
If you wish to find out the current file extension and type association for a specific file type, simply add it as the parameter to the command. For instance, to find the software associated with text files, use the following command:
ftype txtfile
16. The getmac Command
The getmac command retrieves all network cards’ MAC addresses from the computer or network. The command further displays the protocols related to each address
getmac <options>
The command offers several options that let you format the output or get comprehensive information about a remote computer. For instance, use the following command to get the MAC addresses in a CSV file:
getmac /fo csv
17. The label Command
The label command displays, modifies, or deletes a disk’s volume label (also known as the disk name). Note that because of the impact of this command, you need administrator privileges.
The label command launches a prompt to alter the name and, in the absence of any parameters, displays the label for the current drive:
The command prompts you to enter a new name to replace the existing label name (or press Enter to delete the label). Press Y to accept the change, or N to maintain the current name.
18. The makecab Command
As the name suggests, this command creates a cabinet (.cab) file. These Windows-only files are an archive format that supports lossless data compression and archive integrity.
makecab <options> <source> <destination>
19. The msinfo32 Command
The msinfo32 command launches the System Information window that shows essential information about the system.
msinfo32
20. The nslookup Command
The nslookup is a simple tool for diagnosing the issues in DNS infrastructure. The command offers both a non-interactive and an interactive mode.
nslookup <host> <command> <options>
When you launch the command without any parameters, nslookup enters interactive mode. As you can see in the following screenshot, the command shows DNS records for a domain name.
21. The path Command
You can view the contents of the PATH environment variables with this command. This is usually a list of folders pointing to executable files.
Use a semicolon (;) to divide each location into its own PATH entry, like in the example below:
path <location 1>; <location 2>
22. The powercfg Command
This command launches the powercfg.exe program to manage the system’s power plans. The monitoring tool highlights the issues with a device’s battery life and energy efficiency.
powercfg <options> <arguments>
For instance, use the command with the /list parameter to get the details of the active power plan.
> powercfg /list
In the above screenshot, you can see that the star (*) indicates the active power plan.
The prompt command can switch the CMD prompt display with the supplied string. Note that the default prompt is the current directory location followed by the greater-than symbol (>).
prompt <string and variables>
The prompt command provides a number of options for adding unique characters or other functionality to the prompt. For instance, use the following command to transform the prompt into an arrow.
prompt --$g
The change to the prompt will persist throughout the command-line session. To restore the default prompt, simply enter the command without any parameters.
24. The route Command
The local routing table entries are shown and modified using the route command.
route <options> <command> <value>
> route print
25. The schtasks command
The schtasks command facilitates scheduling system-wide operations for commands or programs. The duties are carried out frequently or at set intervals.
schtasks /query
26. The tasklist Command
The tasklist command displays all active processes and their memory utilization on a local or remote machine. The command is a great option for finding more information about the processes.
tasklist <options>
Without any parameters, this command outputs a list of all active processes on the local machine.
27. The tree Command
The tree command shows a tree-like representation of the contents of a disk or directory.
> tree <options> <path>
Conclusion
Whether you are a system administrator, a power user, or simply an individual seeking deeper Windows knowledge, mastering the Command Prompt is an indispensable skill for Windows users. It provides unparalleled control, efficiency, and automation capabilities. You can easily navigate directories, manage files, troubleshoot network issues, and perform various administrative tasks.
You can automate repetitive actions by harnessing the power to batch processing and scripting.
FAQ’s
Q. What does Windows Command Prompt do?
A. Users can communicate with the operating system via text-based commands using the Command Prompt, sometimes called CMD. It offers an easy way to launch programs and carry out different operations without relying on a graphical user interface.
Q. How do I open the Command Prompt?
A. To open the Command Prompt in Windows, you can follow these steps:
Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
Type “cmd” or “cmd.exe” and press Enter.
Alternatively, you can search for “Command Prompt” in the Start menu and click the result.
Q. What are some essential CMD commands every user should know?
A. There are several CMD commands that are very handy for everyday tasks. They include:
1. cd: Change directory.
2. dir: List files and folders in the current directory.
3. mkdir: Create a new directory.
4. copy: Copy files from one location to another.
5. del: Delete files.
6. ipconfig: Display IP configuration information.
7. ping: Send a network request to a specific IP address or domain.
8. tasklist: List all running processes.
9. shutdown: Shut down or restart the computer.
A. If you need assistance with a specific CMD command, you can use the built-in help feature. Simply type the command followed by “/?” and press Enter. This will display detailed information about the command, including its syntax and available options.
Q. Can I customize the appearance of the Command Prompt?
A. Yes, you can customize the appearance of the Command Prompt to suit your preferences. Right-click on the title bar of the Command Prompt window and select “Properties.” You can modify settings such as the font, colors, and window size from there.
Q. Are there any advanced CMD commands for power users?
A. There are advanced CMD commands that offer additional functionality for power users and system
administrators. Some examples include:
diskpart: Manage disks, partitions, and volumes.
sfc: Scan and repair system files.
regedit: Access and modify the Windows Registry.
netstat: Display active network connections and listening ports.
robocopy: Advanced file and directory copying.
powercfg: Configure power settings and check power usage.
When working on the Windows command line, do you remember how often you kept looking for the same commands? Do you easily mistype in the Windows command prompt as if you were using bash commands, such as “rm” instead of “del”? If you’ve ever been in the situations above, this Windows command line cheat sheet is for you.
The Windows command line is only as powerful as the commands at your disposal, which we’ll expand on in this Windows command prompt cheat sheet. It covers every command you need for important tasks and batch scripting, plus a few delightful surprises if you make it to the end.
Keep a copy of this Windows command line cheat sheet on your desk, in your pocket, or wherever you go. When you’re ready, let’s dive in.
Windows Command Line Cheat Sheet Search
Search our Windows command line cheat sheet to find the right cheat for the term you’re looking for. Simply enter the term in the search bar and you’ll receive the matching cheats available.
What Is the Windows Command Line?
The Windows command line (Windows command prompt) is the command-line interface (CLI) on Microsoft Windows machines, analogous to the Terminal in Unix/Linux. It emulates many command-line abilities in Microsoft’s deprecated text-only operating system MS-DOS (but it’s not MS-DOS).
Methods to open the Windows CLI:
- On Windows 10 or above, click Start on the bottom left corner, type cmd, and select Command Prompt.
- On Windows 8.x or earlier, press Ctrl+R to open the Run dialog box, type cmd into it, and press Enter.
Hence, another name for Windows CLI is “cmd.”
Scripts containing Windows commands (batch scripts) have “.bat” as the file extension. All cmd commands are case-insensitive, so arp and ARP are the same. If you need help using any command, add /? to it, e.g., ARP /? will show the manual for ARP:
Table Of Contents
- Windows Command Line Cheat Sheet Search
- Directory Navigation
- File Management
- Disk Management
- Windows Command Generator
- System Information and Networking
- Process Management
- Batch Scripting
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Directory Navigation
These commands help you view directories and move directories around.
| Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
c: |
Change the current drive to the C:\ drive |
d: |
Change the current drive to the D:\ drive |
CD c:\path\to\my_folder |
Change directory to c:\path\to\my_folder |
CD .. |
Navigate to the parent directory of the current working directory |
CD .\new_folder |
Navigate to the folder new_folder located in the current working directory |
CD /D d:\videos\ |
Change the current drive to D:\ and access the folder videos on it. |
DIR |
Display files and folders in the current directory |
DIR /A c:\apps\ |
Display files and folders in the directory c:\apps\ |
DIR /A:D |
Display only folders (D: directories) |
DIR /A:-D |
Display only files (D: directories; -: not) |
DIR /A:H |
Display hidden files and folders |
DIR /O |
Display files and folders sorted alphabetically |
DIR /O:S |
Display files and folders sorted by file size from smallest to largest |
DIR /O:-S |
Display files and folders sorted by file size from largest to smallest |
DIR /B |
Display only the names of files and folders in the current working directory |
SORT |
Take input from a source file/pipeline, sort its contents alphabetically (default: A to Z; in reverse: Z to A), and display the output |
SORT "C:\music\playlist.m3u" |
Sort the contents of C:\music\playlist.m3u line by line |
DIR /B | SORT /R /O ZtoA.txt |
List all file and folder names in the current working directory, sort them in reverse alphabetical order, and save the sorted output to a file ZtoA.txt: |
MOVE |
Move a file or files |
MOVE c:\f1\text.txt c:\f2 |
Move a file text.txt from one folder c:\f1 to another folder c:\f2 |
MD new_folderMAKEDIR new_folder |
Create a new folder called new_folder in the current directory |
RD new_folderRMDIR new_folder |
Delete the folder called new_folder in the current directory |
TREE |
Show the directory structure of a disk/folder |
TREE "C:\Program Files" |
Show the directory structure of the folder “Program Files” on the disk C:\ |
TREE C:\ /F |
Display the names of the files in each folder in the directory structure of the C:\ drive |
ATTRIB |
Display/set the attributes of the files in the current directory |
ATTRIB +H +S +R myItem |
Hide a file/folder myItem |
ATTRIB -H -S -R myItem |
Unhide a file/folder myItem |
File Management
The following commands are for managing and manipulating files.
Like Unix, cmd supports pipelines: you may pass the output of a command to the next one by sandwiching the pipe character “|” between both.
| Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
COPY text.txt C:\schoolwork |
Copy the file text.txt to a folder with the path C:\schoolwork |
DEL text.txtERASE text.txt |
Delete the file text.txt |
REN text.txt script.batRENAME text.txt script.bat |
Rename a file text.txt to script.bat |
REPLACE .\src\hey.txt .\dest |
Overwrite; replace a file named hey.txt in a local folder src with another hey.txt in a local folder dest, both files sharing the same name.Warning: Don’t specify .\dest\hey.txt anywhere here. |
XCOPY |
Copy files and directory trees to another folder. XCOPY is similar to COPY but with additional switches to specify the source and destination paths in detail. |
XCOPY /S folder1 folder2 |
Copy folders and subfolders of folder1 to folder2 |
ROBOCOPY |
Robust copying of files and directories: by default, such copying only occurs if the source and destination differ in time stamps or file sizes. |
EXPAND gameData.cab |
Decompresses the compressed .CAB cabinet file gameData.cab |
FC file1.ext file2.ext |
Compare the contents of two files (file1.ext, file2.ext) and display non-matching lines |
COMP file1.ext file2.ext |
Compare the contents of two files (file1.ext, file2.ext) and display non-matching items |
FIND "python" in run.bat |
Output every line that contains a text string (which you must enclose in quotation marks) «python» in the file run.bat |
FIND /C "python" in run.bat |
Count every line that contains a text string (which you must enclose in quotation marks) «python» in the file run.bat |
PRINT resume.txt |
Print contents of a file resume.txt |
OPENFILES /QUERY |
Query/display open files |
OPENFILES /DISCONNECT |
Disconnect files opened by network users. |
TYPE test.txt |
Displays the contents of the file test.txt |
TYPE playlist.m3u | SORT /unique /o C:\work\unique_play.m3u |
Sort a file playlist.m3u and output only the unique values to a file C:\work\unique_play.m3u |
MORE |
Display contents of one or more files, one screen at a time. |
ASSOC |
Display or change the association between a file extension and a file type |
NOTEPAD |
Open the Notepad application from cmd |
NOTEPAD filename.ext |
Open a file filename.ext in Notepad |
Disk Management
It’s easy to handle and automate the following tasks on cmd.
| Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
CHKDSK |
Check and repair disk problems (local disks only) |
CHKDSK /F A: |
Fix errors on A: drive |
CHKDSK /R A: |
Recover data on A: drive |
CHKDSK /X A: |
Dismount drive A: |
CIPHER /E classified |
Encrypt the folder classified |
CIPHER /D secret_recipe.txt |
Decrypt the file secret_recipe.txt |
DEFRAG |
Disk Defragmentation |
CHKNTFS |
Display/modify disk-checking on startup |
COMPACT |
Display/change the compression of files in NTFS partitions |
CONVERT |
Convert FAT disk volume to NTFS |
DISKPART |
Display and adjust disk partition properties |
FORMAT |
Format the disk |
FSUTIL |
File system management |
LABEL d:x |
Rename disk D:\ to X:\ |
SUBST p: c:\taxes |
Assign drive P:\ to the local folder c:\taxes |
SUBST p: /D |
Remove the path represented by P:\ |
RECOVER d:\data.dat |
Recover a file data.dat from a bad or defective disk D:\ |
VOL |
Display current disk volume label and serial number |
POWERCFG |
Control power settings and configure Hibernate/Standby modes |
SFC /SCANNOW |
Scan and update protected system files |
Windows Command Generator
Say goodbye to the hassle of trying to remember the exact syntax for the Windows command line! With our Windows Command Generator, you can simply say what you need Windows to do, and we will generate the command for you.
System Information and Networking
The following commands are helpful in troubleshooting computers and computer networks.
| Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
VER |
Display the current operating system version |
SYSTEMINFO |
List system configuration |
HOSTNAME |
Show the computer’s hostname on the network |
DRIVERQUERY |
Show all installed device drivers |
DATE |
Display/set system date |
TIME |
Display/set system time |
GPRESULT |
Display Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) information for a remote user and computer. |
GPUPDATE |
Update group policies |
IPCONFIG |
Display Windows IP network configurations |
IPCONFIG /release |
Release your current local IP address |
IPCONFIG /renew |
Request a new local IP address |
IPCONFIG /flushdns |
Reset the contents of the DNS client resolver cache |
PING google.com |
Send ICMP requests to the target google.com and check host availability |
PATHPING |
Trace route and provide network latency and packet loss for each router and link in the path |
NET |
Provide various network services |
NET use M: \\gameServ /user:"ReadyPlayerOne" player1 |
Assign as disk M:\ the path \\gameServ, logging in as “ReadyPlayerOne” and password “player1” |
TRACERT |
Find the IP address of any remote host |
NSLOOKUP |
Find IP addresses on a nameserver |
ROUTE |
Manipulate network routing tables |
ROUTE PRINT |
Displays network route details |
ARP -A |
List IP addresses and corresponding physical addresses (Address Resolution Protocol) |
NETSH |
Configure network interfaces, Windows firewall, routing, and remote access |
NETSTAT |
Display current TCP/IP network connections and protocol statistics |
GETMAC |
Shows all MAC addresses of the network adapters |
Process Management
The commands below are Task Manager-like functions. Note that you call variables in arithmetic or logical expressions by enclosing each with two “%” signs (e.g., “%a%”).
| Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
SCHTASKS |
Create/edit a job on Task Scheduler. Use this to create scheduled tasks in Disk Management. |
SET |
List environment variables |
PATH |
Display/change the list of folders stored in the %PATH% environment variable |
SHUTDOWN /R |
Restart the computer |
SHUTDOWN /S /T 60 |
Shut down the computer 60 seconds from now |
TASKLIST |
List running tasks |
TASKLIST /SVC |
Show services related to each task |
TASKLIST /V |
Display detailed task information |
TASKLIST | FIND "1234" |
Get the name of the executable associated with the process ID (PID) of 1234 |
TASKKILL |
End one or more tasks |
TASKKILL /IM "msedge.exe" |
Terminate all Microsoft Edge instances: |
TASKKILL /PID 10736 |
Terminate process with PID of 10736 |
REGREGEDIT |
Registry Editor |
RUNAS /USER:user2 program1 |
Execute a program program1 as another user user2 |
POWERSHELL |
Open a Powershell instance |
Batch Scripting
These commands are for constructing and debugging batch scripts (.bat). To suppress the output of a certain command, add @ in front of it, e.g., @echo off.
| Command | Explanation |
|---|---|
REM comment. . .:comment. . . |
Prefix for the single-line comment “comment. . .” |
GOTO end<comment_block>:end |
Format of multi-line comments represented by <comment_block> enclosed by delimiters end and :end |
SET /A c = %a% + %b% |
Assign the arithmetic expression a+b to the variable c |
^ |
Escape character |
some_command > output.txt |
Redirect output of some_command to a file output.txt |
? |
Wildcard representing one character |
* |
Wildcard representing multiple characters |
& |
Introduce a new command on the same line |
TIMEOUT 3600 |
Tell the command prompt to sleep for 3600 seconds (= 1 hour) |
PAUSE |
Prompt the user to continue |
CHOICE |
Prompt the user to pick an on-screen option |
CHOICE /T 15 /C ync /CS /D y /M "Press y=Yes, n=No, c=cancel:" |
You have 15 seconds to press Y, N, or C keys without capitalization, defaulting to “y” if time runs out without a decision |
CLS |
Clear screen |
CMD |
Restarts Windows command prompt window: |
COLOR |
Set text and background color of cmd: |
ECHO ON |
Display each command executed |
ECHO OFF |
Only display command output |
ECHO a string of characters |
Display a string of characters |
HELP |
Display help |
PROMPT topSecret^>$$ |
Changes the command line prompt to topSecret>$ for the current session |
PROMPT |
Reset the command line prompt to default |
START X |
Start/open a program/document X in a new window |
TITLE top Secret |
Set the title of the current session of Windows command prompt to top Secret |
/? |
Add this to the end of any command word (shown in ALL CAPS in this cheat sheet) to get help on the command, e.g., CD/? = manual for CD (change directory) command |
| CLIP |
Append this to the end of a command to copy the command output to the clipboard |
EXIT |
Exits the command line |
Flow Control
Note the condition is a Boolean expression e.g., %a%==5.
| Conditional | Syntax |
|---|---|
| If | IF (condition) do_something |
| If-else | If (condition) (do_something)ELSE (do_something_else) |
| Nested if | IF (condition1) IF (condition2) do_something |
| Infinite loop | :markerdo_somethingGOTO marker |
| While loop | :markerIF (condition) ( do_something GOTO :marker) |
Shortcut keys
Any Windows CLI cheat sheet must include methods to speed up your work, such as the following.
| Key | Effect |
|---|---|
| Tab | Autocomplete |
| Ctrl+F | Find text in console (opens dialog box) |
| F1, F3, F5, F8 | Retype command |
| F2 | Copy the current command leftward of the cursor |
| F4 | Delete the current command rightward of the cursor |
| F6 | Insert end-of-file character |
| F7 | List previous commands from which you choose |
| F9 | Retype a command by typing its line number in the command history |
Conclusion
We sincerely hope this Windows cmd commands cheat sheet helps you finish your work quickly and efficiently today, especially if you’re prone to confusing Windows command prompt commands with other terminal scripting languages in the past.
Remember to check out our course offerings on Windows.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use the command line for coding?
Like bash, sh, and zsh, the Windows command line is a shell scripting language suited for automating line-by-line execution of programs callable from a command line interface. It’s not suitable as a programming language because it lacks data structures found in general-purpose programming languages such as Python (interpretive) and C++ (compiled).
What are the basic CLI commands?
They’re DIR, CD, CP, DEL, MOVE, REN, MKDIR, RMDIR, CLS, HELP, EXIT, and NOTEPAD. With these commands, a beginner can operate the Windows command prompt and manage most files and folders.
Is learning the command line useful?
Yes. Learning how to use it will allow you to discover your computer’s latent superpowers. You can automate tasks when combined with Run > shell:startup or Task Scheduler (both on Windows). The command line will help you manage and manipulate files and folders more quickly than comparable actions (e.g., drag and drop) on the graphical user interface.
Can CMD run Python?
If the machine has Python installed, then yes. Python isn’t native to Windows. Note that the command to run Python could be one of the following: python, py -2 (for Python 2); python3, py -3 (for Python 3).
Level Up in Cyber Security: Join Our Membership Today!
-
Cassandra is a writer, artist, musician, and technologist who makes connections across disciplines: cyber security, writing/journalism, art/design, music, mathematics, technology, education, psychology, and more. She’s been a vocal advocate for girls and women in STEM since the 2010s, having written for Huffington Post, International Mathematical Olympiad 2016, and Ada Lovelace Day, and she’s honored to join StationX. You can find Cassandra on LinkedIn and Linktree.
View all posts
