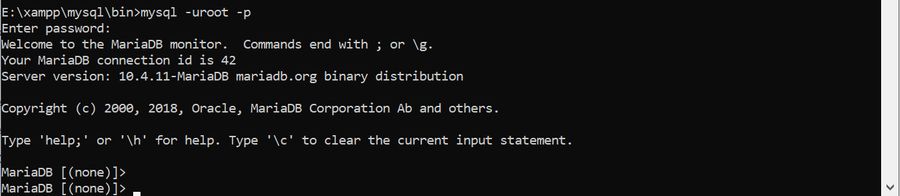
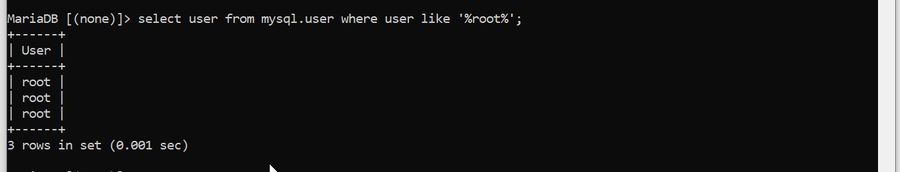
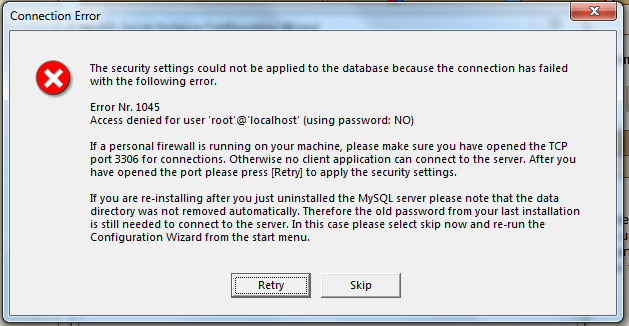
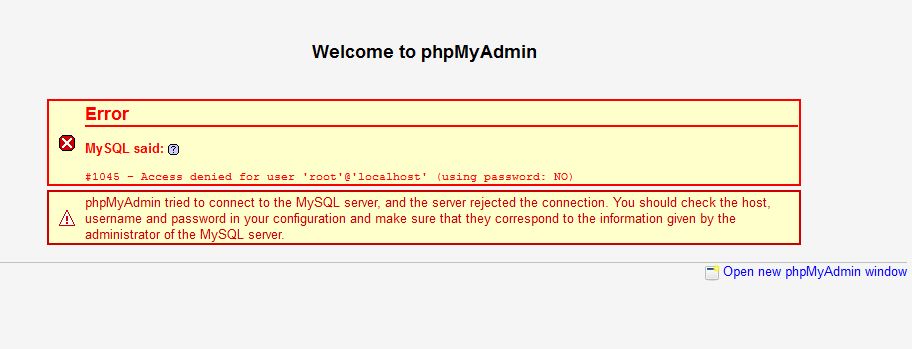
If you have that same problem in MySql 5.7.+ :
Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost'
it’s because MySql 5.7 by default allow to connect with socket, which means you just connect with sudo mysql. If you run sql :
SELECT user,authentication_string,plugin,host FROM mysql.user;
then you will see it :
+------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+
| user | authentication_string | plugin | host |
+------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+
| root | | auth_socket | localhost |
| mysql.session | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost |
| mysql.sys | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost |
| debian-sys-maint | *497C3D7B50479A812B89CD12EC3EDA6C0CB686F0 | mysql_native_password | localhost |
+------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
To allow connection with root and password, then update the values in the table with command :
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'Current-Root-Password';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Then run the select command again and you’ll see it has changed :
+------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+
| user | authentication_string | plugin | host |
+------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+
| root | *2F2377C1BC54BE827DC8A4EE051CBD57490FB8C6 | mysql_native_password | localhost |
| mysql.session | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost |
| mysql.sys | *THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORDTHATCANBEUSEDHERE | mysql_native_password | localhost |
| debian-sys-maint | *497C3D7B50479A812B89CD12EC3EDA6C0CB686F0 | mysql_native_password | localhost |
+------------------+-------------------------------------------+-----------------------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
And that’s it. You can run this process after running and completing the sudo mysql_secure_installation command.
For mariadb, use
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('manager');
to set password.
More at https://mariadb.com/kb/en/set-password/
answered Nov 26, 2018 at 18:59
KeitelDOGKeitelDOG
4,7804 gold badges18 silver badges33 bronze badges
10
Use the instructions for resetting the root password — but instead of resetting the root password, we’ll going to forcefully INSERT a record into the mysql.user table
In the init file, use this instead
INSERT INTO mysql.user (Host, User, Password) VALUES ('%', 'root', password('YOURPASSWORD'));
GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' WITH GRANT OPTION;
answered Jul 31, 2013 at 16:42
Andy JonesAndy Jones
6,2054 gold badges31 silver badges47 bronze badges
9
It didn’t like my user privilege so I SUDO it.
(in bash << sudo set user and password)
(this gives username of root and sets the password to nothing)
(On Mac)
sudo mysql -uroot -p
Pang
9,624146 gold badges81 silver badges122 bronze badges
answered Jun 30, 2017 at 6:48
Dan KaiserDan Kaiser
9918 silver badges7 bronze badges
1
Try the following commands
~$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
~$ sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
~$ mysql -u root
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1 to server version: 4.1.15-Debian_1-log
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the buffer.
mysql>
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> update user set password=PASSWORD("root") where User='root';
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> quit
~$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
Stopping MySQL database server: mysqld
STOPPING server from pid file /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
mysqld_safe[6186]: ended
[1]+ Done mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables
~$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start
~$ mysql -u root -p
* MySQL Community Server 5.6.35 is started
~$ mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 1
Server version: 5.6.35 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
answered Sep 20, 2017 at 13:28
aashishaashish
2,4631 gold badge21 silver badges19 bronze badges
4
for the people who are facing below error in mysql 5.7+ version —
Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
-
Open new terminal
-
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
…
MySQL Community Server 5.7.8-rc is stopped -
sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
this will skipp all grant level privileges and start the mysql in safe mode
Sometimes the process got stucked just because of
grep: write error: Broken pipe
180102 11:32:28 mysqld_safe Logging to ‘/var/log/mysql/error.log’.
Simply press Ctrl+Z or Ctrl+C to interrupt and exit process
mysql -u root
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 2
Server version: 5.7.8-rc MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2015, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type ‘help;’ or ‘\h’ for help. Type ‘\c’ to clear the current input statement.
- mysql>
use mysql;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
-
mysql>
update user set authentication_string=password('password') where user='root';
Query OK, 4 rows affected, 1 warning (0.03 sec)
Rows matched: 4 Changed: 4 Warnings: 1 -
mysql>
flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) -
mysql>
quit
Bye -
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
..180102 11:37:12 mysqld_safe mysqld from pid file /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid ended
.
* MySQL Community Server 5.7.8-rc is stopped
arif@ubuntu:~$ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start
..
* MySQL Community Server 5.7.8-rc is started
-
mysql -u root -pEnter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 2
Server version: 5.7.8-rc MySQL Community Server (GPL)
after mysql 5.7+ version the column password replaced by name authentication_string from the mysql.user table.
hope these steps will help anyone, thanks.
answered Jan 2, 2018 at 6:20
ArifMustafaArifMustafa
4,6575 gold badges40 silver badges48 bronze badges
0
I was using ubuntu 18 and simply installed MySQL (password:root) with the following commands.
sudo apt install mysql-server
sudo mysql_secure_installation
When I tried to log in with the normal ubuntu user it was throwing me this issue.
ERROR 1698 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost'
But I was able to login to MySQL via the super user. Using the following commands I was able to log in via a normal user.
sudo mysql
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'root';
exit;
Then you should be able to login to Mysql with the normal account.
answered Sep 17, 2019 at 7:06
If you are getting this error in Workbench but you are able to log in from terminal then follow this steps.
First simply log in with your current password:
sudo mysql -u root -p
Then change your password because having low strength password gives error sometimes.
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'new-strong-password';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Then simply exit and again login with your new password:
quit
sudo mysql -u root -p
Once you successfully logged in type the command:
use mysql;
It should show a message like ‘Database changed’ then type:
UPDATE user SET plugin='mysql_native_password' WHERE User='root';
After that type:
UPDATE mysql.user set authentication_string=PASSWORD('new-strong-password') where user='root';
Then type:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Then simply exit:
quit
Now try to log in with your new password in your WORKBENCH. Hope it will work. Thank you.
answered Apr 17, 2020 at 17:04
0
For my case, I found this error after fresh installation of mysql on Mac OS Big Sur.
What i did to fix it was:
I click on the apple logo, go to system preferences and then click on mysql.
There’s an initialize database button on the opened settings window, I click on that, and then when I try to access again, it’s solved.
answered Apr 4, 2021 at 4:04
2
I faced this problem while installing Testlink on Ubuntu server, I followed these steps
mysql -u root
use mysql;
update user set password=PASSWORD("root") where User='root';
flush privileges;
quit
Now stop the instance and start again i.e
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start
radbyx
9,38221 gold badges84 silver badges128 bronze badges
answered Aug 4, 2018 at 6:57
Well the easiest way to reset root password is:
-
restart mysqld —skip-grant-tables option. This enables anyone to
connect without a password and with all privileges. Because this is
insecure, you might want to use —skip-grant-tables in conjunction
with —skip-networking to prevent remote clients from connecting. -
Connect to the mysqld server with this command:
-
shell> mysql Issue the following statements in the mysql client.
Replace the password with the password that you want to use. -
mysql> UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘MyNewPass’)
-> WHERE User=’root’; mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; -
Stop the server, then restart it normally (without the —skip-grant-tables and —skip-networking options).
Source Mysql documentation and personal experience:
http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/resetting-permissions.html
answered May 21, 2014 at 10:42
avijendravijendr
3,9982 gold badges31 silver badges46 bronze badges
In my case:
- I set plugin authentication to «» (empty) and I can’t run mysql server:
SOLUTION:
- nano /etc/mysql/my.cnf
- edit:
[mysqld]
skip-grant-tables
- service mysql restart
- mysql -u root
- use mysql
- UPDATE mysql.user SET plugin = ‘mysql_native_password’ WHERE User = ‘root’
- flush privileges
answered Apr 27, 2021 at 12:08
CecherzCecherz
561 silver badge7 bronze badges
alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified with mysql_native_password by '$your_password$';
it worked for me.
note: use strong password
for example
alter user 'root'@'localhost' identified with mysql_native_password by 'root';
answered Mar 31, 2022 at 15:01
I resolved the same issue by running Workbench as administrator.
…I guess it’s because of restrictions on company computers, in my case…
answered Feb 28, 2018 at 12:17
MySQL default password for root is assigned depending on the way you have installed MySQL.
If you have installed it from MySQL Yum repository, MySQL SUSE repository, or RPM packages directly downloaded from Oracle, you can obtain the password using following command:
sudo grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
answered Dec 15, 2020 at 13:50
nayan dhabardenayan dhabarde
1,8141 gold badge20 silver badges38 bronze badges
Try out the following steps to overcome this issue:
- Open terminal / command prompt and navigate to the bin folder of the MySQL installation folder. Then run the command
mysqld --console. - If you can see that line
171010 14:58:22 [Note] --secure-file-privis set to NULL. Operations related to importing and exporting data are disabled, after executing the above command from the command prompt. - Then you need to check that the
mysqldis either blocked by the Windows Firewall or another program. - If it’s blocked by Windows Firewall then need to unblock from it and save settings.
- To unblock the
mysqldormysqlapplication, follow the below steps:- Go to command prompt and type
wf.mscto open the firewall settings. - Click on Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall.
- Check the
mysqldormysqldinstances are available in the list and check the checkbox for the domain, public and private and save the settings.
- Go to command prompt and type
- Return to the bin folder and try the command from step 1 again.
- It should work fine and not show any errors.
It should be possible to run the MySQL console without any problems now!
answered Oct 10, 2017 at 9:42
0
I resolved the same issue using next sql and restarting MySQL server:
update mysql.user set Select_priv='Y',Insert_priv='Y',Update_priv='Y',Delete_priv='Y',Create_priv='Y',Drop_priv='Y',Reload_priv='Y',Shutdown_priv='Y',Process_priv='Y',File_priv='Y',Grant_priv='Y',References_priv='Y',Index_priv='Y',Alter_priv='Y',Show_db_priv='Y',Super_priv='Y',Create_tmp_table_priv='Y',Lock_tables_priv='Y',Execute_priv='Y',Repl_slave_priv='Y',Repl_client_priv='Y',Create_view_priv='Y',Show_view_priv='Y',Create_routine_priv='Y',Alter_routine_priv='Y',Create_user_priv='Y',Event_priv='Y',Trigger_priv='Y',Create_tablespace_priv='Y'
where user='root';
answered Nov 11, 2017 at 19:39
I worked on Access Denied for User ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: YES) for several hours, I have found following solution,
The answer to this problem was that in the my.cnf located within
/etc/mysql/my.cnf
the line was either
bind-address = 127.0.0.1
(or)
bind-address = localhost
(or)
bind-address = 0.0.0.0
I should prefer that 127.0.0.1
I should also prefer 0.0.0.0, it is more flexible
because which will allow all connections
answered Nov 15, 2017 at 6:36
0
I don’t think you have to escape the --init-file parameter:
"C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.6\bin\mysqld.exe" --defaults-file="C:\\Program Files\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 5.6\\my.ini" --init-file=C:\\mysql-init.txt
Should be:
"C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.6\bin\mysqld.exe" --defaults-file="C:\\Program Files\\MySQL\\MySQL Server 5.6\\my.ini" --init-file=C:\mysql-init.txt
answered Nov 30, 2017 at 2:19
JordanJordan
1481 silver badge11 bronze badges
for the above problem ur password in the system should matches with the password u have passed in the program because when u run the program it checks system’s password as u have given root as a user so gives u an error and at the same time the record is not deleted from the database.
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
class Delete
{
public static void main(String []k)
{
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student";
String user="root";
String pass="jacob234";
try
{
Connection myConnection=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,pass);
Statement myStatement=myConnection.createStatement();
String deleteQuery="delete from students where id=2";
myStatement.executeUpdate(deleteQuery);
System.out.println("delete completed");
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Keep ur system password as jacob234 and then run the code.
answered Feb 9, 2018 at 14:11
With me was the same problem, but it was caused, because i was using the mysql server on 32 (bit) and the workbench was running on 64(bit) version. the server and the workbench need to has the same version.
xpress
answered Dec 16, 2018 at 16:24
I was facing the same problem when I’m trying to connecting Mysql database using the Laravel application.
I would like to recommend please check the password for the user. MySQL password should not have special characters like #, &, etc…
answered Mar 13, 2020 at 16:23
1
cause might be missing mysqld file in /var/run/mysqld
sudo service mysql stop
sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables
sudo service mysql start
if file does not exits then create file
mkdir -p /var/run/mysqld
chown mysql:mysql /var/run/mysqld
check now you are able to login mysql -uroot -p123
otherwise do
sudo mysql -u root
use mysql;
show tables;
describe user;
update user set authentication_string=password('1111') where user='root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
exit;
mysql -uroot -p123
link — mysqld_safe Directory ‘/var/run/mysqld’ for UNIX socket file don’t exists
answered Jun 29, 2021 at 12:41
For windows:-
If the instance configuration fails with similar issue and if you cannot log in to the root account.
Steps I followed to fix the issue:—
- Stop MySql service if running.
- Uninstall MySql using ‘remove’ option from the installation wizard.
- If MySql service is not removed from services,
sc delete <MYSQL_SERVICE_NAME>
- Delete all data containing in the MySql folder (‘Program files’, ‘Program data’ or the custom installation directory you have given).
- Remove MySql path from the environmental variable.
- Disable windows firewall.
- Reinstall and config root account with new password.
answered Jun 30, 2022 at 9:55
the only thing that worked was sudo mysql followed by adding skip-grant-tables in [mysqld] section of /etc/my.cnf file — Ubuntu Mysql 5.5
answered Jan 25 at 9:25
Please do crosscheck your password from your phpmyadmin login webpage on localhost, if its correct, then it will work without tempering with yoru credentials
answered Jul 10 at 20:26
Same issue occurred with me also, turned out my db username was wrong
answered Jul 20, 2022 at 6:04
MySQL users often face an issue called Error 1045 (28000) access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: yes). This usually occurs when you enter an incorrect password or password for your database. Fixing these credentials can resolve this error in no time.
In this article, we will look at the ways to resolve this error.
How to fix “Error 1045 (28000) access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: yes)”?
The error looks something like this —
mysql -uroot -proot
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
It arises when you perform a fresh installation of MySQL and try to login with a password. The default password of MySQL is blank () (i.e. empty string).
So, you can login to the MySQL server using the same password.
Example
>mysql -uroot -pEnter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 9
Server version: 10.4.11-MariaDB mariadb.org binary distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type ‘help;’ or ‘\h’ for help. Type ‘\c’ to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]>The best practice is to change the password after the new installation.
Set root user password
You must set the root user password after performing the new installation. Here is the code to set it –
Login as user root with blank password
>mysql -u root
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'abc';Now the new password for root user is abc.
How to fix the Error 1045 (28000)?
Let us look at the ways to fix this problem –
-
Enter the correct credentials
The primary method to fix this error is to enter the correct username and password using the following command –
mysql –u username –p -
Ensure the user is correct
Sometimes, the user you might be trying to access does not exist on the MySQL server. You can check if the user exists using the following code-
MariaDB [(none)]> select user from mysql.user where user like '%root%';
+------+
| User |
+------+
| root |
| root |
| root |
+------+
3 rows in set (0.001 sec) If the user does not exist, create it with the desired username.
-
Enter the correct host name
You might be trying to access the server from a host that is different from the defined host name. You will encounter Error 1045 in this case. You can use this code to view details of the user –
To fix this, you can update the host name for the user using the code below –
mysql> mysql -u root -pabc -h <IP> -P 3306You might encounter the error in due to the following scenarios –
Entered wrong password
>mysql -uroot -pssssss
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
Host doesn’t not have permission to connect databaseThis is a very common error that occurs while connecting to a remote database. While connecting to such a database we need to give access to the HOST IP ADDRESS to connect to it.
This is the IP Address of the source system which connects to the database server.
If access is not given, then run the given command –
CREATE USER ‘dbuser1’@'< Host IP >’ IDENTIFIED VIA mysql_native_password USING ‘***’;GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO ‘dbuser1’@'< Host IP >’ REQUIRE NONE WITH GRANT OPTION MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_UPDATES_PER_HOUR 0 MAX_USER_CONNECTIONS 0;
Conclusion
Apart from all this, make sure the host contains the correct IP address and host name, to avoid the Error 1045 (28000) access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (using password: yes).
grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
Sort date (newest date)
You may see something like this;
[root@SERVER ~]# grep 'temporary password' /var/log/mysqld.log
2016-01-16T18:07:29.688164Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: O,k5.marHfFu
2016-01-22T13:14:17.974391Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: b5nvIu!jh6ql
2016-01-22T15:35:48.496812Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: (B*=T!uWJ7ws
2016-01-22T15:52:21.088610Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: %tJXK7sytMJV
2016-01-22T16:24:41.384205Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: lslQDvgwr3/S
2016-01-22T22:11:24.772275Z 1 [Note] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: S4u+J,Rce_0t
[root@SERVER ~]# mysql_secure_installation
Securing the MySQL server deployment.
Enter password for user root:
The existing password for the user account root has expired. Please set a new password.
New password:
Re-enter new password:
If you see it says
... Failed! Error: Your password does not satisfy the current policy requirements
That means your password needs to have a character such as ! . # - etc...
mix characters well, upper case, lower case, ! . , # etc...
New password:
Re-enter new password:
The 'validate_password' plugin is installed on the server.
The subsequent steps will run with the existing configuration
of the plugin.
Using existing password for root.
Estimated strength of the password: 100
Change the password for root ? ((Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Estimated strength of the password: 100
Do you wish to continue with the password provided?(Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
By default, a MySQL installation has an anonymous user,
allowing anyone to log into MySQL without having to have
a user account created for them. This is intended only for
testing, and to make the installation go a bit smoother.
You should remove them before moving into a production
environment.
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
Success.
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from
'localhost'. This ensures that someone cannot guess at
the root password from the network.
Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
Success.
By default, MySQL comes with a database named 'test' that
anyone can access. This is also intended only for testing,
and should be removed before moving into a production
environment.
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
- Dropping test database...
Success.
- Removing privileges on test database...
Success.
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes
made so far will take effect immediately.
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : Y
Success.
All done!
[root@SERVER ~]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 11
Server version: 5.7.10 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Watch the last 10 minutes of this video, it teaches you how you do it.
This “access denied” error is one of the most common errors you’ll get when working with MySQL.
Learn how to fix it, and see a range of solutions if the suggested fix does not work, in this article.
When you try to connect to a MySQL database on your own computer (called “localhost”), you may get this error:
Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
You might get an error code in front of it:
ERROR 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
You might also get the error with “using password no”:
Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: NO)
You’ll see this if you log into MySQL using the command line:
mysql -u root -p
You might also see this if you log in to MySQL using an IDE such as MySQL Workbench. Or even if you use phpMyAdmin.
What does this mean? How can you fix it?
There are a few solutions to this, which I’ve detailed below. Try one, and if it doesn’t work, try another one.
Also a tip for logging in: don’t enter your password in the command line itself, because this will be stored in your command history. Use the -p option, as mentioned above, and then you’ll be prompted to enter the password.
Solution 1: Sudo then Change Password
If you get the “access denied” error, one way to solve it is by using sudo to log in to mysql and change the root password.
Step 1: Open the command line on your system.
Step 2: Open mysql using the sudo command:
sudo mysql
Step 3: Enter the password for this account.
Step 4: Change the auth_plugin to mysql_native_password, and the password for the root account, in a single command:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost'
IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'your_new_password';Substitute the word your_new_password with a new secure password that you want to use for the root account.
The mysql_native_password method is a traditional method of authentication and will allow you to login.
Step 5: Flush the privileges, which tells the server to refresh the grant tables and apply your changes, with this command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Step 6: You can confirm that the new authentication method, or plugin, is used by selecting from the mysql.user table.
SELECT user, plugin
FROM mysql.userResults:
| user | plugin |
| root | mysql_native_password |
Step 7: Exit the console by pressing CTRL + D or typing exit.
exit;
Step 8: Log in to mysql using the root account and the new password you set, which should work:
mysql -u root -p
You should now be logged in to the root account in mysql.
Solution 2: Edit My.cnf File
If the above solution did not work, you may need to edit the mysql.cnf file to allow for changes to the root account.
Step 1: Open the my.cnf file. This may be stored in:
/etc/my.cnf /etc/mysql/my.cnf
If you’re not sure where it is, search your MySQL installation folder (e.g. on Windows or Mac) for the file.
If you don’t have a my.cnf file (MacOS does not include one by default). You can create one in the /etc folder if you like.
Step 2: Add the word skip-grant-tables under the word [mysqld]. Your file may look like this:
[mysqld] skip-grant-tables
Step 3: Restart the MySQL server.
Step 4: Login to the root account:
mysql -u root -p
Step 5: Flush the privileges, which tells the server to refresh the grant tables and apply your changes, with this command:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Step 6: Set a new password for the account:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your_new_password';Substitute the word your_new_password with a new secure password that you want to use for the root account.
Step 7: Open the my.cnf file you opened in step 1, and remove the line about skip-grant-tables, and save the file.
Step 8: Restart the MySQL server again.
Step 9: Log in to the root account again:
mysql -u root -p
You should now be able to log in successfully with your new password and not get an error.
Conclusion
Either of these two solutions should hopefully solve the problem for you, and you should no longer get the error “Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’”.
If you have any questions, feel free to use the comments section below.
Ошибка: Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (Using password: YES и NO)
При работе с системой MySQL могут возникнуть самые разные ошибки, и на этапе освоения программы разобраться с ними может быть сложно. Одна из наиболее распространенных проблем — ошибка 1045, которая сопровождается сообщением Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (Using password: YES и NO). Сегодня я расскажу, как ее исправить.
Понять суть проблемы можно, переведя сообщение об ошибке на русский язык. Означает оно, что пользователю с именем root на машине localhost запрещен доступ к БД при использовании пароля или без него.
Причины ошибки Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’
Чтобы свободно получить доступ в MySQL, должно совпасть три параметра, описывающих пользователя базы данных — имя, название машины и пароль. Если есть какие-то несовпадения, доступ будет запрещен. Самая простая причина проблемы — неправильный ввод пароля. Кроме этого, вызывать ошибку может неправильный синтаксис.
В системе MySQL нет простой зависимости имя пользователя – пароль, название хоста играет важную роль в получении доступа к БД. Оно может иметь вид IP-адреса, доменного имени, ключевого слова (например, localhost) или символа, объединяющего несколько машин в группу (например, % — любой хост, кроме локального).
Наиболее распространенные ошибки при обращении к БД:
- При присвоении прав новому пользователю не был указан адрес машины, с которой он может подключаться. В таком случае ему автоматически будет разрешено пользоваться БД с любого хоста, кроме локального, и при попытке подключения с localhost возникнет ошибка доступа.
- Неправильно расставленные кавычки. Если при создании пользователя написать ‘username@localhost’, это будет значить, что username@localhost может подключаться с любой машины, кроме локальной, а не что username может подключаться с компьютера localhost. Логин пользователя и имя машины должны иметь свою пару кавычек.
- Использование пароля при его отсутствии в базе данных.
В зависимости от того, при каком способе подключения к БД возникает ошибка Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (Using password: YES или NO), используются разные методы решения проблемы.
Если ошибка Access denied for user появляется с указанием Using password: YES, проблема заключается в неправильном вводе пароля. Проверить это можно, открыв таблицу mysql.user, в которой хранятся данные обо всех пользователях.
Порядок действий таков:
- Откройте таблицу пользователей.
- Проверьте, существует ли пользователь root с хостом localhost. Если он есть, смотрите на поле «password». Если там пусто, зайти в базу можно без ввода пароля. Если там что-то есть, значит, вы вводите неправильный пароль.
- Смените пароль командой SET PASSWORD.
- Если пользователя root нет, создайте его, установите пароль и предоставьте ему права.
После этого в базу данных можно зайти. Если изменить данные не получается, следует использовать параметр —skip-grant-tables, который отменяет все настройки разрешений.
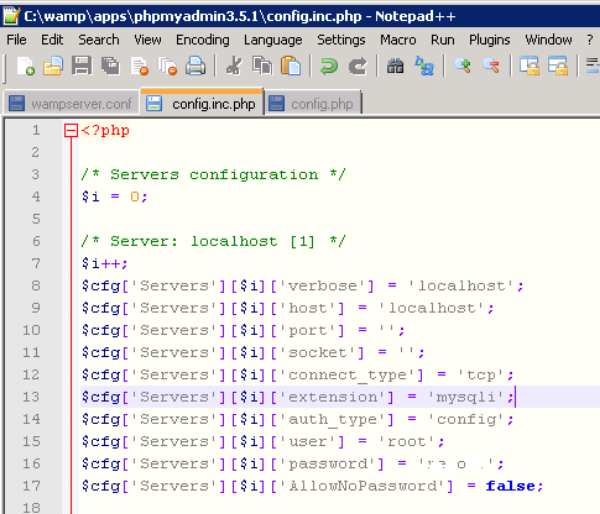
Если ошибка появляется с ключом (Using password: NO), нужно сделать следующее изменить файл config.inc.php, указав в нем правильные данные. Если проблема возникает при установке MySQL, нужно удалить базы данных старой версии программы или сменить пароль для доступа к ним, используя режим —skip-grant-tables.
Таким образом, ошибка Access denied for user ‘root’@’localhost’ (Using password: YES или NO) возникает при несоответствии пароля и имени пользователя и легко исправляется заменой данных для входа.
Опубликовано Обновлено