IIS has a limit for the size of the files users can upload to an application. If the file size exceeds the limit, the application will throw “Error in HTTP request, received HTTP status 413 (Request Entity Too Large)” error.
The default file upload size is 49 KB (49152 bytes). The application records the log below if user tries to upload a file that is bigger than this size.
Why this issue occurs for SSL sites? The reason is that the request body must be preloaded during the SSL handshake process.
Solution
The quickest solution is to increase the upload size limit. IIS uses uploadReadAheadSize parameter in applicationHost.config and web.config files to control this limit.
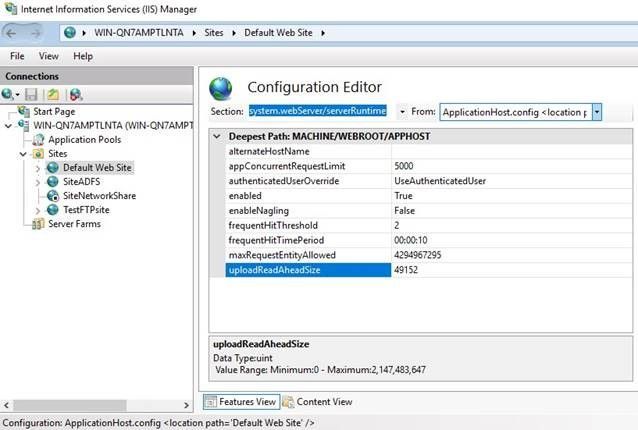
uploadReadAheadSize
Optional uint attribute.
Specifies the number of bytes that a Web server will read into a buffer and pass to an ISAPI extension or module. This occurs once per client request. The ISAPI extension or module receives any additional data directly from the client. The value must be between 0 and 2147483647.
The default value is49152.Server Runtime
Steps to change the value of this parameter:
- Open IIS Manager
- Select the site
- Double click “Configuration Editor”
- Select
system.webServerand thenserverRuntime - Modify the
uploadReadAheadSizevalue - Click “Apply”
You may also want to change maxRequestEntityAllowed parameter. It specifies the maximum number of bytes allowed in the request body.
Note: In another case, the recommendations above didn’t work to solve 413 error. Please check this post for more information
I’ve written a WCF service with .NET 4.0, which is hosted on my Windows 7 x64 Ultimate system with IIS 7.5.
One of the service methods has an ‘object’ as argument and I’m trying to send a byte[] which contains a picture.
As long as the file size of this picture is less then approx. 48KB, all goes well. But if I’m trying to upload a larger picture, the WCF service returns an error: (413) Request Entity Too Large.
So ofcourse I’ve spent 3 hours Googling the error message and every topic I’ve seen about this subject suggests raising the ‘uploadReadAheadSize’ property.
So what I’ve done is using the following commands (10485760 = 10MB):
"appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webserver/serverruntime/uploadreadaheadsize: 10485760 /commit:apphost"
"cscript adsutil.vbs set w3svc/<APP_ID>/uploadreadaheadsize 10485760"
I’ve also used IIS Manager to set the value by opening the site and going to «Configuration Editor» under Management.
Unfortunately I’m still getting the Request Entity Too Large error and it’s getting really frustrating!
So does anybody know what else I can try to fix this error?
Uwe Keim
39.7k57 gold badges175 silver badges291 bronze badges
asked Apr 12, 2012 at 11:49
1
That is not problem of IIS but the problem of WCF. WCF by default limits messages to 65KB to avoid denial of service attack with large messages. Also if you don’t use MTOM it sends byte[] to base64 encoded string (33% increase in size) => 48KB * 1,33 = 64KB
To solve this issue you must reconfigure your service to accept larger messages. This issue previously fired 400 Bad Request error but in newer version WCF started to use 413 which is correct status code for this type of error.
You need to set maxReceivedMessageSize in your binding. You can also need to set readerQuotas.
<system.serviceModel>
<bindings>
<basicHttpBinding>
<binding maxReceivedMessageSize="10485760">
<readerQuotas ... />
</binding>
</basicHttpBinding>
</bindings>
</system.serviceModel>
answered Apr 12, 2012 at 12:39
Ladislav MrnkaLadislav Mrnka
361k59 gold badges660 silver badges670 bronze badges
10
I was having the same issue with IIS 7.5 with a WCF REST Service. Trying to upload via POST any file above 65k and it would return Error 413 «Request Entity too large».
The first thing you need to understand is what kind of binding you’ve configured in the web.config. Here’s a great article…
BasicHttpBinding vs WsHttpBinding vs WebHttpBinding
If you have a REST service then you need to configure it as «webHttpBinding». Here’s the fix:
<system.serviceModel>
<bindings>
<webHttpBinding>
<binding
maxBufferPoolSize="2147483647"
maxReceivedMessageSize="2147483647"
maxBufferSize="2147483647" transferMode="Streamed">
</binding>
</webHttpBinding>
</bindings>
answered Jun 7, 2013 at 18:30
5
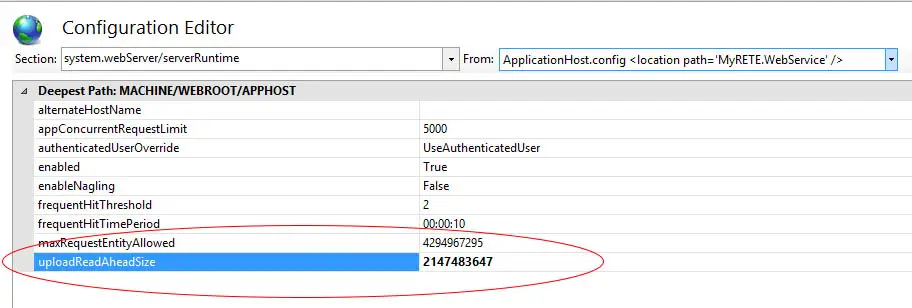
I had the same problem and setting the uploadReadAheadSize solved it:
http://www.iis.net/configreference/system.webserver/serverruntime
«The value must be between 0 and 2147483647.»
It is easily set it in the applicationHost.config-fle if you don’t want to do a cmd-thing.
Its located in WindowsFOLDER\System32\inetsrv\config (2008 server).
You must open it with notepad. Do a Backup of the file first.
According to the comments in config the recommended way to unlock sections is by using a location tag:
<location path="Default Web Site" overrideMode="Allow">
<system.webServer>
<asp />
</system.webServer>
</location>"
So you can write in the bottom (since it doesn’t exist before). I write maxvalue here — write your own value if you want.
<location path="THENAMEOFTHESITEYOUHAVE" overrideMode="Allow">
<system.webServer>
<asp />
<serverRuntime uploadReadAheadSize="2147483647" />
</system.webServer>
</location>
If you put it last before </configuration> for example, you know where you have it.
Hope that solves your problems. It was an SSL overhead issue for me, where too much post freezed the application, raising a (413) Request Entity Too Large error.
abatishchev
98.4k88 gold badges297 silver badges433 bronze badges
answered Mar 29, 2013 at 8:15
Tom PTom P
3093 silver badges2 bronze badges
3
I was receiving this error message, even though I had the max settings set within the binding of my WCF service config file:
<basicHttpBinding>
<binding name="NewBinding1"
receiveTimeout="01:00:00"
sendTimeout="01:00:00"
maxBufferSize="2000000000"
maxReceivedMessageSize="2000000000">
<readerQuotas maxDepth="2000000000"
maxStringContentLength="2000000000"
maxArrayLength="2000000000"
maxBytesPerRead="2000000000"
maxNameTableCharCount="2000000000" />
</binding>
</basicHttpBinding>
It seemed as though these binding settings weren’t being applied, thus the following error message:
IIS7 — (413) Request Entity Too Large when connecting to the service.
The Problem
I realised that the name="" attribute within the <service> tag of the web.config is not a free text field, as I thought it was. It is the fully qualified name of an implementation of a service contract as mentioned within this documentation page.
If that doesn’t match, then the binding settings won’t be applied!
<services>
<!-- The namespace appears in the 'name' attribute -->
<service name="Your.Namespace.ConcreteClassName">
<endpoint address="http://localhost/YourService.svc"
binding="basicHttpBinding" bindingConfiguration="NewBinding1"
contract="Your.Namespace.IConcreteClassName" />
</service>
</services>
I hope that saves someone some pain…
answered Mar 22, 2016 at 16:19
LukeLuke
23k31 gold badges111 silver badges194 bronze badges
3
If you’re running into this issue despite trying all of the solutions in this thread, and you’re connecting to the service via SSL (e.g. https), this might help:
http://forums.newatlanta.com/messages.cfm?threadid=554611A2-E03F-43DB-92F996F4B6222BC0&#top
To summarize (in case the link dies in the future), if your requests are large enough the certificate negotiation between the client and the service will fail randomly. To keep this from happening, you’ll need to enable a certain setting on your SSL bindings. From your IIS server, here are the steps you’ll need to take:
- Via cmd or powershell, run
netsh http show sslcert. This will give you your current configuration. You’ll want to save this somehow so you can reference it again later. - You should notice that «Negotiate Client Certificate» is disabled. This is the problem setting; the following steps will demonstrate how to enable it.
- Unfortunately there is no way to change existing bindings; you’ll have to delete it and re-add it. Run
netsh http delete sslcert <ipaddress>:<port>where<ipaddress>:<port>is the IP:port shown in the configuration you saved earlier. - Now you can re-add the binding. You can view the valid parameters for
netsh http add sslcerthere (MSDN) but in most cases your command will look like this:
netsh http add sslcert ipport=<ipaddress>:<port> appid=<application ID from saved config including the {}> certhash=<certificate hash from saved config> certstorename=<certificate store name from saved config> clientcertnegotiation=enable
If you have multiple SSL bindings, you’ll repeat the process for each of them. Hopefully this helps save someone else the hours and hours of headache this issue caused me.
EDIT: In my experience, you can’t actually run the netsh http add sslcert command from the command line directly. You’ll need to enter the netsh prompt first by typing netsh and then issue your command like http add sslcert ipport=... in order for it to work.
answered Mar 29, 2016 at 19:04
oconnerjoconnerj
3261 gold badge3 silver badges7 bronze badges
1
This helped me to resolve the problem (one line — split for readability / copy-ability):
C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\appcmd set config "YOUR_WEBSITE_NAME"
-section:system.webServer/serverRuntime /uploadReadAheadSize:"2147483647"
/commit:apphost
answered Apr 3, 2014 at 17:51
AnasAnas
5,6325 gold badges39 silver badges71 bronze badges
1
For me, setting the uploadReadAheadSize to int.MaxValue also fixed the problem, after also increasing the limits on the WCF binding.
It seems that, when using SSL, the entire request entity body is preloaded, for which this metabase property is used.
For more info, see:
The page was not displayed because the request entity is too large. iis7
answered Oct 24, 2017 at 13:32
1
In my case, I was getting this error message because I was changed the service’s namespace and services tag was pointed to the older namespace. I refreshed the namespace and the error disapear:
<services>
<service name="My.Namespace.ServiceName"> <!-- Updated name -->
<endpoint address=""
binding="wsHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="MyBindingConfiguratioName"
contract="My.Namespace.Interface" <!-- Updated contract -->
/>
</service>
</services>
answered Jul 12, 2018 at 20:49
Vladimir VenegasVladimir Venegas
3,9145 gold badges25 silver badges46 bronze badges
For anyone else ever looking for an IIS WCF error 413 : Request entity to large and using a WCF service in Sharepoint, this is the information for you. The settings in the application host and web.config suggested in other sites/posts don’t work in SharePoint if using the MultipleBaseAddressBasicHttpBindingServiceHostFactory. You can use SP Powershell to get the SPWebService.Content service, create a new SPWcvSettings object and update the settings as above for your service (they won’t exist). Remember to just use the name of the service (e.g. [yourservice.svc]) when creating and adding the settings. See this site for more info https://robertsep.wordpress.com/2010/12/21/set-maximum-upload-filesize-sharepoint-wcf-service
answered Apr 7, 2015 at 21:16
In my case I had to increase the «Maximum received message size» of the Receive Location in BizTalk. That also has a default value of 64K and so every message was bounced by BizTAlk regardless of what I configured in my web.config
answered May 21, 2015 at 11:45
I’ve been able to solve this by executing a dummy call ( e.g. IsAlive returning true ) just before the request with large content on the same wcf channel/client. Apparently ssl negotation is done on the first call. So no need to increase Uploadreadaheadsize.
answered Sep 18, 2017 at 5:14
reknarekna
5,3137 gold badges45 silver badges54 bronze badges
Got a similar error on IIS Express with Visual Studio 2017.
HTTP Error 413.0 — Request Entity Too Large
The page was not displayed because the request entity is too large.
Most likely causes:
The Web server is refusing to service the request because the request
entity is too large.The Web server cannot service the request because it is trying to
negotiate a client certificate but the request entity is too large.The request URL or the physical mapping to the URL (i.e., the physical
file system path to the URL’s content) is too long.Things you can try:
Verify that the request is valid.
If using client certificates, try:
Increasing system.webServer/serverRuntime@uploadReadAheadSize
Configure your SSL endpoint to negotiate client certificates as part
of the initial SSL handshake. (netsh http add sslcert …
clientcertnegotiation=enable) .vs\config\applicationhost.config
Solve this by editing \.vs\config\applicationhost.config. Switch serverRuntime from Deny to Allow like this:
<section name="serverRuntime" overrideModeDefault="Allow" />
If this value is not edited, you will get an error like this when setting uploadReadAheadSize:
HTTP Error 500.19 — Internal Server Error
The requested page cannot be accessed because the related
configuration data for the page is invalid.This configuration section cannot be used at this path. This happens
when the section is locked at a parent level. Locking is either by
default (overrideModeDefault=»Deny»), or set explicitly by a location
tag with overrideMode=»Deny» or the legacy allowOverride=»false».
Then edit Web.config with the following values:
<system.webServer>
<serverRuntime uploadReadAheadSize="10485760" />
...
answered Feb 25, 2019 at 18:49
OgglasOgglas
62.8k37 gold badges338 silver badges422 bronze badges
1
My problem has gone after I added this:
<system.webServer>
<security>
<requestFiltering>
<requestLimits
maxAllowedContentLength="104857600"
/>
</requestFiltering>
</security>
</system.webServer>
answered Feb 16, 2021 at 23:04
Liam KernighanLiam Kernighan
2,3551 gold badge21 silver badges24 bronze badges
for issue the remote server returned an unexpected response: (413) Request Entity Too Large on WCF with Resful
please see my explain configuration
</client>
<serviceHostingEnvironment multipleSiteBindingsEnabled="false" aspNetCompatibilityEnabled="true"/>
<bindings>
<!-- this for restfull service -->
<webHttpBinding>
<binding name="RestfullwebHttpBinding"
maxBufferPoolSize="2147483647"
maxReceivedMessageSize="2147483647"
maxBufferSize="2147483647" transferMode="Streamed">
<readerQuotas
maxDepth="2147483647"
maxStringContentLength="2147483647"
maxArrayLength="2147483647"
maxBytesPerRead="2147483647" />
</binding>
</webHttpBinding>
<!-- end -->
<!-- this for Soap v.2 -->
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding name="wsBinding1" maxReceivedMessageSize="2147483647" closeTimeout="00:10:00" openTimeout="00:10:00" receiveTimeout="00:10:00" sendTimeout="00:10:00" bypassProxyOnLocal="false" transactionFlow="false" hostNameComparisonMode="StrongWildcard" maxBufferPoolSize="2147483647" messageEncoding="Text" textEncoding="utf-8" useDefaultWebProxy="true" allowCookies="false">
<readerQuotas maxDepth="2147483647" maxStringContentLength="2147483647" maxArrayLength="2147483647" maxBytesPerRead="2147483647" maxNameTableCharCount="2147483647"/>
<reliableSession ordered="true" inactivityTimeout="00:10:00" enabled="false"/>
<!--UsernameToken over Transport Security-->
<security mode="TransportWithMessageCredential">
<message clientCredentialType="UserName" establishSecurityContext="true"/>
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
<!-- this for restfull service -->
<!-- this for Soap v.1 -->
<basicHttpBinding>
<binding name="basicBinding1" maxReceivedMessageSize="2147483647" closeTimeout="00:10:00" openTimeout="00:10:00" receiveTimeout="00:10:00" sendTimeout="00:10:00" bypassProxyOnLocal="false" hostNameComparisonMode="StrongWildcard" maxBufferPoolSize="2147483647" messageEncoding="Text" textEncoding="utf-8" useDefaultWebProxy="true" allowCookies="false" transferMode="Streamed">
<readerQuotas maxDepth="2147483647" maxStringContentLength="2147483647" maxArrayLength="2147483647" maxBytesPerRead="2147483647" maxNameTableCharCount="2147483647"/>
<security mode="None"/>
</binding>
</basicHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<!-- end -->
<services>
<clear/>
<service name="ING.IWCFService.CitisecHashTransfer" >
<endpoint address="http://localhost:8099/CitisecHashTransfer.svc"
behaviorConfiguration="RestfullEndpointBehavior"
binding="webHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="RestfullwebHttpBinding"
name="ICitisecHashTransferBasicHttpBinding"
contract="ING.IWCFService.ICitisecHashTransfer" />
</service>
</services>
<behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior name="ServiceBehavior">
<serviceMetadata httpsGetEnabled="true"/>
<serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="true"/>
<dataContractSerializer maxItemsInObjectGraph="2147483647"/>
<serviceCredentials>
<userNameAuthentication userNamePasswordValidationMode="Custom" customUserNamePasswordValidatorType="ING.IWCFService.IWCFServiceValidator, ING.IWCFService"/>
</serviceCredentials>
<serviceSecurityAudit auditLogLocation="Application" serviceAuthorizationAuditLevel="SuccessOrFailure" messageAuthenticationAuditLevel="SuccessOrFailure"/>
<serviceThrottling maxConcurrentCalls="1000" maxConcurrentSessions="100" maxConcurrentInstances="1000"/>
</behavior>
<behavior>
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="true" httpsGetEnabled="true"/>
<serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="true"/>
<dataContractSerializer maxItemsInObjectGraph="2147483647"/>
</behavior>
</serviceBehaviors>
<endpointBehaviors>
<behavior name="EndpointBehavior">
<dataContractSerializer maxItemsInObjectGraph="2147483647" />
</behavior>
<behavior name="RestfullEndpointBehavior">
<dataContractSerializer maxItemsInObjectGraph="2147483647" />
<webHttp/>
</behavior>
</endpointBehaviors>
</behaviors>
answered Jun 20, 2018 at 9:21
Glued a lot of responses together will ALL info I needed:
IIS Config: C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\config\applicationHost.config (very bottom)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
...
<location path="Default Web Site">
<system.webServer>
<security>
<access sslFlags="SslNegotiateCert" />
<!-- Max upload size in bytes -->
<requestFiltering>
<requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength="104857600" />
</requestFiltering>
</security>
</system.webServer>
</location>
</configuration>
answered Jan 10, 2022 at 15:58
KevinKevin
2,29621 silver badges22 bronze badges
If you have come across this article it is likely that you are trying to configure your ASP.NET application (Core, MVC, Web API, Windows Forms, WCF or other) on an IIS web server which, unlike the development web server , refuses to accept the upload of a file larger than 16kb, returning one of the following errors:
HTTP Error 413.1 — Request Entity Too Large
(413) Request Entity Too Large
Maximum request length exceeded
All these errors are related to exceeding the maximum size of an attachment — or rather, the HTTP Request sent to the server — provided by our ASP.NET application by default. These limitations have been inserted for a valid reason: receiving a file is a rather heavy operation for the server, as it engages a working thread indefinitely. For this reason, the default settings of most ASP.NET applications provide a size generally between 16k and 64k, sufficient for sending / receiving text forms but logically completely inadequate when you need to manage the upload of one or more files.
Luckily enough, solving this problem is quite simple: all we have to do is modify some sections in the application’s Web.config file to extend the limits in bytes normally provided for this type of operation. Since these settings vary according to the versions of IIS, we have entered all the versions for which it is necessary to add (or change) the indicated values.
MaxRequestLength
This value sets the maximum length limit of each Request to a maximum of 1073741824 bytes.
IIS (all versions)
|
<configuration> <system.web> <httpRuntime maxRequestLength=«1048576» /> </system.web> </configuration> |
IIS (version 7.x and higher)
In addition to the above:
|
<system.webServer> <security> <requestFiltering> <requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength=«1073741824» /> </requestFiltering> </security> </system.webServer> |
HttpBindings
If your application is a web service built with ASP.NET WFC (SOAP) or Web API / MVC (REST), you also need to add the following attributes to the bindings you intend to use. The best way to proceed is to open the Web.config for the application and, under each of them, add the following highlighted parameters:
|
<system.serviceModel> <bindings> <basicHttpBinding> <binding maxBufferPoolSize=«2147483647» maxReceivedMessageSize=«2147483647» maxBufferSize=«2147483647» > <!— binding config: security, httpTransport and more —> </binding> </basicHttpBinding> </bindings> </system.serviceModel> |
The above example has the purpose of increasing the maximum size of any upload up to 2147483647 bytes for all basicHttpBinding connections: depending on the characteristics of your web service and the protocols used, it may be necessary to add the above attributes also to the other bindings present, expected and / or supported: webHttpBinding, wsHttpBinding, customBinding and so on.
In case such addition is not enough to solve the problem, it may be necessary to also change the transferMode attribute, setting it to Streamed (the default is Buffered), and also revise the settings related to the readerQuotas, i.e. the limitations that the server gives to the SOAP clients when initiating their connection:
|
<binding maxBufferPoolSize=«2147483647» maxReceivedMessageSize=«2147483647» maxBufferSize=«2147483647» transferMode=«Streamed»> <readerQuotas maxDepth=«2000000» maxStringContentLength=«2147483647» maxArrayLength=«2147483647» maxBytesPerRead=«2147483647» maxNameTableCharCount=«2147483647»/> |
uploadReadAheadSize
In the event that all the operations described above are not sufficient to solve the problem, all that remains is to try to intervene by changing the value of the uploadReadAheadSize property: unfortunately, this setting cannot be changed at the Web.config level but must be defined directly on the machine hosting the publishing IIS Web Server.
The need to modify this setting is particularly frequent when working with the Windows Communication Foundation (WFC), the (not so much) «modern» method of managing SOAP Web Services that we have already had occasion to talk about in this article: in those scenarios, the problem generally occurs in consequence of any upload larger than 42-49kb.
Let’s get to work: access the server using Remote Desktop or physical access, then open a Command Prompt with administrator privileges and type the following command, taking care to replace YOUR_WEBSITE_NAME with the name of the website as you defined it on IIS Manager at the time of creation:
|
C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\appcmd set config «YOUR_WEBSITE_NAME» —section:system.webServer/serverRuntime /uploadReadAheadSize:«2147483647» /commit:apphost |
In case you want to operate in a more general way, you can set this new value as a default setting for all websites with the following PowerShell command:
|
Set-WebConfigurationProperty -pspath ‘MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST’ -filter «system.webserver/serverruntime» -name «uploadreadaheadsize» -value 1048576 |
If you prefer to use the GUI, you can also configure these settings via the Configuration Editor within the Internet Information Services Manager (IISManager) tool:
Once there, select the system.webServer/serverRuntime within the top-left dropdown list, the change the uploadReadAheadSize value to your new desired standard (2147483647 in our example):
IMPORTANT: Make sure the enabled attribute is correctly set to True, otherwise the whole section will not be taken into account and IIS will use the default limitations, blocking uploads larger than 42-49kb.
That’s it for now: happy upload!
413 request entity too large errors occur when the request body is larger than the server is configured to allow but specific to tomcat IIS combination with SSO as for few users header size value and max_packet_size is getting bigger than what is set in IIS and Tomcat configurations.This happens as header encodes the user’s group membership in the authorization header, so if a user is part of large number of groups or multiple SSL chains gets sent, the header/request becomes very large to get processed by IIS & Tomcat with default set limits. For example by default tomcat has an 8k maximum header, whilst users belonging to many groups can have an authorization token that can swell to larger than this size. This explains why it will work for one user and whilst for other user it might not work.
REFRENCE ERRORS AS SEEN IN LOG FILES:
1. 413 Error in IIS Access log:
2016-11-23 17:13:08 10.231.132.212 GET /VERY_LONG_URL 443 USERID 10.15.101.221 Mozilla/4.0+(compatible;+MSIE+7.0;+Windows+NT+6.1;+WOW64;+Trident/7.0;+SLCC2;+.NET+CLR+2.0.50727;+.NET+CLR+3.5.30729;+.NET+CLR+3.0.30729;+.NET4.0C;+.NET4.0E;+InfoPath.3) https://VERY_LONG_URL 413 0 0 15
2. 413 Error in ISAPI_REDIRECT.log:
[Wed Nov 23 12:13:09.132 2016] [2556:1060] [error] ajp_marshal_into_msgb::jk_ajp_common.c (511): failed appending the query string [Wed Nov 23 12:13:09.148 2016] [2556:1060] [error] HttpExtensionProc::jk_isapi_plugin.c (2195): service() failed with http error 413
DETAILED ANALYSIS:
1. User Browser Profiling:
From the browser profiling we were able to see Request Entity Too Large error seen only for the GET requests which are having header sizes more than approx. 5000.
We confirmed the same after analyzing all the failed requests and It was observed that all the failed requests with 413 request entity too large on browser screen and in back end logs had headersSize value greater than 5000 and all successful requests had header size lower than 5000.
Example successful requests header sizes:
The above issue can be solved by making sure higher values are set in regedit for header size. So to solve the headerSize limitation webserver and machine shall have below settings available:
Create the following DWORD values under the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\HTTP\Parameters MaxFieldLength : 65534 MaxRequestBytes : 16777216
References:
Microsoft KB link: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/820129
2. Backend error logs analysis:
ajp_marshal_into_msgb::jk_ajp_common.c (511): failed appending the query string
The above error comes due to request exceeding the default maxHttpHeaderSize for HTTP connections or max_packet_size for AJP connections.
This issue can be addressed by changing the following configs in Tomcat, tomcat connectors and IIS.
Tomcat AJP connector:
worker.ajp13w.max_packet_size=65536 in workers.properties file.
Tomcat Server:
In server.xml file.
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" redirectPort="8443" maxHttpHeaderSize="65536" /> <Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" packetSize="65536" tomcatAuthentication="false" />
In JVM arguments
-Dorg.apache.coyote.ajp.MAX_PACKET_SIZE=65536
IIS Web Server:
maxUrl=”65536” maxQueryString="2097151" maxUrlLength=”65536” maxRequestLength=”20971520” uploadReadAheadSize="4194304”
Detailed Steps To Complete the Changes
1. Login to the Application and open the IIS Manager from the administrative tools.
2. Click on the Website created for the application.
3. Click on Configuration Editor Icon.
4. Navigate as per below screenshot and update the highlighted parameters like below.
maxUrl=”65536” maxQueryString="2097151" maxUrlLength=”65536” maxRequestLength=”20971520”
Note: Make sure the same values are updated in both configuration editors. Local site level and Global.
Screenshot 1:
Screenshot 2:
5. maxHttpHeaderSize setting:
Note: Below settings needs to be done in both App and Web Server machine registries.
Create the following DWORD values under the following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\HTTP\Parameters MaxFieldLength : 65534 MaxRequestBytes : 16777216
6. max_packet_size setting:
max_packet_size : AJP,SUB Default 8192 : This attribute sets the maximal AJP packet size in Bytes. It should be a multiple of 1024. Configuration values that are not a multiple of 1024 will be aligned to the next multiple of 1024. The maximum value is 65536. If you change it from the default, you must also change the packetSize attribute of your AJP connector on the Tomcat side! The attribute packetSize is available in Tomcat 6.0.2 onwards.
Normally it is not necessary to change the maximum packet size. Problems with the default value have been reported when sending certificates or certificate chains.
The above settings needs to be done in the tomcat-connector and tomcat itself.
Step 1: Set max_packet_size in the worker definition
In the workers.properties file referenced by the tomcat-connection definition, set the packet size to the maximum:
worker.<worker name>.max_packet_size=65536
for example:
worker.ajp13w.max_packet_size=65536
Step 2: Set packetSize in the AJP Connector definition
In the server.xml configuration file for tomcat, set the packet size to the maximum:
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" packetSize="65536" tomcatAuthentication="false" />
Step 3: In regedit
Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Apache Software Foundation\Procrun 2.0\TomcatService\Parameters\Java and edit java options and add -Dorg.apache.coyote.ajp.MAX_PACKET_SIZE=65536
7. In the middle pane of the IIS application website click on the icon Request Filtering.
8. In the Request Filtering window, click on the Query Strings sub tab and click on Edit Feature Settings in the right most window.
9. This will open Edit Request Filtering Settings page, in that page change maximum query string like below screenshot and click on OK.
10. Select the site which is configured for Application and as well as Global.
• Select Configuration Editor
• Within Section Dropdown, select “system.webServer/serverRuntime”
• Enter a higher value for “uploadReadAheadSize” such as 4194304 bytes. Default is 49152 bytes.
Once all above configurations are completed restart complete IIS and Tomcat services to make the change take effect.
In case of any ©Copyright or missing credits issue please check CopyRights page for faster resolutions.
Ошибка HTTP 413 Request Entity Too Large появляется, когда пользователь пытается загрузить на сервер слишком большой файл. Размер определяется относительно лимита, который установлен в конфигурации. Изменить его может только администратор сервера.
Что делать, если вы пользователь
Если вы видите ошибку 413, когда пытаетесь загрузить файл на чужом сайте, то вам нужно уменьшить размер передаваемых данных. Вот несколько ситуаций.
- Если вы пытались загрузить одновременно несколько файлов (форма позволяет так делать), попробуйте загружать их по одному.
- Если не загружается изображение, уменьшите его размер перед загрузкой на сервер. Можно сделать это с помощью онлайн-сервисов — например, Tiny PNG.
- Если не загружается видео, попробуйте сохранить его в другом формате и уменьшить размер. Можно сделать это с помощью онлайн-сервисов — я использую Video Converter.
- Если не загружается PDF-документ, уменьшите его размер. Можно сделать это с помощью онлайн-сервисов — я обычно использую PDF.io.
Универсальный вариант — архивация файла со сжатием. Ошибка сервера 413 появляется только в том случае, если вы пытаетесь одновременно загрузить слишком большой объем данных. Поэтому и выход во всех ситуациях один — уменьшить размер файлов.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Исправление ошибки сервера 413 владельцем сайта
Если вы владелец сайта, который при загрузке файлов выдает ошибку 413, то необходимо изменить конфигурацию сервера. Порядок действий зависит от используемых технологий.
Чтобы понять, что стало причиной ошибки, нужно посмотреть логи. Это поможет сэкономить время. Вот подробная инструкция, которая рассказывает, как посмотреть логи в панели управления Timeweb. В зависимости от того, какая информация будет в логах, вы поймете, как исправлять ошибку 413.
Увеличение разрешенного размера для загрузки файлов на Nginx и Apache
На Nginx максимально допустимый размер файла задан в параметре client_max_body_size. По умолчанию он равен 1 МБ. Если запрос превышает установленное значение, пользователь видит ошибку 413 Request Entity Too Large.
Параметр client_max_body_size находится в файле nginx.conf. Для его изменения нужен текстовый редактор — например, vi.
Подключитесь к серверу через SSH и выполните в консоли следующую команду:
Во встроенном редакторе vi откроется файл nginx.conf. В разделе http добавьте или измените следующую строку:
client_max_body_size 20M;
Сохраните и закройте файл. Затем проверьте конфигурацию файла:
Перезагрузите сервер следующей командой:
После перезагрузки будет действовать новая конфигурация с увеличенным лимитом на размер загружаемого файла.
На Apache опция, устанавливающая максимально допустимый размер загружаемого файла, называется LimitRequestBody. По умолчанию лимит не установлен (равен 0).
На CentOS главный конфиг располагается по адресу /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf. На Debian/Ubuntu — по адресу /etc/apache2/apache2.conf.
Значение задается в байтах:
LimitRequestBody 33554432
Эта запись выставляет максимально допустимый размер 32 МБ.
Изменить конфиги можно также через панель управления. Я пользуюсь ISPmanager, поэтому покажу на ее примере.
- Раскройте раздел «Домены» и перейдите на вкладку «WWW-домены».
- Выберите домен, на котором появляется ошибка, и нажмите на кнопку «Конфиг».
Появится вкладка с конфигами Apache и Nginx. Вы можете редактировать их вручную, устанавливая лимит на размер загружаемого файла.
Исправление ошибки на WordPress
На WordPress ошибку можно исправить двумя способами.
Способ первый — изменение разрешенного размера в файле functions.php. Этот файл отвечает за добавление функций и возможностей — например, меню навигации.
- Откройте файловый менеджер.
- Перейдите в папку public.html.
- Откройте директорию wp-content/themes.
- Выберите тему, которая используется на сайте с WordPress.
- Скачайте файл functions.php и откройте его через любой текстовый редактор.
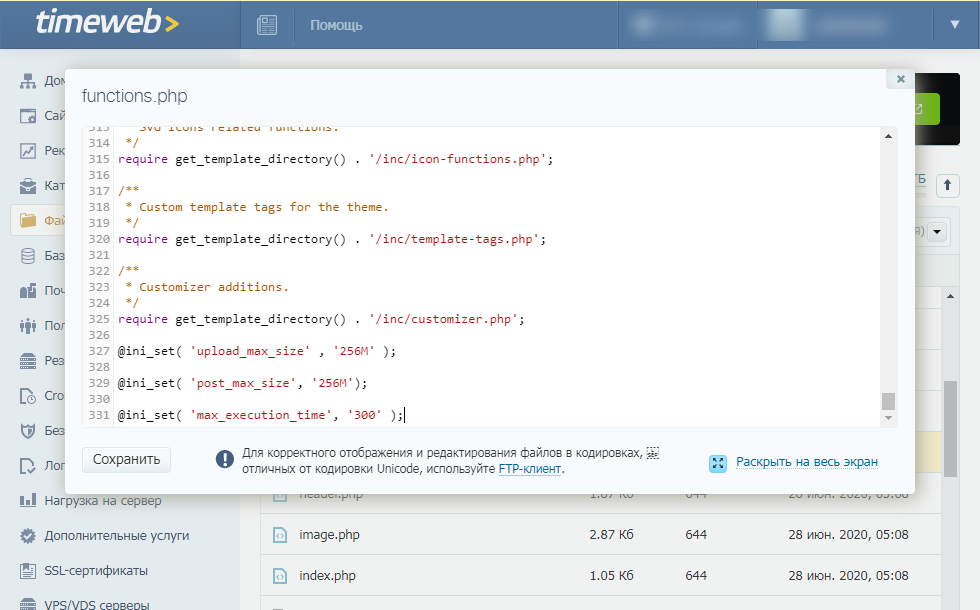
В панели управления на Timeweb можно также воспользоваться встроенным редактором или IDE — путь будет такой же, как указан выше: public.html/wp-content/themes/ваша тема/functions.php.
В конце файла functions.php добавьте следующий код:
@ini_set( 'upload_max_size' , '256M' ); @ini_set( 'post_max_size', '256M'); @ini_set( 'max_execution_time', '300' );
Сохраните изменения и загрузите модифицированный файл обратно на сервер. Проверьте, появляется ли ошибка 413.
Второй способ — изменение файла .htaccess. Это элемент конфигурации, который способен переопределять конфигурацию сервера в плане авторизации, кэширования и даже оптимизации. Найти его можно через файловый менеджер в папке public.html.
Скачайте файл на компьютер, на всякий случай сделайте резервную копию. Затем откройте .htaccess в текстовом редакторе и после строчки #END WORDPRESS вставьте следующий код:
php_value upload_max_filesize 999M php_value post_max_size 999M php_value max_execution_time 1600 php_value max_input_time 1600
Сохраните файл и загрузите его обратно на сервер с заменой исходного файла. То же самое можно сделать через встроенный редактор или IDE в панели управления Timeweb.
Исправление ошибки при использовании PHP-скрипта
Если файлы загружаются с помощью PHP-скрипта, то для исправления ошибки 413 нужно отредактировать файл php.ini. В нем нас интересуют три директивы.:
- upload_max_filesize — в ней указан максимально допустимый размер загружаемого файла (значение в мегабайтах);
- post_max_size — максимально допустимый размер данных, отправляемых методом POST (значение в мегабайтах);
- max_execution_time — максимально допустимое время выполнения скрипта (значение в секундах).
Например, если я хочу, чтобы пользователи могли загружать файлы размером до 20 МБ, то я делаю так:
max_execution_time = 90 post_max_size = 20M upload_max_filesize = 20M
Если все значения указаны верно, то файлы с допустимым размером будут загружаться на сервер без ошибок.
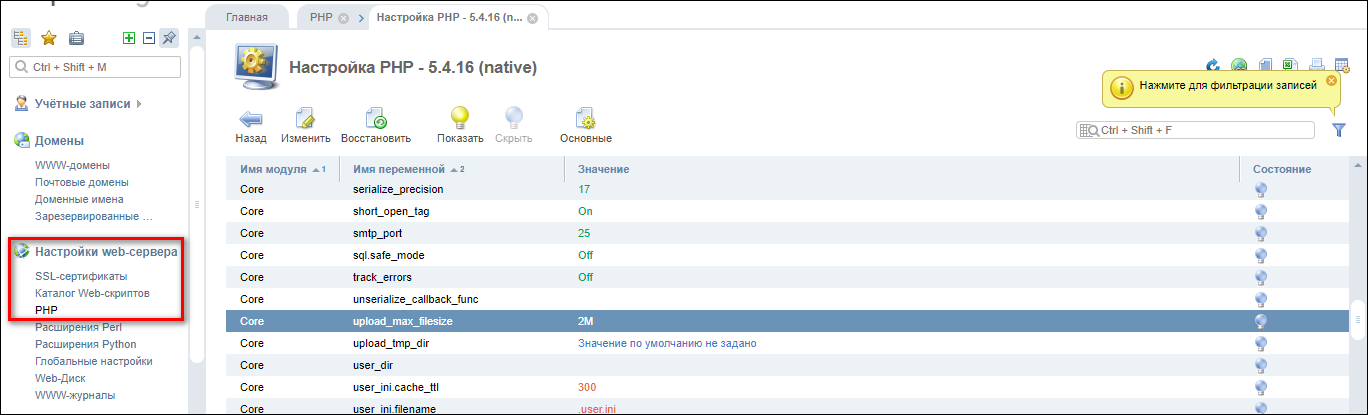
То же самое можно сделать через панель управления. Например, в ISPmanager порядок будет такой:
- Авторизуйтесь с root-правами.
- В левом меню раскройте раздел «Настройки web-сервера» и перейдите на вкладку «PHP».
- Выберите используемую версию и нажмите на кнопку «Изменить».
На экране появится список параметров. Они отсортированы по алфавиту. Установите необходимые значения для параметров max_execution_time, post_max_size и upload_max_filesize. Изменения применяются автоматически.