From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This article is about the character encoding commonly mislabeled as «ANSI». For the actual ANSI character encoding, see ASCII. For the actual «ANSI extended Latin» encoding, see ANSEL.
 |
|
| MIME / IANA | windows-1252[1] |
|---|---|
| Alias(es) | cp1252 (code page 1252) |
| Language(s) | All supported by ISO/IEC 8859-1 plus full support for French and Finnish and ligature forms for English; e.g. Danish (except for a rare exceptional letter), Irish, Italian, Norwegian, Portuguese, Spanish, Swedish, German (missing uppercase ẞ), Icelandic, Faroese, Luxembourgish, Albanian, Estonian, Swahili, Tswana, Catalan, Basque, Occitan, Rotokas, Romansh, Dutch (except the IJ/ij character, substituted by IJ/ÿ), and Slovene (except the č character, substituted by ç). |
| Created by | Microsoft |
| Standard | WHATWG Encoding Standard |
| Classification | extended ASCII, Windows-125x |
| Extends | ISO 8859-1 (excluding C1 controls) |
| Transforms / Encodes | ISO 8859-15 |
|
Windows-1252 or CP-1252 (code page 1252) is a single-byte character encoding of the Latin alphabet that was used by default in Microsoft Windows for English and many Romance and Germanic languages including Spanish, Portuguese, French, and German (though missing uppercase ẞ). This character-encoding scheme is used throughout the Americas, Western Europe, Oceania, and much of Africa.
It is the most-used single-byte character encoding in the world. As of January 2023, 1.4%[2] of all web sites declare ISO 8859-1 which is treated as Windows-1252 by all modern browsers (as demanded by the HTML5 standard[3]), plus 0.3% of all websites declared use of Windows-1252,[2][4] for a total of 1.7% (and only 16 of the top 1000 websites[5]). Pages declared as ASCII, or a missing or invalid charset, are also assumed to be Windows-1252 by browsers.[citation needed]
Depending on the country or language, use can be much higher than the global average,[when?] e.g., for Brazil website use is at 9.2%,[6] and in Germany at 3.9%[7][8] (these are the sums of ISO-8859-1 and CP1252 declarations).
Windows-1252 is often assumed to be the encoding of text in operating systems, in particular on Microsoft Windows;[9] this is only gradually being changed to UTF-8.
All modern operating systems, including Windows, now use Unicode code points and text encodings by default, which are portable across all of the world’s major languages.
Details[edit]
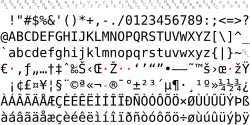
This character encoding is a superset of ISO 8859-1 in terms of printable characters, but differs from the IANA’s ISO-8859-1 by adding additional characters in the 80 to 9F (hex) range (the ISO standards reserve this range for control characters). Notable additional characters include curly quotation marks and all printable characters from ISO 8859-15. It is known to Windows by the code page number 1252, and by the IANA-approved name «windows-1252».
At one stage many Microsoft internet products produced text in Windows-1252 but marked as ISO-8859-1. A result was that all the quotes and apostrophes (produced by «smart quotes») were replaced with question marks or boxes when viewed on non-Windows operating systems. Most modern web browsers and e-mail clients treat the media type charset ISO-8859-1 as Windows-1252 to accommodate such mislabeling. This behavior is now required by the HTML5 specification.[3] Browsers appear to treat the charset «ASCII» and missing charsets the same.
Historically, the phrase «ANSI Code Page» was used in Windows to refer to non-DOS encodings; the intention was that most of these would be ANSI standards such as ISO-8859-1. Even though Windows-1252 was the first and by far most popular code page named so in Microsoft Windows parlance, the code page has never been an ANSI standard. Microsoft explains, «The term ANSI as used to signify Windows code pages is a historical reference, but is nowadays a misnomer that continues to persist in the Windows community.»[10]
In LaTeX packages, CP-1252 is referred to as «ansinew».
IBM uses code page 1252 (CCSID 1252 and euro sign extended CCSID 5348) for Windows-1252.[11][12][13]
It is called «WE8MSWIN1252» by Oracle.[14]
Codepage layout[edit]
The following table shows Windows-1252. Differences from ISO-8859-1 have the Unicode code point number below the character, based on the Unicode.org mapping of Windows-1252 with «best fit». A tooltip, generally available only when one points to the immediate left of the character, shows the Unicode code point name and the decimal Alt code.
| Windows-1252 (CP1252)[15][16][17][18][19] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | NUL | SOH | STX | ETX | EOT | ENQ | ACK | BEL | BS | HT | LF | VT | FF | CR | SO | SI |
| 1_ | DLE | DC1 | DC2 | DC3 | DC4 | NAK | SYN | ETB | CAN | EM | SUB | ESC | FS | GS | RS | US |
| 2_ | SP | ! | » | # | $ | % | & | ‘ | ( | ) | * | + | , | — | . | / |
| 3_ | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | : | ; | < | = | > | ? |
| 4_ | @ | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O |
| 5_ | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | [ | \ | ] | ^ | _ |
| 6_ | ` | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o |
| 7_ | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x | y | z | { | | | } | ~ | DEL |
| 8_ | € 20AC |
‚ 201A |
ƒ 0192 |
„ 201E |
… 2026 |
† 2020 |
‡ 2021 |
ˆ 02C6 |
‰ 2030 |
Š 0160 |
‹ 2039 |
Π0152 |
Ž 017D |
|||
| 9_ | ‘ 2018 |
’ 2019 |
“ 201C |
” 201D |
• 2022 |
– 2013 |
— 2014 |
˜ 02DC |
™ 2122 |
š 0161 |
› 203A |
œ 0153 |
ž 017E |
Ÿ 0178 |
||
| A_ | NBSP | ¡ | ¢ | £ | ¤ | ¥ | ¦ | § | ¨ | © | ª | « | ¬ | SHY | ® | ¯ |
| B_ | ° | ± | ² | ³ | ´ | µ | ¶ | · | ¸ | ¹ | º | » | ¼ | ½ | ¾ | ¿ |
| C_ | À | Á | Â | Ã | Ä | Å | Æ | Ç | È | É | Ê | Ë | Ì | Í | Î | Ï |
| D_ | Ð | Ñ | Ò | Ó | Ô | Õ | Ö | × | Ø | Ù | Ú | Û | Ü | Ý | Þ | ß |
| E_ | à | á | â | ã | ä | å | æ | ç | è | é | ê | ë | ì | í | î | ï |
| F_ | ð | ñ | ò | ó | ô | õ | ö | ÷ | ø | ù | ú | û | ü | ý | þ | ÿ |
According to the information on Microsoft’s and the Unicode Consortium’s websites, positions 81, 8D, 8F, 90, and 9D are unused; however, the Windows API MultiByteToWideChar maps these to the corresponding C1 control codes. The «best fit» mapping documents this behavior, too.[15]
History[edit]
- The first version[when?] of the codepage 1252 used in Microsoft Windows 1.0 did not have positions D7 and F7 defined. All the characters in the ranges 80–9F were undefined too.
- The second version, used in Microsoft Windows 2.0, positions D7, F7, 91, and 92 had been defined.
- The third version, used since Microsoft Windows 3.1, had all the present-day positions defined, except euro sign and Z with caron character pair.
- The final version listed above debuted in Microsoft Windows 98 and was ported to older versions of Windows with the euro symbol update.
OS/2 extensions[edit]
The OS/2 operating system supports an encoding by the name of Code page 1004 (CCSID 1004) or «Windows Extended».[20][21] This mostly matches code page 1252, with the exception of certain C0 control characters being replaced by diacritic characters.
| Code page 1004 (differing rows only)[22][23][24][25] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | NUL | SOH | STX | ETX | ˉ 02C9 |
˘ 02D8 |
˙ 02D9 |
BEL | ˚ 02DA |
HT | ˝ 02DD |
˛ 02DB |
ˇ 02C7 |
CR | SO | SI |
MSDOS extensions [rare][edit]
There is a rarely used, but useful, graphics extended code page 1252 where codes 0x00 to 0x1f allow for box drawing as used in applications such as MSDOS Edit and Codeview. One of the applications to use this code page was an Intel Corporation Install/Recovery disk image utility from mid/late 1995. These programs were written for its P6 User Test Program machines (US example[26]). It was used exclusively in its then EMEA region (Europe, Middle East & Africa). In time the programs were changed to use code page 850.
| Graphics Extended Code Page 1252[citation needed] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | ○ | ■ | ↑ | ↓ | → | ← | ║ | ═ | ╔ | ╗ | ╚ | ╝ | ░ | ▒ | ► | ◄ |
| 1_ | │ | ─ | ┌ | ┐ | └ | ┘ | ├ | ┤ | ┴ | ┬ | ♦ | ┼ | █ | ▄ | ▀ | ▬ |
Palm OS variant[edit]
Each Palm OS device supports a single language and a single character encoding, depending on its locale.[27]
For languages such as English and French, Palm OS uses a custom character encoding based on Windows-1252. For Japanese, it instead uses a multibyte character encoding based on code page 932. Regardless of the system locale, all characters in the range 0x00 to 0x7F are guaranteed to be the same, except 0x5D which is the Yen sign in Japanese and a backslash on all others.[27]
Palm OS 3.1 introduced several changes to the character encoding to better align with Windows-1252:[28]
- The special Palm OS glyphs «shortcut stroke» (0x9D) and «command stroke» (0x9E) were copied to 0x16 and 0x17, to ensure they were in the range guaranteed to be consistent between locales.[28] Starting in Palm OS 3.3, 0x16 and 0x17 are the only code points for those characters,[29] leaving 0x9D and 0x9E undefined.[30]
- The numeric space (0x80) and horizontal ellipsis (0x85) were copied to 0x19 and 0x18 (respectively), to ensure they were in the range guaranteed to be consistent between locales.[28][29]
- The Euro sign was added at 0x80, replacing what was previously the numeric space.[29]
- The playing card suits were copied to the font Symbol 9,[28] although their original code points remain valid.[29][30]
The following is the variant of Windows-1252 used by Palm OS 3.3 onward for English and several other locales.[29] Python gives it the palmos label, describing it as the encoding for Palm OS 3.5.[31] Differences from Windows-1252 have their Unicode code point.
| Palm OS 3.3 character encoding[30][32] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 8_ | €[a] | ‚ | ƒ | „ | …[b] | † | ‡ | ˆ | ‰ | Š | ‹ | Œ | ♦ 2666 |
♣ 2663 |
♥ 2665 |
|
| 9_ | ♠ 2660 |
‘ | ’ | “ | ” | • | – | — | ˜ | ™ | š | › | œ | [c] | [d] | Ÿ |
- ^ Prior to Palm OS 3.1, the character at code point 0x80 was U+2007 NUMERIC SPACE; starting in Palm OS 3.1, 0x80 is the Euro sign and 0x19 is U+2007 NUMERIC SPACE instead.[29]
- ^ Starting in Palm OS 3.1, this character is also duplicated at 0x18.[28][29]
- ^ Prior to Palm OS 3.3, this code point was the Palm OS-exclusive character «shortcut stroke»; starting in Palm OS 3.3, this code point is undefined.[28][29]
- ^ Prior to Palm OS 3.3, this code point was the Palm OS-exclusive character «command stroke»; starting in Palm OS 3.3, this code point is undefined.[28][29]
See also[edit]
- Latin script in Unicode
- Unicode
- Universal Coded Character Set
- European Unicode subset (DIN 91379)
- UTF-8
- Western Latin character sets (computing)
- Windows-1250
- Windows code pages
- ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2
- Extended ASCII
References[edit]
- ^ Character Sets, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), 2018-12-12
- ^ a b «Historical trends in the usage statistics of character encodings for websites, January 2023». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-01-16.
- ^ a b «Encoding». WHATWG. 27 January 2015. sec. 5.2 Names and labels. Archived from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ «Frequenty Asked Questions». w3techs.com.
- ^ «Usage Survey of Character Encodings broken down by Ranking». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ^ «Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use Brazil». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ^ «Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use .de». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ^ «Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use German». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-01-16.
- ^ «c++ — What is the native narrow string encoding on Windows?». Stack Overflow. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ^ Wissink, Cathy (5 April 2002). «Unicode and Windows XP» (PDF). Microsoft. p. 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ «Code page 1252 information document». Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.
- ^ «CCSID 1252 information document». Archived from the original on 2016-03-26.
- ^ «CCSID 5348 information document». Archived from the original on 2014-11-29.
- ^ «Database Client Installation Guide». Oracle. Retrieved 2021-02-14.
- ^ a b «Unicode mappings of Windows-1252 with ‘Best Fit’«. Unicode. Archived from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ Code Page CPGID 01252 (pdf) (PDF), IBM
- ^ Code Page CPGID 01252 (txt), IBM
- ^ International Components for Unicode (ICU), ibm-1252_P100-2000.ucm, 2002-12-03
- ^ International Components for Unicode (ICU), ibm-5348_P100-1997.ucm, 2002-12-03
- ^ «Code page 1004 information document». Archived from the original on 2015-06-25.
- ^ «CCSID 1004 information document». Archived from the original on 2016-03-26.
- ^ «Code Page 01004» (PDF). IBM. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-07-08. (version based on Windows 3.1 version of Windows-1252)
- ^ Code Page CPGID 01004 (pdf) (PDF), IBM
- ^ Code Page CPGID 01004 (txt), IBM
- ^ Borgendale, Ken (2001). «Codepage 1004 — Windows Extended». OS/2 codepages by number. Archived from the original on 2018-05-13. Retrieved 2018-05-13. (version based on current version of Windows-1252)
- ^ Storaasli, Olaf (1996). «Performance of the NASA equation solvers on computational mechanics applications» (PDF). Performance of NASA Equation Solvers on Computational Mechanics Applications. NASA. doi:10.2514/6.1996-1505. S2CID 15711051. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-05-03.
- ^ a b «Chapter 13: Localized Applications». Palm OS Programmer’s Companion (PDF). Palm Computing Platform. March 16, 2000. p. 321.
- ^ a b c d e f g «Appendix B: Compatibility Guide». Palm OS SDK Reference (PDF). Palm Computing Platform. March 16, 2000. pp. 1181–1182.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Walleij, Linus. «Palm Pilot Character Sets And Unicode Mappings». GNU Recode. Datorföreningen vid Lunds Universitet och Lunds Tekniska Högskola. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ a b c Parker, Greg. «Palm OS Built-in Fonts». Sealie Software. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ «codecs — Codec registry and base classes (§ Text Encodings)». The Python Standard Library—Python 3.9.4 Documentation. Python Software Foundation.
- ^ Mullender, Sjoerd (13 July 2002). «Python Character Mapping Codec for Palm OS 3.5». CPython source tree. Python Software Foundation. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft’s code charts for Windows-1252 («Code Page 1252 Windows Latin 1 (ANSI)»)
- Unicode mapping table and code page definition with best fit mappings for Windows-1252
This article is about the character encoding commonly mislabeled as «ANSI». For the actual ANSI character encoding, see ASCII. For the actual «ANSI extended Latin» encoding, see ANSEL.
Windows-1252 or CP-1252 (code page 1252) is a single-byte character encoding of the Latin alphabet that was used by default in Microsoft Windows for English and many Romance and Germanic languages including Spanish, Portuguese, French, and German (though missing uppercase ẞ). This character-encoding scheme is used throughout the Americas, Western Europe, Oceania, and much of Africa.
 |
|
| MIME / IANA | windows-1252[1] |
|---|---|
| Alias(es) | cp1252 (code page 1252) |
| Language(s) | All supported by ISO/IEC 8859-1 plus full support for French and Finnish and ligature forms for English; e.g. Danish (except for a rare exceptional letter), Irish, Italian, Norwegian, Portuguese, Spanish, Swedish, German (missing uppercase ẞ), Icelandic, Faroese, Luxembourgish, Albanian, Estonian, Swahili, Tswana, Catalan, Basque, Occitan, Rotokas, Romansh, Dutch (except the IJ/ij character, substituted by IJ/ÿ), and Slovene (except the č character, substituted by ç). |
| Created by | Microsoft |
| Standard | WHATWG Encoding Standard |
| Classification | extended ASCII, Windows-125x |
| Extends | ISO 8859-1 (excluding C1 controls) |
| Transforms / Encodes | ISO 8859-15 |
|
It is the most-used single-byte character encoding in the world. As of January 2023, 1.4%[2] of all web sites declare ISO 8859-1 which is treated as Windows-1252 by all modern browsers (as demanded by the HTML5 standard[3]), plus 0.3% of all websites declared use of Windows-1252,[2][4] for a total of 1.7% (and only 16 of the top 1000 websites[5]). Pages declared as ASCII, or a missing or invalid charset, are also assumed to be Windows-1252 by browsers.[citation needed]
Depending on the country or language, use can be much higher than the global average,[when?] e.g., for Brazil website use is at 9.2%,[6] and in Germany at 3.9%[7][8] (these are the sums of ISO-8859-1 and CP1252 declarations).
Windows-1252 is often assumed to be the encoding of text in operating systems, in particular on Microsoft Windows;[9] this is only gradually being changed to UTF-8.
All modern operating systems, including Windows, now use Unicode code points and text encodings by default, which are portable across all of the world’s major languages.
Details
Edit
This character encoding is a superset of ISO 8859-1 in terms of printable characters, but differs from the IANA’s ISO-8859-1 by adding additional characters in the 80 to 9F (hex) range (the ISO standards reserve this range for control characters). Notable additional characters include curly quotation marks and all printable characters from ISO 8859-15. It is known to Windows by the code page number 1252, and by the IANA-approved name «windows-1252».
At one stage many Microsoft internet products produced text in Windows-1252 but marked as ISO-8859-1. A result was that all the quotes and apostrophes (produced by «smart quotes») were replaced with question marks or boxes when viewed on non-Windows operating systems. Most modern web browsers and e-mail clients treat the media type charset ISO-8859-1 as Windows-1252 to accommodate such mislabeling. This behavior is now required by the HTML5 specification.[3] Browsers appear to treat the charset «ASCII» and missing charsets the same.
Historically, the phrase «ANSI Code Page» was used in Windows to refer to non-DOS encodings; the intention was that most of these would be ANSI standards such as ISO-8859-1. Even though Windows-1252 was the first and by far most popular code page named so in Microsoft Windows parlance, the code page has never been an ANSI standard. Microsoft explains, «The term ANSI as used to signify Windows code pages is a historical reference, but is nowadays a misnomer that continues to persist in the Windows community.»[10]
In LaTeX packages, CP-1252 is referred to as «ansinew».
IBM uses code page 1252 (CCSID 1252 and euro sign extended CCSID 5348) for Windows-1252.[11][12][13]
It is called «WE8MSWIN1252» by Oracle.[14]
Codepage layout
Edit
The following table shows Windows-1252. Differences from ISO-8859-1 have the Unicode code point number below the character, based on the Unicode.org mapping of Windows-1252 with «best fit». A tooltip, generally available only when one points to the immediate left of the character, shows the Unicode code point name and the decimal Alt code.
| Windows-1252 (CP1252)[15][16][17][18][19] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | NUL | SOH | STX | ETX | EOT | ENQ | ACK | BEL | BS | HT | LF | VT | FF | CR | SO | SI |
| 1_ | DLE | DC1 | DC2 | DC3 | DC4 | NAK | SYN | ETB | CAN | EM | SUB | ESC | FS | GS | RS | US |
| 2_ | SP | ! | » | # | $ | % | & | ‘ | ( | ) | * | + | , | — | . | / |
| 3_ | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | : | ; | < | = | > | ? |
| 4_ | @ | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O |
| 5_ | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | [ | \ | ] | ^ | _ |
| 6_ | ` | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o |
| 7_ | p | q | r | s | t | u | v | w | x | y | z | { | | | } | ~ | DEL |
| 8_ | € 20AC |
‚ 201A |
ƒ 0192 |
„ 201E |
… 2026 |
† 2020 |
‡ 2021 |
ˆ 02C6 |
‰ 2030 |
Š 0160 |
‹ 2039 |
Π0152 |
Ž 017D |
|||
| 9_ | ‘ 2018 |
’ 2019 |
“ 201C |
” 201D |
• 2022 |
– 2013 |
— 2014 |
˜ 02DC |
™ 2122 |
š 0161 |
› 203A |
œ 0153 |
ž 017E |
Ÿ 0178 |
||
| A_ | NBSP | ¡ | ¢ | £ | ¤ | ¥ | ¦ | § | ¨ | © | ª | « | ¬ | SHY | ® | ¯ |
| B_ | ° | ± | ² | ³ | ´ | µ | ¶ | · | ¸ | ¹ | º | » | ¼ | ½ | ¾ | ¿ |
| C_ | À | Á | Â | Ã | Ä | Å | Æ | Ç | È | É | Ê | Ë | Ì | Í | Î | Ï |
| D_ | Ð | Ñ | Ò | Ó | Ô | Õ | Ö | × | Ø | Ù | Ú | Û | Ü | Ý | Þ | ß |
| E_ | à | á | â | ã | ä | å | æ | ç | è | é | ê | ë | ì | í | î | ï |
| F_ | ð | ñ | ò | ó | ô | õ | ö | ÷ | ø | ù | ú | û | ü | ý | þ | ÿ |
According to the information on Microsoft’s and the Unicode Consortium’s websites, positions 81, 8D, 8F, 90, and 9D are unused; however, the Windows API MultiByteToWideChar maps these to the corresponding C1 control codes. The «best fit» mapping documents this behavior, too.[15]
History
Edit
- The first version[when?] of the codepage 1252 used in Microsoft Windows 1.0 did not have positions D7 and F7 defined. All the characters in the ranges 80–9F were undefined too.
- The second version, used in Microsoft Windows 2.0, positions D7, F7, 91, and 92 had been defined.
- The third version, used since Microsoft Windows 3.1, had all the present-day positions defined, except euro sign and Z with caron character pair.
- The final version listed above debuted in Microsoft Windows 98 and was ported to older versions of Windows with the euro symbol update.
OS/2 extensions
Edit
The OS/2 operating system supports an encoding by the name of Code page 1004 (CCSID 1004) or «Windows Extended».[20][21] This mostly matches code page 1252, with the exception of certain C0 control characters being replaced by diacritic characters.
| Code page 1004 (differing rows only)[22][23][24][25] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | NUL | SOH | STX | ETX | ˉ 02C9 |
˘ 02D8 |
˙ 02D9 |
BEL | ˚ 02DA |
HT | ˝ 02DD |
˛ 02DB |
ˇ 02C7 |
CR | SO | SI |
MSDOS extensions [rare]
Edit
There is a rarely used, but useful, graphics extended code page 1252 where codes 0x00 to 0x1f allow for box drawing as used in applications such as MSDOS Edit and Codeview. One of the applications to use this code page was an Intel Corporation Install/Recovery disk image utility from mid/late 1995. These programs were written for its P6 User Test Program machines (US example[26]). It was used exclusively in its then EMEA region (Europe, Middle East & Africa). In time the programs were changed to use code page 850.
| Graphics Extended Code Page 1252[citation needed] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 0_ | ○ | ■ | ↑ | ↓ | → | ← | ║ | ═ | ╔ | ╗ | ╚ | ╝ | ░ | ▒ | ► | ◄ |
| 1_ | │ | ─ | ┌ | ┐ | └ | ┘ | ├ | ┤ | ┴ | ┬ | ♦ | ┼ | █ | ▄ | ▀ | ▬ |
Palm OS variant
Edit
Each Palm OS device supports a single language and a single character encoding, depending on its locale.[27]
For languages such as English and French, Palm OS uses a custom character encoding based on Windows-1252. For Japanese, it instead uses a multibyte character encoding based on code page 932. Regardless of the system locale, all characters in the range 0x00 to 0x7F are guaranteed to be the same, except 0x5D which is the Yen sign in Japanese and a backslash on all others.[27]
Palm OS 3.1 introduced several changes to the character encoding to better align with Windows-1252:[28]
- The special Palm OS glyphs «shortcut stroke» (0x9D) and «command stroke» (0x9E) were copied to 0x16 and 0x17, to ensure they were in the range guaranteed to be consistent between locales.[28] Starting in Palm OS 3.3, 0x16 and 0x17 are the only code points for those characters,[29] leaving 0x9D and 0x9E undefined.[30]
- The numeric space (0x80) and horizontal ellipsis (0x85) were copied to 0x19 and 0x18 (respectively), to ensure they were in the range guaranteed to be consistent between locales.[28][29]
- The Euro sign was added at 0x80, replacing what was previously the numeric space.[29]
- The playing card suits were copied to the font Symbol 9,[28] although their original code points remain valid.[29][30]
The following is the variant of Windows-1252 used by Palm OS 3.3 onward for English and several other locales.[29] Python gives it the palmos label, describing it as the encoding for Palm OS 3.5.[31] Differences from Windows-1252 have their Unicode code point.
| Palm OS 3.3 character encoding[30][32] | ||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| 8_ | €[a] | ‚ | ƒ | „ | …[b] | † | ‡ | ˆ | ‰ | Š | ‹ | Œ | ♦ 2666 |
♣ 2663 |
♥ 2665 |
|
| 9_ | ♠ 2660 |
‘ | ’ | “ | ” | • | – | — | ˜ | ™ | š | › | œ | [c] | [d] | Ÿ |
- ^ Prior to Palm OS 3.1, the character at code point 0x80 was U+2007 NUMERIC SPACE; starting in Palm OS 3.1, 0x80 is the Euro sign and 0x19 is U+2007 NUMERIC SPACE instead.[29]
- ^ Starting in Palm OS 3.1, this character is also duplicated at 0x18.[28][29]
- ^ Prior to Palm OS 3.3, this code point was the Palm OS-exclusive character «shortcut stroke»; starting in Palm OS 3.3, this code point is undefined.[28][29]
- ^ Prior to Palm OS 3.3, this code point was the Palm OS-exclusive character «command stroke»; starting in Palm OS 3.3, this code point is undefined.[28][29]
See also
Edit
- Latin script in Unicode
- Unicode
- Universal Coded Character Set
- European Unicode subset (DIN 91379)
- UTF-8
- Western Latin character sets (computing)
- Windows-1250
- Windows code pages
- ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2
- Extended ASCII
References
Edit
- ^ Character Sets, Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), 2018-12-12
- ^ a b «Historical trends in the usage statistics of character encodings for websites, January 2023». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-01-16.
- ^ a b «Encoding». WHATWG. 27 January 2015. sec. 5.2 Names and labels. Archived from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ «Frequenty Asked Questions». w3techs.com.
- ^ «Usage Survey of Character Encodings broken down by Ranking». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ^ «Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use Brazil». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ^ «Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use .de». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ^ «Distribution of Character Encodings among websites that use German». w3techs.com. Retrieved 2023-01-16.
- ^ «c++ — What is the native narrow string encoding on Windows?». Stack Overflow. Retrieved 2023-02-16.
- ^ Wissink, Cathy (5 April 2002). «Unicode and Windows XP» (PDF). Microsoft. p. 1. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ «Code page 1252 information document». Archived from the original on 2016-03-03.
- ^ «CCSID 1252 information document». Archived from the original on 2016-03-26.
- ^ «CCSID 5348 information document». Archived from the original on 2014-11-29.
- ^ «Database Client Installation Guide». Oracle. Retrieved 2021-02-14.
- ^ a b «Unicode mappings of Windows-1252 with ‘Best Fit’«. Unicode. Archived from the original on 4 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ Code Page CPGID 01252 (pdf) (PDF), IBM
- ^ Code Page CPGID 01252 (txt), IBM
- ^ International Components for Unicode (ICU), ibm-1252_P100-2000.ucm, 2002-12-03
- ^ International Components for Unicode (ICU), ibm-5348_P100-1997.ucm, 2002-12-03
- ^ «Code page 1004 information document». Archived from the original on 2015-06-25.
- ^ «CCSID 1004 information document». Archived from the original on 2016-03-26.
- ^ «Code Page 01004» (PDF). IBM. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-07-08. (version based on Windows 3.1 version of Windows-1252)
- ^ Code Page CPGID 01004 (pdf) (PDF), IBM
- ^ Code Page CPGID 01004 (txt), IBM
- ^ Borgendale, Ken (2001). «Codepage 1004 — Windows Extended». OS/2 codepages by number. Archived from the original on 2018-05-13. Retrieved 2018-05-13. (version based on current version of Windows-1252)
- ^ Storaasli, Olaf (1996). «Performance of the NASA equation solvers on computational mechanics applications» (PDF). Performance of NASA Equation Solvers on Computational Mechanics Applications. NASA. doi:10.2514/6.1996-1505. S2CID 15711051. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2019-05-03.
- ^ a b «Chapter 13: Localized Applications». Palm OS Programmer’s Companion (PDF). Palm Computing Platform. March 16, 2000. p. 321.
- ^ a b c d e f g «Appendix B: Compatibility Guide». Palm OS SDK Reference (PDF). Palm Computing Platform. March 16, 2000. pp. 1181–1182.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Walleij, Linus. «Palm Pilot Character Sets And Unicode Mappings». GNU Recode. Datorföreningen vid Lunds Universitet och Lunds Tekniska Högskola. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ a b c Parker, Greg. «Palm OS Built-in Fonts». Sealie Software. Retrieved 10 October 2023.
- ^ «codecs — Codec registry and base classes (§ Text Encodings)». The Python Standard Library—Python 3.9.4 Documentation. Python Software Foundation.
- ^ Mullender, Sjoerd (13 July 2002). «Python Character Mapping Codec for Palm OS 3.5». CPython source tree. Python Software Foundation. Retrieved 9 December 2021.
External links
Edit
- Microsoft’s code charts for Windows-1252 («Code Page 1252 Windows Latin 1 (ANSI)»)
- Unicode mapping table and code page definition with best fit mappings for Windows-1252
Кодировка windows 1252, также известная как кодировка Latin-1 или кодировка Windows Western, является одной из наиболее популярных кодировок, используемых в операционной системе Windows. Она предназначена для отображения символов латинского алфавита и распространена в странах западной Европы и Северной Америки.
В кодировке windows 1252 каждому символу соответствует определенный числовой код. Это позволяет компьютерам и программам правильно интерпретировать и отображать текст, содержащий символы этой кодировки. Кодировка windows 1252 включает в себя широкий набор символов, включая основные символы латинского алфавита, специальные символы, знаки пунктуации и символы валют.
Для использования кодировки windows 1252 вам нужно убедиться, что ваш текстовый редактор или программа поддерживает эту кодировку. В большинстве редакторов есть возможность выбрать нужную кодировку при сохранении файла или открытии нового проекта. Если вы работаете с веб-страницей, то вам также потребуется указать кодировку в заголовке страницы, чтобы браузер правильно отображал текст.
Например, если вы создаете веб-страницу с кодировкой windows 1252, то вам нужно добавить следующую строку в заголовок страницы: <meta charset=»windows-1252″>. Это сообщает браузеру о том, как правильно интерпретировать символы на странице и отобразить их пользователю.
Использование кодировки windows 1252 может быть полезно в тех случаях, когда вам нужно работать с текстом, содержащим символы латинского алфавита или специальные символы, которые отсутствуют в других кодировках. Также, если вы взаимодействуете с системами, которые используют эту кодировку, то использование windows 1252 обеспечит совместимость и правильную обработку текста.
Содержание
- Что представляет собой кодировка windows 1252 и для чего она нужна?
- Windows 1252: основные характеристики и история создания
- В чем отличие кодировки windows 1252 от других кодировок?
- Примеры использования кодировки windows 1252
Что представляет собой кодировка windows 1252 и для чего она нужна?
Она представляет собой символьную таблицу, которая определяет соответствие между числовыми значениями и буквами, цифрами, знаками препинания и другими символами, используемыми в тексте.
Кодировка Windows-1252 особенно полезна для работы с символами, которые не представлены в стандартной кодировке ASCII, таких как символы с диакритическими знаками (например, умляуты, акценты) и специальные символы (например, символы математических операций, символы валюты).
Она широко используется при создании веб-страниц и обработке текстовых данных в различных приложениях, таких как текстовые редакторы, электронные таблицы, базы данных и другие программы.
Windows 1252: основные характеристики и история создания
Windows 1252 представляет собой 8-битную кодировку, каждому символу из таблицы символов Unicode сопоставляется уникальное число. Коды символов от 0 до 127 включительно совпадают с кодами ASCII. Кодировка содержит символы различных языков, включая латинский алфавит, немецкие буквы, французские символы, испанские буквы и другие символы, часто используемые в европейских языках.
Одна из особенностей Windows 1252 заключается в том, что она включает несколько символов, которые отсутствуют в таблице символов ASCII. Например, это включает символы с диакритическими знаками, такие как французская «é», немецкие «ä», «ö», «ü», испанская «ñ» и другие символы, которые не представлены в ASCII.
Windows 1252 поддерживается многими программными продуктами и операционными системами, включая Microsoft Windows, MacOS, Linux и другие. Важно отметить, что кодировка Windows 1252 не содержит символов ряда других языков, таких как русский или китайский. Для поддержки символов этих языков используются другие кодировки, например, UTF-8 или UTF-16.
Использование кодировки Windows 1252 может быть полезно, если вы работаете с текстом на европейских языках и хотите обеспечить совместимость вашего текста с программами и операционными системами, которые не поддерживают более современные кодировки символов.
В чем отличие кодировки windows 1252 от других кодировок?
Отличительной особенностью кодировки Windows 1252 является то, что она включает символы, отсутствующие в других популярных кодировках, таких как ASCII и UTF-8. Например, она содержит символы с западноевропейскими знаками препинания, специальными символами, символами валюты, математическими символами и символами, используемыми в декоративном искусстве.
Кодировка Windows 1252 имеет фиксированное отображение каждого символа на бит. Каждый символ представлен одним байтом (8 бит), поэтому может быть представлено 256 различных символов. Это позволяет использовать кодировку Windows 1252 для представления текста, который содержит символы из западноевропейских алфавитов, таких как английский, французский, немецкий, итальянский и испанский.
Однако кодировка Windows 1252 не поддерживает символы, используемые в других алфавитах, таких как кириллический или японский. Это ограничение может вызывать проблемы при отображении и обработке некоторых иностранных языков на компьютерах, использующих кодировку Windows 1252. В таких случаях рекомендуется использовать другие кодировки, такие как UTF-8 или UTF-16, которые поддерживают широкий спектр символов.
Примеры использования кодировки windows 1252
Пример 1:
Предположим, у вас есть текстовый файл, который использует кодировку windows 1252. Чтобы правильно отобразить содержимое этого файла, вы можете использовать следующий HTML-код:
<meta charset=»windows-1252″>
Этот код гарантирует, что браузер правильно интерпретирует символы из кодировки windows 1252 и отображает их на веб-странице.
Пример 2:
Если вам необходимо вставить специальные символы, такие как символ копирайта (©) или торговой марки (™), в ваш HTML-код, вы можете использовать соответствующие числовые коды символов для кодировки windows 1252.
Например, чтобы вставить символ копирайта, вы можете использовать следующий код:
©
Это преобразуется в символ копирайта на веб-странице.
Пример 3:
Еще одним примером использования кодировки windows 1252 является отправка данных с помощью HTML-формы. Если вы хотите, чтобы введенные данные пользователя отображались корректно на сервере, вы должны указать кодировку формы следующим образом:
<form accept-charset=»windows-1252″>
Это гарантирует, что данные будут отправлены с использованием кодировки windows 1252 и будут корректно интерпретированы на сервере.
Windows-1252 или CP-1252 (кодовая страница 1252) — это однобайтовая кодировка символов латинского алфавита, используемая по умолчанию в устаревших компонентах Microsoft Windows для английского и многих европейских языков, включая испанский, французский и немецкий.
Это наиболее часто используемая однобайтовая кодировка символов в мире.По состоянию на ноябрь 2022 года в Интернете [обновление] 0,3% всех веб-сайтов заявили об использовании Windows-1252[2][3], но в то же время 1,3% [2] использовали ISO 8859-1 (в то время как только 8 из 1000 лучших веб-сайтов [4]),которая по стандартам HTML5 должна считаться той же кодировкой[5], так что 1,6% веб-сайтов эффективно используют Windows-1252. Страницы, объявленные как US-ASCII, также будут учитываться как этот набор символов. Неизвестное (но, вероятно, большое) подмножество других страниц использует только ASCII-часть UTF-8 или только коды, соответствующие Windows-1252 из их объявленного набора символов, и их также можно подсчитать.
В зависимости от страны, использование может быть намного выше, чем в среднем по миру, например, для Бразилии, согласно использованию веб-сайта (включая ISO-8859-1), использование составляет 7,9%[6], а в Германии — 4,0%[7][8].
Эта кодировка символов является надмножеством стандарта ISO 8859-1 с точки зрения символов, доступных для печати, но отличается от стандарта IANA ISO-8859-1 использованием отображаемых символов, а не управляющих символов в диапазоне от 80 до 9F (hex). Заметные дополнительные символы включают фигурные кавычки и все доступные для печати символы, которые есть в ISO 8859-15 (в разных местах, чем ISO 8859-15). Он известен Windows под номером кодовой страницы 1252 и одобренным IANA именем «windows-1252».
Очень часто текст Windows-1252 ошибочно помечается кодировкой ISO-8859-1. Общим результатом было то, что все кавычки и апострофы (создаваемые «умными кавычками» в текстовых редакторах) были заменены вопросительными знаками или прямоугольниками в операционных системах, отличных от Windows, что затрудняло чтение текста. Большинство современных веб-браузеров и почтовых клиентов обрабатывают кодировку типа носителя ISO-8859-1 как Windows-1252, чтобы учесть такую неправильную маркировку. Теперь это стандартное поведение в спецификации HTML5, которая требует, чтобы документы, объявленные как ISO-8859-1, фактически анализировались в кодировке Windows-1252.[5]
Исторически фраза «Кодовая страница ANSI» использовалась в Windows для обозначения кодировок, отличных от DOS; предполагалось, что большинство из них будут стандартами ANSI, такими как ISO-8859-1. Несмотря на то, что Windows-1252 была первой и на сегодняшний день самой популярной кодовой страницей, названной так на языке Microsoft Windows, кодовая страница никогда не была стандартом ANSI. Microsoft объясняет: «Термин ANSI, используемый для обозначения кодовых страниц Windows, является исторической ссылкой, но в настоящее время это неправильное название, которое продолжает сохраняться в сообществе Windows».[9]
В пакетах LaTeX CP-1252 упоминается как «ansinew».
IBM использует кодовую страницу 1252 (CCSID 1252 и расширенный CCSID 5348 знака евро) для Windows-1252.[10][11][12]
Oracle называет его «WE8MSWIN1252″[13].
Распространенные кодировки
Функционал сайта временно ограничен. Приносим свои извинения
Для преобразования или определения кодировки скопируйте исходный текст в это поле:
Выберите исходную кодировку:
Выберите нужную кодировку:
Результат перекодирования появится здесь:
Кодовая страница, используемая для латинских алфавитов западноевропейских языков
 |
|
| MIME / IANA | windows-1252 |
|---|---|
| Язык (и) | Практически все поддерживаются ISO / IEC 8859-1 например английский, ирландский, итальянский, норвежский, португальский, испанский, шведский. Плюс еще немецкий, финский и французский. И голландский, кроме символа. И словенский, за исключением символа č. |
| Создано | Microsoft |
| Standard | WHATWG Encoding Standard |
| Classification | расширенный ASCII, Windows-125x |
| Расширяет | ISO 8859-1 (за исключением элементов управления C1) |
| Преобразует / кодирует | ISO 8859-15 |
|
Windows-1252 или CP -1252 (кодовая страница 1252) — однобайтовая кодировка символов из латинского алфавита, используемая по умолчанию в устаревшем компоненты Microsoft Windows для английского и многих европейских языков, включая испанский, французский и немецкий.
Это наиболее часто используемая кодировка однобайтовых символов в мире. По состоянию на октябрь 2020 года 0,4% всех веб-сайтов заявили об использовании Windows-1252, но в то же время 1,9% использовали ISO 8859-1 (в то время как только 0,8% из 1000 сайтов), что, по Стандарты HTML5 следует рассматривать как одну и ту же кодировку, так что 2,3% веб-сайтов эффективно используют Windows-1252. Страницы, объявленные как US- ASCII, также будут считаться этим набором символов. Неизвестное (но, вероятно, большое) подмножество других страниц использует только часть ASCII UTF-8 или только коды, соответствующие Windows-1252 из их объявленного набора символов, и также может быть подсчитано.
Содержание
- 1 Подробности
- 2 Набор символов
- 2.1 История
- 2.2 Расширения OS / 2
- 2.3 Расширения MSDOS [редко]
- 3 См. Также
- 4 Ссылки
- 5 Внешние ссылки
Подробности
Эта кодировка символов является надмножеством из ISO 8859-1 с точки зрения печатаемых символов, но отличается от ISO- 8859-1, используя отображаемые символы вместо управляющих символов в диапазоне от 80 до 9F (шестнадцатеричный ). Примечательные дополнительные символы включают фигурные кавычки и все печатаемые символы, которые находятся в ISO 8859-15 (в местах, отличных от ISO 8859-15). Он известен Windows по кодовой странице номер 1252 и по одобренному IANA имени «windows-1252».
Очень часто неправильно маркировать текст Windows-1252 меткой кодировки ISO-8859-1. Обычным результатом было то, что все кавычки и апострофы (созданные «умными кавычками» в текстовых редакторах) были заменены вопросительными знаками или квадратами в операционных системах, отличных от Windows, что затрудняло чтение текста. Большинство современных веб-браузеров и клиентов электронной почты обрабатывают кодировку типа носителя ISO-8859-1 как Windows-1252, чтобы избежать такой неправильной маркировки. Теперь это стандартное поведение в спецификации HTML5, которое требует, чтобы документы, рекламируемые как ISO-8859-1, фактически анализировались в кодировке Windows-1252.
Исторически фраза «Кодовая страница ANSI» использовалась в Windows для обозначения кодировок, отличных от DOS; Предполагалось, что большинство из них будут стандартами ANSI, такими как ISO-8859-1. Несмотря на то, что Windows-1252 была первой и, безусловно, самой популярной кодовой страницей, названной так на языке Microsoft Windows, кодовая страница никогда не была стандартом ANSI. Microsoft объясняет: «Термин ANSI, используемый для обозначения кодовых страниц Windows, является исторической справкой, но в настоящее время это неправильное название, которое продолжает сохраняться в сообществе Windows».
В пакетах LaTeX, CP-1252 упоминается как «ансинью».
IBM использует кодовую страницу 1252 (CCSID 1252 и знак евро расширенный CCSID 5348) для Windows-1252.
Набор символов
В следующей таблице показан Windows-1252. Каждый символ отображается с его эквивалентом Unicode на основе сопоставления Unicode.org Windows-1252 с «наилучшим соответствием». Десятичные числа (стиль 0123 ) — это альтернативный код, который можно использовать для их ввода в системах Windows. Отличия от ISO-8859-1 показаны более темным оттенком поверх цвета их легенды.
| _0 | _1 | _2 | _3 | _4 | _5 | _6 | _7 | _8 | _9 | _A | _B | _C | _D | _E | _F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0_. 0 | NUL. 0000. 0 | SOH. 0001. 01 | STX. 0002. 02 | ETX. 0003. 03 | EOT. 0004. 04 | ENQ. 0005. 05 | ACK. 0006. 06 | BEL. 0007. 07 | BS. 0008. 08 | HT. 0009. 09 | LF. 000A. 010 | VT. 000B. 011 | FF. 000C. 012 | CR. 000D. 013 | SO. 000E. 014 | SI. 000F. 015 |
| 1_. 16 | DLE. 0010. 016 | DC1. 0011. 017 | DC2. 0012. 018 | DC3. 0013. 019 | DC4. 0014. 020 | NAK. 0015. 021 | SYN. 0016. 022 | ETB. 0017. 023 | CAN. 0018. 024 | EM. 0019. 025 | SUB. 001A. 026 | ESC. 001B. 027 | FS. 001C. 028 | GS. 001D. 029 | RS. 001E. 030 | US. 001F. 031 |
| 2_. 32 | SP. 0020. 32 | !. 0021. 33 | «. 0022. 34 | #. 0023. 35 | $. 0024. 36 | %. 0 025. 37 | . 0026. 38 | ‘. 0027. 39 | (. 0028. 40 | ). 0029. 41 | *. 002A. 42 | +. 002B. 43 | ,. 002C. 44 | -. 002D. 45 | .. 002E. 46 | /. 002F. 47 |
| 3_. 48 | 0. 0030. 48 | 1. 0031. 49 | 2. 0032. 50 | 3. 0033. 51 | 4. 0034. 52 | 5. 0035. 53 | 6. 0036. 54 | 7. 0037. 55 | 8. 0038. 56 | 9. 0039. 57 | :. 003A. 58 | ;. 003B. 59 | <. 003C. 60 | =. 003D. 61 | >. 003E. 62 | ?. 003F. 63 |
| 4_. 64 | @. 0040. 64 | A. 0041. 65 | B. 0042. 66 | C. 0043. 67 | D. 0044. 68 | E. 0045. 69 | F. 0046. 70 | G. 0047. 71 | H. 0048. 72 | I. 0049. 73 | J. 004A. 74 | K. 004B. 75 | L. 004C. 76 | M. 004D. 77 | N. 004E. 78 | O. 004F. 79 |
| 5_. 80 | P. 0050. 80 | Q. 0051. 81 | R. 0052. 82 | S. 0053. 83 | T. 0054. 84 | U. 0055. 85 | V. 0056. 86 | W. 0057. 87 | X. 0058. 88 | Y. 0059. 89 | Z. 005A. 90 | [. 005B. 91 | \. 005C. 92 | ]. 005D. 93 | ^. 005E. 94 | _. 005F. 95 |
| 6_. 96 | `. 0060. 96 | a. 0061. 97 | b. 0062. 98 | c. 0063. 99 | d. 0064. 100 | e. 0065. 101 | f. 0066. 102 | g. 0067. 103 | h. 0068. 104 | i. 0069. 105 | j. 006A. 106 | k. 006B. 107 | l. 006C. 108 | m. 006D. 109 | n. 006E. 110 | o. 006F. 111 |
| 7_. 112 | p. 0070. 112 | q. 0071. 113 | r. 0072. 114 | s. 0073. 115 | t. 0074. 116 | u. 0075. 117 | v. 0076. 11 8 | w. 0077. 119 | x. 0078. 120 | y. 0079. 121 | z. 007A. 122 | {. 007B. 123 | |. 007C. 124 | }. 007D. 125 | ~. 007E. 126 | DEL. 007F. 0127 |
| 8_. 128 | €. 20AC. 0128 | ‚. 201A. 0130 | ƒ. 0192. 0131 | „. 201E. 0132 | …. 2026. 0133 | †. 2020. 0134 | ‡. 2021. 0135 | ˆ. 02C6. 0136 | ‰. 2030. 0137 | Š. 0160. 0138 | ‹. 2039. 0139 | Œ. 0152. 0140 | Ž. 017D. 0142 | |||
| 9_. 144 | ‘. 2018. 0145 | ’. 2019. 0146 | “. 201C. 0147 | ”. 201D. 0148 | •. 2022. 0149 | –. 2013. 0150 | —. 2014. 0151 | ˜. 02DC. 0152 | ™. 2122. 0153 | š. 0161. 0154 | ›. 203A. 0155 | œ. 0153. 0156 | ž. 017E. 0158 | Ÿ. 0178. 0159 | ||
| A_. 160 | NBSP. 00A0. 0160 | ¡. 00A1. 0161 | ¢. 00A2. 0162 | £. 00A3. 0163 | ¤. 00A4. 0164 | ¥. 00A5. 0165 | ¦. 00A6. 0166 | §. 00A7. 0167 | ¨. 00A8. 0168 | ©. 00A9. 0169 | ª. 00AA. 0170 | «. 00AB. 0171 | ¬. 00AC. 0172 | SHY. 00AD. 0173 | ®. 00AE. 0174 | ¯. 00AF. 0175 |
| B_. 176 | °. 00B0. 0176 | ±. 00B1. 0177 | ². 00B2. 0178 | ³. 00B3. 0179 | ´. 00B4. 0180 | µ. 00B5. 0181 | ¶. 00B6. 0182 | ·. 00B7. 0183 | ¸. 00B8. 0184 | ¹. 00B9. 0185 | º. 00BA. 0186 | ». 00BB. 0187 | ¼. 00BC. 0188 | ½. 00BD. 0189 | ¾. 00BE. 0190 | ¿. 00BF. 0191 |
| C_. 192 | À. 00C0. 0192 | Á. 00C1. 0193 | Â. 00C2. 0194 | Ã. 00C3. 0195 | Ä. 00C4. 0196 | Å. 00C5. 0197 | Æ. 00C6. 0198 | Ç. 00C7. 0199 | È. 00C8. 0200 | É. 00C9. 0201 | Ê. 00CA. 0202 | Ë. 00CB. 0203 | Ì. 00CC. 0204 | Í. 00CD. 0205 | Î. 00CE. 0206 | Ï. 00CF. 0207 |
| D_. 208 | Ð. 00D0. 0208 | Ñ. 00D1. 0209 | Ò. 00D2. 0210 | Ó. 00D3. 0211 | Ô. 00D4. 0212 | Õ. 00D5. 0213 | Ö. 00D6. 0214 | ×. 00D7. 0215 | Ø. 00D8. 0216 | Ù. 00D9. 0217 | Ú. 00DA. 0218 | Û. 00DB. 0219 | Ü. 00DC. 0220 | Ý. 00DD. 0221 | Þ. 00DE. 0222 | ß. 00DF. 0223 |
| E_. 224 | à. 00E0. 0224 | á. 00E1. 0225 | â. 00E2. 0226 | ã. 00E3. 0227 | ä. 00E4. 0228 | å. 00E5. 0229 | æ. 00E6. 0230 | ç. 00E7. 0231 | è. 00E8. 0232 | é. 00E9. 0233 | ê. 00EA. 0234 | ë. 00EB. 0235 | ì. 00EC. 0236 | í. 00ED. 0237 | î. 00EE. 0238 | ï. 00EF. 0239 |
| F_. 240 | ð. 00F0. 0240 | ñ. 00F1. 0241 | ò. 00F2. 0242 | ó. 00F3. 0243 | ô. 00F4. 0244 | õ. 00F5. 0245 | ö. 00F6. 0246 | ÷. 00F7. 0247 | ø. 00F8. 0248 | ù. 00F9. 0249 | ú. 00FA. 0250 | û. 00FB. 0251 | ü. 00FC. 0252 | ý. 00FD. 0253 | þ. 00FE. 0254 | ÿ. 00FF. 0255 |
L etter Число Знаки пунктуации Символ Другое Не определено
Согласно информации на сайтах Microsoft и Консорциума Unicode, позиции 81, 8D, 8F, 90 и 9D не используются; однако Windows API MultiByteToWideChar сопоставляет их с соответствующими управляющими кодами C1. Отображение «наилучшего соответствия» также документирует это поведение.
История
- В первой версии кодовой страницы 1252, используемой в Microsoft Windows 1.0, не были определены позиции D7 и F7. Все символы в диапазонах 80–9F также не были определены.
- Вторая версия, используемая в Microsoft Windows 2.0, позиции D7, F7, 91 и 92 были определены.
- Третья версия версия, используемая с Microsoft Windows 3.1, имела все современные позиции, кроме знака евро и Z с парой символов caron.
- Последняя версия, указанная выше дебютировал в Microsoft Windows 98 и был перенесен на более старые версии Windows с обновлением символа евро.
Расширения OS / 2
Операционная система OS / 2 поддерживает кодировку по имени из Кодовая страница 1004 (CCSID 1004) или «Windows Extended». Это в основном соответствует кодовой странице 1252, за исключением некоторых управляющих символов C0, замененных на диакритические символы. Отличия от ISO-8859-1 показаны более темным оттенком поверх цветов их легенды.
| _0 | _1 | _2 | _3 | _4 | _5 | _6 | _7 | _8 | _9 | _A | _B | _C | _D | _E | _F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0_. 0 | NUL. 0000 | SOH. 0001 | STX. 0002 | ETX. 0003 | ˉ. 02C9 | ˘. 02D8 | ˙. 02D9 | BEL. 0007 | ˚. 02DA | HT. 0009 | ˝. 02DD | ˛. 02DB | ˇ. 02C7 | CR. 000D | SO. 000E | SI. 000F |
Расширения MSDOS [редко]
Существует редко используемая, но полезная расширенная кодовая страница 1252 графики, где коды от 0x00 до 0x1f позволяют рисовать прямоугольники, как это используется в таких приложениях, как MSDOS Edit и Codeview. Одним из приложений, использующих эту кодовую страницу, была утилита установки / восстановления образа диска корпорации Intel, выпущенная в середине / конце 1995 года. Эти программы были написаны для компьютеров с пользовательской тестовой программой P6 (пример для США). Он использовался исключительно в тогдашнем регионе EMEA (Европа, Ближний Восток и Африка). Со временем программы были изменены для использования кодовой страницы 850.
| _0 | _1 | _2 | _3 | _4 | _5 | _6 | _7 | _8 | _9 | _A | _B | _C | _D | _E | _F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0_. 0 | ○. 25CB | ■. 25A0 | ↑. 2191 | ↓. 2193 | →. 2192 | ←. 2190 | ║. 2551 | ═. 2550 | ╔. 2554 | ╗. 2557 | ╚. 255A | ╝. 255D | ░. 2591 | ▒. 2592 | ►. 25BA | ◄. 25C4 |
| 1_. 16 | │. 2502 | ─. 2500 | ┌. 250C | ┐. 2510 | └. 2514 | ┘. 2518 | ├. 251C | ┤. 2524 | ┴. 2534 | ┬. 252C | ♦. 2666 | ┼. 253C | █. 2588 | ▄. 2584 | ▀. 2580 | ▬. 25AC |
См. Также
- Наборы символов западной латиницы (вычисления)
- Windows-1250
Ссылки
Внешние ссылки
- Microsoft кодовые диаграммы для Windows-1252 («Кодовая страница 1252 Windows Latin 1 (ANSI)»)
- Таблица сопоставления Unicode и определение кодовой страницы с наиболее подходящими сопоставлениями для Windows-1252