Идея беспроводной мобильной связи зародилась в головах ученых еще в начале 20-го века. Работы по созданию системы радиотелефонной связи активно велись и в западных странах и в Советском Союзе, однако первая рабочая модель сотового телефона появилась в лишь в 1973 году, когда американская компания Motorola представила миру DynaTac — первый прототип портативного сотового телефона.
Сегодня жизнь человека практически невозможно представить без мобильных устройств, использующих технологии беспроводной связи. За последние 35 лет сменилось 4 поколения сотовой связи, и на смену четвертому приходит пятое поколение, внедрение которого ожидается к 2020 году. Об истории развития сотовой связи, поколениях и применяемых технологиях пойдет речь в данной статье.
Первое поколение — 1G
Все стандарты первого поколения были аналоговыми и имели массу недостатков. Проблемы были как с качеством сигнала, так и с совместимостью технологий.
Среди стандартов мобильной связи первого поколения, наибольшее распространение получили следующие:
• AMPS (Advanced Mobile Phone Service – усовершенствованная подвижная телефонная служба). Использовался в США, Канаде, Австралии и странах Южной Америки;
• TACS (Total Access Communications System — тотальная система доступа к связи) Использовался в европейских странах, таких как Англия, Италия, Испания, Австрия и ещё ряд стран;
• NMT (Nordic Mobile Telephone – северный мобильный телефон). Применялся в скандинавских странах.
• TZ-801 (TZ-802,TZ-803), разработанные в Японии.
Не смотря на имеющиеся проблемы с качеством и совместимостью стандартов, аналоговым сетям мобильной связи все же нашли коммерческое применение. Первыми это сделали японцы в 1979 году, затем в 1981 году аналоговая сеть была запущена в Дании, Финляндии, Норвегии и Швеции, и в 1983 году в США.
Второе поколение — 2G
В 1982 году Европейской конференцией почтовых и телекоммуникационных ведомств была сформирована рабочая группа, названная GSM (франц. Groupe Spécial Mobile — специальная группа по подвижной связи). Целью создания группы, является изучение и разработка пан-Европейской наземной системы подвижной связи общего применения.
В 1989 году изучение и разработку второго поколения мобильной связи продолжил Европейский институт стандартов в телекоммуникации. Аббревиатура GSM тогда приобрела иное значение — Global System for Mobile Communications (глобальная система для подвижной связи).
В 1991 году появились первые коммерческие мобильные сети второго поколения. Главным отличием сетей второго поколения от первого является цифровой метод передачи данных. Технологии передачи данных в цифровом виде позволили внедрить сервис обмена текстовыми сообщениями (SMS), а позднее, с помощью протокола WAP (Wireless Application Protocol — беспроводной протокол передачи данных) стал возможен выход в Интернет с мобильных устройств. Скорость передачи данных в сетях второго поколения составляла не более 19,5 кбит/с.
Дальнейший рост потребности пользователей в мобильном интернете послужил толчком для разработки сетей следующих поколений. Промежуточными этапами между сетями 2G и 3G стали поколения, условно называемые 2,5G и 2,7G.
Поколением 2,5G обозначили технологию GPRS (General Packet Radio Service — пакетная радиосвязь общего пользования), которая позволила увеличить скорость передачи данных до 172 кбит/с в теории, и до 80 кбит/с в реальности.
Поколением 2,7G назвали технологию EDGE (EGPRS) (Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution), которая функционирует как надстройка над 2G и 2.5G. Скорость передачи данных в таких сетях теоретически может достигать 474 кбит/с, однако на практике редко доходит до 150 кБит/с.
Третье поколение — 3G
Работы по созданию технологий третьего поколения начались в 1990-х годах, а внедрение состоялось только в начале 2000-х (в 2002 году в России). Разработанные к тому времени стандарты основывались на технологии CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access — множественный доступ с кодовым разделением).
Третье поколение мобильной связи включает 5 стандартов: UMTS/WCDMA, CDMA2000/IMT-MC, TD-CDMA/TD-SCDMA, DECT и UWC-136. Наиболее распространенными из них являются стандарты UMTS/WCDMA и CDMA2000/IMT-MC. В России популярность получил стандарт UMTS/WCDMA. Далее предлагаем остановиться на основных технологиях 3G:
UMTS
UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System – универсальная сисема мобильной электросвязи) – технология сотовой связи разработанная для внедрения 3G в Европе. Используемый диапазон частот 2110-2200 МГц. (зачастую ширина канала 5 МГц). Скорость передачи данных в режиме UMTS составляет не более 2 Мбит/с (для неподвижного абонента), а при движении абонента, в зависимости от скорости движения, может опуститься до 144 Кбит/с.
HSDPA
HSDPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access — высокоскоростная пакетная передача данных от базовой станции к мобильному телефону) – первый из семейства протоколов сотовой связи HSPA (High Speed Packet Access — высокоскоростная пакетная передача данных), основанный на UMTS технологии. Данный протокол и последующие его версии позволили значительно увеличить скорость передачи данных в сетях 3G. В первой своей реализации протокол HSDPA имел максимальную скорость передачи данных 1,2 Мбит/с. Скорость передачи данных в следующей реализации протокола HSDPA составляла уже 3,6 Мбит/с. На этот момент 3G модемы получили большую популярность и у большинства пользователей были модемы поддерживающие именно этот стандарт, наиболее популярные модель Huawei E1550, ZTE mf180 (такие экземпляры встречаются до сих пор). В результате дальнейшего развития протокола HSDPA удалось увеличить скорость сначала до 7,2 Мбит/с (наиболее популяные модемы Huawei E173, ZTE MF112), а затем до 14,4 Мбит/с. (Huawei E1820, ZTE MF658) Вершиной технологии HSDPA стала технология DC-HSDPA скорость которой могла достигать 28.8 Мбит/с. DC-HSDPA по сути двухканальный вариант HSDPA.
HSPA+
HSPA+ – технология, базирующаяся на HSDPA, в которой реализованы более сложные методы модуляции сигнала (16QAM, 64QAM) и технология MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output – множественный вход множественный выход). Максимальная скорость 3G может достигать 21 Мбит/с. Подобную технологию уже относят к 3,5G.
DC-HSPA+
DC-HSPA+ технология с самым быстрым 3G Интернетом 42,2 Мбит/с. По сути это двухканальный HSPA+ с шириной канала 10 МГц. Часто это технологию называют 3.75G.
Все устройства, поддерживающие режим работы в сетях третьего поколения, поддерживают также стандарты предыдущих поколений. К примеру, уже устаревший на сегодняшний день USB-модем Huawei E173 для сетей 2G/3G поддерживает стандарты GSM, GPRS, EDGE (до 236,8 Кбит/c), UMTS (до 384 Кбит/c), HSDPA (до 7,2 Мбит/с), т.е. стандарты сетей как второго так и третьего поколений. Максимальная скорость с которой может работать данное устройство равна 7,2 Мбит/с. Более «продвинутая» модель Huawei E3131 для сетей 2G/3G поддерживает набор стандартов, включающий кроме вышеперечисленных еще и HSPA+. Максимальная достижимая скорость загрузки данных на этом устройстве значительно больше и составляет 21 Мбит/сек. Но следует учесть, что максимальная теоретическая и реальная скорости отличаются довольно сильно.Например на модемах huawei E1550, zte mf180, где максимальная скорость 3.6 Мбит/с, на практике можно добиться скорости 1-2 Мит/с, на модемах Huawei E173, ZTE MF112 (максимальная скорость 7,2 Мбит/с) на практике 2-3,5 Мбит/с, это при условии хорошего уровня сигнала и низкой загруженности вышки мобильного оператора. Одним из факторов повышения скорости 3G Интернета является использования модема поддерживающего максимальную скорость 3G. Мы рекомендуем модем Huawei E3372, он не только поддерживает максимальную скорость 3G Интернета (до 42,2 Мбит/с), но и 4G (до 150 Мбит/с). Кто то может возразить и сказать что в его «дыре» 4G не будет никогда, однако не забывайте, что несколько лет назад вы и о 3G не мечтали. Технологии не стоят на месте!
Четвертое поколение — 4G
На смену еще не исчерпавшему свои возможности 3G приходят новые технологии, технологии четвертого поколения (4G), в большей степени отвечающие запросам времени. Технологии поколения 4G обозначили совершенно новые требования к качеству сигнала связи и его стабильности.
Детищем совместных исследований компаний Hewlett-Packard и NTT DoCoMo в области разработки технологий передачи данных в беспроводных сетях четвертого поколения стали стандарты LTE и WiMax.
• Стандарт WiMAX был разработан в 2001 году организацией WiMAX Forum, в состав которой входят такие производители, как Samsung, Huawei Technologies, Intel и другие известные компании. Концептуально WiMAX является продолжением беспроводного стандарта Wi-Fi. Версии стандарта WiMAX подразделяются на фиксированные, предназначенные для неподвижных абонентов, и мобильные, для движущихся абонентов со скоростью, не превышающей 115 км/час. Первая коммерческая WiMAX-сеть была запущена в эксплуатацию в Канаде в 2005 году.
• Стандарт LTE (Long-Term Evolution — долговременное развитие) по сути является продолжением развития стандартов GSM/UMTS и первоначально не относился к четвёртому поколению мобильной связи. На сегодняшний день именно LTE является основным стандартом сетей четвертого поколения (4G). Впервые представленный вышеупомянутой компанией NTT DoCoMo, крупнейшим в мире японским оператором сотовой связи, стандарт LTE, в десятом его релизе LTE Advanced, был избран Международным союзом электросвязи в качестве стандарта, отвечающего требованиям беспроводной связи четвертого поколения. Первая коммерческая реализация LTE-сети была осуществлена в 2009 году в Швеции и Норвегии.
Максимальная теоретическая скорость передачи данных в LTE-сетях составляет 326.4 Мбит/с. На практике скорость передачи данных существенно зависит от используемой оператором ширины диапазона частот. Наибольшую ширину диапазона частот на сегодняшний день имеет сотовый оператор Мегафон (40 МГц), что является серьезным преимуществом перед другими отечественными операторами сотовой связи, которые используют ширину 10 МГц. Максимальная скорость передачи данных в LTE-сети при ширине диапазона 10 МГЦ равна 75 Мбит/с. Ну а предельная скорость передачи данных при использовании ширины диапазона 40 МГц может достигать 300 Мбит/с.
Пятое поколение — 5G
Работы по разработке новых стандартов беспроводной передачи данных идут не останавливаясь. В основном при спонсорской поддержке одного из крупнейших производителей сетевого оборудования китайской компании Huawei. Повсеместное внедрение технологий пятого поколения прогнозируется в 2020 году. Однозначных сведений относительно максимальных скоростей передачи данных в сетях 5G пока нет, однако известно, что в опытных испытаниях сетей 5G удавалось достичь скорости 25 Гбит/с. Это в десятки раз превышает максимальные значения скорости передачи данных в сетях четвертого поколения.
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators.
UMTS specifies a complete network system, which includes the radio access network (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network, or UTRAN), the core network (Mobile Application Part, or MAP) and the authentication of users via SIM (subscriber identity module) cards.
The technology described in UMTS is sometimes also referred to as Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access (FOMA)[1] or 3GSM.
Unlike EDGE (IMT Single-Carrier, based on GSM) and CDMA2000 (IMT Multi-Carrier), UMTS requires new base stations and new frequency allocations.
Features[edit]
UMTS supports maximum theoretical data transfer rates of 42 Mbit/s when Evolved HSPA (HSPA+) is implemented in the network.[2] Users in deployed networks can expect a transfer rate of up to 384 kbit/s for Release ’99 (R99) handsets (the original UMTS release), and 7.2 Mbit/s for High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) handsets in the downlink connection. These speeds are significantly faster than the 9.6 kbit/s of a single GSM error-corrected circuit switched data channel, multiple 9.6 kbit/s channels in High-Speed Circuit-Switched Data (HSCSD) and 14.4 kbit/s for CDMAOne channels.
Since 2006, UMTS networks in many countries have been or are in the process of being upgraded with High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA), sometimes known as 3.5G. Currently, HSDPA enables downlink transfer speeds of up to 21 Mbit/s. Work is also progressing on improving the uplink transfer speed with the High-Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA). The 3GPP LTE standard succeeds UMTS and initially provided 4G speeds of 100 Mbit/s down and 50 Mbit/s up, with scalability up to 3 Gbps, using a next generation air interface technology based upon orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing.
The first national consumer UMTS networks launched in 2002 with a heavy emphasis on telco-provided mobile applications such as mobile TV and video calling. The high data speeds of UMTS are now most often utilised for Internet access: experience in Japan and elsewhere has shown that user demand for video calls is not high, and telco-provided audio/video content has declined in popularity in favour of high-speed access to the World Wide Web – either directly on a handset or connected to a computer via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or USB.[citation needed]
Air interfaces[edit]
UMTS combines three different terrestrial air interfaces, GSM’s Mobile Application Part (MAP) core, and the GSM family of speech codecs.
The air interfaces are called UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA).[3] All air interface options are part of ITU’s IMT-2000. In the currently most popular variant for cellular mobile telephones, W-CDMA (IMT Direct Spread) is used. It is also called «Uu interface», as it links User Equipment to the UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network.
Please note that the terms W-CDMA, TD-CDMA and TD-SCDMA are misleading. While they suggest covering just a channel access method (namely a variant of CDMA), they are actually the common names for the whole air interface standards.[4]
W-CDMA (UTRA-FDD)[edit]
W-CDMA (WCDMA; Wideband Code-Division Multiple Access), along with UMTS-FDD, UTRA-FDD, or IMT-2000 CDMA Direct Spread is an air interface standard found in 3G mobile telecommunications networks. It supports conventional cellular voice, text and MMS services, but can also carry data at high speeds, allowing mobile operators to deliver higher bandwidth applications including streaming and broadband Internet access.[5]
W-CDMA uses the DS-CDMA channel access method with a pair of 5 MHz wide channels. In contrast, the competing CDMA2000 system uses one or more available 1.25 MHz channels for each direction of communication. W-CDMA systems are widely criticized for their large spectrum usage, which delayed deployment in countries that acted relatively slowly in allocating new frequencies specifically for 3G services (such as the United States).
The specific frequency bands originally defined by the UMTS standard are 1885–2025 MHz for the mobile-to-base (uplink) and 2110–2200 MHz for the base-to-mobile (downlink). In the US, 1710–1755 MHz and 2110–2155 MHz are used instead, as the 1900 MHz band was already used.[6] While UMTS2100 is the most widely deployed UMTS band, some countries’ UMTS operators use the 850 MHz (900 MHz in Europe) and/or 1900 MHz bands (independently, meaning uplink and downlink are within the same band), notably in the US by AT&T Mobility, New Zealand by Telecom New Zealand on the XT Mobile Network and in Australia by Telstra on the Next G network. Some carriers such as T-Mobile use band numbers to identify the UMTS frequencies. For example, Band I (2100 MHz), Band IV (1700/2100 MHz), and Band V (850 MHz).
UMTS-FDD is an acronym for Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) – frequency-division duplexing (FDD) and a 3GPP standardized version of UMTS networks that makes use of frequency-division duplexing for duplexing over an UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (UTRA) air interface.[7]
W-CDMA is the basis of Japan’s NTT DoCoMo’s FOMA service and the most-commonly used member of the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) family and sometimes used as a synonym for UMTS.[8] It uses the DS-CDMA channel access method and the FDD duplexing method to achieve higher speeds and support more users compared to most previously used time-division multiple access (TDMA) and time-division duplex (TDD) schemes.
While not an evolutionary upgrade on the airside, it uses the same core network as the 2G GSM networks deployed worldwide, allowing dual-mode mobile operation along with GSM/EDGE; a feature it shares with other members of the UMTS family.
Development[edit]
In the late 1990s, W-CDMA was developed by NTT DoCoMo as the air interface for their 3G network FOMA. Later NTT DoCoMo submitted the specification to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) as a candidate for the international 3G standard known as IMT-2000. The ITU eventually accepted W-CDMA as part of the IMT-2000 family of 3G standards, as an alternative to CDMA2000, EDGE, and the short range DECT system. Later, W-CDMA was selected as an air interface for UMTS.
As NTT DoCoMo did not wait for the finalisation of the 3G Release 99 specification, their network was initially incompatible with UMTS.[9] However, this has been resolved by NTT DoCoMo updating their network.
Code-Division Multiple Access communication networks have been developed by a number of companies over the years, but development of cell-phone networks based on CDMA (prior to W-CDMA) was dominated by Qualcomm, the first company to succeed in developing a practical and cost-effective CDMA implementation for consumer cell phones and its early IS-95 air interface standard has evolved into the current CDMA2000 (IS-856/IS-2000) standard. Qualcomm created an experimental wideband CDMA system called CDMA2000 3x which unified the W-CDMA (3GPP) and CDMA2000 (3GPP2) network technologies into a single design for a worldwide standard air interface. Compatibility with CDMA2000 would have beneficially enabled roaming on existing networks beyond Japan, since Qualcomm CDMA2000 networks are widely deployed, especially in the Americas, with coverage in 58 countries as of 2006. However, divergent requirements resulted in the W-CDMA standard being retained and deployed globally. W-CDMA has then become the dominant technology with 457 commercial networks in 178 countries as of April 2012.[10] Several CDMA2000 operators have even converted their networks to W-CDMA for international roaming compatibility and smooth upgrade path to LTE.
Despite incompatibility with existing air-interface standards, late introduction and the high upgrade cost of deploying an all-new transmitter technology, W-CDMA has become the dominant standard.
Rationale for W-CDMA[edit]
W-CDMA transmits on a pair of 5 MHz-wide radio channels, while CDMA2000 transmits on one or several pairs of 1.25 MHz radio channels. Though W-CDMA does use a direct-sequence CDMA transmission technique like CDMA2000, W-CDMA is not simply a wideband version of CDMA2000 and differs in many aspects from CDMA2000. From an engineering point of view, W-CDMA provides a different balance of trade-offs between cost, capacity, performance, and density[citation needed]; it also promises to achieve a benefit of reduced cost for video phone handsets. W-CDMA may also be better suited for deployment in the very dense cities of Europe and Asia. However, hurdles remain, and cross-licensing of patents between Qualcomm and W-CDMA vendors has not eliminated possible patent issues due to the features of W-CDMA which remain covered by Qualcomm patents.[11]
W-CDMA has been developed into a complete set of specifications, a detailed protocol that defines how a mobile phone communicates with the tower, how signals are modulated, how datagrams are structured, and system interfaces are specified allowing free competition on technology elements.
Deployment[edit]
The world’s first commercial W-CDMA service, FOMA, was launched by NTT DoCoMo in Japan in 2001.
Elsewhere, W-CDMA deployments are usually marketed under the UMTS brand.
W-CDMA has also been adapted for use in satellite communications on the U.S. Mobile User Objective System using geosynchronous satellites in place of cell towers.
J-Phone Japan (once Vodafone and now SoftBank Mobile) soon followed by launching their own W-CDMA based service, originally branded «Vodafone Global Standard» and claiming UMTS compatibility. The name of the service was changed to «Vodafone 3G» (now «SoftBank 3G») in December 2004.
Beginning in 2003, Hutchison Whampoa gradually launched their upstart UMTS networks.
Most countries have, since the ITU approved of the 3G mobile service, either «auctioned» the radio frequencies to the company willing to pay the most, or conducted a «beauty contest» – asking the various companies to present what they intend to commit to if awarded the licences. This strategy has been criticised for aiming to drain the cash of operators to the brink of bankruptcy in order to honour their bids or proposals. Most of them have a time constraint for the rollout of the service – where a certain «coverage» must be achieved within a given date or the licence will be revoked.
Vodafone launched several UMTS networks in Europe in February 2004. MobileOne of Singapore commercially launched its 3G (W-CDMA) services in February 2005. New Zealand in August 2005 and Australia in October 2005.
AT&T Mobility utilized a UMTS network, with HSPA+, from 2005 until its shutdown in February 2022.
Rogers in Canada March 2007 has launched HSDPA in the Toronto Golden Horseshoe district on W-CDMA at 850/1900 MHz and plan the launch the service commercial in the top 25 cities October, 2007.
TeliaSonera opened W-CDMA service in Finland October 13, 2004, with speeds up to 384 kbit/s. Availability only in main cities. Pricing is approx. €2/MB.[citation needed]
SK Telecom and KTF, two largest mobile phone service providers in South Korea, have each started offering W-CDMA service in December 2003. Due to poor coverage and lack of choice in handhelds, the W-CDMA service has barely made a dent in the Korean market which was dominated by CDMA2000. By October 2006 both companies are covering more than 90 cities while SK Telecom has announced that it will provide nationwide coverage for its WCDMA network in order for it to offer SBSM (Single Band Single Mode) handsets by the first half of 2007. KT Freecel will thus cut funding to its CDMA2000 network development to the minimum.
In Norway, Telenor introduced W-CDMA in major cities by the end of 2004, while their competitor, NetCom, followed suit a few months later. Both operators have 98% national coverage on EDGE, but Telenor has parallel WLAN roaming networks on GSM, where the UMTS service is competing with this. For this reason Telenor is dropping support of their WLAN service in Austria (2006).
Maxis Communications and Celcom, two mobile phone service providers in Malaysia, started offering W-CDMA services in 2005.
In Sweden, Telia introduced W-CDMA in March 2004.
UTRA-TDD[edit]
UMTS-TDD, an acronym for Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) – time-division duplexing (TDD), is a 3GPP standardized version of UMTS networks that use UTRA-TDD.[7] UTRA-TDD is a UTRA that uses time-division duplexing for duplexing.[7] While a full implementation of UMTS, it is mainly used to provide Internet access in circumstances similar to those where WiMAX might be used.[citation needed] UMTS-TDD is not directly compatible with UMTS-FDD: a device designed to use one standard cannot, unless specifically designed to, work on the other, because of the difference in air interface technologies and frequencies used.[citation needed] It is more formally as IMT-2000 CDMA-TDD or IMT 2000 Time-Division (IMT-TD).[12][13]
The two UMTS air interfaces (UTRAs) for UMTS-TDD are TD-CDMA and TD-SCDMA. Both air interfaces use a combination of two channel access methods, code-division multiple access (CDMA) and time-division multiple access (TDMA): the frequency band is divided into time slots (TDMA), which are further divided into channels using CDMA spreading codes. These air interfaces are classified as TDD, because time slots can be allocated to either uplink or downlink traffic.
TD-CDMA (UTRA-TDD 3.84 Mcps High Chip Rate (HCR))[edit]
TD-CDMA, an acronym for Time-Division-Code-Division Multiple Access, is a channel-access method based on using spread-spectrum multiple-access (CDMA) across multiple time slots (TDMA). TD-CDMA is the channel access method for UTRA-TDD HCR, which is an acronym for UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access-Time Division Duplex High Chip Rate.[12]
UMTS-TDD’s air interfaces that use the TD-CDMA channel access technique are standardized as UTRA-TDD HCR, which uses increments of 5 MHz of spectrum, each slice divided into 10 ms frames containing fifteen time slots (1500 per second).[12] The time slots (TS) are allocated in fixed percentage for downlink and uplink. TD-CDMA is used to multiplex streams from or to multiple transceivers. Unlike W-CDMA, it does not need separate frequency bands for up- and downstream, allowing deployment in tight frequency bands.[14]
TD-CDMA is a part of IMT-2000, defined as IMT-TD Time-Division (IMT CDMA TDD), and is one of the three UMTS air interfaces (UTRAs), as standardized by the 3GPP in UTRA-TDD HCR. UTRA-TDD HCR is closely related to W-CDMA, and provides the same types of channels where possible. UMTS’s HSDPA/HSUPA enhancements are also implemented under TD-CDMA.[15]
In the United States, the technology has been used for public safety and government use in the New York City and a few other areas.[16] In Japan, IPMobile planned to provide TD-CDMA service in year 2006, but it was delayed, changed to TD-SCDMA, and bankrupt before the service officially started.
TD-SCDMA (UTRA-TDD 1.28 Mcps Low Chip Rate (LCR))[edit]
Time-Division Synchronous Code-Division Multiple Access (TD-SCDMA) or UTRA TDD 1.28 Mcps low chip rate (UTRA-TDD LCR)[13][4] is an air interface[13] found in UMTS mobile telecommunications networks in China as an alternative to W-CDMA.
TD-SCDMA uses the TDMA channel access method combined with an adaptive synchronous CDMA component[13] on 1.6 MHz slices of spectrum, allowing deployment in even tighter frequency bands than TD-CDMA. It is standardized by the 3GPP and also referred to as «UTRA-TDD LCR». However, the main incentive for development of this Chinese-developed standard was avoiding or reducing the license fees that have to be paid to non-Chinese patent owners. Unlike the other air interfaces, TD-SCDMA was not part of UMTS from the beginning but has been added in Release 4 of the specification.
Like TD-CDMA, TD-SCDMA is known as IMT CDMA TDD within IMT-2000.
The term «TD-SCDMA» is misleading. While it suggests covering only a channel access method, it is actually the common name for the whole air interface specification.[4]
TD-SCDMA / UMTS-TDD (LCR) networks are incompatible with W-CDMA / UMTS-FDD and TD-CDMA / UMTS-TDD (HCR) networks.
Objectives[edit]
TD-SCDMA was developed in the People’s Republic of China by the Chinese Academy of Telecommunications Technology (CATT), Datang Telecom, and Siemens AG in an attempt to avoid dependence on Western technology. This is likely primarily for practical reasons, since other 3G formats require the payment of patent fees to a large number of Western patent holders.
TD-SCDMA proponents also claim it is better suited for densely populated areas.[13] Further, it is supposed to cover all usage scenarios, whereas W-CDMA is optimised for symmetric traffic and macro cells, while TD-CDMA is best used in low mobility scenarios within micro or pico cells.[13]
TD-SCDMA is based on spread-spectrum technology which makes it unlikely that it will be able to completely escape the payment of license fees to western patent holders. The launch of a national TD-SCDMA network was initially projected by 2005[17] but only reached large scale commercial trials with 60,000 users across eight cities in 2008.[18]
On January 7, 2009, China granted a TD-SCDMA 3G licence to China Mobile.[19]
On September 21, 2009, China Mobile officially announced that it had 1,327,000 TD-SCDMA subscribers as of the end of August, 2009.
TD-SCDMA is not commonly used outside of China.[20]
Technical highlights[edit]
TD-SCDMA uses TDD, in contrast to the FDD scheme used by W-CDMA. By dynamically adjusting the number of timeslots used for downlink and uplink, the system can more easily accommodate asymmetric traffic with different data rate requirements on downlink and uplink than FDD schemes. Since it does not require paired spectrum for downlink and uplink, spectrum allocation flexibility is also increased. Using the same carrier frequency for uplink and downlink also means that the channel condition is the same on both directions, and the base station can deduce the downlink channel information from uplink channel estimates, which is helpful to the application of beamforming techniques.
TD-SCDMA also uses TDMA in addition to the CDMA used in WCDMA. This reduces the number of users in each timeslot, which reduces the implementation complexity of multiuser detection and beamforming schemes, but the non-continuous transmission also reduces coverage (because of the higher peak power needed), mobility (because of lower power control frequency) and complicates radio resource management algorithms.
The «S» in TD-SCDMA stands for «synchronous», which means that uplink signals are synchronized at the base station receiver, achieved by continuous timing adjustments. This reduces the interference between users of the same timeslot using different codes by improving the orthogonality between the codes, therefore increasing system capacity, at the cost of some hardware complexity in achieving uplink synchronization.
History[edit]
On January 20, 2006, Ministry of Information Industry of the People’s Republic of China formally announced that TD-SCDMA is the country’s standard of 3G mobile telecommunication. On February 15, 2006, a timeline for deployment of the network in China was announced, stating pre-commercial trials would take place starting after completion of a number of test networks in select cities. These trials ran from March to October, 2006, but the results were apparently unsatisfactory. In early 2007, the Chinese government instructed the dominant cellular carrier, China Mobile, to build commercial trial networks in eight cities, and the two fixed-line carriers, China Telecom and China Netcom, to build one each in two other cities. Construction of these trial networks was scheduled to finish during the fourth quarter of 2007, but delays meant that construction was not complete until early 2008.
The standard has been adopted by 3GPP since Rel-4, known as «UTRA TDD 1.28Mbps Option».[13]
On March 28, 2008, China Mobile Group announced TD-SCDMA «commercial trials» for 60,000 test users in eight cities from April 1, 2008. Networks using other 3G standards (WCDMA and CDMA2000 EV/DO) had still not been launched in China, as these were delayed until TD-SCDMA was ready for commercial launch.
In January 2009, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) in China took the unusual step of assigning licences for 3 different third-generation mobile phone standards to three carriers in a long-awaited step that is expected to prompt $41 billion in spending on new equipment. The Chinese-developed standard, TD-SCDMA, was assigned to China Mobile, the world’s biggest phone carrier by subscribers. That appeared to be an effort to make sure the new system has the financial and technical backing to succeed. Licences for two existing 3G standards, W-CDMA and CDMA2000 1xEV-DO, were assigned to China Unicom and China Telecom, respectively. Third-generation, or 3G, technology supports Web surfing, wireless video and other services and the start of service is expected to spur new revenue growth.
The technical split by MIIT has hampered the performance of China Mobile in the 3G market, with users and China Mobile engineers alike pointing to the lack of suitable handsets to use on the network.[21] Deployment of base stations has also been slow, resulting in lack of improvement of service for users.[22] The network connection itself has consistently been slower than that from the other two carriers, leading to a sharp decline in market share. By 2011 China Mobile has already moved its focus onto TD-LTE.[23][24] Gradual closures of TD-SCDMA stations started in 2016.[25][26]
Frequency bands & Deployments[edit]
The following is a list of mobile telecommunications networks using third-generation TD-SCDMA / UMTS-TDD (LCR) technology.
| Operator | Country | Frequency (MHz) |
Band | Launch date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China Mobile | 2100 | A+ (Band 34) |
Jan 2009 | [24][26][27] (↓↑) 2010–2025 MHz Network being phased out in favour of LTE. |
|
| China Mobile | 1900 | A- (Band 33) |
Jan 2009 | [24][26][27] (↓↑) 1900–1920 MHz (Subset of Band 39) Previously used by Xiaolingtong (PHS). Network being phased out in favour of LTE. |
|
| none | 1900 | F (Band 39) |
N/A | (↓↑) 1880–1920 MHz No deployments, later used for TD-LTE instead. |
|
| none | 2300 | E (Band 40) |
N/A | (↓↑) 2300–2400 MHz No deployments, later used for TD-LTE instead. |
|
| Xinwei (CooTel) |
1800 | N/A | Apr 2016 | [28][29][30] (↓↑) 1785–1805 MHz |
Unlicensed UMTS-TDD[edit]
In Europe, CEPT allocated the 2010–2020 MHz range for a variant of UMTS-TDD designed for unlicensed, self-provided use.[31] Some telecom groups and jurisdictions have proposed withdrawing this service in favour of licensed UMTS-TDD,[32] due to lack of demand, and lack of development of a UMTS TDD air interface technology suitable for deployment in this band.
Comparison with UMTS-FDD[edit]
Ordinary UMTS uses UTRA-FDD as an air interface and is known as UMTS-FDD. UMTS-FDD uses W-CDMA for multiple access and frequency-division duplex for duplexing, meaning that the up-link and down-link transmit on different frequencies. UMTS is usually transmitted on frequencies assigned for 1G, 2G, or 3G mobile telephone service in the countries of operation.
UMTS-TDD uses time-division duplexing, allowing the up-link and down-link to share the same spectrum. This allows the operator to more flexibly divide the usage of available spectrum according to traffic patterns. For ordinary phone service, you would expect the up-link and down-link to carry approximately equal amounts of data (because every phone call needs a voice transmission in either direction), but Internet-oriented traffic is more frequently one-way. For example, when browsing a website, the user will send commands, which are short, to the server, but the server will send whole files, that are generally larger than those commands, in response.
UMTS-TDD tends to be allocated frequency intended for mobile/wireless Internet services rather than used on existing cellular frequencies. This is, in part, because TDD duplexing is not normally allowed on cellular, PCS/PCN, and 3G frequencies. TDD technologies open up the usage of left-over unpaired spectrum.
Europe-wide, several bands are provided either specifically for UMTS-TDD or for similar technologies. These are 1900 MHz and 1920 MHz and between 2010 MHz and 2025 MHz. In several countries the 2500–2690 MHz band (also known as MMDS in the USA) have been used for UMTS-TDD deployments. Additionally, spectrum around the 3.5 GHz range has been allocated in some countries, notably Britain, in a technology-neutral environment. In the Czech Republic UTMS-TDD is also used in a frequency range around 872 MHz.[33]
Deployment[edit]
UMTS-TDD has been deployed for public and/or private networks in at least nineteen countries around the world, with live systems in, amongst other countries, Australia, Czech Republic, France, Germany, Japan, New Zealand, Botswana, South Africa, the UK, and the USA.
Deployments in the US thus far have been limited. It has been selected for a public safety support network used by emergency responders in New York,[34] but outside of some experimental systems, notably one from Nextel, thus far the WiMAX standard appears to have gained greater traction as a general mobile Internet access system.
Competing standards[edit]
A variety of Internet-access systems exist which provide broadband speed access to the net. These include WiMAX and HIPERMAN. UMTS-TDD has the advantages of being able to use an operator’s existing UMTS/GSM infrastructure, should it have one, and that it includes UMTS modes optimized for circuit switching should, for example, the operator want to offer telephone service. UMTS-TDD’s performance is also more consistent. However, UMTS-TDD deployers often have regulatory problems with taking advantage of some of the services UMTS compatibility provides. For example, the UMTS-TDD spectrum in the UK cannot be used to provide telephone service, though the regulator OFCOM is discussing the possibility of allowing it at some point in the future. Few operators considering UMTS-TDD have existing UMTS/GSM infrastructure.
Additionally, the WiMAX and HIPERMAN systems provide significantly larger bandwidths when the mobile station is near the tower.
Like most mobile Internet access systems, many users who might otherwise choose UMTS-TDD will find their needs covered by the ad hoc collection of unconnected Wi-Fi access points at many restaurants and transportation hubs, and/or by Internet access already provided by their mobile phone operator. By comparison, UMTS-TDD (and systems like WiMAX) offers mobile, and more consistent, access than the former, and generally faster access than the latter.
Radio access network[edit]
UMTS also specifies the Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (UTRAN), which is composed of multiple base stations, possibly using different terrestrial air interface standards and frequency bands.
UMTS and GSM/EDGE can share a Core Network (CN), making UTRAN an alternative radio access network to GERAN (GSM/EDGE RAN), and allowing (mostly) transparent switching between the RANs according to available coverage and service needs. Because of that, UMTS’s and GSM/EDGE’s radio access networks are sometimes collectively referred to as UTRAN/GERAN.
UMTS networks are often combined with GSM/EDGE, the latter of which is also a part of IMT-2000.
The UE (User Equipment) interface of the RAN (Radio Access Network) primarily consists of RRC (Radio Resource Control), PDCP (Packet Data Convergence Protocol), RLC (Radio Link Control) and MAC (Media Access Control) protocols. RRC protocol handles connection establishment, measurements, radio bearer services, security and handover decisions. RLC protocol primarily divides into three Modes – Transparent Mode (TM), Unacknowledge Mode (UM), Acknowledge Mode (AM). The functionality of AM entity resembles TCP operation whereas UM operation resembles UDP operation. In TM mode, data will be sent to lower layers without adding any header to SDU of higher layers. MAC handles the scheduling of data on air interface depending on higher layer (RRC) configured parameters.
The set of properties related to data transmission is called Radio Bearer (RB). This set of properties decides the maximum allowed data in a TTI (Transmission Time Interval). RB includes RLC information and RB mapping. RB mapping decides the mapping between RB<->logical channel<->transport channel. Signaling messages are sent on Signaling Radio Bearers (SRBs) and data packets (either CS or PS) are sent on data RBs. RRC and NAS messages go on SRBs.
Security includes two procedures: integrity and ciphering. Integrity validates the resource of messages and also makes sure that no one (third/unknown party) on the radio interface has modified the messages. Ciphering ensures that no one listens to your data on the air interface. Both integrity and ciphering are applied for SRBs whereas only ciphering is applied for data RBs.
Core network[edit]
With Mobile Application Part, UMTS uses the same core network standard as GSM/EDGE. This allows a simple migration for existing GSM operators. However, the migration path to UMTS is still costly: while much of the core infrastructure is shared with GSM, the cost of obtaining new spectrum licenses and overlaying UMTS at existing towers is high.
The CN can be connected to various backbone networks, such as the Internet or an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) telephone network. UMTS (and GERAN) include the three lowest layers of OSI model. The network layer (OSI 3) includes the Radio Resource Management protocol (RRM) that manages the bearer channels between the mobile terminals and the fixed network, including the handovers.
Frequency bands and channel bandwidths[edit]
UARFCN[edit]
A UARFCN (abbreviation for UTRA Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number, where UTRA stands for UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access) is used to identify a frequency in the UMTS frequency bands.
Typically channel number is derived from the frequency in MHz through the formula Channel Number = Frequency * 5. However, this is only able to represent channels that are centered on a multiple of 200 kHz, which do not align with licensing in North America. 3GPP added several special values for the common North American channels.
Spectrum allocation[edit]
|
|
This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (October 2013) |
Over 130 licenses have already been awarded to operators worldwide (as of December 2004), specifying W-CDMA radio access technology that builds on GSM. In Europe, the license process occurred at the tail end of the technology bubble, and the auction mechanisms for allocation set up in some countries resulted in some extremely high prices being paid for the original 2100 MHz licenses, notably in the UK and Germany. In Germany, bidders paid a total €50.8 billion for six licenses, two of which were subsequently abandoned and written off by their purchasers (Mobilcom and the Sonera/Telefónica consortium). It has been suggested that these huge license fees have the character of a very large tax paid on future income expected many years down the road. In any event, the high prices paid put some European telecom operators close to bankruptcy (most notably KPN). Over the last few years some operators have written off some or all of the license costs. Between 2007 and 2009, all three Finnish carriers began to use 900 MHz UMTS in a shared arrangement with its surrounding 2G GSM base stations for rural area coverage, a trend that is expected to expand over Europe in the next 1–3 years.[needs update]
The 2100 MHz band (downlink around 2100 MHz and uplink around 1900 MHz) allocated for UMTS in Europe and most of Asia is already used in North America. The 1900 MHz range is used for 2G (PCS) services, and 2100 MHz range is used for satellite communications. Regulators have, however, freed up some of the 2100 MHz range for 3G services, together with a different range around 1700 MHz for the uplink. [needs update]
AT&T Wireless launched UMTS services in the United States by the end of 2004 strictly using the existing 1900 MHz spectrum allocated for 2G PCS services. Cingular acquired AT&T Wireless in 2004 and has since then launched UMTS in select US cities. Cingular renamed itself AT&T Mobility and rolled out[35] some cities with a UMTS network at 850 MHz to enhance its existing UMTS network at 1900 MHz and now offers subscribers a number of dual-band UMTS 850/1900 phones.
T-Mobile’s rollout of UMTS in the US was originally focused on the 1700 MHz band. However, T-Mobile has been moving users from 1700 MHz to 1900 MHz (PCS) in order to reallocate the spectrum to 4G LTE services.[36]
In Canada, UMTS coverage is being provided on the 850 MHz and 1900 MHz bands on the Rogers and Bell-Telus networks. Bell and Telus share the network. Recently, new providers Wind Mobile, Mobilicity and Videotron have begun operations in the 1700 MHz band.
In 2008, Australian telco Telstra replaced its existing CDMA network with a national UMTS-based 3G network, branded as NextG, operating in the 850 MHz band. Telstra currently provides UMTS service on this network, and also on the 2100 MHz UMTS network, through a co-ownership of the owning and administrating company 3GIS. This company is also co-owned by Hutchison 3G Australia, and this is the primary network used by their customers. Optus is currently rolling out a 3G network operating on the 2100 MHz band in cities and most large towns, and the 900 MHz band in regional areas. Vodafone is also building a 3G network using the 900 MHz band.
In India, BSNL has started its 3G services since October 2009, beginning with the larger cities and then expanding over to smaller cities. The 850 MHz and 900 MHz bands provide greater coverage compared to equivalent 1700/1900/2100 MHz networks, and are best suited to regional areas where greater distances separate base station and subscriber.
Carriers in South America are now also rolling out 850 MHz networks.
Interoperability and global roaming[edit]
UMTS phones (and data cards) are highly portable – they have been designed to roam easily onto other UMTS networks (if the providers have roaming agreements in place). In addition, almost all UMTS phones are UMTS/GSM dual-mode devices, so if a UMTS phone travels outside of UMTS coverage during a call the call may be transparently handed off to available GSM coverage. Roaming charges are usually significantly higher than regular usage charges.
Most UMTS licensees consider ubiquitous, transparent global roaming an important issue. To enable a high degree of interoperability, UMTS phones usually support several different frequencies in addition to their GSM fallback. Different countries support different UMTS frequency bands – Europe initially used 2100 MHz while the most carriers in the USA use 850 MHz and 1900 MHz. T-Mobile has launched a network in the US operating at 1700 MHz (uplink) /2100 MHz (downlink), and these bands also have been adopted elsewhere in the US and in Canada and Latin America. A UMTS phone and network must support a common frequency to work together. Because of the frequencies used, early models of UMTS phones designated for the United States will likely not be operable elsewhere and vice versa. There are now 11 different frequency combinations used around the world – including frequencies formerly used solely for 2G services.
UMTS phones can use a Universal Subscriber Identity Module, USIM (based on GSM’s SIM card) and also work (including UMTS services) with GSM SIM cards. This is a global standard of identification, and enables a network to identify and authenticate the (U)SIM in the phone. Roaming agreements between networks allow for calls to a customer to be redirected to them while roaming and determine the services (and prices) available to the user. In addition to user subscriber information and authentication information, the (U)SIM provides storage space for phone book contact. Handsets can store their data on their own memory or on the (U)SIM card (which is usually more limited in its phone book contact information). A (U)SIM can be moved to another UMTS or GSM phone, and the phone will take on the user details of the (U)SIM, meaning it is the (U)SIM (not the phone) which determines the phone number of the phone and the billing for calls made from the phone.
Japan was the first country to adopt 3G technologies, and since they had not used GSM previously they had no need to build GSM compatibility into their handsets and their 3G handsets were smaller than those available elsewhere. In 2002, NTT DoCoMo’s FOMA 3G network was the first commercial UMTS network – using a pre-release specification,[37] it was initially incompatible with the UMTS standard at the radio level but used standard USIM cards, meaning USIM card based roaming was possible (transferring the USIM card into a UMTS or GSM phone when travelling). Both NTT DoCoMo and SoftBank Mobile (which launched 3G in December 2002) now use standard UMTS.
Handsets and modems[edit]
|
|
This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (August 2015) |
All of the major 2G phone manufacturers (that are still in business) are now manufacturers of 3G phones. The early 3G handsets and modems were specific to the frequencies required in their country, which meant they could only roam to other countries on the same 3G frequency (though they can fall back to the older GSM standard). Canada and USA have a common share of frequencies, as do most European countries. The article UMTS frequency bands is an overview of UMTS network frequencies around the world.
Using a cellular router, PCMCIA or USB card, customers are able to access 3G broadband services, regardless of their choice of computer (such as a tablet PC or a PDA). Some software installs itself from the modem, so that in some cases absolutely no knowledge of technology is required to get online in moments. Using a phone that supports 3G and Bluetooth 2.0, multiple Bluetooth-capable laptops can be connected to the Internet. Some smartphones can also act as a mobile WLAN access point.
There are very few 3G phones or modems available supporting all 3G frequencies (UMTS850/900/1700/1900/2100 MHz). In 2010, Nokia released a range of phones with Pentaband 3G coverage, including the N8 and E7. Many other phones are offering more than one band which still enables extensive roaming. For example, Apple’s iPhone 4 contains a quadband chipset operating on 850/900/1900/2100 MHz, allowing usage in the majority of countries where UMTS-FDD is deployed.
Other competing standards[edit]
The main competitor to UMTS is CDMA2000 (IMT-MC), which is developed by the 3GPP2. Unlike UMTS, CDMA2000 is an evolutionary upgrade to an existing 2G standard, cdmaOne, and is able to operate within the same frequency allocations. This and CDMA2000’s narrower bandwidth requirements make it easier to deploy in existing spectra. In some, but not all, cases, existing GSM operators only have enough spectrum to implement either UMTS or GSM, not both. For example, in the US D, E, and F PCS spectrum blocks, the amount of spectrum available is 5 MHz in each direction. A standard UMTS system would saturate that spectrum. Where CDMA2000 is deployed, it usually co-exists with UMTS. In many markets however, the co-existence issue is of little relevance, as legislative hurdles exist to co-deploying two standards in the same licensed slice of spectrum.
Another competitor to UMTS is EDGE (IMT-SC), which is an evolutionary upgrade to the 2G GSM system, leveraging existing GSM spectrums. It is also much easier, quicker, and considerably cheaper for wireless carriers to «bolt-on» EDGE functionality by upgrading their existing GSM transmission hardware to support EDGE rather than having to install almost all brand-new equipment to deliver UMTS. However, being developed by 3GPP just as UMTS, EDGE is not a true competitor. Instead, it is used as a temporary solution preceding UMTS roll-out or as a complement for rural areas. This is facilitated by the fact that GSM/EDGE and UMTS specifications are jointly developed and rely on the same core network, allowing dual-mode operation including vertical handovers.
China’s TD-SCDMA standard is often seen as a competitor, too. TD-SCDMA has been added to UMTS’ Release 4 as UTRA-TDD 1.28 Mcps Low Chip Rate (UTRA-TDD LCR). Unlike TD-CDMA (UTRA-TDD 3.84 Mcps High Chip Rate, UTRA-TDD HCR) which complements W-CDMA (UTRA-FDD), it is suitable for both micro and macrocells. However, the lack of vendors’ support is preventing it from being a real competitor.
While DECT is technically capable of competing with UMTS and other cellular networks in densely populated, urban areas, it has only been deployed for domestic cordless phones and private in-house networks.
All of these competitors have been accepted by ITU as part of the IMT-2000 family of 3G standards, along with UMTS-FDD.
On the Internet access side, competing systems include WiMAX and Flash-OFDM.
Migrating from GSM/GPRS to UMTS[edit]
From a GSM/GPRS network, the following network elements can be reused:
- Home Location Register (HLR)
- Visitor Location Register (VLR)
- Equipment Identity Register (EIR)
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC)
- Gateway Mobile Switching Center (GMSC)
- Authentication Center (AUC)
- Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN)
- Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN)
From a GSM/GPRS communication radio network, the following elements cannot be reused:
- Base transceiver station (BTS)
- Base station controller (BSC)
- Packet Control Unit (PCU)
They can remain in the network and be used in dual network operation where 2G and 3G networks co-exist while network migration and new 3G terminals become available for use in the network.
The UMTS network introduces new network elements that function as specified by 3GPP:
- Node B (base transceiver station)
- Radio Network Controller (RNC)
- Media Gateway (MGW)
The functionality of MSC changes when going to UMTS. In a GSM system the MSC handles all the circuit switched operations like connecting A- and B-subscriber through the network. In UMTS the Media gateway (MGW) takes care of data transfer in circuit switched networks. MSC controls MGW operations.
Problems and issues[edit]
Some countries, including the United States, have allocated spectrum differently from the ITU recommendations, so that the standard bands most commonly used for UMTS (UMTS-2100) have not been available.[citation needed] In those countries, alternative bands are used, preventing the interoperability of existing UMTS-2100 equipment, and requiring the design and manufacture of different equipment for the use in these markets. As is the case with GSM900 today[when?], standard UMTS 2100 MHz equipment will not work in those markets. However, it appears as though UMTS is not suffering as much from handset band compatibility issues as GSM did, as many UMTS handsets are multi-band in both UMTS and GSM modes. Penta-band (850, 900, 1700, 2100, and 1900 MHz bands), quad-band GSM (850, 900, 1800, and 1900 MHz bands) and tri-band UMTS (850, 1900, and 2100 MHz bands) handsets are becoming more commonplace.[38]
In its early days[when?], UMTS had problems in many countries: Overweight handsets with poor battery life were first to arrive on a market highly sensitive to weight and form factor.[citation needed] The Motorola A830, a debut handset on Hutchison’s 3 network, weighed more than 200 grams and even featured a detachable camera to reduce handset weight. Another significant issue involved call reliability, related to problems with handover from UMTS to GSM. Customers found their connections being dropped as handovers were possible only in one direction (UMTS → GSM), with the handset only changing back to UMTS after hanging up. In most networks around the world this is no longer an issue.[citation needed]
Compared to GSM, UMTS networks initially required a higher base station density. For fully-fledged UMTS incorporating video on demand features, one base station needed to be set up every 1–1.5 km (0.62–0.93 mi). This was the case when only the 2100 MHz band was being used, however with the growing use of lower-frequency bands (such as 850 and 900 MHz) this is no longer so. This has led to increasing rollout of the lower-band networks by operators since 2006.[citation needed]
Even with current technologies and low-band UMTS, telephony and data over UMTS requires more power than on comparable GSM networks. Apple Inc. cited[39] UMTS power consumption as the reason that the first generation iPhone only supported EDGE. Their release of the iPhone 3G quotes talk time on UMTS as half that available when the handset is set to use GSM. Other manufacturers indicate different battery lifetime for UMTS mode compared to GSM mode as well. As battery and network technology improve, this issue is diminishing.
Security issues[edit]
As early as 2008, it was known that carrier networks can be used to surreptitiously gather user location information.[40] In August 2014, the Washington Post reported on widespread marketing of surveillance systems using Signalling System No. 7 (SS7) protocols to locate callers anywhere in the world.[40]
In December 2014, news broke that SS7’s very own functions can be repurposed for surveillance, because of its lax security, in order to listen to calls in real time or to record encrypted calls and texts for later decryption, or to defraud users and cellular carriers.[41]
Deutsche Telekom and Vodafone declared the same day that they had fixed gaps in their networks, but that the problem is global and can only be fixed with a telecommunication system-wide solution.[42]
Releases[edit]
The evolution of UMTS progresses according to planned releases. Each release is designed to introduce new features and improve upon existing ones.
Release ’99[edit]
- Bearer services
- 64 kbit/s circuit switch
- 384 kbit/s packet switched
- Location services
- Call service: compatible with Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), based on Universal Subscriber Identity Module (USIM)
- Voice quality features – Tandem Free Operation
- Frequency 2.1 GHz
Release 4[edit]
- Edge radio
- Multimedia messaging
- MExE (Mobile Execution Environment)
- Improved location services
- IP Multimedia Services (IMS)
- TD-SCDMA (UTRA-TDD 1.28 Mcps low chip rate)
Release 5[edit]
- IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)
- IPv6, IP transport in UTRAN
- Improvements in GERAN, MExE, etc.
- HSDPA
Release 6[edit]
- WLAN integration
- Multimedia broadcast and multicast
- Improvements in IMS
- HSUPA
- Fractional DPCH
Release 7[edit]
- Enhanced L2
- 64 QAM, MIMO
- Voice over HSPA
- CPC – continuous packet connectivity
- FRLC – Flexible RLC
Release 8[edit]
- Dual-Cell HSDPA
Release 9[edit]
- Dual-Cell HSUPA
See also[edit]
- List of UMTS networks
- Long Term Evolution, the 3GPP 4G successor for UMTS and CDMA2000.
- GAN/UMA: A standard for running GSM and UMTS over wireless LANs.
- Opportunity-Driven Multiple Access (ODMA): a UMTS TDD mode communications relaying protocol
- HSDPA, HSUPA: updates to the W-CDMA air interface.
- PDCP
- Subscriber Identity Module
- UMTS-TDD: a variant of UMTS largely used to provide wireless Internet service.
- UMTS frequency bands
- UMTS channels
- W-CDMA: the primary air interface standard used by UMTS.
- TD-SCDMA
Other, non-UMTS, 3G and 4G standards[edit]
- CDMA2000: evolved from cdmaOne (also known as IS-95 or «CDMA»), managed by the 3GPP2
- FOMA
- WiMAX
- GSM
- GPRS
- EDGE
- ETSI
Other information[edit]
- Cellular frequencies
- CDMA
- Comparison of wireless data standards
- DECT
- Dynamic TDMA
- Evolution-Data Optimized/CDMA2000
- FOMA
- GSM/EDGE
- HSPA
- PN sequences
- Spectral efficiency comparison table
- UMTS frequency bands
- WiMAX
- Telecommunications industry in China
- Communications in China
- Standardization in China
- Mobile modem
- Spectral efficiency comparison table
- Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA)
- Common pilot channel or CPICH, a simple synchronisation channel in WCDMA.
- Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) is the major issue of multiple antenna research.
- Wi-Fi: a local area wireless technology that is complementary to UMTS.
- List of device bandwidths
- Operations and Maintenance Centre
- Radio Network Controller
- UMTS security
- Huawei SingleRAN: a RAN technology allowing migration from GSM to UMTS or simultaneous use of both
References[edit]
Citations[edit]
- ^ «Draft summary minutes, decisions and actions from 3GPP Organizational Partners Meeting#6, Tokyo, 9 October 2001» (PDF). 3GPP. p. 7.
- ^ Tindal, Suzanne (8 December 2008). «Telstra boosts Next G to 21Mbps». ZDNet Australia. Retrieved 2009-03-16.
- ^ «3G Glossary – UTRA». 3GNewsroom.com. 2003-11-29. Archived from the original on 2011-04-06.
- ^ a b c ITU-D Study Group 2. «Guidelines on the smooth transition of existing mobile networks to IMT-2000 for developing countries (GST); Report on Question 18/2» (PDF). pp. 4, 25–28. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
- ^ «What is 3G/WCDMA?». GSMA.com. Retrieved 2014-06-24.
- ^ «Advanced Wireless Services (AWS) Band Plan» (PDF). Federal Communications Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-07-05.
- ^ a b c 3GPP. «TS 25.201». Retrieved 2009-02-23.
- ^ 3GPP notes that «there currently existed many different names for the same system (eg FOMA, W-CDMA, UMTS, etc)»; 3GPP. «Draft summary minutes, decisions and actions from 3GPP Organizational Partners Meeting#6, Tokyo, 9 October 2001» (PDF). p. 7.
- ^ Hsiao-Hwa Chen (2007), The Next Generation CDMA Technologies, John Wiley and Sons, pp. 105–106, ISBN 978-0-470-02294-8
- ^ «GSM Association HSPA Market update April 2012».
- ^ «Qualcomm says it doesn’t need Nokia patents».
- ^ a b c Forkel; et al. (2002). «Performance Comparison Between UTRA-TDD High Chip Rate And Low Chip Rate Operation». CiteSeerX 10.1.1.11.3672.
- ^ a b c d e f g Siemens (2004-06-10). «TD-SCDMA Whitepaper: the Solution for TDD bands» (PDF). TD Forum. pp. 6–9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-03-30. Retrieved 2009-06-15.
- ^ «UMTS World TD-CDMA information». umtsworld.com. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- ^ «IPWireless Ships First Commercial 3GPP Chipset with Full HSDPA Implementation». ipwireless.com. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- ^ «IPWireless introduces TD-CDMA Network in a Box targeting rural operators, public safety». Fiercewireless. 2 May 2010.
- ^ Clendenin, Mike (30 January 2007). «3G in China still held up». EE Times Asia.
- ^ «China Mobile to Test TD-SCDMA on 60,000 Phones From April 1». Cellular News. Archived from the original on 2008-06-28.
- ^ Wei, Michael (January 7, 2009). «China issues 3G licences to main carriers». Reuters.
- ^ «What is 3G TD-SCDMA». Electronics Notes.
- ^ Lau, Justine (August 28, 2008). «China Mobile trails on 3G technology». Financial Times. Archived from the original on 2022-12-10.(subscription required)
- ^ «China’s 3G Network Deployment Update – IHS Technology». IHS Market: Technology. Archived from the original on 9 August 2019. Retrieved 9 August 2019.
- ^ «China Mobile Not Serious About TD-SCDMA, Betting Big on TD-LTE». TechNode. 9 May 2011.
- ^ a b c «China Mobile Said to Begin Closing Its 3G Base Stations». CaixinOnline. 2016-03-14. Retrieved 2016-12-17.
- ^ «Closing of China Mobile 3G Base Stations Signifies End of China’s Self-owned Standard». People’s Daily Online. 2016.
- ^ a b c «China Mobile’s Dead End on the 3G Highway». CaixinOnline. 2014-12-15. Retrieved 2016-12-17.
- ^ a b «China Mobile Announces Commercial Deployment of TD-SCDMA Technology». Spreadtrum Communications, Inc. 2008-03-28. Archived from the original on 2014-07-25. Retrieved 2014-07-17.
- ^ «Xinwei belatedly launches as CooTel in Nicaragua». TeleGeography. 2016-04-29. Retrieved 2016-04-29.
- ^ «Xinwei finally stages user trials; will trade under CooTel brand». TeleGeography. 2016-01-19. Retrieved 2016-01-20.
- ^ «Xinwei outlines November launch plan for Nicaragua». TeleGeography. 2015-10-14. Retrieved 2015-10-14.
- ^ «ERC/DEC/(99)25 EU Recommendation on UMTS TDD» (PDF). ero.dk. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- ^ «Award_of_available_spectrum:_2500-2690_MHz,_2010-2025_MHz_and_2290-2300_MHz» (PDF). ofcom.org.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-30. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- ^ «T-Mobile launches UMTS TDD network in the Czech Republic». 21 June 2005.
- ^ «Northrop Grumman Wins $500 Million New York City Broadband Mobile Wireless Contract». ipwireless.com. Archived from the original on 2007-11-24. Retrieved 2008-02-28.
- ^ Vries, Lloyd. «From AT&T To Cingular And Back Again». CBS News. Retrieved 30 June 2017.
- ^ «T-Mobile shifting 1700 MHz HSPA+ users to 1900 MHz band». TeleGeography. 2015-06-24. Retrieved 2016-04-07.
- ^ Hsiao-Hwa Chen (2007), The Next Generation CDMA Technologies, John Wiley and Sons, pp. 105–106, ISBN 978-0-470-02294-8
- ^ «GSM World Coverage Map — GSM Country List by frequency bands».
- ^ Wingfield, Nick; Sharma, Amol (30 June 2007). «iPhone ‘Surfing’ On AT&T Network Isn’t Fast, Jobs Concedes». Wall Street Journal – via www.wsj.com.
- ^ a b Craig Timberg (24 August 2014). «For sale: Systems that can secretly track where cellphone users go around the globe». Washington Post. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ Craig Timberg (18 December 2014). «German researchers discover a flaw that could let anyone listen to your cell calls». The Switch- Washington Post. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ Peter Onneken (18 December 2014). «Sicherheitslücken im UMTS-Netz». Tagesschau (in German). ARD-aktuell / tagesschau.de. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
Bibliography[edit]
- Martin Sauter: Communication Systems for the Mobile Information Society, John Wiley, September 2006, ISBN 0-470-02676-6.
- Ahonen and Barrett (editors), Services for UMTS (Wiley, 2002) first book on the services for 3G, ISBN 978-0-471-48550-6.
- Holma and Toskala (editors), WCDMA for UMTS, (Wiley, 2000) first book dedicated to 3G technology, ISBN 978-0-471-72051-5.
- Kreher and Ruedebusch, UMTS Signaling: UMTS Interfaces, Protocols, Message Flows and Procedures Analyzed and Explained (Wiley 2007), ISBN 978-0-470-06533-4.
- Laiho, Wacker and Novosad, Radio Network Planning and Optimization for UMTS (Wiley, 2002) first book on radio network planning for 3G, ISBN 978-0-470-01575-9.
- Muratore, Flavio. UMTS: mobile communications for the future. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2000. ISBN 978-0-471-49829-2.
Documentation[edit]
- 3GPP specification series 25 – Radio aspects of 3G, including UMTS
- TS 25.201 Physical Layer – General Description – Describes basic differences between FDD and TDD.
- TS 25.211 Physical channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (FDD)
- TS 25.221 Physical channels and mapping of transport channels onto physical channels (TDD)
- TS 25.212 Multiplexing and channel coding (FDD)
- TS 25.222 Multiplexing and channel coding (TDD)
- TS 25.213 Spreading and modulation (FDD)
- TS 25.223 Spreading and modulation (TDD)
- TS 25.214 Physical layer procedures (FDD)
- TS 25.224 Physical layer procedures (TDD)
- TS 25.215 Physical layer – Measurements (FDD)
- TS 25.225 Physical layer – Measurements (TDD)
External links[edit]
- 3gpp.org – 3rd Generation Partnership Project Standard
- 3GPP Specifications Numbering Schemes
- Vocabulary for 3GPP Specifications, up to Release 8
- UMTS LTE Link Budget Comparison
- UMTS FAQ on UMTS World
- Worldwide W-CDMA frequency allocations on UMTS World
- UMTS TDD Alliance The Global UMTS TDD Alliance
- 3GSM World Congress
- UMTS Provider Chart
- LTE Encyclopedia
- TD-SCDMA Forum
- TD-SCDMA Industry Alliance
- UMTS FAQ
UMTS роутер – это устройство, которое позволяет организовать доступ к интернету через сеть кардинально мобильной связи. UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) – это стандарт, который позволяет передавать данные с высокой скоростью по сотовой связи. Роутер, в свою очередь, является устройством, которое распределяет сигнал интернета по разным устройствам, подключенным к нему.
Главное преимущество использования UMTS роутера – это возможность получить доступ к интернету там, где нет проводной сети или она непригодна для использования, например, в поезде, в походе или вдали от города. UMTS роутер ловит сигнал сотовой связи и преобразует его в Wi-Fi сигнал, который может быть использован компьютерами, смартфонами и другими устройствами. Это позволяет подключиться к интернету в любое время и в любом месте, где есть сигнал сотовой связи.
UMTS роутеры находят широкое применение как в быту, так и в бизнесе. В быту они используются, например, когда проводной интернет недоступен или сигнал Wi-Fi слишком слабый. Благодаря UMTS роутеру, семья или группа друзей могут одновременно получить доступ к интернету, используя свои устройства, в то время как они находятся далеко от дома или офиса. В бизнесе UMTS роутеры могут использоваться для организации мобильного офиса или при необходимости быстро организовать доступ в интернет на выставке или мероприятии.
UMTS роутер является незаменимым устройством для тех, кому нужен надежный и удобный доступ к интернету, где бы они ни находились. Благодаря ему можно быть всегда на связи, не зависеть от наличия проводной сети и обеспечивать доступ к интернету нескольким устройствам одновременно. UMTS роутеры предоставляют высокую скорость передачи данных и дают возможность использовать интернет везде, где есть сигнал сотовых операторов.
Содержание
- UMTS роутер: функции и преимущества использования
- Основные характеристики UMTS роутера
- Практическое применение UMTS роутера
UMTS роутер: функции и преимущества использования
Основные функции UMTS роутера:
1. Подключение к интернету через сети UMTS – главная функция этого типа роутера. Подключение к мобильному интернету через UMTS сеть позволяет получить доступ к широкому спектру онлайн-ресурсов, включая сайты, приложения, видео и многое другое.
2. Создание беспроводной Wi-Fi сети – UMTS роутер также может создавать локальную Wi-Fi сеть, чтобы подключать к ней различные устройства, такие как ноутбуки, планшеты и смартфоны. Это позволяет распространить интернет-соединение на все устройства в пределах Wi-Fi зоны покрытия роутера.
3. Поддержка множества устройств – UMTS роутер обычно имеет несколько портов, которые позволяют подключать к нему различные устройства через проводное подключение. Это удобно, когда требуется подключить не только устройства с Wi-Fi, но и устройства без беспроводных возможностей.
4. Мобильная мощность – UMTS роутер обычно работает на аккумуляторе, что позволяет его использовать везде, где есть охват сети UMTS. Это делает его идеальным выбором для тех, кто нуждается в постоянном доступе к интернету в дороге или в местах, где нет стабильного проводного подключения.
Преимущества использования UMTS роутера:
1. Подключение в любом месте – одним из главных преимуществ использования UMTS роутера является возможность подключения к интернету в любом месте, где есть охват сети UMTS. Это особенно полезно для путешественников, бизнесменов и всех, кто нуждается в надежном интернет-подключении в любых условиях.
2. Большая гибкость – использование UMTS роутера позволяет быть гибким в выборе места для работы или использования интернета. Вам больше не нужно ограничиваться только домом или офисом — вы можете работать где угодно, где есть охват UMTS сети.
3. Безопасность и конфиденциальность – UMTS роутер обеспечивает защищенное соединение с интернетом, что гарантирует безопасность ваших данных и информации, передаваемых через сеть. Это особенно важно, если вы работаете с конфиденциальными данными или осуществляете онлайн-транзакции.
UMTS роутер – это надежное и удобное решение для получения доступа к интернету через сети UMTS. Он предлагает широкий спектр функций и преимуществ, которые позволяют быть связанным и работать в любое время и в любом месте.
Основные характеристики UMTS роутера
Основные характеристики UMTS роутера:
1. Скорость передачи данных: UMTS роутеры могут предоставлять высокую скорость передачи данных, позволяя пользователям быстро скачивать и загружать файлы, просматривать видео, играть в онлайн-игры и многое другое.
2. Покрытие: UMTS роутеры могут работать в различных областях и обеспечивать стабильное подключение даже в удаленных или сложно доступных местах.
3. Мобильность: UMTS роутеры позволяют пользователям оставаться подключенными к интернету во время перемещений. Мобильные роутеры обычно имеют встроенную батарею и поддерживают подключение нескольких устройств одновременно.
4. Безопасность: UMTS роутеры обеспечивают защиту данных и конфиденциальность соединения. Они поддерживают различные методы шифрования и стандарты безопасности.
5. Гибкость: UMTS роутеры обладают гибкими настройками и функциями. Пользователи могут настраивать параметры соединения, управлять доступом к интернету и устанавливать дополнительные функции, такие как VPN и фильтрация контента.
UMTS роутеры стали очень популярными среди людей, которые нуждаются в быстром и надежном интернете, особенно в отдаленных или плохо охваченных проводным интернетом местах. Они предлагают удобный способ подключения ко всему миру и сохранения продуктивности в любой ситуации.
Практическое применение UMTS роутера
1. Доступ в интернет в поездках и на отдыхе
UMTS роутер может быть очень полезен во время путешествий и отдыха. Благодаря ему, вы сможете оставаться на связи, отвечать на электронные письма и использовать интернет в любом месте, где есть сеть UMTS.
2. Работа в удаленном офисе
Если вам приходится работать в удаленном офисе или постоянно ездить по командировкам, UMTS роутер может стать незаменимым помощником. Он обеспечит вас постоянным доступом в интернет, что значительно упростит выполнение рабочих задач и связь с коллегами.
3. Резервное подключение к интернету
UMTS роутер может использоваться как резервное подключение к интернету в случае, если основное подключение отключается или нестабильно. Таким образом, вы сможете сохранить доступ в интернет и продолжить работу или использование онлайн-сервисов.
4. Обеспечение интернета для нескольких устройств
UMTS роутер может обеспечить доступ в интернет для нескольких устройств одновременно, таких как ноутбуки, планшеты и смартфоны. Это может быть особенно удобно для семей или рабочих групп, где каждому участнику требуется независимый доступ в интернет.
5. Использование мобильных приложений
UMTS роутер позволяет использовать мобильные приложения, которые требуют постоянного интернет-соединения. Вы сможете управлять умным домом, отслеживать геолокацию или просматривать видео без прерываний.
Таким образом, UMTS роутер – это надежное и удобное устройство, которое может быть использовано в различных ситуациях для обеспечения доступа в мобильный интернет.
Система UMTS:
архитектура системы, пользовательское
оборудование, каналы
UMTS
(англ. Universal Mobile
Telecommunications System
— Универсальная Мобильная
Телекоммуникационная Система) —
технология сотовой связи, разработана
Европейским Институтом Стандартов
Телекоммуникаций (ETSI) для
внедрения 3G в Европе. В
качестве способа передачи данных через
воздушное пространство используется
технология W-CDMA,
стандартизованный в соответствии с
проектом 3GPP ответ
европейских учёных и производителей
на требование IMT-2000,
опубликованное Международным союзом
электросвязи как набор минимальных
критериев сети сотовой связи третьего
поколения.
С целью отличия от
конкурирующих решений, UMTS
также часто называют 3GSM
с целью подчеркнуть принадлежность
технологии к сетям 3G и
его преемственность в разработках с
сетями стандарта GSM.
Архитектура каналов
UMTS
Как уже говорилось
выше, система 3G в основном
рассматривается как инфраструктура,
предоставляющая оконечным пользователям
и пользовательским приложениям
оборудование, соответствующую полосу
частот и необходимое качество. Обеспечение
техническими средствами, распределение
частот и качество соединения вместе
образуют понятие «качество обслуживания»
(QoS). В случае сквозного
режима обслуживания (соединения) между
пользователями для данной конкретной
услуги устанавливается свой набор
требований к качеству обслуживания,
которые должны выполняться по всей
сети. В различных частях сети MTS
выполнение требований QoS
к услугам обеспечивается по-разному.
Чтобы смоделировать
эту ситуацию, требования к сквозному
режиму обслуживания разделили на три
категории: обслуживание местного канала,
обслуживание канала UMTS
и обслуживание внешнего канала.
Обслуживание местного канала включает
механизмы реализации сквозного режима
на участке между оконечным оборудованием
и мобильным окончанием (МТ). МТ представляет
собой часть оборудования пользователя
(UE), которая устанавливает
радиосоединение с сетью и адаптирует
возможности оконечного оборудования
к условиям радиопередачи. Обслуживание
канала UMTS, в свою очередь,
предусматривает механизмы выполнения
требований качества обслуживания (QoS)
в сети UMTS/3G,
включающей сеть доступа UTRAN
и базовую сеть. Когда сеть UMTS
соединяется с другой сетью (или сетями),
то требования QoS для
сквозного режима должны поддерживаться
и в направлении этих внешних сетей. Это
область ответственности внешнего
канала.
Внутри сети UMTS
сеть доступа UTRAN и базовая
сеть по-разному поддерживают требования
QoS. С точки зрения базовой
сети UTRAN создает иллюзию
фиксированного канала, предоставляя
оконечному пользователю необходимое
качество обслуживания (QoS).
Этот воображаемый канал называют услугой
по предоставлению канала радиодоступа.
Базовая сеть CN использует
собственный метод передачи, который
называется «службой канала базовой
сети». Такое разделение обусловлено
необходимостью гарантировать определенное
качество обслуживания в очень разных
транспортных средах, для каждой из
которых требуются свои механизмы
передачи и протоколы. Так, канал базовой
сети по своей природе достаточно
постоянен, поскольку базовая транспортная
сеть обеспечивает стабильные (устойчивые)
физические соединения. В системе UTRAN
канал радиодоступа претерпевает
множество изменений с течением времени
и при перемещениях оборудования
пользователя, что создает различные
условия с точки зрения выполнения
требований QoS. Кроме того,
при разделении каналов сети доступа и
базовой сети (CN) выполняется
основной принцип архитекторы сети UMTS
— независимость инфраструктуры всей
сети от технологии радиодоступа.
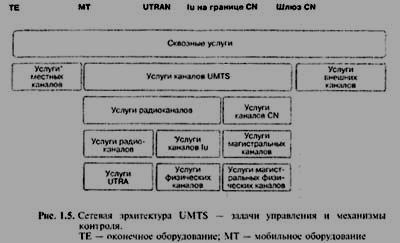
На рис. 1.5 приведена
модель сетевой архитектуры, в основе
которой лежат понятия каналов и качества
обслуживания (QoS). На
нашем сайте этим понятиям уделяется
большое внимание, поскольку обеспечение
QoS — одна из важнейших
задач UMTS.
Распределение частот
К декабрю 2004 года по
всему миру было выдано более 120 лицензий
на предоставление услуг связи операторам,
внедряющих технологию радиодоступа
W-CDMA на
оборудовании стандарта GSM.
В Европе процесс выдачи лицензий пришёлся
на время повышенного спроса на акции
технологических компаний, и в таких
странах как Великобритания и Германия
стоимость лицензий была по мнению многих
специалистов неоправданно завышена. В
Германии покупатели выложили в сумме
более 50 миллиардов евро за шесть лицензий,
две из которых позже были аннулированы
без возмещения стоимости (компании
Mobilcom и консорциума финской
Sonera и испанской Telefonica).
Помимо оплаты стоимости лицензии,
операторы брали на себя бремя достаточно
высоких налоговых выплат в течение
последующих десяти лет, что, по прогнозам
финансистов, не могло окупить затрат
участников и привело бы к банкротству
(в числе наиболее рискованных игроков
оказалась нидерландская KPN).
Спустя несколько лет часть операторов
предпочла частично или полностью
отказаться от полученных лицензий.
Спектр частот,
отведённый под использование UMTS
в Европе, является уже занятым под
предоставление других услуг на территории
США: частота в 1900 МГц отведена под
Personal Communications
Service (PCS)
стандарта 2G, частота 2100
МГц используется для спутниковой связи.
Тем не менее, по решению государственных
органов США часть диапазона 2100 МГц
освобождается под услуги 3G,
также как и часть диапазона 1700 МГц (для
передачи данных в режиме «от мобильного
терминала к базовой станции»).
AT&T
Wireless запустила сеть UMTS
в Соединённых Штатах Америки в конце
2004 г. в диапазоне 1900 МГц. Компания сотовой
связи Cingular, приобретённая
AT&T в том
же 2004 году, смогла применить эту технологию
на своей сети в ряде американских
городов. В соседней Канаде запуск UMTS
также анонсируется на частоте 1900 МГц.
Другая компания, T-Mobile,
предполагает развернуть сеть в диапазоне
2100/1700 МГц.
С целью расширения
абонентской базы AT&T
также осваивает диапазон в 850 МГц в части
американских штатов. Австралийский
оператор Telstra планирует
к февралю 2008 года перейти от эксплуатации
сети CDMA в диапазоне 850 МГц
к UMTS на частоте 2100 МГц.
Стоит отметить то, что диапазон 850 МГц
позволяет охватывать большую зону
действия в пределах одной базовой
станции по отношению к сетям 1700/1900/2100
МГЦ.
Оборудование
Доступ пользователей
к услуге передачи данных сети UMTS
может обеспечиваться вне зависимости
от типа используемого компьютера, путём
применения шлюза доступа к сети (cellular
router), использующего
интерфейс PCMCIA либо USB.
Часть программного обеспечения
устанавливается автоматически при
обнаружении операционной системой
модема, и не требует дополнительных
знаний по настройке подключения к сети.
Использование
мобильного терминала, имеющего доступ
к сетям 3G, в качестве
маршрутизатора(модема)позволяет
установить соединение с сетью Интернет
посредством Bluetooth или USB
ноутбукам самых разных марок и
производителей.
Возможности
UMTS,
используя разработки W-CDMA,
позволяет поддерживать скорость передачи
информации на теоретическом уровне до
21 Мбит в сек. (при использовании HSPA+).
В настоящий момент самыми высокими
скоростями считаются 384 Кбит/сек для
мобильных станций технологии R99
и 7,2 Мбит/сек для станций HSDPA
в режиме передачи данных от базовой
станции к мобильному терминалу. Это
является скачком по сравнению со
значением в 9,6 Кбит/сек при передаче
данных по каналу GSM, или
использованием в соответствии с
технологией HSCSD нескольких
каналов 9,6 Кбит/сек (при этом максимально
достигаемая скорость — 14,4 Кбит/сек в
CDMAOne), и, наряду с другими
технологиями беспроводной передачи
данных (CDMA2000, PHS,
WLAN) позволяет получить
доступ к Всемирной Паутине и другим
сервисам посредством использования
мобильных станций.
Предшествующее
поколению 3G второе
поколение мобильной связи включает в
себя такие технологии как GSM,
IS-95, PHS,
используемый в Японии PDC
и некоторые другие, принятые на вооружение
в самых разных странах. Эволюционным
этапом на этом пути развития телекоммуникаций
является поколение «2,5G»,
обозначающее применение на сетях
технологии GPRS. Теоретически
скорость передачи данных с GPRS
может составлять максимально 171,2
Кбит/сек, но на практике она колеблется
в пределах 56 Кбит/сек, что тем не менее
повышает привлекательность технологии,
основанной на пакетной коммутации по
сравнению с более медленными в передаче
данных способах, основанных на коммутации
каналов. GPRS применена на
многих сотовых сетях стандарта GSM,
а следующий этап в этой технологии —
EDGE, использующий более
сложные схемы кодирования информации
— позволяет поднять скорость передачи
данных до 473,6 Кбит/с в теории и до 180
Кбит/сек на практике. Сети, развёрнутые
с применением EDGE, относят
к поколению «2,75G». Улучшенный
GPRS это и есть EDGE.
GSM/EDGE
составляют один из уровней доступа
3G/UMTS — GERAN.
Начиная с 2006 года на
сетях UMTS повсеместно
распространяется технология
высокоскоростной пакетной передачи
данных от базовой станции к мобильному
терминалу HSDPA, которую
принято относить к сетям поколения
«3,5G». К началу 2008 года
HSDPA поддерживала скорость
передачи данных в режиме «от базовой
станции к мобильному терминалу» до 7,2
Мбит/сек. Также ведутся разработки по
повышению скорости передачи данных в
режиме от мобильного терминала к базовой
станции HSUPA. В долгосрочной
перспективе, согласно проектам 3GPP,
планируется эволюция UMTS
в сети четвёртого поколения 4G,
позволяющие базовым станциям передавать
и принимать информацию на скоростях
100 Мбит/сек и 50 Мбит/сек соответственно,
благодаря усовершенствованному
использованию воздушной среды посредством
мультиплексирования с ортогональным
частотным (скорее, имеется в виду фазовое)
разделением сигналов OFDM.
UMTS
позволяет пользователям проводить
сеансы видеоконференций посредством
мобильного терминала, однако опыт работы
операторов связи Японии и некоторых
других стран показал невысокий интерес
абонентов к данной услуге. Гораздо более
перспективным представляется развитие
сервисов, предлагающих загрузку
музыкального и видео контента: высокий
спрос на услуги такого рода был
продемонстрирован в сетях 2,5G.
Процедуры мягкого
и жёсткого хэндовера
Х
эндовер
(англ. Handover) — в сотовой связи процесс
передачи сессии абонента от одной
базовой станции к другой. В спутниковой
связи процесс передачи контроля над
спутником от одного научно-измерительного
пункта к другому без нарушения и потери
обслуживания.
Демонстрация «мягкого»
хендовера
Назначение
В сотовой связи может
быть несколько причин для проведения
передачи сессии:
Когда телефон уходит
с зоны покрытия одной ячейкой сети и
входит в зону покрытия другой ячейкой.
Хэндовер позволяет абонентам не быть
привязанным к какой-либо географической
точке и дает возможность передвигаться
в пределах сети оператора без разрыва
соединения;
Когда ёмкость сети в
текущей ячейке израсходована при
существовании нового звонка с телефона,
который находится в зоне, перекрытой
другой ячейкой, передаётся к этой ячейке
в порядке освобождения ёмкости первой
ячейки для других ее пользователей,
которые могут быть соединены только с
первой ячейкой;
В не-CDMA сетях, когда
канал используемый телефоном зашумлён
помехами другого телефона, использующего
тот же канал в другой ячейке, звонок
передаётся другому каналу в той же
ячейке или другому каналу в другой
ячейке для устранения помех;
В не-CDMA сетях, когда
изменяется поведение пользователя, то
есть когда пользователь, быстро изменяющий
местоположение, подключённый к большой
зонтообразной ячейке, останавливается,
звонок может быть передан макроячейке
или даже микроячейке для освобождения
ёмкости большой сети для других быстро
передвигающихся абонентов и для
уменьшения потенциальных помех другим
ячейкам или пользователям. Это работает
и в противоположной ситуации, когда
абонент передвигается быстрее
определенного порога, звонок может быть
передан большей ячейке для уменьшения
частоты передач.
Принцип действия
Процесс передачи
сессии может быть инициирован при
переходе пользователя из зоны покрытия
одной ячейки в зону покрытия другой. В
случае использования традиционного
метода «жёсткого» хендовера
соединение с текущей ячейкой прерывается,
после чего создаётся соединение с новой
ячейкой. Этот метод известен как
«break-before-make» хендовер. Так как все
ячейки в CDMA используют общие частоты,
возможно создание соединения с новой
ячейкой без прерывания соединения с
предыдущей. Этот метод также известен
как «make-before-break» или «мягкий»
хендовер. Мягкие хендоверы требуют
меньших мощностей, что уменьшает
интерференцию и увеличивает возможности
нагрузки. Мобильный телефон может также
быть соединён с несколькими BTS. «Более
мягкий» хендовер — частный случай
мягкого хендовера, в котором радиосвязи,
добавленные и удалённые одному и тому
же узлу.
Жёсткий хендовер –
может внести искажения, задержки в
передачу данных и речи.
Физический уровень
UMTS
Физический уровень
определяет услуги обмена информацией
в виде транспортных каналов. На этом
уровне выполняются все функции, связанные
с обработкой сигналов, канальным
кодированием, перемещением, модуляцией,
синхронизацией и т.д. В число этих функций
входит отображение транспортных каналов
в физические каналы.
Уровень звена данных
разделен на следующие подуровни:
— подуровень управления
доступом к среде (MAC-подуровень);
— подуровень управления
радиоканалом (RLC-подуровень);
— подуровень протокола
сходимости пакетных данных (англ. Packet
Data Convergence Protocol — PDCP);
— подуровень управления
вещанием/широковещанием (англ. Broadcast/
Multicast Control — BMC).
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Сотовые беспроводные сети стали использоваться операторами для выхода Интернет достаточно давно. Сначала скорости передачи данных не поражали воображение, иными словами «интернет был медленным». В сетях первого поколения 1G скорость не превышала 9600 Бит/с, т.е. меньше 10 Кбит/с. Однако, рынок рос, сетевые услуги становилось всё более и более востребованными, соответственно росли и объёмы информации, требовались более высокие скорости. В сетях второго поколения 2G было реализовано несколько стандартов, некоторые из которых используются до сих пор: GPRS (до 171,2 Кбит/с) и EDGE (до 384 Кбит/с). В современных реалиях такие скорости конечно уже не могут отвечать возросшим потребностям пользователей. Наиболее распространенными сетями в России сейчас являются сотовые сети стандарта 3G.
Однако, 3G тоже бывает разный. Рассмотрим все популярные стандарты в сетях 3G.
UMTS
Основной несущей частотой в стандарте 3G является 2100 МГц, а точнее диапазон 2110-2200 МГц. Для UMTS характерная ширина канала 5 МГц. Скорость доступа в Интернет в режиме UMTS не превышает 2 Мбит/с.
HSDPA
Этот стандарт так же можно отнести к первому поколению сетей 3G, но он уже значительно быстрее UMTS. Пропускная способность в начальной версии HSDPA (High-Speed Downlink Packet Access) составила 1,8 Мбит/с, но наибольшее распространение, в том числе и в России, получила вторая версия HSDPA со скоростью до 3,6 Мбит/с. Было выпущено достаточно много 3G модемов именно с такими скоростными характеристиками. Многие из этих «динозавров» используются до сих пор. Следующим развитием стандартна HSDPA стало достижение скорости 7,2 Мбит/с, а затем 14,4 Мбит/с. Это уже вполне неплохие скорости, но следует понимать, что это теоретический пропускной канал, реальные скорости обычно значительно меньше. Апогеем эволюции HSDPA стал его двухканальный вариант, называемый также DC-HSDPA, скорость достигла 28,8 Мбит/с. Сети 3G HSDPA/DC-HSDPA до сих пор используются во многих регионах России, однако при модернизации уступают своё место или HSPA+, или уже сразу 4G LTE.
HSPA+
Технология базируется на предшествующем стандарте HSDPA, однако позволяет получить значительно большую скорость. Уже в стартовом варианте HSPA+ (High Speed Packet Access) даёт скорость до 21,6 Мбит/с. Именно такой вариант сейчас в основном используется в сетях 3G. Ширина канала также составляет 5 МГц, и все современные 3G/4G модемы поддерживают данный режим работы. Многие относят сети HSPA+ к так называемому переходному поколению 3.5G, однако это не совсем корректно.
DC-HSPA+
Самый быстрый из используемых стандартов сетей 3G. По сути это двухканальный HSPA+ с шириной канала 10 МГц. Соответственно и максимальная скорость в 2 раза выше — до 43,2 Мбит/с. Такие сети часто называют даже 3.75G, т.е. уже почти 4G. И действительно, в сетях DC-HSPA+ реальная скорость доступа в Интернет часто сопоставима с показателями 4G.