on August 5, 2015
Deleting files is one of the frequently done operation from Windows command prompt. This post explains how to use ‘del’ command from CMD for different use cases like deleting a single file, deleting files in bulk using wild cards etc. Before we start to look at the syntax, note that the command works only for files and can’t handle folders.
How to delete a file
Run del command with the name of the file to be deleted, you are done!
del filename
You do not see message after running the command if the file is deleted successfully. Error message is shown only when something goes wrong.
Delete files in bulk
Del command recognizes wildcard(*) and so can be used to delete files in bulk from CMD. Some examples below.
To delete all the files in current folder
del *
To delete all the files with ‘log’ extension
del *.log
Delete all files having the prefix ‘abc’
del abc*
Delete all files having ‘PIC’ somewhere in the file name.
del *PIC*
The above are the basic use cases of del command. Continue to read below for non trivial use cases.
Delete multiple files
‘Del’ command can accept multiple files as argument
del filename1 filename2 filename3 filename4....
Example:
D:\>dir /s /b 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\>del 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\> D:\>dir /s /b D:\>
Delete Read only files
We can’t delete a read-only file using simple‘del’ command. We get access denied error in this scenario.
c:\>attrib readonlyfile.txt A R C:\readonlyfile.txt c:\>del readonlyfile.txt c:\readonlyfile.txt Access is denied. c:\>
A read-only file can be deleted by adding /F flag.
del /F readonlyfile.txt
Alternatively, we can use the below command too
del /A:R readonlyfile.txt
Windows Command Prompt Overview
What is Command Prompt? It is a command-line interpreter application also known as cmd.exe or cmd. It can only be used in Windows operating system, and it is a gorgeous tool that can help you do a lot of advanced operations and solve some Windows issues.
Command Prompt is functional, you can deal with USB virus remove with cmd or activate Windows using cmd, and you can use it to delete files and folders very fast with the del command and rmdir command, especially if you have several items to erase. We will teach you how to use cmd delete files with a detailed tutorial.
First, you can check a video to help understand how to use Command Prompt to delete files, and we have listed the essential moments:
- 00:15 How to open Command Prompt
- 00:27 Use the del command to delete files
- 01:56 Use the del command to delete folders
How to Use CMD Delete File Step by Step
First, you need to know that using cmd to delete files is not like putting files and folders into Windows Recycle Bin. You can recover files from Recycle Bin folder directly, but it is not easy to recover cmd deleted files without third-party recovery software. So be careful when you are deleting files with cmd. Make sure you delete the files you don’t want anymore. Now let us learn how to open cmd first.
How to Open Command Prompt on Windows 11/10
We will teach you the easiest way to open the Command Prompt on Windows.
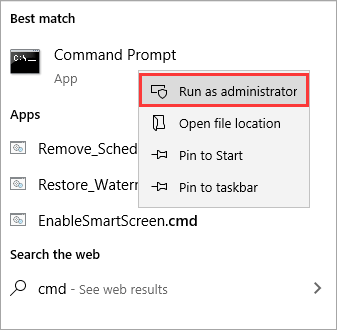
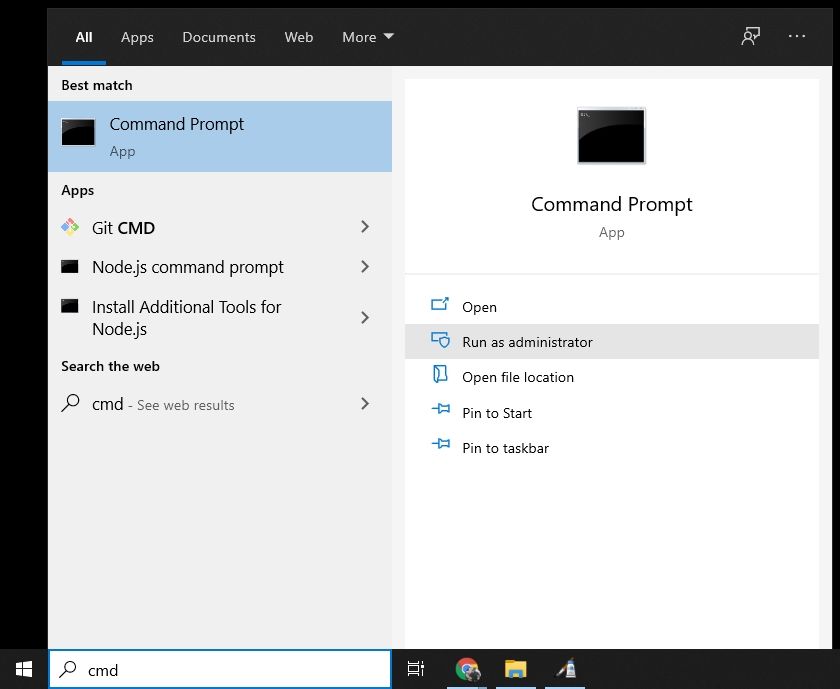
Step 1. Click «Start», and you’ll see the search box.
Step 2. Type in cmd.
Step 3. Right-click cmd and select «Run as Administrator».
Step 4. Now you can use Command Prompt to delete files.
How to Use CMD Delete File with del
Once you have learned how to open the Command Prompt, you can type in command lines. Follow the tutorial and type in the correct command lines to delete files.
Step 1. Type in del with a space after it.
Step 2. Then type the path for each file you want to delete, and remember to add spaces to separate each file name.
Step 3. Make sure you type in the right path and press the Enter key.
How to Use CMD Delete Folders with rmdir
You will need a different command to delete folders with cmd on your computer. Keep reading and follow the operations:
Step 1. Type in rmdir with a space after it.
Step 2. Then type the path for each folder you want to delete.
Step 3. Make sure you type in the right path and press the Enter key.
Recover Deleted Files/Folders from CMD with the File Recovery Tool
It is possible that you accidentally delete key files and folders, and you don’t know how to recover permanently deleted files. You can easily return these essential items with EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard.
No matter it is you delete file with PowerShell or with Command Prompt, EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard can help you recover deleted files easily. This professional recovery tool also can be handy for home users.
You don’t have to worry about how to recover deleted videos, photos, music, emails, and documents. EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard can ensure you don’t bother with data loss anymore.
It is also a handy tool, and you can recover deleted files and folders in three steps.
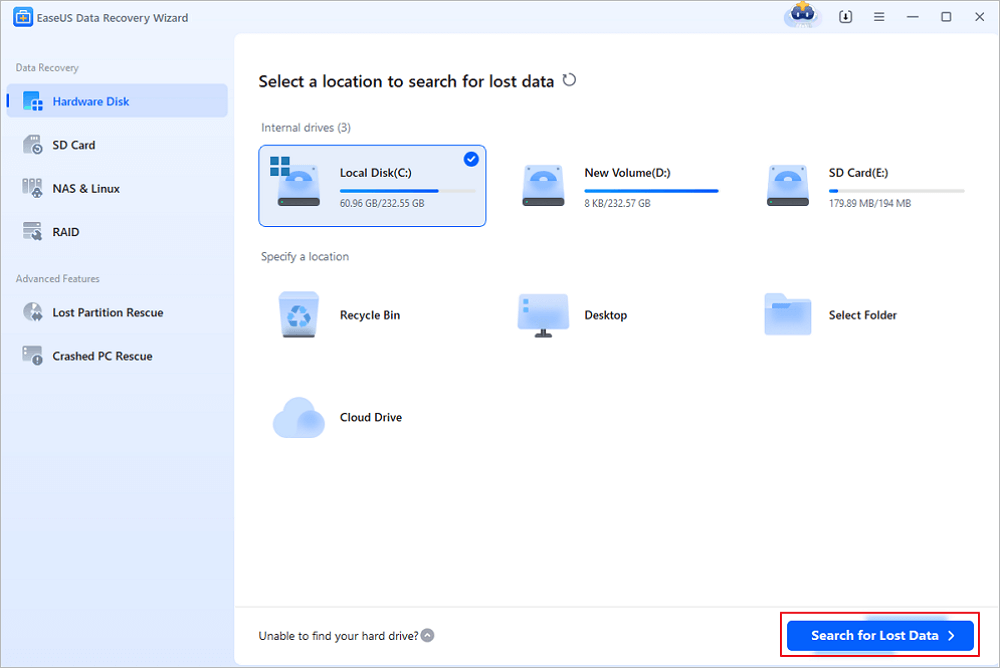
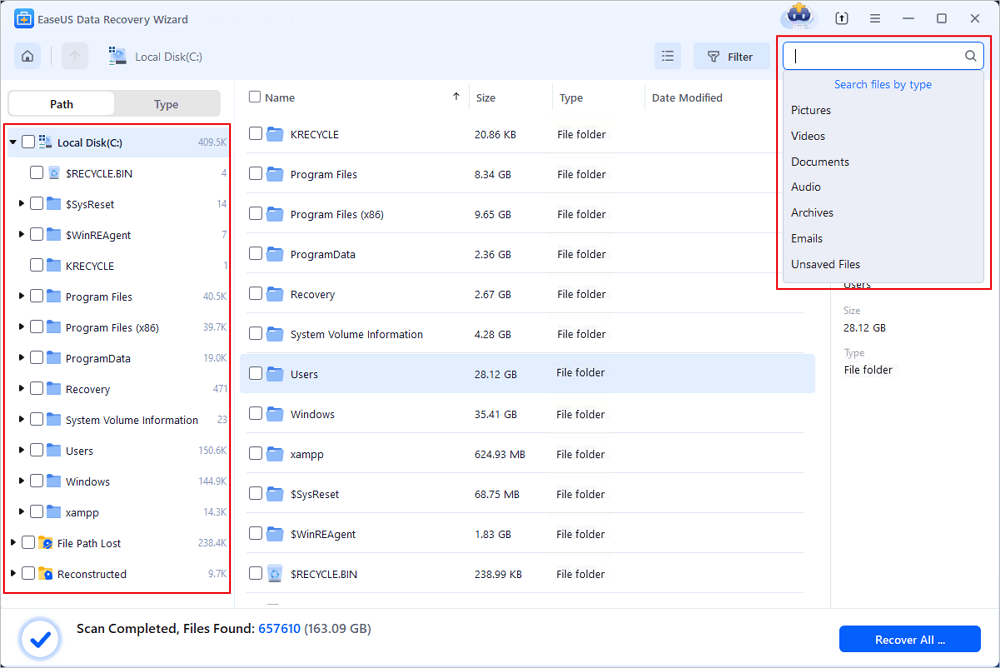
Step 1. Run EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard. Choose the drive where you lost files and start scanning. This software allows you to recover lost data from all devices, including HDD, SSD, USB drive, SD card, pen drive, camera, etc.
Step 2. Browse the full scan results. You can choose the file type you need by clicking on the file type filter. EaseUS data recovery software supports 1000+ file types like photos, videos, documents, emails, audio files, and many more.
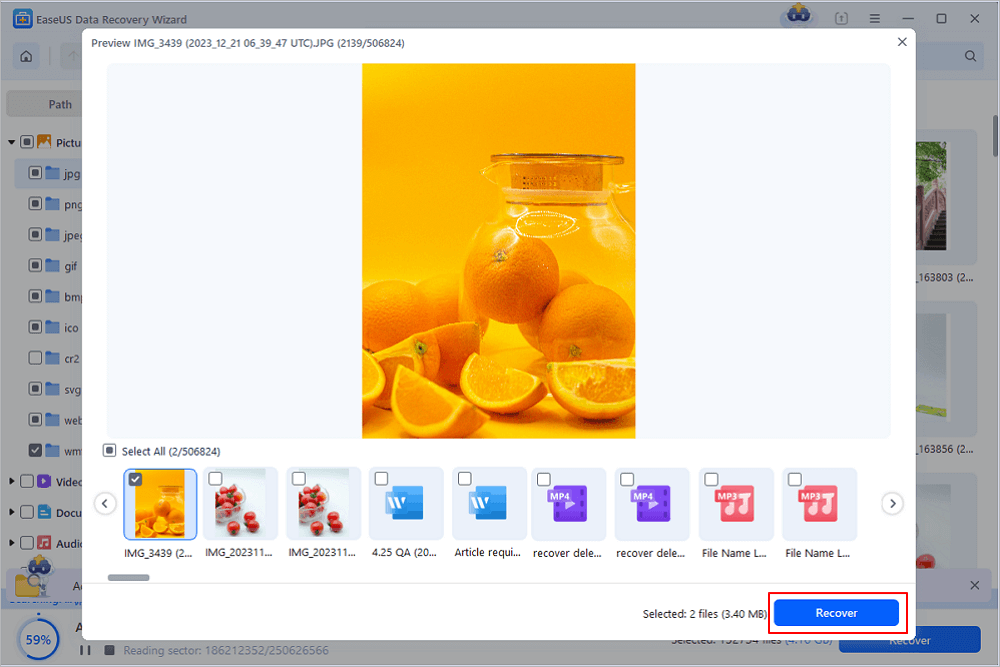
Step 3. Select the files you want to preview. Click «Recover» and set a storage location to save the recovered data.
Summary
Except for deleting files with Command Prompt, there are many other things cmd can do on Windows. For example, if you can’t find the file and find it is hidden. It is possible to show hidden files using cmd.
When you are using the computer or laptop, if you want to get back deleted videos, photos, or files, download EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard immediately, and you can find your lost files in one click.
Command Prompt Delete File FAQs
We have listed some further questions and answers here:
What is delete command in cmd?
You will need the del command and rmdir command to delete files and folders with Command Prompt. And the del command is the most common command to erase one or multiple files.
How do I delete corrupted files in cmd?
When you find you can’t commonly delete corrupted files, you can try deleting files with cmd.
- 1. Click «Start», and you’ll see the search box.
- 2. Type in cmd.
- 3. Right-click cmd and select «Run as Administrator».
- 4. Type the following command Del /F /Q /A, and add the path of corrupted files.
- 4. Press the Enter key.
How do I delete multiple files in command prompt?
You can delete a single file and multiple files with the del command.
- 1. Type in del with a space after it.
- 2. Then type the path for each file you want to delete, and remember to add spaces to separate each file name.
- 3. Make sure you type in the right path and press the Enter key.
How delete all files and folders using cmd?
You can use cmd to delete all the files and folders using del and the /S flag ( to tell cmd to remove all files from all subdirectories).
Sometimes it’s just faster to do things with the command line.
In this quick tutorial we’ll go over how to open Command Prompt, some basic commands and flags, and how to delete files and folders in Command Prompt.
If you’re already familiar with basic DOS commands, feel free to skip ahead.
How to open Command Prompt
To open Command Prompt, press the Windows key, and type in «cmd».
Then, click on «Run as Administrator»:
After that, you’ll see a Command Prompt window with administrative privileges:
If you can’t open Command Prompt as an administrator, no worries. You can open a normal Command Prompt window by clicking «Open» instead of «Run as Administrator».
The only difference is that you may not be able to delete some protected files, which shouldn’t be a problem in most cases.
How to delete files with the del command
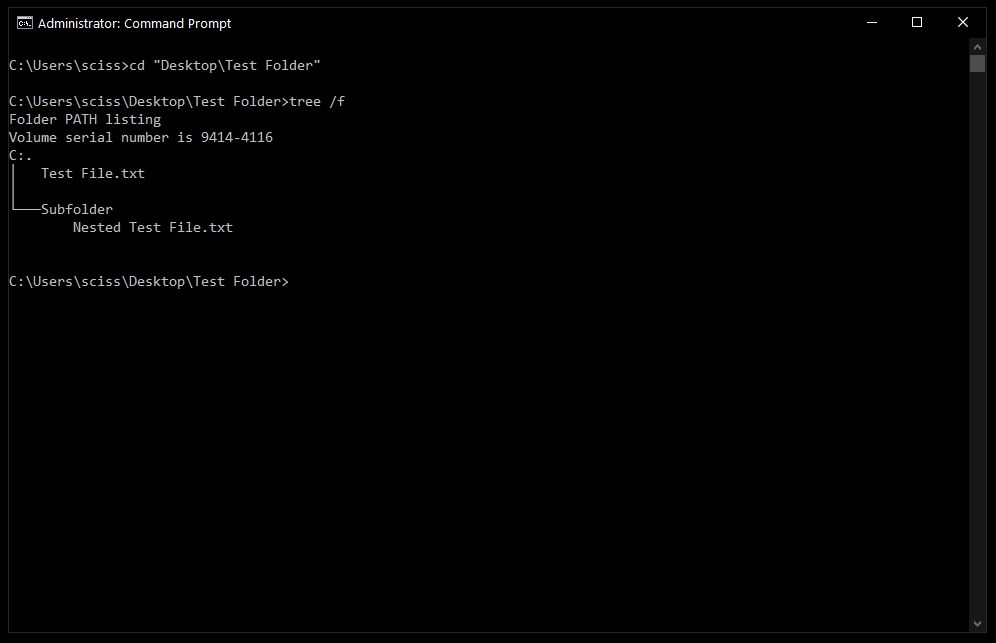
Now that Command Prompt is open, use cd to change directories to where your files are.
I’ve prepared a directory on the desktop called Test Folder. You can use the command tree /f to see a, well, tree, of all the nested files and folders:
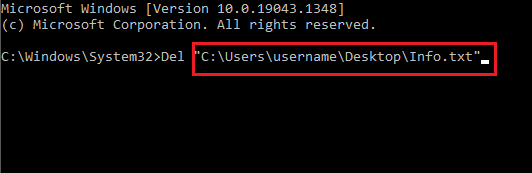
To delete a file, use the following command: del "<filename>".
For example, to delete Test file.txt, just run del "Test File.txt".
There may be a prompt asking if you want to delete the file. If so, type «y» and hit enter.
Note: Any files deleted with the del command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
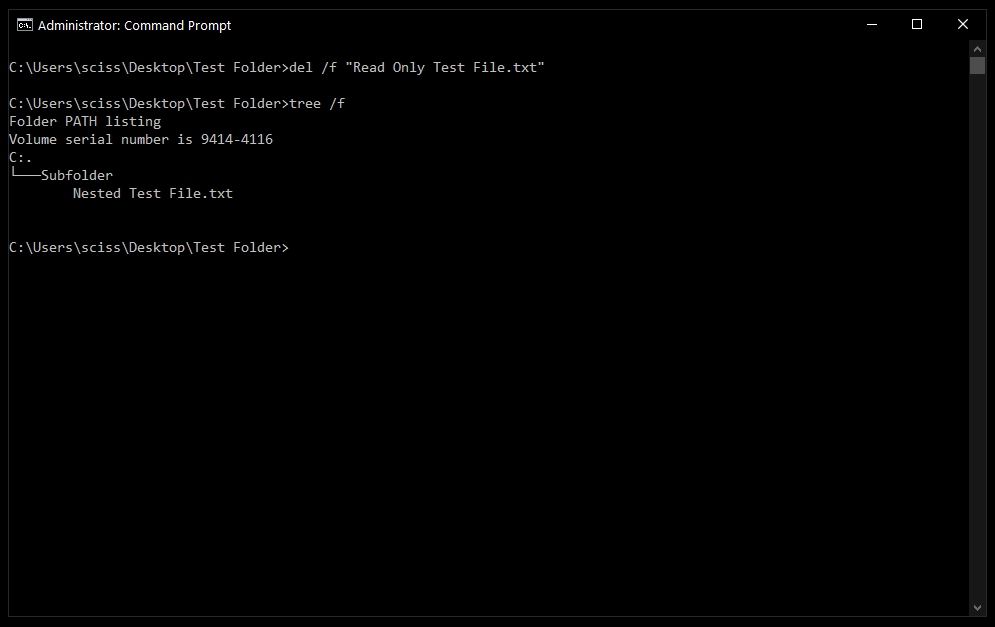
After that, you can run tree /f to confirm that your file was deleted:
Also, bonus tip – Command Prompt has basic autocompletion. So you could just type in del test, press the tab key, and Command Prompt will change it to del "Test File.txt".
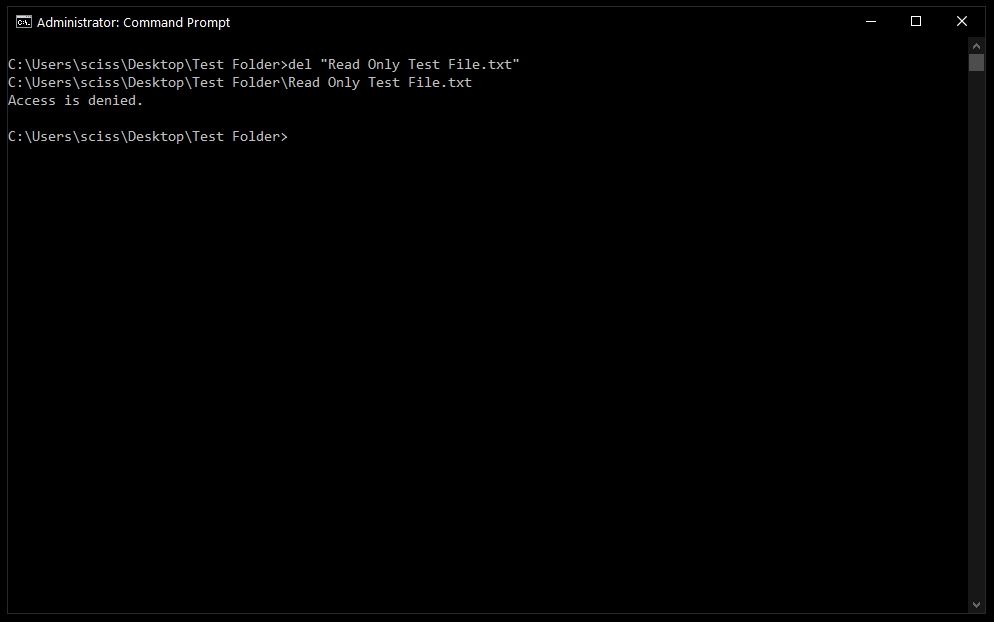
How to force delete files with the del command
Sometimes files are marked as read only, and you’ll see the following error when you try to use the del command:
To get around this, use the /f flag to force delete the file. For example, del /f "Read Only Test File.txt":
How to delete folders with the rmdir command
To delete directories/folders, you’ll need to use the rmdir or rd command. Both commands work the same way, but let’s stick with rmdir since it’s a bit more expressive.
Also, I’ll use the terms directory and folder interchangeably for the rest of the tutorial. «Folder» is a newer term that became popular with early desktop GUIs, but folder and directory basically mean the same thing.
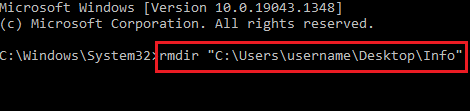
To remove a directory, just use the command rmdir <directory name>.
Note: Any directories deleted with the rmdir command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
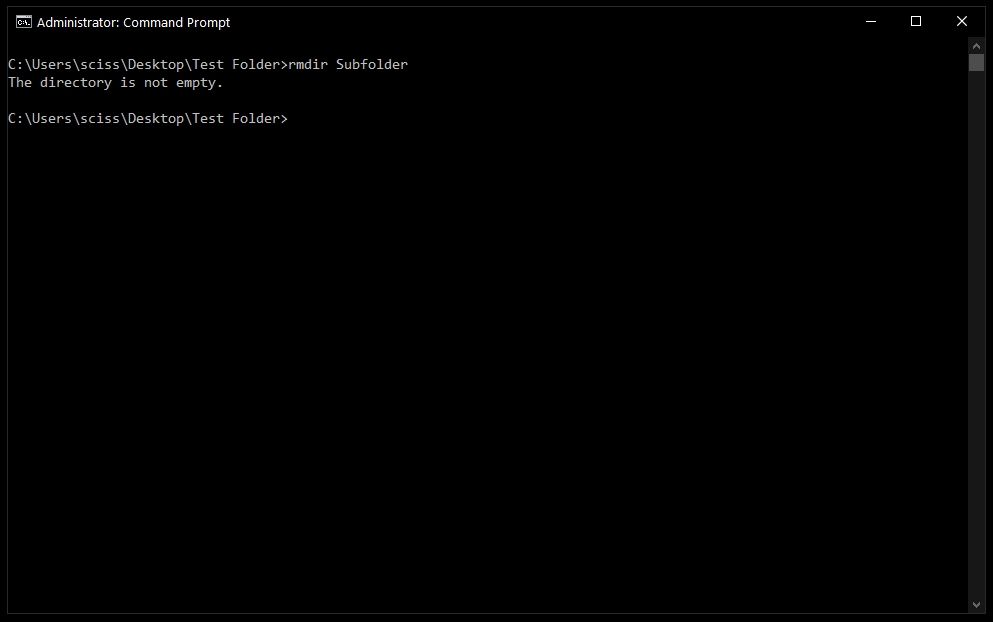
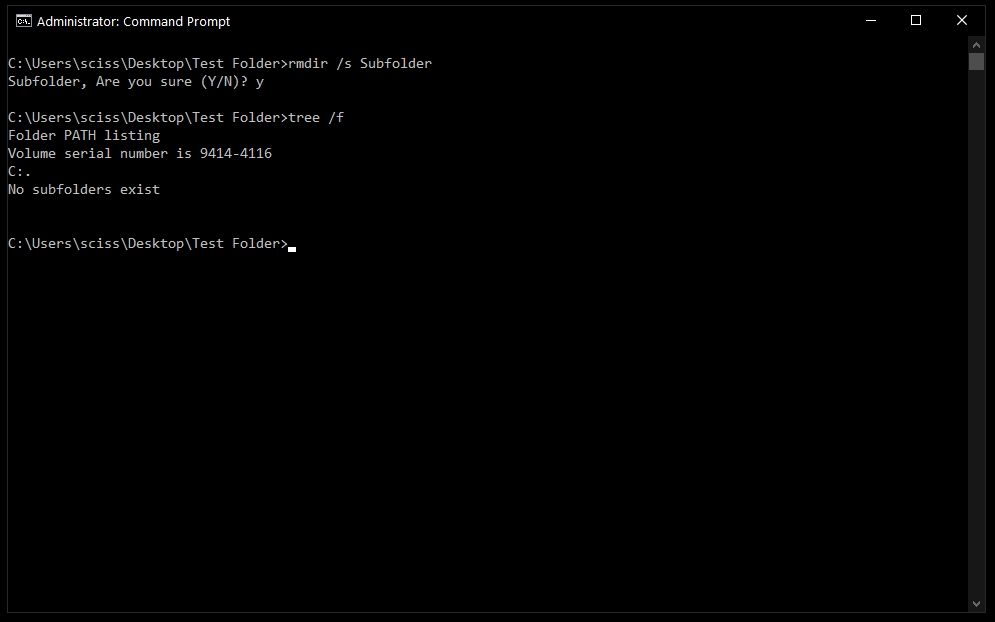
In this case I want to remove a directory named Subfolder, so I’ll use the command rmdir Subfolder:
But, if you remember earlier, Subfolder has a file in it named Nested Test File.
You could cd into the Subfolder directory and remove the file, then come back with cd .. and run the rmdir Subfolder command again, but that would get tedious. And just imagine if there were a bunch of other nested files and directories!
Like with the del command, there’s a helpful flag we can use to make things much faster and easier.
How to use the /s flag with rmdir
To remove a directory, including all nested files and subdirectories, just use the /s flag:
There will probably be a prompt asking if you want to remove that directory. If so, just type «y» and hit enter.
And that’s it! That should be everything you need to know to remove files and folders in the Windows Command Prompt.
All of these commands should work in PowerShell, which is basically Command Prompt version 2.0. Also, PowerShell has a bunch of cool aliases like ls and clear that should feel right at home if you’re familiar with the Mac/Linux command line.
Did these commands help you? Are there any other commands that you find useful? Either way, let me know over on Twitter.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
In some cases, for whatever reason, Windows will make sure that the provided file is used by the system and prevent it from being deleted. This file situation is very frustrating, especially if you know the file is not in use.
If you are having trouble in deleting any file or folder directly by right-clicking, then you can delete it using cmd. The commands below delete the specific file or folder and place them in the recycle bin:
- del
- rmdir
Here we have created a sample File and a Folder to delete it using CMD:
del command
del command is used to delete a file. Here, we will take our sample file “hello.txt” located at the desktop and try to delete it using the del command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the file:
Step 1: Change the path of the directory in CMD and set it to the path of the file. Type the following command in cmd and press Enter:
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the file “hello.txt” with following command:
del hello.txt
rmdir command
rmdir command is used to delete the entire folder or directory. Here, we will take our sample folder named “Tasks” placed at desktop and try to delete it using rmdir command in CMD. Follow the steps given below to delete the folder:
Step 1: Change the path of the directory in CMD and set it to the path of the folder. Type the following command in cmd and press Enter:
cd desktop
Step 2: Delete the folder “Tasks” with following command:
rmdir tasks
Last Updated :
03 Jul, 2022
Like Article
Save Article
Some folders and files are impossible to delete using Windows Explorer. These include files with long paths, names or reserved names like CON, AUX, COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, LPT1, LPT2, LPT3, PRN, NUL etc. You will get an Access Denied error message when you try to delete these files using Windows Explorer, even if you are an administrator.
Regardless of the reason, these can only be force deleted using command line only. This article explains using cmd to delete folder or file successfully.
Table of contents
- Before we begin
- How to remove files and folders using Command Prompt
- Del/Erase command in cmd
- Rmdir /rd command in cmd
- Delete multiple files and folders
- Delete files and folders in any directory
- Check the existence of file or folder then remove using IF command
- How to remove files and folders using Windows PowerShell
- Delete multiple files and folders
- Delete files and folders in any directory
- Delete files and folders with complex and long paths using the command line
- Closing words
Before we begin
Here are some important things for you to understand before we dig into removing files and folders using Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell. These tips will help you understand the terms and some basic rules of the commands that will be used further in the article.
The most important thing to remember here is the syntax of the path and file/folder name. When typing file name, notice whether there is a gap (space) in it. For example, if the folder name has no space in it, it can be written as-is. However, if there is a gap in it, it will need to be written within parenthesis (“”). Here is an example:
Another thing to remember is that you might see different outcomes while removing folders that are already empty, and folders that have some content in them. Having said that, you will need to use the dedicated options in the command to remove content from within a folder along with the main folder itself. This is called a recursive action.
Furthermore, you must also know how to change your working directory when inside a Command Line Interface. Use the command cd to change your directory, followed by the correct syntax. Here are some examples:
One last thing that might come in handy is being able to view what content is available in the current working directory. This is especially helpful so that you type in the correct spelling of the target file or folder. To view the contents of the current working directory in Command Prompt and PowerShell, type in Dir.
Now that we have the basic knowledge, let us show you how you can delete files and folders using the command line on a Windows PC.
By default, there are 2 command-line interfaces built into Windows 10 – Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell. Both of these are going to be used to delete content from a computer.
How to remove files and folders using Command Prompt
Let us start with the very basic commands and work our way up from there for Command Prompt. We recommend that you use Command Prompt with administrative privileges so that you do not encounter any additional prompts that you already might have.
Del/Erase command in cmd
Del and Erase commands in Command Prompt are aliases of one another. Meaning, both perform the same function regardless of which one you use. These can be used to remove individual items (files) in the current working directory. Remember that it cannot be used to delete the directories (folders) themselves.
Use either of the following commands to do so:
Tip: Use the Tab button to automatically complete paths and file/folder names.
Del File/FolderName Erase File/FolderName
Replace File/FolderName with the name of the item you wish to remove. Here is an example of us removing files from the working directory:
If you try to remove items from within a folder, whether empty or not, you will be prompted for a confirmation action, such as the one below:
In such a scenario, you will need to enter Y for yes and N for no to confirm. If you select yes, the items directly within the folder will be removed, but the directory (folder) will remain. However, the subdirectories within the folder will not be changed at all.
This problem can be resolved by using the /s switch. In order to remove all of the content within the folder and its subdirectories, you will need to add the recursive option in the command (/s). The slash followed by “s” signifies the recursive option. Refer to the example below to fully understand the concept:
We will be using the Del command here to recursively remove the text files within the folder “Final folder,” which also has a subdirectory named “Subfolder.” Subfolder also has 2 sample text files that we will be recursively removing with the following command:
Del /s "Final folder"
Here is its output:
As you can see in the image above, we had to enter “y” twice – once for each folder. with each confirmation, 2 text files were removed, as we had stated earlier in this example. However, if we use File Explorer, we can still see that both the directories – “Final folder” and “Subfolder” – are still there, but the content inside them is removed.
You can also make another tweak to the command so that it is executed silently and you will not be prompted for confirmation. Here is how:
Del /s /q "Final folder"
The /q illustrates that the action be taken quietly.
Rmdir /rd command in cmd
Similar to Del and Erase, rmdir and rd are also aliases for one another, which means to remove directory. These commands are used to remove the entire directory and subdirectories (recursively) including their contents. Use the command below to do so:
rmdir "New Folder"
The above command will remove the “New folder” only if it is empty. If a folder has subdirectories, you might get the following prompt:
In this case, we will need to apply the option for recursive deletion of items as we have done earlier with the Del command.
rmdir /s "Final folder"
Of course, this can also be performed with the /q option so that you are not prompted with a confirmation.
rmdir /s /q "Final folder"
Delete multiple files and folders
Up until now, we have completed the task of deleting single items per command. Now let’s see how you can remove multiple selective files or folders. Use the command below to do so:
For files:
Del "File1.txt" "File3.txt" "File5.txt"
For directories:
rd "Folder1" "Folder3" "Folder5"
Here is a before and after comparison of the directory where both of the above commands were executed:
You can also use an asterisk (*) concatenated with a file type or file name to perform bulk removal of files with the Del command. However, Microsoft has removed the support for the use of asterisks with rmdir so that users do not accidentally remove entire folders.
Here is an example of us removing all .txt files from our current working directory:
Del "*.txt"
Delete files and folders in any directory
We are working on removing content within the current working directory. However, you can also use the commands we have discussed till now to remove files and folders from any directory within your computer.
Simply put the complete path of the item you want to delete in enclosed parenthesis, and it shall be removed, as in the example below:
Check the existence of file or folder then remove using IF command
We have already discussed that you can view the contents of the working directory by typing in Dir in Command Prompt. However, you can apply an “if” condition in Command Prompt to remove an item if it exists. If it will not, the action would not be taken. Here is how:
if exist File/FolderName (rmdir /s/q File/FolderName)
Replace File/FolderName in both places with the name of the item (and extension if applicable) to be deleted. Here is an example:
if exist Desktop (rmdir /s/q Desktop)
How to remove files and folders using Windows PowerShell
The commands in Windows PowerShell to delete and remove content from your PC are very much similar to those of Command Prompt, with a few additional aliases. The overall functionality and logic are the same.
We recommend that you launch Windows PowerShell with administrative privileges before proceeding.
The main thing to note here is that unlike Command Prompt, all commands can be used for both purposes – removing individual files as well as complete directories. We ask you to be careful while using PowerShell to delete files and folders, as the directory itself is also removed.
The good thing is that you do not need to specify recursive action. If a directory has sub-directories, PowerShell will confirm whether you wish to continue with your deletion, which will also include all child objects (subdirectories).
Here is a list of all the commands/aliases that can be used in PowerShell to remove an item:
- Del
- Rm-dir
- remove-item
- Erase
- Rd
- Ri
- Rm
We tested all of these commands in our working directory and each of them was successful in deleting the folders as well as individual items, as can be seen below:
As can be seen above, the syntax of all the aliases is the same. You can use any of the commands below to delete an item using PowerShell:
Del File/FolderName Rm-dir File/FolderName remove-item File/FolderName Erase File/FolderName Rd File/FolderName Ri File/FolderName Rm File/FolderName
Delete multiple files and folders
You can also delete multiple selective files and folders just as we did while using Command Prompt. The only difference is that you will need to provide the complete path of each item, even if you are in the same working directory. Use the command below to do so:
Del "DriveLetter:\Path\ItemName", "DriveLetter:\Path\ItemName"
Remember to append the file type if the item is not a directory (.txt, .png, etc.), as we have done in the example below:
You can also use an asterisk (*) concatenated with a file type or file name to perform bulk removal of files with the Del command, as done in Command Prompt. Here is an example:
The command shown above will remove all.txt files in the directory “New folder.”
Delete files and folders in any directory
You can also remove an item in a different directory, just like we did in Command Prompt. Simply enter the complete path to the item in PowerShell, as we have done below:
Delete files and folders with complex and long paths using the command line
Sometimes you may encounter an error while trying to delete an item that may suggest that the path is too long, or the item cannot be deleted as it is buried too deep. Here is a neat trick you can apply using both Command Prompt and PowerShell to initially empty the folder, and then remove it using any of the methods above.
Use the command below to copy the contents of one folder (which is empty) into a folder that cannot be deleted. This will also make the destination folder empty, hence making it removable.
robocopy "D:\EmptyFolder" D:\FolderToRemove /MIR
In this scenario, the EmptyFolder is the source folder that we have deliberately kept empty to copy it to the target folder “FolderToRemove.”
You will now see that the folder that was previously unremovable is now empty. You can proceed to delete it using any of the methods discussed in this article.
Closing words
The command line is a blessing for Windows users. You can use any of these commands to remove even the most stubborn files and folders on your computer.
Let us know which solution worked for you in the comments section down below.