Базовая настройка маршрутизатора для CCNA и ICND. Назначение IP-адресов на интерфейсы маршрутизатора.
Предположим, что после деления сети 192.168.0.0/24 на 3 подсети A, B и C (по 100, 50, 2 хоста соответственно) мы получили такие подсети: A — 192.168.0.0/25, B — 192.168.0.128/26, C — 192.168.0.192/30.
Первый адрес подсети A надо назначить на интерфейс маршрутизатора fastethernet 0/0.
Первый адрес подсети B надо назначить на интерфейс маршрутизатора fastethernet 0/1.
Первый адрес подсети C надо назначить на интерфейс маршрутизатора serial 0/0/0. Причем на один конец кабеля (DCE) для интерфейса serial необходимо назначить clock rate (задать время для синхронизации сигнала), а для другого (DTE) этого делать не надо.
// Так я буду обозначать комментарии.
-
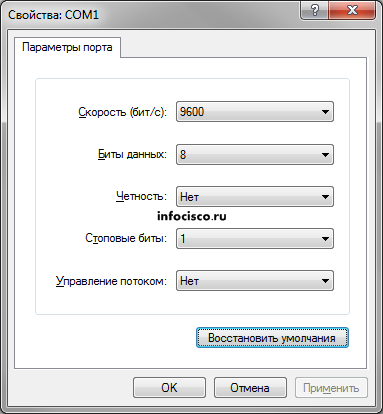
Устанавливаем консольное соединение через гипертерминал со следующими настройками:
- Скорость: 9600; Биты данных: 8; Четность: Нет; Стоповые биты: 1; Управление потоком: Нет;
- Router>enable//Входим в привилегированный режим.
- Router#
- Router#erase startup-config//Очищаем маршрутизатор от предыдущих настроек.
- Router#reload//Перезагружаем маршрутизатор.
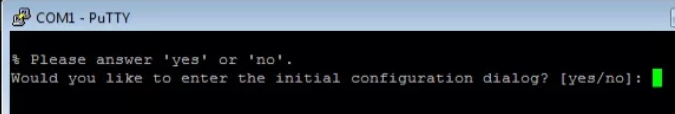
- Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: no//После перезагрузки маршрутизатора IOS спросит, надо ли настраивать маршрутизатор в режиме диалога. Откажитесь.
- Router>enable//Снова входим в привилегированный режим.
- Router#
- Router#configure terminal//входим в режим глобальной конфигурации
- Router(config)#hostname R1//даём имя маршрутизатору, в данном случае R1
- R1(config)#no ip domain-lookup//выключаем поиск DNS
- R1(config)#enable secret class//включаем пароль на вход привилегированного режима
- R1(config)#banner motd #//Настраиваем сообщение дня (message of the day). Между знаками «#» пишем сообщение.
!!!ACCESS DENIED!!!
# - R1(config)#line console 0//Входим в режим настройки консоли.
- R1(config-line)#password cisco//Назначаем пароль на вход.
- R1(config-line)#login//Включаем запрос пароля перед входом в консоль.
- R1(config-line)#exit
- R1(config)#line vty 0 4//Входим в режим настройки телнета.
- R1(config-line)#password cisco//Назначаем пароль на вход.
- R1(config-line)#login//Включаем запрос пароля перед входом с помощью телнета.
- R1(config-line)#end
- R1#show running-config//Проверяем введенные данные.
- R1#copy running-config startup-config//Сохраняем произведенную настройку в энерго-независимую память. Сейвы помогают не только геймерам
Были случаи когда ПакетТрейсер вис и приходилось всё делать заново.
- R1#configure terminal//снова заходим в режим глобальной конфигурации
- R1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0//заходим в режим конфигурации интерфейса
- R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.128//назначаем IP-адрес интерфейсу и маску 255.255.255.128 (эта маска является расшифровкой префикса /25)
- R1(config-if)#des Subnet A//краткое описание интерфейса
- R1(config-if)#no shutdown//включаем интерфейс
- R1(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1//заходим в режим конфигурации интерфейса
- R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.129 255.255.255.192//назначаем IP-адрес интерфейсу и маску 255.255.255.128 (эта маска является расшифровкой префикса /25)
- R1(config-if)#des Subnet B//краткое описание интерфейса
- R1(config-if)#no shutdown//включаем интерфейс
- R1(config)#interface serial 0/0/0//заходим в режим конфигурации интерфейса
- R1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.193 255.255.255.252//назначаем IP-адрес интерфейсу и маску 255.255.255.128 (эта маска является расшифровкой префикса /25)
- R1(config-if)#des Link to R2//краткое описание интерфейса
- R1(config-if)#clock rate 64000//задаем время сигнала для синхронизации со вторым роутером. На втором роутере этого делать не надо!
- R1(config-if)#no shutdown//включаем интерфейс
- R1(config-line)#end//выходим в привилегированный режим EXEC Mode
- R1#show running-config//Проверяем введенные данные.
- R1#copy running-config startup-config//Сохраняем произведенную настройку в энерго-независимую память.
Скачать выполненное задание настройки роутера
Предлагаю скачать файл с выполненным заданием для программы эмулятора PacketTracer, открыть его и посмотреть на реализацию (пароль на консольный вход — cisco, на привилегированный режим — class).
Заметьте, что компьютер PC1 может нормально пинговать компьютер PC2, но не может пинговать PC3. Это происходит из-за не настроенной маршрутизации. А настроим мы её в следующей шпаргалке 
Настройка роутера копированием конфигурации
-
Для автоматической базовой настройки (всё, что выше) маршрутизатора выполните следующие действия:
- 1. Скопируйте текст ниже в буфер обмена: выделите всё, кликните правой кнопкой по выделенному и выберите «Копировать».
- 2. При необходимости очистите роутер от всех настроек и перезагрузите его.
- 3. Войдите в режим глобальной конфигурации и вызовите меню Гипер Терминала «Правка», а в нём «Передать главному компьютеру».
- 4. Обязательно проверьте настройки с помощью команды
show running-config - 5. При необходимости включите интерфейсы командой no shutdown из режима каждого интерфейса
Read the article BASIC CONFIGURATION OF THE CISCO ROUTER. ACCESS TO THE INTERNET in English
Рассмотрим схему подключения офиса к сети Интернет с помощью маршрутизатора Cisco. Для примера возьмем модель Cisco 881. Команды для настройки других маршрутизаторов (1841, 2800, 3825…) будут аналогичными Различия могут быть в настройке интерфейсов, вернее в их названиях и нумерации.
В схеме присутствуют:
- канал в Интернет со статическим адресом
- несколько компьютеров в локальной сети офиса
- маршрутизатор
- коммутатор, который используется для организации локальной сети офиса
Задача: обеспечить доступ компьютеров локальной сети в Интернет.
Шаг 0. Очистка конфигурации
Первое, с чего стоит начать настройку нового маршрутизатора – полностью очистить стартовую конфигурацию устройства. (Выполнять только на новом или тестовом оборудовании!) Для этого нужно подключиться с помощью специального кабеля к консольному порту маршрутизатора, зайти в командную строку и выполнить следующее:
Войти в привилегированный режим(#), возможно потребуется ввести логин/пароль.
router> enable
Удалить стартовую конфигурацию
router# write erase
/подтверждение/
Перезагрузить маршрутизатор
router# reload
/подтверждение/
После выполнения маршрутизатор должен перезагрузиться в течение 3ех минут, а при старте вывести запрос о начале базовой настройки. Следует отказаться.
Would you like to enter the basic configuration dialog (yes/no): no
В текущей конфигурации маршрутизатора будут только технологические строки по умолчанию, и можно приступать к основной настройке.
Шаг 1. Имя устройства
Задание имени маршрутизатора для удобства последующего администрирования выполняется командой hostname «название устройства»
router#conf t
router (config)#hostname R-DELTACONFIG
R-DELTACONFIG(config)#
Шаг 2. Настройка интерфейсов
Необходимо настроить 2 интерфейса: внешний и внутренний.
Через внешний интерфейс будет осуществляться связь с Интернет. На нем будут те ip адрес и маска сети, которые предоставил Интернет провайдер.
Внутренний интерфейс будет настроен для локальной сети 192.168.0.0 /24
Предположим, что оператор связи предоставил нам следующие адреса:
- Сеть 200.150.100.0
- Маска подсети 255.255.255.252 или /30
- Шлюз по умолчанию 200.150.100.1
Настроим внешний интерфейс: зададим ip адрес и сетевую маску, и включим его командой no shut
R-DELTACONFIG#conf t
R-DELTACONFIG (config)#
interface Fa 4
ip address 200.150.100.2 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
После этого соединяем этот интерфейс маршрутизатора с портом оборудования провайдера при помощи прямого патч корда и далее проверяем его доступность командой ping.
Сначала собственный интерфейс
R-DELTACONFIG#ping 200.150.100.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 200.150.100.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
Затем соседний адрес — шлюз провайдера
R-DELTACONFIG#ping 200.150.100.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 200.150.100.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 2/4/10 ms
Убедившись в доступности шлюза Провайдера, переходим к настройке внутреннего интерфейса.
В локальной сети будет использоваться следующая адресация
- Сеть 192.168.0.0
- Маска подсети 255.255.255.0
- Внутренний адрес маршрутизатора, который выполняет роль шлюза в Интернет для всех хостов в сети, 192.168.0.1
- Диапазон внутренних адресов сети (пользователи, принтеры, серверы и.т.д.) советую начинать с адреса 192.168.0.5
- Максимально возможный доступный для использования адрес в этой сети будет 192.168.0.254
- Адреса с 192.168.0.2 до 192.168.0.4 оставим про запас для непредвиденных технологических нужд
Для настройки внутреннего интерфейса локальной сети следует зайти в режим конфигурирования виртуального интерфейса Vlan 1, задать на нем ip адрес и соотнести ему один из физических интерфейсов маршрутизатора (Fa 0).
R-DELTACONFIG#conf t
interface Vlan 1
Ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
Выбираем физический интерфейс маршрутизатора и соотносим его с виртуальным Vlan
interface Fa 0
switchport access vlan 1
no shutdown
Для наглядности:
ip address => interface Vlan X => interface Fastethernet Y
Ip адрес присваивается виртуальному интерфейсу Vlan X, а он привязывается к физическому интерфейсу Fastethernet Y.
Интерфейс маршрутизатора Fa 0 нужно соединить с коммутатором, где располагаются рабочие станции локальной сети или напрямую с рабочей станцией администратора. После этого проверить доступность этого интерфейса маршрутизатора с помощью ping из командной строки.
Шаг 3 Настройка удаленного доступа к маршрутизатору
Получить доступ к консоли маршрутизатора можно не только с помощью консольного кабеля, но и удаленно с помощью протоколов Telnet(данные передаются в открытом виде) или SSH(защищенное соединение).
Рассмотрим настройку безопасного подключения.
Включаем протокол SSH 2 версии и задаем произвольное имя домена
R-DELTACONFIG (config)#
ip ssh ver 2
ip domain-name xxx.ru
Генерируем ключи rsa, необходимые для подключения. При запросе указываем 1024.
crypto key generate rsa
How many bits in the modulus [512]: 1024
Задаем имя пользователя с правами администратора и его пароль (*****)
username admin privilege 15 secret 0 *****
Включаем авторизацию через локальную базу устройства (тот пользователь, которого создали строчкой выше)
line vty 0 4
login local
Задаем пароль на привилегированный режим
enable secret 0 *****
После этого при помощи специальной программы, поддерживающей протокол SSH можно зайти в командную строку маршрутизатора удаленно с любой из рабочих станций локальной сети. При авторизации следует ввести логин и пароль, которые были задан. Подробнее про доступ на устройство по протоколу SSH написано в этой статье.
Шаг 4. Шлюз по умолчанию
Для маршрутизации пакетов в сеть Интернет на устройстве необходимо указать шлюз по умолчанию(default gateway).
R-DELTACONFIG (config)#
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 200.150.100.1
После этого можно проверить не только доступность оборудования провайдера, но и полностью канала в Интернет. Для этого необходимо запустить ping до любого адреса во внешней сети в цифровой форме(DNS для локальной сети лучше настраивать после настройки маршрутизатора). Для примера возьмем адрес лидера на рынке ping – www.yandex.ru (93.158.134.3)
R-DELTACONFIG#ping 93.158.134.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 93.158.134.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/5/10 ms
Важно!
Обратите внимание, что на данный момент ping внешних адресов работает только(!) будучи запущенным из консоли управления маршрутизатором. Рабочие станции локальной сети все еще не имеют доступа в Интернет.
Шаг 5 Настройка трансляции адресов (NAT)
Для доступа в Интернет из локальной сети необходимо динамически транслировать все внутренние адреса в определенный внешний ip адрес. В нашем случае, так как провайдер предоставляет только один внешний адрес 200.150.100.2 (определяется маской подсети /30 в условиях примера), то все адреса локальной сети должны транслироваться в него.
Указываем список внутренних адресов, которые будем транслировать во внешний адрес.
R-DELTACONFIG (config)#
ip access-list standard ACL_NAT
permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.255
Указываем внутренний интерфейс для процедуры трансляции
Interface Vlan 1
ip nat inside
Указываем внешний интерфейс для процедуры трансляции
Interface Fa 4
ip nat outside
Создаем правило трансляции (NAT)
ip nat inside source list ACL_NAT interface fa4
В результате должен появиться доступ с любой рабочей станции локальной сети в Интернет при условии, что шлюзом по умолчанию указан внутренний ip адрес маршрутизатора (192.168.0.1). Проверить можно с помощью команды ping до адреса в Интернет из командной строки. Желательно, чтобы проверяемый адрес был в цифровом виде, чтобы исключить потенциальные проблемы с DNS именами.
Важно!
В указанном примере меняется собственный адрес источника. Если в процессе работы необходимо транслировать адрес назначения — пускать траффик на вымышленный адрес, чтобы попасть на некий настоящий, то прочитайте статью ip nat outside.
Важно!
Не стоит оставлять полный доступ в Интернет со всех адресов локальной сети. Советую после проверки работоспособности соединения для безопасности ограничить доступ в Интернет и разрешить его только с конкретных адресов — например с прокси сервера и рабочих станций администратора и/или директора. О том как это сделать можно прочитать в статье «немного об access lists«.
Важно!
Не забудьте сохранить конфигурацию на всех устройствах командой write или copy run start. Иначе после перезагрузки все изменения будут потеряны.
R-DELTACONFIG#write
Building configuration...
[OK]
Перейти к оглавлению
Table Of Contents
Basic Router Configuration
Interface Port Labels
Viewing the Default Configuration
Information Needed for Configuration
Configuring Basic Parameters
Configure Global Parameters
Configure Fast Ethernet LAN Interfaces
Configure WAN Interfaces
Configure the Fast Ethernet WAN Interface
Configure the ATM WAN Interface
Configure the Wireless Interface
Configuring a Loopback Interface
Configuration Example
Verifying Your Configuration
Configuring Command-Line Access to the Router
Configuration Example
Configuring Static Routes
Configuration Example
Verifying Your Configuration
Configuring Dynamic Routes
Configuring RIP
Configuration Example
Verifying Your Configuration
Configuring Enhanced IGRP
Configuration Example
Verifying Your Configuration
Basic Router Configuration
This chapter provides procedures for configuring the basic parameters of your Cisco router, including global parameter settings, routing protocols, interfaces, and command-line access. It also describes the default configuration on startup.
Note Individual router models may not support every feature described throughout this guide. Features not supported by a particular router are indicated whenever possible.
This chapter contains the following sections:
•Interface Port Labels
•Viewing the Default Configuration
•Information Needed for Configuration
•Configuring Basic Parameters
•Configuring Static Routes
•Configuring Dynamic Routes
•Configuring Enhanced IGRP
Each section includes a configuration example and verification steps, as available.
For complete information on how to access global configuration mode, see the «Entering Global Configuration Mode» section in Appendix A, «Cisco IOS Basic Skills.» For more information on the commands used in the following tables, see the Cisco IOS Release 12.3 documentation set.
Interface Port Labels
Table 1-1 lists the interfaces supported for each router and their associated port labels on the equipment.
|
Router |
Interface |
Port Label |
|---|---|---|
|
Cisco 851 |
Fast Ethernet LAN |
LAN (top), FE0-FE3 (bottom) |
|
Fast Ethernet WAN |
WAN (top), FE4 (bottom) |
|
|
Wireless LAN |
(no label) |
|
|
Cisco 871 |
Fast Ethernet LAN |
FE0-FE3 |
|
Fast Ethernet WAN |
FE4 |
|
|
Wireless LAN |
LEFT, RIGHT/PRIMARY |
|
|
USB |
1-0 |
|
|
Cisco 857 |
Fast Ethernet LAN |
LAN (top), FE0-FE3 (bottom) |
|
ATM WAN |
ADSLoPOTS |
|
|
Wireless LAN |
(no label) |
|
|
Cisco 876 |
Fast Ethernet LAN |
LAN (top), FE0-FE3 (bottom) |
|
ATM WAN |
ADSLoISDN |
|
|
Wireless LAN |
LEFT, RIGHT/PRIMARY |
|
|
BRI |
ISDN S/T |
|
|
Cisco 877 |
Fast Ethernet LAN |
LAN (top), FE0-FE3 (bottom) |
|
ATM WAN |
ADSLoPOTS |
|
|
Wireless LAN |
LEFT, RIGHT/PRIMARY |
|
|
Cisco 878 |
Fast Ethernet LAN |
FE0-FE3 |
|
ATM WAN |
G.SHDSL |
|
|
Wireless LAN |
LEFT, RIGHT/PRIMARY |
|
|
BRI |
ISDN S/T |
Viewing the Default Configuration
When you first boot up your Cisco router, some basic configuration has already been performed. All of the LAN and WAN interfaces have been created, console and VTY ports are configured, and the inside interface for Network Address Translation has been assigned. Use the show running-config command to view the initial configuration, as shown in Example 1-1.
Example 1-1 Cisco 851 Default Configuration on Startup
Router# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 1090 bytes
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
no ftp-server write-enable
speed basic-1.0 basic-2.0 basic-5.5 6.0 9.0 basic-11.0 12.0 18.0 24.0 36.0 48.0
Information Needed for Configuration
You need to gather some or all of the following information, depending on your planned network scenario, prior to configuring your network
•If you are setting up an Internet connection, gather the following information:
– Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) client name that is assigned as your login name
–PPP authentication type: Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) or Password Authentication Protocol (PAP)
–PPP password to access your Internet service provider (ISP) account
–DNS server IP address and default gateways
•If you are setting up a connection to a corporate network, you and the network administrator must generate and share the following information for the WAN interfaces of the routers:
–PPP authentication type: CHAP or PAP
–PPP client name to access the router
–PPP password to access the router
•If you are setting up IP routing:
–Generate the addressing scheme for your IP network.
–Determine the IP routing parameter information, including IP address, and ATM permanent virtual circuits (PVCs). These PVC parameters are typically virtual path identifier (VPI), virtual circuit identifier (VCI), and traffic shaping parameters.
–Determine the number of PVCs that your service provider has given you, along with their VPIs and VCIs.
–For each PVC determine the type of AAL5 encapsulation supported. It can be one of the following:
AAL5SNAP—This can be either routed RFC 1483 or bridged RFC 1483. For routed RFC 1483, the service provider must provide you with a static IP address. For bridged RFC 1483, you may use DHCP to obtain your IP address, or you may obtain a static IP address from your service provider.
AAL5MUX PPP—With this type of encapsulation, you need to determine the PPP-related configuration items.
•If you plan to connect over an ADSL or G.SHDSL line:
–Order the appropriate line from your public telephone service provider.
For ADSL lines—Ensure that the ADSL signaling type is DMT (also called ANSI T1.413) or DMT Issue 2.
For G.SHDSL lines—Verify that the G.SHDSL line conforms to the ITU G.991.2 standard and supports Annex A (North America) or Annex B (Europe).
Once you have collected the appropriate information, you can perform a full configuration on your router, beginning with the tasks in the «Configuring Basic Parameters» section.
Configuring Basic Parameters
To configure the router, perform one or more of these tasks:
•Configure Global Parameters
•Configure Fast Ethernet LAN Interfaces
•Configure WAN Interfaces
•Configuring a Loopback Interface
•Configuring Command-Line Access to the Router
A configuration example is presented with each task to show the network configuration following completion of that task.
Configure Global Parameters
Perform these steps to configure selected global parameters for your router:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
configure terminal Example: Router> enable Router# configure terminal Router(config)# |
Enters global configuration mode, when using the console port. If you are connecting to the router using a remote terminal, use the following: telnet router name or address Login: login id Password: ********* Router> enable |
|
Step 2 |
hostname name Example: Router(config)# hostname Router Router(config)# |
Specifies the name for the router. |
|
Step 3 |
enable secret password Example: Router(config)# enable secret cr1ny5ho Router(config)# |
Specifies an encrypted password to prevent unauthorized access to the router. |
|
Step 4 |
no ip domain-lookup Example: Router(config)# no ip domain-lookup |
Disables the router from translating unfamiliar words (typos) into IP addresses. |
For complete information on the global parameter commands, see the Cisco IOS Release 12.3 documentation set.
Configure Fast Ethernet LAN Interfaces
The Fast Ethernet LAN interfaces on your router are automatically configured as part of the default VLAN and as such, they are not configured with individual addresses. Access is afforded through the VLAN. You may assign the interfaces to other VLANs if desired. For more information about creating VLANs, see Chapter 5 «Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs.»
Configure WAN Interfaces
The Cisco 851 and Cisco 871 routers each have one Fast Ethernet interface for WAN connection. The Cisco 857, Cisco 877, and Cisco 878 routers each have one ATM interface for WAN connection.
Based on the router model you have, configure the WAN interface(s) using one of the following procedures:
•Configure the Fast Ethernet WAN Interface
•Configure the ATM WAN Interface
Configure the Fast Ethernet WAN Interface
This procedure applies only to the Cisco 851 and Cisco 871 router models. Perform these steps to configure the Fast Ethernet interface, beginning in global configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
interface type number Example: Router(config)# interface fastethernet 4
Router(config-int)# |
Enters the configuration mode for a Fast Ethernet WAN interface on the router. |
|
Step 2 |
ip address ip-address mask Example: Router(config-int)# ip address 192.168.12.2
255.255.255.0
Router(config-int)# |
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the specified Fast Ethernet interface. |
|
Step 3 |
no shutdown Example: Router(config-int)# no shutdown
Router(config-int)# |
Enables the Ethernet interface, changing its state from administratively down to administratively up. |
|
Step 4 |
exit Example: Router(config-int)# exit
Router(config)# |
Exits configuration mode for the Fast Ethernet interface and returns to global configuration mode. |
Configure the ATM WAN Interface
This procedure applies only to the Cisco 857, Cisco 876, Cisco 877 and Cisco 878 models.
Perform these steps to configure the ATM interface, beginning in global configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
For the Cisco 878 model only:
controller dsl 0 Example: Router(config)# controller dsl 0
Router(config-controller)# mode atm
Router(config-controller)# exit Router(config)# |
For routers using the G.SHDSL signaling, perform these commands. Ignore this step for routers using ADSL signaling. |
|
Step 2 |
interface type number Example: Router(config)# interface atm0
Router(config-int)# |
Identifies and enters the configuration mode for an ATM interface. |
|
Step 3 |
ip address ip-address mask Example: Router(config-int)# ip address 10.10.10.100
255.255.255.0
Router(config-int)# |
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the ATM interface. |
|
Step 4 |
no shutdown Example: Router(config-int)# no shutdown
Router(config-int)# |
Enables the ATM 0 interface. |
|
Step 5 |
exit Example: Router(config-int)# exit
Router(config)# |
Exits configuration mode for the ATM interface and returns to global configuration mode. |
Configure the Wireless Interface
The wireless interface enables connection to the router through a wireless LAN connection. For more information about configuring a wireless connection, see Chapter 9 «Configuring a Wireless LAN Connection,» and the Cisco Access Router Wireless Configuration Guide.
Configuring a Loopback Interface
The loopback interface acts as a placeholder for the static IP address and provides default routing information.
For complete information on the loopback commands, see the Cisco IOS Release 12.3 documentation set.
Perform these steps to configure a loopback interface:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
interface type number Example: Router(config)# interface Loopback 0
Router(config-int)# |
Enters configuration mode for the loopback interface. |
|
Step 2 |
ip address ip-address mask Example: Router(config-int)# ip address 10.108.1.1
255.255.255.0
Router(config-int)# |
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the loopback interface. |
|
Step 3 |
exit Example: Router(config-int)# exit
Router(config)# |
Exits configuration mode for the loopback interface and returns to global configuration mode. |
Configuration Example
The loopback interface in this sample configuration is used to support Network Address Translation (NAT) on the virtual-template interface. This configuration example shows the loopback interface configured on the Fast Ethernet interface with an IP address of 10.10.10.100/24, which acts as a static IP address. The loopback interface points back to virtual-template1, which has a negotiated IP address.
ip address 10.10.10.100 255.255.255.0 (static IP address)
interface Virtual-Template1
Verifying Your Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured the loopback interface, enter the show interface loopback command. You should see verification output similar to the following example.
Router# show interface loopback 0
Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet address is 10.10.10.100/24
MTU 1514 bytes, BW 8000000 Kbit, DLY 5000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation LOOPBACK, loopback not set
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Output queue 0/0, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Another way to verify the loopback interface is to ping it:
Router# ping 10.10.10.100
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.10.10.100, timeout is 2 seconds:
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
Configuring Command-Line Access to the Router
Perform these steps to configure parameters to control access to the router, beginning in global configuration mode.
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
line [aux | console | tty | vty] line-number Example: Router(config)# line console 0
Router(config)# |
Enters line configuration mode, and specifies the type of line. This example specifies a console terminal for access. |
|
Step 2 |
password password Example: Router(config)# password 5dr4Hepw3
Router(config)# |
Specifies a unique password for the console terminal line. |
|
Step 3 |
login Example: Router(config)# login
Router(config)# |
Enables password checking at terminal session login. |
|
Step 4 |
exec-timeout minutes [seconds] Example: Router(config)# exec-timeout 5 30
Router(config)# |
Sets the interval that the EXEC command interpreter waits until user input is detected. The default is 10 minutes. Optionally, add seconds to the interval value. This example shows a timeout of 5 minutes and 30 seconds. Entering a timeout of 0 0 specifies never to time out. |
|
Step 5 |
line [aux | console | tty | vty] line-number Example: Router(config)# line vty 0 4
Router(config)# |
Specifies a virtual terminal for remote console access. |
|
Step 6 |
password password Example: Router(config)# password aldf2ad1
Router(config)# |
Specifies a unique password for the virtual terminal line. |
|
Step 7 |
login Example: Router(config)# login
Router(config)# |
Enables password checking at the virtual terminal session login. |
|
Step 8 |
end Example: Router(config)# end
Router# |
Exits line configuration mode, and returns to privileged EXEC mode. |
For complete information about the command line commands, see the Cisco IOS Release 12.3 documentation set.
Configuration Example
The following configuration shows the command-line access commands.
You do not need to input the commands marked «default.» These commands appear automatically in the configuration file generated when you use the show running-config command.
transport input none (default)
Configuring Static Routes
Static routes provide fixed routing paths through the network. They are manually configured on the router. If the network topology changes, the static route must be updated with a new route. Static routes are private routes unless they are redistributed by a routing protocol. Configuring static routes on the Cisco 850 and Cisco 870 series routers is optional.
Perform these steps to configure static routes, beginning in global configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
ip route prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type interface-number [ip-address]} Example: Router(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0
255.255.0.0 10.10.10.2
Router(config)# |
Specifies the static route for the IP packets. For details about this command and additional parameters that can be set, see the Cisco IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 4: Routing Protocols. |
|
Step 2 |
end Example: Router(config)# end
Router# |
Exits router configuration mode, and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
For complete information on the static routing commands, see the Cisco IOS Release 12.3 documentation set. For more general information on static routing, see «Concepts.»
Configuration Example
In the following configuration example, the static route sends out all IP packets with a destination IP address of 192.168.1.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 on the Fast Ethernet interface to another device with an IP address of 10.10.10.2. Specifically, the packets are sent to the configured PVC.
You do not need to enter the commands marked «(default).» These commands appear automatically in the configuration file generated when you use the show running-config command.
ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2!
Verifying Your Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured static routing, enter the show ip route command and look for static routes signified by the «S.»
You should see verification output similar to the following example.
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0
Configuring Dynamic Routes
In dynamic routing, the network protocol adjusts the path automatically, based on network traffic or topology. Changes in dynamic routes are shared with other routers in the network.
The Cisco routers can use IP routing protocols, such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), to learn routes dynamically. You can configure either of these routing protocols on your router.
Configuring RIP
Perform these steps to configure the RIP routing protocol on the router, beginning in global configuration mode:
|
Command |
Task |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
router rip Example: Router> configure terminal
Router(config)# router rip
Router(config-router)# |
Enters router configuration mode, and enables RIP on the router. |
|
Step 2 |
version {1 | 2} Example: Router(config-router)# version 2
Router(config-router)# |
Specifies use of RIP version 1 or 2. |
|
Step 3 |
network ip-address Example: Router(config-router)# network 192.168.1.1
Router(config-router)# network 10.10.7.1
Router(config-router)# |
Specifies a list of networks on which RIP is to be applied, using the address of the network of directly connected networks. |
|
Step 4 |
no auto-summary Example: Router(config-router)# no auto-summary
Router(config-router)# |
Disables automatic summarization of subnet routes into network-level routes. This allows subprefix routing information to pass across classful network boundaries. |
|
Step 5 |
end Example: Router(config-router)# end
Router# |
Exits router configuration mode, and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
For complete information on the dynamic routing commands, see the Cisco IOS Release 12.3 documentation set. For more general information on RIP, see «Concepts.»
Configuration Example
The following configuration example shows RIP version 2 enabled in IP network 10.0.0.0 and 192.168.1.0.
Execute the show running-config command from privileged EXEC mode to see this configuration.
Verifying Your Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured RIP, enter the show ip route command and look for RIP routes signified by «R.» You should see a verification output like the example shown below.
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
R 3.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 2.2.2.1, 00:00:02, Ethernet0/0
Configuring Enhanced IGRP
Perform these steps to configure Enhanced IGRP (EIGRP), beginning in global configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
router eigrp as-number Example: Router(config)# router eigrp 109
Router(config)# |
Enters router configuration mode, and enables EIGRP on the router. The autonomous-system number identifies the route to other EIGRP routers and is used to tag the EIGRP information. |
|
Step 2 |
network ip-address Example: Router(config)# network 192.145.1.0
Router(config)# network 10.10.12.115
Router(config)# |
Specifies a list of networks on which EIGRP is to be applied, using the IP address of the network of directly connected networks. |
|
Step 3 |
end Example: Router(config-router)# end
Router# |
Exits router configuration mode, and enters privileged EXEC mode. |
For complete information on the IP EIGRP commands, see the Cisco IOS Release 12.3 documentation set. For more general information on EIGRP concepts, see «Concepts.»
Configuration Example
The following configuration example shows the EIGRP routing protocol enabled in IP networks 192.145.1.0 and 10.10.12.115. The EIGRP autonomous system number is 109.
Execute the show running-config command from privileged EXEC mode to see this configuration.
Verifying Your Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured IP EIGRP, enter the show ip route command, and look for EIGRP routes indicated by «D.» You should see verification output similar to the following example.
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
D 3.0.0.0/8 [90/409600] via 2.2.2.1, 00:00:02, Ethernet0/0
Всем привет! Сегодня я на простом примере расскажу вам про настройку роутера Cisco (2911, 1841, 881 и другие модели). Я выдумал некую простую схему с примером, которая позволит вам понять, как подключить локальную сеть к интернету через наш маршрутизатор. Я покажу пример настройки через консоль. Но вы можете делать конфигурирование через программу «Cisco Packet Tracer» – видеоинструкцию смотрим в конце статьи.
Содержание
- Пример подключения
- ШАГ 1: Подключение к маршрутизатору
- ШАГ 2: Reset настроек
- ШАГ 3: Конфигурация интерфейсов
- ШАГ 4: Удаленный доступ к роутеру
- ШАГ 5: Настройка шлюза
- ШАГ 6: Настройка NAT
- Видео
- Задать вопрос автору статьи
Пример подключения
Представим себе, что у нас есть один роутер Cisco. С помощью маршрутизатора мы должны подключить офис с несколькими компьютерами. Для коннекта всех локальных машин будем использовать коммутатор. Fa 4 и Fa 0 – это внешний и внутренний физический интерфейс. Также у нас есть:
- 277.146.101.1 – это шлюз провайдера.
- 277.146.101.2 – это внешний IP адрес роутера, его выдает провайдер.
- 192.168.1.1 – это локальный IP адрес.
Я думаю, схема достаточно понятная и простая.
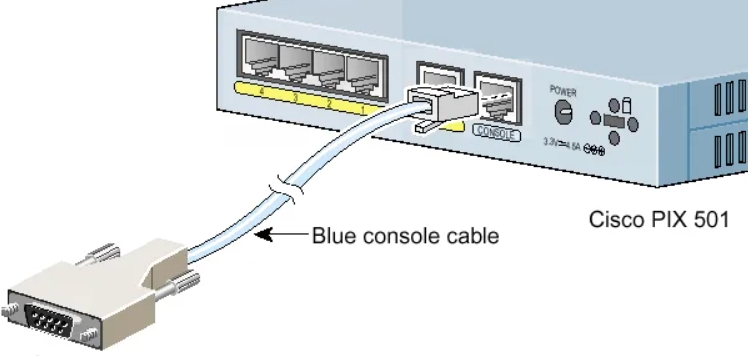
ШАГ 1: Подключение к маршрутизатору
Для подключения мы будем использовать вот такой вот кабель, который обычно идет в комплекте со всем подобным оборудованием.
С одной стороны консольного кабеля должен быть COM-порт (RS 232). Подключаем один конец в CONSOLE (может иметь надпись CON) порты.
Вы можете столкнуться с проблемой, что у современных компов и ноутов нет подобного входа. Поэтому можно использовать USB переходник.
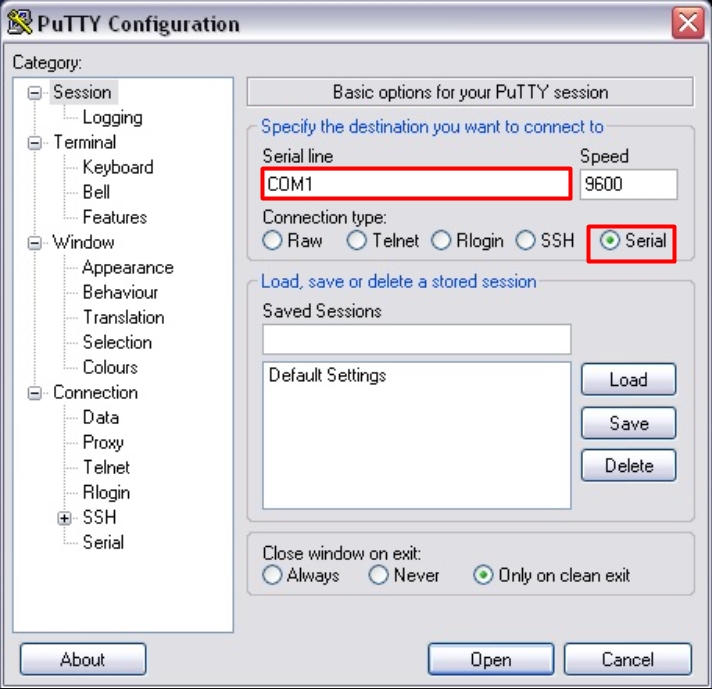
После подключения скачиваем программку PuTTY – она бесплатная и достаточно удобная. Очень важный момент – в разделе «Connection type» после запуска установите значение «Serial».
И далее нажимаем по кнопке «Open». Если у вас возникли трудности и подключение не происходит, то проверьте в «Диспетчере устройств», какой COM порт используется. Может быть баг, что порт указан не тот. Особенно этот баг проявляется при использовании переходника USB-COM.
Далее вы должны увидеть приветственную надпись в запрос ввода логина и пароля.
ШАГ 2: Reset настроек
Итак, в первую очередь нам нужно полностью очистить старые настройки – они нам ни к чему, все будем делать с нуля (так сказать). Изначально вы увидите вот такую надпись:
router>
Но нам нужно запустить роутер с правами администратора, чтобы вместо стрелочки стояла решетка (#). Для этого вводим команду:
router> enable
Теперь сначала удаляем старый конфиг, а потом ребутаем аппарат:
router# write erase
router# reload
Нужно будет немного подождать. После этого роутер загрузится и выведет сообщение – использовать стандартную конфигурацию? – отвечаем:
no
ШАГ 3: Конфигурация интерфейсов
В первую очередь давайте назовем наше устройство для удобства обращения через команду. Я назвал его: «WIFIGID-ROUTER» – смотрим на картинку. Вообще, если у вас будут возникать какие-то вопросы по командам, то смотрите на схему в начале статьи. Итак, обзываем наш роутер:
router#conf t
router (config)#hostname WIFIGID-ROUTER
После этого вместо «router» вы должны увидеть свое название. Вспомним, что у роутера есть два интерфейса,
Внутренний (связь с локальной сетью) – с адресацией:
192.168.1.0/24
Внешний (связь с глобальным интернетом) – понятное дело, что у нас тут будут статические настройки:
- Сеть провайдера: 277.146.101.0
- Маска: 255.255.255.252 (/30)
- Шлюз: 277.146.101.1
Я придумал все эти значения, просто чтобы показать настройку – вы же подставляйте свои циферки. Маршрутизатор будет выступать шлюзом, и наша задача связать две эти сети и дать клиентам доступ в интернет.
Давайте введем настройки внешнего статического адреса:
WIFIGID-ROUTER #conf t
WIFIGID-ROUTER (config)#
interface Fa 4
ip address 227.146.101.2 255.255.255.252
no shutdown
Для подключения к интернету мы используем четвёртый интерфейс. Выше я задал внешний IP как 227.146.101.2, после этого прописал маску и запустил настройку последней командой. Ах да, не забудьте подключить интернет кабель от провайдера. В качестве проверки пингуем сначала сам роутер:
WIFIGID-ROUTER #ping 227.146.101.2
А потом шлюз провайдера:
WIFIGID-ROUTER #ping 227.146.101.1
Если все хорошо, и оба устройства пингуются, идем настраивать интерфейс для связи с локальной сетью. Локальная сеть у нас будет с адресацией:
192.168.1.0
Локальный адрес роутера:
192.168.1.1
Маска стандартная:
255.255.255.0
И еще один совет – обязательно оставьте пару адресов про запас. То есть диапазон адресов будет примерно от 192.168.1.2 до 192.168.1.10. Остальные уже будут использоваться клиентами и другими устройствами в локалке.
Локальный адрес роутера мы будем прописывать в VLAN:
R-DELTACONFIG#conf t
interface Vlan 1
Ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
no shutdown
interface Fa 0
switchport access vlan 1
no shutdown
А для подключения будем использовать интерфейс «Fa 0». Что мы сделали, мы привязали сначала локальный адрес к Vlan. А потом уже VLAN привязали к физическому интерфейсу. Подключаем к этому физическому интерфейсу наш коммутатор, к которому уже будут подключены все рабочие машины, принтеры и другие сетевые устройства.
ШАГ 4: Удаленный доступ к роутеру
Чтобы вам постоянно не сидеть рядом с роутером и подключенным к нему консольным кабелем, я вам советую сразу настроить удалённый доступ. Мы будем использовать подключение по защищенному каналу SSH (второй версии).
WIFIGID-ROUTER (config)#
ip ssh ver 2
ip domain-name wifigid-router-c.ru
Сначала мы запустили SSH-2, а потом прописали произвольный домен. Теперь создаем ключ с помощью команды.
crypto key generate rsa
Далее вылезет вот такая вот надпись:
Вписываем число:
1024
Создаем пользователя с правами админа и паролем. Вместо «password» введите свой пароль.
username admin privilege 15 secret 0 password
Включаем пользователя в базу устройства:
line vty 0 4
login local
И задаем пароль для режима доступа:
enable secret 0 password-2
Опять же вместо «password-2» вводим свой пароль. После этого вы можете использовать любую программу с поддержкой SSH для доступа из локальной сети к этому роутеру.
ШАГ 5: Настройка шлюза
Теперь нам нужно подключиться к шлюзу провайдера:
WIFIGID-ROUTER (config)#
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 227.146.101.1
После этого пингуем любой внешний сайт, но лучше использовать именно IP, а не DNS адрес. Можно даже пропинговать один из DNS-серверов.
WIFIGID-ROUTER#ping 8.8.8.8
ШАГ 6: Настройка NAT
Опять же локальные компьютеры пользователя пока не имеют доступа в интернет, но мы это исправим. Для этого нам нужно настроить динамическую трансляцию локальных IP во внешний. У нас всего один внешний адрес, поэтому локальные адреса должны превращаться в него, проходя через наш роутер, выполняющий роль шлюза.
Прописываем диапазон тех адресов, которые в теории могут использоваться локальными машинами:
WIFIGID-ROUTER (config)#
ip access-list standard ACL_NAT
permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
Далее указываем наш VLAN:
Interface Vlan 1
ip nat inside
Они будет неким локальным интерфейсом, ведь в VLAN может быть сразу несколько адресов. Теперь указываем физический внешний интерфейс, к которому мы подключили провайдерский кабель:
Interface Fa 4
ip nat outside
А теперь мы создаем NAT правило:
ip nat inside source list WIFIGID_NAT interface fa4
Далее мы уже можем из локальной сети с любого компа клиента пинговать любые интернет-адреса. Также в качестве пробы используем внешний IP адрес. Ну и в самом конце не забудьте сохранить конфиг в память роутера:
WIFIGID-ROUTER#write
Видео

Configuring and checking router interfaces are the main tasks of a network engineer, whether it’s the initial configuration of a router or trouble shooting the network connectivity.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to configure serial interface of a Cisco router.
- How to configure Fast Ethernet interface of a Cisco Router.
- And How to Enable an interface of Cisco router.
There is a command which displays all the IP interfaces, which is helpful in troubleshooting and knowing the IP address used on a specific interface.
Show ip interface brief // this is an enable/privileged mode command.
You have to be at the enable mode/privileged mode for executing this command, this command can also be used to know if an interface is enabled or administratively down.
How to find Cisco router IP addresses:
IP addresses of each functional and configured interface of a router must be different, “show ip interface brief” command will display all the configured interfaces along with their assigned ip addresses. Open your routers command line interface.
UpaaeRouter1> enable // go to enable mode/ privileged mode. UpaaeRouter1# show ip interface brief // display all the ip interface of this router

How to configure Ethernet Interface on Cisco Router:
For configuring any interface of a router you should be at global configuration mode.
Assuming you are at user exe mode.
UpaaeRouter1> enable // entering to enable/privileged mode UpaaeRouter1# configure terminal // entering to global configuration mode UpaaeRouter1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0 // 0/0 specifies the port number UpaaeRouter1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.5 255.0.0.0

Confirm if ip address is assigned successfully.
Switch to enable mode, type “show ip interface brief” command and press enter, just like the screenshot below.

How to configure serial interface on cisco router:
Before executing the commands for setting the ip address for serial interface you need to be at the line configuration mode of that specific interface.
For configuring IP Address for any interface you must be in global configuration mode and then enter to the line configuration mode of required interface. In this case we are going to set ip address for serial 0/0/0 interface. Assuming you are at user exe mode.
UpaaeRouter1> enable // entering enable/privileged mode
UpaaeRouter1# configure terminal // entering global configuration mode
UpaaeRouter1(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 // 0/0/0 specifies the port number
UpaaeRouter1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0

Confirming if ip address is assigned successfully.

As you can see that serial interface is properly configured but it is still administratively down, in order to get any interface of cisco router working we need to enable that specific interface.
How to Enable Cisco Router Interface:
By default all of the Cisco router’s interfaces are in down state for security sake, if you want to enable any interface you need to be at the line interface mode, in this example we will enable serial 0/0/0 interface. no shutdown is the command for enabling serial interface.
UpaaeRouter1> enable // entering enable/privileged mode UpaaeRouter1# configure terminal // entering global configuration mode UpaaeRouter1(config)# interface serial 0/0/0 // 0/0/0 specifies the port number UpaaeRouter1(config-if)# no shutdown // command for enabling cisco router interface
That’s it, we hope you enjoyed and learned from this tutorial.