The cat command in Linux is used to concatenate files and print to a standard output.
The type command is a Windows cat equivalent that works across a command-line prompt (CMD) and a Windows PowerShell.
In this short note i will show how to concatenate files and how to print the contents of a text file to the screen in Windows.
Cool Tip: Windows grep command equivalent in CMD and PowerShell! Read more →
Print the contents of a text file in CMD or Windows PowerShell (cat a file):
C:\> type file.txt
Create files:
C:\> echo "line from file1" > file1.txt C:\> echo "line from file2" > file2.txt
Concatenate files:
C:\> type file1.txt file2.txt > result.txt C:\> type result.txt line from file1 line from file2
Type: The type command in PowerShell is the alias of the Get-Content command.
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
Время на прочтение
5 мин
Количество просмотров 89K
Разделы можно пропускать без ущерба для понимания, ровно как и любые непонятные/неинтересные места в них.
Перенаправления
Как обычно:
echo foo > bar
echo foo 2> bar
echo foo > bar 2>&1cat
Да, в Windows есть аналог многоликой команды cat, которая является одной из команд, выражающих суть UNIX’а. Это команда type. Она принимает один или несколько аргументов — имена файлов.
type fileЕсли нужно, чтоб type читал с экрана (например, если нужно создать файл, на лету наполнив его содержимым), то нужно набрать
type con > filecon — это аналог /dev/tty (подробнее об этом в следующем разделе).
То есть вышеприведённая команда является аналогом UNIX’овой команды cat /dev/tty > file или cat - > file или просто cat > file.
Когда вы закончите набирать файл, нажмите на новой строке Ctrl-Z и Enter. Это признак конца файла, аналог Ctrl-D в UNIX’е.
Сейчас будет куча технических подробностей про Ctrl-D и Ctrl-Z, их можно пропустить и перейти к следующему разделу.
В UNIX’е, когда юзер нажимает Ctrl-D, эта комбинация не обрабатывается самим приложением (например, в GNU/Linux в tty1 она обрабатывается ядром, если включен CONFIG_VT [на сегодняшний день (2012) CONFIG_VT включен по дефолту на десктопе, хотя есть планы по её выкидыванию]). А запущенное приложение получает EOF (End Of File, конец файла) в чистом виде (а не саму комбинацию клавиш или символ Ctrl-D). То есть как если бы ввод просто закончился. Иными словами, getchar в приложении возвращает EOF, а read — 0.
В Windows то же самое, Ctrl-Z и Enter заставляют getchar вернуть EOF.
/dev/null, /dev/tty и т. д.
Аналог /dev/null — это устройство nul. Причём оно как бы присутствует в каждой папке. Это тянется со времён старых версий DOS’а, когда не было папок.
Теперь о других устройствах. Аналог /dev/tty — это con, от слова console. Причём con — это аналог именно /dev/tty, а не /dev/console, так как в Windows у каждого окна командной строки con свой.
Аналоги /dev/ttyS0, /dev/ttyS1, /dev/ttyS2, /dev/ttyS3 — это com1, com2, com3, com4 (но винде есть ещё com5 и т. д.). Это устройства serial console, они же COM-порты, они же последовательные порты.
Обычными средствами винды нельзя создать файл или папку с именем con или nul и т. д. Но можно исхитриться: mkdir \\.\c:\con.
Есть шуточная версия того, почему в Windows трудно создать файл с именем con. А именно: у Билла Гейтса было прозвище con, то есть ботаник. Подробнее см., например, здесь: vk.com/wall-31439745_2474 (естественно, этой информации нельзя доверять).
Подробнее про эти устройства тут: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Device_file#MS-DOS.
/dev, /dev/sda1, …
После прочтения предыдущего раздела у вас мог возникнуть вопрос: и что, всё? /dev/null, /dev/tty и ещё несколько штук девайсов? А где /dev/sda1 и прочие бесчисленные устройства? Ведь в GNU/Linux’е папка /dev может содержать сотни устройств!
Ответ таков: да, в Windows есть целая папка с такими устройствами. Это \Device. Её сложно посмотреть через обычный пользовательский интерфейс. Там лежат устройства типа \Device\HarddiskVolume1 — это аналог GNU/Linux’ового /dev/sda1.
Эти устройства появились в NT-шных версиях Windows’а и не тянутся с DOS’овых времён, в отличие от устройств из предыдущего раздела.
Пайпы, они же конвееры
cmd1 | cmd2, так же, как и в UNIX.
/etc/fstab
Его аналог — это ветка HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\MountedDevices в реестре Windows (да, да, в винде, как и в UNIX, есть понятие монтирования). Кстати, если у вас до этого были проблемы с переносом установленного Windows’а с одного раздела на другой, или с переименованием дисков в Windows’е или с чем-то ещё подобным, то — вот оно, решение!
Сейчас будет рассказ для тех, кто задумал перенести винду с одного раздела на другой. Остальные могут его пропустить и перейти к следующему разделу.
Если, скажем, вы перенесли Windows с одного раздела на другой, то после этого нужно сделать два шага: разобраться с загрузчиком и его конфигами (об этом в следующем разделе) и подредактировать этот самый ключ реестра (в общем-то так же, как и в GNU/Linux’е: GRUB + fstab). Если ключ не подредактировать, то винда загрузиться не сможет, так начнёт грузиться с нового раздела (то есть того, на который мы копирнули винду), а продолжит — со старого (то есть того, с которого мы копирнули винду). Все системные вещи будут загружены с нового, а всякие Касперские — со старого. Итак, нужно удалить из этой ветки все записи, кроме записи «(По умолчанию)». Тогда винда забудет всё, что знала о разделах и при следующем запуске будет считать своим разделом тот, с которого запустилась (что нам и надо). Короче говоря, автоматически определит разделы.
Правда, тут возникает вопрос: а как подредактировать реестр какой-нибудь винды, не загружаясь в неё? Хм, я для этого использовал Windows PE, который входил в комплект пиратской сборки винды, поэтому я подробности рассказывать не буду. (См. другие способы в этой ветке: geektimes.ru/post/156749/#comment_5355987 от EndUser.)
Ещё несколько вариантов:
- Почистить реестр, выключить компьютер (можно «жёстко»), а потом копирнуть винду. Однако, я это не проверял. Не факт, что винда даст вам отредактировать этот ключ реестра и что она не заполнит его снова при выключении
- Отредактировать реестр, и сразу же, не выключая комп, копирнуть запущенную винду на другой раздел. Но и это тоже не проверялось
- Если вы копируете винду с одного физического диска на другой, можно после копирования вынуть из компьютера старый физический диск и загрузиться в новый хотя бы один раз (чтоб винда обновила MountedDevices). Потом можно вставить старый диск обратно. Такой же трюк можно проделать даже с разделами на одном физическом диске: просто временно удалить старый раздел, а потом восстановить его обратно (ясно, что делать это нужно крайне осторожно). Ну и конечно же, всё это не проверялось :))
- Смонтировать реестр Windows в GNU/Linux как winregfs
И наконец: использовать разные программы для копирования/бекапов разделов (типа Acronis) бесполезно: все они не меняют реестр (скорее всего), поэтому работать в такой ситуации (копирование винды в пределах одного компа) не будут.
И ещё: весь материал этого раздела проверялся только на Windows XP.
/boot/grub/grub.cfg
В Windows XP его аналог — это файл boot.ini в корне раздела с Windows, а в Windows 7 — это Windows Boot Manager.
Мощный командный интерпретатор
В стандартном интерпретаторе (то есть в cmd.exe) есть много разных фич типа ветвления, так же, как и в UNIX’овых интерпретаторах. Там даже есть дебаговый вывод (а-ля set -x), а именно echo on, правда он включен по дефолту и обычно первым действием в скрипте его отключают (echo off, разумеется).
Вообще, виндовая команда echo крайне непоследовательна: её действие довольно странным образом зависит от аргумента:
| cmd.exe | bash |
|---|---|
| echo foo | echo foo |
| echo on | set -x |
| echo off | set +x |
| echo | shopt -o xtrace |
После лицезрения этой таблицы все юниксоиды, конечно же, схватились за голову и сказали: «Что за идиоты проектировали винду?» Впрочем, в UNIX’е тоже не всё гладко: с какой стати set -x включает дебаг, а set +x выключает его??? То же самое относится к остальным режимам, включаемым командой set.
Ах да, я же обещал мощный командный интерпретатор. 
Спасибо Evgeny_Shiryaev, 6opoDuJIo, amdf, easyman, EndUser, risik, NoOne и aik за ценные замечания и исправления ошибок.
I want to do exactly what unix «cat» does, but on my PC. Is there a simple equivalent command for the Windows command line?
Specifically I want to create a file from all the files of a given type in a folder
In Unix:
cat *fna >all_fna_files.fna
(which joins all the «.fna» text files into one big text file)
asked Jun 10, 2012 at 7:22
5
type
It works across command.com, cmd, and PowerShell (though in the latter it’s an alias for Get-Content, so is cat, so you could use either).
From the Wikipedia article (emphasis mine):
In computing, type is a command in various VMS. AmigaDOS, CP/M, DOS, OS/2 and Microsoft Windows command line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS/4NT and Windows PowerShell. It is used to display the contents of specified files. It is analogous to the Unix cat command.
C:\>echo hi > a.txt
C:\>echo bye > b.txt
C:\>type a.txt b.txt > c.txt
C:\>type c.txt
hi
bye
answered Jun 10, 2012 at 7:47
ckhanckhan
7,8112 gold badges17 silver badges16 bronze badges
16
From the command shell:
copy a.txt + b.txt + c.txt output.txt
(But that follows the command shells use of control-Z as an end of file marker, so not suitable in some cases).
In PowerShell:
get-content a.txt,b.txt,c.txt | out-file output.txt
and you can control (using -Encoding parameter) the file encoding (which allows transcoding by using different encoding for the read and write).
answered Jun 10, 2012 at 7:33
RichardRichard
8,9623 gold badges26 silver badges27 bronze badges
6
I have just used the cat command in DOS (Windows 7 Pro) in the following manner and successfully merged 3 files (log1.txt, log2.txt, log3.txt) into a single file:
cat log*.txt >> myBigLogFile.txt
Note: cat log*.txt > myBigLogFile2.txt also provide the same result, but it’ll override the previous file.
kenorb
24.8k27 gold badges129 silver badges199 bronze badges
answered Mar 20, 2015 at 13:41
HeidiHeidi
671 silver badge1 bronze badge
3
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
I need to join two binary files with a *.bat script on Windows.
How can I achieve that?
Demurgos
1,57618 silver badges40 bronze badges
asked Sep 13, 2008 at 1:28
Artem TikhomirovArtem Tikhomirov
21.5k10 gold badges48 silver badges68 bronze badges
4
Windows type command works similarly to UNIX cat.
Example 1:
type file1 file2 > file3
is equivalent of:
cat file1 file2 > file3
Example 2:
type *.vcf > all_in_one.vcf
This command will merge all the vcards into one.
Greg Dubicki
6,0903 gold badges56 silver badges68 bronze badges
answered Sep 13, 2008 at 1:53
8
You can use copy /b like this:
copy /b file1+file2 destfile
answered Sep 13, 2008 at 1:29
Greg HewgillGreg Hewgill
955k184 gold badges1151 silver badges1286 bronze badges
3
If you have control over the machine where you’re doing your work, I highly recommend installing GnuWin32. Just «Download All» and let the wget program retrieve all the packages. You will then have access to cat, grep, find, gzip, tar, less, and hundreds of others.
GnuWin32 is one of the first things I install on a new Windows box.
answered Sep 13, 2008 at 3:45
David CitronDavid Citron
43.2k21 gold badges63 silver badges72 bronze badges
2
Shameless PowerShell plug (because I think the learning curve is a pain, so teaching something at any opportunity can help)
Get-Content file1,file2
Note that type is an alias for Get-Content, so if you like it better, you can write:
type file1,file2
answered Sep 13, 2008 at 2:00
Jay BazuziJay Bazuzi
45.3k16 gold badges112 silver badges168 bronze badges
5
Just use the dos copy command with multiple source files and one destination file.
copy file1+file2 appendedfile
You might need the /B option for binary files
VFDan
83110 silver badges26 bronze badges
answered Sep 13, 2008 at 1:32
simonsimon
5,7977 gold badges31 silver badges36 bronze badges
0
In Windows 10’s Redstone 1 release, the Windows added a real Linux subsystem for the NTOS kernel. I think originally it was intended to support Android apps, and maybe docker type scenarios. Microsoft partnered with Canonical and added an actual native bash shell. Also, you can use the apt package manager to get many Ubuntu packages. For example, you can do apt-get gcc to install the GCC tool chain as you would on a Linux box.
If such a thing existed while I was in university, I think I could have done most of my Unix programming assignments in the native Windows bash shell.
answered May 17, 2016 at 20:15
sam msftsam msft
5576 silver badges18 bronze badges
If you simply want to append text to the end of existing file, you can use the >> pipe. ex:
echo new text >>existingFile.txt
answered May 30, 2014 at 3:49
So i was looking for a similar solution with the abillity to preserve EOL chars and found out there was no way, so i do what i do best and made my own utillity
This is a native cat executable for windows — https://mega.nz/#!6AVgwQhL!qJ1sxx-tLtpBkPIUx__iQDGKAIfmb21GHLFerhNoaWk
Usage: cat file1 file2 file3 file4 -o output.txt
-o | Specifies the next arg is the output, we must use this rather than ">>" to preserve the line endings
I call it sharp-cat as its built with C#, feel free to scan with an antivirus and source code will be made available at request
answered Jan 13, 2019 at 10:03
I try to rejoin tar archive which has been splitted in a Linux server.
And I found if I use type in Windows’s cmd.exe, it will causes the file being joined in wrong order.(i.e. type sometimes will puts XXXX.ad at first and then XXXX.ac , XXXX.aa etc …)
So, I found a tool named bat in GitHub https://github.com/sharkdp/bat which has a Windows build, and has better code highlight and the important thing is, it works fine on Windows to rejoin tar archive!
answered Nov 10, 2018 at 5:17
1
Windows type command has problems, for example with Unicode characters on 512 bytes boundary. Try Cygwin’s cat.
answered May 13, 2020 at 14:44
user42391user42391
211 silver badge1 bronze badge
If you have to use a batch script and have python installed here is a polyglot answer in batch and python:
1>2# : ^
'''
@echo off
python "%~nx0" " %~nx1" "%~nx2" "%~nx3"
exit /b
rem ^
'''
import sys
import os
sys.argv = [argv.strip() for argv in sys.argv]
if len(sys.argv) != 4:
sys.exit(1)
_, file_one, file_two, out_file = sys.argv
for file_name in [file_one, file_two]:
if not os.path.isfile(file_name):
print "Can't find: {0}".format(file_name)
sys.exit(1)
if os.path.isfile(out_file):
print "Output file exists and will be overwritten"
with open(out_file, "wb") as out:
with open(file_one, "rb") as f1:
out.write(f1.read())
with open(file_two, "rb") as f2:
out.write(f2.read())
If saved as join.bat usage would be:
join.bat file_one.bin file_two.bin out_file.bin
Thanks too this answer for the inspiration.
YorSubs
3,2847 gold badges37 silver badges60 bronze badges
answered Oct 15, 2014 at 13:40
NoelkdNoelkd
7,7262 gold badges30 silver badges43 bronze badges
What is the cat command and how to use cat in Windows or windows cat equivalent?
cat command ( short for concatenate) is one of the powerful commands to create single or multiple files, view the contents of the file, concatenate multiple files, copy the content to other files, and print output to the terminal or file.
The cat command is mostly used in Linux and other operating systems. The cat command is called cat as it is used to concatenate files. For example, to display the contents of a file, use cat filename.txt, to view the large file, use cat filename.txt | more
If you use the cat command in windows cmd (command prompt/command line), it will throw an exception as 'cat' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program, or batch file.
In the Microsoft Windows operating system, if you use the help cat command in Windows PowerShell terminal, it gives the below output
PS C:\> help cat
NAME
Get-Content
SYNTAX
Get-Content [-Path] <string[]> [-ReadCount <long>] [-TotalCount <long>]
[-Tail <int>] [-Filter <string>] [-Include
<string[]>] [-Exclude <string[]>] [-Force] [-Credential <pscredential>]
[-UseTransaction] [-Delimiter <string>]
[-Wait] [-Raw] [-Encoding {Unknown | String | Unicode | Byte |
BigEndianUnicode | UTF8 | UTF7 | UTF32 | Ascii |
Default | Oem | BigEndianUTF32}] [-Stream <string>] [<CommonParameters>]
Get-Content -LiteralPath <string[]> [-ReadCount <long>] [-TotalCount <long>]
[-Tail <int>] [-Filter <string>]
[-Include <string[]>] [-Exclude <string[]>] [-Force] [-Credential <pscredential>]
[-UseTransaction] [-Delimiter
<string>] [-Wait] [-Raw] [-Encoding {Unknown | String | Unicode | Byte |
BigEndianUnicode | UTF8 | UTF7 | UTF32 |
Ascii | Default | Oem | BigEndianUTF32}] [-Stream <string>] [<CommonParameters>]
ALIASES
gc
cat
type
REMARKS
Get-Help cannot find the Help files for this cmdlet on this computer.
It is displaying only partial help.
-- To download and install Help files for the module that includes
this cmdlet, use Update-Help.
-- To view the Help topic for this cmdlet online, type:
"Get-Help Get-Content -Online" or
go to https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=113310.
Help cat command in windows PowerShell output.
Cool Tip: cat in Windows alias are type, gc, and Get-Content
In the above PowerShell terminal, the help cat command gives output as Get-Content and other aliases used for cat alternative in windows. You can use the windows cat equivalent cmdlets like type, gc and Get-Content.
The type command is a Windows cat equivalent that works across a command-line prompt (cmd) and a Windows PowerShell. type command used in Windows to view the contents of the given file without modifying it.
In this post, we will discuss how to display the contents of a file on the screen using the cat equivalent in windows.
Windows Cat equivalent in cmd & PowerShell : type
type command syntax in windows
Syntax
type [<Drive>:][<Path>]<FileName>
Parameters
[<Drive>:][<Path>] : location and name of the file to use for viewing contents.
<FileName> : Single file name or separate multiple file names with spaces on cmd
Windows Cat equivalent – type command Examples
To get help on type command
type /?
The above command in cmd gets help on windows cat equivalent type command and displays contents of a text file or files. Help command gives output as
TYPE [drive:][path]filename
To view single file content using type command
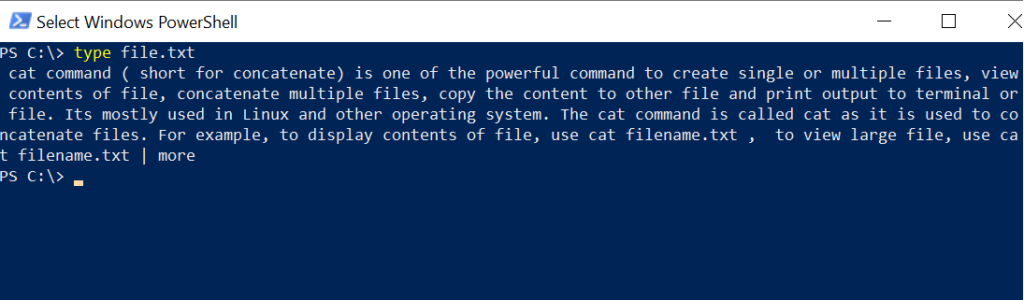
C:\>type file.txt
It will display a view of the file.txt file as given in the below image
Cool Tip: How to get permissions on folders and subfolders!
Windows Cat equivalent – view multiple file content using type
Sometimes, it is necessary to view the content of the file which is locked by another program and also copy the content to another file. type command in windows provides an easy way of doing it.
C:\> type file1.txt ,file2.txt > resultfile.txt C:\> type resultfile.txt
In the above command, we have used two files separated by, (comma) in PowerShell. If you are using a command prompt use separator as space. Two files of concatenated output will be stored in resultfile.txt.
The second command, type resultfile.txt display contents on the screen. windows cat equivalent type command doesn’t lock the file it is viewing on the screen.
Cool Tip: Use set-aduser to modify active directory user attributes!
To view large-sized file content
C:\>type logs.txt | more
Sometimes, we may need to view the contents of a lengthy file like a log file. In order to view lengthy content, use more a filter to view content on the screen one line at a time.
type Command FAQ
What is the cat equivalent command in windows?
The type command is a Windows cat equivalent that works on command-line prompt and a Windows PowerShell.
You can also use GC-Content cmdlet as an alias for the cat command in windows.
How to use cat command in windows?
Use type command in windows to view the contents of the text file or files. If you need more help, use type /?type command syntax is TYPE [drive:][path]filename
what is the windows equivalent of the Unix command cat?
cat command in Unix is used to concatenate files and print content. windows type command is used to display the content of the text file. You can also use Get-Content cmdlet to display content
‘cat’ is not recognized as an internal or external command
cat command not used in windows. If you use cat in windows command prompt (cmd), it will display a message as `cat` is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable command, or batch script.
use type command in the command line or PowerShell. However, if you use Get-Help cat on PowerShell, it gives output as Get-Content which is an alias of type command.
Best type command windows example
type command best feature is to view the content of the file without locking the file and even copy the contents of the file which are locked by another program to a different file
How to concatenate two text files in PowerShell?
Let’s consider two files file1.txt and file2.txt, to concatenate two files using PowerShell, use the below command
type file1.txt file2.txt > resultfile.txt
above command concatenate file1.txt and file2.txt into resultfile.txt file.
Does cat command work in Windows?
The cat command is used to create single or multiple files, concatenate files, and view the contents of the file.
cat command in windows doesn’t work. If you type cat in windows cmd, it will throw an error as `cat` is not recognized as an internal or external command.
However, you can use the cat alias command Get-Content or type to perform the same operation as the cat command.
Why is the cat command used?
The cat command in Unix/Linux systems is used to read the content of the file and print the output of the file on to the console.
Cool Tip: Know more about how to get aduser using userprincipalname!
Conclusion:
Windows operating system doesn’t have the cat command in Windows. using the cat command in cmd line, it will throw an exception as “‘cat’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file”.
However, using the cat command in PowerShell displays its alias command as Get-Content and type.
type command is a built-in alias of the Get-Content cmdlet which also displays the contents but with a different syntax.
In the above post, I explained how to use cat equivalent command in Windows using a built-in command type to display file contents, view lengthy files, and view multiple files contents.
You can find more topics about PowerShell Active Directory commands and PowerShell basics on the ShellGeek home page.